Correlation between 25-hydroxy vitamin D levels and COVID-19 severity in pregnant women: a cross-sectional study
et al., The Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine, doi:10.1080/14767058.2021.2005564, Nov 2021
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Prospective study of 403 pregnant COVID+ hospitalized women in Turkey, showing higher risk of severe disease or poor prognostic factors with vitamin D deficiency.
This is the 106th of 228 COVID-19 sufficiency studies for vitamin D, which collectively show higher levels reduce risk with p<0.0000000001.
|
risk of severe disease or poor prognostic factor, 46.5% lower, RR 0.53, p = 0.006, cutoff 14.5ng/ml, inverted to make RR<1 favor high D levels (≥14.5ng/ml).
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Seven et al., 23 Nov 2021, prospective, Turkey, peer-reviewed, 6 authors, study period September 2020 - November 2020.
Correlation between 25-hydroxy vitamin D levels and COVID-19 severity in pregnant women: a cross-sectional study
The Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine, doi:10.1080/14767058.2021.2005564
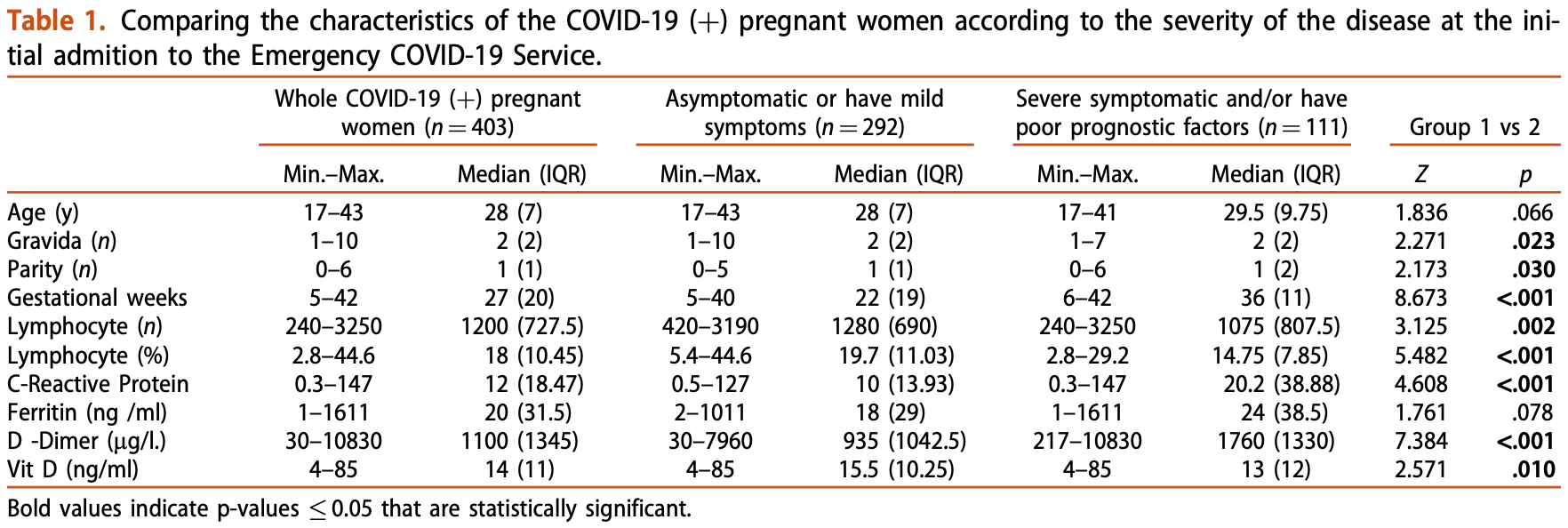
Objective: To evaluate the relationship between 25-hydroxy vitamin D (25(OH)D) levels and disease severity in hospitalized COVID-19 positive pregnant women Methods: The COVID-19 (þ) pregnant women (confirmed by PCR test) were classified as asymptomatic, mild symptomatic, and severe disease according to their symptoms and laboratory results. Severe COVID-19 criteria were respiratory symptoms and/or findings. The following laboratory results were considered as poor prognostic factors: the number of lymphocytes <800/ml and/or CRP value >10 times the upper limit of the normal range and/or ferritin value >500 ng/ml and/or D-Dimer value >1000 mg/l. The patients were divided into two groups; asymptomatic or mild symptomatic group (Group 1), and severe disease and/or poor prognostic factor group (Group 2). The 25(OH)D levels were compared between groups. ROC curve analysis was used to analyze the cutoff value for vitamin D to predict the severity of COVID-19. Results: 25(OH)D levels were found to be statistically significantly lower in group 2 (15.5 (10.25) ng/ml in Group 1, 13 (12) ng/ml in Group 2, p ¼ .010). The 25(OH)D level under 14.5 ng/ml was associated with severe COVID-19 and/or poor prognostic factors (p ¼ .010). The risk of severe COVID-19 and/or having poor prognostic factors was 1.87 times higher among pregnant women who had 25(OH)D levels below 14.5 ng/ml. This value was found to have 54.1% sensitivity and 61.3% specificity in predicting severe COVID-19 and/or poor prognostic laboratory findings in pregnant women Conclusion: There is a relationship between vitamin D status and the severity of COVID-19 in pregnant women. During the pandemic period, vitamin D supplementation for pregnant women should gain more importance.
Disclosure statement No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
References
Alipio, Vitamin D supplementation could possibly improve clinical outcomes of patients infected with Coronavirus
Bilezikian, Bikle, Hewison, Mechanisms in endocrinology: vitamin D and COVID-19, Eur J Endocrinol
Castillo, Costa, Barrios, Effect of calcifediol treatment and best available therapy versus best available therapy on intensive care unit admission and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: a pilot randomized clinical study, J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol
Cucinotta, Vanelli, WHO declares COVID-19 a pandemic, Acta Biomed
Cyprian, Lefkou, Varoudi, Immunomodulatory effects of vitamin D in pregnancy and Beyond, Front Immunol
D'avolio, Avataneo, Manca, 25-Hydroxyvitamin D concentrations are lower in patients with positive PCR for SARS-CoV-2, Nutrients
Dey, Singh, Tiwari, Pregnancy outcome in first 50 SARS-Cov-2 positive patients at our center, Gynecol Obstet Reprod Med
Eggemoen, Falk, Knutsen, Vitamin D deficiency and supplementation in pregnancy in a multiethnic population-based cohort, BMC Pregnancy Childbirth
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Evidence that vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of influenza and COVID-19 infections and deaths, Nutrients
Haussler, Jurutka, Mizwicki, Vitamin D receptor (VDR)-mediated actions of 1a,25(OH)(2) vitamin D 3 : genomic and non-genomic mechanisms, Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab
Henry, De Oliveira, Benoit, Hematologic, biochemical and immune biomarker abnormalities associated with severe illness and mortality in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a metaanalysis, Clin Chem Lab Med
Holick, Vitamin D deficiency, N Engl J Med
Huang, Wang, Li, Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet
Jovanovich, Ginde, Holmen, Vitamin D level and risk of community-acquired pneumonia and sepsis, Nutrients
Lokken, Taylor, Huebner, Higher severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection rate in pregnant patients, Am J Obstet Gynecol
Martineau, Jolliffe, Hooper, Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data, BMJ
Medical, World medical association declaration of Helsinki: ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects, JAMA
Mohan, Cherian, Sharma, Exploring links between vitamin D deficiency and COVID-19, PLOS Pathog
Mor, Cardenas, The immune system in pregnancy: a unique complexity, Am J Reprod Immunol
Ozdemir, Gundemir, Kucuk, Vitamin D deficiency in pregnant women and their infants, J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol
Phoswa, Khaliq, Is pregnancy a risk factor of COVID-19?, Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol
Pike, Christakos, Biology and mechanisms of action of the vitamin D Hormone, Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am
Radujkovic, Hippchen, Tiwari-Heckler, Vitamin D deficiency and outcome of COVID-19 patients, Nutrients
Singh, Nair, Singh, Pregnancy-specific concerns and psychological impact of COVID-19 on antenatal women, Gynecol Obstet Reprod Med
Soy, Keser, Atagunduz, Cytokine storm in COVID-19: pathogenesis and overview of anti-inflammatory agents used in treatment, Clin Rheumatol
Tabatabaeizadeh, Avan, Bahrami, High dose supplementation of vitamin D affects measures of systemic inflammation: reductions in high sensitivity C-Reactive protein level and neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) distribution, J Cell Biochem
Tuten, Acikgoz, Mammadov, Is there a role of 25-Hydroxy vitamin D in the pathogenesis of mild and moderate-to-severe endometriosis?, Gynecol Obstet Reprod Med
Van Schoor, Lips, Worldwide vitamin D status, Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab
Wang, Nestel, Bourdeau, Cutting edge: 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 is a direct inducer of antimicrobial peptide gene expression, J Immunol
Wu, Zhao, Yu, A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China, Nature
Yes ¸iltepe-Mutlu, Aksu, Bereket, Vitamin D status across age groups in Turkey: results of 108,742 samples from a single laboratory, Jcrpe
Zhao, Meng, Kumar, Lymphopenia is associated with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infections: a systemic review and metaanalysis, Int J Infect Dis
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1080/14767058.2021.2005564",
"ISSN": [
"1476-7058",
"1476-4954"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/14767058.2021.2005564",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1080/14767058.2021.2005564"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "Peer Review Statement",
"name": "peerreview_statement",
"order": 1,
"value": "The publishing and review policy for this title is described in its Aims & Scope."
},
{
"URL": "http://www.tandfonline.com/action/journalInformation?show=aimsScope&journalCode=ijmf20",
"label": "Aim & Scope",
"name": "aims_and_scope_url",
"order": 2,
"value": "http://www.tandfonline.com/action/journalInformation?show=aimsScope&journalCode=ijmf20"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2021-06-10"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Revised",
"name": "revised",
"order": 1,
"value": "2021-09-19"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "2021-11-09"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 3,
"value": "2021-11-23"
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4731-4755",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Ob&Gyn, Ankara City Hospital, Ankara, Turkey"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Seven",
"given": "B.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5868-4861",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Ob&Gyn, Ankara City Hospital, Ankara, Turkey"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Gunduz",
"given": "O.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6132-5779",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Ob&Gyn, Ankara City Hospital, Ankara, Turkey"
},
{
"name": "Department of Ob&Gyn, University of Health Sciences, Turkey"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ozgu-Erdinc",
"given": "A. S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8567-9048",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Ob&Gyn, Ankara City Hospital, Ankara, Turkey"
},
{
"name": "Department of Ob&Gyn, University of Health Sciences, Turkey"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Sahin",
"given": "Dilek",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8167-3837",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Ob&Gyn, Ankara City Hospital, Ankara, Turkey"
},
{
"name": "Department of Ob&Gyn, University of Health Sciences, Turkey"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Moraloglu Tekin",
"given": "O.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2268-3821",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Ob&Gyn, Ankara City Hospital, Ankara, Turkey"
},
{
"name": "Department of Ob&Gyn, University of Health Sciences, Turkey"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Keskin",
"given": "H. L.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"The Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"www.tandfonline.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-23T14:00:55Z",
"timestamp": 1637676055000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-23T14:01:00Z",
"timestamp": 1637676060000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-24T06:51:27Z",
"timestamp": 1637736687544
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "1476-7058"
},
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "1476-4954"
}
],
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
23
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/14767058.2021.2005564",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "301",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1-6",
"prefix": "10.1080",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
23
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
23
]
]
},
"publisher": "Informa UK Limited",
"reference": [
{
"author": "Cucinotta D",
"first-page": "157",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Acta Biomed",
"key": "CIT0001",
"volume": "91",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21613/GORM.2021.1176",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21613/GORM.2021.1172",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2008-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10067-020-05190-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1008874",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.i6583",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ecl.2017.07.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMra070553",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.beem.2011.05.010",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.173.5.2909",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2019.02739",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1530/EJE-20-0665",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21613/GORM.2019.949",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12051359",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2013.281053",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0017"
},
{
"key": "CIT0018",
"unstructured": "Turkish Ministry of Health, General Directorate of Public Health, COVİD-19 (SARS-CoV-2 infection) Guideline, Scientific Committee Report 2020. Available from: https://hsgm.saglik.gov.tr/depo/birimler/goc_sagligi/covid19/rehber/COVID-19_Rehberi20200414_eng_v4_002_14.05.2020.pdf"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1515/cclm-2020-0369",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.04.086",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcb.26084",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu6062196",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.beem.2011.06.007",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12884-016-0796-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4274/jcrpe.galenos.2019.2019.0097",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0025"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4274/jcrpe.4706",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0026"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12092757",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0027"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105751",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0028"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2139/ssrn.3571484",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "CIT0029",
"unstructured": "Alipio M. Vitamin D supplementation could possibly improve clinical outcomes of patients infected with Coronavirus-2019 (COVID-19). Available at SSRN 3571484. 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejogrb.2020.06.058",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0030"
},
{
"author": "Lokken EM",
"journal-title": "Am J Obstet Gynecol",
"key": "CIT0031",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1600-0897.2010.00836.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0032"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12040988",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "CIT0033"
}
],
"reference-count": 33,
"references-count": 33,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"The Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Obstetrics and Gynaecology",
"Pediatrics, Perinatology, and Child Health"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Correlation between 25-hydroxy vitamin D levels and COVID-19 severity in pregnant women: a cross-sectional study"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/tandf_crossmark_01"
}
