Frequency, type and severity of drug-related problems and pharmacist interventions in Paxlovid® prescribing: a descriptive analysis
et al., International Journal of Clinical Pharmacy, doi:10.1007/s11096-024-01852-5, Oct 2024 (preprint)
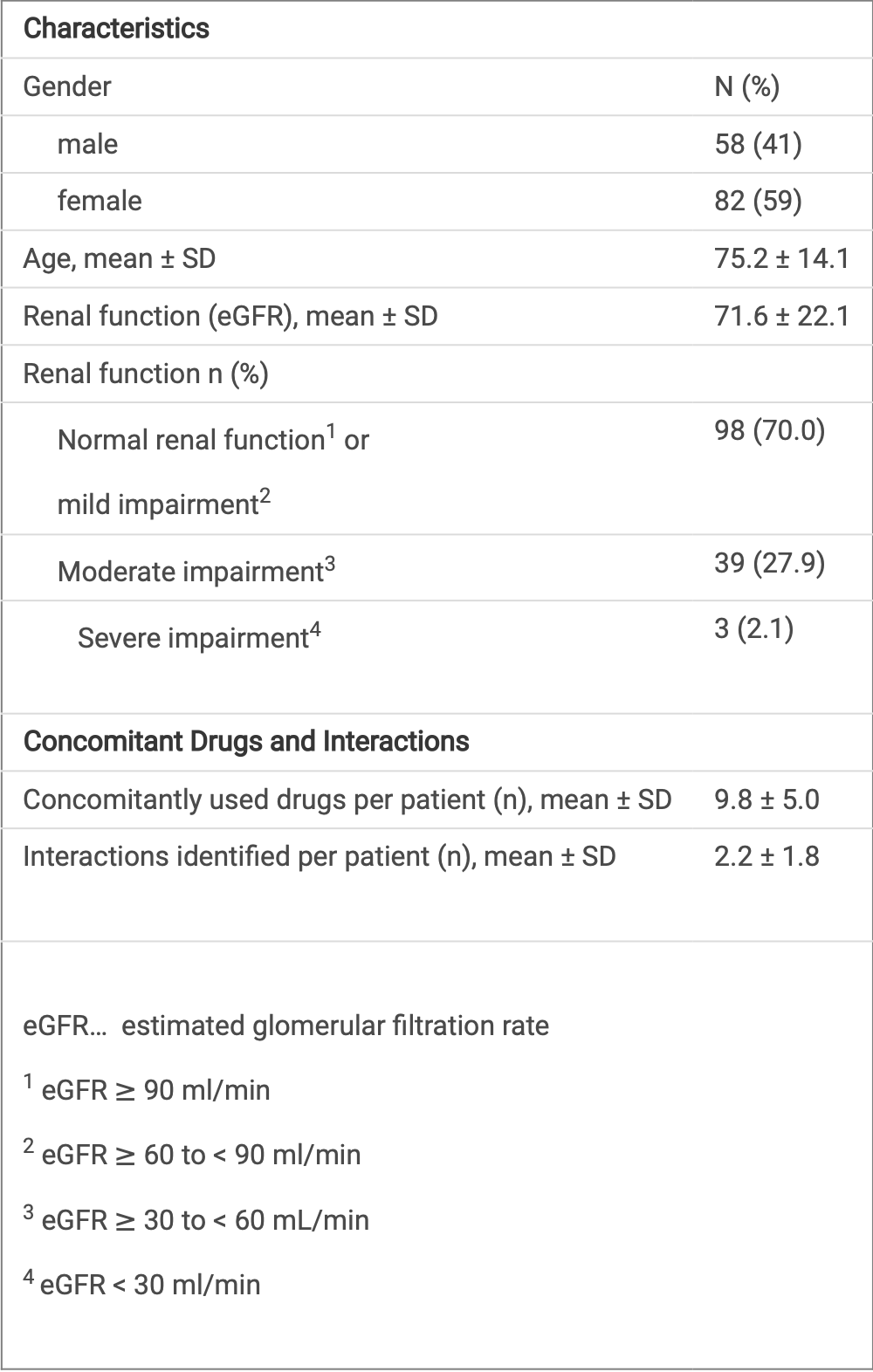
Retrospective 140 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in Austria showing that pharmacist review identified a high rate of drug-related problems (DRPs) with paxlovid prescribing, including drug-drug interactions (DDIs) and inappropriate dosing based on renal function. In 87% of cases, pharmacist interventions were required to prevent DRPs.
Resistance. Variants may be resistant to paxlovid1-8. Use may promote the emergence of variants that weaken host immunity and potentially contribute to long COVID9. Confounding by contraindication. Hoertel et al. find that over 50% of patients that died had a contraindication for the use of Paxlovid10. Retrospective studies that do not exclude contraindicated patients may significantly overestimate efficacy. Black box warning. The FDA notes that severe, life-threatening, and/or fatal adverse reactions due to drug interactions have been reported in patients treated with paxlovid11. Kidney and liver injury. Studies show significantly increased risk of acute kidney injury12 and liver injury13,14. Viral rebound. Studies show significantly increased risk of replication-competent viral rebound15-17.
1.
Zhou et al., Nirmatrelvir-resistant SARS-CoV-2 variants with high fitness in an infectious cell culture system, Science Advances, doi:10.1126/sciadv.add7197.
2.
Moghadasi et al., Rapid resistance profiling of SARS-CoV-2 protease inhibitors, npj Antimicrobials and Resistance, doi:10.1038/s44259-023-00009-0.
3.
Jochmans et al., The Substitutions L50F, E166A, and L167F in SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro Are Selected by a Protease Inhibitor In Vitro and Confer Resistance To Nirmatrelvir, mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.02815-22.
4.
Lopez et al., SARS-CoV-2 Resistance to Small Molecule Inhibitors, Current Clinical Microbiology Reports, doi:10.1007/s40588-024-00229-6.
5.
Zvornicanin et al., Molecular Mechanisms of Drug Resistance and Compensation in SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease: The Interplay Between E166 and L50, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2025.01.24.634813.
6.
Vukovikj et al., Impact of SARS-CoV-2 variant mutations on susceptibility to monoclonal antibodies and antiviral drugs: a non-systematic review, April 2022 to October 2024, Eurosurveillance, doi:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2025.30.10.2400252.
7.
Deschenes et al., Functional and structural characterization of treatment-emergent nirmatrelvir resistance mutations at low frequencies in the main protease (Mpro) reveals a unique evolutionary route for SARS-CoV-2 to gain resistance, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiaf294.
8.
Zhou (B) et al., SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor ensitrelvir: asymmetrical cross-resistance with nirmatrelvir and emerging resistance hotspots, Emerging Microbes & Infections, doi:10.1080/22221751.2025.2552716.
9.
Thomas et al., Nirmatrelvir-Resistant Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 Mpro Enhance Host Immune Evasion via Cleavage of NF-κB Essential Modulator, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2024.10.18.619137.
10.
Hoertel et al., Prevalence of Contraindications to Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir Among Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19 at Risk for Progression to Severe Disease, JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.42140.
11.
FDA, Fact sheet for healthcare providers: emergency use authorization for paxlovid, www.fda.gov/media/155050/download.
12.
Kamo et al., Association of Antiviral Drugs for the Treatment of COVID-19 With Acute Renal Failure, In Vivo, doi:10.21873/invivo.13637.
13.
Wang et al., Development and validation of a nomogram to assess the occurrence of liver dysfunction in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in the ICU, BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-025-10684-1.
14.
Siby et al., Temporal Trends in Serious Adverse Events Associated with Oral Antivirals During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights from the FAERS Database (2020–2023), Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf695.1825.
15.
Edelstein et al., SARS-CoV-2 virologic rebound with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir therapy, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.06.23.23288598.
Stoiber et al., 17 Oct 2024, retrospective, Austria, peer-reviewed, mean age 75.2, 5 authors, study period September 2022 - March 2023.
A descriptive analysis of drug related problems identified when prescribing the COVID-19 antiviral drug Paxlovid®
doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-4973191/v1
Background Paxlovid® is the only licensed oral COVID - 19 antiviral containing nirmatrelvir and ritonavir. Ritonavir is a potent inhibitor of cytochrome P450 enzymes resulting in clinically signi cant drug-drug interactions (DDIs).
Aim To describe the frequency, type, and severity of detected drug related problems (DRPs) with Paxlovid®
Method This study involved a retrospective, quantitative data analysis. All patients prescribed Paxlovid® in a public hospital in Vienna, were included. Data was collected from the patients' records and recorded on a customised and piloted data collection form. Any DRPs were also noted. The severity of DDIs was classi ed using an established checker tool.
Results 122 of 140 (87.1%) patients required interventions to prevent DRPs; 63.6% of cases required intervention by the pharmacist at dispensing. The most common DRPs were DDIs (57.1%). In 24.3% of cases both renal impairment and DDIs were noted. 313 DDIs were recorded in 114 patients; in 24 patients, the interactions recorded were severe. In 3 patients (2.1%), Paxlovid® was prescribed despite being contraindicated due to severe renal impairment requiring pharmacist intervention.
Conclusion This study demonstrated that numerous DRPs involving Paxlovid® were identi ed by the pharmacist following prescribing. Pharmacists' involvement in prescribing highly interacting drugs such as Paxlovid® is bene cial to enhance patient safety.
Impact on Practice Pharmacist screening for drug related problems at the point of dispensing is likely to increase patient safety and mitigate risk associated with high-risk drugs. The study con rms that a strong focus needs to be placed on reviewing the patients´ renal function and adjusting dosing accordingly both as part of the prescribing and screening processes.
Con ict of Interests The authors declare that they have no con ict of interest.
Characteristics
Supplementary Files This is a list of supplementary les associated with this preprint. Click to download. Appendices.docx
References
Doogue, Polasek, Drug Dosing in Renal Disease, The Clinical Biochemist Reviews
Hassan, Al-Ramahi, Aziz, Impact of a renal drug dosing service on dose adjustment in hospitalized patients with chronic kidney disease, The Annals of Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.1345/aph.1M187
Hull, Montaner, Ritonavir-boosted protease inhibitors in HIV therapy, Annals of Medicine, doi:10.3109/07853890.2011.572905
Igho-Osagie, Puenpatom, Williams, Prevalence of potential drug-drug interactions with ritonavir-containing COVID-19 therapy, J Manag Care Spec Pharm, doi:10.18553/jmcp.2023.22366
Kieck, Mahalick, Vo, Medication-Related Problems Identi ed and Addressed by Pharmacists Dispensing COVID-19 Antivirals at a Community Pharmacy, Pharmacy, doi:10.3390/pharmacy11030087
Kucukarslan, Peters, Mlynarek, Pharmacists on rounding teams reduce preventable adverse drug events in hospital general medicine units, Arch Intern Med, doi:10.1001/archinte.163.17.2014
Mahase, Covid-19: NICE plans to expand Paxlovid eligibility to 1.4 million more people, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.q59TablesTable1:Characteristicsofpatients
Mchugh, Interrater reliability: the kappa statistic, Biochemia Medica
Portman, Scolese, Facilitating oral COVID-19 therapy utilization through a pharmacy consult service, JAPhA, doi:10.1016/j.japh.2023.04.010
Roblek, Deticek, Leskovar, Clinical-pharmacist intervention reduces clinically relevant drug-drug interactions in patients with heart failure: A randomized, double-blind, controlled trial, International Journal of Cardiology, doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2015.10.206
Tanne, Covid-19: FDA authorises pharmacists to prescribe Paxlovid, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.o1695
Tasaka, Tanaka, Yasunaga, Potential drug-related problems detected by routine pharmaceutical interventions: safety and economic contributions made by hospital pharmacists in Japan, Journal of Pharmaceutical Health Care and Sciences, doi:10.1186/s40780-018-0125-z
Traynor, Québec authorizes pharmacists to prescribe Paxlovid, American Journal of Health-System Pharmacy, doi:10.1093/ajhp/zxac163
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11096-024-01852-5",
"ISSN": [
"2210-7703",
"2210-7711"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11096-024-01852-5",
"alternative-id": [
"1852"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "25 August 2024"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "2 December 2024"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "21 December 2024"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Conflicts of interest",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1,
"value": "The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stoiber",
"given": "Alina",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gray",
"given": "Gwen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sailer",
"given": "Gudrun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Huf",
"given": "Wolfgang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2659-6901",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Tonna",
"given": "Antonella",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "International Journal of Clinical Pharmacy",
"container-title-short": "Int J Clin Pharm",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2024-12-21T08:14:26Z",
"timestamp": 1734768866000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2024-12-21T09:06:55Z",
"timestamp": 1734772015000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2024-12-22T05:06:19Z",
"timestamp": 1734843979398,
"version": "3.32.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
21
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.springernature.com/gp/researchers/text-and-data-mining",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2024-12-21T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1734739200000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.springernature.com/gp/researchers/text-and-data-mining",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2024-12-21T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1734739200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s11096-024-01852-5.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11096-024-01852-5/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s11096-024-01852-5.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1007",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
21
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
21
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"key": "1852_CR1",
"unstructured": "Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). People with certain medical conditions and Covid-19 risk factors. CDC. 2024. http://www.cdc.gov/covid/risk-factors/?CDC_AAref_Val=https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/need-extra-precautions/people-with-medical-conditions.html. Accessed 23 Nov 2024."
},
{
"key": "1852_CR2",
"unstructured": "Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Types of Covid-19 treatment. CDC. 2024. http://www.cdc.gov/covid/treatment/?CDC_AAref_Val=https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/your-health/treatments-for-severe-illness.html Accessed 23 Nov 2024."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMcp2009575",
"author": "DA Berlin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2451",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "1852_CR3",
"unstructured": "Berlin DA, Gulick RM, Martinez FJ. Severe Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:2451–60. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMcp2009575.",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "Y Chao",
"first-page": "572",
"journal-title": "Hum Biol",
"key": "1852_CR4",
"unstructured": "Chao Y, Haiqiang L, Daoquan W, et al. A realworld Pharmacovigilance study of FDA adverse event reporting system (FAERS) events for paxlovid and molnupiravir. Hum Biol. 2024;94:572–80.",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"key": "1852_CR5",
"unstructured": "Electronic Medicines Compendium (EMC). Paxlovid 150 mg/100 mg film-coated tablets—summary of product characteristics (SmPC)-(emc). EMC. 2024. https://www.medicines.org.uk/emc/product/13145/smpc. Accessed 23 Nov 2024."
},
{
"key": "1852_CR6",
"unstructured": "Liverpool Interaction Group. Evaluating the drug-drug interaction risk of COVID-19 therapies (licensed or under clinical investigation). University of Liverpool. 2022. http://www.covid19-druginteractions.org/prescribing_resources/methods-metabolism. Accessed 23 Nov 2024."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3109/07853890.2011.572905",
"author": "MW Hull",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "375",
"journal-title": "Ann Med",
"key": "1852_CR7",
"unstructured": "Hull MW, Montaner JSG. Ritonavir-boosted protease inhibitors in HIV therapy. Ann Med. 2011;43:375–88. https://doi.org/10.3109/07853890.2011.572905.",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"key": "1852_CR8",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization (WHO). WHO model list of essential medicines—22nd list, 2021. WHO. 2021. https://www.who.int/publications-detail-redirect/WHO-MHP-HPS-EML-2021.02. Accessed 23 Nov 2024."
},
{
"key": "1852_CR9",
"unstructured": "National Health Service (NHS). Chronic kidney disease—Diagnosis—NHS. NHS. 2019. https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/kidney-disease/diagnosis/. Accessed 14 March 2023."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.q59",
"author": "E Mahase",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "59",
"journal-title": "Br Med J",
"key": "1852_CR10",
"unstructured": "Mahase E. Covid-19: NICE plans to expand Paxlovid eligibility to 1 million more people. Br Med J. 2024;384:59. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.q59.",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.o1695",
"author": "JH Tanne",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1659",
"journal-title": "Br Med J",
"key": "1852_CR11",
"unstructured": "Tanne JH. Covid-19: FDA authorises pharmacists to prescribe Paxlovid. Br Med J. 2022;378:1659. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.o1695.",
"volume": "378",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajhp/zxac163",
"author": "K Traynor",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1126",
"journal-title": "Am J Health Syst Pharm",
"key": "1852_CR12",
"unstructured": "Traynor K. Québec authorizes pharmacists to prescribe Paxlovid. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2022;79:1126–7. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajhp/zxac163.",
"volume": "79",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "1852_CR13",
"unstructured": "Bundesministerium für Finanzen. RIS [Rechtsinformationssystem des Bundes]—Rezeptpflichtgesetz—Bundesrecht konsolidiert, Fassung vom 22.03.2023. Bundesministerium für Finanzen. 2023. [Federal Ministry of Finance. RIS (Federal Information System for Laws)—Compulsory Prescription Act—Federal law consolidated, version dated March 22, 2023. Federal Ministry of Finance. 2023.] https://www.ris.bka.gv.at/GeltendeFassung.wxe?Abfrage=Bundesnormen&Gesetzesnummer=10010351. Accessed 22 Mar 2023."
},
{
"DOI": "10.11613/BM.2012.031",
"author": "M McHugh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "276",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Biochem Med (Zagreb)",
"key": "1852_CR14",
"unstructured": "McHugh M. Interrater reliability: the kappa statistic. Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2012;22(3):276–82.",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"key": "1852_CR15",
"unstructured": "The University of Liverpool. Liverpool COVID-19 drug interactions. The University of Liverpool. 2023. https://www.covid19-druginteractions.org/checker#. Accessed 23 Nov 2024."
},
{
"key": "1852_CR16",
"unstructured": "Liverpool Interaction Group. Interactions with outpatient medicines & Nirmatrelvir/ritonavir (NMV/r). University of Liverpool. 2023. www.covid19-druginteractions.org/prescribing_resources/paxlovid-outpatient-medicines. Accessed 23 Nov 2024."
},
{
"DOI": "10.18553/jmcp.2023.22366",
"author": "E Igho-Osagie",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "509",
"journal-title": "J Manag Care Spec Pharm",
"key": "1852_CR17",
"unstructured": "Igho-Osagie E, Puenpatom A, Williams MG, et al. Prevalence of potential drug-drug interactions with ritonavir-containing COVID-19 therapy. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2023;29:509–28. https://doi.org/10.18553/jmcp.2023.22366.",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2221857120",
"author": "Y Kim",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e2221857120",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci",
"key": "1852_CR18",
"unstructured": "Kim Y, Ryu JY, Kim HU, et al. Computational prediction of interactions between Paxlovid and prescription drugs. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2023;120:e2221857120. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2221857120.",
"volume": "120",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cpt.2646",
"author": "C Marzolini",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1191",
"journal-title": "Clin Pharmacol Ther",
"key": "1852_CR19",
"unstructured": "Marzolini C, Kuritzkes DR, Marra F, et al. Recommendations for the management of drug-drug interactions between the COVID-19 antiviral Nirmatrelvir/ritonavir (Paxlovid) and comedications. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2022;112:1191–200. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpt.2646.",
"volume": "112",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/phar.2860",
"author": "X Xiao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1251",
"journal-title": "Pharmacotherapy",
"key": "1852_CR20",
"unstructured": "Xiao X, Mehta HB, Curran J, et al. Potential drug-drug interactions among US adults treated with nirmatrelvir/ritonavir: a cross-sectional study of the National Covid Cohort Collaborative (N3C). Pharmacotherapy. 2023;43:1251–61. https://doi.org/10.1002/phar.2860.",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/pharmacy11030087",
"author": "D Kieck",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "87",
"journal-title": "Pharmacy (Basel)",
"key": "1852_CR21",
"unstructured": "Kieck D, Mahalick L, Vo TT. Medication-related problems identified and addressed by pharmacists dispensing COVID-19 antivirals at a community pharmacy. Pharmacy (Basel). 2023;11:87. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy11030087.",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.japh.2023.04.010",
"author": "DB Portman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1237",
"journal-title": "J Am Pharm Assoc",
"key": "1852_CR22",
"unstructured": "Portman DB, Scolese CJ. Facilitating oral COVID-19 therapy utilization through a pharmacy consult service. J Am Pharm Assoc. 2023;63:1237–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.japh.2023.04.010.",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1345/aph.1M187",
"author": "Y Hassan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1598",
"journal-title": "Ann Pharmacother",
"key": "1852_CR23",
"unstructured": "Hassan Y, Al-Ramahi RJ, Aziz NA, et al. Impact of a renal drug dosing service on dose adjustment in hospitalized patients with chronic kidney disease. Ann Pharmacother. 2009;43:1598–605. https://doi.org/10.1345/aph.1M187.",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"author": "MP Doogue",
"first-page": "69",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Clin Biochem Rev",
"key": "1852_CR24",
"unstructured": "Doogue MP, Polasek TM. Drug dosing in renal disease. Clin Biochem Rev. 2011;32(2):69–73.",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijcard.2015.10.206",
"author": "T Roblek",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "647",
"journal-title": "Int J Cardiol",
"key": "1852_CR25",
"unstructured": "Roblek T, Deticek A, Leskovar B, et al. Clinical-pharmacist intervention reduces clinically relevant drug–drug interactions in patients with heart failure: a randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. Int J Cardiol. 2016;203:647–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2015.10.206.",
"volume": "203",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40780-018-0125-z",
"author": "Y Tasaka",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "33",
"journal-title": "J Pharm Health Care Sci",
"key": "1852_CR26",
"unstructured": "Tasaka Y, Tanaka A, Yasunaga A, et al. Potential drug-related problems detected by routine pharmaceutical interventions: safety and economic contributions made by hospital pharmacists in Japan. J Pharm Health Care Sci. 2018;4:33. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40780-018-0125-z.",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/jrpp.JRPP_18_88",
"author": "M Shafiekhani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "143",
"journal-title": "J Res Pharm Pract",
"key": "1852_CR27",
"unstructured": "Shafiekhani M, Moosavi N, Firouzabadi D, et al. Impact of clinical pharmacist’s interventions on potential drug-drug interactions in the cardiac care units of two university hospitals in Shiraz, South of Iran. J Res Pharm Pract. 2019;8:143–8. https://doi.org/10.4103/jrpp.JRPP_18_88.",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5005/jp-journals-10071-23919",
"author": "M Aghili",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1226",
"journal-title": "Indian J Crit Care Med",
"key": "1852_CR28",
"unstructured": "Aghili M, Kasturirangan MN. Management of drug-drug interactions among critically ill patients with chronic kidney disease: impact of clinical pharmacist’s interventions. Indian J Crit Care Med. 2021;25:1226–31. https://doi.org/10.5005/jp-journals-10071-23919.",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11096-015-0199-8",
"author": "SH Chau",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "46",
"journal-title": "Int J Clin Pharm",
"key": "1852_CR29",
"unstructured": "Chau SH, Jansen AP, van de Ven PM, et al. Clinical medication reviews in elderly patients with polypharmacy: a cross-sectional study on drug-related problems in the Netherlands. Int J Clin Pharm. 2016;38:46–53. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11096-015-0199-8.",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/hsr2.1971",
"author": "JC Kanninen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e1971",
"journal-title": "Health Sci Rep",
"key": "1852_CR30",
"unstructured": "Kanninen JC, Toivo T, Airaksinen M, et al. Collaborative medication reviews in community pharmacies-drug-related problems and the process of communicating them with physicians: a retrospective validation study. Health Sci Rep. 2024;7:e1971. https://doi.org/10.1002/hsr2.1971.",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.sapharm.2016.10.016",
"author": "HM Seidling",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1127",
"journal-title": "Res Soc Adm Pharm",
"key": "1852_CR31",
"unstructured": "Seidling HM, Send AFJ, Bittmann J, et al. Medication review in German community pharmacies—Post-hoc analysis of documented drug-related problems and subsequent interventions in the ATHINA-project. Res Soc Adm Pharm. 2017;13:1127–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sapharm.2016.10.016.",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2020.01176",
"author": "E Schindler",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1176",
"journal-title": "Front Pharmacol",
"key": "1852_CR32",
"unstructured": "Schindler E, Hohmann C, Culmsee C. Medication review by community pharmacists for type 2 diabetes patients in routine care: results of the DIATHEM-study. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:1176. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.01176.",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.sapharm.2021.07.017",
"author": "DE Michel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2944",
"journal-title": "Res Social Adm Pharm",
"key": "1852_CR33",
"unstructured": "Michel DE, Tonna AP, Dartsh DC, Weidmann AE. Experiences of key stakeholders with the implementation of medication reviews in community pharmacies: a systematic review using the consolidated framework for implementation research (CFIR). Res Social Adm Pharm. 2022;18:2944–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sapharm.2021.07.017.",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 33,
"references-count": 33,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s11096-024-01852-5"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Frequency, type and severity of drug-related problems and pharmacist interventions in Paxlovid® prescribing: a descriptive analysis",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy"
}