Oxidative stress status and vitamin D levels of asymptomatic to mild symptomatic COVID-19 infections during the third trimester of pregnancy: A retrospective study in Metz, France
et al., Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.27606, Jan 2022
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
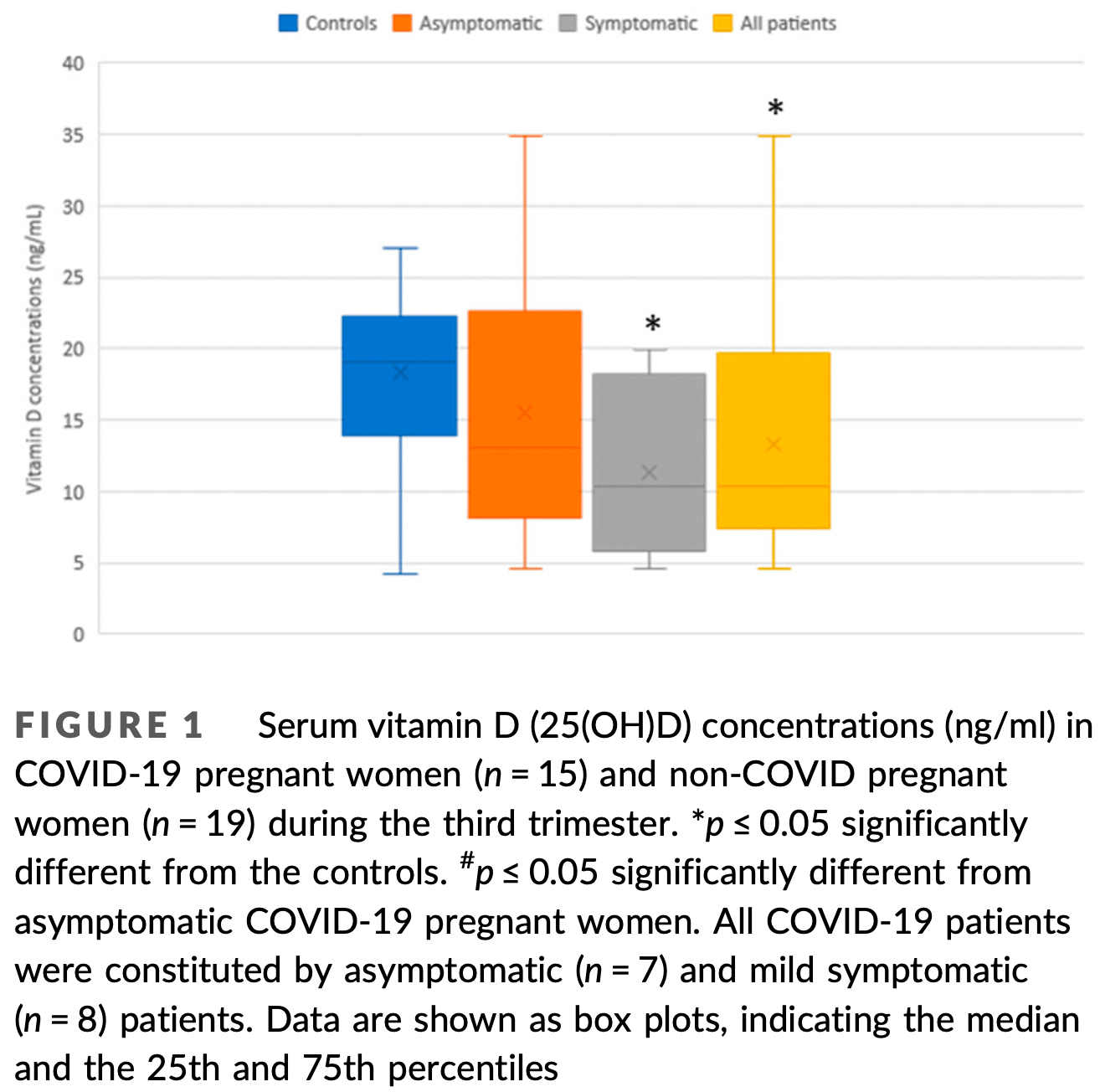
Retrospective 15 COVID+ pregnant women and 20 healthy controls in France, showing that all COVID+ patients were vitamin D deficient, and vitamin D levels were significantly lower in symptomatic patients compared to controls or asymptomatic patients.
Schmitt et al., 27 Jan 2022, France, peer-reviewed, 5 authors.
Oxidative stress status and vitamin D levels of asymptomatic to mild symptomatic COVID‐19 infections during the third trimester of pregnancy: A retrospective study in Metz, France
Journal of Medical Virology, doi:10.1002/jmv.27606
It is believed that the subtle equilibrium between tolerance and immunity during the unique biological state of pregnancy, which is characterized by further physiological and hormonal changes, rends pregnant women more vulnerable to coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). In this retrospective study, confirmed COVID-19-positive pregnant women (n = 15) during their third trimester, comprising asymptomatic (n = 7) and mild symptomatic (n = 8), and healthy pregnant controls (n = 20), were
CONFLICT OF INTERESTS The authors declare that there are no conflict of interests.
ETHICS STATEMENT In this retrospective study, analyzed serum samples were leftovers in CHR Metz-Thionville hospital laboratories. They were processed in
References
Antoun, Taweel, Ahmed, Patni, Honest, Maternal COVID-19 infection, clinical characteristics, pregnancy, and neonatal outcome: a prospective cohort study, Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol
Asgari, Pousaz, Human genetic variants identified that affect COVID susceptibility and severity, Nature, doi:10.1038/d41586-021-01773-7
Bansal, Pandey, Asthana, C-reactive protein (CRP) and its association with periodontal disease: a brief review, J Clin Diagn Res
Beltrán-García, Osca-Verdegal, Pallardó, Oxidative stress and inflammation in COVID-19-associated sepsis: the potential role of anti-oxidant therapy in avoiding disease progression, Antioxidants
Bouayed, Bohn, Adapted sickness behavior-why it is not enough to limit the COVID-19 spread?, Brain Behav Immun
Bouayed, Bohn, Dietary derived antioxidants: implications on health, Nutrition, Well-Being and Health. Intech
Bouayed, Bohn, The link between microglia and the severity of COVID-19: the 'two-hit' hypothesis, J Med Virol
Cao, Yin, Chen, Clinical analysis of ten pregnant women with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective study, Int J Infect Dis
Cecchini, Cecchini, SARS-CoV-2 infection pathogenesis is related to oxidative stress as a response to aggression, Med Hypotheses
Chen, Guo, Wang, Clinical characteristics and intrauterine vertical transmission potential of COVID-19 infection in nine pregnant women: a retrospective review of medical records, Lancet
De Melo, De Araújo, COVID-19 infection in pregnant women, preterm delivery, birth weight, and vertical transmission: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Cad Saude Publica
Demir, Demir, Aygun, Vitamin D deficiency is associated with COVID-19 positivity and severity of the disease, J Med Virol
Derouiche, Oxidative stress associated with SARS-Cov-2 (COVID-19) increases the severity of the lung disease-a systematic review, J Infect Dis Epidemiol
Elsori, Hammoud, Vitamin D deficiency in mothers, neonates and children, J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol
Fahmi, Brügger, Démoulins, SARS-CoV-2 can infect and propagate in human placenta explants, Cell Rep Med
Gandhi, Lynch, Del Rio, Mild or moderate Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Getachew, Tizabi, Vitamin D and COVID-19: role of ACE2, age, gender, and ethnicity, J Med Virol
Gupta, Kumar, Sharma, SARS-CoV-2 prevalence and maternal-perinatal outcomes among pregnant women admitted for delivery: experience from COVID-19-dedicated maternity hospital in Jammu, Jammu and Kashmir (India), J Med Virol
Iddir, Brito, Dingeo, Strengthening the immune system and reducing inflammation and oxidative stress through diet and nutrition: considerations during the COVID-19 crisis, Nutrients
Jering, Claggett, Cunningham, Clinical characteristics and outcomes of hospitalized women giving birth with and without COVID-19, JAMA Intern Med, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.9241
Jha, Ho, Dan, Jandeleit-Dahm, A causal link between oxidative stress and inflammation in cardiovascular and renal complications of diabetes, Clin Sci
Juan, Gil, Rong, Zhang, Yang et al., Effect of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) on maternal, perinatal and neonatal outcome: systematic review, Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol
Karkhanei, Ghane, Mehri, Evaluation of oxidative stress level: total antioxidant capacity, total oxidant status and glutathione activity in patients with COVID-19, New Microbes New Infect
Lips, Cashman, Lamberg-Allardt, Current vitamin D status in European and Middle East countries and strategies to prevent vitamin D defciency: a position statement of the European Calcifed Tissue Society, Eur J Endocrinol
Mandò, Savasi, Anelli, Mitochondrial and oxidative unbalance in placentas from mothers with SARS-CoV-2 infection, Antioxidants
Masood, Nadeem, Mustafa, Donnell, Reversal of oxidative stress-induced anxiety by inhibition of phosphodiesterase-2 in mice, J Pharmacol Exp Ther
Menzel, Samouda, Dohet, Loap, Ellulu et al., Common and novel markers for measuring inflammation and oxidative stress ex vivo in research and clinical practice-which to use regarding disease outcomes?, Antioxidants
Mor, Aldo, Alvero, The unique immunological and microbial aspects of pregnancy, Nat Rev Immunol
Ovies, Semmes, Coyne, Pregnancy influences immune responses to SARS-CoV-2, Sci Transl Med
Petrelli, Luciani, Perego, Dognini, Colombelli et al., Therapeutic and prognostic role of vitamin D for COVID-19 infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 43 observational studies, J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol
Salem, Leghouchi, Soulimani, Bouayed, Reduction of paw edema and liver oxidative stress in carrageenan-induced acute inflammation by Lobaria pulmonaria and Parmelia caperata, lichen species, in mice, Int J Vitam Nutr Res
Sinaci, Ocal, Yucel, Yetiskin, Impact of vitamin D on the course of COVID-19 during pregnancy: a case control study, J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol
Tekin, Yassa, Birol, Vitamin D status is not associated with clinical severity of COVID-19 in pregnant women, Eur J Nutr
Wei, Vitamin D and pregnancy outcomes, Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol
Yan, Guo, Fan, Coronavirus disease 2019 in pregnant women: a report based on 116 cases, Am J Obstet Gynecol
Yang, Wang, Liu, Clinical characteristics and risk assessment of newborns born to mothers with COVID-19, J Clin Virol
Zeberg, Pääbo, The major genetic risk factor for severe COVID-19 is inherited from Neanderthals, Nature
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.27606",
"ISSN": [
"0146-6615",
"1096-9071"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/jmv.27606",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1002/jmv.27606"
],
"archive": [
"Portico"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2021-11-19"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 1,
"value": "2022-01-17"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 2,
"value": "2022-01-27"
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Université de Lorraine, LCOMS /Neurotoxicologie Alimentaire et Bioactivité Metz France"
},
{
"name": "CHR Metz‐Thionvillle Hôpital de Mercy Ars‐Laquenexy France"
}
],
"family": "Schmitt",
"given": "Guillaume",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "CHR Metz‐Thionvillle Hôpital de Mercy Ars‐Laquenexy France"
}
],
"family": "Labdouni",
"given": "Sary",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Université de Lorraine, LCOMS /Neurotoxicologie Alimentaire et Bioactivité Metz France"
}
],
"family": "Soulimani",
"given": "Rachid",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "CHR Metz‐Thionvillle Hôpital de Mercy Ars‐Laquenexy France"
}
],
"family": "Delamare",
"given": "Catherine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8410-2105",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Université de Lorraine, LCOMS /Neurotoxicologie Alimentaire et Bioactivité Metz France"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Bouayed",
"given": "Jaouad",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Journal of Medical Virology"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"onlinelibrary.wiley.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-21T11:56:00Z",
"timestamp": 1642766160000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-27T15:51:39Z",
"timestamp": 1643298699000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-28T06:42:16Z",
"timestamp": 1643352136709
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "0146-6615"
},
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "1096-9071"
}
],
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
27
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/termsAndConditions#vor",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-27T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1643241600000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://doi.wiley.com/10.1002/tdm_license_1.1",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-27T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1643241600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/jmv.27606",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full-xml/10.1002/jmv.27606",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/jmv.27606",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1002",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
27
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
27
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference": [
{
"key": "e_1_2_12_2_1",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization. WHO timeline—COVID‐19. April 27 2020. https://www.who.int/news-room/detail/27-04-2020-who-timeline--covid-19"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.04.047",
"article-title": "Clinical analysis of ten pregnant women with COVID‐19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective study",
"author": "Cao D",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "294",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis",
"key": "e_1_2_12_3_1",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30360-3",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics and intrauterine vertical transmission potential of COVID‐19 infection in nine pregnant women: a retrospective review of medical records",
"author": "Chen H",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "809",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "e_1_2_12_4_1",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejogrb.2020.07.008",
"article-title": "Maternal COVID‐19 infection, clinical characteristics, pregnancy, and neonatal outcome: a prospective cohort study",
"author": "Antoun L",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "559",
"journal-title": "Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol",
"key": "e_1_2_12_5_1",
"volume": "252",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nri.2017.64",
"article-title": "The unique immunological and microbial aspects of pregnancy",
"author": "Mor G",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "469",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Immunol",
"key": "e_1_2_12_6_1",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/uog.22088",
"article-title": "Effect of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19) on maternal, perinatal and neonatal outcome: systematic review",
"author": "Juan J",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "15",
"journal-title": "Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol",
"key": "e_1_2_12_7_1",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26984",
"article-title": "The link between microglia and the severity of COVID‐19: the ‘two‐hit’ hypothesis",
"author": "Bouayed J",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4111",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "e_1_2_12_8_1",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2818-3",
"article-title": "The major genetic risk factor for severe COVID‐19 is inherited from Neanderthals",
"author": "Zeberg H",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "610",
"issue": "7835",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "e_1_2_12_9_1",
"volume": "587",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/d41586-021-01773-7",
"article-title": "Human genetic variants identified that affect COVID susceptibility and severity",
"author": "Asgari S",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "390",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "e_1_2_12_10_1",
"volume": "600",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26832",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency is associated with COVID‐19 positivity and severity of the disease",
"author": "Demir M",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2992",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "e_1_2_12_11_1",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.27074",
"article-title": "SARS‐CoV‐2 prevalence and maternal‐perinatal outcomes among pregnant women admitted for delivery: experience from COVID‐19‐dedicated maternity hospital in Jammu, Jammu and Kashmir (India)",
"author": "Gupta P",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5505",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "e_1_2_12_12_1",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.abm2070",
"article-title": "Pregnancy influences immune responses to SARS‐CoV‐2",
"author": "Ovies C",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "eabm2070",
"issue": "13617",
"journal-title": "Sci Transl Med",
"key": "e_1_2_12_13_1",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.xcrm.2021.100456",
"article-title": "SARS‐CoV‐2 can infect and propagate in human placenta explants",
"author": "Fahmi A",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100456",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep Med",
"key": "e_1_2_12_14_1",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajog.2020.04.014",
"article-title": "Coronavirus disease 2019 in pregnant women: a report based on 116 cases",
"author": "Yan J",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "111.e1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Am J Obstet Gynecol",
"key": "e_1_2_12_15_1",
"volume": "223",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1590/0102-311x00087320",
"article-title": "COVID‐19 infection in pregnant women, preterm delivery, birth weight, and vertical transmission: a systematic review and meta‐analysis",
"author": "Melo GC",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e00087320",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Cad Saude Publica",
"key": "e_1_2_12_16_1",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104356",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics and risk assessment of newborns born to mothers with COVID‐19",
"author": "Yang P",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "104356",
"journal-title": "J Clin Virol",
"key": "e_1_2_12_17_1",
"volume": "127",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.9241",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics and outcomes of hospitalized women giving birth with and without COVID‐19",
"author": "Jering KS",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "714",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern Med",
"key": "e_1_2_12_18_1",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.27075",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and COVID‐19: role of ACE2, age, gender, and ethnicity",
"author": "Getachew B",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5285",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "e_1_2_12_19_1",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105964",
"article-title": "Impact of vitamin D on the course of COVID‐19 during pregnancy: a case control study",
"author": "Sinaci S",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "105964",
"journal-title": "J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol",
"key": "e_1_2_12_20_1",
"volume": "213",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/GCO.0000000000000117",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and pregnancy outcomes",
"author": "Wei SQ",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "438",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol",
"key": "e_1_2_12_21_1",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2017.01.023",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency in mothers, neonates and children",
"author": "Elsori DH",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "195",
"journal-title": "J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol",
"key": "e_1_2_12_22_1",
"volume": "175",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105883",
"article-title": "Therapeutic and prognostic role of vitamin D for COVID‐19 infection: a systematic review and meta‐analysis of 43 observational studies",
"author": "Petrelli F",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "105883",
"issue": "26",
"journal-title": "J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol",
"key": "e_1_2_12_23_1",
"volume": "211",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1530/EJE-18-0736",
"article-title": "Current vitamin D status in European and Middle East countries and strategies to prevent vitamin D defciency: a position statement of the European Calcifed Tissue Society",
"author": "Lips P",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "23",
"journal-title": "Eur J Endocrinol",
"key": "e_1_2_12_24_1",
"volume": "180",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D status is not associated with clinical severity of COVID‐19 in pregnant women",
"author": "Tekin AB",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Eur J Nutr",
"key": "e_1_2_12_25_1",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "C‐reactive protein (CRP) and its association with periodontal disease: a brief review",
"author": "Bansal T",
"first-page": "ZE21",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "J Clin Diagn Res",
"key": "e_1_2_12_26_1",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12061562",
"article-title": "Strengthening the immune system and reducing inflammation and oxidative stress through diet and nutrition: considerations during the COVID‐19 crisis",
"author": "Iddir M",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1562",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "e_1_2_12_27_1",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMcp2009249",
"article-title": "Mild or moderate Covid‐19",
"author": "Gandhi RT",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1757",
"issue": "18",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "e_1_2_12_28_1",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbi.2020.12.028",
"article-title": "Adapted sickness behavior–why it is not enough to limit the COVID‐19 spread?",
"author": "Bouayed J",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4",
"journal-title": "Brain Behav Immun",
"key": "e_1_2_12_29_1",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5772/1864",
"author": "Bouayed J",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"key": "e_1_2_12_30_1",
"volume-title": "Nutrition, Well‐Being and Health",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"article-title": "Oxidative stress associated with SARS‐Cov‐2 (COVID‐19) increases the severity of the lung disease‐a systematic review",
"author": "Derouiche S",
"first-page": "121",
"journal-title": "J Infect Dis Epidemiol",
"key": "e_1_2_12_31_1",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antiox9100936",
"article-title": "Oxidative stress and inflammation in COVID‐19‐associated sepsis: the potential role of anti‐oxidant therapy in avoiding disease progression",
"author": "Beltrán‐García J",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "936",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Antioxidants",
"key": "e_1_2_12_32_1",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110102",
"article-title": "SARS‐CoV‐2 infection pathogenesis is related to oxidative stress as a response to aggression",
"author": "Cecchini R",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "110102",
"journal-title": "Med Hypotheses",
"key": "e_1_2_12_33_1",
"volume": "143",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100897",
"article-title": "Evaluation of oxidative stress level: total antioxidant capacity, total oxidant status and glutathione activity in patients with COVID‐19",
"author": "Karkhanei B",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100897",
"journal-title": "New Microbes New Infect",
"key": "e_1_2_12_34_1",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antiox10030414",
"article-title": "Common and novel markers for measuring inflammation and oxidative stress ex vivo in research and clinical practice—which to use regarding disease outcomes?",
"author": "Menzel A",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "414",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Antioxidants (Basel)",
"key": "e_1_2_12_35_1",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antiox10101517",
"article-title": "Mitochondrial and oxidative unbalance in placentas from mothers with SARS‐CoV‐2 infection",
"author": "Mandò C",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1517",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Antioxidants",
"key": "e_1_2_12_36_1",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1024/0300-9831/a000620",
"article-title": "Reduction of paw edema and liver oxidative stress in carrageenan‐induced acute inflammation by Lobaria pulmonaria and Parmelia caperata, lichen species, in mice",
"author": "Salem S",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "143",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Int J Vitam Nutr Res",
"key": "e_1_2_12_37_1",
"volume": "91",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/CS20171459",
"article-title": "A causal link between oxidative stress and inflammation in cardiovascular and renal complications of diabetes",
"author": "Jha JC",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1811",
"issue": "16",
"journal-title": "Clin Sci",
"key": "e_1_2_12_38_1",
"volume": "132",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1124/jpet.108.137208",
"article-title": "Reversal of oxidative stress‐induced anxiety by inhibition of phosphodiesterase‐2 in mice",
"author": "Masood A",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "369",
"journal-title": "J Pharmacol Exp Ther",
"key": "e_1_2_12_39_1",
"volume": "326",
"year": "2008"
}
],
"reference-count": 38,
"references-count": 38,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"Journal of Medical Virology"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Virology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Oxidative stress status and vitamin D levels of asymptomatic to mild symptomatic COVID‐19 infections during the third trimester of pregnancy: A retrospective study in Metz, France"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/crossmark_policy"
}
