A multi-mechanism approach reduces length of stay in the ICU for severe COVID-19 patients
et al., PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0245025, Jan 2021
Colchicine for COVID-19
5th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.0000049 from 54 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
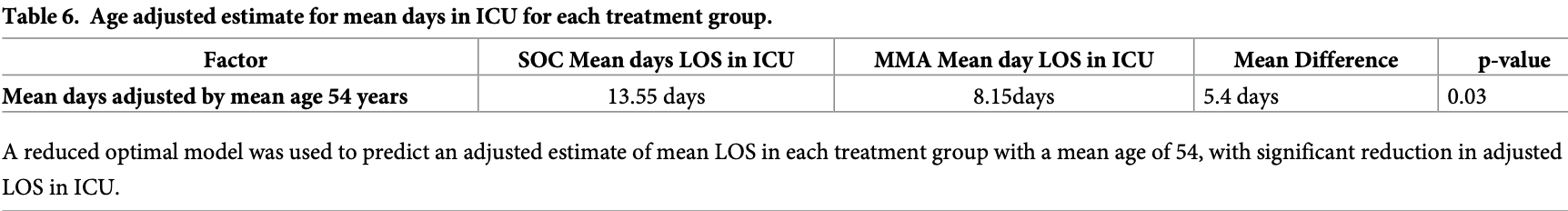
Retrospective 65 ICU patients in the USA and Honduras, showing shorter ICU stay with combined treatment including colchicine, LMWH, tocilizumab, dexamethasone, and methylprednisolone.
|
risk of death, 22.8% lower, RR 0.77, p = 0.60, treatment 5 of 35 (14.3%), control 12 of 30 (40.0%), NNT 3.9, adjusted per study, odds ratio converted to relative risk, multivariable.
|
|
ICU time, 39.9% lower, relative time 0.60, p = 0.03, treatment 35, control 30, adjusted per study, multivariable.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Valerio Pascua et al., 7 Jan 2021, retrospective, multiple countries, peer-reviewed, 19 authors, study period 10 June, 2020 - 6 August, 2020, average treatment delay 6.1 days, dosage 1.5mg day 1, 1mg days 2-5, varied by location, this trial uses multiple treatments in the treatment arm (combined with LMWH, tocilizumab, dexamethasone, methylprednisolone) - results of individual treatments may vary.
A multi-mechanism approach reduces length of stay in the ICU for severe COVID-19 patients
PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0245025
Purpose COVID-19 pandemic has multifaceted presentations with rising evidence of immune-mediated mechanisms underplay. We sought to explore the outcomes of severe COVID-19 patients treated with a multi-mechanism approach (MMA) in addition to standard-of-care (SC) versus patients who only received SC treatment.
Materials and methods Data were collected retrospectively for patients admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU). This observational cohort study was performed at five institutions, 3 in the United States and 2 in Honduras. Patients were stratified for MMA vs. SC treatment during ICU stay. MMA treatment consists of widely available medications started immediately upon hospitalization. These interventions target immunomodulation, anticoagulation, viral suppression, and oxygenation. Primary outcomes included in-hospital mortality and length of stay (LOS) for the index hospitalization and were measured using logistic regression.
References
Alam, Hobbelink, Van Tienhoven, Van De Ven, Jansma et al., The impact of the use of the Early Warning Score (EWS) on patient outcomes: a systematic review, Resuscitation, doi:10.1016/j.resuscitation.2014.01.013
Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, Mehta, Zingman et al., Remdesivir for the Treatment of Covid-19-Preliminary Report, N Engl J Med
Cao, Li, COVID-19: towards understanding of pathogenesis, Cell Res, doi:10.1038/s41422-020-0327-4
Chao, Woo, Hospitals pushed to the brink in Wuhan: 'I just want to save his life, Wall Street Journal
Cummings, Baldwin, Abrams, Jacobson, Meyer et al., Epidemiology, clinical course, and outcomes of critically ill adults with COVID-19 in New York City: a prospective cohort study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736%2820%2931189-2
Dasta, Mclaughlin, Mody, Piech, Daily cost of an intensive care unit day: the contribution of mechanical ventilation, Crit Care Med, doi:10.1097/01.ccm.0000164543.14619.00
De Wit, Van Doremalen, Falzarano, Munster, SARS and MERS: recent insights into emerging coronaviruses, Nat Rev Microbiol, doi:10.1038/nrmicro.2016.81
Deftereos, Giannopoulos, Vrachatis, Siasos, Giotaki et al., GRECCO-19 investigators. Effect of Colchicine vs Standard Care on Cardiac and Inflammatory Biomarkers and Clinical Outcomes in Patients Hospitalized With Coronavirus Disease 2019: The GRECCO-19 Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA Netw Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.13136
Despres, Brunin, Berthier, Pili-Floury, Besch, Prone positioning combined with high-flow nasal or conventional oxygen therapy in severe Covid-19 patients, Crit Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-020-03001-6
Edgar, Najmabadi, Platoff, Texas hospitals are running out of drugs, beds, ventilators and even staff, Texas Tribune
Elharrar, Trigui, Dols, Touchon, Martinez et al., Use of Prone Positioning in Nonintubated Patients With COVID-19 and Hypoxemic Acute Respiratory Failure, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.8255
Finkelsztein, Jones, Ma, Pabo ´n, Delgado et al., Comparison of qSOFA and SIRS for predicting adverse outcomes of patients with suspicion of sepsis outside the intensive care unit, Crit Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-017-1658-5
Fox, Akmatbekov, Harbert, Li, Brown et al., Pulmonary and cardiac pathology in African American patients with COVID-19: an autopsy series from New Orleans, Lancet Respir Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600%2820%2930243-5
Helms, Tacquard, Severac, Leonard-Lorant, Ohana et al., High risk of thrombosis in patients with severe SARS-CoV-2 infection: a multicenter prospective cohort study, Intensive Care Med, doi:10.1007/s00134-020-06062-x
Kewan, Covut, Mj, Rose, Gopalakrishna et al., Tocilizumab for treatment of patients with severe COVID-19: A retrospective cohort study, EClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100418
Mafham, COVID-19 pandemic and admission rates for and management of acute coronary syndromes in England, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736%2820%2931356-8
Rosa, Reduction of hospitalizations for myocardial infarction in Italy in the COVID-19 era, Eur Heart J, doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa409
Rothan, Byrareddy, The epidemiology and pathogenesis of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak, J Autoimmun, doi:10.1016/j.jaut.2020.102433
Sabatino, Impact of cardiovascular risk profile on COVID-19 outcome. A meta-analysis, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0237131
Sanche, Lin, Xu, Romero-Severson, Hengartner et al., High Contagiousness and Rapid Spread of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2, Emerg Infect Dis, doi:10.3201/eid2607.200282
Semple, In some nations, coronavirus is only one of many outbreaks
Soy, Keser, ¨ndu ¨z, Tabak, ¨ndu ¨z et al., Cytokine storm in COVID-19: pathogenesis and overview of anti-inflammatory agents used in treatment, Clin Rheumatol, doi:10.1007/s10067-020-05190-5
Tang, Bai, Chen, Gong, Li et al., Anticoagulant treatment is associated with decreased mortality in severe coronavirus disease 2019 patients with coagulopathy, J Thromb Haemost, doi:10.1111/jth.14817
Toniati, Piva, Cattalini, Garrafa, Regola et al., Tocilizumab for the treatment of severe COVID-19 pneumonia with hyperinflammatory syndrome and acute respiratory failure: A single center study of 100 patients in Brescia, Italy, Autoimmun Rev, doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102568
Valerio Pascua, Diaz, Medina, Contreras, Mistroff et al., Project administration: Fernando Valerio Pascua
Valerio Pascua, Diaz, Medina, Contreras, Mistroff et al., Vincent
Villar, Confalonieri, Pastores, Meduri, Rationale for Prolonged Corticosteroid Treatment in the Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Caused by Coronavirus Disease 2019, Crit Care Explor
Wang, Zhang, Du, Du, Zhao et al., Remdesivir in adults with severe COVID-19: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736%2820%2931022-9
Zhou, Yu, Du, Fan, Liu et al., Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736%2820%2930566-3
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0245025",
"ISSN": [
"1932-6203"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0245025",
"abstract": "<jats:sec id=\"sec001\">\n<jats:title>Purpose</jats:title>\n<jats:p>COVID-19 pandemic has multifaceted presentations with rising evidence of immune-mediated mechanisms underplay. We sought to explore the outcomes of severe COVID-19 patients treated with a multi-mechanism approach (MMA) in addition to standard-of-care (SC) versus patients who only received SC treatment.</jats:p>\n</jats:sec>\n<jats:sec id=\"sec002\">\n<jats:title>Materials and methods</jats:title>\n<jats:p>Data were collected retrospectively for patients admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU). This observational cohort study was performed at five institutions, 3 in the United States and 2 in Honduras. Patients were stratified for MMA vs. SC treatment during ICU stay. MMA treatment consists of widely available medications started immediately upon hospitalization. These interventions target immunomodulation, anticoagulation, viral suppression, and oxygenation. Primary outcomes included in-hospital mortality and length of stay (LOS) for the index hospitalization and were measured using logistic regression.</jats:p>\n</jats:sec>\n<jats:sec id=\"sec003\">\n<jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n<jats:p>Of 86 patients admitted, 65 (76%) who had severe COVID-19 were included in the study; 30 (46%) patients were in SC group, compared with 35 (54%) patients treated with MMA group. Twelve (40%) patients in the SC group died, compared with 5 (14%) in the MMA group (p-value = 0.01, Chi squared test). After adjustment for gender, age, treatment group, Q-SOFA score, the MMA group had a mean length of stay 8.15 days, when compared with SC group with 13.55 days. ICU length of stay was reduced by a mean of 5.4 days (adjusted for a mean age of 54 years, p-value 0.03) and up to 9 days (unadjusted for mean age), with no significant reduction in overall adjusted mortality rate, where the strongest predictor of mortality was the use of mechanical ventilation.</jats:p>\n</jats:sec>\n<jats:sec id=\"sec004\">\n<jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title>\n<jats:p>The finding that MMA decreases the average ICU length of stay by 5.4 days and up to 9 days in older patients suggests that implementation of this treatment protocol could allow a healthcare system to manage 60% more COVID-19 patients with the same number of ICU beds.</jats:p>\n</jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5880-7849",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Valerio Pascua",
"given": "Fernando",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5268-3320",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Diaz",
"given": "Oscar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9668-1135",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Medina",
"given": "Rina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Contreras",
"given": "Brian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8969-4069",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Mistroff",
"given": "Jeff",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4231-7300",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Espinosa",
"given": "Daniel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sekhon",
"given": "Anupamjeet",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6481-7181",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Paz Handal",
"given": "Diego",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pineda",
"given": "Estela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7912-4011",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Vargas Pineda",
"given": "Miguel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3237-3517",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Pineda",
"given": "Hector",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3542-3949",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Diaz",
"given": "Maribel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lewis",
"given": "Anita S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hesse",
"given": "Heike",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Castro Lainez",
"given": "Miriams T.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stevens",
"given": "Mark L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9851-3976",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Sierra- Hoffman",
"given": "Miguel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ontai",
"given": "Sidney C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7612-6388",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "VanBuren",
"given": "Vincent",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"PLOS ONE"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"www.plosone.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2021-01-07T20:47:23Z",
"timestamp": 1610052443000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2021-01-07T20:47:52Z",
"timestamp": 1610052472000
},
"editor": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kou",
"given": "Yu Ru",
"sequence": "first"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-21T19:28:40Z",
"timestamp": 1642793320595
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 1,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "1932-6203"
}
],
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
7
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
7
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2021-01-07T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1609977600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0245025",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "340",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e0245025",
"prefix": "10.1371",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
7
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
7
]
]
},
"publisher": "Public Library of Science (PLoS)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaut.2020.102433",
"article-title": "The epidemiology and pathogenesis of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak.",
"author": "HA Rothan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "102433",
"journal-title": "J Autoimmun",
"key": "pone.0245025.ref001",
"volume": "109",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "World Health Organization",
"key": "pone.0245025.ref002",
"volume-title": "Clinical management of Severe Acute Respiratory Infection (SARI) when COVID-19 disease is suspected: interim guidance, 13 March 2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrmicro.2016.81",
"article-title": "SARS and MERS: recent insights into emerging coronaviruses",
"author": "E de Wit",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "523",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Microbiol",
"key": "pone.0245025.ref003",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41422-020-0327-4",
"article-title": "COVID-19: towards understanding of pathogenesis",
"author": "W Cao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "367",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Cell Res",
"key": "pone.0245025.ref004",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10067-020-05190-5",
"article-title": "Cytokine storm in COVID-19: pathogenesis and overview of anti-inflammatory agents used in treatment",
"author": "M Soy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2085",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Clin Rheumatol",
"key": "pone.0245025.ref005",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Rationale for Prolonged Corticosteroid Treatment in the Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Caused by Coronavirus Disease",
"author": "J Villar",
"first-page": "e0111",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Crit Care Explor. 2020 Apr 29",
"key": "pone.0245025.ref006",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.13136",
"article-title": "Effect of Colchicine vs Standard Care on Cardiac and Inflammatory Biomarkers and Clinical Outcomes in Patients Hospitalized With Coronavirus Disease 2019: The GRECCO-19 Randomized Clinical Trial",
"author": "GRECCO-19 investigators",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e2013136",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "pone.0245025.ref007",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102568",
"article-title": "Tocilizumab for the treatment of severe COVID-19 pneumonia with hyperinflammatory syndrome and acute respiratory failure: A single center study of 100 patients in Brescia, Italy",
"author": "P Toniati",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "102568",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Autoimmun Rev",
"key": "pone.0245025.ref008",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30243-5",
"article-title": "Pulmonary and cardiac pathology in African American patients with COVID-19: an autopsy series from New Orleans",
"author": "SE Fox",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "681",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "pone.0245025.ref009",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00134-020-06062-x",
"article-title": "High risk of thrombosis in patients with severe SARS-CoV-2 infection: a multicenter prospective cohort study",
"author": "J Helms",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1089",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Intensive Care Med.",
"key": "pone.0245025.ref010",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jth.14817",
"article-title": "Anticoagulant treatment is associated with decreased mortality in severe coronavirus disease 2019 patients with coagulopathy",
"author": "N Tang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1094",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "J Thromb Haemost",
"key": "pone.0245025.ref011",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.8255",
"article-title": "Use of Prone Positioning in Nonintubated Patients With COVID-19 and Hypoxemic Acute Respiratory Failure",
"author": "X Elharrar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2336",
"issue": "22",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "pone.0245025.ref012",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-03001-6",
"article-title": "Prone positioning combined with high-flow nasal or conventional oxygen therapy in severe Covid-19 patients",
"author": "C Despres",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "256",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Crit Care.",
"key": "pone.0245025.ref013",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "The impact of the use of the Early Warning Score (EWS) on patient outcomes: a systematic review. Resuscitation",
"author": "N Alam",
"first-page": "587",
"issue": "5",
"key": "pone.0245025.ref014",
"volume": "85",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"article-title": "Comparison of qSOFA and SIRS for predicting adverse outcomes of patients with suspicion of sepsis outside the intensive care unit. Crit Care",
"author": "EJ Finkelsztein",
"first-page": "73",
"issue": "1",
"key": "pone.0245025.ref015",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3201/eid2607.200282",
"article-title": "High Contagiousness and Rapid Spread of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2",
"author": "S Sanche",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1470",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Emerg Infect Dis",
"key": "pone.0245025.ref016",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Hospitals pushed to the brink in Wuhan: ‘I just want to save his life’",
"author": "D Chao",
"journal-title": "Wall Street Journal",
"key": "pone.0245025.ref017",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "In some nations, coronavirus is only one of many outbreaks",
"author": "K. Semple",
"journal-title": "New York Times",
"key": "pone.0245025.ref018",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Texas hospitals are running out of drugs, beds, ventilators and even staff.",
"author": "W Edgar",
"journal-title": "Texas Tribune",
"key": "pone.0245025.ref019",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "pone.0245025.ref020",
"unstructured": "Texas Department of State Health Services [Internet]. Austin. 2020 [cited August 12, 2020] Available from: https://dshs.texas.gov/coronavirus/additionaldata.aspx"
},
{
"article-title": "Daily cost of an intensive care unit day: the contribution of mechanical ventilation. Crit Care Med",
"author": "JF Dasta",
"first-page": "1266",
"issue": "6",
"key": "pone.0245025.ref021",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"key": "pone.0245025.ref022",
"unstructured": "Centers for Disease Control [Internet]. Atlanta. 2020 [cited August 12, 2020] National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases (NCIRD), Division of Viral Diseases. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/covid-data/covidview/index.html#hospitalizations"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31189-2",
"article-title": "Epidemiology, clinical course, and outcomes of critically ill adults with COVID-19 in New York City: a prospective cohort study",
"author": "MJ Cummings",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1763",
"issue": "10239",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "pone.0245025.ref023",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Remdesivir for the Treatment of Covid-19—Preliminary Report",
"author": "JH Beigel",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "pone.0245025.ref024",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31022-9",
"article-title": "Remdesivir in adults with severe COVID-19: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial",
"author": "Y Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1569",
"issue": "10236",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "pone.0245025.ref025",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100418",
"article-title": "Tocilizumab for treatment of patients with severe COVID-19: A retrospective cohort study",
"author": "T Kewan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100418",
"journal-title": "EClinicalMedicine.",
"key": "pone.0245025.ref026",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"article-title": "Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "F Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1054",
"issue": "10229",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "pone.0245025.ref027",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31356-8",
"article-title": "COVID-19 pandemic and admission rates for and management of acute coronary syndromes in England",
"author": "M. M. Mafham",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "381",
"issue": "10248",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "pone.0245025.ref028",
"volume": "396",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Reduction of hospitalizations for myocardial infarction in Italy in the COVID-19 era",
"author": "S. De Rosa",
"first-page": "2083",
"issue": "22",
"journal-title": "Eur Heart J",
"key": "pone.0245025.ref029",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0237131",
"article-title": "Impact of cardiovascular risk profile on COVID-19 outcome. A meta-analysis",
"author": "J. Sabatino",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e0237131",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "pone.0245025.ref030",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 30,
"references-count": 30,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"PLoS ONE"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Multidisciplinary"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"A multi-mechanism approach reduces length of stay in the ICU for severe COVID-19 patients"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.corrections_policy",
"volume": "16"
}
