Efficacy and safety of Ensitrelvir in asymptomatic or mild to moderate COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
et al., Infection, doi:10.1007/s15010-025-02582-0, PROSPERO CRD42024572306, Jul 2025
50th treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2023, now with p = 0.015 from 8 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
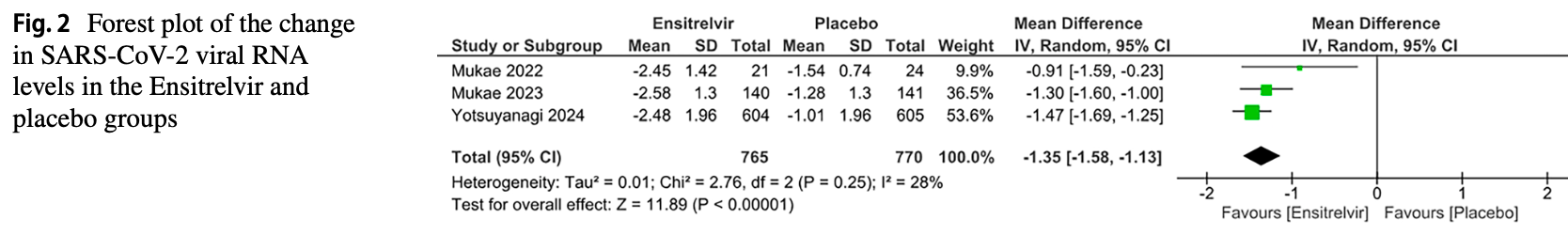
Meta-analysis of 6 RCTs with 2,793 participants showing significantly lower viral load with ensitrelvir. However, treatment was associated with significant adverse effects including decreased HDL levels, elevated triglycerides, increased bilirubin, more headaches, and higher overall treatment-emergent adverse events.
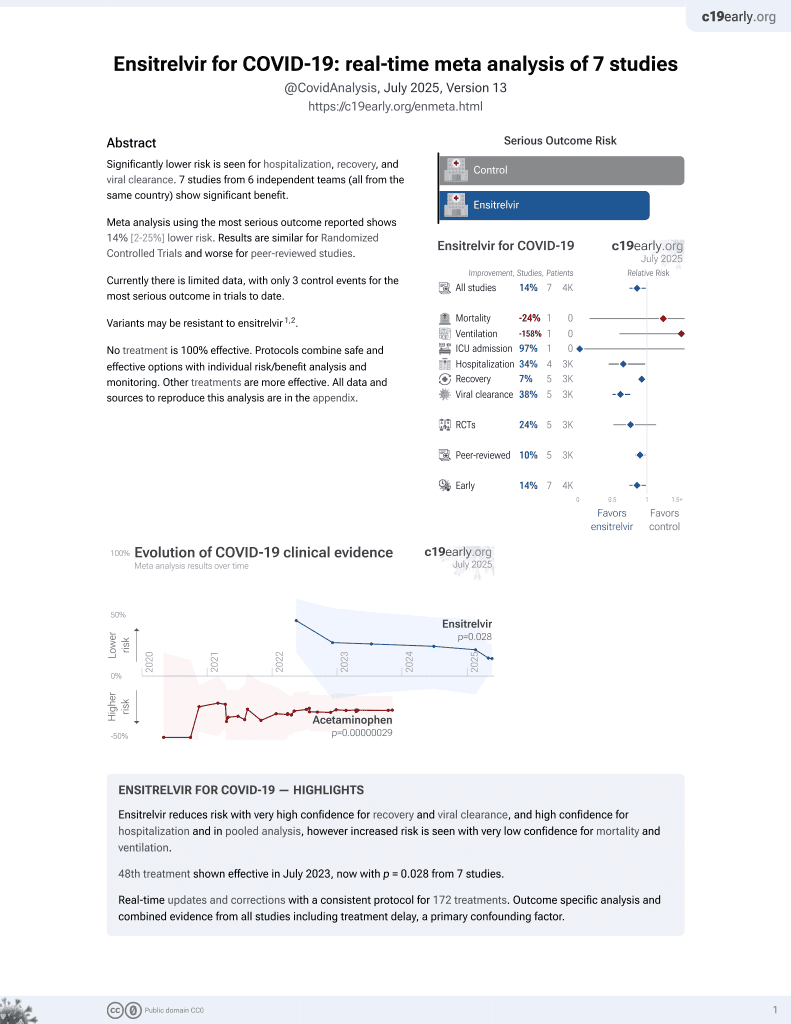
Currently there are 8 ensitrelvir studies and meta-analysis shows:
| Outcome | Improvement |
|---|---|
| Mortality | 24% higher [-83‑805%] |
| Ventilation | 158% higher [-40‑1012%] |
| ICU admission | 97% lower [-3585978‑100%] |
| Hospitalization | 34% lower [3‑55%] |
| Cases | 68% fewer [52‑78%] |
Ul Haq et al., 31 Jul 2025, peer-reviewed, 11 authors, trial PROSPERO CRD42024572306.
Efficacy and safety of Ensitrelvir in asymptomatic or mild to moderate COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Infection, doi:10.1007/s15010-025-02582-0
Introduction Since late 2019, COVID-19 has had a catastrophic impact on public health. Ensitrelvir, a new antiviral targeting the SARS-CoV-2 main protease, has reduced viral replication and disease severity. This meta-analysis and systematic review assessed Ensitrelvir's efficacy and safety in patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19 symptoms. Methods A comprehensive search was conducted in PubMed (Medline), Scopus, Embase, and CENTRAL up to July 2024 to retrieve randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing Ensitrelvir to placebo in adults with mild to moderate, RT-PCRconfirmed COVID-19. Outcomes were assessed at standardized time points, with viral RNA measured at day 4. Mean differences (MD) for continuous outcomes and risk ratios (RR) for binary outcomes, both with 95% confidence intervals (CIs), were calculated using the Mantel-Haenszel random-effects model. Efficacy outcomes included SARS-CoV-2 viral RNA, while safety outcomes included HDL, triglycerides, bilirubin, AST, headache, diarrhea, TEAEs, TRAEs, serious TEAEs, and treatment discontinuation. The quality of the included RCTs was assessed with the Cochrane Risk of Bias 2 (ROB2) tool.
Results The analysis included six RCTs with 2,793 participants: 1,860 received Ensitrelvir and 933 were given a placebo. Ensitrelvir gave significant results for reduced viral RNA levels of SARS-CoV-2 [MD: -1.35; 95% CI -1.58 to -1.13; p < 0.01] and the incidence of lower cholesterol levels [RR: 8.83; 95% CI 4.05 to 19.27; p < 0.01] compared to the placebo group. However, it was associated with increased risks of decreased HDL levels, elevated triglycerides, increased bilirubin, more headaches, and a higher overall occurrence of treatment-emergent adverse events. Conclusion Ensitrelvir effectively reduces viral load in COVID-19 patients, but its safety profile raises concerns due to significant adverse effects. The benefits must be carefully weighed against the risks, and further research is needed to confirm its role in treatment and to find ways to mitigate these adverse effects.
Authors and Affiliations Muhammad Zain Ul Haq
References
Auvigne, Vaux, Strat, Severe hospital events following symptomatic infection with Sars-CoV-2 Omicron and Delta variants in France, December 2021-January 2022: a retrospective, population-based, matched cohort study, EClin Med, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101455
Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19-final report, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2007764
Bernal, Da Silva, Musungaie, Molnupiravir for oral treatment of Covid-19 in nonhospitalized patients, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2116044
Butler, Hobbs, Gbinigie, Molnupiravir plus usual care versus usual care alone as early treatment for adults with COVID-19 at increased risk of adverse outcomes (PANO-RAMIC): an open-label, platform-adaptive randomised controlled trial, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02597-1
Hammond, Fountaine, Yunis, Nirmatrelvir for vaccinated or unvaccinated adult outpatients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2309003
Hammond, Leister-Tebbe, Gardner, Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2118542
Imran, Zubair, Mughal, Shakeel, Ritonavir-boosted nirmatrelvir and COVID-19 outcomes in the age of Omicron variant, Ann Med Surg, doi:10.1097/MS9.0000000000000169
Marzolini, Kuritzkes, Marra, Recommendations for the management of drug-drug interactions between the COVID-19 antiviral nirmatrelvir/ritonavir (Paxlovid) and comedications, Clin Pharmacol Ther, doi:10.1002/cpt.2646
Mukae, Yotsuyanagi, Ohmagari, A randomized phase 2/3 study of Ensitrelvir, a novel oral SARS-CoV-2 3C-like protease inhibitor, in Japanese patients with mild-tomoderate COVID-19 or asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection: results of the phase 2a part, Antimicrob Agents Chemother, doi:10.1128/aac.00697-22
Mukae, Yotsuyanagi, Ohmagari, Efficacy and safety of Ensitrelvir in patients with mild-to-moderate coronavirus disease 2019: the phase 2b part of a randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 2/3 study, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciac933
Nalbandian, Sehgal, Gupta, Post-acute COVID-19 syndrome, Nat Med, doi:10.1038/s41591-021-01283-z
Nobori, Fukao, Kuroda, Efficacy of Ensitrelvir against SARS-CoV-2 in a delayed-treatment mouse model, J Antimicrob Chemother, doi:10.1093/jac/dkac257
Ohmagari, Yotsuyanagi, Doi, Efficacy and safety of Ensitrelvir for asymptomatic or mild COVID-19: an exploratory analysis of a multicenter, randomized, phase 2b/3 clinical trial, Influenza Other Respir Viruses, doi:10.1111/irv.13338
Onder, Rezza, Brusaferro, Case-fatality rate and characteristics of patients dying in relation to COVID-19 in Italy, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.4683
Page, Mckenzie, Bossuyt, The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.n71
Rauch, Costacurta, Schöppe, Highly specific SARS-CoV-2 main protease (M pro ) mutations against the clinical antiviral Ensitrelvir selected in a safe, VSV-based system, Antivir Res, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2024.105969
Research, De, Assessing COVID-19-related symptoms in outpatient adult and adolescent subjects in clinical trials of drugs and biological products for COVID-19 prevention or treatment
Sanders, Monogue, Jodlowski, Cutrell, Pharmacologic treatments for Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a review, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.6019
Shimizu, Sonoyama, Fukuhara, Kuwata, Matsuo et al., A phase 1 study of Ensitrelvir fumaric acid tablets evaluating the safety, pharmacokinetics and food effect in healthy adult populations, Clin Drug Investig, doi:10.1007/s40261-023-01309-z
Shimizu, Sonoyama, Fukuhara, Kuwata, Matsuo et al., Safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of the novel antiviral agent Ensitrelvir fumaric acid, a SARS-CoV-2 3CL protease inhibitor, in healthy adults, Antimicrob Agents Chemother, doi:10.1128/aac.00632-22
Sterne, Savović, Page, RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.l4898
Wu, Mcgoogan, Characteristics of and important lessons from the Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.2648
Yotsuyanagi, Ohmagari, Doi, Efficacy and safety of 5-day oral Ensitrelvir for patients with mild to moderate COVID-19 the SCORPIO-SR randomized clinical trial, JAMA Netw Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.54991
Zhang, Jackson, Mou, SARS-CoV-2 spike-protein D614G mutation increases virion spike density and infectivity, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-020-19808-4
Zhou, Yang, Wang, A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s15010-025-02582-0",
"ISSN": [
"0300-8126",
"1439-0973"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s15010-025-02582-0",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Introduction</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Since late 2019, COVID-19 has had a catastrophic impact on public health. Ensitrelvir, a new antiviral targeting the SARS-CoV-2 main protease, has reduced viral replication and disease severity. This meta-analysis and systematic review assessed Ensitrelvir’s efficacy and safety in patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19 symptoms.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>A comprehensive search was conducted in PubMed (Medline), Scopus, Embase, and CENTRAL up to July 2024 to retrieve randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing Ensitrelvir to placebo in adults with mild to moderate, RT-PCR–confirmed COVID-19. Outcomes were assessed at standardized time points, with viral RNA measured at day 4. Mean differences (MD) for continuous outcomes and risk ratios (RR) for binary outcomes, both with 95% confidence intervals (CIs), were calculated using the Mantel–Haenszel random-effects model. Efficacy outcomes included SARS-CoV-2 viral RNA, while safety outcomes included HDL, triglycerides, bilirubin, AST, headache, diarrhea, TEAEs, TRAEs, serious TEAEs, and treatment discontinuation. The quality of the included RCTs was assessed with the Cochrane Risk of Bias 2 (ROB2) tool.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>The analysis included six RCTs with 2,793 participants: 1,860 received Ensitrelvir and 933 were given a placebo. Ensitrelvir gave significant results for reduced viral RNA levels of SARS-CoV-2 [MD: − 1.35; 95% CI − 1.58 to − 1.13; p < 0.01] and the incidence of lower cholesterol levels [RR: 8.83; 95% CI 4.05 to 19.27; p < 0.01] compared to the placebo group. However, it was associated with increased risks of decreased HDL levels, elevated triglycerides, increased bilirubin, more headaches, and a higher overall occurrence of treatment-emergent adverse events.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Ensitrelvir effectively reduces viral load in COVID-19 patients, but its safety profile raises concerns due to significant adverse effects. The benefits must be carefully weighed against the risks, and further research is needed to confirm its role in treatment and to find ways to mitigate these adverse effects.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"2582"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "9 March 2025"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "5 June 2025"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "31 July 2025"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Declarations",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Conflict of interest",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "The authors declare no conflicts of interest."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Ethical compliance",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 3,
"value": "No ethical approval was required for this study design, as all data were obtained from publicly available sources."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ul Haq",
"given": "Muhammad Zain",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ashraf",
"given": "Saad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shah",
"given": "Muhammad Shahmeer Ullah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sulaiman",
"given": "Samia Aziz",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shaukat",
"given": "Ayesha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ansari",
"given": "Muhammad Ahsan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Basaria",
"given": "Areeba Aamir Ali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fatima",
"given": "Laveeza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saeed",
"given": "Humza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Goyal",
"given": "Aman",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Daoud",
"given": "Mohamed",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Infection",
"container-title-short": "Infection",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2025-07-31T06:34:10Z",
"timestamp": 1753943650000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2025-07-31T06:34:14Z",
"timestamp": 1753943654000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2025-07-31T07:10:03Z",
"timestamp": 1753945803768,
"version": "3.41.2"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
31
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2025-07-31T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1753920000000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2025-07-31T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1753920000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s15010-025-02582-0.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s15010-025-02582-0/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s15010-025-02582-0.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1007",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
31
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
31
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7",
"author": "P Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "270",
"issue": "7798",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "2582_CR1",
"unstructured": "Zhou P, Yang XL, Wang XG, et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature. 2020;579(7798):270–3. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7.",
"volume": "579",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.2648",
"author": "Z Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1239",
"issue": "13",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "2582_CR2",
"unstructured": "Wu Z, McGoogan JM. Characteristics of and important lessons from the Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA. 2020;323(13):1239–42. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2020.2648.",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.4683",
"author": "G Onder",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1775",
"issue": "18",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "2582_CR3",
"unstructured": "Onder G, Rezza G, Brusaferro S. Case-fatality rate and characteristics of patients dying in relation to COVID-19 in Italy. JAMA. 2020;323(18):1775–6. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2020.4683.",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-021-01283-z",
"author": "A Nalbandian",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "601",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "2582_CR4",
"unstructured": "Nalbandian A, Sehgal K, Gupta A, et al. Post-acute COVID-19 syndrome. Nat Med. 2021;27(4):601–15. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-021-01283-z.",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2007764",
"author": "JH Beigel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1813",
"issue": "19",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2582_CR5",
"unstructured": "Beigel JH, Tomashek KM, Dodd LE, et al. Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19—final report. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(19):1813–26. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2007764.",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021436",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2582_CR6",
"unstructured": "null null. Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(8):693–704. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2021436."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cpt.2646",
"author": "C Marzolini",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1191",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Clin Pharmacol Ther",
"key": "2582_CR7",
"unstructured": "Marzolini C, Kuritzkes DR, Marra F, et al. Recommendations for the management of drug–drug interactions between the COVID-19 antiviral nirmatrelvir/ritonavir (Paxlovid) and comedications. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2022;112(6):1191–200. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpt.2646.",
"volume": "112",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.6019",
"author": "JM Sanders",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1824",
"issue": "18",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "2582_CR8",
"unstructured": "Sanders JM, Monogue ML, Jodlowski TZ, Cutrell JB. Pharmacologic treatments for Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a review. JAMA. 2020;323(18):1824–36. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2020.6019.",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-19808-4",
"author": "L Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "6013",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "2582_CR9",
"unstructured": "Zhang L, Jackson CB, Mou H, et al. SARS-CoV-2 spike-protein D614G mutation increases virion spike density and infectivity. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):6013. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-19808-4.",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.54991",
"author": "H Yotsuyanagi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "2582_CR10",
"unstructured": "Yotsuyanagi H, Ohmagari N, Doi Y, et al. Efficacy and safety of 5-day oral Ensitrelvir for patients with mild to moderate COVID-19 the SCORPIO-SR randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw Open. 2024. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.54991.",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.n71",
"author": "MJ Page",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "2582_CR11",
"unstructured": "Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021;372: n71. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.n71.",
"volume": "372",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.l4898",
"author": "JAC Sterne",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "2582_CR12",
"unstructured": "Sterne JAC, Savović J, Page MJ, et al. RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. 2019;366: l4898. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.l4898.",
"volume": "366",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/irv.13338",
"author": "N Ohmagari",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Influenza Other Respir Viruses",
"key": "2582_CR13",
"unstructured": "Ohmagari N, Yotsuyanagi H, Doi Y, et al. Efficacy and safety of Ensitrelvir for asymptomatic or mild COVID-19: an exploratory analysis of a multicenter, randomized, phase 2b/3 clinical trial. Influenza Other Respir Viruses. 2024;18(6): e13338. https://doi.org/10.1111/irv.13338.",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40261-023-01309-z",
"author": "R Shimizu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "785",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Clin Drug Investig",
"key": "2582_CR14",
"unstructured": "Shimizu R, Sonoyama T, Fukuhara T, Kuwata A, Matsuo Y, Kubota R. A phase 1 study of Ensitrelvir fumaric acid tablets evaluating the safety, pharmacokinetics and food effect in healthy adult populations. Clin Drug Investig. 2023;43(10):785–97. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40261-023-01309-z.",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/aac.00632-22",
"author": "R Shimizu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e0063222",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob Agents Chemother",
"key": "2582_CR15",
"unstructured": "Shimizu R, Sonoyama T, Fukuhara T, Kuwata A, Matsuo Y, Kubota R. Safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of the novel antiviral agent Ensitrelvir fumaric acid, a SARS-CoV-2 3CL protease inhibitor, in healthy adults. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2022;66(10):e0063222. https://doi.org/10.1128/aac.00632-22.",
"volume": "66",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/aac.00697-22",
"author": "H Mukae",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e0069722",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob Agents Chemother",
"key": "2582_CR16",
"unstructured": "Mukae H, Yotsuyanagi H, Ohmagari N, et al. A randomized phase 2/3 study of Ensitrelvir, a novel oral SARS-CoV-2 3C-like protease inhibitor, in Japanese patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19 or asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection: results of the phase 2a part. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2022;66(10):e0069722. https://doi.org/10.1128/aac.00697-22.",
"volume": "66",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciac933",
"author": "H Mukae",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1403",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "2582_CR17",
"unstructured": "Mukae H, Yotsuyanagi H, Ohmagari N, et al. Efficacy and safety of Ensitrelvir in patients with mild-to-moderate coronavirus disease 2019: the phase 2b part of a randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 2/3 study. Clin Infect Dis. 2023;76(8):1403–11. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciac933.",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jac/dkac257",
"author": "H Nobori",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2984",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "J Antimicrob Chemother",
"key": "2582_CR18",
"unstructured": "Nobori H, Fukao K, Kuroda T, et al. Efficacy of Ensitrelvir against SARS-CoV-2 in a delayed-treatment mouse model. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2022;77(11):2984–91. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkac257.",
"volume": "77",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MS9.0000000000000169",
"author": "L Imran",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "313",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Ann Med Surg",
"key": "2582_CR19",
"unstructured": "Imran L, Zubair R, Mughal S, Shakeel R. Ritonavir-boosted nirmatrelvir and COVID-19 outcomes in the age of Omicron variant. Ann Med Surg. 2023;85(2):313–5. https://doi.org/10.1097/MS9.0000000000000169.",
"volume": "85",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2024.105969",
"author": "S Rauch",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Antivir Res",
"key": "2582_CR20",
"unstructured": "Rauch S, Costacurta F, Schöppe H, et al. Highly specific SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro) mutations against the clinical antiviral Ensitrelvir selected in a safe, VSV-based system. Antivir Res. 2024;231: 105969. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.antiviral.2024.105969.",
"volume": "231",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2116044",
"author": "A Jayk Bernal",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "509",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med.",
"key": "2582_CR21",
"unstructured": "Jayk Bernal A, Gomes da Silva MM, Musungaie DB, et al. Molnupiravir for oral treatment of Covid-19 in nonhospitalized patients. N Engl J Med. 2022;386(6):509–20. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2116044.",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2118542",
"author": "J Hammond",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1397",
"issue": "15",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2582_CR22",
"unstructured": "Hammond J, Leister-Tebbe H, Gardner A, et al. Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2022;386(15):1397–408. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2118542.",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101455",
"author": "V Auvigne",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "EClin Med",
"key": "2582_CR23",
"unstructured": "Auvigne V, Vaux S, Strat YL, et al. Severe hospital events following symptomatic infection with Sars-CoV-2 Omicron and Delta variants in France, December 2021-January 2022: a retrospective, population-based, matched cohort study. EClin Med. 2022;48: 101455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101455.",
"volume": "48",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02597-1",
"author": "CC Butler",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "281",
"issue": "10373",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "2582_CR24",
"unstructured": "Butler CC, Hobbs FDR, Gbinigie OA, et al. Molnupiravir plus usual care versus usual care alone as early treatment for adults with COVID-19 at increased risk of adverse outcomes (PANORAMIC): an open-label, platform-adaptive randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2023;401(10373):281–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02597-1.",
"volume": "401",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"key": "2582_CR25",
"unstructured": "Research C for DE and. Assessing COVID-19-related symptoms in outpatient adult and adolescent subjects in clinical trials of drugs and biological products for COVID-19 prevention or treatment. February 22, 2024. https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/assessing-covid-19-related-symptoms-outpatient-adult-and-adolescent-subjects-clinical-trials-drugs. Accessed 26 Aug 2024."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2309003",
"author": "J Hammond",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1186",
"issue": "13",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2582_CR26",
"unstructured": "Hammond J, Fountaine RJ, Yunis C, et al. Nirmatrelvir for vaccinated or unvaccinated adult outpatients with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2024;390(13):1186–95. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2309003.",
"volume": "390",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"key": "2582_CR27",
"unstructured": "Study Details | A study to compare S-217622 with placebo in non-hospitalized participants with COVID-19 | ClinicalTrials.gov. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05305547. Accessed 26 Aug 2024."
},
{
"key": "2582_CR28",
"unstructured": "Study Details | Strategies and treatments for respiratory infections & viral emergencies (STRIVE): Shionogi protease inhibitor (Ensitrelvir) | ClinicalTrials.gov. https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05605093. Accessed 26 Aug 2024."
}
],
"reference-count": 28,
"references-count": 28,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s15010-025-02582-0"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Efficacy and safety of Ensitrelvir in asymptomatic or mild to moderate COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy"
}