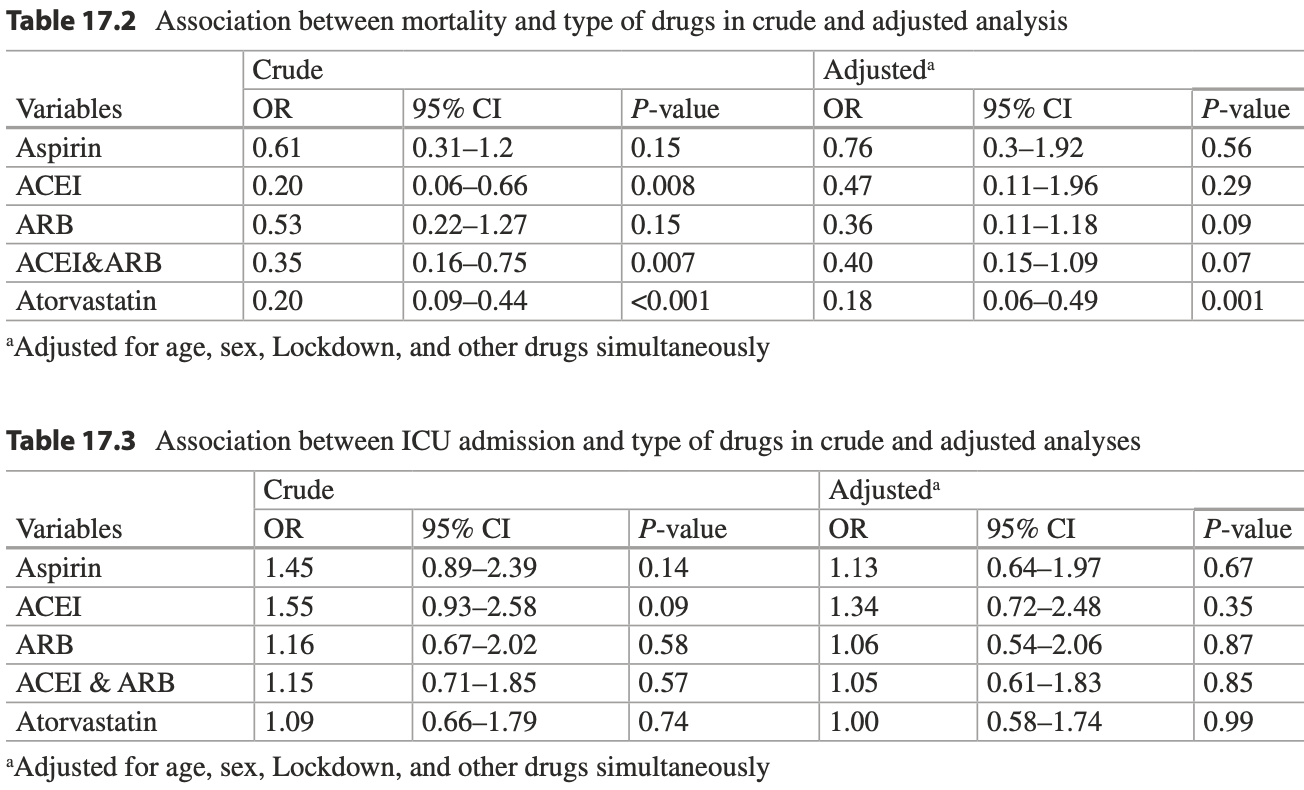
Association of In-hospital Use of Statins, Aspirin, and Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Inhibitors with Mortality and ICU Admission Due to COVID-19
et al., Identification of Biomarkers, New Treatments, and Vaccines for COVID-19, doi:10.1007/978-3-030-71697-4_17, Jul 2021
Retrospective 587 COVID+ hospitalized patients in Iran, showing no significant differences in outcomes with aspirin treatment.
|
risk of death, 21.9% lower, RR 0.78, p = 0.56, treatment 13 of 337 (3.9%), control 28 of 250 (11.2%), adjusted per study, odds ratio converted to relative risk, multivariable, primary outcome.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 10.5% higher, RR 1.10, p = 0.67, treatment 36 of 337 (10.7%), control 44 of 250 (17.6%), adjusted per study, odds ratio converted to relative risk, multivariable.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Vahedian-Azimi et al., 20 Jul 2021, retrospective, Iran, peer-reviewed, 9 authors.
Identification of Biomarkers, New Treatments, and Vaccines for COVID-19
doi:10.1007/978-3-030-71697-4
This series of volumes focuses on concepts, techniques and recent advances in the field of proteomics, interactomics, metabolomics and systems biology. Recent advances in various 'omics' technologies enable quantitative monitoring of myriad various biological molecules in a high-throughput manner, and allow determination of their variation between different biological states on a genomic scale. Now that the sequencing of various genomes, from prokaryotes to humans, has provided the list and linear sequence of proteins and RNA that build living organisms, defining the complete set of interactions that sustain life constitutes one of the key challenges of the postgenomic era. This series is intended to cover experimental approaches for defining protein-protein, protein-RNA, protein-DNA and protein-lipid interactions; as well as theoretical approaches dealing with data
Authors Tamires Duarte Afonso Serdan and Yuanji Tang have equally contributed to this chapter.
Abstract There have been recent encouraging reports about the development of vaccines for COVID-19. Given the scale and effects of this pandemic on public health and economies worldwide, there has been an unprecedented approach across the globe, leading to the emergence of vaccine candidates many times faster than the normal process would allow. This review gives up-to-date information as of November 28, 2020, on the latest developments in this area and covers the plans to roll out the most promising vaccines across the entire world to halt the spread of this devastating virus. response after the first dose and all patients showing a response after the second [16] . The EMA Human Medicines Committee (CHMP) and Health Canada had initiated a rolling review of this vaccine candidate to minimize the amount of time for making conclusions on its safety and effectiveness, and the Australian Therapeutic Good Administration (TGA) has already taken the first step in the process for approval. In the UK, the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) has also begun an accelerated review of Covishield. Four million doses of the vaccine will be available in the UK by the end of 2020, assuming and a phase 1 trial showed only a few adverse effects [21] . Pfizer and BioNTech have now received Food and Drug Administration (FDA) fast-tracking for two BNT162 candidates. BNT162b2..
References
Abate, Kassie, Kassaw, Aragie, Masresha, Sex difference in coronavirus disease (COVID-19): a systematic review and metaanalysis, BMJ Open, doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-040129
Abdi, Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in Iran: actions and problems, Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol
Abdi, Mobedi, Mosaffa, Dolatian, Tehrani, Effects of hormone replacement therapy on immunological factors in the postmenopausal period, Climacteric
Abdullah, Chai, Chong, Tohit, Ramasamy et al., Gender effect on in vitro lymphocyte subset levels of healthy individuals, Cell Immunol
Abiri, None
Ackermann, Verleden, Kuehnel, Haverich, Welte et al., Pulmonary vascular endothelialitis, thrombosis, and angiogenesis in Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Agostoni, Braegger, Decsi, Kolacek, Koletzko et al., Breast-feeding: a commentary by the ESPGHAN Committee on Nutrition, J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr
Akalin, Azzi, Bartash, Seethamraju, Parides et al., Covid-19 and kidney transplantation, N Engl J Med
Al-Attar, Presnell, Peterson, Thomas, Lutz, The effect of sex on immune cells in healthy aging: elderly women have more robust natural killer lymphocytes than do elderly men, Mech Ageing Dev
Alberici, Delbarba, Manenti, Econimo, Valerio et al., A report from the Brescia Renal COVID Task Force on the clinical characteristics and short-term outcome of hemodialysis patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection, Kidney Int
Alberici, Delbarba, Manenti, Econimo, Valerio et al., A single center observational study of the clinical characteristics and short-term outcome of 20 kidney transplant patients admitted for SARS-CoV2 pneumonia, Kidney Int
Alehagen, Johansson, Björnstedt, Rosén, Dahlström, Cardiovascular mortality and N-terminal-proBNP reduced after combined selenium and coenzyme Q10 supplementation: a 5-year prospective randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial among elderly Swedish citizens, Int J Cardiol
Alehagen, Lindahl, Aaseth, Svensson, Johansson, Levels of sP-selectin and hs-CRP decrease with dietary intervention with selenium and coenzyme Q10 combined: a secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0137680
Alexandraki, Piperi, Ziakas, Apostolopoulos, Makrilakis et al., Cytokine secretion in long-standing diabetes mellitus type 1 and 2: associations with low-grade systemic inflammation, J Clin Immunol
Alexandre, Cracowski, Richard, Bouhanick, Drugs, COVID-19' working group of the French Society of Pharmacology, Therapeutics (2020) Reninangiotensin-aldosterone system and COVID-19 infection, Ann Endocrinol
Algaadi, Urticaria and COVID-19: a review, Dermatol Ther, doi:10.1111/dth.14290
Alghamdi, Hussain, Almalki, Alghamdi, Alghamdi et al., The pattern of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus in Saudi Arabia: a descriptive epidemiological analysis of data from the Saudi Ministry of Health, Int J Gen Med
Alikiaii, Bagherniya, Askari, Johnston, Sahebkar, The role of phytochemicals in sepsis: a mechanistic and therapeutic perspective, BioFactors, doi:10.1002/biof.1694
Alikiaii, Bagherniya, Askari, Sathyapalan, Sahebkar, Evaluation of the effect of curcumin on pneumonia: a systematic review of preclinical studies, Phytother Res. Nov, doi:10.1002/ptr.6939
Alikiaii, Bagherniya, Askari, Sathyapalan, Sahebkar, Evaluation of the effect of curcumin on pneumonia: a systematic review of preclinical studies, Phytother Res. Nov, doi:10.1002/ptr.6939
Allorto, Oxygen-ozone therapy: an extra weapon for the general practitioners and their patients, Ozone Ther, doi:10.4081/ozone.2019.8424
Alyasin, Nabavizadeh, Houshmand, Esmaeilzadeh, Jelodar et al., Short time efficiency of rhinophototherapy in management of patients with allergic rhinitis resistant to medical therapy, Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol
An, Yue, Zhao, Droplets and aerosols in dental clinics and prevention and control measures of infection, Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi
Anand, Kunnumakkara, Newman, Aggarwal, Bioavailability of curcumin: problems and promises, Mol Pharm
Anand, Sundaram, Jhurani, Kunnumakkara, Aggarwal, Curcumin and cancer: an "oldage" disease with an "age-old" solution, Cancer Lett
Anirudh, Mathematical modeling and the transmission dynamics in predicting the Covid-19 -what next in combating the pandemic, Infect Dis Model
Antonioli, Fornai, Pellegrini, Blandizzi, NKG2A and COVID-19: another brick in the wall, Cell Mol Immunol
Antunes, Fachi, De Paula, Da Silva, Pral et al., Microbiotaderived acetate protects against respiratory syncytial virus infection through a GPR43-type 1 interferon response, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-019-11152-6
Arachchillage, Laffan, Abnormal coagulation parameters are associated with poor prognosis in patients with novel coronavirus pneumonia, J Thromb Haemost
Aragão, Júnior, Ataide, Neto, Aragão et al., Case report COVID-19 presenting as an exanthematic disease: a case report, Rev Soc Bras Med Trop, doi:10.1590/0037-8682-0533-2020
Aramaki, Maskawa, Morita, John McIntyre Conference Centre, Edinburgh, UK, A meeting of SIGDAT, a Special Interest Group of the ACL
Arruvito, Giulianelli, Flores, Paladino, Barboza et al., NK cells expressing a 6 Sex Differences and COVID-19 progesterone receptor are susceptible to progesteroneinduced apoptosis, J Immunol
Asadi, Tabatabaei, Safinejad, Mohammadi, New corona virus (COVID-19) management in pregnancy and childbirth, Arch Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.5812/archcid.102938
Ascenzi, Handbook of disinfectants and antiseptics
Asg, Potential use of ozone in SARS-CoV-2/COVID
Ashing-Giwa, Padilla, Tejero, Kraemer, Wright et al., Understanding the breast cancer experience of women: a qualitative study of African American, Asian American, Latina and Caucasian cancer survivors, Psychooncology
Ashour, Elkhatib, Rahman, Elshabrawy, Insights into the recent 2019 novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) in light of past human coronavirus outbreaks, Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens9030186
Atri, Siddiqi, Lang, Nauffal, Morrow et al., COVID-19 for the cardiologist: a current Review of the virology, clinical epidemiology, cardiac and other clinical manifestations and potential therapeutic strategies, JACC Basic Transl Sci
Avasarala, Zhang, Liu, Wang, London et al., Curcumin modulates the inflammatory response and inhibits subsequent fibrosis in a mouse model of viral-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0057285
Azar, Shin, Kang, Landry, Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection in the setting of the cytokine release syndrome, Expert Rev Mol Diagn, doi:10.1080/14737159.2020.1830760
Azarpazhooh, Limeback, The application of ozone in dentistry: a systematic review of literature, J Dent
Azkur, Akdis, Azkur, Sokolowska, Van De Veen et al., Immune response to SARS-CoV-2 and mechanisms of immunopathological changes in COVID-19, Allergy
Baden, Rubin, Covid-19-the search for effective therapy, N Engl J Med
Bagheri, Ghasemi, Barreto, Rafiee, Sathyapalan et al., Effects of curcumin on mitochondria in neurodegenerative diseases, Biofactors
Baglivo, Baronio, Natalini, Beccari, Chiurazzi et al., Natural small molecules as inhibitors of coronavirus lipid-dependent attachment to host cells: a possible strategy for reducing SARS-COV-2 infectivity? SARS-COV-2 lipid-dependent attachment to host cells, Acta Bio Med Atenei Parmensis
Bahrami, Sattarzadeh, Koochaksariie, Ghojazadeh, Comparing depression and sexual satisfaction in fertile and infertile couples, J Reprod Infert
Baker, Charlie Swanton, Nature
Baker, Williams, Tropsha, Ekins, Repurposing quaternary ammonium compounds as potential treatments for COVID-19, Pharm Res, doi:10.1007/s11095-020-02842-8
Bakovic, Risner, Bhalla, Brilacidin, a COVID-19 drug candidate, exhibits potent in vitro antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2, Microbiology
Balasubramanian, Ultraviolet radiation and cataract, J Ocul Pharmacol Ther
Banerjee, Popoola, Shah, Ster, Quan et al., COVID-19 infection in kidney transplant recipients, Kidney Int
Bang, Choi, Sur, Lim, Kim et al., Anti-inflammatory and antiarthritic effects of piperine in human interleukin 1β-stimulated fibroblast-like synoviocytes and in rat arthritis models, Arthritis Res Ther
Bansal, Jonsson, Taylor, Figueroa, Dugour et al., Iota-carrageenan and xylitol inhibit SARS-CoV-2 in cell culture, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.08.19.225854
Barrett, Yaffe, COVID-19: all the wrong moves in all the wrong places, Sci Signal, doi:10.1126/scisignal.abe4242
Bassetti, Puente, Magnasco, Giacobbe, Innovative therapies for acute bacterial skin and skin-structure infections (ABSSSI) caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: advances in phase I and II trials, Expert Opin Investig Drugs
Baud, Qi, Nielsen-Saines, Musso, Pomar et al., Real estimates of mortality following COVID-19 infection, Lancet Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/s1473-3099(20)30195-x
Baumgaertner, Rainy, Trump administration ended pandemic early-warning program to detect coronaviruses, Los Angeles Times
Becker, Tanzi, Kalil, Shibata, Cain, Early statin use is associated with increased risk of infection after stroke, J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis
Belkacem, Serafini, Wheeler, Derrien, Boucinha et al., Lactobacillus paracasei feeding improves immune control of influenza infection in mice, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0184976
Ben-Zur, Gilbar, Coping with breast cancer: Patient, spouse, and dyad models, Psychosom Med
Benahmed, Gasmi, Arshad, Shanaida, Lysiuk et al., Health benefits of xylitol, Appl Microbiol Biotechnol
Benvenuto, Angeletti, Giovanetti, Bianchi, Pascarella et al., Evolutionary analysis of SARS-CoV-2: how mutation of non-structural protein 6 (NSP6) could affect viral autophagy, J Infect
Benzakoun, Hmeydia, Delabarde, Hamza, Meder et al., Excess out-of-hospital deaths during the COVID-19 outbreak: evidence of pulmonary embolism as a main determinant, Eur J Heart Fail
Berger, Th1 and Th2 responses: what are they?, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.321.7258.424
Berghella, Burd, Anderson, Boelig, Decreased incidence of preterm birth during COVID-19 pandemic, Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM, doi:10.1016/j.ajogmf.2020.100258
Bergquist, COVID-19: end of the beginning?, Geospat Health, doi:10.4081/gh.2020.897
Bergquist, Rinaldi, Covid-19: pandemonium in our time, Geospat Health, doi:10.4081/gh.2020.880
Bergquist, Rinaldi, Covid-19: pandemonium in our time, Geospatial Health, doi:10.4081/gh.2020.880
Bernheim, Mei, Huang, Yang, Fayad et al., Chest CT findings in Coronavirus Disease-19 (COVID-19): relationship to duration of infection, Radiology, doi:10.1148/radiol.2020200463
Bernstein, Schiff, Echler, Prince, Feller et al., In vitro virucidal effectiveness of a 0.12%-chlorhexidine gluconate mouthrinse, J Dent Res
Betjes, Immune cell dysfunction and inflammation in end-stage renal disease, Nat Rev Nephrol
Bhat, Hamid, Kunin, Saboo, Batra et al., Chest imaging in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 infection -A case series, Curr Probl Diagn Radiol
Bi, Wu, Mei, Ye, Zou et al., Epidemiology and transmission of COVID-19 in Shenzhen China: analysis of 391 cases and 1,286 of their close contacts, MedRxiv, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30287-5
Bialek, Gierke, Hughes, Mcnamara, Pilishvili et al., Coronavirus disease 2019 in children -United States, MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep
Bidra, Pelletier, Westover, Bidra, Pelletier et al., Rapid in-vitro inactivation of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) using povidone-iodine Oral antiseptic rinse, J Prosthodont
Bidra, Pelletier, Westover, Frank, Brown et al., Comparison of in vitro inactivation of SARS CoV-2 with hydrogen peroxide and povidone-iodine oral antiseptic rinses, J Prosthodont, doi:10.1111/jopr.13220
Bioithas, The intestinal microbiota as a therapeutic target in hospitalized patients With COVID-19 infection
Biosearch, Multicentric study to assess the effect of consumption of lactobacillus coryniformis K8 on healthcare personnel exposed to COVID
Biotech, Study to investigate if sucking a Coldamaris Lozenge Elutes Sufficient Iota-carrageenan to inactivate usual common cold viruses
Bisht, Feldmann, Soni, Ravi, Karikar et al., Polymeric nanoparticleencapsulated curcumin ("nanocurcumin"): a novel strategy for human cancer therapy, J Nanobiotechnol, doi:10.1186/1477-3155-5-3
Bocci, The case for oxygen-ozonetherapy, Br J Biomed Sci
Boe, Boule, Kovacs, Innate immune responses in the ageing lung, Clin Exp Immunol
Boettler, Newsome, Mondelli, Maticic, Cordero et al., Care of patients with liver disease during the COVID-19 pandemic: EASL-ESCMID position paper, JHEP Rep, doi:10.1016/j.jhepr.2020.100113
Borrelli, Bocci, Oxygen ozone therapy in the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: an integrative approach, Am J Clin Exp Med
Boswell, Cannon, Introduction to nursing research
Bouaziz, Duong, Jachiet, Velter, Lestang et al., Vascular skin symptoms in COVID-19: a French observational study, J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol, doi:10.1111/jdv.16544
Brazil, None
Brosnihan, Li, Ganten, Ferrario, Estrogen protects transgenic hypertensive rats by shifting the vasoconstrictor-vasodilator balance of RAS, Am J Phys
Buck, Thompson, Roberts, Müller, Lowy et al., Carrageenan is a potent inhibitor of papillomavirus infection, PLoS Pathog, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.0020069
Budden, Gellatly, Wood, Cooper, Morrison et al., Emerging cal superinfection through altered short-chain fatty acid production, Cell Rep
Bukowska, Spiller, Wolke, Lendeckel, Weinert et al., Protective regulation of the ACE2/ACE gene expression by estrogen in human atrial tissue from elderly men, Exp Biol Med (Maywood)
Burki, COVID-19 in Latin America, Lancet Infect Dis
Busse, Mathur, Age-related changes in immune function: effect on airway inflammation, J Allergy Clin Immunol
Bárcena, Oostergetel, Bartelink, Faas, Verkleij et al., Cryo-electron tomography of mouse hepatitis virus: insights into the structure of the coronavirion, Proc Natl Acad Sci
Cai, Xu, Lin, Yang, Xu et al., A case series of children with 2019 novel coronavirus infection: clinical and epidemiological features, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa198
Caillard, Anglicheau, Matignon, Durrbach, Greze et al., An initial report from the French SOT COVID Registry suggests high mortality due to Covid-19 in recipients of kidney transplants, Kidney Int, doi:10.1016/j.kint.2020.08.005
Callaway, Making sense of coronavirus mutations, Nature
Calunga, Paz, Menéndez, Martínez, Hernández, Rectal ozone therapy for patients with pulmonary emphysema, Rev Med Chil
Cameron, Bermejo-Martin, Danesh, Muller, Kelvin, Human immunopathogenesis of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), Virus Res
Candido, Watts, Abade, Kraemer, Pybus et al., Routes for COVID-19 importation in Brazil, J Travel Med, doi:10.1093/jtm/taaa042
Cao, Chen, Chen, Chiu, SARS-CoV-2 infection in children: transmission dynamics and clinical characteristics, J Formos Med Assoc
Cao, Wang, Wen, Liu, Wang, A trial of lopinavir-ritonavir in adults hospitalized with severe Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Cariou, Goronflot, Timbert, Boullu, Wargny, Routine use of statins and increased COVID-19 related mortality in inpatients with type 2 diabetes: results from the CORONADO study, Diabetes Metab, doi:10.1016/j.diabet.2020.10.001
Carlos, Cruz, Cao, Pasnick, Jamil, Novel Wuhan (2019-nCoV) coronavirus
Carpendale, Freeberg, Ozone inactivates HIV at noncytotoxic concentrations, Antivir Res
Carroll, Daszak, Wolfe, Gao, Morel et al., The global virome project, Science
Carrouel, Conte, Fisher, Gonçalves, Dussart et al., COVID-19: a recommendation to examine the effect of mouthrinses with β-cyclodextrin combined with citrox in preventing infection and progression, J Clin Med, doi:10.3390/jcm9041126
Carrouel, Gonçalves, Conte, Campus, Fisher et al., None
Caruso, Accardi, Virruso, Candore, Sex, gender and immunosenescence: a key to understand the different lifespan between men and women?, Immun Ageing
Caruso, Prete, Lazzarino, Capaldi, Grumetto, Might hydrogen peroxide reduce the hospitalization rate and complications of SARS-CoV-2 infection?, Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol
Caruso, Rossi, Pedersen, Incerpi, Computational studies reveal mechanism by which quinone derivatives can inhibit SARS-CoV-2. Study of embelin and two therapeutic compounds of interest, methyl prednisolone and dexamethasone, J Infect Public Health. Oct, doi:10.1016/j.jiph.2020.09.015
Casas, Català, Hernández, Rodríguez-Jiménez, Fernández-Nieto et al., Classification of the cutaneous manifestations of COVID-19: a rapid prospective nationwide consensus study in Spain with 375 cases, Br J Dermatol
Cascella, Rajnik, Cuomo, Dulebohn, Napoli, Features, evaluation, and treatment of coronavirus, StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing
Casteels, Pünt, Brämswig, Transient neonatal hypothyroidism during breastfeeding after post-natal maternal topical iodine treatment, Eur J Pediatr
Català, Galván-Casas, Carretero-Hernández, Rodríguez-Jiménez, Fernández-Nieto et al., Maculopapular eruptions associated to COVID-19: a subanalysis of the COVID-Piel study, Dermatol Ther, doi:10.1111/dth.14170
Cdc, Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) considerations for inpatient obstetric healthcare settings
Cdc, Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Centers for disease control and prevention
Cdc, People with underlying medical conditions, immunocompromised state (Weakened immune system) from solid organ transplant
Cerdá, Mohan, Garcia-Garcia, Jha, Samavedam et al., Acute kidney injury recognition in low-and middle-income countries, Kidney Int Rep
Cevik, Bamford, Ho, COVID-19 pandemic -a focused review for clinicians, Clin Microbiol Infect
Chambers, Krogstad, Bertrand, Contreras, Bode et al., Evaluation of SARS-CoV-2 in breastmilk from 18 infected women, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.06.12.20127944
Chan, Chaudhary, Saha, Chauhan, Vaid et al., AKI in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, J Am Soc Nephrol, doi:10.1681/ASN.2020050615
Chan, Huang, Liao, Tsai, Chu, Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors and risks of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Hypertension
Chan, Yuan, Kok, To, Chu et al., A familial cluster of pneumonia associated with the 2019 novel coronavirus indicating person-to-person transmission: a study of a family cluster, Lancet
Chan-Yeung, Xu, SARS: epidemiology, Respirology, doi:10.1046/j.1440-1843.2003.00518.x
Chang, Ding, Freund, Johnson, Schwarz et al., Prior diagnoses and medications as risk factors for COVID-19 in a Los Angeles Health System, doi:10.1101/2020.07.03.20145581
Chang, Sun, Lactoferrin may reduce the incidence and attenuate the severity of COVID-19 in infants and children, doi:10.22541/au.158630054.41052564
Chang, Yu, Chang, Galvin, Liu et al., Pulmonary sequelae in convalescent patients after severe acute respiratory syndrome: evaluation with thin-section CT, Radiology
Channappanavar, Fett, Mack, Eyck, Meyerholz et al., Sex-based differences in susceptibility to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection, J Immunol
Channappanavar, Fett, Mack, Eyck, Meyerholz et al., Sex-based differences in susceptibility to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection, J Immunol
Chappell, Yamaleyeva, Westwood, Estrogen and salt sensitivity in the female mRen(2). Lewis rat, Am J Phys Regul Integr Comp Phys
Chase, Cocchi, Liu, Andersen, Holmberg et al., Coenzyme Q10 in acute influenza, Influenza Other Respir Viruses
Chaux, UVA light device to treat COVID
Chen, Fu, Shu, Chen, Hua et al., Diagnosis and treatment recommendation for pediatric coronavirus disease-19, Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban
Chen, Fu, Shu, Chen, Hua et al., Diagnosis and treatment recommendations for pediatric respiratory infection caused by the 2019 novel coronavirus, World J Pediatr
Chen, Guo, Wang, Luo, Yu et al., Clinical characteristics and intrauterine vertical transmission potential of COVID-19 infection in nine pregnant women: a retrospective review of medical records, Lancet
Chen, Guo, Wang, Wang, Luo et al., Clinical characteristics and intrauterine vertical transmission potential of COVID-19 infection in nine pregnant women: a retrospective review of medical records, Lancet
Chen, Lan, Yuan, Deng, Li et al., Detectable 2019-nCoV viral RNA in blood is a strong indicator for the further clinical severity, Emerg Microbes Infect
Chen, Li, Gong, Zhang, Li, Predictors of health-related quality of life and influencing factors for COVID-19 patients, a follow-up at one month, Front Psychiatry, doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00668
Chen, Li, Song, Hu, Su et al., Assessment of hypokalemia and clinical characteristics in patients with Coronavirus Disease, JAMA Netw Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.11122
Chen, Liu, Sun, Huang, Wang et al., 25-Dihydroxyvitamin D promotes negative feedback regulation of TLR signaling via targeting microRNA-155-SOCS1 in macrophages, J Immunol
Chen, Liu, Zhang, Xiong, Chen et al., Frist case of severe childhood novel coronavirus pneumonia in China, Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi
Chen, Rui, Wang, Zhao, Cui et al., A mathematical model for simulating the phase-based transmissibility of a novel coronavirus, Infect Dis Poverty, doi:10.1186/s40249-020-00640-3
Chen, Tin, Peralta, Appel, Choi et al., APOL1 risk variants, incident proteinuria, and subsequent eGFR decline in blacks with hypertension-attributed CKD, Clin J Am Soc Nephrol
Chen, Wang, Antiplatelet and calcium inhibitory properties of eugenol and sodium eugenol acetate, Gen Pharmacol
Chen, Zhou, Dong, Qu, Gong et al., Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study, Lancet
Chen, Zhou, Dong, Qu, Gong et al., Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study, Lancet
Chen, Zhou, Dong, Qu, Gong et al., Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study, Lancet
Cheng, Luo, Wang, Wang, Zhang et al., The incidence, risk factors, and prognosis of acute kidney injury in adult patients with Coronavirus Disease, Clin J Am Soc Nephrol
Cheng, Luo, Wang, Zhang, Wang et al., Kidney disease is associated with inhospital death of patients with COVID-19, Kidney Int
Chiba, Tomosada, Vizoso-Pinto, Salva, Takahashi et al., Immunobiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus improves resistance of infant mice against respiratory syncytial virus infection, Int Immunopharmacol
Chin, Chu, Perera, Hui, Yen et al., Stability of SARS-CoV-2 in different environmental conditions, Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/S2666-5247(20)30003-3
Chiu, Chan, Tsai, Li, Wu, Prevention of human enterovirus 71 infection by kappa carrageenan, Antivir Res
Chng, Tan, Kuperan, Establishment of adult peripheral blood lymphocyte subset reference range for an Asian population by singleplatform flow cytometry: influence of age, sex, and race and comparison with other published studies, Clin Diagn Lab Immunol
Choi, Aizaki, Lai, Murine coronavirus requires lipid rafts for virus entry and cell-cell fusion but not for virus release, J Virol
Choi, Qi, Yoon, Park, Lee et al., Extension of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) on chest CT and implications for chest radiograph interpretation, Radiol Cardiothorac Imaging, doi:10.1148/ryct.2020200107
Chollet, Allaire, Deep learning with R, Manning Publications, Shelter Island. ISBN
Chow, Khanna, Kethireddy, Yamane, Levine et al., Aspirin use is associated with decreased mechanical ventilation, ICU admission, and INhospital mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, Anesth Anal
Chowdhury, Anwar, Management of hemoglobin disorders during the COVID-19 pandemic, Front Med (Lausanne), doi:10.3389/fmed.2020.00306
Chu, Aid, Duda, Solo, Yaacoub et al., on behalf of the COVID-19 SURGE study authors (2020) Physical distancing, face masks, and eye protection to prevent person-toperson transmission of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Lancet
Chugh, Awasthi, Agarwal, Gaur, Dhawan et al., A comprehensive review on potential therapeutics interventions for COVID-19
Chumakov, Benn, Aaby, Kottilil, Gallo, Can existing live vaccines prevent COVID-19?, Science
Chung, Bernheim, Mei, Zhang, Huang et al., CT imaging features of 2019 novel coronavirus
Cinatl, Morgenstern, Bauer, Chandra, Rabenau et al., Treatment of SARS with human interferons, Lancet
Cingi, Cakli, Yaz, Songu, Bal, Phototherapy for allergic rhinitis: a prospective, randomized, single-blind, placebo-controlled study, Ther Adv Respir Dis
Clavo, Rodriguez-Esparragon, Rodriguez-Abreu, Martinez-Sanchez, Llontop et al., Modulation of oxidative stress by ozone therapy in the prevention and treatment of chemotherapy-induced toxicity: review and prospects, Antioxidants (Basel), doi:10.3390/antiox8120588
Clavo, Santana-Rodríguez, Llontop, Gutiérrez, Suárez et al., Ozone therapy as adjuvant for cancer treatment: is further research warranted? Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, doi:10.1155/2018/7931849
Clay, Donart, Fomukong, Knight, Lei et al., Primary severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection limits replication but not lung inflammation upon homologous rechallenge, J Virol
Codo, Davanzo, Monteiro, De Souza, Muraro et al., Elevated glucose levels favor SARS-CoV-2 infection and monocyte response through a HIF-1α/ glycolysis-dependent axis, Cell Metab, doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2020.07.007
Cohall, Scantlebury-Manning, James, Hall, Ferrario, Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system gender differences in an Afro-Caribbean population, J Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Syst
Cohen, Hörl, Immune dysfunction in uremia-An update, Toxins (Basel)
Colafrancesco, Scrivo, Barbati, Conti, Priori, Targeting the immune system for pulmonary inflammation and cardiovascular complications in COVID-19 patients, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.01439
Conte, Ronconi, Caraffa, Gallenga, Ross et al., Induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1 and IL-6) and ling inflammation by COVID-19 or SARS-COV-2: anti-inflammatory strategies, J Biol Regul Homeost Agents
Cooper, Existential psychotherapy and counselling: contributions to a pluralistic practice
Coppa, Gabrielli, Zampini, Galeazzi, Ficcadenti et al., Oligosaccharides in 4 different milk groups, Bifidobacteria, and Ruminococcus Obeum, J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr
Corbett, Blakey, Nitsch, Loucaidou, Mclean et al., Epidemiology of COVID-19 in an Urban Dialysis Center, J Am Soc Nephrol
Corman, Landt, Kaiser, Molenkamp, Meijer et al., Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR, Eurosurveillance, doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.3.2000045
Cornish, Filipovic, Åsenius, Williams, Mcdonnell, Innate immune responses to acute viral infection during pregnancy, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.572567
Coronavirus, Oxford vaccine to be rolled out within weeks, and 70 million doses by Easter. Two-dose candidate found to be up to 90 per cent effective in preventing Covid
Covid-19, Coenzyme Q10 and Selenium, doi:10.1016/j.exger.2020.111147
Crackower, Sarao, Oudit, Yagil, Kozieradzki et al., Angiotensinconverting enzyme 2 is an essential regulator of heart function, Nature
Crackower, Sarao, Oudit, Yagil, Kozieradzki et al., Angiotensinconverting enzyme 2 is an essential regulator of heart function, Nature
Crane, Biochemical functions of CoQ10, J Am Coll Nutr
Cravedi, Suraj, Azzi, Haverly, Farouk et al., COVID-19 and kidney transplantation: results from the TANGO International Transplant Consortium, Am J Transplant, doi:10.1111/ajt.16185
Criado, Abdalla, De Assis, Van Blarcum De, Mello et al., Are the cutaneous manifestations during or due to SARS-CoV-2 infection/COVID-19 frequent or not? Revision of possible pathophysiologic mechanisms, Inflamm Res
Cristiani, Mancino, Matera, Nenna, Pierangeli et al., Will children reveal their secret? The coronavirus dilemma, Eur Respir J, doi:10.1183/13993003.00749-202026
Cristiani, Mancino, Matera, Nenna, Pierangeli et al., Will children reveal their secret? The coronavirus dilemma, Eur Respir J, doi:10.1183/13993003.01617-2020
Crowe, Jolly, Macarthur, Manaseki-Holland, Gittoes et al., Trends in the incidence of testing for vitamin D deficiency in primary care in the UK, BMJ Open, doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2018-028355
Császár-Nagy, Bókkon, Mother-newborn separation at birth in hospitals: a possible risk for neurodevelopmental disorders?, Neurosci Biobehav Rev
Cui, Li, Shi, Origin and evolution of pathogenic coronaviruses, Nat Rev Microbiol
Cui, Yu, Wu, Huang, Tian et al., Acute kidney injury in patients with the Coronavirus Disease 2019: a multicenter study, Kidney Blood Press Res
Curcumin-Piperine, None
Cyranoski, Why healthy arteries might help kids avoid COVID complications, Nature
Dai, Gu, Su, Wang, Zhao et al., Inhibition of curcumin on influenza A virus infection and influenzal pneumonia via oxidative stress, TLR2/4, p38/JNK MAPK and NF-κB pathways, Int Immunopharmacol
Dai, Zhao, Zeng, Wan, Yang et al., Drug screening for autophagy inhibitors based on the dissociation of Beclin1-Bcl2 complex using BiFC technique and mechanism of eugenol on anti-influenza A virus activity, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0061026
Dancer, Parekh, Lax, Souza, Zheng et al., Vitamin D deficiency contributes directly to Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS), Thorax
Daneshgaran, Dubin, Gould, Cutaneous manifestations of COVID-19: an evidencebased review, Am J Clin Dermatol
Danzi, Loffi, Galeazzi, Gherbesi, Acute pulmonary embolism and COVID-19 pneumonia: a random association?, Eur Heart J, doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa254
Dargahi, Johnson, Donkor, Vasiljevic, Apostolopoulos, Immunomodulatory effects of probiotics: can they be used to treat allergies and autoimmune diseases?, Maturitas
Datta, Liu, Fischer, Rappaport, Qin, SARS-CoV-2 pandemic and research gaps: understanding SARS-CoV-2 interaction with the ACE2 receptor and implications for therapy, Theranostics
Davanzo, Moro, Sandri, Agosti, Moretti et al., Ad interim indications of the Italian Society of Neonatology endorsed by the Union of European Neonatal & Perinatal Societies, Matern Child Nutr, doi:10.1111/mcn.13010
De Andrea, Ravera, Gioia, Gariglio, Landolfo, The interferon system: an overview, Eur J Paediatr Neurol
De Chazal, Buono, Keyser-Marcus, Ma, Moeller et al., Stress cardiomyopathy diagnosis and treatment: JACC state-of-the-art review, J Am Coll Cardiol
De Opitz, Sass, Tackling antimicrobial resistance by exploring new mechanisms of antibiotic action, Future Microbiol
De Souza, Buss, Candido, Carrera, Li et al., Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of the COVID-19 epidemic in Brazil, Nat Hum Behav
Dentaid, Efecto de un Enjuague Bucal Con Clorhexidina al 0.12% y Cloruro de Cetil Piridinio al 0.05% en la Carga Viral en Saliva en Pacientes COVID-19 + Hospitalizados o Que Esten Recibiendo Cuidado médico en Casa en Cali -2020
Derosa, Maffioli, Sahebkar, Piperine and its role in chronic diseases, Adv Exp Med Biol
Dhama, Khan, Tiwari, Sircar, Bhat et al., Coronavirus disease 2019-COVID-19, Microbiol Rev, doi:10.1128/CMR.00028-20
Dhar, Mohanty, Gut microbiota and Covid-19-possible link and implications, Virus Res, doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2020.198018
Dhillon, Aggarwal, Newman, Wolff, Kunnumakkara et al., Phase II trial of curcumin in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer, Clin Cancer Res
Dhochak, Singhal, Kabra, Lodha, Pathophysiology of COVID-19: why children fare better than adults?, Indian J Pediatr
Diao, Wang, Tan, Chen, Liu et al., Reduction and functional exhaustion of T cells in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Medrxiv, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.00827
Diao, Wang, Wang, Feng, Tan et al., Human kidney is a target for Novel Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.03.04.20031120
Diaz-Guimaraens, Dominguez-Santas, Suarez-Valle, Pindado-Ortega, Selda-Enriquez et al., Petechial skin rash associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection, JAMA Dermatol
Ding, Cao, Zhou, Wang, Jiang, Ozone disinfection of chlorine-resistant bacteria in drinking water, Water Res
Ding, Zhang, Li, Wu, Huang, Correlation analysis of the severity and clinical prognosis of 32 cases of patients with COVID-19, Respir Med, doi:10.1016/j.rmed.2020.105981
Ding, Zhang, Wang, Cui, Chen et al., Potential influence of menstrual status and sex hormones on female SARS-CoV-2 infection: a crosssectional study from multicentre in Wuhan, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa1022
Djukanović, Harrison, Johnston, Gabbay, Wark et al., The effect of inhaled IFN-β on worsening of asthma symptoms caused by viral infections. A randomized trial, Am J Respir Crit Care Med
Dong, Mo, Hu, Qi, Jiang et al., Epidemiological characteristics of 2143 pediatric patients with 2019 coronavirus disease in China, Pediatrics, doi:10.1542/peds.2020-0702
Dong, Tian, He, Zhu, Wang et al., Possible vertical transmission of SARS-CoV-2 from an infected mother to her newborn, JAMA
Dong, Tian, He, Zhu, Wang et al., Possible vertical transmission of SARS-CoV-2 from an infected mother to her newborn, JAMA
Drageset, Lindstrøm, Underlid, I just have to move on": women's coping experiences and reflections following their first year after primary breast cancer surgery, Eur J Oncol Nurs
Drago, Rampini, Rampini, Rebora, Atypical exanthems: morphology and laboratory investigations may lead to an aetiological diagnosis in about 70% of cases, Br J Dermatol
Dudas, Rambaut, MERS-CoV recombination: implications about the reservoir and potential for adaptation, Virus Evol, doi:10.1093/ve/vev023
Duffy, Biegelsen, Eberhardt, Kahn, Kingwell et al., Low-renin hypertension with relative aldosterone excess is associated with impaired NO-mediated vasodilation, Hypertension
Dulguerov, Guinand, Courvoisier, Landis, Lacroix et al., Rhinophototherapy in chronic rhinosinusitis: a double blind randomized placebo-controlled trial, Rhinology
Dumas, Safe skin-to-skin contact between mother and baby
Dumpa, Kamity, Vinci, Noyola, Noor, Neonatal coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) infection: a case report and review of literature, Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.8165
Duran, Berman, Niermeyer, Jaenisch, Forster et al., COVID-19 and newborn health: systematic review, Rev Panam Salud Publica, doi:10.26633/RPSP.2020.54
Díaz, Maestro, Pumarega, Antón, Alonso, First case of neonatal infection due to SARS-CoV-2 in Spain, An Pediatr
Dörnemann, Burzio, Ronsse, Sprecher, Clerck et al., First newborn baby to receive experimental therapies survives ebola virus disease, J Infect Dis
Eccles, Martensson, Chen, Effects of intranasal xylometazoline, alone or in combination with ipratropium, in patients with common cold, Curr Med Res Opin
Editorial, The COVID-19 testing debacle, Nature Biotech, doi:10.1038/s41587-020-0575-3
Eggers, Koburger-Janssen, Eickmann, Zorn, In vitro bactericidal and virucidal efficacy of povidone-iodine gargle/mouthwash against respiratory and oral tract pathogens, Infect Dis Ther
Eguchi, Fujitani, Nakagawa, Miyazaki, Prevention of respiratory syncytial virus infection with probiotic lactic acid bacterium Lactobacillus gasseri SBT2055, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-019-39602-7
Eguchi, Fujitani, Nakagawa, Miyazaki, Prevention of respiratory syncytial virus infection with probiotic lactic acid bacterium Lactobacillus gasseri SBT2055, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-019-39602-7
Eickmann, Becker, Klenk, Doerr, Stadler et al., Phylogeny of the SARS coronavirus, Science
Elias, Pievani, Randoux, Louis, Denis et al., None
Elo, Kyngäs, The qualitative content analysis process, J Adv Nurs
Elvis, Ekta, Ozone therapy: a clinical review, J Nat Sci Biol Med
Emami, Javanmardi, Pirbonyeh, Akbari, Prevalence of underlying diseases in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a systematic Review and meta-analysis, Arch Acad Emerg Med, doi:10.22037/aaem.v8i1.600
Emani, Goswami, Nandanoor, Emani, Reddy et al., Randomized controlled trials for COVID-19: evaluation of optimal randomization methodologies -Need for the data validation of the completed trials, and to improve the ongoing and future randomized trial designs, Int J Antimicrob Agents, doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.106222
Erden, Demir, Filibeli, Disintegration of biological sludge: effect of ozone oxidation and ultrasonic treatment on aerobic digestibility, Bioresour Technol
Eren, Saribek, Kalayci, Yilmaz, How to cripple SARS-COV-2 virus with ozone treatment Thiol groups in viruses and SARS-COV-2. £rd WorldConference on Traditional and Complementary Medicine. Scheduled December 10-11 in Dubai, UAE (now Webinar due to COVID-19 restrictions
Esmaily, Sahebkar, Iranshahi, Ganjali, Mohammadi et al., An investigation of the effects of curcumin on anxiety and depression in obese individuals: a randomized controlled trial, Chin J Integr Med
Estébanez, Pérez-Santiago, Silva, Guillen-Climent, García-Vázquez et al., Cutaneous manifestations in COVID-19: a new contribution, J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol
Evans, Rainger, Mason, Guzik, Osto et al., Endothelial dysfunction in COVID-19: a position paper of the ESC Working 17 Statin Use and COVID-19 group for atherosclerosis and vascular biology, and the ESC council of basic cardiovascular science, Cardiovasc Res
Falony, Joossens, Vieira-Silva, Wang, Darzi et al., Population-level analysis of gut microbiome variation, Science
Fan, Chong, Chan, Lim, Lim et al., Hematologic parameters in patients with COVID-19 infection, Am J Hematol, doi:10.1002/ajh.25774
Fan, Lei, Fang, Li, Wang et al., Perinatal transmission of COVID-19 associated SARS-CoV-2: should we worry?, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa226
Fan, Pedersen, Gut microbiota in human metabolic health and disease, Nat Rev Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41579-020-0433-9
Fang, Zhang, Xie, Lin, Ying et al., Sensitivity of chest CT for COVID-19: comparison to RT-PCR, Radiology
Farag, Deal, Mckinney, Thorp, Senior et al., Single-blind randomized controlled trial of surfactant vs hypertonic saline irrigation following endoscopic endonasal surgery, Int Forum Allergy Rhinol
Farazi, Sofian, Jabbariasl, Nayebzadeh, Coenzyme Q10 administration in communityacquired pneumonia in the elderly, Iran Red Crescent Med J, doi:10.5812/ircmj.18852.
Farrell, Klatt-Cromwell, Schneider, Benefits and safety of nasal saline irrigations in a pandemic-washing COVID-19 away, JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg
Fatima, Zaidi, Amraiz, Afzal, In vitro antiviral activity of Cinnamomum cassia and its nanoparticles against H7N3 influenza a virus, J Microbiol Biotechnol
Fazekas, Eickhoff, Pruckner, Vollnhofer, Fischmeister et al., Lessons learned from a double-blind randomised placebocontrolled study with a iota-carrageenan nasal spray as medical device in children with acute symptoms of common cold, BMC Complement Altern Med, doi:10.1186/1472-6882-12-147
Fedson, Treating the host response to emerging virus diseases: lesson learned from sepsis, pneumonia, influenza and Ebola, Ann Translat Med, doi:10.21037/atm.2016.11.03
Feng, Liu, Lv, Zhong, A case report of COVID-19 with false negative RT-PCR test: necessity of chest CT, Jpn J Radiol
Fenizia, Biasin, Cetin, Vergani, Mileto et al., Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 vertical transmission during pregnancy, Nat Commun
Ferigato, Fernandez, Amorim, Ambrogi, Fernandes et al., The Brazilian Government's mistakes in responding to the COVID-19 pandemic, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32164-4
Fernandez, Manuel, Obesity, respiratory disease and pulmonary infections, Ann Res Hosp
Fernandez-Nieto, Ortega-Quijano, Segurado-Miravalles, Pindado-Ortega, Prieto-Barrios et al., Cutaneous manifestations in COVID-19: a first perspective. Safety concerns of clinical images and skin biopsies, J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol
Fernández-Ayala, Navas, López-Lluch, Age-related mitochondrial dysfunction as a key factor in COVID-19 disease, Exp Gerontol
Ferreira, Castro, Guatimosim, Almeida, Gomes et al., Attenuation of isoproterenol-induced cardiac fibrosis in transgenic rats harboring an angiotensin-(1-7)-producing fusion protein in the heart, Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis
Figuero, Herrera, Tobías, Serrano, Roldán et al., Efficacy of adjunctive anti-plaque chemical agents in managing gingivitis: a systematic review and network meta-analyses, J Clin Periodontol
Fini, Oral saliva and COVID-19, Oral Oncol, doi:10.1016/j.oraloncology.2020.104821
Fink, Klein, Sex and gender impact immune responses to vaccines among the elderly, Physiology
Fischer, Hoffmann, Voelkl, Meidenbauer, Ammer et al., Inhibitory effect of tumor cell-derived lactic acid on human T cells, Blood
Fish, The X-files in immunity: sex-based differences predispose immune responses, Nat Rev Immunol
Fisher, Neugarten, Bellin, Yunes, Stahl et al., AKI in hospitalized patients with and without COVID-19: a comparison study, J Am Soc Nephrol
Flacco, Martellucci, Bravi, Parruti, Cappadona, Treatment with ACE inhibitors or ARBs and risk of severe/lethal COVID-19: a meta-analysis, Heart
Flanagan, Fink, Plebanski, Klein, Sex and gender differences in the outcomes of vaccination over the life course, Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol
Flaxman, Mishra, Gandy, Hjt, Mellan, Imperial College COVID-19 Response Team et al (2020) Estimating the effects of non-pharmaceutical interventions on COVID-19 in Europe, Nature
Flaxman, Mishra, Gandy, Hjt, Mellan, Imperial College COVID-19 Response Team et al (2020) Estimating the effects of non-pharmaceutical interventions on COVID-19 in Europe, Nature
Fogarty, Townsend, Cheallaigh, Bergin, Martin-Loeches et al., COVID-19 Coagulopathy in caucasian patients, Br J Haematol
Frank, Brown, Capriotti, Westover, Pelletier et al., In vitro efficacy of a povidone-iodine nasal Antiseptic for rapid inactivation of SARS-CoV-2, JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, doi:10.1001/jamaoto.2020.3053
Frank, Capriotti, Brown, Tessema, Povidone-iodine use in sinonasal and oral cavities: a review of safety in the COVID-19 era, Ear Nose Throat J
Frater, Zini, Onofrio, Rogers, COVID-19 and the clinical hematology laboratory, Int J Lab Hematol
Friedland, Virucidal pilot study of Nasodine® Antiseptic Nasal Spray (povidoneiodine 0.5%) in people with COVID-19 and confirmed nasal shedding of SARS-CoV-2 virus
Friedman, Kozlitina, Genovese, Jog, Pollak, Population-based risk assessment of APOL1 on renal disease, J Am Soc Nephrol
Friedman, Pollak, Apolipoprotein L1 and kidney disease in African Americans, Trends Endocrinol Metab
Fromm-Dornieden, Rembe, Schäfer, Böhm, Stuermer, Cetylpyridinium chloride and miramistin as antiseptic substances in chronic wound management -prospects and limitations, J Med Microbiol
Fu, Zhou, Zhang, Balaji, Wei et al., Expressions and significances of the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 gene, the receptor of SARS-CoV-2 for COVID-19, Mol Biol Rep
Furuta, Komeno, Nakamura, Favipiravir (T-705), a broad spectrum inhibitor of viral RNA polymerase, Proc Jpn Acad Ser B
Gabarre, Dumas, Dupont, Darmon, Azoulay et al., Acute kidney injury in critically ill patients with COVID-19, Intensive Care Med
Gadi, Wu, Spihlman, Moulton, What's sex got to do with COVID-19? Genderbased differences in the host immune response to coronaviruses, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.0214
Galbadage, Peterson, Awada, Buck, Ramirez, Systematic review and meta-analysis of sex-specific COVID-19 clinical outcomes, Front Med (Lausanne), doi:10.3389/fmed.2020.00348
Galoforo, Scassellati, Bonvicini, Coronavirus: Dall' Ozono una possibile soluzione? Il Popolo Veneto
Gameiro, Romao, Changes in the immune system during menopause and aging, Front Biosci (Elite Ed)
Gao, Cai, Zhang, Zhou, Zhang, Association of hypertension and antihypertensive treatment with COVID-19 mortality: a retrospective observational study, Eur Heart J
Gao, Hu, Zhang, Li, Zhu et al., Highly pathogenic coronavirus N protein aggravates lung injury by MASP-2-mediated complement over-activation, doi:10.1101/2020.03.29.20041962
Gao, Jiang, Wen, Cheng, Sun et al., Prognostic value of NT-proBNP in patients with severe COVID-19, Respir Res, doi:10.1186/s12931-020-01352-w
Gautier-Vargas, Baldacini, Benotmane, Keller, Perrin et al., Thrombotic microangiopathy in a patient with COVID-19, Kidney Int
Geleris, Sun, Platt, Zucker, Baldwin et al., Observational study of hydroxychloroquine in hospitalized patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Genovese, Colonna, Marzano, Varicella-like exanthem associated with COVID-19 in an 8-year-old girl: a diagnostic clue?, Pediatr Dermatol
Gentles, Guth, Rozins, Brook, A review of mechanistic models of viral dynamics in bat reservoirs for zoonotic disease, Pathog Glob Health, doi:10.1080/20477724.2020.1833161
George, Brandenburg, Fabian, Crowther, Agongo et al., Kidney damage and associated risk factors in rural and urban sub-Saharan Africa (AWI-Gen): a cross-sectional population study, Lancet Glob Health
Gera, Sharma, Ghosh, Huynh, Lee, Nanoformulations of curcumin: an emerging paradigm for improved remedial application, Oncotarget
Gern, Mosser, Swenson, Rennie, England et al., Inhibition of rhinovirus replication in vitro and in vivo by acidbuffered saline, J Infect Dis
Ghosh, Dellibovi-Ragheb, Kerviel, Pak, Qiu et al., ) β-Coronaviruses use lysosomes for egress instead of the biosynthetic secretory pathway, Cell S, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.10.039
Giannis, Ziogas, Gianni, Coagulation disorders in coronavirus infected patients: COVID-19, SARS-CoV-1, MERS-CoV and lessons from the past, J Clin Virol, doi:10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104362
Giannouchos, Sussman, Mier, Poulas, Farsalinos, Characteristics and risk factors for COVID-19 diagnosis and adverse outcomes in Mexico: an analysis of 89,756 laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 cases, Eur Respir J, doi:10.1183/13993003.02144-2020
Gianotti, Veraldi, Recalcati, Cusini, Ghislanzoni et al., Cutaneous clinico-pathological findings in three covid-19-positive patients observed in the metropolitan area of Milan, Italy, Acta Derm Venereol, doi:10.2340/00015555-3490
Giefing-Kröll, Berger, Lepperdinger, Grubeck-Loebenstein, How sex and age affect immune responses, susceptibility to infections, and response to vaccination, Aging Cell
Girón-González, Moral, Elvira, García-Gil, Guerrero et al., Consistent production of a higher TH1:TH2 cytokine ratio by stimulated T cells in men compared with women, Eur J Endocrinol
Gisondi, Piaserico, Bordin, Alaibac, Girolomoni, Cutaneous manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 infection: a clinical update, J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol, doi:10.1111/jdv.16774
Glende, Pfefferle, Drosten, Schwegmann-Weßels, Herrler, Lipid microdomains are important for the entry process of SARS coronavirus to target cells, FASEB J
Goebel, Hsue, Dombrowski, Masters, Characterization of the RNA components of a putative molecular switch in the 3′ untranslated region of the murine coronavirus genome, J Virol
Goicoechea, Cámara, Macías, De Morales, Rojas et al., COVID-19: clinical course and outcomes of 36 hemodialysis patients in Spain, Kidney Int
Golmai, Larsen, Devita, Wahl, Weins et al., Histopathologic and ultrastructural findings in postmortem kidney biopsy material in 12 patients with AKI and COVID-19, J Am Soc Nephrol
Gomez-Arango, Barrett, Mcintyre, Callaway, Morrison et al., Increased systolic and diastolic blood pressure is associated with altered gut microbiota composition and butyrate production in early pregnancy, Hypertension
Gorbalenya, Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus -the species and its viruses, a statement of the Coronavirus Study Group, BioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.02.07.937862
Gordon, Tchesnokov, Woolner, Perry, Feng et al., Remdesivir is a direct-acting antiviral that inhibits RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 with high potency, J Biol Chem
Goshayeshi, Milani, Bergqueist, Sadrzadeh, Rajabzadeh et al., Covid-19 infection without respiratory symptoms: case report of diagnosing a 14 year-old patient with acute abdomen, Res Sq, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-27389/v1
Goshayeshi, Rad, Bergquist, Allahyari, Hoseini, Demographic and clinical characteristics of the severe Covid-19 infections: first report from, Iran. medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.05.20.20108068
Goto, Sagitani, Ashida, Kato, Hirota et al., Anti-influenza virus effects of both live and non-live Lactobacillus acidophilus L-92 accompanied by the activation of innate immunity, Br J Nutr
Gottlieb, Long, Dermatologic manifestations and complications of COVID-19, Am J Emerg Med
Gottsauner, Michaelides, Schmidt, Scholz, Buchalla et al., A prospective clinical pilot study on the effects of a hydrogen peroxide mouthrinse on the intraoral viral load of SARS-CoV-2, Clin Oral Investig
Goyal, Chander, Yezli, Otter, Evaluating the virucidal efficacy of hydrogen peroxide vapour, J Hosp Infect
Graneheim, Lundman, Qualitative content analysis in nursing research: concepts, procedures and measures to achieve trustworthiness, Nurse Educ Today
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Baggerly, French et al., Evidence that vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of influenza and COVID-19 infection and deaths, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12040988
Grassauer, Weinmuellner, Meier, Pretsch, Prieschl-Grassauer et al., Iota-Carrageenan is a potent inhibitor of rhinovirus infection, Virol J, doi:10.1186/1743-422X-5-107
Grasselli, Greco, Zanella, Risk factors associated with mortality among patients with COVID-19 in intensive care units in Lombardy, Italy, JAMA Intern Med
Grasselli, Zangrillo, Zanella, Antonelli, Cabrini et al., Baseline charac-P. B. Rodrigues et al. teristics and outcomes of 1591 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 admitted to ICUs of the Lombardy Region, JAMA
Greenhalgh, Koh, Choon, Car, Covid-19: a remote assessment in primary care, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.m1182
Griffin, Cabot, Wallwork, Panizza, Alternative therapies for chronic rhinosinusitis: a review, Ear Nose Throat J
Groneberg, Hilgenfeld, Zabel, Molecular mechanisms of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), Respir Res, doi:10.1186/1465-9921-6-8
Gruenwald, Freder, Armbruester, Cinnamon and health, Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr
Gu, Chen, Wu, Gao, Lv et al., Alterations of the gut microbiota in patients with COVID-19 or H1N1 influenza, Clin Infect Dis:ciaa, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa709
Guan, Ni, Hu, Liang, Ou et al., Clinical characteristics of 2019 novel coronavirus infection in China, N Engl J Med
Guan, Ni, Hu, Liang, Ou et al., Clinical characteristics of 2019 novel coronavirus infection in China, N Engl J Med
Guan, Ni, Hu, Liang, Ou et al., Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China, N Engl J Med
Guan, Ni, Hu, Liang, Ou et al., Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China, N Engl J Med
Guarner, Three emerging coronaviruses in two decades, Am J Clin Pathol
Guglielmi, Fast coronavirus tests are coming, Nature
Guillin, Vindry, Ohlmann, Chavatte, Selenium, selenoproteins and viral infection, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu11092101
Guo, Cao, Hong, Tan, Chen et al., The origin, transmission and clinical therapies on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak -an update on the status, Mil Med Res, doi:10.1186/s40779-020-00240-0
Guo, Cao, Hong, Tan, Chen et al., The origin, transmission and clinical therapies on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak -an update on the status, Mil Med Res, doi:10.1186/s40779-020-00240-0
Guo, Cao, Hong, Tan, Chen, The origin, transmission and clinical therapies on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak -An update on the status, Mil Med Res, doi:10.1186/s40779-020-00240-0
Gupta, Madhavan, Poterucha, Defilippis, Parikh, Association between antecedent statin use and decreased mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, Res Sq, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-56210/v1.1
Gupta, Madhavan, Sehgal, Nair, Mahajan et al., Extrapulmonary manifestations of COVID-19, Nat Med
Gupta, Madhavan, Sehgal, Nair, Mahajan et al., Extrapulmonary manifestations of COVID-19, Nat Med
Gurung, Li, You, Rodrigues, Jump et al., Role of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes pathophysiology, Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.11.051
Gustafson, Raju, Wu, Ching, Veitch et al., Overcoming barriers: the endothelium as a linchpin of coronavirus disease 2019 pathogenesis?, Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol
Guzmán-Flores, Briones, Cells of innate and adaptive immunity in type 2 diabetes and obesity, Gac Med Mex
Gvozdjakova, Klauco, Kucharska, Sumbalova, Is mitochondrial bioenergetics and coenzyme Q10 the target of a virus causing COVID-19?, Bratisl Lek Listy
Hajiahmadi, Yegdaneh, Homayoni, Parishani, Moshkelgosha et al., Comparative evaluation of efficacy of "green tea" and "green tea with xylitol" mouthwashes on the salivary streptococcus mutans and lactobacillus colony count in children: a randomized clinical trial, J Contemp Dent Pract
Hamada, Torre, Drancourt, Ghigo, Trained immunity carried by non-immune cells, Front Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2018.03225
Hamming, Cooper, Haagmans, Hooper, Korstanje et al., The emerging role of ACE2 in physiology and disease, J Pathol
Hamming, Timens, Bulthuis, Lely, Navis et al., Tissue distribution of ACE2 protein, the functional receptor for SARS coronavirus. A first step in understanding SARS pathogenesis, J Pathol
Hamming, Timens, Bulthuis, Lely, Navis et al., Tissue distribution of ACE2 protein, the functional receptor for SARS coronavirus. A first step in understanding SARS pathogenesis, J Pathol
Hamosh, Bioactive factors in human milk, Pediatr Clin N Am
Han, Xu, Guo, Huang, Curcumin ameliorates severe influenza pneumonia via attenuating lung injury and regulating macrophage cytokines production, Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol
Hansell, Bankier, Macmahon, Mcloud, Muller, Fleischner Society: glossary of terms for thoracic imaging, Radiology
Hanson, Breastfeeding provides passive and likely long-lasting active immunity, Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol
Hao, Cheng, Wu, Wu, Lin et al., Reconstruction of the full transmission dynamics of COVID-19 in Wuhan, Nature
Hao, Yan, Zhang, Lian, Cai et al., Interferon-alpha2b spray inhalation did not shorten virus shedding time of SARS-CoV-2 in hospitalized patients: a preliminary matched casecontrol study, J Zhejiang Univ Sci B
Harada, Yano S, Pharmacological studies on Chinese cinnamon. II. Effects of cinnamaldehyde on the cardiovascular and digestive systems, Chem Pharm Bull
Harata, He, Hiruta, Kawase, Kubota et al., Intranasal administration of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG protects mice from H1N1 influenza virus infection by regulating respiratory immune responses, Lett Appl Microbiol
Harding, Siefker, Vu Dinh, You, Devincenzo et al., Altered gut microbiota in infants is associated with respiratory syncytial virus disease severity, BMC Microbiol, doi:10.1186/s12866-020-01816-5
Hargreaves, Duncan, Heales, Land, The effect of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors on coenzyme Q10: possible biochemical/clinical implications, Drug Saf
Hargreaves, Mantle, Supplementation with selenium and coenzyme Q10 in critically ill patients, Br J Hosp Med
Hargreaves, Ubiquinone: cholesterol's reclusive cousin, Ann Clin Biochem
He, Lau, Wu, Deng, Wang et al., Temporal synamics in viral shedding and transmissibility of COVID-19, Nat Med
He, Luo, Lei, Fan, Shao et al., Risk factors for severe cases of COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study, Aging (Albany NY)
Heaton, Heales, Rahman, Sexton, Hargreaves, The effect of cellular coenzyme Q(10) deficiency on lysosomal acidification, J Clin Med, doi:10.3390/jcm9061923
Heemskerk, Sage, Calcium signalling in platelets and other cells, Platelets
Hemming, Viral respiratory diseases in children: classification, etiology, epidemiology, and risk factors, J Pediatr
Henry, Ackerman, Sancelme, Finon, Esteve, Urticarial eruption in COVID-19 infection, J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol
Henry, Oliveira, Preliminary epidemiological analysis on children and adolescents with novel coronavirus disease 2019 outside Hubei Province, China: an observational study utilizing crowd sourced data, doi:10.1101/2020.03.01.20029884
Her, Venier-Julienne, Improvement of curcumin bioavailability for medical applications, Med Aromat Plants (Los Angel), doi:10.4172/2167-0412.1000326
Hernández, Calunga, Turrent, Menéndez, Montenegro, Ozone therapy effects on biomarkers and lung function in asthma, Arch Med Res
Herrera, Serrano, Roldán, Sanz, Is the oral cavity relevant in SARS-CoV-2 pandemic?, Clin Oral Investig
Hewlings, Kalman, Curcumin: a review of its' effects on human health, Foods, doi:10.3390/foods6100092
Higgins, Wu, Illing, Sokoloski, Weaver et al., Intranasal antiviral drug delivery and coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a state of the art review, Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg
Hirose, Ikegaya, Naito, Watanabe, Yoshida et al., Survival of SARS-CoV-2 and influenza virus on the human skin: importance of hand hygiene in COVID-19, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa1517
Hirsch, Ng, Ross, Sharma, Shah et al., Acute kidney injury in patients hospitalized with COVID-19, Kidney Int
Ho, Alhazzani, Alhuraiji, Coomes, Chemaly et al., A practical approach to the management of cancer patients during the novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic: an international collaborative group, The Oncologist
Ho, Chang, Chang, Inhibition of neuroinflammation by cinnamon and its main components, Food Chem
Hoel, Heggelund, Reikvam, Stiksrud, Ueland et al., Elevated markers of gut leakage and inflammasome activation in COVID-19 patients with cardiac involvement, J Intern Med, doi:10.1111/joim.13178
Hoffmann, Kleine-Weber, Krueger, Mueller, Drosten et al., The novel coronavirus 2019 (2019-nCoV) uses the SARScoronavirus receptor ACE2 and the cellular protease TMPRSS2 for entry into target cells, BioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.01.31.929042v1
Hofmann, Geier, Marzi, Krumbiegel, Peipp et al., Susceptibility to SARS coronavirus S protein-driven infection correlates with expression of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 and infection can be blocked by soluble receptor, Biochem Biophys Res Commun
Hofmann, Pyrc, Van Der Hoek, Geier, Berkhout et al., Human coronavirus NL63 employs the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus receptor for cellular entry, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
Holcar, Goropevšek, Ihan, Avčin, Age-related differences in percentages of regulatory and effector T lymphocytes and their subsets in healthy individuals and characteristic STAT1/ STAT5 signalling response in helper T lymphocytes, J Immunol Res, doi:10.1155/2015/352934
Holloway, Galvin, Qualitative research in nursing and healthcare, 4th edn
Holmes, Coronaviruses
Holshue, Debolt, Lindquist, Lofy, Wiesman et al., First Case of 2019 Novel Coronavirus in the United States, N Engl J Med
Holshue, Debolt, Lindquist, Lofy, Wiesman et al., First case of 2019 novel coronavirus in the United States, N Engl J Med
Hsiang, Allen, Annan-Phan, Bell, Bollinger et al., The effect of large-scale anti-contagion policies on the COVID-19 pandemic, Nature
Hsieh, Shannon, Three approaches to qualitative content analysis, Qual Health Res
Hsue, None
Hsue, None
Hu, Huang, Yin, The cytokine storm and COVID-19, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.26232
Hu, Wang, Wang, Langley, Liu, Prediction of influenza-like illness based on the improved artificial tree algorithm and artificial neural network, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-018-23075-1
Huang, Lee, Hsiao, Hospitalization for ambulatory-care-sensitive conditions in Taiwan following the SARS outbreak: a population-based interrupted time series study, J Formos Med Assoc
Huang, Liu, Huang, Liu, Lei et al., Use of chest CT in combination with negative RT-PCR assay for the 2019 novel coronavirus but high clinical suspicion, Radiology
Huang, Rose, Hoffmann, The role of selenium in inflammation and immunity: from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic opportunities, Antioxid Redox Signal
Huang, Su, Tien, Huang, Lan et al., Epidemiology of human coronavirus NL63 infection among hospitalized patients with pneumonia in Taiwan, J Microbiol Immunol Infect
Huang, Wang, Li, Ren, Zhao et al., Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, Lancet
Huang, Wang, Li, Ren, Zhao et al., Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, Lancet
Huang, Wang, Li, Ren, Zhao et al., Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, Lancet
Huang, Wang, Li, Ren, Zhao et al., Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, Lancet
Huang, Wang, Luo, Xie, Shi, Cinnamaldehyde reduction of platelet aggregation and thrombosis in rodents, Thromb Res
Huang, Zhang, Chen, Zhang, Wei, Clinical characteristics of COVID-19 in patients with preexisting ILD: a retrospective study in a single center in Wuhan, China. J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.26174
Hudson, Sharma, Petric, Inactivation of norovirus by ozone gas in conditions relevant to healthcare, J Hosp Infect
Hudson, Sharma, Vimalanathan, Development of a practical method for using ozone gas as a virus decontaminating agent, Ozone Sci Eng
Hydroxychloroquine, Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed)
Ichinohe, Pang, Kumamoto, Peaper, Ho et al., Microbiota regulates immune defense against respiratory tract influenza A virus infection, Proc Natl Acad Sci
Ilyas, Katare, Aeri, Naseef, A review on hepatoprotective and immunomodulatory herbal plants, Pharmacogn Rev
Imai, Kuba, Rao, Huan, Guo et al., Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 protects from severe acute lung failure, Nature
Infante-Duarte, Kamradt, Th1/Th2 balance in infection, Springer Semin Immunopathol
Iranshahi, Sahebkar, Hosseini, Takasaki, Konoshima et al., Cancer chemopreventive activity of diversin from Ferula diversivittata in vitro and in vivo, Phytomedicine
Isaacs, Fakhri, Luong, Whited, Citardi, The effect of dilute baby shampoo on nasal mucociliary clearance in healthy subjects, Am J Rhinol Allergy, doi:10.2500/ajra.2011.25.3583
Iser, Sliva, Raymundo, Poleto, Schuelter-Trevisol et al., None
Israel, Schaffer, Cicurel, Feldhamer, Tal et al., Large population study identifies drugs associated with reduced COVID 19 severity, doi:10.1101/2020.10.13.20211953
Jaafar, Ho, Lee, Rooming-in for new mother and infant versus separate care for increasing the duration of breastfeeding, Cochrane Database Syst Rev, doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006641.pub2
Jackson, Anderson, Rouphael, Roberts, Makhene et al., An mRNA P. C. Guest and S. E. Ozanne vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 -preliminary report, N Engl J Med
Jacobi, Chung, Bernheim, Eber, Portable chest X-ray in coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19): a pictorial review, Clin Imaging
Jakhetia, Patel, Khatri, Pahuja, Garg et al., Cinnamon: a pharmacological review, J Adv Sci Res
Jalali, Nasiri, Abedi, Patients and family members' experiences regarding receiving bad news from health providers, Iran J Med Ethics Hist Med
Jambhekar, Breen, Cyclodextrins in pharmaceutical formulations I: structure and physicochemical properties, formation of complexes, and types of complex, Drug Discov Today
Jaramillo, Vendruscolo, Fülber, Seidel, Barbosa et al., Effects of transrectal medicinal ozone in horses-clinical and laboratory aspects, Arq Bras Med Vet Zootec
Jardim, Dias, Grande, 'keeffe, Dazzan et al., COVID-19 experience among Brasil's indigenous people, Rev Assoc Med Bras
Jassim, Whitford, Understanding the experiences and quality of life issues of Bahraini women with breast cancer, Soc Sci Med
Java, Apicelli, Liszewski, Coler-Reilly, Atkinson et al., The complement system in COVID-19: friend and foe?, JCI Insight, doi:10.1172/jci.insight.140711
Java, Apicelli, Liszewski, Coler-Reilly, Atkinson et al., The complement system in COVID-19: friend and foe?, JCI Insight, doi:10.1172/jci.insight.140711
Jennings, Parks, Curcumin as an antiviral agent, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v12111242
Jeong, Ryu, Park, Kim, Kwon et al., Neuraminidase inhibitory activities of flavonols isolated from Rhodiola rosea roots and their in vitro anti-influenza viral activities, Bioorg Med Chem
Jia, Kamceva, Rao, Linos, Cutaneous manifestations of COVID-19: a preliminary review, J Am Acad Dermatol
Jiang, Chin, Tsui, A universal deep learning approach for modeling the flow of patients under different severities, Comput Methods Prog Biomed
Jiang, Han, Song, Xue, Zhang et al., Efficacy and safety of aerosol inhalation of recombinant human interferon α1b (IFNα1b) injection for noninfluenza viral pneumonia, a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebocontrolled trial, J Inflamm (Lond), doi:10.1186/s12950-020-00249-1
Jin, Cai, Cheng, Cheng, Deng et al., A rapid advice guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) infected pneumonia (standard version), Mil Med Res, doi:10.1186/s40779-020-0233-6
Jin, Lian, Hu, Gao, Zheng et al., Epidemiological, clinical and virological characteristics of 74 cases of coronavirus-infected disease 2019 (COVID-19) with gastrointestinal symptoms, Gut
Jo, Kim, Kim, Shin, Kim, Characteristics of flavonoids as potent MERS-CoV 3C-like protease inhibitors, Chem Biol Drug Des
Johnson, Mukhtar, Curcumin for chemoprevention of colon cancer, Cancer Lett
Joob, Wiwanitkit, COVID-19 can present with a rash and be mistaken for dengue, J Am Acad Dermatol, doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.03.036
Jose, Manuel, COVID-19 cytokine storm: the interplay between inflammation and coagulation, Lancet Respir Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30216-2
Jung, Lim, Kang, Kim, Lee et al., Outcomes of COVID-19 among patients on in-center hemodialysis: an experience from the epicenter in South Korea, J Clin Med, doi:10.3390/jcm9061688
Kabashima, Honda, Ginhoux, Egawa, The immunological anatomy of the skin, Nat Rev Immunol
Kadel, Kovats, Sex hormones regulate innate immune cells and promote sex differences in respiratory virus infection, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2018.01653
Kakarala, Brenner, Korkaya, Cheng, Tazi et al., Targeting breast stem cells with the cancer preventive compounds curcumin and piperine, Breast Cancer Res Treat
Kalén, Appelkvist, Dallner, Agerelated changes in the lipid compositions of rat and human tissues, Lipids
Kampf, Todt, Pfaender, Steinmann, Persistence of coronaviruses on inanimate surfaces and their inactivation with biocidal agents, J Hosp Infect
Kanda, Tamaki, Estrogen enhances immunoglobulin production by human PBMCs, J Allergy Clin Immunol
Kanjanaumporn, Aeumjaturapat, Snidvongs, Seresirikachorn, Chusakul, Smell and taste dysfunction in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: a review of epidemiology, pathogenesis, prognosis, and treatment options, Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol
Kanjanawasee, Seresirikachorn, Chitsuthipakorn, Snidvongs, Hypertonic saline versus isotonic saline nasal irrigation: systematic review and meta-analysis, Am J Rhinol Allergy
Kanwar, Kumar, Ng-Wong, Thakur, Cadnum et al., Evaluation of an alcohol-based antiseptic for nasal decolonization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in colonized patients, Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol
Karimi, None
Karimi, Sadeghi, Maleki-Saghooni, Khadivzadeh, The effect of mother-infant skin to skin contact on success and duration of first breastfeeding: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Kariwa, Fujii, Takashima, Inactivation of SARS coronavirus by means of povidoneiodine, physical conditions and chemical reagents, Dermatology
Kasembeli, Duarte, Ramsay, Mosiane, Dickens et al., APOL1 risk variants are strongly associated with HIV-associated nephropathy in Black South Africans, J Am Soc Nephrol
Kassaa, New insights on antiviral probiotics: from research to applications
Kawahara, Takahashi, Oishi, Tanaka, Masuda et al., Consecutive oral administration of Bifidobacterium longum MM-2 improves the defense system against influenza virus infection by enhancing natural killer cell activity in a murine model, Microbiol Immunol
Kawase, He, Kubota, Harata, Hiramatsu, Oral administration of lactobacilli from human intestinal tract protects mice against influenza virus infection, Lett Appl Microbiol
Kazazian, Woodhead, Hemoglobin A synthesis in the developing fetus, N Engl J Med
Keech, Albert, Cho, Robertson, Reed et al., Phase 1-2 trial of a SARS-CoV-2 recombinant spike protein nanoparticle vaccine, N Engl J Med. NEJMoa, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2026920
Keidar, Strizevsky, Raz, Gamliel-Lazarovich, ACE2 activity is increased in monocytederived macrophages from prehypertensive subjects, Nephrol Dial Transplant
Keil, Bengrine, Bowen, Marschner, Hovenga et al., Inactivation of viruses in platelet and plasma products using a riboflavin-and-UV-based photochemical treatment, Transfusion
Keil, Bowen, Marschner, Inactivation of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) in plasma products using a riboflavinbased and ultraviolet light-based photochemical treatment, Transfusion
Keil, Ragan, Yonemura, Hartson, Dart et al., Inactivation of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 in plasma and platelet products using a riboflavin and ultraviolet light-based photochemical treatment, Vox Sang
Kejner, Povidone-iodine intranasal for prophylaxis in front-line health-care personnel and inpatients during the sars-CoV-2 pandemic
Kelekci, Sen, Yolbas, Uluca, Tan et al., The relationships between clinical outcome and the levels of total antioxidant capacity and CoQ10 in children with pandemic influenza (H1N1) and seasonal flu, Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci
Kelly, Karesh, Johnson, Gilardi, Anthony et al., One Health proof of concept: bringing a transdisciplinary approach to surveillance for zoonotic viruses at the human-wild animal interface, Prev Vet Med
Kelvin, Rubino, Fear of the novel coronavirus, J Infect Dev Ctries
Khalil, Kalafat, Benlioglu, 'brien, Morris et al., SARS-CoV-2 infection in pregnancy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical features and pregnancy outcomes, EClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100446
Khan, A clinical trial of gargling agents in reducing intraoral viral load among COVID-19 patients (GARGLES)
Khan, Vesel, Bahl, Martines, Timing of breastfeeding initiation and exclusivity of breastfeeding during the first month of life: effects on neonatal mortality and morbidity-A systematic review and meta-analysis, Matern Child Health J
Khansari, Saeedinejad, Raoofi, Gooshki, Psychological experiences of women with breast cancer after passing through the critical stage; a qualitative study, Iran Q J Breast Diseas
Kim, Garg, 'halloran, Whitaker, Pham et al., Risk factors for intensive care unit admission and in-hospital mortality among hospitalized adults identified through the U.S. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)-associated hospitalization surveillance network (COVID-NET), doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa1012
Kim, Kim, Kim, Kim, Jung et al., Suppression of age-related inflammatory NF-κB activation by cinnamaldehyde, Biogerontology
Kim, Koo, Koo, Ngoc, Kang et al., Platelet anti-aggregation activities of compounds from Cinnamomum cassia, J Med Food
Kim, Ku, Bae, Anticoagulant activities of curcumin and its derivative, BMB Rep
Kim, Rimmer, Mrad, Ahmadzada, Harvey, Betadine has a ciliotoxic effect on ciliated human respiratory cells, J Laryngol Otol
Kimura, Freeman, Wessinger, Gupta, Sheng et al., Interim analysis of an open-label randomized controlled trial evaluating nasal irrigations in non-hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease, Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, doi:10.1002/alr.22703
Kimura, Impact of nasal saline irrigations on viral load in patients with COVID
Kirk-Bayley, A pilot study of the ability of povidone-iodine (PVP-I) 0•5% aqueous solution oral/nasal spray and mouthwash to kill the SARS-CoV-2 virus
Klein, Flanagan, Sex differences in immune responses, Nat Rev Immunol
Kliegman, Behrman, Jenson, Stanton, Nelson textbook of pediatrics e-book
Klok, Kruip, Van Der Meer, Arbous, Gommers et al., Incidence of thrombotic complications in critically ill ICU patients with COVID-19, Thromb Res
Knapp, Diabetes and infection: is there a link? -a mini-review, Gerontology
Knight, Bunch, Vousden, Morris, Simpson et al., Characteristics and outcomes of pregnant women admitted to hospital with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection in UK: national population based cohort study, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.m2107
Koelsch, Tschaikin, Sacher, Anti-rhinovirus-specific activity of the alpha-sympathomimetic oxymetazoline, Arzneimittelforschung
Koenighofer, Lion, Bodenteich, Prieschl-Grassauer, Grassauer et al., Carrageenan nasal spray in virus confirmed common cold: individual patient data analysis of two randomized controlled trials, Multidiscip Respir Med, doi:10.1186/2049-6958-9-57
Koh, Dipietro, Inflammation and wound healing: the role of the macrophage, Expert Rev Mol Med, doi:10.1017/S1462399411001943
Kolivras, Dehavay, Delplace, Feoli, Meiers et al., Coronavirus (COVID-19) infection e induced chilblains: a case report with histopathologic findings
Komukai, Mochizuki, Yoshimura, Gender and the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, Fundam Clin Pharmacol
Koreck, Csoma, Bodai, Ignacz, Kenderessy et al., Rhinophototherapy: a new therapeutic tool for the management of allergic rhinitis, J Allergy Clin Immunol
Koreck, Szechenyi, Morocz, Cimpean, Bella et al., Effects of intranasal phototherapy on nasal mucosa in patients with allergic rhinitis, J Photochem Photobiol B
Korkina, Afanas, Ib, Antioxidant and chelating properties of flavonoids, Adv Pharmacol
Kow, Hasan, Meta-analysis of effect of statins on patients with COVID-19, Am J Cardiol
Kowalski, Romanowski, Yates, Mah, An independent evaluation of a novel peptide mimetic, Brilacidin (PMX30063), for ocular antiinfective, J Ocul Pharmacol Ther
Kratzel, Todt, 'kovski, Steiner, Gultom et al., Inactivation of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 by WHOrecommended hand rub formulations and alcohols, Emerg Infect Dis
Kraus, Perry, Nickerson, Salivary catalase and peroxidase values in normal subjects and in persons with periodontal disease, Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol
Krippendorff, Content analysis: an introduction to its methodology
Ksiazek, Erdman, Goldsmith, Zaki, Peret et al., A novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome, N Engl J Med
Kuba, Imai, Rao, Gao, Guo et al., A crucial role of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in SARS coronavirus-induced lung injury, Nat Med
Kudose, Batal, Santoriello, Xu, Barasch et al., Kidney biopsy findings in patients with COVID-19, J Am Soc Nephrol
Kumar, Management of infants born to mothers with COVID-19: initial guidance for pediatric hospitals
Kumar, Mishra, Dunn, Townsend, Oguadinma et al., Biocides and novel antimicrobial agents for the mitigation of coronaviruses, Front Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2020.01351
Kumru, Godekmerdan, Yılmaz, Immune effects of surgical menopause and estrogen replacement therapy in peri-menopausal women, J Reprod Immunol
Kunutsor, Laukkanen, Markers of liver injury and clinical outcomes in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis, J Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2020.05.045
Kunutsor, Laukkanen, Renal complications in COVID-19: a systematic review and metaanalysis, Ann Med
Kurkov, Loftsson, Cyclodextrins, Int J Pharm
Kurts, Panzer, Anders, Rees, The immune system and kidney disease: basic concepts and clinical implications, Nat Rev Immunol
Kuster, Pfister, Burkard, Zhou, Twerenbold et al., SARS-CoV2: should inhibitors of the renin-angiotensin system be withdrawn in patients with COVID-19?, Eur Heart J
Kutner, Nachtsheim, Neter, Li, Applied linear statistical models
Kwon, Oh, Kwon, Zhang, Fraser, Sulfated polysaccharides effectively inhibit SARS-CoV-2 in vitro, doi:10.1038/s41421-020-00192-8
Lai, Baric, Makino, Keck, Egbert et al., Recombination between nonsegmented RNA genomes of murine coronaviruses, J Virol
Lai, Cavanagh, The molecular biology of coronaviruses, Adv Virus Res
Lai, Recombination in large RNA viruses: coronaviruses, Semin Virol
Lai, Ruktanonchai, Zhou, Prosper, Luo et al., Effect of non-pharmaceutical interventions to contain COVID-19 in China, Nature
Lai, Shih, Ko, Tang, Hsueh, Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and corona virus disease-2019 (COVID-19): the epidemic and the challenges, Int J Antimicrob Agents, doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105924
Lai, Stohlman, Comparative analysis of RNA genomes of mouse hepatitis viruses, J Virol
Lai, Tang, Fung, Li, Reply to "does hand hygiene reduce SARS-CoV-2 transmission?, Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol, doi:10.1007/s00417-020-04653-4
Lalani, Poh, Flavonoids as antiviral agents for Enterovirus A71 (EV-A71), Viruses, doi:10.3390/v12020184
Lam, Chow, Vo, Hou, Li et al., Continued in-hospital angiotensinconverting enzyme inhibitor and angiotensin II receptor blocker use in hypertensive COVID-19 patients is associated with positive clinical outcome, J Infect Dis
Lam, Shum, Zhu, Tong, Ni et al., Identification of 2019-nCoV related coronaviruses in Malayan pangolins in southern China, BioRxiv
Lan, Ge, Yu, Shan, Zhou, Crystal structure of the 2019-nCoV spike receptorbinding domain bound with the ACE2 receptor, BioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.02.19.956235
Landa, Mendieta-Eckert, Aguirre, Chilblain-like lesions on feet and hands during the COVID-19 pandemic, Int J Dermatol
Lane, Anantpadma, Freundlich, Davey, Madrid et al., The natural product eugenol is an inhibitor of the ebola virus in vitro, Pharm Res, doi:10.1007/s11095-019-2629-0
Lang, Yang, Deng, Liu, Yang et al., Inhibition of SARS pseudovirus cell entry by lactoferrin binding to heparan sulfate proteoglycans, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0023710
Larsen, Bourne, Wilson, Saqqa, Collapsing glomerulopathy in a patient with COVID-19, Kidney Int Rep
Lauer, Grantz, Bi, Jones, Zheng et al., The incubation period of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) from publicly reported confirmed cases: estimation and application, Ann Intern Med
Lavezzo, Franchin, Ciavarella, Cuomo-Dannenburg, Barzon, Imperial College COVID-19 Response Team et al (2020) Suppression of a SARS-CoV-2 outbreak in the Italian municipality of Vo', Nature
Le, Andreadakis, Kumar, Roman, Tollefsen et al., The COVID-19 vaccine development landscape, Nat Rev Drug Discov
Le, Nguyen, Tran, Do, Tran et al., The first infant case of COVID-19 acquired from a secondary transmission in Vietnam, Lancet Child Adolesc Health
Lee, Hu, Chen, Huang, Hsueh, Are children less susceptible to COVID-19?, J Microbiol Immunol Infect
Lee, Hui, Wu, Chan, Cameron et al., A major outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome in Hong Kong, N Engl J Med
Lee, Kim, Cho, Lee, You et al., Effect of sex hormones on coronavirus disease 2019: an analysis of 5,061 laboratoryconfirmed cases in South Korea, Menopause, doi:10.1097/GME.0000000000001657
Lee, Yap, Chew, Quah, Prabhakaran et al., Age-and sex-related changes in lymphocyte subpopulations of healthy Asian subjects: from birth to adulthood, Cytometry
Leibbrandt, Meier, König-Schuster, Weinmüllner, Kalthoff et al., Iota-Carrageenan is a potent inhibitor of influenza a virus infection, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0014320
Leong, Rhinophototherapy: gimmick or an emerging treatment option for allergic rhinitis?, Rhinology
Leslie, Zhou, Macinga, Inactivation of SARS-CoV-2 by commercially available alcoholbased hand sanitizers, Am J Infect Control:S, doi:10.1016/j.ajic.2020.08.020
Li, Chest CT features and their role in COVID-19, Radiol Infect Dis
Li, Cui, Li, Fang, Li, Chest computed tomography in children with COVID-19 respiratory infection, Pediatr Radiol
Li, Guan, Wu, Wang, Zhou et al., Early transmission dynamics in Wuhan, China, of novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia, N Engl J Med
Li, Li, Zhang, Wang, An investigation of the expression of 2019 novel coronavirus cell receptor gene ACE2 in a wide variety of human tissues, Infect Dis Poverty, doi:10.1186/s40249-020-00662-x
Li, Liu, Yu, Tang, Tang, Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): current status and future perspectives, Int J Antimicrob Agents, doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105951
Li, Pei, Chen, Song, Zhang, Substantial undocumented infection facilitates the rapid dissemination of novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2), Science
Li, Qin, Xu, Yin, Wang et al., Artificial intelligence distinguishes COVID-19 from community acquired pneumonia on chest CT, Radiology, doi:10.1148/radiol.2020200905
Li, Wu, Wu, Guo, Chen et al., The clinical and chest CT features associated with severe and critical COVID-19 pneumonia, Investig Radiol, doi:10.1097/RLI.0000000000000672
Li, Yan, Zhai, Qi, Lei, Chest CT findings in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a comprehensive review, doi:10.5152/dir.2020.20212
Li, Zai, Zhao, Nie, Li et al., Evolutionary history, potential intermediate animal host, and cross-species analyses of SARS-CoV-2, J Med Virol
Li, Zeng, Li, Chen, Shi et al., CT imaging changes of corona virus disease 2019(COVID-19): a multi-center study in Southwest China, J Transl Med, doi:10.1186/s12967-020-02324-w
Li, Zhai, Jiang, Huang, Liu et al., Curcumin-piperine mixtures in selfmicroemulsifying drug delivery system for ulcerative colitis therapy, Int J Pharm
Li, Zhao, Wang, Chen, Tao et al., Gut microbiota dysbiosis contributes to the development of hypertension, Microbiome, doi:10.1186/s40168-016-0222-x
Li, Zhu, Research and development of next generation of antibody-based therapeutics, Acta Pharmacol Sin
Liao, Hsieh, Liu, Tzeng, Sun et al., Cinnamaldehyde inhibits the tumor necrosis factor-α-induced expression of cell adhesion molecules in endothelial cells by suppressing NF-κB activation: effects upon IκB and Nrf2, Toxicol Appl Pharmacol
Liao, Liang, Chen, Hsu, Yang et al., IL-19 induces production of IL-6 and TNF-alpha and results in cell apoptosis through TNF-alpha, J Immunol
Liao, Wang, Tan, Wei, Cinnamon extracts exert intrapancreatic cytoprotection against streptozotocin in vivo, Gene
Libby, Loscalzo, Ridker, Farkouh, Hsue et al., Inflammation, immunity, and infection in atherothrombosis: JACC review topic of the week, J Am Coll Cardiol
Lin, Tang, Wei, Dai, Sun, Xylitol nasal irrigation in the treatment of chronic rhinosinusitis, Am J Otolaryngol
Lindsley, Schwartz, Rothenberg, Mechanisms of allergic diseases Eosinophil responses during COVID-19 infections and coronavirus vaccination, J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol, doi:10.18176/jiaci.0624
Ling, Xu, Lin, Tian, Zhu et al., Persistence and clearance of viral RNA in 2019 novel coronavirus disease rehabilitation patients, Chin Med J
Lipkowitz, Freedman, Langefeld, Comeau, Bowden et al., Apolipoprotein L1 gene variants associate with hypertension-attributed nephropathy and the rate of kidney function decline in African Americans, Kidney Int
Lippi, Plebani, Laboratory abnormalities in patients with COVID-2019 infection, Clin Chem Lab Med
Lippi, Plebani, The critical role of laboratory medicine during coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and other viral outbreaks, Clin Chem Lab Med
Lippi, South, Henry, Electrolyte imbalances in patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Ann Clin Biochem
Liu, Chen, Viral metagenomics revealed sendai virus and coronavirus infection of malayan pangolins (Manis javanica), Viruses, doi:10.3390/v11110979
Liu, Cui, Zeng, Wang, Feng et al., Risk factors for developing into critical COVID-19 patients in Wuhan, China: a multicenter, retrospective, cohort study, EClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100471
Liu, Jiang, Hua, Wang, Hou et al., Are pangolins the intermediate host of the, Biorxiv, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1008421
Liu, Li, COVID-19: attacks the 1-beta chain of hemoglobin and captures the porphyrin to inhibit human heme metabolism
Liu, Ning, Chen, Guo, Liu et al., Aerodynamic analysis of SARS-CoV-2 in two Wuhan hospitals, Nature
Liu, Tao, Wang, Yuan, Liu et al., Analysis of factors associated with disease outcomes in hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus disease, Chin Med J
Liu, Xu, Lv, Qiu, Yao et al., CT manifestations of coronavirus disease-2019: a retrospective analysis of 73 cases by disease severity, Eur J Radiol, doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2020.108941
Liu, Yan, Wan, Xiang, Le et al., Viral dynamics in mild and severe cases of COVID-19, Lancet Infect Dis
Liu, Yang, Zhang, Huang, Wang et al., Clinical and biochemical indexes from 2019-nCoV infected patients linked to viral loads and lung injury, Sci China Life Sci
Liu, Zhang, COVID-19: face masks and human-to-human transmission, doi:10.1111/irv.12740
Liu, Zhang, Huang, Yang, Wang et al., 2019-novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) infections trigger an exaggerated cytokine response aggravating lung injury, ChinaXiv, doi:10.12074/202002.00018
Logunov, Dolzhikova, Zubkova, Tukhvatullin, Shcheblyakov et al., Safety and immunogenicity of an rAd26 and rAd5 vector-based heterologous primeboost COVID-19 vaccine in two formulations: two open, non-randomised phase 1/2 studies from Russia, Lancet
Long, Brady, Koyfman, Gottlieb, Cardiovascular complications in COVID-19, Am J Emerg Med
Long, Nie, Xiang, Li, Zhang et al., D-Dimer and Prothrombin Time Are the Significant Indicators of Severe COVID-19 and Poor Prognosis, Biomed Res Int
Lorizate, Kräusslich, Role of lipids in virus replication, Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol, doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a004820
Lorusso, Calistri, Petrini, Savini, Decaro, Novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) epidemic: a veterinary perspective, Vet Ital
Lovato, De Filippis, Clinical presentation of COVID-19: a systematic review focusing on upper airway symptoms, Ear Nose Throat J
Lu, Liu, Li, Gu, Piperine ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via modulating NF-κB signaling pathways, Inflammation
Lu, Liu, Tam, Lipid rafts are involved in SARS-CoV entry into Vero E6 cells, Biochem Biophys Res Commun
Lu, Shi, Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) and neonate: what neonatologist need to know, J Med Virol
Lu, Shi, Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) and neonate: what neonatologist need to know, J Med Virol
Lu, Zhang, Du, Zhang, Li et al., SARS-CoV-2 infection in children, N Engl J Med
Lu, Zhang, Du, Zhang, Li, Chinese Pediatric Novel Coronavirus Study T (2020) SARS-CoV-2 infection in children, N Engl J Med
Lu, Zhao, Li, Niu, Yang et al., Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: implications for virus origins and receptor binding, Lancet
Lu, Zhao, Li, Niu, Yang et al., Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: implications for virus origins and receptor binding, Lancet
Lu, Zhao, Li, Niu, Yang et al., Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: implications for virus origins and receptor binding, Lancet
Lu, Zhao, Li, Niu, Yang et al., Genomic characterisation and epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: implications for virus origins and receptor binding, Lancet
Lucas, Heinlein, Kim, Hernandez, Malik et al., The androgen-regulated protease TMPRSS2 activates a proteolytic cascade involving components of the tumor microenvironment and promotes prostate cancer metastasis, Cancer Discov
Ludvigsson, Systematic review of COVID-19 in children shows milder cases and a better prognosis than adults, Acta Paediatr
Ludwig, Enzenhofer, Schneider, Rauch, Bodenteich et al., Efficacy of a carrageenan nasal spray in patients with common cold: a randomized controlled trial, Respir Res, doi:10.1186/1465-9921-14-124
Luna-Castro, Samaniego-Barrón, Serrano-Rubio, Ceballos-Olivera, Avalos-Gómez et al., Lactoferrin: a powerful antimicrobial protein present in milk, J Adv Dairy Res, doi:10.4172/2329-888X.1000195(195)
Lynch, Werder, Loh, Sikder, Curren et al., Plasmacytoid dendritic cells protect from viral bronchiolitis and asthma through semaphorin 4a-mediated T reg expansion, J Exp Med
López-Lluch, Pozo-Cruz, Sánchez-Cuesta, Cortés-Rodríguez, Navas, Bioavailability of coenzyme Q10 supplements depends on carrier lipids and solubilization, Nutrition
Lönnerdal, Atkinson, Nitrogenous components of milk: a human milk proteins
Lü, Qiu, Jia, Guo, Leng, Singlecell expression profiles of ACE2 and TMPRSS2 reveals potential vertical transmission and fetus infection of SARS-CoV-2, Aging (Albany NY)
Ma, Xie, Li, Shi, Mao et al., Effect of SARS-CoV-2 infection upon male gonadal function: a single center-based study, doi:10.1101/2020.03.21.20037267
Madhyastha, Madhyastha, Nakajima, Omura, Maruyama, Curcumin facilitates fibrinolysis and cellular migration during wound healing by modulating urokinase plasminogen activator expression, Pathophysiol Haemost Thromb
Madjid, Safavi-Naeini, Solomon, Vardeny, Potential effects of coronaviruses on the cardiovascular system: a review, JAMA Cardiol, doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2020.1286
Magro, Mulvey, Berlin, Nuovo, Salvatore et al., Complement associated microvascular injury and thrombosis in the pathogenesis B, Transl Res
Magro, Mulvey, Berlin, Nuovo, Salvatore et al., Complement associated microvascular injury and thrombosis in the pathogenesis of severe COVID-19 infection: a report of five cases, Transl Res
Maguire, Zacharopoulos, Phillips, Carrageenan-based nonoxynol-9 spermicides for prevention of sexually transmitted infections, Sex Transm Dis
Mahmoodpoor, The effect of intravenous selenium on oxidative stress in critically ill patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome, Immunol Investig
Maier, Chu, Use of ozone for inactivation of bacteria and viruses in cryostats, J Cytol Histol, doi:10.4172/2157-7099.1000428
Majdic, Could sex/gender differences in ACE2 expression in the lungs contribute to the large gender disparity in the morbidity and mortality of patients infected with the SARS-CoV-2 virus?, Front Cell Infect Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2020.00327
Mak, Chan, Ng, Probiotics and COVID-19: one size does not fit all, Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol
Malik, Properties of coronavirus and SARS-CoV-2, Malays J Pathol
Mallapaty, The coronavirus is most deadly if you are old and male, Nature
Mallapaty, What the cruise-ship outbreaks reveal about COVID-19, Nature, doi:10.1038/d41586-020-00885-w
Managutti, Managutti, Patel, Puthanakar, Evaluation of post-surgical bacteremia with use of povidone-iodine and chlorhexidine during mandibular third molar surgery, J Maxillofac Oral Surg
Manalo, Smith, Cheeley, Jacob, A dermatologic manifestation of COVID-19: transient livedo reticularis, J Am Acad Dermatol, doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2020.04.018
Mancuso, Mcnish, Peters-Golden, Brock, Evaluation of phagocytosis and arachidonate metabolism by alveolar macrophages and recruited neutrophils from F344xBN rats of different ages, Mech Ageing Dev
Mangum, Graham, Lopinavirritonavir: a new protease inhibitor, Pharmacotherapy
Manikandan, Sumitra, Aishwarya, Manohar, Lokanadam et al., Curcumin modulates free radical quenching in myocardial ischaemia in rats, Int J Biochem Cell Biol
Marazuela, Giustina, Puig-Domingo, Endocrine and metabolic aspects of the COVID-19 pandemic, Rev Endocr Metab Disord
Marchese, Barbieri, Coppo, Orhan, Daglia et al., Antimicrobial activity of eugenol and essential oils containing eugenol: a mechanistic viewpoint, Crit Rev Microbiol
Marra, Jones, Astell, Holt, Brooks-Wilson et al., The genome sequence of the SARS-associated coronavirus, Science
Marzano, Genovese, Fabbrocini, Pigatto, Monfrecola et al., Varicellalike exanthem as a specific COVID-19-associated skin manifestation: multicenter case series of 22 patients, J Am Acad Dermatol
Matos, New coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2): advances to flatten the curve the prison population, Rev Soc Bras Med Trop, doi:10.1590/0037-8682-0219-2020
Matsumura, Ananthaswamy, Toxic effects of ultraviolet radiation on the skin, Toxicol Appl Pharmacol
Matthay, Zemans, Zimmerman, Arabi, Beitler et al., Acute respiratory distress syndrome, Nat Rev Dis Primers, doi:10.1038/s41572-019-0069-0
Mauro, Cantarella, Bernardini, Rosa, Barbagallo et al., The biochemical and pharmacological properties of ozone: the smell of protection in acute and chronic diseases, Int J Mol Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms20030634
Mauvais-Jarvis, Klein, Levin, Estradiol, progesterone, immunomodulation, and COVID-19 outcomes, Endocrinology, doi:10.1210/endocr/bqaa127
Mcintosh, Hirsch, Bloom, Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): Epidemiology, virology, and prevention, Lancet Infect Dis
Medico, Magno, Primo Report -Ossigeno Ozono Sioot Nei Pazienti Ricoverati Con COVID-19
Medico, Magno, Secondo Report -Ossigeno Ozono Sioot Nei Pazienti Ricoverati Con COVID-19
Meester, Manilla-Muñoz, León-Cachón, Paniagua-Frausto, Carrión-Alvarez et al., SeXY chromosomes and the immune system: reflections after a comparative study, Biol Sex Differ, doi:10.1186/s13293-019-0278-y
Mehta, Mcauley, Brown, Sanchez, Tattersall et al., COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression, Lancet
Meng, Wang, Li, Chen, Li et al., An experimental trial of recombinant human interferon alpha nasal drops to prevent coronavirus disease 2019 in medical staff in an epidemic area, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.04.11.20061473
Meng, Xiao, Zhang, He, Ou et al., Renin-angiotensin system inhibitors improve the clinical outcomes of COVID-19 patients with hypertension, Emerg Microbe Infect
Mensa, Howell, Scott, Degrado, Comparative mechanistic studies of brilacidin, daptomycin, and the antimicrobial peptide LL16, Antimicrob Agents Chemother
Mercado, Zahn, Wegmann, Loos, Chandrashekar et al., Single-shot Ad26 vaccine protects against SARS-CoV-2 in rhesus macaques, Nature
Meshkani, Vakili, Tissue resident macrophages: key players in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes and its complications, Clin Chim Acta
Meyers, Robison, Milici, Alam, Quillen et al., Lowering the transmission and spread of human coronavirus, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.26514
Meyers, Robison, Milici, Alam, Quillen et al., Virucidal efficacy of different oral rinses against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, J Infect Dis, doi:10.1002/jmv.26514
Microbiota, None
Microbiota, None
Mirhafez, Farimani, Gholami, Hooshmand, Tavallaie et al., The effect of curcumin with piperine supplementation on pro-oxidant and antioxidant balance in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, Drug Metab Pers Ther, doi:10.1515/dmpt-2018-0040
Mirzaei, Shakeri, Rashidi, Jalili, Banikazemi et al., Phytosomal curcumin: a review of pharmacokinetic, experimental and clinical studies, Biomed Pharmacother
Mitchell, Paniker, Sanchez, Bella, Garaczi et al., Molecular response of nasal mucosa to therapeutic exposure to broad-band ultraviolet radiation, J Cell Mol Med
Mitra, Dwyre, Schivo, Thompson, Cohen et al., Leukoerythroblastic reaction in a patient with COVID-19 infection, Am J Hematol
Mizumoto, Kagaya, Zarebski, Chowell, Estimating the asymptomatic proportion of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) cases on board the Diamond Princess cruise ship, Euro Surveillance, doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.10.2000180
Modi, Roy, Brahmachari, Rangasamy, Pahan, Cinnamon and its metabolite sodium benzoate attenuate the activation of p21rac and protect memory and learning in an animal model of Alzheimer's disease, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0130398
Moghadamtousi, Kadir, Hassandarvish, Tajik, Abubakar et al., A review on antibacterial, antiviral, and antifungal activity of curcumin, Biomed Res Int, doi:10.1155/2014/186864
Mohamed, Lukitsch, Torres-Ortiz, Walker, Varghese et al., Acute kidney injury associated with Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Urban New Orleans, Kidney
Mohamud, Griffith, Rehman, Miller, Chebl et al., Intraluminal carotid artery thrombus in COVID-19: another danger of cytokine storm?, Am J Neuroradiol
Mohd, Tawfiq, Memish, Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) origin and animal reservoir, Virol J, doi:10.1186/s12985-016-0544-0
Mollazadeh, Cicero, Blesso, Pirro, Majeed et al., Immune modulation by curcumin: the role of interleukin-10, Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr
Molony, Nguyen, Kong, Montgomery, Shaw et al., Aging impairs both primary and secondary RIG-1 signaling for interferon induction in human monocytes, Sci Signal, doi:10.1126/scisignal.aan2392
Momtazi, Derosa, Maffioli, Banach, Sahebkar, Role of microRNAs in the therapeutic effects of curcumin in non-cancer diseases, Mol Diagn Ther
Monga, Alexandrescu, Katz, Stein, Ganiats, Impact of infertility on quality of life, marital adjustment, and sexual function, Urology
Moore, Anderson, Bergman, Dowswell, Early skin-to-skin contact for mothers and their healthy newborn infants, Cochrane Database Syst Rev, doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003519.pub3
Moorthi, Kathiresan, Curcumin-Piperine/ curcumin-quercetin/curcumin-Silibinin dual drugloaded nanoparticulate combination therapy: a novel approach to target and treat multidrug-resistant cancers, J Med Hypotheses Ideas
Morawska, Cao, Airborne transmission of SARS-CoV-2: the world should face the reality, Environ Int, doi:10.1016/j.envint.2020.105730
Morra, Van Thanh, Kamel, Ghazy, Altibi et al., Clinical outcomes of current medical approaches for Middle East respiratory syndrome: a systematic review and metaanalysis, Rev Med Virol, doi:10.1002/rmv.1977
Morrow, Ruiz-Palacios, Altaye, Jiang, Guerrero et al., Human milk oligosaccharides are associated with protection against diarrhea in breast-fed infants, J Pediatr
Morse, Mazet, Woolhouse, Parrish, Carroll et al., Prediction and prevention of the next pandemic zoonosis, Lancet
Moss, Hoffbrand, Essential haematology, 6th edn
Moulton, Sex hormones in acquired immunity and autoimmune disease, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2018.02279
Mujumdar, Dhuley, Deshmukh, Raman, Naik, Anti-inflammatory activity of piperine, Jpn J Med Sci Biol
Mukherjee, Esper, Buchheit, Arters, Adkins et al., Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial to assess the safety and effectiveness of a novel dualaction oral topical formulation against upper respiratory infections, BMC Infect Dis, doi:10.1186/s12879-016-2177-8
Mulligan, Lyke, Kitchin, Absalon, Gurtman et al., Phase I/II study of COVID-19 RNA vaccine BNT162b1 in adults, Nature
Muniyappa, Gubbi, COVID-19 pandemic, coronaviruses, and diabetes mellitus, Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab
Munster, Koopmans, Van Doremalen, Van Riel, De, A novel coronavirus emerging in China-key questions for impact assessment, N Engl J Med
Musa, Hepatic and gastrointestinal involvement in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): what do we know till now? Arab, J Gastroenterol
Myśliwska, Trzonkowski, Szmit, Brydak, Machała et al., Immunomodulating effect of influenza vaccination in the elderly differing in health status, Exp Gerontol
Márquez, Chung, Marches, Rossi, Nehar-Belaid et al., Sexual-dimorphism in human immune system aging, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-020-14396-9
Mäkelä, Puhakka, Ruuskanen, Leinonen, Saikku et al., Viruses and bacteria in the etiology of the common cold, J Clin Microbiol
Mörelius, Theodorsson, Nelson, Salivary cortisol and mood and pain profiles during skin-to-skin care for an unselected group of mothers and infants in neonatal intensive care, Pediatrics
Nagatake, Ahmed, Oishi, Prevention of respiratory infections by povidone-iodine gargle, Dermatology
Nagpal, Mainali, Ahmadi, Wang, Singh et al., Gut microbiome and aging: physiological and mechanistic insights, Nutr Healthy Aging
Nair, Jandovitz, Hirsch, Nair, Abate et al., COVID-19 in kidney transplant recipients, Am J Transplant
Najarian, Morbilliform exanthem associated with COVID-19, JAAD Case Rep
Narasaraju, Yang, Samy, Ng, Poh et al., Excessive neutrophils and 5 COVID-19 and Age References
Netea, Joosten, Latz, Mills, Natoli et al., Trained immunity: a program of innate immune memory in health and disease, Science, doi:10.1126/science.aaf1098
Netea, Rovina, Akinosoglou, Antoniadou, Antonakos, Complex immune dysregulation in COVID-19 patients with severe respiratory failure, Cell Host Microbe
Netea, Rovina, Akinosoglou, Antoniadou, Antonakos, Complex immune dysregulation in COVID-19 patients with severe respiratory failure, Cell Host Microbe
Neuman, Adair, Yoshioka, Quispe, Orca et al., Supramolecular architecture of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus revealed by electron cryomicroscopy, J Virol
News, Covid, None
Ng, Hirsch, Hazzan, Wanchoo, Shah et al., Outcomes among patients hospitalized with COVID-19 and acute kidney injury, Am J Kidney Dis, doi:10.1053/j.ajkd.2020.09.002
Nicastri, Petrosillo, Bartoli, Lepore, Mondi et al., National institute for the infectious diseases "L. Spallanzani", IRCCS. recommendations for COVID-19 clinical management, Infect Dis Rep, doi:10.4081/idr.2020.8543
Nieto, Sánchez-Lasheras, García-Gonzalo, De, Juez, PM10 concentration forecasting in the metropolitan area of Oviedo (northern Spain) using models based on SVM, MLP, VARMA and ARIMA: a case study, Sci Total Environ
Nimkar, Naaraayan, Hasan, Pant, Durdevic et al., Incidence and risk factors for acute kidney injury and its effect on mortality in patients hospitalized from Covid-19, Mayo Clin Proc: Innov Qual Outcomes, doi:10.1016/j.mayocpiqo.2020.07.003
Nobukuni, Hayakawa, Namba, Ihara, Sato et al., The influence of long-term treatment with povidone-iodine on thyroid function, Dermatology
Noor, Islam, Prevalence and associated risk factors of mortality among COVID-19 patients: a meta-analysis, J Community Health
Normile, Japan ends its COVID-19 state of emergency, Asia/Pacific, Health, Coronavirus: Science News
Novel, The epidemiological characteristics of an outbreak of 2019 novel coronavirus diseases (COVID-19) in China, Zhonghua liu xing bing xue za zhi
Numata, Chu, Dakhama, Voelker, Pulmonary surfactant phosphatidylglycerol inhibits respiratory syncytial virus-induced inflammation and infection, Proc Natl Acad Sci
Numata, Mitchell, Tipper, Brand, Trombley et al., Pulmonary surfactant lipids inhibit infections with the pandemic H1N1 influenza virus in several animal models, J Biol Chem
Olaimat, Aolymat, Holy, Ayyash, Ghoush et al., The potential application of probiotics and prebiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19, NPJ Sci Food, doi:10.1038/s41538-020-00078-9
Onder, Rezza, Brusaferro, Case-fatality rate and characteristics of patients dying in relation to COVID-19 in Italy, JAMA
Onder, Rezza, Brusaferro, Casefatality rate and characteristics of patients dying in relation to COVID-19 in Italy, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.4683
Oran, Topol, Prevalence of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection : a narrative review, Ann Intern Med
Organization, Health topics. Coronavírus. Coronavirus: symptoms. World Health Organization
Ortega, Rech, Haje, Gallo, Pérez-Sayáns et al., Short-term inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 by hydrogen peroxide in persistent nasopharyngeal carriers, J Hosp Infect. Oct, doi:10.1002/jmv.26485
Ortona, Pierdominici, Rider, Editorial: sex hormones and gender differences in immune responses, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2019.01076
Ose, Tu, Schink, Maxeiner, Schuster et al., Cinnamon extract inhibits allergenspecific immune responses in human and murine allergy models, Clin Exp Allergy
Overcash, Using narrative research to understand the quality of life of older women with breast cancer, Oncol Nurs Forum
Oxford, Group, Folegatti, Ewer, Aley et al., Safety and immunogenicity of the ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccine against SARS-CoV-2: a preliminary report of a phase 1/2, single-blind, randomised controlled trial, Lancet
Oyelade, Alqahtani, Canciani, Prognosis of COVID-19 in patients with liver and kidney diseases: an early systematic review and meta-analysis, Trop Med Infect Dis, doi:10.3390/tropicalmed5020080
Pachiega, Afonso, Sinhorin, Alencar, Araújo et al., Chronic heart diseases as the most prevalent comorbidities among deaths by COVID-19 in Brazil, Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo, doi:10.1590/S1678-9946202062045
Page, Bryant, Cheng, Dow, Ky et al., Drugs that may cause or exacerbate heart failure: a scientific statement from the american heart association, Circulation
Paim, Bowman, Miller, Feehan, Marthaler et al., None, Epidemiology
Pan, Mu, Yang, Sun, Wang et al., Clinical characteristics of COVID-19 patients with digestive symptoms in Hubei, China: a descriptive, cross-sectional, multicenter study, Am J Gastroenterol
Pan, Peto, Karim, Alejandria, Swaminathan, Repurposed antiviral drugs for COVID-19 -interim WHO SOLIDARITY trial results, MedRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.10.15.20209817
Pan, Xu, Zhang, Zhou, Wang et al., Identification of a potential mechanism of acute kidney injury during the COVID-19 outbreak: a study based on single-cell transcriptome analysis, Intensive Care Med
Pan, Xue, Snow, Xiao, Tailor-made antimicrobial/antiviral star polymer via ATRP of cyclodextrin and guanidine-based macromonomer, Macromol Chem Phys
Panahi, Ahmadi, Teymouri, Johnston, Sahebkar, Curcumin as a potential candidate for treating hyperlipidemia: a review of cellular and metabolic mechanisms, J Cell Physiol
Panahi, Badeli, Karami, Sahebkar, Investigation of the efficacy of adjunctive therapy with bioavailability-boosted curcuminoids in major depressive disorder, Phytother Res
Panahi, Hosseini, Khalili, Naimi, Majeed et al., Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of curcuminoid-piperine combination in subjects with metabolic syndrome: a randomized controlled trial and an updated metaanalysis, Clin Nutr
Panahi, Khalili, Hosseini, Abbasinazari, Sahebkar, Lipid-modifying effects of adjunctive therapy with curcuminoids-piperine combination in patients with metabolic syndrome: results of a randomized controlled trial, Complemen Ther Med
Panahi, Khalili, Sahebi, Namazi, Atkin et al., Curcuminoids plus piperine modulate adipokines in type 2 diabetes mellitus, Curr Clin Pharmacol
Panahi, Khalili, Sahebi, Namazi, Reiner et al., Curcuminoids modify lipid profile in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized controlled trial, Complemen Ther Med
Panahi, Khalili, Sahebi, Namazi, Simental-Mendía et al., Effects of Curcuminoids plus piperine on glycemic, hepatic and inflammatory biomarkers in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized double-blind placebocontrolled trial, Drug Res (Stuttg)
Panahi, Valizadegan, Ahamdi, Ganjali, Majeed et al., Curcuminoids plus piperine improve nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a clinical trial, J Cell Biochem
Panche, Diwan, Chandra, Flavonoids: an overview, J Nutr Sci, doi:10.1017/jns.2016.41
Pang, Tang, Sex differences in the serum concentrations of testosterone in mice and hamsters during their critical periods of neural sexual differentiation, J Endocrinol
Paraskevis, Kostaki, Magiorkinis, Panayiotakopoulos, Sourvinos et al., Full-genome evolutionary analysis of the novel corona virus (2019-nCoV) rejects the hypoth-Z. N. Ghale-Noie et al. esis of emergence as a result of a recent recombination event, Infect Genet Evol, doi:10.1016/j.meegid.2020.104212
Pascoal, Rodrigues, Genaro, Gomes, Toledo-Teixeira et al., Microbiota-derived shortchain fatty acids do not interfere with SARS-CoV-2 infection of human colonic samples, Gut Microbes
Patel, Verma, COVID-19 and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers: what is the evidence?, JAMA
Paterlini, Closing borders is ridiculous': the epidemiologist behind Sweden's controversial coronavirus strategy, Nature, doi:10.1038/d41586-020-01098-x
Patoulias, Katsimardou, Stavropoulos, Imrialos, Doumas, Renin-anfiotensin system inhibitors and COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Evidence for significant geographic disparities, Curr Hypertens Rep, doi:10.1007/s11906-020-01101-w
Paules, Marston, Fauci, Coronavirus infections-more than just the common cold, JAMA
Peeples, What the data say about wearing face masks, Nature
Pei, Zhang, Peng, Liu, Zhang et al., Renal involvement and early prognosis in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia, J Am Soc Nephrol
Peiris, Lai, Poon, Guan, Yam et al., Coronavirus as a possible cause of severe acute respiratory syndrome, Lancet
Pelayo, Lo, Bhargav, Gul, Peterson et al., Clinical characteristics and outcomes of community-and hospital-acquired acute kidney injury with COVID-19 in a US inner city hospital system, Cardioren Med
Peleng, Kudose, Agati, Siddall, Ahmad, Acute kidney injury due to collapsing glomerulopathy following COVID-19 infection, Kidney Int Rep
Pendergrass, Pirro, Westwood, Ferrario, Brosnihan et al., Sex dif-N. Thomas et al. ferences in circulating and renal angiotensins of hypertensive mRen(2). Lewis but not normotensive Lewis rats, Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol
Peng, Liu, Zhang, Fu, Mei et al., Breast milk concentration of hydroxychloroquine in Chinese lactating women with connective tissue diseases, Eur J Clin Pharmacol
Peng, Xu, Li, Cheng, Zhou et al., Transmission routes of 2019-nCoV and controls in dental practice, Int J Oral Sci, doi:10.1038/s41368-020-0075-9
Peri, Calabrese, Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) modulation by synthetic and natural compounds: an update: miniperspective, J Med Chem
Perrotta, Corbi, Mazzeo, Boccia, Aronne et al., COVID-19 and the elderly: insights into pathogenesis and clinical decisionmaking, Aging Clin Exp Res
Pestka, Langer, Zoon, Samuel, Interferons and their actions, Annu Rev Biochem
Peter, Wesselborg, Lauber, Molecular suicide notes: last call from apoptosing cells, J Mol Cell Biol
Phoswa, Khaliq, Is pregnancy a risk factor of COVID-19?, Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol
Pi-Sunyer, The medical risks of obesity, Postgrad Med
Piccinni, Giudizi, Biagiotti, Beloni, Giannarini et al., Progesterone favors the development of human T helper cells producing Th2-type cytokines and promotes both IL-4 production and membrane CD30 expression in established Th1 cell clones, J Immunol
Pierce, Preston-Hurlburt, Dai, Aschner, Cheshenko, Immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection in hospitalized pediatric and adult patients, Sci Transl Med, doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.abd5487
Pinto, Oliveira, Singh, Jimenez, Gonçalves et al., ACE2 expression is increased in the lungs of patients with comorbidities associated with severe COVID-19, J Infect Dis
Pivotto, Banhuk, Staffen, Daga, Ayala et al., Clinical uses and molecular aspects of ozone therapy: a review, Online J Biol Sci, doi:10.3844/ojbsci.2020.37.49
Pluznick, A novel SCFA receptor, the microbiota, and blood pressure regulation, Gut Microbes
Pollitt, Peccia, Ko, Kaminski, Cruz et al., COVID-19 vulnerability: the potential impact of genetic susceptibility and airborne transmission, Hum Genomics, doi:10.1186/s40246-020-00267-3
Poltajainen, Matikainena, Nymanb, Aleniusa, Veckman, Beta-glucan inducible microRNAs negatively regulate inflammatory response, doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2013.06.202
Portolés, Marques, López-Sánchez, De Valdenebro, Muñez et al., Chronic kidney disease and acute kidney injury in the COVID-19 Spanish outbreak, Nephrol Dial Transplant
Poston, Patel, Davis, Management of critically ill adults with COVID-19, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.4914
Pourhoseingholi, None
Poutanen, Low, Henry, Finkelstein, Rose et al., Identification of severe acute respiratory syndrome in Canada, N Engl J Med
Preprint, Brilacidin, a COVID-19 Drug Candidate, Exhibits Potent In Vitro Antiviral Activity Against SARS-CoV-2
Prompetchara, Ketloy, Palaga, Immune responses in COVID-19 and potential vaccines: lessons learned from SARS and MERS epidemic, Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol
Qiao, What are the risks of COVID-19 infection in pregnant women?, Lancet
Qiao, What are the risks of COVID-19 infection in pregnant women?, Lancet
Qin, Huang, Gong, Shen, Huang et al., Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of 4 weeks or longer suggest that curcumin may afford some protection against oxidative stress, Nutr Res
Qin, Qiu, Yuan, Zong, Tuo et al., Clinical characteristics and treatment of patients infected with COVID-19 in Shishou, Lancet preprints, doi:10.2139/ssrn.3541147
Qin, Zhou, Hu, Zhang, Yang et al., Dysregulation of immune response in patients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, Clin Infect Dis
Rabenau, Kampf, Cinatl, Doerr, Efficacy of various disinfectants against SARS coronavirus, J Hosp Infect
Ragan, Hartson, Pidcoke, Bowen, Goodrich, Pathogen reduction of SARS-CoV-2 virus in plasma and whole blood using riboflavin and UV light, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0233947
Raghavendra, Naidu, Spice active principles as the inhibitors of human platelet aggregation and thromboxane biosynthesis, Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fat Acids
Rahimnia, Panahi, Alishiri, Sharafi, Sahebkar, Impact of supplementation with curcuminoids on systemic inflammation in patients with knee osteoarthritis: findings from a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial, Drug Res
Rainville, Tsyglakova, Hodes, Deciphering sex differences in the immune system and depression, Front Neuroendocrinol
Ramalingam, Cai, Wong, Twomey, Chen et al., Antiviral innate immune response in non-myeloid cells is augmented by chloride ions via an increase in intracellular hypochlorous acid levels, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-018-31936-y
Ramalingam, Graham, Dove, Morrice, Sheikh, A pilot, open labelled, randomised controlled trial of hypertonic saline nasal irrigation and gargling for the common cold, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-018-37703-3
Ramezanpour, Smith, Psaltis, Wormald, Vreugde, In vitro safety evaluation of a povidone-iodine solution applied to human nasal epithelial cells, Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. Apr, doi:10.1002/alr.22575
Ranasinghe, Pigera, Premakumara, Galappaththy, Constantine et al., Medicinal properties of 'true'cinnamon (Cinnamomum zeylanicum): a systematic review, BMC Complement Altern Med, doi:10.1186/1472-6882-13-275
Rao, Gan, Cinnamon: a multifaceted medicinal plant, Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, doi:10.1155/2014/642942
Raoofi, Takian, Sari, Olyaeemanesh, Haghighi et al., COVID-19 pandemic and comparative health policy learning in Iran, Arch Iran Med
Ravioli, Niebuhr, Ruchti, Pluess, Stoeckli et al., The syndrome of inappropriate antidiuresis in COVID-19 pneumonia: report of two cases, Clin Kidney J
Ravskov, Rapid response: cholesterollowering treatment may worsen the outcome of a COVID-19 infection, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.m1182
Rawat, Kumari, Saha, COVID-19 vaccine: a recent update in pipeline vaccines, their design and development strategies, Eur J Pharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173751
Read, COVID-19: attacks the 1-beta chain of hemoglobin and captures the porphyrin to inhibit human heme metabolism, Chemrxiv, doi:10.26434/chemrxiv.12120912.v1
Rebhan, Kohlhuber, Schwegler, Fromme, Abou-Dakn et al., Breastfeeding duration and exclusivity associated with infants' health and growth: data from a prospective cohort study in Bavaria, Acta Paediatr
Recalcati, Barbagallo, Frasin, Prestinari, Cogliardi et al., Acral cutaneous lesions in the time of COVID-19, J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol
Recalcati, Cutaneous manifestations in COVID-19: a first perspective, J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol
Redd, Hathorn, Mccarty, Bazarbashi, Thompson et al., Prevalence and characteristics of gastrointestinal symptoms in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection in the United States: a multicenter cohort study, Gastroenterology, doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.04.045
Reed, The history of ultraviolet germicidal irradiation for air disinfection, Public Health Rep
Reich, Oudit, Penninger, Scholey, Herzenberg, Decreased glomerular and tubular expression of ACE2 in patients with type 2 diabetes and kidney disease, Kidney Int
Reiner, Hatamipour, Banach, Pirro, Sahebkar, Statins and the COVID-19 main protease: in silico evidence on direct interaction, Arch Med Sci
Rennie, Bowtell, Hull, Charbonneau, Lambkin-Williams, Low pH gel intranasal sprays inactivate influenza viruses in vitro and protect ferrets against influenza infection, Respir Res, doi:10.1186/1465-9921-8-38
Rest, Mindell, SARS associated coronavirus has a recombinant polymerase and coronaviruses have a history of host-shifting, Infect Genet Evol
Reyes-Engel, Morcillo, Aranda, Ruiz, Gaitan et al., Influence of gender and genetic variability on plasma angiotensin peptides, J Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Syst
Reynolds, Adhikari, Pulgarin, Troxel, Iturrate et al., Renin-angiotensinaldosterone system inhibitors and risk of COVID-19
Rezaie, Leite, Melmed, Mathur, Villanueva-Millan et al., Ultraviolet A light effectively reduces bacteria and viruses including coronavirus, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0236199
Rezapoor, Nicholson, Tabatabaee, Chen, Maltenfort et al., Povidoneiodine-based solutions for decolonization of nasal Staphylococcus aureus: a randomized, prospective, placebo-controlled study, J Arthroplast
Ricevuti, Franzini, Valdenassi, Oxygenozone immunoceutical therapy in COVID-19 outbreak: facts and figures, Ozone Ther, doi:10.4081/ozone.2020.9014
Richardson, Hirsch, Narasimhan, Crawford, Mcginn et al., Presenting characteristics, comorbidities, and outcomes among 5700 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in the New York City area, JAMA
Ridaura, Faith, Rey, Cheng, Duncan et al., Gut microbiota from twins discordant for obesity modulate metabolism in mice, Science, doi:10.1126/science.1241214
Rivera, Mastronardi, Silva-Aldana, Arcos-Burgos, Lidbury, Myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome: a comprehensive review, Diagnostics (Basel), doi:10.3390/diagnostics9030091
Rodick, Seibels, Babu, Huggins, Mathews, Potential role of CoQ10 in health and disease, Nutr Diet Suppl
Rodriguez-Nava, Garcia, Yanez-Bello, Chung, Friedman, Atorvastatin associated with decreased hazard for death in COVID-19 patients admitted to an ICU: a retrospective cohort study, Crit Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-020-03154-4
Rodríguez-Morales, Macgregor, Kanagarajah, Patel, Schlagenhauf, Going globaltravel and the 2019 novel coronavirus, Travel Med Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/j.tmaid.2020.101578
Romagnani, T-cell subsets (Th1 versus Th2), Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol, doi:10.1016/s1081-1206(10)62426-x
Rosen, Palmer, Malley, Cohen, Surfactants in the management of rhinopathologies, Am J Rhinol Allergy
Rossi, Lasagni, Trakatelli, Rowan, Magnoni, Acute maculopapular eruption in Covid-19 patient: a case report, Dermatol Ther, doi:10.1111/dth.13812
Rossi, Talarico, Coppi, Boriani, Protective role of statins in COVID 19 patients: importance of pharmacokinetic characteristics rather than intensity of action, Intern Emerg Med
Roth, Solbakken, Tørresen, Bayer, Matschiner et al., Evolution of male pregnancy associated with remodeling of canonical vertebrate immunity in seahorses and pipefishes, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
Rothan, Byrareddy, The epidemiology and pathogenesis of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak, J Autoimmun, doi:10.1016/j.jaut.2020.102433
Rowen, Robins, A plausible "penny" costing effective treatment for Corona virus ozone therapy, J Infect Dis Epidemiol, doi:10.23937/2474-3658/1510113
Rowen, Robins, Carew, Kamara, Jalloh, Rapid resolution of hemorrhagic fever (Ebola) in Sierra Leone with ozone therapy, Afr J Infect Dis
Roy, Impact of UV radiation on genome stability and human health, Adv Exp Med Biol
Rubin, Orieux, Prevel, Garric, Bats et al., Characterization of acute kidney injury in critically ill patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019, Clin Kidney J
Russell, Hellewell, Jarvis, Zandvoort, Abbott, CMMID COVID-19 working group et al (2020) Estimating the infection and case fatality ratio for coronavirus disease (COVID-19) using ageadjusted data from the outbreak on the Diamond Princess cruise ship, Euro Surveillance, doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.12.2000256
Russo, Esposito, Taramasso, Magnasco, Saio et al., Kidney disease and all-cause mortality in patients with COVID-19 hospitalized in Genoa, Northern Italy, J Nephrol, doi:10.1007/s40620-020-00875-1
Ryu, Jeong, Kim, Kim, Park et al., Biflavonoids from Torreya nucifera displaying SARS-CoV 3CL(pro) inhibition, Bioorg Med Chem
Saal, Sexual differentiation in litterbearing mammals: influence of sex of adjacent fetuses in utero, J Anim Sci
Saberi-Karimian, Keshvari, Ghayour-Mobarhan, Salehizadeh, Rahmani et al., Effects of curcuminoids on inflammatory status in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a randomized controlled trial, Complemen Ther Med, doi:10.1016/j.ctim.2020.102322
Saberi-Karimian, Keshvari, Ghayour-Mobarhan, Salehizadeh, Rahmani et al., Effects of curcuminoids on inflammatory status in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a randomized controlled trial, Complemen Ther Med, doi:10.1016/j.ctim.2020.102322
Sachdeva, Gianotti, Shah, Bradanini, Tosi et al., Cutaneous manifestations of COVID-19: report of three cases and a review of literature, J Dermatol Sci
Saeed, Castagna, Agalliu, Xue, Jorde, Statin use and in-hospital mortality in diabetics with COVID-19, J Am Heart Assoc, doi:10.1161/JAHA.120.018475
Sahin, Muik, Derhovanessian, Vogler, Kranz et al., COVID-19 vaccine BNT162b1 elicits human antibody and T(H)1 T cell responses, Nature
Saini, Ozone therapy in dentistry: a strategic review, J Nat Sci Biol Med
Sakallioğlu, Güvenç, Cingi, Xylitol and its usage in ENT practice, J Laryngol Otol
Salata, Calistri, Parolin, Palu, Coronaviruses: a paradigm of new emerging zoonotic diseases, Pathog Dis, doi:10.1093/femspd/ftaa006
Salavastru, Stanciu, Fritz, Tiplica, A burst in the incidence of viral exanthems, Indian Dermatol Online J
Salazar, Arboleya, Fernández-Navarro, De, Reyes-Gavilán et al., Age-associated changes in gut microbiota and dietary components related with the immune system in adulthood and old age: a cross-sectional study, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu11081765
Salciccia, Giudice, Gentile, Mastroianni, Pasculli et al., Interplay between male testosterone levels and the risk for subsequent invasive respiratory assistance among COVID-19 patients at hospital admission, Endocrine
Salehi, Stojanovic-Radic, Matejic, Sharifi-Rad, Kumar et al., The therapeutic potential of curcumin: a review of clinical trials, Eur J Med Chem
Samanta, Das, Das, Roles of flavonoids in Plants, Int J Pharm Sci Technol
Sankaran, Khanal, Pometto, Van Leeuwen, Ozone as a selective disinfectant for nonaseptic fungal cultivation on corn-processing wastewater, Bioresour Technol
Santoriello, Khairallah, Bomback, Xu, Kudose et al., Postmortem kidney pathology findings in patients with COVID-19, J Am Soc Nephrol
Sanyaolu, Okorie, Marinkovic, Patidar, Younis et al., Comorbidity and its impact on patients with COVID-19, SN Compr Clin Med, doi:10.1007/s42399-020-00363-4
Saokham, Muankaew, Jansook, Loftsson, Solubility of cyclodextrins and drug/cyclodextrin complexes, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules23051161
Sarilumab, Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed)
Sars-Cov, It is typically characterized by high fever, dry cough, difficulty in breathing, severe atypical pneumonia, and other symptoms such as gastrointestinal difficulties
Savasi, Parisi, Patanè, Ferrazzi, Frigerio et al., Clinical findings and disease severity in hospitalized pregnant women with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Obstet Gynecol
Schmelzer, Lindner, Rimbach, Niklowitz, Menke et al., Functions of CoQ10 in inflammation and gene expression, Biofactors
Schochetman, Stevens, Simpson, Presence of infectious polyadenylated RNA in the coronavirus avian bronchitis virus, Virology
Schoen, Horvat, Guerreiro, De Castro, De Giassi, Spectrum of clinical and radiographic findings in patients with diagnosis of H1N1 and correlation with clinical severity, BMC Infect Dis, doi:10.1186/s12879-019-4592-0
Schwartz, Sánchez, Ozone therapy and its scientific foundations, Ozone Ther Glob J
Scotland, Stables, Madalli, Watson, Gilroy, Sex differences in resident immune cell phenotype underlie more efficient acute inflammatory responses in female mice, Blood
Section On Breastfeeding, Johnston, Landers, Noble, Szucs et al., Breastfeeding and the use of human milk, Pediatrics, doi:10.1542/peds.2011-3552
Seidler, Linetskiy, Hubálková, Stankova, Smucler et al., Ozone and its usage in general medicine and dentistry. A review article, Prague Med Rep
Sekizuka, Itokawa, Kageyama, Saito, Takayama et al., Haplotype networks of SARS-CoV-2 infections in the Diamond Princess cruise ship outbreak, doi:10.1101/2020.03.23.20041970
Serdan, Masi, Gorjao, Pithon-Curi, Curi et al., COVID-19 in Brazil: Historical cases, disease milestones, and estimated outbreak peak, Travel Med Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/j.tmaid.2020.101733
Serdan, Masi, Gorjao, Pithon-Curi, Curi et al., COVID-19 in Brazil: Historical cases, disease milestones, and estimated outbreak peak, Travel Med Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/j.tmaid.2020.101733
Serdan, None
Serhan, Dalli, Colas, Winkler, Chiang, Protectins and maresins: new pro-resolving families of mediators in acute inflammation and resolution bioactive metabolome, Biochim Biophys Acta
Service, Spit shines for easier coronavirus testing, Science
Servick, Coronavirus creates a flu season guessing game, Science
Setlow, Grist, Thompson, Woodhead, Wavelengths effective in induction of malignant melanoma, Proc Natl Acad Sci
Sex, Gender and Covid-19 Project
Shadnoush, Zahedi, Norouzy, Sahebkar, Sadeghi et al., Piperinemediated inhibition of glucuronidation activity in isolated epithelial cells of the guinea-pig small intestine: evidence that piperine lowers the endogeneous UDP-glucuronic acid content, J Pharmacol Exp Ther, doi:10.1002/ptr.6749
Shafique, Ihsan, Liu, Evolutionary Trajectory for the Emergence of Novel Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens9030240
Sharma, Nasr, Larsen, Amy, Ormsby et al., COVID-19-associated collapsing focal segmental glomerulosclerosis: a report of 2 cases, Kidney Med
Sharma, Uppal, Wanchoo, Shah, Yang et al., COVID-19-associated kidney injury: a case series of kidney biopsy findings, J Am Soc Nephrol
Shastri, Wheat, Agrawal, Chaterjee, Pradhan et al., Delayed clearance of SARS-CoV2 in male compared to female patients: high ACE2 expression in testes suggests possible existence of gender-specific viral reservoirs, doi:10.1101/2020.04.16.20060566
Shell, The United Kingdom's mask crusader, Science
Shen, Wang, Zhao, Yang, Li et al., Treatment of 5 critically ill patients with COVID-19 with convalescent plasma, JAMA
Shen, Yang, Wang, Zhao, Jiang, Diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of 2019 novel coronavirus infection in children: experts' consensus statement, World J Pediatr
Shi, Hu, A review of studies on animal reservoirs of the SARS coronavirus, Virus Res
Shi, Wang, Shao, Huang, Gan et al., COVID-19 infection: the perspectives on immune responses, Cell Death Differ
Shibata, Arima, Asayama, Hoshide, Ichihara et al., Hypertension and related diseases in the era of COVID-19: a report from the Japanese Society of Hypertension Task Force on COVID-19, Hypertens Res
Shimizu, Lima, Pereira, Bittar, Batista et al., Flavonoids from pterogyne nitens inhibit hepatitis C virus entry, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-017-16336-y
Shoba, Joy, Joseph, Rajendran, Srinivas, Influence of piperine on the pharmacokinetics of curcumin in animals and human volunteers, Planta Med
Shu, Benoist, Mathis, The immune system's involvement in obesity-driven type 2 diabetes, Semin Immunol
Siddharta, Pfaender, Vielle, Dijkman, Friesland et al., Virucidal activity of World Health Organization-recommended formulations against enveloped viruses, including Zika, Ebola, and Emerging Coronaviruses, J Infect Dis
Silverman, Hupert, Washburne, Using influenza surveillance networks to estimate statespecific prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 in the United States, Sci Transl Med, doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.abc1126
Simet, Sisson, Alcohol's effects on lung health and immunity, Alcohol Res
Simonnet, Chetboun, Poissy, Raverdy, Noulette et al., High prevalence of obesity in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) requiring invasive mechanical ventilation, Obesity (Silver Spring)
Simões E Silva, Silveira, Ferreira, Teixeira, ACE2, angiotensin-(1-7) and Mas receptor axis in inflammation and fibrosis, Br J Pharmacol
Singh, Gillies, Singh, Singh, Chudasama et al., Prevalence of co-morbidities and their association with mortality in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and metaanalysis, Diabetes Obes Metab, doi:10.1111/dom.14124
Singh, Joshi, Samuel, Patra, Mahindroo, Alcohol-based hand sanitisers as first line of defence against SARS-CoV-2: a review of biology, chemistry and formulations, Epidemiol Infect, doi:10.1017/S0950268820002319
Singh-Grewal, Lucas, Mccarthy, Cheng, Wood et al., Update on the COVID-19-associated inflammatory syndrome in children and adolescents; paediatric inflammatory multisystem syndrome-temporally associated with SARS-CoV-2, J Paediatr Child Health, doi:10.1111/jpc.15049
Singhal, A review of coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19), Indian J Pediatr
Siqueiros-Cendon, Arevalo-Gallegos, Iglesias-Figueroa, Garcia-Montoya, Salazar-Martinez et al., Immunomodulatory effects of lactoferrin, Acta Pharmacol Sin
Siviero, Gallo, Maggini, Gori, Mugelli et al., Curcumin, a golden spice with a low bioavailability, J Herb Med
Sivro, Lajoie, Kimani, Jaoko, Plummer et al., Age and menopause affect the expression of specific cytokines/chemokines in plasma and cervical lavage samples from female sex workers in Nairobi, Kenya. Immun Ageing, doi:10.1186/1742-4933-10-42
Smith, Wilson, Gandhi, Vatsia, Khan, Ozone therapy: an overview of pharmacodynamics, current research, and clinical utility, Med Gas Res
Smits, De Lang, Van Den Brand, Leijten, Van et al., Exacerbated innate host response to SARS-CoV in aged nonhuman primates, PLoS Pathog, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1000756
Snape, Viner, COVID-19 in children and young people, Science
Snijder, Bredenbeek, Dobbe, Thiel, Ziebuhr et al., Unique and conserved features of genome and proteome of SARScoronavirus, an early split-off from the coronavirus group 2 lineage, J Mol Biol
Sokol, Contreras, Maisonnasse, Desmons, Delache et al., SARS-CoV-2 infection in nonhuman primates alters the composition and functional activity of the gut microbiota, Gut Microbes
Soleimani, Sahebkar, Hosseinzadeh, Turmeric (Curcuma longa) and its major constituent (curcumin) as nontoxic and safe substances: review, Phytother Res
Soler, Wysocki, Batlle, ACE2 alterations in kidney disease, Nephrol Dial Transplant
Sommerstein, Gräni, Rapid response: re: preventing a covid-19 pandemic: ACE inhibitors as a potential risk factor for fatal, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.m810
Somparn, Phisalaphong, Nakornchai, Unchern, Morales, Comparative antioxidant activities of curcumin and its demethoxy and hydrogenated derivatives, Biol Pharm Bull
Son, Akiba, Hong, Yun, Hwang et al., Piperine inhibits the activities of platelet cytosolic phospholipase A2 and thromboxane A2 synthase without affecting cyclooxygenase-1 activity: different mechanisms of action are involved in the inhibition of platelet aggregation and macrophage inflammatory response, Nutrients
Song, Li, Xie, Hou, You, Cytokine storm induced by SARS-CoV-2, Clin Chim Acta
Speziale, Streubert, Carpenter, Qualitative research in nursing: advancing the humanistic imperative
Srivastava, Bordia, Verma, Curcumin, a major component of food spice turmeric (Curcuma longa) inhibits aggregation and alters eicosanoid metabolism in human blood platelets, Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fat Acids
Sriwilaijaroen, Wilairat, Hiramatsu, Takahashi, Suzuki et al., Mechanisms of the action of povidone-iodine against human and avian influenza A viruses: its effects on hemagglutination and sialidase activities, Virol J, doi:10.1186/1743-422X-6-124
Starr, How Italy's 'father of the swabs' fought the virus, Science
Steed, Christophi, Kaiko, Sun, Goodwin et al., The microbial metabolite desaminotyrosine protects from influenza through type I interferon, Science
Steed, Costello, Lohia, Jones, Spannhake et al., Reduction of nasal Staphylococcus aureus carriage in health care professionals by treatment with a nonantibiotic, alcohol-based nasal antiseptic, Am J Infect Control
Steeg, Klein, Sex and sex steroids impact influenza pathogenesis across the life course, Semin Immunol, doi:10.1007/s00281-018-0718-5
Stockman, Massoudi, Helfand, Erdman, Siwek et al., Severe acute respiratory syndrome in children, Pediatr Infect Dis J
Stuebe, 19. World Health Organization. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) technical guidance: infection prevention and control, doi:10.1089/bfm.2020.29153.ams
Su, Aerosol transmission risk and comprehensive prevention and control strategy in dental treatments, Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi
Su, Yang, Wan, Yi, Tang et al., Renal histopathological analysis of 26 postmortem findings of patients with COVID-19 in China, Kidney Int
Suez, Zmora, Segal, Elinav, The pros, cons, and many unknowns of probiotics, Nat Med
Sun, Chen, Viboud, Early epidemiological analysis of the coronavirus disease 2019 outbreak based on crowd sourced data: a population-level observational study, Lancet Digit Health
Sun, Chen, Viboud, Early epidemiological analysis of the coronavirus disease 2019 outbreak based on crowd sourced data: a populationlevel observational study, Lancet Digit Health
Sun, Jiang, Tien, Liu, Li, IFN-λ: a new spotlight in innate immunity against influenza virus infection, Protein Cell
Sun, Lulla, Sioda, Winglee, Wu et al., Gut microbiota composition and blood pressure, Hypertension
Sunila, Kuttan, Immunomodulatory and antitumor activity of Piper longum Linn. and piperine, J Ethnopharmacol
Sánchez, Jiménez, Laviada, Correa, Suñé et al., Antigenic homology among coronaviruses related to transmissible gastroenteritis virus, Virology
Tabibzadeh, Esghaei, Soltani, Yousefi, Taherizadeh et al., Evolutionary study of COVID-19, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) as an emerging coronavirus: phylogenetic analysis and literature review, Vet Med Sci, doi:10.1002/vms3.394
Takada, Matsushita, Horioka, Furuichi, Sumi, Bactericidal effects of 310 nm ultraviolet light-emitting diode irradiation on oral bacteria, BMC Oral Health, doi:10.1186/s12903-017-0382-5
Tanaka, Masuda, Matsuo, Sasaki, Yamakage et al., Hyperglycemia and inflammatory property of circulating monocytes are associated with inflammatory property of carotid plaques in patients undergoing carotid endarterectomy, J Atheroscler Thromb
Tang, Bai, Chen, Gong, Li et al., Anticoagulant treatment is associated with decreased mortality in severe coronavirus disease 2019 patients with coagulopathy, J Thromb Haemost
Tang, Serdan, Masi, Tang, Gorjao et al., Epidemiology of COVID-19 in Brazil: using a mathematical model to estimate the outbreak peak and temporal evolution, Emerg Microbes Infect
Tang, Serdan, Masi, Tang, Gorjao et al., Epidemiology of COVID-19 in Brazil: using a mathematical model to estimate the outbreak peak and temporal evolution, Emerg Microbes Infect
Tang, Wang, Mathematic modeling of COVID-19 in the United States, Emerg Microbes Infect
Tang, Wu, Li, Song, Yao et al., On the origin and continuing evolution of SARS-CoV-2, Natl Sci Rev:nwaa, doi:10.1093/nsr/nwaa036
Tapak, Hamidi, Amini, Poorolajal, Prediction of kidney graft rejection using artificial neural network, Healthc Inform Res
Tapparel, Antiviral activity of Xlear spray against SARS-CoV2
Tchernof, Després, Pathophysiology of human visceral obesity: an update, Physiol Rev
Teymouri, Pirro, Johnston, Sahebkar, Curcumin as a multifaceted compound against human papilloma virus infection and cervical cancers: a review of chemistry, cellular, molecular, and preclinical features, Biofactors
Thomas, None
Thompson, Pandemic potential of 2019-nCoV, Lancet Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30068-2
Thygesen, Alpert, Jaffe, Chaitman, Bax et al., Fourth universal definition of myocardial infarction (2018), J Am Coll Cardiol
Tipnis, Hooper, Hyde, Karran, Christie et al., A human homolog of angiotensinconverting enzyme. Cloning and functional expression as a captopril-insensitive carboxypeptidase, J Biol Chem
Toering, Gant, Visser, Graaf, Laverman, Sex differences in reninangiotensin-aldosterone system affect extracellular volume in healthy subjects, Am J Physiol Ren Physiol
Tomosada, Chiba, Zelaya, Takahashi, Tsukida et al., Nasally administered Lactobacillus rhamnosus strains differentially modulate respiratory antiviral immune responses and induce protection against respiratory syncytial virus infection, BMC Immunol, doi:10.1186/1471-2172-14-40
Tostanoski, Wegmann, Martinot, Loos, Mcmahan et al., Ad26 vaccine protects against SARS-CoV-2 severe clinical disease in hamsters, Nat Med
Touret, De Lamballerie, Of chloroquine and COVID-19, Antiviral Res, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104762
Trandem, Anghelina, Zhao, Perlman, Regulatory T cells inhibit T cell proliferation and decrease demyelination in mice chronically infected with a coronavirus, J Immunol Res
Troeger, Forouzanfar, Rao, Khalil, Brown et al., Estimates of the global, regional, and national morbidity, mortality, and aetiologies of lower respiratory tract infections in 195 countries: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study, Lancet Infect Dis
Trøseid, Andersen, Broch, Hov, The gut microbiome in coronary artery disease and heart failure: current knowledge and future directions, doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102649
Tsai, Lu, Bau, Chiu, Yen et al., Approaches towards fighting the COVID-19 pandemic (Review), Int J Mol Med, doi:10.3892/ijmm.2020.4794
Tsang, Ho, Ooi, Yee, Wang et al., A cluster of cases of severe acute respiratory syndrome in Hong Kong, N Engl J Med
Turnbaugh, Hamady, Yatsunenko, Cantarel, Duncan et al., A core gut microbiome in obese and lean twins, Nature
Turner, Wu, Dorminy, Chandra, Safety and tolerability of surfactant nasal irrigation, Int Forum Allergy Rhinol
Udugama, Kadhiresan, Kozlowski, Malekjahani, Osborne et al., None
Vaduganathan, Vardeny, Michel, Mcmurray, Pfeffer et al., Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors in patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Vaduganathan, Vardeny, Michel, Mcmurray, Pfeffer et al., Reninangiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors in patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Vakili, Savardashtaki, Jamalnia, Tabrizi, Nematollahi et al., Laboratory findings of COVID-19 infection are conflicting in different age groups and pregnant women: a literature review, Arch Med Res
Valdenassi, Franzini, Ricevuti, Rinaldi, Galoforo et al., Potential mechanisms by which the oxygen-ozone (O2-O3) therapy could contribute to the treatment against the coronavirus COVID-19, Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci
Valente-Acosta, Moreno-Sanchez, Fueyo-Rodriguez, Palomar-Lever, Rhabdomyolysis as an initial presentation in a patient diagnosed with COVID-19, BML Case Rep, doi:10.1136/bcr-2020-236719
Valizadeh, Abdolmohammadi-Vahid, Danshina, Gencer, Ammari et al., Nano-curcumin therapy, a promising method in modulating inflammatory cytokines in COVID-19 patients, Int Immunopharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107088
Van Boheemen, De Graaf, Lauber, Bestebroer, Raj et al., Genomic characterization of a newly discovered coronavirus associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome in humans, MBio, doi:10.1128/mBio.00473-12
Van De Pol, Wolfs, Jansen, Van Loon, Rossen, Diagnostic value of real-time polymerase chain reaction to detect viruses in young children admitted to the paediatric intensive care unit with lower respiratory tract infection, Crit Care, doi:10.1186/cc4895
Van Der Hoek, Pyrc, Jebbink, Vermeulen-Oost, Berkhout et al., Identification of a new human coronavirus, Nat Med
Van Der Meer, Joosten, Riksen, Netea, Trained immunity: a smart way to enhance innate immune defence, Mol Immunol
Van Kerkhove, Vandemaele, Shinde, Jaramillo-Gutierrez, Koukounari et al., Risk factors for severe outcomes following 2009 influenza A (H1N1) infection: a global pooled analysis, PLoS Med, doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1001053
Vanhook, Why aging attenuates antiviral responses, Science
Varga, Flammer, Steiger, Haberecker, Andermatt et al., Endothelial cell infection and Endotheliitis in COVID-19, Lancet
Victora, Bahl, Barros, França, Horton et al., Breastfeeding in the 21st century: epidemiology, mechanisms, and lifelong effect, Lancet
Viebahn-Hänsler, Os, Fahmy, Systemic ozone applications, major autohemotherapy and rectal insufflation, evaluated according to the international classification of evidence-based medicine. A new basis for reimbursement of medical expenses by private and social insurances, J Ozone Ther, doi:10.7203/jo3t.3.4.2019.15550
Virtue, Mccright, Wright, Jimenez, Mowel et al., The gut microbiota regulates white adipose tissue inflammation and obesity via a family of microRNAs, Sci Transl Med, doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.aav1892
Voelker, Numata, Phospholipid regulation of innate immunity and respiratory viral infection, J Biol Chem
Vogel, Sweden's gamble, Science
Voigt, Ovsyannikova, Kennedy, Grill, Goergen et al., Sex differences in older adults' immune responses to seasonal influenza vaccination, Front Immunol
Wakabayashi, Oda, Yamauchi, Abe, Lactoferrin for prevention of common viral infections, J Infect Chemother
Waki, Yajima, Suganuma, Buddle, Luo et al., Oral administration of Lactobacillus brevisKB290 to mice alleviates clinical symptoms following influenza virus infection, Lett Appl Microbiol
Walsh, Frenck, Jr, Falsey, Kitchin et al., Safety and immunogenicity of two RNA-based Covid-19 vaccine candidates, Online ahead of print, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2027906
Walsh, Safety issues relating to the use of hydrogen peroxide in dentistry, Aust Dent J
Wang, Horby, Hayden, Gao, A novel coronavirus outbreak of global health concern, Lancet
Wang, Hu, Hu, Zhu, Liu et al., Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 Novel Coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, JAMA
Wang, Hu, Hu, Zhu, Liu et al., Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, JAMA
Wang, Jiang, Chen, Montaner, Cytokine storm and leukocyte changes in mild versus severe SARS-CoV-2 infection: review of 3939 COVID-19 patients in China and emerging pathogenesis and therapy concepts, J Leukoc Biol
Wang, Liu, Chen, Huang, Xu et al., The establishment of reference sequence for SARS-CoV-2 and variation analysis, J Med Virol
Wang, Liu, Hu, Zhou, Yu et al., Nasopharyngeal swabs are more sensitive than oropharyngeal swabs for COVID-19 diagnosis and monitoring the SARS-CoV-2 load, Front Med, doi:10.3389/fmed.2020.00334
Wang, Liu, Wang, Liu, Chen et al., Dynamic changes of chest CT imaging in patients with COVID-19, Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban
Wang, Ma, Zhang, Song, Wang et al., Fasting blood glucose at admission is an independent predictor for 28-day mortality in patients with COVID-19 without previous diagnosis of diabetes: a multi-centre retrospective study, Diabetologia
Wang, Maintenance hemodialysis and COVID-19: saving lives with caution, care, and courage, Kidney Med
Wang, Shi, Xiao, Fu, Feng et al., Chinese expert consensus on the perinatal and neonatal management for the prevention and control of the 2019 novel coronavirus infection, Ann Transl Med
Wang, Tang, Wei, Updated understanding of the outbreak of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in Wuhan, China. J Med Virol
Wang, Xu, scRNA-seq profiling of human testes reveals the presence of the ACE2 receptor, a target for SARS-CoV-2 infection in Spermatogonia, Leydig and Sertoli cells, Cell, doi:10.3390/cells9040920
Wang, Zhou, Lin, Liu, Wu et al., Experience of clinical management for pregnant women and newborns with novel coronavirus pneumonia in Tongji hospital, Curr Med Sci
Weber, Bysted, Hłlmer, The coenzyme Q10 content of the average Danish diet, Int J Vitam Nutr Res
Wege, Müller, Meulen, Genomic RNA of the murine coronavirus JHM, J Gen Virol
Wei, Xiao, Wang, Chen, Zhang et al., Sex differences in severity and mortality among patients with covid-19: evidence from pooled literature analysis and insights from integrated bioinformatic analysis
Wei, Yuan, Liu, Fu, Yu et al., Novel coronavirus infection in hospitalized infants under 1 year of age in China, JAMA
Wei, Zeng, Su, Wan, Yu et al., Hypolipidemia is associated with the severity of Covid-19, J Clin Lipidol
Weiss, Murdoch, Clinical course and mortality risk of severe COVID-19, Lancet
Weiss, Navas-Martin, Coronavirus pathogenesis and the emerging pathogen severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus, Microbiol Mol Biol Rev
Wells, Latino, Gavalchin, Poiesz, Inactivation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 by ozone in vitro, Blood
Wenham, Smith, Morgan, Gender, Group, COVID-19: the gendered impacts of the outbreak, Lancet
Werion, Belkhir, Perrot, Schmit, Aydin et al., SARS-CoV-2 causes a specific dysfunction of the kidney proximal tubule, Kidney Int
Westover, Virucidal activity of Xlear compounds vs SARS-CoV-2 virus and rhinovirus-16
White, Pasupuleti, Roman, Li, Hernandez, Oral turmeric/curcumin effects on inflammatory markers in chronic inflammatory diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Pharmacol Res, doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2019.104280
Who, Disease, COVID-19): situation report-31
Who, None
Who, None
Who, None
Who, None
Who, None
Who, None
Who, Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS): status of the outbreak and lessons for the immediate future
Williams, Price, Shafii, Yahvah, Bode et al., Relationships among microbial communities, maternal cells, oligosaccharides, and macronutrients in human Milk, J Hum Lact
Williams, Zhang, Hypertension, reninangiotensin-aldosterone system inhibition, and COVID-19, Lancet
Williamson, Walker, Bhaskaran, Bacon, Bates et al., Factors associated with COVID-19-related death using OpenSAFELY, Nature
Willyard, Ageing and COVID vaccines, Nature
Winther, Buchert, Turner, Hendley, Tschaikin, Decreased rhinovirus shedding after intranasal oxymetazoline application in adults with induced colds compared with intranasal saline, Am J Rhinol Allergy
Wolff, Nee, Hickey, Marschollek, Risk factors for Covid-19 severity and fatality: a structured literature review, Infection
Wong, Chow, Leung, Ng, Ng et al., Pregnancy and perinatal outcomes of women with severe acute respiratory syndrome, Am J Obstet Gynecol
Wong, Liu, Liu, Zhou, Bi et al., MERS, SARS, and Ebola: the role of superspreaders in infectious disease, Cell Host Microbe
Woo, Huang, Lau, Yuen, Coronavirus genomics and bioinformatics analysis
Woo, Huang, Lau, Yuen, None
Woo, Lau, Chu, Chan, Tsoi et al., Characterization and complete genome sequence of a novel coronavirus, coronavirus HKU1, from patients with pneumonia, J Virol
Woo, Lau, Huang, Yuen, Coronavirus diversity, phylogeny and interspecies jumping, Exp Biol Med
Woo, Lau, Li, Poon, Wong et al., Molecular diversity of coronaviruses in bats, Virology
Worobey, Pekar, Larsen, Nelson, Hill et al., The emergence of SARS-CoV-2 in Europe and North America
Wu, Chen, Cai, Ja, Zhou et al., Risk factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with Coronavirus Disease, JAMA Intern Med
Wu, Chen, Chan, The outbreak of COVID-19: an overview, J Chin Med Assoc
Wu, Larsen, Hernadez-Arroyo, Mohamed, Caza et al., AKI and collapsing glomerulopathy associated with COVID-19 and APOL1 high-risk genotype, J Am Soc Nephrol
Wu, Mcgoogan, Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, JAMA
Wu, Mcgoogan, Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72,314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, JAMA
Wu, Peng, Huang, Ding, Wang et al., Genome composition and divergence of the novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) originating in China, Cell Host Microbe
Xia, Duan, Zhang, Zhao, Zhang et al., Effect of an inactivated vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 on safety and immunogenicity outcomes: interim analysis of 2 randomized clinical trials, JAMA
Xiao, Zhai, Feng, Zhou, Zhang et al., Isolation and characterization of 2019-nCoV-like coronavirus from Malayan pangolins, BioRxiv
Xie, Pay attention to SARS-CoV-2 infection in children, Pediatr Investig
Xie, Zhong, Zhao, Zheng, Wang et al., Chest CT for typical 2019-nCoV pneumonia: relationship to negative RT-PCR testing, Radiology
Xiong, Tang, Liu, Tu, Tian et al., Clinical characteristics of and medical interventions for COVID-19 in hemodialysis patients in Wuhan, China. J Am Soc Nephrol
Xu, Cui, Duan, Zhang, Zhou et al., Saliva: potential diagnostic value and transmission of 2019-nCoV, Int J Oral Sci, doi:10.1038/s41368-020-0080-z
Xu, Li, Zhu, Liang, Fang et al., Characteristics of pediatric SARS-CoV-2 infection and potential evidence for persistent fecal viral shedding, Nat Med
Xu, Qi, Yang, Wei, Gong, Orchitis: a complication of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), Biol Reprod
Xu, Shi, Wang, Zhang, Huang et al., Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome, Lancet Respir Med
Xu, Wi, Kim, Kim, Ameliorating effect of dietary xylitol on human respiratory syncytial virus (hRSV) infection, Biol Pharm Bull
Xu, Wu, Jiang, Xu, Ying et al., Clinical findings in a group of patients infected with the 2019 novel coronavirus (SARS-Cov-2) outside of Wuhan, China: retrospective case series, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.m606
Xu, Wu, Jiang, Xu, Ying et al., Clinical findings in a group of patients infected with the 2019 novel coronavirus (SARS-Cov-2) outside of Wuhan, China: retrospective case series, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.m606
Xu, Wu, Jiang, Xu, Ying et al., Clinical findings in a group of patients infected with the 2019 novel coronavirus (SARS-Cov-2) outside of Wuhan, China: retrospective case series, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.m606
Xu, Wu, Jiang, Xu, Ying et al., Clinical findings in a group of patients infected with the 2019 novel coronavirus (SARS-Cov-2) outside of Wuhan, China: retrospective case series, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.m606
Xu, Zhong, Deng, Peng, Dan et al., High expression of ACE2 receptor of 2019-nCoV on the epithelial cells of oral mucosa, Int J Oral Sci
Xu, Zhong, Deng, Peng, Dan et al., High expression of ACE2 receptor of 2019-nCoV on the epithelial cells of oral mucosa, Int J Oral Sci
Xue, Mi, Wang, Pang, Liu et al., High expression of ACE2 on keratinocytes reveals skin as a potential target for SARS-CoV-2, J Invest Dermatol, doi:10.1016/j.jid.2020.05.087
Yan, Li, Wang, Yan, Zhu et al., Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio as prognostic and predictive factor in patients with coronavirus disease 2019: a retrospective cross-sectional study, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.26061
Yan, Ma, Wang, Wu, Huang et al., Luteolin decreases the yield of influenza a virus in vitro by interfering with the coat protein I complex expression, J Nat Med
Yan, Valdes, Vijay, Wang, Liang, Role of drugs affecting the renin-angiotensinaldosterone system on susceptibility and severity of COVID-19: a large case-control study from Zheijang Province, MedRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.04.24.20077875
Yan, Wu, Wang, Yu, Hu et al., Involvement of Cathepsins in innate and adaptive immune responses in periodontitis, Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, doi:10.1155/2020/4517587
Yang, Cao, Qin, Wang, Cheng et al., Clinical characteristics and imaging manifestations of the 2019 novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19): a multi-center study in Wenzhou city, China. J Infect
Yang, Does hand hygiene reduce SARS-CoV-2 transmission?, Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol
Yang, Li, Zhang, Sun, Chen, Prevalence and impact of acute renal impairment on COVID-19: a systematic review and metaanalysis, Crit Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-020-03065-4
Yang, Mei, Zheng, Fu, Zhang et al., Pregnant women with COVID-19 and risk of adverse birth outcomes and maternal-fetal vertical transmission: a population-based cohort study in Wuhan, China, BMC Med, doi:10.1186/s12916-020-01798-1
Yang, Yang, Ding, Liu, Lou et al., The crystal structures of severe acute respiratory syndrome virus main protease and its complex with an inhibitor, Proc Natl Acad Sci
Yasuhara, Kuno, Takagi, Sumitomo, Clinical characteristics of COVID-19 in children: a systematic review, Pediatr Pulmonol, doi:10.1002/ppul.24991
Ye, Wysocki, William, Soler, Cokic et al., Glomerular localization and expression of Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and Angiotensinconverting enzyme: implications for albuminuria in diabetes, J Am Soc Nephrol
Ye, Yuan, Yuen, Fung, Chan et al., Zoonotic origins of human coronaviruses, Int J Biol Sci
Ye, Zhang, Wang, Huang, Song, Chest CT manifestations of new coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a pictorial review, Eur Radiol
Yi, Li, Yuan, Qu, Chen et al., Small molecules blocking the entry of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus into host cells, J Virol
Yoon, Yoon, Song, Yoon, Lim et al., Clinical significance of a high SARS-CoV-2 viral load in the saliva, J Korean Med Sci, doi:10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e195
Youn, Lee, Choi, Saitoh, Miyake et al., Cinnamaldehyde suppresses toll-like receptor 4 activation mediated through the inhibition of receptor oligomerization, Biochem Pharmacol
Youn, Lee, Lee, Park, Yuk et al., Intranasal administration of live Lactobacillus species facilitates protection against influenza virus infection in mice, Antivir Res
Yount, Roberts, Lindesmith, Baric, Rewiring the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) transcription circuit: engineering a recombination-resistant genome, Proc Natl Acad Sci
Zareie, Sahebkar, Khorvash, Bagherniya, Hasanzadeh et al., Effect of cinnamon on migraine attacks and inflammatory markers: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial, Phytother Res
Zeighami, Nesami, Oskouie, Nikravesh, Content analysis, Iran J Nursing
Zelaya, Tada, Vizoso-Pinto, Salva, Kanmani et al., Nasal priming with immunobiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus modulates inflammation-coagulation interactions and reduces influenza virus-associated pulmonary damage, Inflamm Res
Zeng, Tao, Yuan, Wang, Liu et al., First case of neonate infected with novel coronavirus pneumonia in China, Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi, doi:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0578-1310.2020.0009
Zeng, Xia, Yuan, Yan, Xiao et al., Neonatal early-onset infection with SARS-CoV-2 in 33 neonates born to mothers with COVID-19 in Wuhan, JAMA Pediatr
Zeng, Xu, Fan, Tang, Deng et al., Antibodies in infants born to mothers with COVID-19 pneumonia, JAMA
Zeng, Xu, Fan, Tang, Deng et al., Antibodies in infants born to mothers with COVID-19 pneumonia, JAMA
Zhang, Hu, Feng, Hu, Wang et al., Influenza infection elicits an expansion of gut population of endogenous Bifidobacterium animalis which protects mice against infection
Zhang, Nawata, A comparative study on predicting influenza outbreaks, Biosci Trends
Zhang, Penninger, Li, Zhong, Slutsky, Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) as a SARS-CoV-2 receptor: molecular mechanisms and potential therapeutic target, Intensive Care Med
Zhang, Penninger, Li, Zhong, Slutsky, Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) as a SARS-CoV-2 receptor: molecular mechanisms and potential therapeutic target, Intensive Care Med
Zhang, Taylor, Bennett, Saad, Rayman, Association between regional selenium status and reported outcome of COVID 19 cases in China, Am J Clin Nutr
Zhang, Wu, Zhang, Probable pangolin origin of SARS-CoV-2 associated with the COVID-19 outbreak, Curr Biol
Zhang, Wu, Zhang, Probable pangolin origin of SARS-CoV-2 associated with the COVID-19 outbreak, Curr Biol
Zhang, Xiao, Zhang, Xia, Cao et al., Coagulopathy and antiphospholipid antibodies in patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMc2007575
Zhang, Xiao, Zhang, Xia, Cao et al., Coagulopathy and antiphospholipid antibodies in patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMc2007575
Zhang, Yeh, Ding, Liu, Zhang, Prospective study of probiotic supplementation results in immune stimulation and improvement of upper respiratory infection rate, Synth Syst Biotechnol
Zhang, Yibin, Cai, Guo, Li, In hospital use of statin is associated with a reduced risk of mortality among individuals with COVID-19, Cell Metab
Zhang, Zeng, Pan, Li, Hu et al., Safety, tolerability, and immunogenicity of an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in healthy adults aged 18-59 years: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 1/2 clinical trial, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30843-4
Zhang, Zhu, Cai, Lei, Qin et al., Association of inpatient use of angiotensinconverting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers with mortality among patients with hypertension hospitalized with COVID-19, Circ Res
Zhong, Cao, Zhong, Peng, Jiang et al., Immunity and coagulation/fibrinolytic processes may reduce the risk of severe illness in pregnant women with COVID-19, Am J Obstet Gynecol:S, doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2020.10.032
Zhou, Wang, Zhu, Xia, CT features of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pneumonia in 62 patients in Wuhan, China, AJR Am J Roentgenol
Zhou, Yang, Feng, Huang, Yun et al., Clinical features and chest CT findings of coronavirus disease 2019 in infants and young children, Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi
Zhou, Yang, Wang, Hu, Zhang et al., A pneumonia outbreak associated Z. N. Ghale-Noie et al. 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, J Am Coll Cardiol
Zhou, Yang, Wang, Hu, Zhang et al., A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin, Nature
Zhou, Yu, Du, Fan, Liu et al., Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet
Zhu, Guo, Li, Wang, Fang et al., Host and infectivity prediction of Wuhan 2019 novel coronavirus using deep learning algorithm, BioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.01.21.914044
Zhu, Wang, Fang, Peng, Zhang et al., Clinical analysis of 10 neonates born to mothers with 2019-nCoV pneumonia, Transl Pediatr
Zhu, Zhang, Li, Yang, Song, A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, N Engl J Med
Zhu, Zhang, Li, Yang, Song, A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, N Engl J Med
Zhu, Zhang, Li, Yang, Song, China Novel Coronavirus Investigating and Research Team. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China
Ziegler, Allon, Nyquist, Mbano, Miao et al., SARS-CoV-2 receptor ACE2 Is an interferon-stimulated gene in human airway epithelial cells and is detected in specific cell subsets across tissues, Cell
Zou, Chen, Zou, Han, Hao et al., Single-cell RNA-seq data analysis on the receptor ACE2 expression reveals the potential risk of different human organs vulnerable to 2019-nCoV infection, Front Med
Zou, Chen, Zou, Han, Hao et al., Single-cell RNA-seq data analysis on the receptor ACE2 expression reveals the potential risk of different human organs vulnerable to 2019-nCoV infection, Front Med
Zou, Chen, Zou, Han, Hao et al., Single-cell RNA-seq data analysis on the receptor ACE2 expression reveals the potential risk of different human organs vulnerable to 2019-nCoV infection, Front Med
Zou, Ruan, Huang, Liang, Huang et al., SARS-CoV-2 viral load in upper respiratory specimens of infected patients, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMc2001737
Zulfiqar, Villalba, Hassler, Andrès, Immune thrombocytopenic purpura in a patient with covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMc2010472
Zuo, Zhan, Zhang, Liu, Tso et al., Alterations in fecal fungal microbiome of patients with COVID-19 during time of hospitalization until discharge, Gastroenterology, doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.06.048
Zuo, Zhang, Lui, Yeoh, Li et al., Alterations in gut microbiota of patients with COVID-19 during time of hospitalization, Gastroenterology, doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.048
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-3-030-71697-4_17",
"ISBN": [
"9783030716967",
"9783030716974"
],
"ISSN": [
"0065-2598",
"2214-8019"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-71697-4_17",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Chapter History",
"name": "ChapterHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 1,
"value": "20 July 2021"
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vahedian-Azimi",
"given": "Amir",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rahimibashar",
"given": "Farshid",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Najafi",
"given": "Ali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kidde",
"given": "Jason",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shahriary",
"given": "Alireza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shojaei",
"given": "Sajad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pourhoseingholi",
"given": "Mohamad Amin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jamialahmadi",
"given": "Tannaz",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sahebkar",
"given": "Amirhossein",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Identification of Biomarkers, New Treatments, and Vaccines for COVID-19",
"Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-19T08:03:45Z",
"timestamp": 1626681825000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2021-08-04T06:15:41Z",
"timestamp": 1628057741000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-29T20:32:48Z",
"timestamp": 1643488368213
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 1,
"isbn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "9783030716967"
},
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "9783030716974"
}
],
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "0065-2598"
},
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "2214-8019"
}
],
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.springer.com/tdm",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-01-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1609459200000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.springer.com/tdm",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-01-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1609459200000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.springer.com/tdm",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-01-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1609459200000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.springer.com/tdm",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-01-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1609459200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/978-3-030-71697-4_17",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"page": "205-214",
"prefix": "10.1007",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
20
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer International Publishing",
"publisher-location": "Cham",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.10.15.20209817",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "17_CR1",
"unstructured": "Pan H, Peto R, Karim QA, Alejandria M, Swaminathan S (2020) Repurposed antiviral drugs for COVID-19 – interim WHO SOLIDARITY trial results. MedRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.10.15.20209817"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/ATVBAHA.120.314558",
"author": "D Gustafson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1818",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol",
"key": "17_CR2",
"unstructured": "Gustafson D, Raju S, Wu R, Ching C, Veitch S, Rathnakumar K et al (2020) Overcoming barriers: the endothelium as a linchpin of coronavirus disease 2019 pathogenesis? Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 40(8):1818–1829",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30937-5",
"author": "Z Varga",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1417",
"issue": "10234",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "17_CR3",
"unstructured": "Varga Z, Flammer AJ, Steiger P, Haberecker M, Andermatt R, Zinkernagel AS et al (2020) Endothelial cell infection and Endotheliitis in COVID-19. Lancet 395(10234):1417–1418",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cvr/cvaa230",
"author": "PC Evans",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2177",
"issue": "14",
"journal-title": "Cardiovasc Res",
"key": "17_CR4",
"unstructured": "Evans PC, Rainger GE, Mason JC, Guzik TJ, Osto E, Stamataki Z et al (2020) Endothelial dysfunction in COVID-19: a position paper of the ESC Working group for atherosclerosis and vascular biology, and the ESC council of basic cardiovascular science. Cardiovasc Res 116(14):2177–2184",
"volume": "116",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m810",
"author": "R Sommerstein",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "m810",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "17_CR5",
"unstructured": "Sommerstein R, Gräni C (2020) Rapid response: re: preventing a covid-19 pandemic: ACE inhibitors as a potential risk factor for fatal. BMJ 368:m810. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.m810",
"volume": "368",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m1182",
"author": "U Ravskov",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "m1182",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "17_CR6",
"unstructured": "Ravskov U (2020) Rapid response: cholesterol-lowering treatment may worsen the outcome of a COVID-19 infection. BMJ 368:m1182. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.m1182",
"volume": "368",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jacl.2020.04.008",
"author": "X Wei",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "297",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "J Clin Lipidol",
"key": "17_CR7",
"unstructured": "Wei X, Zeng W, Su J, Wan H, Yu X, Cao X (2020) Hypolipidemia is associated with the severity of Covid-19. J Clin Lipidol 14(3):297–304",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21037/atm.2016.11.03",
"author": "DS Fedson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "421",
"journal-title": "Ann Translat Med",
"key": "17_CR8",
"unstructured": "Fedson DS (2016) Treating the host response to emerging virus diseases: lesson learned from sepsis, pneumonia, influenza and Ebola. Ann Translat Med 4:421. https://doi.org/10.21037/atm.2016.11.03",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5114/aoms.2020.94655",
"author": "Z Reiner",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "490",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Arch Med Sci",
"key": "17_CR9",
"unstructured": "Reiner Z, Hatamipour M, Banach M, Pirro M, Sahebkar A (2020) Statins and the COVID-19 main protease: in silico evidence on direct interaction. Arch Med Sci 16(3):490–496",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.amjcard.2020.08.004",
"author": "CS Kow",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "153",
"journal-title": "Am J Cardiol",
"key": "17_CR10",
"unstructured": "Kow CS, Hasan SS (2020) Meta-analysis of effect of statins on patients with COVID-19. Am J Cardiol 134:153–155",
"volume": "134",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.3539",
"author": "G Grasselli",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1345",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern Med",
"key": "17_CR11",
"unstructured": "Grasselli G, Greco M, Zanella A (2020) Risk factors associated with mortality among patients with COVID-19 in intensive care units in Lombardy, Italy. JAMA Intern Med 180(10):1345–1355",
"volume": "180",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.04.24.20077875",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "17_CR12",
"unstructured": "Yan H, Valdes AM, Vijay A, Wang S, Liang L (2020) Role of drugs affecting the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system on susceptibility and severity of COVID-19: a large case-control study from Zheijang Province, China. MedRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.04.24.20077875"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-56210/v1.1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "17_CR13",
"unstructured": "Gupta A, Madhavan MV, Poterucha TJ, DeFilippis EM, Parikh SA (2020) Association between antecedent statin use and decreased mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19. Res Sq. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-56210/v1.1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11739-020-02504-y",
"author": "R Rossi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1573",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Intern Emerg Med",
"key": "17_CR14",
"unstructured": "Rossi R, Talarico M, Coppi F, Boriani G (2020) Protective role of statins in COVID 19 patients: importance of pharmacokinetic characteristics rather than intensity of action. Intern Emerg Med 15(8):1573–1576",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-03154-4",
"author": "G Rodriguez-Nava",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "429",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "17_CR15",
"unstructured": "Rodriguez-Nava G, Trelles-Garcia DP, Yanez-Bello MA, Chung CW, Friedman HJ (2020) Atorvastatin associated with decreased hazard for death in COVID-19 patients admitted to an ICU: a retrospective cohort study. Crit Care 24(1):429. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054-020-03154-4",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabet.2020.10.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "17_CR16",
"unstructured": "Cariou B, Goronflot T, Timbert A, Boullu S, Wargny M (2020) Routine use of statins and increased COVID-19 related mortality in inpatients with type 2 diabetes: results from the CORONADO study. Diabetes Metab 47(2):101202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabet.2020.10.001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/JAHA.120.018475",
"author": "O Saeed",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "24",
"journal-title": "J Am Heart Assoc",
"key": "17_CR17",
"unstructured": "Saeed O, Castagna F, Agalliu I, Xue X, Jorde UP (2020) Statin use and in-hospital mortality in diabetics with COVID-19. J Am Heart Assoc 9(24):e018475. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.120.018475",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmet.2020.06.015",
"author": "XJ Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "176",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Cell Metab",
"key": "17_CR18",
"unstructured": "Zhang XJ, Yibin W, Cai J, Guo J, Li H (2020) In hospital use of statin is associated with a reduced risk of mortality among individuals with COVID-19. Cell Metab 32(2):176–187",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "17_CR19",
"unstructured": "Social Security Health Insurance National Fund (2013) Use of statins: a consumption structure to be improved, major savings potential for the healthcare system. https://www.ameli.fr/fileadmin/user_upload/documents/29052013_DP_Usage_statines_mai_2013_vdef.pdf"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11906-020-01101-w",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "17_CR20",
"unstructured": "Patoulias D, Katsimardou A, Stavropoulos K, Imrialos K, Doumas M (2020) Renin-anfiotensin system inhibitors and COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Evidence for significant geographic disparities. Curr Hypertens Rep 22(11). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11906-020-01101-w"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa235",
"author": "GM Kuster",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1801",
"issue": "19",
"journal-title": "Eur Heart J",
"key": "17_CR21",
"unstructured": "Kuster GM, Pfister O, Burkard T, Zhou Q, Twerenbold R, Haaf P et al (2020) SARS-CoV2: should inhibitors of the renin-angiotensin system be withdrawn in patients with COVID-19? Eur Heart J 41(19):1801–1803",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2008975",
"author": "H Reynolds",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2441",
"issue": "25",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "17_CR22",
"unstructured": "Reynolds H, Adhikari S, Pulgarin C, Troxel A, Iturrate E, Johnson SB et al (2020) Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors and risk of COVID-19. N Engl J Med 382(25):2441–2448",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiaa447",
"author": "KW Lam",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1256",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "J Infect Dis",
"key": "17_CR23",
"unstructured": "Lam KW, Chow KW, Vo J, Hou W, Li H, Richman PS et al (2020) Continued in-hospital angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor and angiotensin II receptor blocker use in hypertensive COVID-19 patients is associated with positive clinical outcome. J Infect Dis 222(8):1256–1264",
"volume": "222",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa433",
"author": "C Gao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2058",
"issue": "22",
"journal-title": "Eur Heart J",
"key": "17_CR24",
"unstructured": "Gao C, Cai Y, Zhang K, Zhou L, Zhang Y (2020) Association of hypertension and antihypertensive treatment with COVID-19 mortality: a retrospective observational study. Eur Heart J 41(22):2058–2066",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317134",
"author": "P Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1671",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Circ Res",
"key": "17_CR25",
"unstructured": "Zhang P, Zhu L, Cai J, Lei F, Qin JJ, Xie J et al (2020) Association of inpatient use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers with mortality among patients with hypertension hospitalized with COVID-19. Circ Res 126(12):1671–1681",
"volume": "126",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2020.1746200",
"author": "J Meng",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "757",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Emerg Microbe Infect",
"key": "17_CR26",
"unstructured": "Meng J, Xiao G, Zhang J, He X, Ou M, Bi J et al (2020) Renin-angiotensin system inhibitors improve the clinical outcomes of COVID-19 patients with hypertension. Emerg Microbe Infect 9(1):757–760",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.15989",
"author": "C-K Chan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1563",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Hypertension",
"key": "17_CR27",
"unstructured": "Chan C-K, Huang Y-S, Liao H-W, Tsai IJ, Chu T-S (2020) Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors and risks of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hypertension 76(5):1563–1571",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1213/ANE.0000000000005292",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "17_CR28",
"unstructured": "Chow JH, Khanna AK, Kethireddy S, Yamane D, Levine A, Jackson AM et al (2021) Aspirin use is associated with decreased mechanical ventilation, ICU admission, and INhospital mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19. Anesth Anal 132(4):930–941"
}
],
"reference-count": 28,
"references-count": 28,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Association of In-hospital Use of Statins, Aspirin, and Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Inhibitors with Mortality and ICU Admission Due to COVID-19"
],
"type": "book-chapter",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy"
}