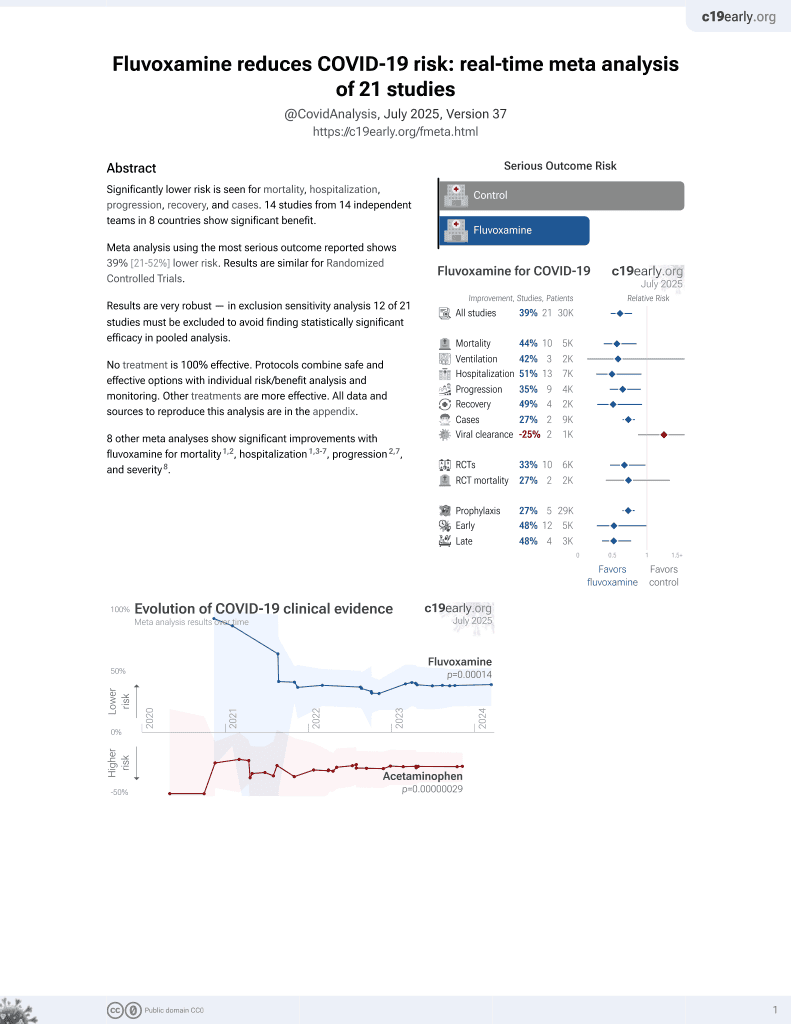
Impact of fluvoxamine on outpatient treatment of COVID-19 in Honduras in a prospective observational real-world study
et al., Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.1054644, Oct 2022 (preprint)
30th treatment shown to reduce risk in
November 2021, now with p = 0.00014 from 21 studies, recognized in 2 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
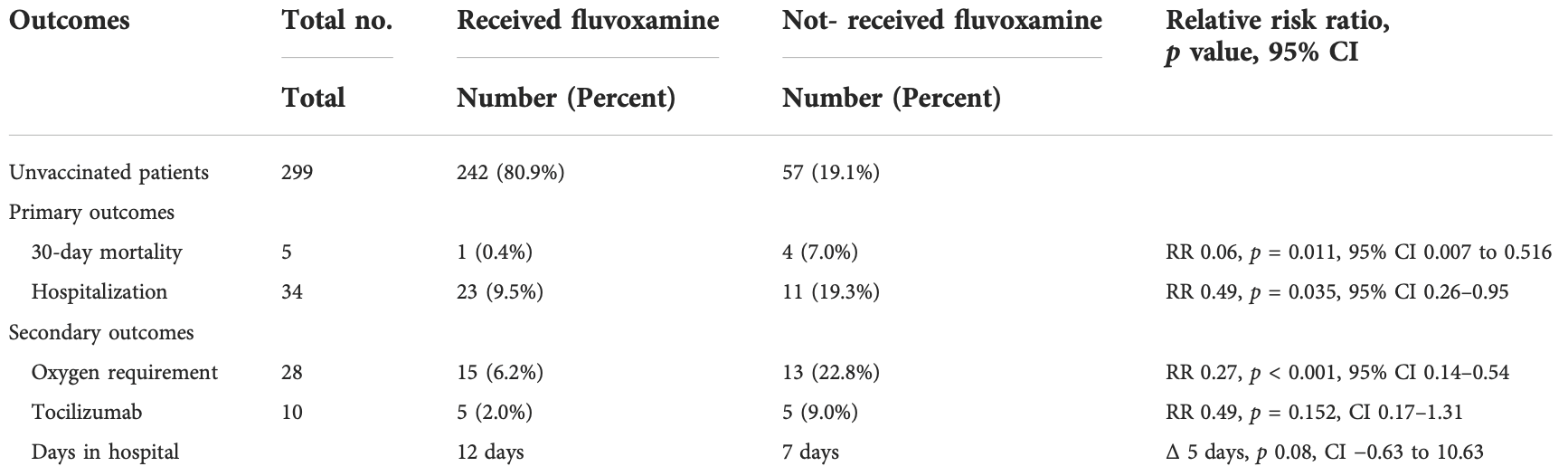
Prospective study of 657 COVID+ outpatients in Honduras, 594 accepting fluvoxamine treatment, showing significantly lower mortality and hospitalization with treatment.
|
risk of death, 94.0% lower, RR 0.06, p = 0.01, treatment 1 of 594 (0.2%), control 4 of 63 (6.3%), NNT 16, adjusted per study.
|
|
risk of oxygen therapy, 73.0% lower, RR 0.27, p < 0.001, treatment 15 of 594 (2.5%), control 13 of 63 (20.6%), NNT 5.5, adjusted per study.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 51.0% lower, RR 0.49, p = 0.04, treatment 23 of 594 (3.9%), control 11 of 63 (17.5%), NNT 7.4, adjusted per study.
|
|
hospitalization time, 71.4% higher, relative time 1.71, p = 0.08, treatment 23, control 11.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Pineda et al., 4 Oct 2022, prospective, Honduras, peer-reviewed, mean age 48.1, 24 authors, study period November 2020 - January 2022.
Contact: anupamsekhon@yahoo.com.
Impact of fluvoxamine on outpatient treatment of COVID-19 in Honduras in a prospective observational real-world study
Frontiers in Pharmacology, doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.1054644
Background: The COVID-19 pandemic has impacted millions of lives globally. While COVID-19 did not discriminate against developed or developing nations, it has been a significant challenge for third world countries like Honduras to have widespread availability of advanced therapies. The concept of early treatment was almost unheard of when early outpatient treatments utilizing repurposed drugs in Latin American countries began showing promising results. One such drug is fluvoxamine, which has shown tremendous potential in two major studies. As a direct result, fluvoxamine was added to the standard of care in a major medical center outpatient COVID-19 clinic.
Ethics statement The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by Institutional Review Board (IRB) of the Hospital Centro Médico Sanpedrano and the Ethics committee of investigation of infectious and zoonotic disease masters of the Universidad Nacional Autónoma de Honduras. The patients/ participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions All authors listed have made a substantial, direct, and intellectual contribution to the work and approved it for publication.
Conflict of interest The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Adnot, Houssaini, Abid, Marcos, Amsellem, Serotonin transporter and serotonin receptors, Handb. Exp. Pharmacol, doi:10.1007/978-3-642-38664-0_15
Akbari, Tabrizi, Lankarani, Aria, Vakili et al., The role of cytokine profile and lymphocyte subsets in the severity of coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19): A systematic review and meta-analysis, Life Sci, doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118167
Almqvist, Skudder, Kuenzig, Schwartz, Effect of cyproheptadine on endotoxin-induced pulmonary platelet trapping, Am. Surg
Alsabhan, Alshammari, New use of the SSRI fluvoxamine in the treatment of Covid-19 symptoms, COVID-19 pandemic, mental Health and neuroscience -new scenarios for understanding and treatment
Bhuta, Khokher, Kesireddy, Iftikhar, Beran et al., Fluvoxamine in nonhospitalized patients with acute COVID-19 infection and the lack of efficacy in reducing rates of hospitalization, mechanical ventilation, and mortality in placebo-controlled trials: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Am. J. Ther, doi:10.1097/mjt.0000000000001496
Bortolotti, Gentili, Rizzo, Rotola, Rizzo, SARS-COV-2 spike 1 protein controls Natural Killer cell activation via the HLA-E/NKG2A pathway, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells9091975
Brimson, Prasanth, Malar, Brimson, Thitilertdecha, None
Calusic, Marcec, Luksa, Jurkovic, Kovac et al., Safety and efficacy of fluvoxamine in COVID-19 ICU patients: An open label, prospective cohort trial with matched controls, Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol, doi:10.1111/bcp.15126
Cheema, Jafar, Elrashedy, Shahid, Awan et al., Efficacy and safety of fluvoxamine for the treatment of COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis, J. Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2022.10.012
Chen, Subbarao, The immunobiology of sars, Annu. Rev
Cloutier, Paré, Farndale, Schumacher, Nigrovic et al., Platelets can enhance vascular permeability, Blood, doi:10.1182/blood-2012-02-413047
Dalton, Johansen, Mellemkjaer, Sørensen, Nørgård, None
Dawson, Christensen, Rickaby, Linehan, Johnston, Lung damage and pulmonary uptake of serotonin in intact dogs, J. Appl. Physiol, doi:10.1152/jappl.1985.58.6.1761
Duerschmied, Suidan, Demers, Herr, Carbo et al., Platelet serotonin promotes the recruitment of neutrophils to sites of acute inflammation in mice, Blood, doi:10.1182/blood-2012-06-437392
Facente, Reiersen, Lenze, Boulware, Klausner et al., Changes in histamine and serotonin secretion from rat peritoneal mast cells caused by antidepressants, Inflamm. Res, doi:10.1007/bf02265168
Fung, Huang, Liu, Coronavirus-induced ER stress response and its involvement in regulation of coronavirus-host interactions, Virus Res, doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2014.09.016
Halperin, Reber, Hayashi, Su, Sigma-1 receptor chaperones at the ERmitochondrion interface regulate ca2+ signaling and cell survival, Dialogues Clin. Neurosci, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.08.036
Iqubal, Hoda, Najmi, Haque, Macrophage activation and cytokine release syndrome in COVID-19: Current updates and analysis of repurposed and investigational anti-cytokine drugs, Drug Res, doi:10.1055/a-1291-7692
Jalali, Rezaie, Rola, Kyle-Sidell, Covid-19 pathophysiology: Are platelets and serotonin hiding in plain sight?, SSRN J, doi:10.2139/ssrn.3800402
Lenze, Mattar, Zorumski, Stevens, Schweiger et al., Fluvoxamine vs placebo and clinical deterioration in outpatients with symptomatic COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.22760
Liu, Li, Liu, Liang, Wang et al., Longitudinal characteristics of lymphocyte responses and cytokine profiles in the peripheral blood of SARS-COV-2 infected patients, EBioMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102763
Liu, Tan, Chen, Zhu, Wan et al., Dynamic changes in lymphocyte subsets and parallel cytokine levels in patients with severe and critical COVID-19, BMC Infect. Dis, doi:10.1186/s12879-021-05792-7
Maclean, Herve, Eddahibi, Adnot, 5-hydroxytryptamine and the pulmonary circulation: Receptors, transporters and relevance to pulmonary arterial hypertension, Br. J. Pharmacol, doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0703570
Marik, Iglesias, Varon, Kory, A scoping review of the pathophysiology of Covid-19, Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol, doi:10.1177/20587384211048026
Martins-Gonçalves, Campos, Palhinha, Azevedo-Quintanilha, Mendes et al., Persisting platelet activation and hyperactivity in COVID-19 survivors, Circ. Res, doi:10.1161/circresaha.122.321659
Mazzoni, Salvati, Maggi, Capone, Vanni et al., Impaired immune cell cytotoxicity in severe COVID-19 is IL-6 dependent, J. Clin. Invest, doi:10.1172/jci138554
Mcgonagle, Ramanan, Bridgewood, Immune cartography of macrophage activation syndrome in the COVID-19 ERA, Nat. Rev. Rheumatol, doi:10.1038/s41584-020-00571-1
Mcgonagle, Sharif, O'regan, Bridgewood, The role of cytokines including interleukin-6 in COVID-19 induced pneumonia and macrophage activation syndrome-like disease, Autoimmun. Rev, doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102537
Meikle, Creeden, Mccullumsmith, Worth, SSRIs: Applications in inflammatory lung disease and implications for Covid-19, Neuropsychopharmacol. Rep, doi:10.1002/npr2.12194
Merad, Martin, Pathological inflammation in patients with COVID-19: A key role for monocytes and macrophages, Nat. Rev. Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41577-020-0331-4
Motta Junior, Miggiolaro, Nagashima, De Paula, Baena et al., Mast cells in alveolar septa of COVID-19 patients: A pathogenic pathway that may link interstitial edema to immunothrombosis, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.574862
Nochaiwong, Ruengorn, Awiphan, Chai-Adisaksopha, Tantraworasin et al., Use of serotonin reuptake inhibitor antidepressants and the risk of bleeding complications in patients on anticoagulant or antiplatelet agents: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Ann. Med, doi:10.1080/07853890.2021.2017474
Olsen, Use of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and risk of upper gastrointestinal tract bleeding: A population-based cohort study, Arch. Intern. Med, doi:10.1001/archinte.163.1.59
Ontai, Zeng, Choi, Sierra Hoffman, Valerio Pascua et al., Early multidrug treatment of SARS-COV-2 (COVID-19) and decreased case fatality rates in Honduras, Epidemiol. Int. J, doi:10.23880/eij-16000217
Pineda, None
Reis, Dos, Moreira-Silva, Silva, Thabane et al., Effect of early treatment with fluvoxamine on risk of emergency care and hospitalisation among patients with Covid-19: The together randomised, platform clinical trial, Lancet. Glob. Health, doi:10.1016/s2214-109x(21)00448-4
Retamozo, Brito-Zerón, Sisó-Almirall, Flores-Chávez, Soto-Cárdenas et al., Haemophagocytic syndrome and Covid-19, Clin. Rheumatol, doi:10.1007/s10067-020-05569-4
Samuel, Seifert, Risk of bleeding in patients on full-dose enoxaparin with venous thromboembolism and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, Ann. Pharmacother, doi:10.1177/1060028016677309
Scala, Pacelli, Fighting the host reaction to SARS-COV-2 in critically ill patients: The possible contribution of off-label drugs, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.01201
Sciacchitano, Giovagnoli, Amodeo, Santino, Simmaco et al., AIDS and Covid-19 are two diseases separated by a common lymphocytopenia, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-43462/v1
Seftel, Boulware, Prospective cohort of fluvoxamine for early treatment of coronavirus disease 19, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofab050
Skurikhin, Andreeva, Khmelevskaya, Ermolaeva, Pershina et al., Effect of antiserotonin drug on the development of lung fibrosis and blood system reactions after intratracheal administration of Bleomycin, Bull. Exp. Biol. Med, doi:10.1007/s10517-012-1567-1
Tan, Anderson, Rathore, Neill, Mantri et al., Signatures of mast cell activation are associated with severe COVID-19, doi:10.1101/2021.05.31.21255594
Tencomnao, Drugs that offer the potential to reduce hospitalization and mortality from SARS-COV-2 infection: The possible role of the sigma-1 receptor and autophagy, Expert Opin. Ther. Targets, doi:10.1080/14728222.2021.1952987
Valerio Pascua, Baires, Diaz, Sierra, Palou et al., Repurposing drugs for Covid-19 by a developing country, Epidemiol. Int. J
Valerio Pascua, Diaz, Medina, Contreras, Mistroff et al., A multi-mechanism approach reduces length of stay in the ICU for severe COVID-19 patients, PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0245025
Wang, Hu, Hu, Zhu, Liu et al., Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.1585
Zaid, Guessous, Puhm, Elhamdani, Chentoufi et al., Platelet reactivity to thrombin differs between patients with COVID-19 and those with Ards unrelated to COVID-19, Blood Adv, doi:10.1182/bloodadvances.2020003513
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2022.1054644",
"ISSN": [
"1663-9812"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.1054644",
"abstract": "<jats:p><jats:bold>Background:</jats:bold> The COVID-19 pandemic has impacted millions of lives globally. While COVID-19 did not discriminate against developed or developing nations, it has been a significant challenge for third world countries like Honduras to have widespread availability of advanced therapies. The concept of early treatment was almost unheard of when early outpatient treatments utilizing repurposed drugs in Latin American countries began showing promising results. One such drug is fluvoxamine, which has shown tremendous potential in two major studies. As a direct result, fluvoxamine was added to the standard of care in a major medical center outpatient COVID-19 clinic.</jats:p><jats:p><jats:bold>Methods:</jats:bold> This is a prospective observational study performed at the Hospital Centro Médico Sampedrano (CEMESA) in San Pedro Sula, Cortes, Honduras in the COVID-19 outpatient clinic. All patients were at least 15 years of age who had presented with mild or moderate signs and symptoms of COVID-19, and who also had a documented positive SARS-CoV-2 antigen or Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) were included in the study. These patients then were all prescribed fluvoxamine. The cohort of patients who decided to take fluvoxamine were compared for primary endpoints of mortality and hospitalization risk to the cohort who did not take fluvoxamine. Patients were then monitored for 30 days with the first follow up at 7 days and the second follow up at 10–14 days of symptom onset. Categorical variables were compared by Pearson Chi-square test. The Relative risk was calculated using regression models. Continuous variables were compared by t-test and Wilcoxon rank-sum tests.</jats:p><jats:p><jats:bold>Results:</jats:bold> Out of total 657 COVID-19 cases, 594 patients took fluvoxamine and 63 did not take fluvoxamine. A total of five patients (0.76 percent) died, with only one death occurring in the fluvoxamine group. Patients who received fluvoxamine had a significantly lower relative risk of mortality (RR 0.06, <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> 0.011, 95% CI 0.007–0.516). There was a lower relative risk of hospitalization in the patients who in the fluvoxamine group. (−10 vs. 30 hospitalizations, RR 0.49, <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.035, 95% CI 0.26–0.95). There was 73 percent reduction in relative risk of requiring oxygen in the fluvoxamine group (RR 0.27, <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> &lt; 0.001, 95% CI 0.14–0.54 Mean lymphocytes count on the first follow-up visit was significantly higher in the fluvoxamine group (1.72 vs. 1.38, Δ 0.33, <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> 0.007, CI 0.09–0.58).</jats:p><jats:p><jats:bold>Conclusion:</jats:bold> The results of our study suggest that fluvoxamine lowers the relative risk of death, hospitalization, and oxygen requirement in COVID 19 patients.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.3389/fphar.2022.1054644"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pineda",
"given": "Estela",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Singh",
"given": "Jarmanjeet",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pineda",
"given": "Miguel Vargas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Umanzor",
"given": "Jose Garay",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baires",
"given": "Fernando",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Benitez",
"given": "Luis G.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Burgos",
"given": "Cesar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sekhon",
"given": "Anupamjeet Kaur",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Crisp",
"given": "Nicole",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lewis",
"given": "Anita S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Radwanski",
"given": "Jana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bermudez",
"given": "Marco",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barjun",
"given": "Karen Sanchez",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Diaz",
"given": "Oscar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Palou",
"given": "Elsa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Escalante",
"given": "Rossany E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hernandez",
"given": "Carlos Isai",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stevens",
"given": "Mark L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Eberhard",
"given": "Deke",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sierra",
"given": "Manuel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alvarado",
"given": "Tito",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Videa",
"given": "Omar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sierra-Hoffman",
"given": "Miguel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Valerio-Pascua",
"given": "Fernando",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Frontiers in Pharmacology",
"container-title-short": "Front. Pharmacol.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"frontiersin.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-30T06:16:23Z",
"timestamp": 1669788983000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-30T06:16:29Z",
"timestamp": 1669788989000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-21T14:30:49Z",
"timestamp": 1679409049267
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 1,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
30
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-30T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1669766400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2022.1054644/full",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1965",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.3389",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
30
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
30
]
]
},
"publisher": "Frontiers Media SA",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-3-642-38664-0_15",
"article-title": "Serotonin transporter and serotonin receptors",
"author": "Adnot",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "365",
"journal-title": "Handb. Exp. Pharmacol.",
"key": "B1",
"volume": "218",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118167",
"article-title": "The role of cytokine profile and lymphocyte subsets in the severity of coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19): A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Akbari",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "118167",
"journal-title": "Life Sci.",
"key": "B2",
"volume": "258",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Effect of cyproheptadine on endotoxin-induced pulmonary platelet trapping",
"author": "Almqvist",
"first-page": "503",
"journal-title": "Am. Surg.",
"key": "B3",
"volume": "50",
"year": "1984"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5772/intechopen.105023",
"article-title": "New use of the SSRI fluvoxamine in the treatment of Covid-19 symptoms",
"author": "Alsabhan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "B4",
"volume-title": "COVID-19 pandemic, mental Health and neuroscience - new scenarios for understanding and treatment [working title]",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/mjt.0000000000001496",
"article-title": "Fluvoxamine in nonhospitalized patients with acute COVID-19 infection and the lack of efficacy in reducing rates of hospitalization, mechanical ventilation, and mortality in placebo-controlled trials: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Bhuta",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e298",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Ther.",
"key": "B5",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cells9091975",
"article-title": "SARS-COV-2 spike 1 protein controls Natural Killer cell activation via the HLA-E/NKG2A pathway",
"author": "Bortolotti",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1975",
"journal-title": "Cells",
"key": "B6",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/14728222.2021.1952987",
"article-title": "Drugs that offer the potential to reduce hospitalization and mortality from SARS-COV-2 infection: The possible role of the sigma-1 receptor and autophagy",
"author": "Brimson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "435",
"journal-title": "Expert Opin. Ther. Targets",
"key": "B7",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bcp.15126",
"article-title": "Safety and efficacy of fluvoxamine in COVID‐19 ICU patients: An open label, prospective cohort trial with matched controls",
"author": "Calusic",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2065",
"journal-title": "Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol.",
"key": "B8",
"volume": "88",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2022.10.012",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of fluvoxamine for the treatment of COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Cheema",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J. Infect.",
"key": "B9",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev.immunol.25.022106.141706",
"article-title": "The immunobiology of sars",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "443",
"journal-title": "Annu. Rev. Immunol.",
"key": "B10",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood-2012-02-413047",
"article-title": "Platelets can enhance vascular permeability",
"author": "Cloutier",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1334",
"journal-title": "Blood",
"key": "B11",
"volume": "120",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/archinte.163.1.59",
"article-title": "Use of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and risk of upper gastrointestinal tract bleeding: A population-based cohort study",
"author": "Dalton",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "59",
"journal-title": "Arch. Intern. Med.",
"key": "B12",
"volume": "163",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/jappl.1985.58.6.1761",
"article-title": "Lung damage and pulmonary uptake of serotonin in intact dogs",
"author": "Dawson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1761",
"journal-title": "J. Appl. Physiol.",
"key": "B13",
"volume": "58",
"year": "1985"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood-2012-06-437392",
"article-title": "Platelet serotonin promotes the recruitment of neutrophils to sites of acute inflammation in mice",
"author": "Duerschmied",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1008",
"journal-title": "Blood",
"key": "B14",
"volume": "121",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40265-021-01636-5",
"article-title": "Fluvoxamine for the early treatment of SARS-COV-2 infection: A review of current evidence",
"author": "Facente",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2081",
"journal-title": "Drugs",
"key": "B15",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/bf02265168",
"article-title": "Changes in histamine and serotonin secretion from rat peritoneal mast cells caused by antidepressants",
"author": "Ferjan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "141",
"journal-title": "Inflamm. Res.",
"key": "B16",
"volume": "45",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virusres.2014.09.016",
"article-title": "Coronavirus-induced ER stress response and its involvement in regulation of coronavirus–host interactions",
"author": "Fung",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "110",
"journal-title": "Virus Res.",
"key": "B17",
"volume": "194",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.31887/dcns.2007.9.1/dhalperin",
"article-title": "Influence of antidepressants on hemostasis",
"author": "Halperin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "47",
"journal-title": "Dialogues Clin. Neurosci.",
"key": "B18",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2007.08.036",
"article-title": "Sigma-1 receptor chaperones at the ER- mitochondrion interface regulate ca2+ signaling and cell survival",
"author": "Hayashi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "596",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "B19",
"volume": "131",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1055/a-1291-7692",
"article-title": "Macrophage activation and cytokine release syndrome in COVID-19: Current updates and analysis of repurposed and investigational anti-cytokine drugs",
"author": "Iqubal",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "173",
"journal-title": "Drug Res.",
"key": "B20",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2139/ssrn.3800402",
"article-title": "Covid-19 pathophysiology: Are platelets and serotonin hiding in plain sight?",
"author": "Jalali",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "SSRN J.",
"key": "B21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.22760",
"article-title": "Fluvoxamine vs placebo and clinical deterioration in outpatients with symptomatic COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Lenze",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2292",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "B22",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102763",
"article-title": "Longitudinal characteristics of lymphocyte responses and cytokine profiles in the peripheral blood of SARS-COV-2 infected patients",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "102763",
"journal-title": "EBioMedicine",
"key": "B23",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-021-05792-7",
"article-title": "Dynamic changes in lymphocyte subsets and parallel cytokine levels in patients with severe and critical COVID-19",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "79",
"journal-title": "BMC Infect. Dis.",
"key": "B24",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/sj.bjp.0703570",
"article-title": "5-hydroxytryptamine and the pulmonary circulation: Receptors, transporters and relevance to pulmonary arterial hypertension",
"author": "MacLean",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "161",
"journal-title": "Br. J. Pharmacol.",
"key": "B25",
"volume": "131",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/20587384211048026",
"article-title": "A scoping review of the pathophysiology of Covid-19",
"author": "Marik",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "20587384211048026",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol.",
"key": "B26",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/circresaha.122.321659",
"article-title": "Persisting platelet activation and hyperactivity in COVID-19 survivors",
"author": "Martins-Gonçalves",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "944",
"journal-title": "Circ. Res.",
"key": "B27",
"volume": "131",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/jci138554",
"article-title": "Impaired immune cell cytotoxicity in severe COVID-19 is IL-6 dependent",
"author": "Mazzoni",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4694",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Invest.",
"key": "B28",
"volume": "130",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41584-020-00571-1",
"article-title": "Immune cartography of macrophage activation syndrome in the COVID-19 ERA",
"author": "McGonagle",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "145",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Rheumatol.",
"key": "B29",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102537",
"article-title": "The role of cytokines including interleukin-6 in COVID-19 induced pneumonia and macrophage activation syndrome-like disease",
"author": "McGonagle",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "102537",
"journal-title": "Autoimmun. Rev.",
"key": "B30",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/npr2.12194",
"article-title": "SSRIs: Applications in inflammatory lung disease and implications for Covid‐19",
"author": "Meikle",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "325",
"journal-title": "Neuropsychopharmacol. Rep.",
"key": "B31",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-020-0331-4",
"article-title": "Pathological inflammation in patients with COVID-19: A key role for monocytes and macrophages",
"author": "Merad",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "355",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Immunol.",
"key": "B32",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.574862",
"article-title": "Mast cells in alveolar septa of COVID-19 patients: A pathogenic pathway that may link interstitial edema to immunothrombosis",
"author": "Motta Junior",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "574862",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "B33",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07853890.2021.2017474",
"article-title": "Use of serotonin reuptake inhibitor antidepressants and the risk of bleeding complications in patients on anticoagulant or antiplatelet agents: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Nochaiwong",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "80",
"journal-title": "Ann. Med.",
"key": "B34",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.23880/eij-16000217",
"article-title": "Early multidrug treatment of SARS-COV-2 (COVID-19) and decreased case fatality rates in Honduras",
"author": "Ontai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Epidemiol. Int. J.",
"key": "B35",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s2214-109x(21)00448-4",
"article-title": "Effect of early treatment with fluvoxamine on risk of emergency care and hospitalisation among patients with Covid-19: The together randomised, platform clinical trial",
"author": "Reis",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e42",
"journal-title": "Lancet. Glob. Health",
"key": "B37",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10067-020-05569-4",
"article-title": "Haemophagocytic syndrome and Covid-19",
"author": "Retamozo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1233",
"journal-title": "Clin. Rheumatol.",
"key": "B38",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1060028016677309",
"article-title": "Risk of bleeding in patients on full-dose enoxaparin with venous thromboembolism and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors",
"author": "Samuel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "226",
"journal-title": "Ann. Pharmacother.",
"key": "B39",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.01201",
"article-title": "Fighting the host reaction to SARS-COV-2 in critically ill patients: The possible contribution of off-label drugs",
"author": "Scala",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1201",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "B40",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "B41",
"unstructured": "AIDS and Covid-19 are two diseases separated by a common lymphocytopenia\n SciacchitanoS.\n GiovagnoliS.\n AmodeoR.\n SantinoI.\n SimmacoM.\n AnibaldiP.\n 10.21203/rs.3.rs-43462/v12020"
},
{
"key": "B36",
"unstructured": "Protocolo de Manejo Clinico de Pacientes con segun estadios clinico Y nivel de atencion Covid-192020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofab050",
"article-title": "Prospective cohort of fluvoxamine for early treatment of coronavirus disease 19",
"author": "Seftel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "ofab050",
"journal-title": "Open Forum Infect. Dis.",
"key": "B42",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10517-012-1567-1",
"article-title": "Effect of antiserotonin drug on the development of lung fibrosis and blood system reactions after intratracheal administration of Bleomycin",
"author": "Skurikhin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "519",
"journal-title": "Bull. Exp. Biol. Med.",
"key": "B43",
"volume": "152",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.05.31.21255594",
"article-title": "Signatures of mast cell activation are associated with severe COVID-19",
"author": "Tan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B44",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.23880/eij-16000234",
"article-title": "Repurposing drugs for Covid-19 by a developing country",
"author": "Valerio Pascua",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Epidemiol. Int. J.",
"key": "B45",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0245025",
"article-title": "A multi-mechanism approach reduces length of stay in the ICU for severe COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Valerio Pascua",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e0245025",
"journal-title": "PLOS ONE",
"key": "B46",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.1585",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus–infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1061",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "B47",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/bloodadvances.2020003513",
"article-title": "Platelet reactivity to thrombin differs between patients with COVID-19 and those with Ards unrelated to COVID-19",
"author": "Zaid",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "635",
"journal-title": "Blood Adv.",
"key": "B48",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 48,
"references-count": 48,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2022.1054644/full"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Pharmacology (medical)",
"Pharmacology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Impact of fluvoxamine on outpatient treatment of COVID-19 in Honduras in a prospective observational real-world study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/crossmark-policy",
"volume": "13"
}