Impact of vitamin D on the course of COVID-19 during pregnancy: A case control study
et al., The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964, Aug 2021
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 159 COVID-19+ pregnant women in Turkey and 332 healthy pregnant controls, showing significantly lower vitamin D levels in COVID-19+ patients. 23% of COVID-19 patients where on vitamin D supplementation, while none of the 7 severe cases were on supplementation.
This is the 47th of 135 COVID-19 controlled studies for vitamin D, which collectively show efficacy with p<0.0000000001.
40 studies are RCTs, which show efficacy with p=0.0000001.
|
risk of severe case, 90.0% lower, RR 0.10, p = 0.35, treatment 0 of 36 (0.0%), control 7 of 123 (5.7%), NNT 18, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), supplementation.
|
|
risk of moderate/severe case, 18.8% higher, RR 1.19, p = 0.64, treatment 8 of 36 (22.2%), control 23 of 123 (18.7%), supplementation.
|
|
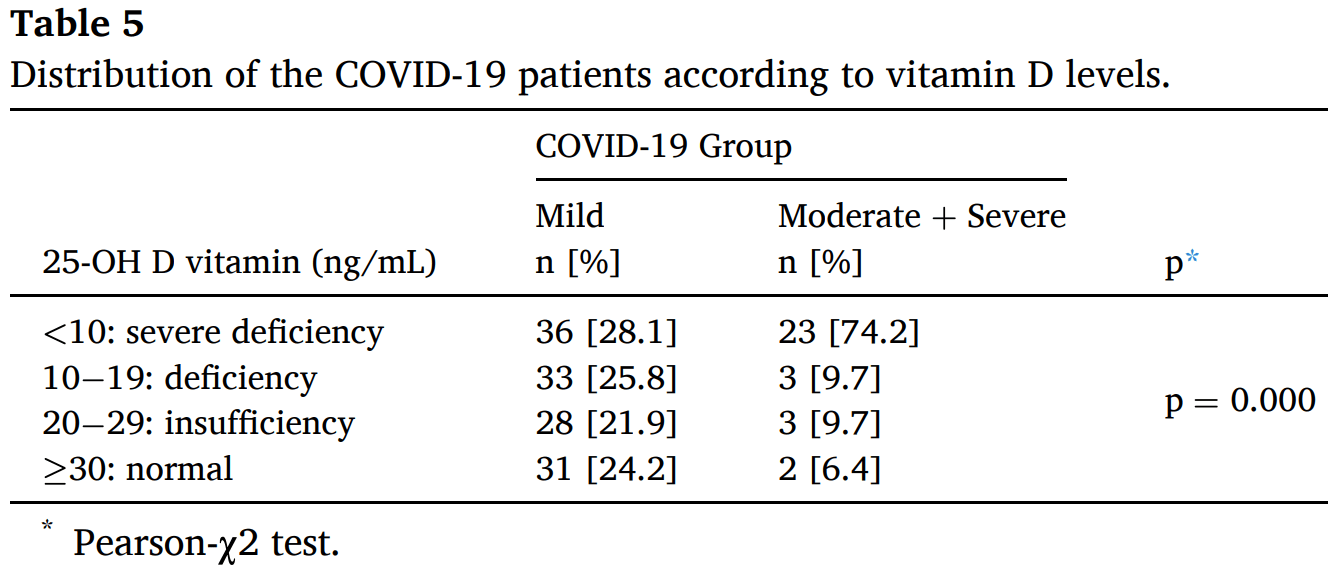
risk of moderate/severe case, 79.5% lower, RR 0.21, p < 0.001, high D levels (≥10ng/mL) 8 of 100 (8.0%), low D levels (<10ng/mL) 23 of 59 (39.0%), NNT 3.2, outcome based on serum levels.
|
|
risk of case, 59.9% lower, RR 0.40, p < 0.001, high D levels (≥10ng/mL) 100 of 397 (25.2%), low D levels (<10ng/mL) 59 of 94 (62.8%), NNT 2.7, outcome based on serum levels.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Sinaci et al., 11 Aug 2021, retrospective, Turkey, peer-reviewed, 10 authors, dosage not specified.
Impact of vitamin D on the course of COVID-19 during pregnancy: A case control study
The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964
We aimed to evaluate the vitamin D status of pregnant women with COVID-19, and the association between vitamin D level and severity of COVID-19. Methods: In this case control study, 159 women with a single pregnancy and tested positive for SARS-CoV-2, and randomly selected 332 healthy pregnant women with similar gestational ages were included. COVID-19 patients were classified as mild, moderate, and severe. Vitamin D deficiency was defined as 25-hydroxycholecalciferol <20 ng/mL (50 nmol/L), and 25-OH D vitamin <10 ng/mL was defined as severe vitamin D deficiency, also 25-OH D vitamin level between 20− 29 ng/mL (525− 725 nmol/L) was defined as vitamin D insufficiency. Results: Vitamin D levels of the pregnant women in the COVID-19 group (12.46) were lower than the control group (18.76). 25-OH D vitamin levels of those in the mild COVID-19 category (13.69) were significantly higher than those in the moderate/severe category (9.06). In terms of taking vitamin D supplementation, there was no statistically significant difference between the groups. However, it was observed that all of those who had severe COVID-19 were the patients who did not take vitamin D supplementation.
Conclusion: The vitamin D levels are low in pregnant women with COVID-19. Also, there is a significant difference regarding to vitamin D level and COVID-19 severity in pregnant women. Maintenance of adequate vitamin D level can be useful as an approach for the prevention of an aggressive course of the inflammation induced by this novel coronavirus in pregnant women.
Author contributions SS: conceptualization, methodology, data collection, investigation, visualization and writing the article; DFO: reviewing and editing; FDYY, DUH, GBU, SGA: data collection; AT, SOE: formal analysis, visualization; OMT: supervision; DS: conceptualization, methodology, reviewing, and editing, project administration.
Ethics approval This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Ankara City Hospital on December 23, 2020, with the number E1-20-1192.
Consent to participate Written informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors report no declarations of interest.
References
Abdelazim, Abufaza, Al-Munaifi, COVID-19 positive woman presented with preterm labor: case report, Gynecol. Obstet. Reprod. Med
Ali, Role of vitamin D in preventing of COVID-19 infection, progression and severity, J. Infect. Public Health, doi:10.1016/j.jiph.2020.06.021
Baeke, Takiishi, Korf, Vitamin D: modulator of the immune system, Curr. Opin. Pharmacol
Bassatne, Basbous, Chakhtoura, Zein, Rahme et al., The link between COVID-19 and VItamin D (VIVID): a systematic review and metaanalysis, Metabolism, doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2021.154753
Bokharee, Khan, Wasim, Mallhi, Alotaibi et al., Daily versus stat vitamin D supplementation during pregnancy; a prospective cohort study, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0231590
Brannon, Vitamin D and adverse pregnancy outcomes: beyond bone health and growth, Proc. Nutr. Soc
Calder, Carr, Gombart, Eggersdorfer, Optimal nutritional status for a well-functioning immune system is an important factor to protect against viral infections, Nutrients
Chang, Ding, Freund, Johnson, Schwarz et al., Prior diagnoses and medications as risk factors for COVID-19 in a Los Angeles Health System, doi:10.1101/2020.07.03.20145581
Chen, Wu, Guo, Clinical and immunological features of severe and moderate coronavirus disease 2019, J. Clin. Invest
Cheng, Can early and high intravenous dose of vitamin C prevent and treat coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)?, Med. Drug Discov
D'avolio, Avataneo, Manca, 25-Hydroxyvitamin D concentrations are lower in patients with positive PCR for SARS-CoV-2, Nutrients
Dey, Singh, Tiwari, Nair, Arora et al., Pregnancy outcome in first 50 SARS-Cov-2 positive patients at our center, Gynecol. Obstet. Reprod. Med
Dubey, Reddy, Manuel, Dwivedi, Maternal and neonatal characteristics and outcomes among COVID-19 infected women: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis, Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol
Ergür, Berberoglu, Atasay, Vitamin D deficiency in Turkish mothers and their neonates and in women of reproductive age, J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol, doi:10.4274/jcrpe.v1i6.266
Fisher, Rahimzadeh, Brierley, Gration, Doree et al., The role of vitamin D in increasing circulating T regulatory cell numbers and modulating T regulatory cell phenotypes in patients with inflammatory disease or in healthy volunteers: a systematic review, PLoS One
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Evidence that vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of influenza and COVID-19 infections and deaths, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12040988
Hastie, Mackay, Ho, Vitamin D concentrations and COVID-19 infection in UK Biobank, Diabetes Metab. Syndr
Hernández, Nan, Fernandez-Ayala, García-Unzueta, Hernández-Hernández et al., Vitamin D status in hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab, doi:10.1210/clinem/dgaa733
Holick, Binkley, Bischoff-Ferrari, Gordon, Hanley et al., Endocrine Society, Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab, doi:10.1210/jc.2011-0385
Huang, Zhang, Liu, Identification of amitriptyline HCl, flavin adenine dinucleotide, azacitidine and calcitriol as repurposing drugs for influenza A H5N1 virus-induced lung injury, PLoS Pathog
Ilie, Stefanescu, Smith, The role of vitamin D in the prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 infection and mortality, Aging Clin. Exp. Res, doi:10.1007/s40520-020-01570-8
Jakovac, COVID-19 and vitamin D-is there a link and an opportunity for intervention?, Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab
Javaid, Crozier, Harvey, Maternal vitamin D status during pregnancy and childhood bone mass at age 9 years: a longitudinal study, Lancet
Jude, Ling, Allcock, Yeap, Pappachan, Vitamin D deficiency is associated with higher hospitalisation risk from COVID-19: a retrospective casecontrol study, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab, doi:10.1210/clinem/dgab439
Marik, Kory, Varon, Does vitamin D status impact mortality from SARS-CoV-2 infection?, Med. Drug Discov, doi:10.1016/j.medidd.2020.100041
Martineau, Jolliffe, Hooper, Greenberg, Aloia et al., Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.i6583
Martineau, Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data, BMJ
Mccartney, Byrne, Optimisation of vitamin d status for enhanced immunoprotection against Covid-19, Ir. Med. J
Mehta, Mcauley, Brown, Sanchez, Tattersall et al., HLH Across Speciality Collaboration, UK, COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression, Lancet
Mena-Bravo, Calderón-Santiago, Lope, Kogevinas, Pollán et al., Vitamin D3 levels in women and factors contributing to explain metabolic variations, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105884
Merzon, Tworowski, Gorohovski, Low plasma 25(OH) vitamin D level is associated with increased risk of COVID-19 infection: an Israeli populationbased study, FEBS J, doi:10.1111/febs.15495
Peterson, Heffernan, Serum tumor necrosis factor-alpha concentrations are negatively correlated with serum 25(OH)D concentrations in healthy women, J. Inflamm. (Lond.)
Petrelli, Luciani, Perego, Dognini, Colombelli et al., Therapeutic and prognostic role of vitamin D for COVID-19 infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 43 observational studies, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105883
Prietl, Treiber, Piber, Amrein, Vitamin D and immune function, Nutrients
Sahin, Tanacan, Erol, Anuk, Yetiskin et al., Updated experience of a tertiary pandemic center on 533 pregnant women with COVID-19 infection: a prospective cohort study from Turkey, Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet, doi:10.1002/ijgo.13460
Shin, Choi, Longtine, Nelson, Vitamin D effects on pregnancy and the placenta, Placenta
Slominski, Stefan, Athar, Holick, Jetten et al., COVID-19 and Vitamin D: a lesson from the skin, Exp. Dermatol, doi:10.1111/exd.14170
Teymoori-Rad, Shokri, Salimi, Marashi, The interplay between vitamin D and viral infections, Rev. Med. Virol
Vuichard Gysin, Dao, Gysin, Lytvyn, Loeb, Effect of vitamin D3 supplementation on respiratory tract infections in healthy individuals: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, PLoS One
Wang, Hu, Hu, Zhu, Liu et al., Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.1585
Wei, Vitamin D and pregnancy outcomes, Curr. Opin. Obstet. Gynecol, doi:10.1097/GCO.0000000000000117
Wu, Mcgoogan, Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese center for disease control and prevention, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.2648
Ye, Wang, Mao, The pathogenesis and treatment of the 'Cytokine Storm' in COVID-19, J. Infect
Zhu, Zhang, Wang, A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019, N. Engl. J. Med
Öcal, Aycan, Dagdeviren, Kanbur, Küçüközkan et al., Vitamin D deficiency in adolescent pregnancy and obstetric outcomes, Taiwan J. Obstet. Gynecol, doi:10.1016/j.tjog.2019.09.008
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964",
"ISSN": [
"0960-0760"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964",
"alternative-id": [
"S0960076021001576"
],
"article-number": "105964",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Impact of vitamin D on the course of COVID-19 during pregnancy: A case control study"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3118-4036",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Sinaci",
"given": "Selcan",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4727-7982",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ocal",
"given": "Doga Fatma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1726-3256",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Yucel Yetiskin",
"given": "Didem Fatma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1866-7295",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Uyan Hendem",
"given": "Derya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4405-2876",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Buyuk",
"given": "Gul Nihal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5770-7555",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Goncu Ayhan",
"given": "Sule",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8209-8248",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Tanacan",
"given": "Atakan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6132-5779",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ozgu-Erdinc",
"given": "A. Seval",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8167-3837",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Moraloglu Tekin",
"given": "Ozlem",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8567-9048",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Sahin",
"given": "Dilek",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology",
"container-title-short": "The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2021-08-11T18:15:34Z",
"timestamp": 1628705734000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-13T01:34:39Z",
"timestamp": 1678671279000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2024-02-22T14:04:35Z",
"timestamp": 1708610675962
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 22,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-10-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1633046400000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-017",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-10-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1633046400000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-037",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-10-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1633046400000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-012",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-10-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1633046400000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-029",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-10-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1633046400000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-004",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-10-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1633046400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0960076021001576?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0960076021001576?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "105964",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001017",
"article-title": "A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019",
"author": "Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "727",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964_bib0005",
"volume": "328",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964_bib0010",
"unstructured": "WHO Director-General’s opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19. World Health Organization (WHO) (Press release). 11 March 2020."
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964_bib0015",
"unstructured": "WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard Data last updated: 2020/12/31, 3:41pm CEST. https://covid19.who.int/WHOCOVID-19-global-data.csv. (Accessed 31 December 2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.2648",
"article-title": "Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese center for disease control and prevention",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1239",
"issue": "13",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964_bib0020",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Pregnancy outcome in first 50 SARS-Cov-2 positive patients at our center",
"author": "Dey",
"first-page": "11",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Gynecol. Obstet. Reprod. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964_bib0025",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejogrb.2020.07.034",
"article-title": "Maternal and neonatal characteristics and outcomes among COVID-19 infected women: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Dubey",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "490",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964_bib0030",
"volume": "252",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Updated experience of a tertiary pandemic center on 533 pregnant women with COVID-19 infection: a prospective cohort study from Turkey",
"author": "Sahin",
"issue": "November (1)",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964_bib0035",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "COVID-19 positive woman presented with preterm labor: case report",
"author": "Abdelazim",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Gynecol. Obstet. Reprod. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964_bib0040",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(06)67922-1",
"article-title": "Maternal vitamin D status during pregnancy and childhood bone mass at age 9 years: a longitudinal study",
"author": "Javaid",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "36",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964_bib0045",
"volume": "367",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4274/jcrpe.v1i6.266",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency in Turkish mothers and their neonates and in women of reproductive age",
"author": "Ergür",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "266",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964_bib0050",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tjog.2019.09.008",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency in adolescent pregnancy and obstetric outcomes",
"author": "Öcal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "778",
"issue": "November (6)",
"journal-title": "Taiwan J. Obstet. Gynecol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964_bib0055",
"volume": "58",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0029665111003399",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and adverse pregnancy outcomes: beyond bone health and growth",
"author": "Brannon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "205",
"journal-title": "Proc. Nutr. Soc.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964_bib0060",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.placenta.2010.08.015",
"article-title": "Vitamin D effects on pregnancy and the placenta",
"author": "Shin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1027",
"journal-title": "Placenta",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964_bib0065",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/GCO.0000000000000117",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and pregnancy outcomes",
"author": "Wei",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "438",
"issue": "December (6)",
"journal-title": "Curr. Opin. Obstet. Gynecol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964_bib0070",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"article-title": "The link between COVID-19 and VItamin D (VIVID): a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Bassatne",
"issue": "June",
"journal-title": "Metabolism",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964_bib0075",
"volume": "119",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.i6583",
"article-title": "Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data",
"author": "Martineau",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "i6583",
"issue": "February (15)",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964_bib0080",
"volume": "356",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"article-title": "Role of vitamin D in preventing of COVID-19 infection, progression and severity",
"author": "Ali",
"issue": "June",
"journal-title": "J. Infect. Public Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964_bib0085",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Optimisation of vitamin d status for enhanced immunoprotection against Covid-19",
"author": "McCartney",
"first-page": "58",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Ir. Med. J.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964_bib0090",
"volume": "113",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/febs.15495",
"article-title": "Low plasma 25(OH) vitamin D level is associated with increased risk of COVID-19 infection: an Israeli population-based study",
"author": "Merzon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3693",
"issue": "17",
"journal-title": "FEBS J",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964_bib0095",
"volume": "287",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Pasaniuc B. Prior diagnoses and medications as risk factors for COVID-19 in a Los Angeles Health System",
"author": "Chang",
"issue": "July (4)",
"journal-title": "medRxiv [Preprint]",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964_bib0100",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105883",
"article-title": "Therapeutic and prognostic role of vitamin D for COVID-19 infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 43 observational studies",
"author": "Petrelli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "105883",
"issue": "March (26)",
"journal-title": "J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964_bib0105",
"volume": "211",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency is associated with higher hospitalisation risk from COVID-19: a retrospective case-control study",
"author": "Jude",
"issue": "June (17)",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964_bib0110",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/clinem/dgaa733",
"article-title": "Vitamin D status in hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Hernández",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e1343",
"issue": "March (3)",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964_bib0115",
"volume": "106",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12040988",
"article-title": "Evidence that vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of influenza and COVID-19 infections and deaths",
"author": "Grant",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "988",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964_bib0120",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "COVID-19 and Vitamin D: a lesson from the skin",
"author": "Slominski",
"issue": "August",
"journal-title": "Exp. Dermatol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964_bib0125",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.2032",
"article-title": "The interplay between vitamin D and viral infections",
"author": "Teymoori‐Rad",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e2032",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Rev. Med. Virol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964_bib0130",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1008341",
"article-title": "Identification of amitriptyline HCl, flavin adenine dinucleotide, azacitidine and calcitriol as repurposing drugs for influenza A H5N1 virus-induced lung injury",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "PLoS Pathog.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964_bib0135",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.medidd.2020.100028",
"article-title": "Can early and high intravenous dose of vitamin C prevent and treat coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)?",
"author": "Cheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Med. Drug Discov.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964_bib0140",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12051359",
"article-title": "25-Hydroxyvitamin D concentrations are lower in patients with positive PCR for SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "D’Avolio",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964_bib0145",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.050",
"article-title": "Vitamin D concentrations and COVID-19 infection in UK Biobank",
"author": "Hastie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "561",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab. Syndr.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964_bib0150",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40520-020-01570-8",
"article-title": "The role of vitamin D in the prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 infection and mortality",
"author": "Ilie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1195",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Aging Clin. Exp. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964_bib0155",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajpendo.00138.2020",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and vitamin D-is there a link and an opportunity for intervention?",
"author": "Jakovac",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "E589",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964_bib0160",
"volume": "318",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.medidd.2020.100041",
"article-title": "Does vitamin D status impact mortality from SARS-CoV-2 infection?",
"author": "Marik",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100041",
"journal-title": "Med. Drug Discov.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964_bib0165",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964_bib0170",
"series-title": "Chinese Management Guideline for COVID-19 (Version 6.0)",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/jc.2011-0385",
"article-title": "Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline",
"author": "Holick",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1911",
"issue": "July (7)",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964_bib0175",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.1585",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1061",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964_bib0180",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2020.03.037",
"article-title": "The pathogenesis and treatment of the ‘Cytokine Storm’ in COVID-19",
"author": "Ye",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "607",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "J. Infect.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964_bib0185",
"volume": "80",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0",
"article-title": "COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression",
"author": "Mehta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1033",
"issue": "10229",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964_bib0190",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI137244",
"article-title": "Clinical and immunological features of severe and moderate coronavirus disease 2019",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2620",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Invest.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964_bib0195",
"volume": "130",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "The role of vitamin D in increasing circulating T regulatory cell numbers and modulating T regulatory cell phenotypes in patients with inflammatory disease or in healthy volunteers: a systematic review",
"author": "Fisher",
"issue": "September (9)",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964_bib0200",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.i6583",
"article-title": "Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data",
"author": "Martineau",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6583",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964_bib0205",
"volume": "356",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu5072502",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and immune function",
"author": "Prietl",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2502",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964_bib0210",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.coph.2010.04.001",
"article-title": "Vitamin D: modulator of the immune system",
"author": "Baeke",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "482",
"journal-title": "Curr. Opin. Pharmacol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964_bib0215",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1476-9255-5-10",
"article-title": "Serum tumor necrosis factor-alpha concentrations are negatively correlated with serum 25(OH)D concentrations in healthy women",
"author": "Peterson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "10",
"journal-title": "J. Inflamm. (Lond.)",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964_bib0220",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0162996",
"article-title": "Effect of vitamin D3 supplementation on respiratory tract infections in healthy individuals: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials",
"author": "Vuichard Gysin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964_bib0225",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"article-title": "Daily versus stat vitamin D supplementation during pregnancy; a prospective cohort study",
"author": "Bokharee",
"issue": "April (4)",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964_bib0230",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12041181",
"article-title": "Optimal nutritional status for a well-functioning immune system is an important factor to protect against viral infections",
"author": "Calder",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1181",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964_bib0235",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105884",
"article-title": "Vitamin D3 levels in women and factors contributing to explain metabolic variations",
"author": "Mena-Bravo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "105884",
"issue": "March (26)",
"journal-title": "J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964_bib0240",
"volume": "211",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 48,
"references-count": 48,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0960076021001576"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Cell Biology",
"Clinical Biochemistry",
"Endocrinology",
"Molecular Biology",
"Molecular Medicine",
"Biochemistry",
"Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Impact of vitamin D on the course of COVID-19 during pregnancy: A case control study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "213"
}
