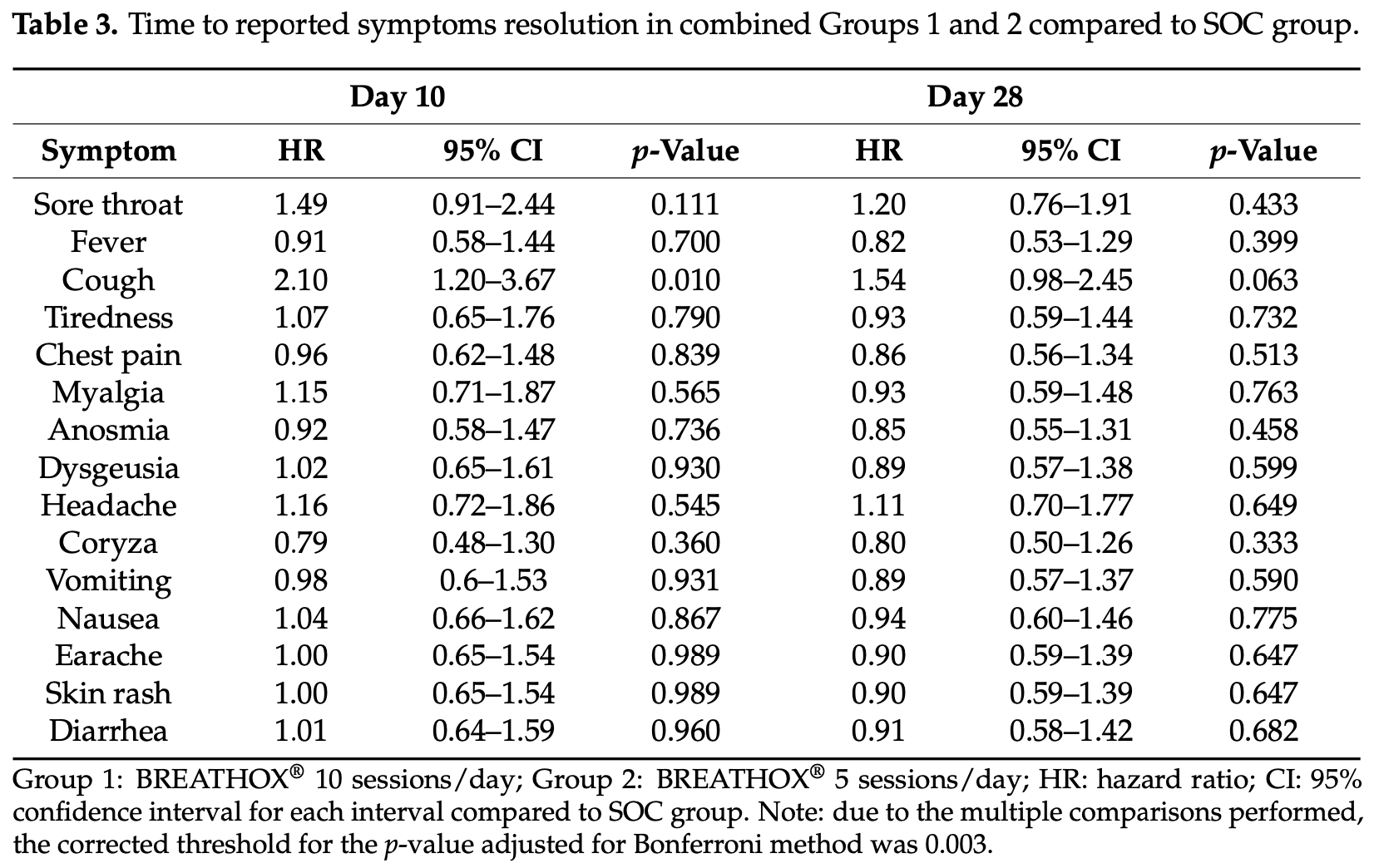
Efficacy of BREATHOX® Device Inhalation on Acute Symptoms Associated with COVID-19 (BREATH Study): A Randomized Pilot Clinical Trial
et al., Journal of Clinical Medicine, doi:10.3390/jcm12186075, Sep 2023
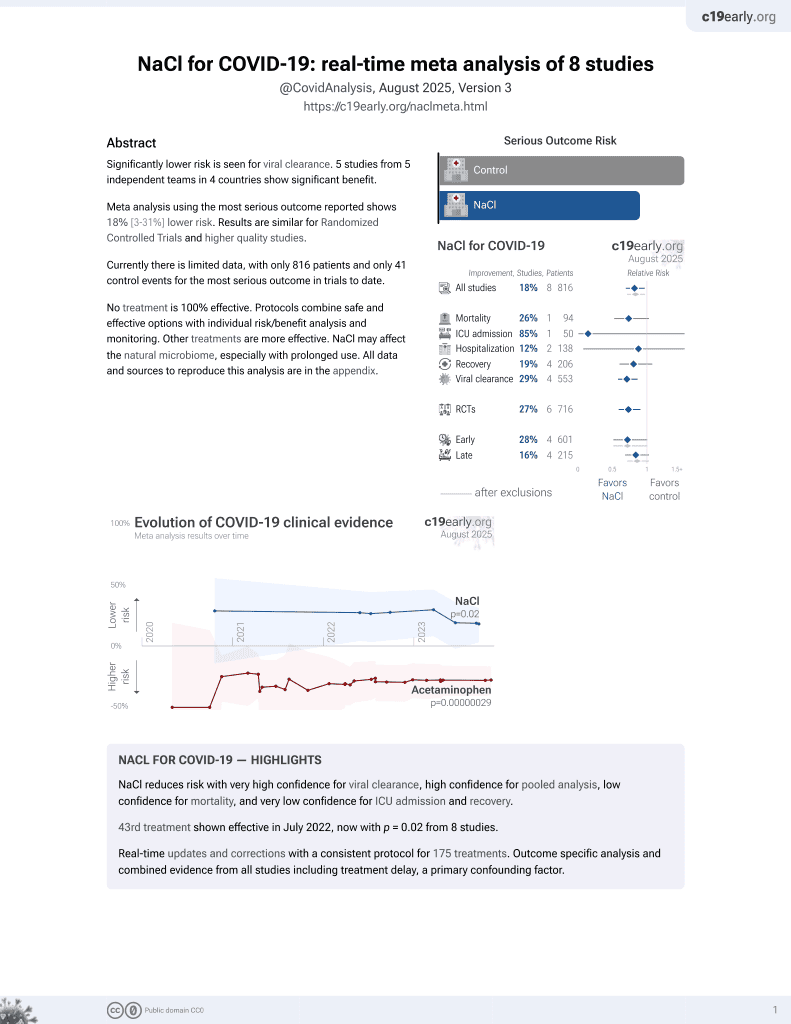
NaCl for COVID-19
44th treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2022, now with p = 0.0028 from 9 studies.
Lower risk for progression and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
RCT 98 outpatients in Brazil, showing faster recovery from cough with inhaled hypertonic saline. Authors note that the effect on coughing may hypothetically be related to a hyperosmotic response influencing the function of different membrane channels and preventing virus entry into the cells; and that the hypertonic solution may increase mucociliary clearance and reduce the destructive inflammatory process in the airways with a decrease in respiratory symptoms.
|
risk of hospitalization, 74.8% lower, RR 0.25, p = 0.34, treatment 0 of 65 (0.0%), control 1 of 33 (3.0%), NNT 33, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
risk of no recovery, 9.9% higher, HR 1.10, p = 0.70, treatment 65, control 33, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, fever.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 52.4% lower, HR 0.48, p = 0.009, treatment 65, control 33, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, cough.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 32.9% lower, HR 0.67, p = 0.11, treatment 65, control 33, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, sore throat.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 2.0% lower, HR 0.98, p = 0.94, treatment 65, control 33, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, dysgeusia.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 8.7% higher, HR 1.09, p = 0.74, treatment 65, control 33, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, anosmia.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
de Gabory et al., Seawater nasal wash to reduce symptom duration and viral load in COVID-19 and upper respiratory tract infections: a randomized controlled multicenter trial, European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology, doi:10.1007/s00405-024-08518-y.
Tanni et al., 20 Sep 2023, Randomized Controlled Trial, Brazil, peer-reviewed, 20 authors.
Contact: robsonapp@gmail.com (corresponding author), suzanapneumo@gmail.com, felipedamatto@hotmail.com, ctbredaneto@gmail.com, lrs.oliveira@unesp.br, luanapagan@alunos.fmb.unesp.br, marianagatto11@hotmail.com, leticiadv@gmail.com, lianascoelho@gmail.com, dianerezende@gmail.com, lh.machado@unesp.br, gustavo.mota@unesp.br, marina.monte@unesp.br, felipe.santaella@unesp.br, elisenf21@gmail.com, mcallegari10@gmail.com, marina.okoshi@unesp.br, fcwehrmeister@gmail.com, estefania.franco@unesp.br, ulw@rn.dk.
Efficacy of BREATHOX® Device Inhalation on Acute Symptoms Associated with COVID-19 (BREATH Study): A Randomized Pilot Clinical Trial
Journal of Clinical Medicine, doi:10.3390/jcm12186075
1) Background: A high concentration of sodium chloride on in vitro cell culture leads to reduced SARS-CoV-2 replication. Therefore, our aim was to evaluate the effects of inhaling hypertonic NaCl particles (BREATHOX ® ) on the duration of COVID-19-induced acute symptoms. (2) Methods: A prospective, open label, randomized, standard of care-controlled group (SOC) pilot trial compared inhaled oral and nasal administered BREATHOX ® (2.0 mg NaCl, particles size between 1-10 µm), with five or ten inhalations per day for ten days. The primary endpoint was the time to resolve COVID-19-related symptoms. Safety outcomes included adverse clinical and laboratory events. (3) Results: A total of 101 individuals were screened and 98 were randomly assigned to BREATHOX ® ten sessions per day (Group 1; 33 patients), BREATHOX ® five sessions per day (Group 2; 32 patients), or SOC (33 patients), and followed up for 28 days. There was an association with cough frequency after 10 days BREATHOX ® compared to SOC [Group 1: hazard ratio (HR) 2.01, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.06-3.81; Group 2: HR 2.17, 95% CI 1.17-4.04]. No differences between the groups for the reported symptoms' resolution time were seen after 28 days. After combining both BREATHOX ® groups, the period to cough resolution 10 days after randomization was significantly lower than in SOC (HR 2.10,). An adverse event occurred in 30% of Group 1, 36% of Group 2, and 9% in SOC individuals. One patient from SOC had a serious adverse event. Nasal burning, sore or itchy nose, and dry mouth were considered related to BREATHOX ® use and resolved after stopping inhalations. (4) Conclusion: BREATHOX ® inhalation is safe and may be effective in reducing the duration of COVID-19-induced coughing.
Funding: This research was funded by LIITA Care.
Institutional Review Board Statement: The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee (Approval number 5.627.523). The study protocol was registered on the clinical trials registry (NCT05196581). All study activities, including project coordination, data management, and site monitoring were performed at the Botucatu Medical School, São Paulo State University, Brazil. The trial was overseen by a data-safety monitoring board of independent experts.
Informed Consent Statement: Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
Brito, Braga, Cunha, Takenami, Mecanismos imunopatológicos envolvidos na infecção por SARS-CoV-2, J. Bras. Patol. Med. Lab
Chen, Geng, Xu, Chen, Gao et al., The features comparison between patients in the ICU and general wards and between patients with different outcomes: A 2020 COVID-19 study, Ann. Palliat. Med, doi:10.21037/apm-21-25
De Souza, Rivera, Almeida, Ge, De Souza et al., Molecular Dynamics Reveals Complex Compensatory Effects of Ionic Strength on the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Spike/Human Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 Interaction, J. Phys. Chem. Lett, doi:10.1021/acs.jpclett.0c02602
Guan, Ni, Hu, Liang, Ou et al., Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2002032
Huang, Wang, Li, Ren, Zhao et al., Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5
Jin, Cai, Cheng, Cheng, Deng et al., A rapid advice guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) infected pneumonia (standard version), Mil. Med. Res, doi:10.1186/s40779-020-0233-6
Li, Geng, Peng, Meng, Lu, Molecular immune pathogenesis and diagnosis of COVID-19, J. Pharm. Anal, doi:10.1016/j.jpha.2020.03.001
Machado, Glaser, Araujo, Petiz, Oliveira et al., Inhibition of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Replication by Hypertonic Saline Solution in Lung and Kidney Epithelial Cells, ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci, doi:10.1021/acsptsci.1c00080
Rytilä, Lindqvist, Laitinen, Safety of sputum induction in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, Eur. Respir. J, doi:10.1034/j.1399-3003.2000.01522.x
Schoeffei, Anderson, Altounyan, Bronchial hyperreactivity in response to inhalation of ultrasonically nebulised solutions of distilled water and saline, Br. Med. J, doi:10.1136/bmj.283.6302.1285
Taube, Holz, Mücke, Jorres, Magnussen, Airway response to inhaled hypertonic saline in patients with moderate to severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med, doi:10.1164/ajrccm.164.10.2104024
Tay, Poh, Rénia, Macary, Ng, The trinity of COVID-19: Immunity, inflammation and intervention, Nat. Rev. Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41577-020-0311-8
Wang, Ding, From SARS to COVID-19: Pathogens, receptor, pathogenesis and principles of the treatment, Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi
Wark, Mcdonald, Nebulised hypertonic saline for cystic fibrosis, Cochrane Database Syst. Rev, doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001506.pub4
Who, WHO COVID-19 Dashboard
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm12186075",
"ISSN": [
"2077-0383"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/jcm12186075",
"abstract": "<jats:p>(1) Background: A high concentration of sodium chloride on in vitro cell culture leads to reduced SARS-CoV-2 replication. Therefore, our aim was to evaluate the effects of inhaling hypertonic NaCl particles (BREATHOX®) on the duration of COVID-19-induced acute symptoms. (2) Methods: A prospective, open label, randomized, standard of care-controlled group (SOC) pilot trial compared inhaled oral and nasal administered BREATHOX® (2.0 mg NaCl, particles size between 1–10 μm), with five or ten inhalations per day for ten days. The primary endpoint was the time to resolve COVID-19-related symptoms. Safety outcomes included adverse clinical and laboratory events. (3) Results: A total of 101 individuals were screened and 98 were randomly assigned to BREATHOX® ten sessions per day (Group 1; 33 patients), BREATHOX® five sessions per day (Group 2; 32 patients), or SOC (33 patients), and followed up for 28 days. There was an association with cough frequency after 10 days BREATHOX® compared to SOC [Group 1: hazard ratio (HR) 2.01, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.06–3.81; Group 2: HR 2.17, 95% CI 1.17–4.04]. No differences between the groups for the reported symptoms’ resolution time were seen after 28 days. After combining both BREATHOX® groups, the period to cough resolution 10 days after randomization was significantly lower than in SOC (HR 2.10, 95% CI 1.20–3.67). An adverse event occurred in 30% of Group 1, 36% of Group 2, and 9% in SOC individuals. One patient from SOC had a serious adverse event. Nasal burning, sore or itchy nose, and dry mouth were considered related to BREATHOX® use and resolved after stopping inhalations. (4) Conclusion: BREATHOX® inhalation is safe and may be effective in reducing the duration of COVID-19-induced coughing.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"jcm12186075"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2587-2759",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical School, São Paulo State University (Unesp), Distrito de Rubião Junior s/n, Botucatu 18618-970, São Paulo, Brazil"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Tanni",
"given": "Suzana",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Departament of Social Medicine, The Faculty of Medicine, Federal University of Pelotas, Avenida Duque de Caxias 250, Pelotas 96030-002, Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil"
}
],
"family": "Wehrmeister",
"given": "Fernando",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinical Hospital of Botucatu Medical School, São Paulo State University (Unesp), Distrito de Rubião Junior s/n, Botucatu 18618-970, São Paulo, Brazil"
}
],
"family": "Prudente",
"given": "Robson",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical School, São Paulo State University (Unesp), Distrito de Rubião Junior s/n, Botucatu 18618-970, São Paulo, Brazil"
}
],
"family": "Damatto",
"given": "Felipe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical School, São Paulo State University (Unesp), Distrito de Rubião Junior s/n, Botucatu 18618-970, São Paulo, Brazil"
}
],
"family": "Breda Neto",
"given": "Carlos",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical School, São Paulo State University (Unesp), Distrito de Rubião Junior s/n, Botucatu 18618-970, São Paulo, Brazil"
}
],
"family": "Oliveira",
"given": "Leiliane",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical School, São Paulo State University (Unesp), Distrito de Rubião Junior s/n, Botucatu 18618-970, São Paulo, Brazil"
}
],
"family": "Pagan",
"given": "Luana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical School, São Paulo State University (Unesp), Distrito de Rubião Junior s/n, Botucatu 18618-970, São Paulo, Brazil"
}
],
"family": "Gatto",
"given": "Mariana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical School, São Paulo State University (Unesp), Distrito de Rubião Junior s/n, Botucatu 18618-970, São Paulo, Brazil"
}
],
"family": "Vieira",
"given": "Letícia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical School, São Paulo State University (Unesp), Distrito de Rubião Junior s/n, Botucatu 18618-970, São Paulo, Brazil"
}
],
"family": "Coelho",
"given": "Liana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical School, São Paulo State University (Unesp), Distrito de Rubião Junior s/n, Botucatu 18618-970, São Paulo, Brazil"
}
],
"family": "Rezende",
"given": "Diane",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical School, São Paulo State University (Unesp), Distrito de Rubião Junior s/n, Botucatu 18618-970, São Paulo, Brazil"
}
],
"family": "Machado",
"given": "Luiz",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8103-3338",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical School, São Paulo State University (Unesp), Distrito de Rubião Junior s/n, Botucatu 18618-970, São Paulo, Brazil"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Mota",
"given": "Gustavo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4060-870X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical School, São Paulo State University (Unesp), Distrito de Rubião Junior s/n, Botucatu 18618-970, São Paulo, Brazil"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Gaiato",
"given": "Marina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical School, São Paulo State University (Unesp), Distrito de Rubião Junior s/n, Botucatu 18618-970, São Paulo, Brazil"
}
],
"family": "Santaella",
"given": "Felipe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8529-7637",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical School, São Paulo State University (Unesp), Distrito de Rubião Junior s/n, Botucatu 18618-970, São Paulo, Brazil"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Campos",
"given": "Elisângela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinical Hospital of Botucatu Medical School, São Paulo State University (Unesp), Distrito de Rubião Junior s/n, Botucatu 18618-970, São Paulo, Brazil"
}
],
"family": "Franco",
"given": "Estefânia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9557-3968",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical School, São Paulo State University (Unesp), Distrito de Rubião Junior s/n, Botucatu 18618-970, São Paulo, Brazil"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Callegari",
"given": "Matheus",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7728-4505",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical School, São Paulo State University (Unesp), Distrito de Rubião Junior s/n, Botucatu 18618-970, São Paulo, Brazil"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Okoshi",
"given": "Marina Politi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1975-3654",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Clinical Medicine, The Faculty of Medicine, Aalborg University Hospital, Hobrovej 18-22, 9000 Aalborg, Denmark"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Weinreich",
"given": "Ulla",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of Clinical Medicine",
"container-title-short": "JCM",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2023-09-21T02:38:45Z",
"timestamp": 1695263925000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2023-09-21T03:27:40Z",
"timestamp": 1695266860000
},
"funder": [
{
"name": "Liita Care"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2023-09-22T05:09:40Z",
"timestamp": 1695359380985
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "18",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9,
20
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "18",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2023-09-20T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1695168000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2077-0383/12/18/6075/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "6075",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9,
20
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9,
20
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"key": "ref_1",
"unstructured": "WHO (2020). WHO COVID-19 Dashboard, World Health Organization. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-020-0311-8",
"article-title": "The trinity of COVID-19: Immunity, inflammation and intervention",
"author": "Tay",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "363",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_2",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2002032",
"article-title": "Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China",
"author": "Guan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1708",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21037/apm-21-25",
"article-title": "The features comparison between patients in the ICU and general wards and between patients with different outcomes: A 2020 COVID-19 study",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "672",
"journal-title": "Ann. Palliat. Med.",
"key": "ref_4",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"article-title": "Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "P497",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref_5",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "ref_6",
"unstructured": "COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines Panel (2023, April 22). Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Treatment Guidelines, Available online: https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/."
},
{
"article-title": "Mecanismos imunopatológicos envolvidos na infecção por SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Brito",
"first-page": "e3352020",
"journal-title": "J. Bras. Patol. Med. Lab.",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "A rapid advice guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) infected pneumonia (standard version)",
"author": "Jin",
"first-page": "4",
"journal-title": "Mil. Med. Res.",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jpha.2020.03.001",
"article-title": "Molecular immune pathogenesis and diagnosis of COVID-19",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "102",
"journal-title": "J. Pharm. Anal.",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "From SARS to COVID-19: Pathogens, receptor, pathogenesis and principles of the treatment",
"author": "Wang",
"first-page": "647",
"journal-title": "Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi",
"key": "ref_10",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acsptsci.1c00080",
"article-title": "Inhibition of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Replication by Hypertonic Saline Solution in Lung and Kidney Epithelial Cells",
"author": "Machado",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1514",
"journal-title": "ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci.",
"key": "ref_11",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jpclett.0c02602",
"article-title": "Molecular Dynamics Reveals Complex Compensatory Effects of Ionic Strength on the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Spike/Human Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 Interaction",
"author": "Rivera",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "10446",
"journal-title": "J. Phys. Chem. Lett.",
"key": "ref_12",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "ref_13",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization (2020). WHO R&D Blueprint Novel Coronavirus COVID-19 Therapeutic Trial Synopsis, World Health Organization."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.283.6302.1285",
"article-title": "Bronchial hyperreactivity in response to inhalation of ultrasonically nebulised solutions of distilled water and saline",
"author": "Schoeffei",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1285",
"journal-title": "Br. Med. J.",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "283",
"year": "1981"
},
{
"article-title": "Nebulised hypertonic saline for cystic fibrosis",
"author": "Wark",
"first-page": "CD001506",
"journal-title": "Cochrane Database Syst. Rev.",
"key": "ref_15",
"volume": "2018",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/ajrccm.164.10.2104024",
"article-title": "Airway response to inhaled hypertonic saline in patients with moderate to severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease",
"author": "Taube",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1810",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med.",
"key": "ref_16",
"volume": "164",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1034/j.1399-3003.2000.01522.x",
"article-title": "Safety of sputum induction in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease",
"author": "Lindqvist",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1116",
"journal-title": "Eur. Respir. J.",
"key": "ref_17",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"key": "ref_18",
"unstructured": "(2023, April 22). COVID-19 Rapid Guideline: Managing COVID-19—The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). 28.0 published on 29.03.2023. Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng191."
}
],
"reference-count": 18,
"references-count": 18,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2077-0383/12/18/6075"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Efficacy of BREATHOX® Device Inhalation on Acute Symptoms Associated with COVID-19 (BREATH Study): A Randomized Pilot Clinical Trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "12"
}