Serum Vitamin D Concentrations and Covid-19 In Pregnant Women, Does Vitamin D Supplementation Impact Results? A Comprehensive Study
et al., Cukurova Anestezi ve Cerrahi Bilimler Dergisi, doi:10.36516/jocass.1185181, Dec 2022
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
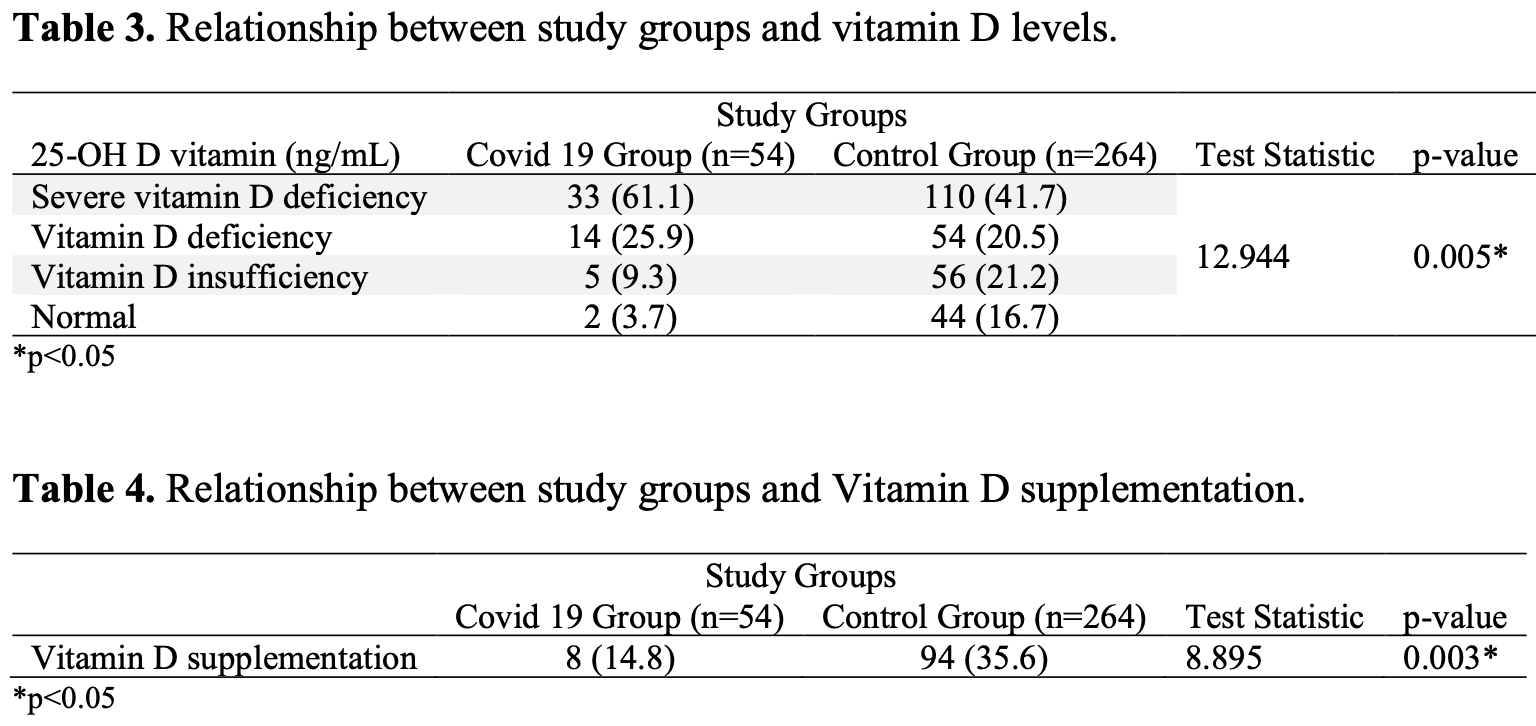
Retrospective 318 pregnant women, 54 COVID+ and 264 healthy controls, showing lower risk of COVID-19 with vitamin D supplementation, and with higher vitamin D levels.
This is the 109th of 135 COVID-19 controlled studies for vitamin D, which collectively show efficacy with p<0.0000000001.
40 studies are RCTs, which show efficacy with p=0.0000001.
|
risk of case, 68.5% lower, OR 0.31, p = 0.004, treatment 8 of 54 (14.8%) cases,
94 of 264 (35.6%) controls, NNT 7.4, case control OR.
|
|
risk of case, 75.6% lower, OR 0.24, p < 0.001, high D levels (≥20ng/mL) 7 of 54 (13.0%) cases,
100 of 264 (37.9%) controls, NNT 6.4, case control OR, outcome based on serum levels.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Şengül et al., 31 Dec 2022, retrospective, Turkey, peer-reviewed, 4 authors, study period March 2020 - December 2021, dosage not specified.
Contact: dr.mustafasengul@gmail.com.
Serum Vitamin D Concentrations and Covid-19 In Pregnant Women, Does Vitamin D Supplementation Impact Results? A Comprehensive Study
Cukurova Anestezi ve Cerrahi Bilimler Dergisi, doi:10.36516/jocass.1185181
Aim: Low vitamin D levels were related to an increased risk of upper respiratory tract infection and pneumonia. Vitamin D might therefore protect against symptoms of the Covid 19. The present study aims to evaluate the relationship between the acquisition and course of Covid 19 and serum vitamin D levels and investigate the prophylactic efficacy of vitamin D supplementation in pregnant women. Methods: This case-control study was conducted on 318 pregnant women admitted to our tertiary clinic to give birth between March 2020 and December 2021. All cases were tested for Covid 19 via nasopharyngeal swab. Fifty-four patients with positive PCR for SARS-CoV-2 (Group 1) were matched with 264 consecutive healthy controls (Group 2). 25 OH D Vitamin levels were measured and compared between the two groups, along with the frequency of vitamin D supplementation. Results: Group 1 showed significantly low mean 25 OH D levels, compared to Group 2 (10,22 ± 7,10 (3-37) ng/ml vs. 16,63 ± 10,80 (3,40-48,90) ng/ml, p = 0,000). Sixteen point seven % of controls and 3,7% of cases had normal Vitamin D levels (>30 ng/mL); the difference was also statistically significant (p=0,005). The frequency of vitamin D supplementation was also detected higher in controls than those with positive SARS-CoV-2 (35,6% vs. 14,8%, p=0,003). Conclusions: Sustaining adequate levels of Vitamin D may positively impact protection against Covid 19 during pregnancy. In this context, Vitamin D supplementation should be considered for the pregnant population, particularly in settings where profound vitamin D deficiency is common.
Author contributions All authors read and approved the final manuscript. M. Sengül: Project development, Data Collection, data analyzing Manuscript writing H. Sen Selim: Data collection, data analyzing, manuscript writing S. Sen: Data analyzing, manuscript writing H.Erbak Yılmaz: Data Collection K.Kurt: Project development
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval Informed consent was obtained from pregnant women both for herself and the newborn. This study was approved by the ethical committee with date 21.09.2021 and number 408 of Izmir Katip Celebi Univesity, Faculty of Medicine and the Turkish Ministry of Health.
References
Aygün, Vitamin D can prevent multi-organ damage caused by COVID-19 infection, Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol
Bahat, Talmac, Bestel, Micronutrients in COVID-19 Positive Pregnancies, Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.10609
Bassatne, Basbous, Chakhtoura, The link between COVID-19 and VItamin D (VIVID): a systematic review and meta-analysis, Metabolism, doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2021.154753
Capobianco, Covid-19 in pregnant women: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Euro. J. Obstet. Gynecol. again. biol, doi:10.1016/j.ejogrb.2020.07.034
Charoenngam, Holick, Immunologic Effects of Vitamin D on Human Health and Disease, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12072097
Ferrer-Sánchez, Díaz-Goicoechea, Mayoral-Cesar, Serum 25(OH) Vitamin D Levels in Pregnant Women with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Case-Control Study, Int J Environ Res Public Health, doi:10.3390/ijerph19073965
Holick, Binkley, Bischoff-Ferrari, Endocrine Society Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab
Jovanovich, Ginde, Holmen, Vitamin D level and risk of community-acquired pneumonia and sepsis, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu6062196
Liu, Why are pregnant women susceptible to COVID-19? An immunological perspective, J Reprod. immunol, doi:10.1016/j.jri.2020.103122
Martineau, Jolliffe, Hooper, Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.i6583
Mascio, Khalil, Saccone, Outcome of coronavirus spectrum infections (SARS, MERS, COVID-19) during pregnancy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. I am, J Obstet Gynecol, doi:10.1016/j.ajogmf.2020.100107
Mercola, Grant, Wagner, Evidence Regarding Vitamin D and Risk of COVID-19 and Its Severity, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12113361
Salmon, Sorge, Pneumonia in pregnant women: exploring this high-risk complication and its links to preterm birth
Schmitt, Labdouni, Soulimani, Oxidative stress status and vitamin D levels of asymptomatic to mild symptomatic COVID-19 infections during the third trimester of pregnancy: A retrospective study in Metz, France, Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.27606
Seven, Gunduz, Correlation between 25-hydroxy vitamin D levels and COVID-19 severity in pregnant women: a cross-sectional study, J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med, doi:10.1080/14767058.2021.2005564
Sinaci, Ocal, Yetiskin, Impact of vitamin D on the course of COVID-19 during pregnancy: A case control study, J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol
Smaha, Kužma, Jackuliak, Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D Concentration Significantly Decreases in Patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia during the First 48 Hours after Hospital Admission, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14122362
Tekin, Yassa, Birol, Vitamin D status is not associated with the clinical severity of COVID-19 in pregnant women, European Journal of Nutrition, doi:10.1007/s00394-021-02709-7
Teymoori-Rad, Shokri, Salimi, Interaction between vitamin D and viral infections, Rev Med Virol, doi:10.1002/rmv.2032
Wu, Mcgoogan, Characteristics and key lessons of the 2019 coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak in China: Summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese center for disease control and prevention, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.2648
Zhu, Zhang, A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019, N. Engl. J.Med, doi:10.1056/nejmoa2001017
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.36516/jocass.1185181",
"ISSN": [
"2667-498X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.36516/jocass.1185181",
"abstract": "<jats:p xml:lang=\"en\">Aim: Low vitamin D levels were related to an increased risk of upper respiratory tract infection and pneumonia. Vitamin D might therefore protect against symptoms of the Covid 19. The present study aims to evaluate the relationship between the acquisition and course of Covid 19 and serum vitamin D levels and investigate the prophylactic efficacy of vitamin D supplementation in pregnant women.
\nMaterials and Methods: This case-control study was conducted on 318 pregnant women admitted to our tertiary clinic to give birth between March 2020 and December 2021. All cases were tested for Covid 19 via nasopharyngeal swab. Fifty-four patients with positive PCR for SARS-CoV-2 (Group 1) were matched with 264 consecutive healthy controls (Group 2). 25 OH D Vitamin levels were measured and compared between the two groups, along with the frequency of vitamin D supplementation. 
\nResults: Group 1 showed significantly low mean 25 OH D levels, compared to Group 2 (10,22 ± 7,10 (3-37)ng/ml vs. 16,63 ± 10,80 (3,40-48,90)ng/ml, p = 0,000). Sixteen point seven % of controls and 3,7% of cases had normal Vitamin D levels (>30 ng/mL); the difference was also statistically significant (p=0,005). The frequency of vitamin D supplementation was also detected higher in controls than those with positive SARS-CoV-2 (35,6% vs. 14,8%, p=0,003).
\nConclusions: Sustaining adequate levels of Vitamin D may positively impact protection against Covid 19 during pregnancy. In this context, Vitamin D supplementation should be considered for the pregnant population, particularly in settings where profound vitamin D deficiency is common.</jats:p>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
5
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "İZMİR KATİP ÇELEBİ ÜNİVERSİTESİ, TIP FAKÜLTESİ"
}
],
"family": "ŞENGÜL",
"given": "Mustafa",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "İZMİR KATİP ÇELEBİ ÜNİVERSİTESİ"
}
],
"family": "ŞEN SELİM",
"given": "Halime",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "İZMİR KATİP ÇELEBİ ÜNİVERSİTESİ"
}
],
"family": "ŞEN",
"given": "Serhat",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "İZMİR KATİP ÇELEBİ ÜNİVERSİTESİ"
}
],
"family": "ERBAK YILMAZ",
"given": "Huriye",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Cukurova Anestezi ve Cerrahi Bilimler Dergisi",
"container-title-short": "JoCASS",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-06T16:52:19Z",
"timestamp": 1673023939000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-06T16:52:34Z",
"timestamp": 1673023954000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-07T06:07:28Z",
"timestamp": 1673071648150
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "3",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
31
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "3",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
31
]
]
}
},
"language": "tr",
"member": "22431",
"original-title": [],
"page": "368-374",
"prefix": "10.36516",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
31
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
31
]
]
},
"publisher": "Cukurova Anestezi ve Cerrahi Bilimler Dergisi",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001017",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref1",
"unstructured": "Zhu N, Zhang D, Wang W. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J.Med. 2020; 328 :727–733. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2001017."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.2648",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref2",
"unstructured": "Wu Z, McGoogan JM. Characteristics and key lessons of the 2019 coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak in China: Summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese center for disease control and prevention. JAMA. 2020; 323 (13):1239–1242. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.2648."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1091592303251728",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref3",
"unstructured": "Salmon B, Bruick Sorge C. Pneumonia in pregnant women: exploring this high-risk complication and its links to preterm birth [Internet]. AWHONN Lifelines. 2003; 7 ( 1 ): 48-52. https://doi.org/10.1177/1091592303251728."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejogrb.2020.07.034",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref4",
"unstructured": "Capobianco G. Covid-19 in pregnant women: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Euro. J. Obstet. Gynecol. again. biol. 2020; 252 :490-501. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2020.07.034."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajogmf.2020.100107",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref5",
"unstructured": ".Di Mascio D, Khalil A., Saccone G, et al. Outcome of coronavirus spectrum infections (SARS, MERS, COVID-19) during pregnancy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. I am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2020; 2 (2) . doi: 10.1016/j.ajogmf.2020.100107."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jri.2020.103122",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref6",
"unstructured": ".Liu H. Why are pregnant women susceptible to COVID-19? An immunological perspective. J Reprod. immunol. 2020; 139. doi: 10.1016/j.jri.2020.103122."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu6062196",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref7",
"unstructured": "Jovanovich AJ, Ginde AA, Holmen J, et al. Vitamin D level and risk of community-acquired pneumonia and sepsis. Nutrients 2014 ;6(6): 2196 – 2205. doi: 10.3390/nu6062196."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.i6583",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref8",
"unstructured": "Martineau AR, Jolliffe DA, Hooper RL, et al. Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data. BMJ. 2017 ;356:i6583. doi: 10.1136/bmj.i6583."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.2032",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref9",
"unstructured": "Teymoori-Rad M, Shokri F, Salimi V, et al.Interaction between vitamin D and viral infections. Rev Med Virol. 2019; 29 :e2032. doi: 10.1002/rmv.2032."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00210-020-01911-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref10",
"unstructured": ".Aygün H. Vitamin D can prevent multi-organ damage caused by COVID-19 infection. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2020; 393(7):1157-1160. doi: 10.1007/s00210-020-01911-4."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.metabol.2021.154753",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref11",
"unstructured": ".Bassatne A, Basbous M, Chakhtoura M, et al.The link between COVID-19 and VItamin D (VIVID): a systematic review and meta-analysis. Metabolism. 2021; 119 (June). doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2021.154753."
},
{
"DOI": "10.15557/PiMR.2020.0004",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref12",
"unstructured": ".World Health Organization (WHO) (2020) Clinical management of COVID-19: interim guidance, 27 May 2020. World Health Organization. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/332196. Retrieved March 25, 2021."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/jc.2011-0385",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref13",
"unstructured": "Holick M.F, Binkley N.C, Bischoff-Ferrari H.A, et al. Endocrine Society Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011;96(July (7)):1911–1930. doi: 10.1210/jc.2011-0385."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14122362",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref14",
"unstructured": "Smaha J, Kužma M, Jackuliak P, et al.Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D Concentration Significantly Decreases in Patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia during the First 48 Hours after Hospital Admission. Nutrients. 2022 Jun 7;14(12):2362. doi: 10.3390/nu14122362."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12072097",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref15",
"unstructured": "Nipith Charoenngam and Michael F. Holick. Immunologic Effects of Vitamin D on Human Health and Disease. Nutrients. 2020 Jul; 12(7): 207. doi: 10.3390/nu12072097."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12113361",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref16",
"unstructured": ".Mercola J, Grant WB, Wagner CL.Evidence Regarding Vitamin D and Risk of COVID-19 and Its Severity. Nutrients. 2020 Oct 31;12(11):3361. doi: 10.3390/nu12113361."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/14767058.2021.2005564",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref17",
"unstructured": "Seven B, Gunduz O, Ozgu-Erdinc A S, et al.Correlation between 25-hydroxy vitamin D levels and COVID-19 severity in pregnant women: a cross-sectional study. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2021 Nov 23;1-6. doi: 10.1080/14767058.2021.2005564."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijerph19073965",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref18",
"unstructured": ".Ferrer-Sánchez N, Díaz-Goicoechea M, Mayoral-Cesar V, et al.Serum 25(OH) Vitamin D Levels in Pregnant Women with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Case-Control Study. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Mar 26;19(7):3965. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19073965."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref19",
"unstructured": "Sinaci S, Ocal D F,Yucel Yetiskin D F, et al.Impact of vitamin D on the course of COVID-19 during pregnancy: A case control study. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2021 Oct;213:105964. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.27606",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref20",
"unstructured": ".Schmitt G, Labdouni S, Soulimani R, et al. Oxidative stress status and vitamin D levels of asymptomatic to mild symptomatic COVID-19 infections during the third trimester of pregnancy: A retrospective study in Metz, France.Journal of Medical Virology.21 January 2022. doi: 10.1002/jmv.27606."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00394-021-02709-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref21",
"unstructured": "Tekin A B, Yassa M, Birol P, et al. Vitamin D status is not associated with the clinical severity of COVID-19 in pregnant women. European Journal of Nutrition (2021). doi: 10.1007/s00394-021-02709-7."
},
{
"DOI": "10.7759/cureus.10609",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref22",
"unstructured": ".Yalcin Bahat P, Aldikactioglu Talmac M,Bestel A, et al. Micronutrients in COVID-19 Positive Pregnancies. Cureus. 2020 Sep 23;12(9):e10609. doi: 10.7759/cureus.10609."
}
],
"reference-count": 22,
"references-count": 22,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://dergipark.org.tr/en/doi/10.36516/jocass.1185181"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Materials Science"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Serum Vitamin D Concentrations and Covid-19 In Pregnant Women, Does Vitamin D Supplementation Impact Results? A Comprehensive Study",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "5"
}
