Association of dietary intake of polyphenols, lignans, and phytosterols with immune-stimulating microbiota and COVID-19 risk in a group of Polish men and women
et al., Frontiers in Nutrition, doi:10.3389/fnut.2023.1241016, Aug 2023
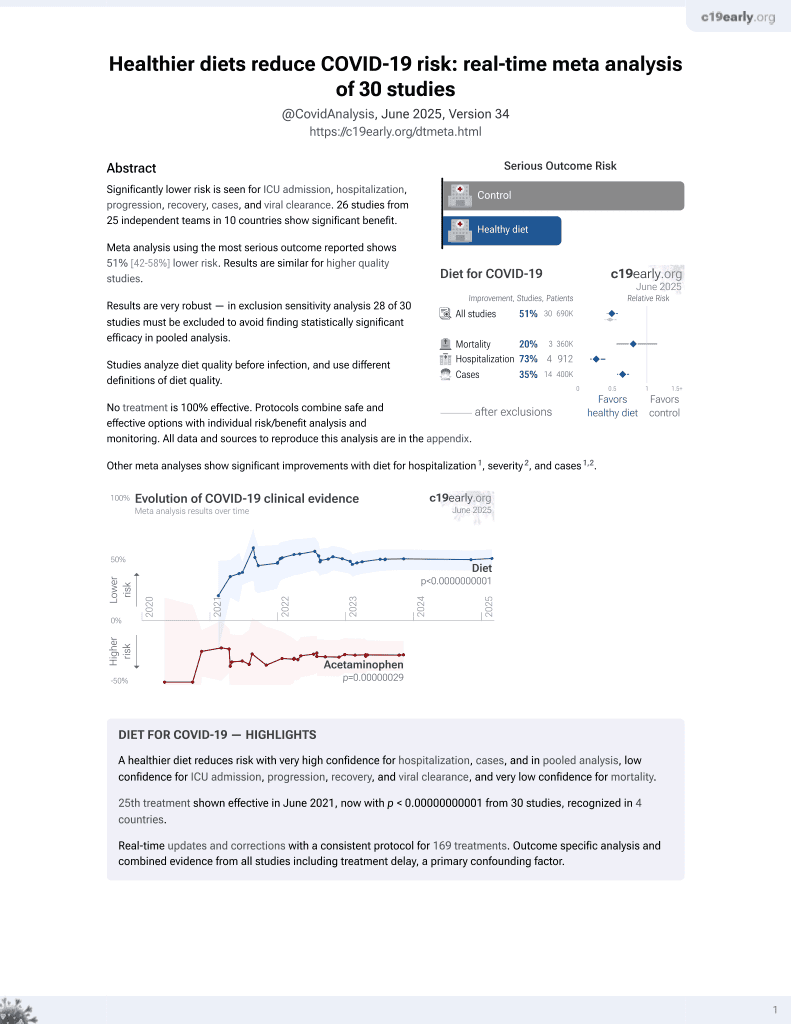
Diet for COVID-19
26th treatment shown to reduce risk in
June 2021, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 30 studies, recognized in 4 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
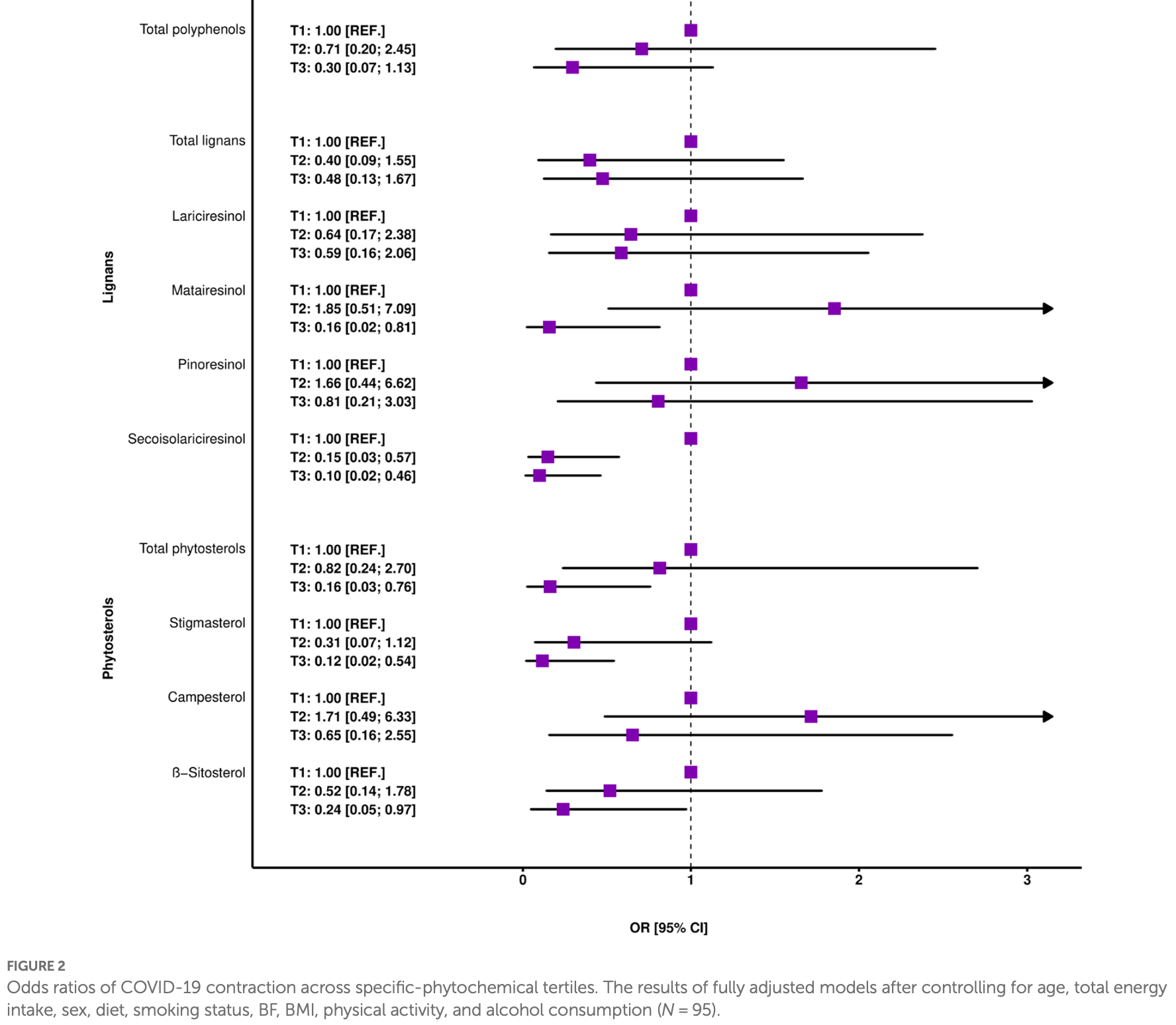
Dietary analysis of 95 adults in Poland, showing lower risk of COVID-19 with higher intake of polyphenols, lignans, and phytosterols. Results were statistically significant for total phytosterols, secoisolariciresinol, β-sitosterol, matairesinol, and stigmasterol. Authors suggest that beneficial effects on gut microbiota and immune function may contribute to the lower risk.
|
risk of case, 70.0% lower, OR 0.30, p = 0.09, higher quality diet 32, lower quality diet 21, adjusted per study, total polyphenols, T3 vs. T1, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Micek et al., 3 Aug 2023, retrospective, Poland, peer-reviewed, survey, 8 authors, study period July 2020 - December 2020.
Contact: agnieszka.micek@uj.edu.pl.
Association of dietary intake of polyphenols, lignans, and phytosterols with immune-stimulating microbiota and COVID-19 risk in a group of Polish men and women
Frontiers in Nutrition, doi:10.3389/fnut.2023.1241016
Objectives: Devastating consequences of COVID-19 disease enhanced the role of promoting prevention-focused practices. Among targeted efforts, diet is regarded as one of the potential factors which can affect immune function and optimal nutrition is postulated as the method of augmentation of people's viral resistance. As epidemiological evidence is scarce, the present study aimed to explore the association between dietary intake of total polyphenols, lignans and plant sterols and the abundance of immunomodulatory gut microbiota such as Enterococcus spp. and Escherichia coli and the risk of developing COVID-19 disease. Methods: Demographic data, dietary habits, physical activity as well as the composition of body and gut microbiota were analyzed in a sample of 95 young healthy individuals. Dietary polyphenol, lignan and plant sterol intakes have been retrieved based on the amount of food consumed by the participants, the phytochemical content was assessed in laboratory analysis and using available databases. Results: For all investigated polyphenols and phytosterols, except campesterol, every unit increase in the tertile of intake category was associated with a decrease in the odds of contracting COVID-19. The risk reduction ranged from several dozen percent to 70 %, depending on the individual plant-based chemical, and after controlling for basic covariates it was statistically significant for secoisolariciresinol (OR = 0.28, 95% CI: 0.11-0.61), total phytosterols (OR = 0.47, 95% CI: 0.22-0.95) and for stigmasterols (OR = 0.34, 95% CI: 0.14-0.72). We found an inverse association between increased β-sitosterol intake and phytosterols in total and the occurrence of Escherichia coli in stool samples outside reference values, with 72% (OR = 0.28, 95% CI: 0.08-0.86) and 66% (OR = 0.34, 95% CI: 0.10-1.08) reduced odds of abnormal level of bacteria for the highest compared with the lowest tertile of phytochemical consumption. Additionally, there was a
Ethics statement The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by the Bioethics Committee of Jagiellonian University No. 1072.6120.5.2020 and 1072.6120.202.2019. The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions AM, PJ, IB, and JG contributed to conception and design of the study. AM, IB, and JG wrote the first draft of the manuscript. AM performed the statistical analysis. PJ, AW, and AMW investigation. AM, IB, PJ, KK, AW, AMW, JP, and JG wrote sections of the manuscript. All authors contributed to manuscript revision, read, and approved the submitted version.
Conflict of interest The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2023.1241016/ full#supplementary-material
References
Akkuş, Atalay, Parlak, COVID-19 pandemic: changes in the emotions, body weights and nutrition habits of individuals during social intervention measures, Med J Nutrition Metab, doi:10.3233/MNM-210006
Allam, Amen, Ashour, Assaf, Hassan et al., In silico study of natural compounds from sesame against COVID-19 by targeting Mpro, PLpro and RdRp, RSC Adv, doi:10.1039/d1ra03937g
Alwani, Yassin, Al-Zoubi, Aboumarzouk, Nettleship et al., Sex-based differences in severity and mortality in COVID-19, Rev Med Virol, doi:10.1002/rmv.2223
Andriamiarina, Laraki, Pelletier, Debry, Effects of stigmasterolsupplemented diets on fecal neutral sterols and bile acid excretion in rats, Ann Nutr Metab, doi:10.1159/000177548
Annunziata, Zamparelli, Santoro, Ciampaglia, Stornaiuolo et al., May polyphenols have a role against coronavirus infection? An overview of in vitro evidence, Front Med (Lausanne), doi:10.3389/fmed.2020.00240
Babu, Jayaraman, An update on β-sitosterol: a potential herbal nutraceutical for diabetic management, Biomed Pharmacother, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110702
Bajpai, Shukla, Paek, Lim, Kumar et al., Efficacy of (+)-Lariciresinol to control bacterial growth of Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli O157:H7, Front Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2017.00804
Barre, Van Damme, Simplicien, Poder, Klonjkowski et al., Man-specific lectins from plants, fungi, algae and cyanobacteria, as potential blockers for SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) coronaviruses: biomedical perspectives, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells10071619
Bonaccio, Gianfagna, Stival, Amerio, Bosetti et al., Changes in a Mediterranean lifestyle during the COVID-19 pandemic among elderly Italians: an analysis of gender and socioeconomic inequalities in the "LOST in Lombardia" study, Int J Food Sci Nutr, doi:10.1080/09637486.2022.2040009
Bonaccio, Pounis, Cerletti, Donati, Iacoviello et al., Mediterranean diet, dietary polyphenols and low grade inflammation: results from the MOLI-SANI study, Med J Nutrition Metab, doi:10.3233/MNM-200597
Boto-Ordóñez, Urpi-Sarda, Queipo-Ortuño, Tulipani, Tinahones, Andres-Lacueva C. High levels of Bifidobacteria are associated with increased levels of anthocyanin microbial metabolites: a randomized clinical trial, Food Funct, doi:10.1039/c4fo00029c
Bottari, Castellone, Neviani, Probiotics and COVID-19, Int J Food Sci Nutr, doi:10.1080/09637486.2020.1807475
Brito, Zang, A review of lignan metabolism, milk enterolactone concentration, and antioxidant status of dairy cows fed flaxseed, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules24010041
Cai, Wu, Zhang, Lignans from Mosla scabra ameliorated influenza a virus-induced pneumonia via inhibiting macrophage activation, Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, doi:10.1155/2022/1688826
Calcuttawala, Nutrition as a key to boost immunity against COVID-19, Clin Nutr ESPEN, doi:10.1016/j.clnesp.2022.04.007
Cao, Ou, Chen, Zhang, Szkudelski et al., Dietary polyphenols and type 2 diabetes: human study and clinical trial, Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr, doi:10.1080/10408398.2018.1492900
Cherian, Vadivel, Thiruganasambandham, Madhavankutty, Phytocompounds and their molecular targets in immunomodulation: a review, J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol, doi:10.1515/jbcpp-2021-0172
Dai, Tan, Ren, Shao, Tao et al., COVID-19 risk appears to vary across different alcoholic beverages, Front Nutr, doi:10.3389/fnut.2021.772700
Ding, Jiang, Fang, Regulation of immune function by polyphenols, J Immunol Res, doi:10.1155/2018/1264074
Ebrahimzadeh-Attari, Panahi, Hebert, Ostadrahimi, Saghafi-Asl et al., Nutritional approach for increasing public health during pandemic of COVID-19: a comprehensive review of antiviral nutrients and nutraceuticals, Health Promot Perspect, doi:10.34172/hpp.2021.17
Enaru, Socaci, Farcas, Socaciu, Danciu et al., Novel delivery systems of polyphenols and their potential health benefits, Pharmaceuticals (Basel), doi:10.3390/ph14100946
Fraga, Croft, Kennedy, Tomás-Barberán, The effects of polyphenols and other bioactives on human health, Food Funct, doi:10.1039/c8fo01997e
Gallagher, Heymsfield, Heo, Jebb, Murgatroyd et al., Healthy percentage body fat ranges: an approach for developing guidelines based on body mass index, Am J Clin Nutr, doi:10.1093/ajcn/72.3.694
Gałecka, Basińska, Bartnicka, Znaczenie mikrobioty jelitowej w kształtowaniu zdrowia człowieka-implikacje w praktyce lekarza rodzinnego, Forum Medycyny Rodzinnej
Giovinazzo, Gerardi, Uberti-Foppa, Lopalco, Can natural polyphenols help in reducing cytokine storm in COVID-19 patients? Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules25245888
Gliozzi, Walker, Muscoli, Vitale, Gratteri et al., Bergamot polyphenolic fraction enhances rosuvastatin-induced effect on LDL-cholesterol, LOX-1 expression and protein kinase B phosphorylation in patients with hyperlipidemia, Int J Cardiol, doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2013.08.125
Godos, Vitale, Micek, Ray, Martini et al., Dietary polyphenol intake, blood pressure, and hypertension: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies, Antioxidants (Basel), doi:10.3390/antiox8060152
Grosso, Godos, Currenti, Micek, Falzone et al., The effect of dietary polyphenols on vascular health and hypertension: current evidence and mechanisms of action, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14030545
Grosso, Godos, Lamuela-Raventos, Ray, Micek et al., A comprehensive meta-analysis on dietary flavonoid and lignan intake and cancer risk: level of evidence and limitations, Mol Nutr Food Res, doi:10.1002/mnfr.201600930
Grosso, Micek, Godos, Pajak, Sciacca et al., Dietary flavonoid and lignan intake and mortality in prospective cohort studies: systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis, Am J Epidemiol, doi:10.1093/aje/kww207
Gu, Zhao, Yang, Du, Li et al., A new perspective to improve the treatment of Lianhuaqingwen on COVID-19 and prevent the environmental health risk of medication, Environ Sci Pollut Res Int, doi:10.1007/s11356-022-21125-w
Jagielski, Wnęk, Łuszczki, Bolesławska, Micek et al., Proposition of a new POLA index to assess the immunomodulatory properties of the diet and its relationship with the gut microbiota, using the example of the incidence of COVID-19 in a Group of People without comorbidities, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14204227
Jagielski, Łuszczki, Wnęk, Micek, Bolesławska et al., Associations of nutritional behavior and gut microbiota with the risk of COVID-19 in healthy young adults in Poland, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14020350
Khan, Nath, Rauf, Emran, Mitra et al., Multifunctional roles and pharmacological potential of β-sitosterol: emerging evidence toward clinical applications, Chem Biol Interact, doi:10.3390/ph15101225
Khan, Siddiqui, Beta-sitosterol: as immunostimulant, antioxidant and inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein, Arch Pharmacol Ther, doi:10.33696/Pharmacol.2.014
Koistinen, Tuomainen, Lehtinen, Peltola, Auriola et al., Side-stream products of malting: a neglected source of phytochemicals, NPJ Sci Food, doi:10.1038/s41538-020-00081-0
Kočar, Režen, Rozman, Cholesterol, lipoproteins, and COVID-19: basic concepts and clinical applications, Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids, doi:10.1016/j.bbalip.2020.158849
Li, Xin, Mo, Marozik, He et al., The bioavailability and biological activities of phytosterols as modulators of cholesterol metabolism, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules27020523
López-García, Cilla, Barberá, Alegría, Anti-inflammatory and cytoprotective effect of plant sterol and Galactooligosaccharides-enriched beverages in Caco-2 cells, J Agric Food Chem, doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.9b03025
Magrone, Jirillo, The interplay between the gut immune system and microbiota in health and disease: nutraceutical intervention for restoring intestinal homeostasis, Curr Pharm Des, doi:10.2174/138161213804805793
Merino, Joshi, Nguyen, Leeming, Mazidi et al., Diet quality and risk and severity of COVID-19: a prospective cohort study, Gut, doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2021-325353
Micek, Godos, Brzostek, Gniadek, Favari et al., Dietary phytoestrogens and biomarkers of their intake in relation to cancer survival and recurrence: a comprehensive systematic review with meta-analysis, Nutr Rev, doi:10.1093/nutrit/nuaa043
Micek, Godos, Rio, Galvano, Grosso, Dietary flavonoids and cardiovascular disease: a comprehensive dose-response meta-analysis, Mol Nutr Food Res, doi:10.1002/mnfr.202001019
Mileo, Nisticò, Miccadei, Polyphenols: immunomodulatory and therapeutic implication in colorectal cancer, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2019.00729
Mohajeri, Mohajery, Nemati, Pourfarzi, The difference in the dietary inflammatory index, functional food, and antioxidants intake between COVID -19 patients and healthy persons, Med J Nutrition Metab, doi:10.3233/MNM-211521
Muller, Walker, Brauer, Sanduzzi Zamparelli, Capitelli et al., A phase II study on the effect of Taurisolo ® administered via AEROsol in hospitalized patients with mild to moderate COVID-19 pneumonia: the TAEROVID-19 study, J Inst Brew, doi:10.3390/cells11091499
Name, Souza, Vasconcelos, Prado, Pereira, Zinc, vitamin D and vitamin C: perspectives for COVID-19 with a focus on physical tissue barrier integrity, Front Nutr, doi:10.3389/fnut.2020.606398
Ngwa, Kumar, Thompson, Lyerly, Moore et al., Potential of flavonoid-inspired phytomedicines against COVID-19, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules25112707
O'driscoll, Santos, Wang, Cummings, Azman et al., Age-specific mortality and immunity patterns of SARS-CoV-2, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2918-0
Palacios-Rápalo, Jesús-González, Cordero-Rivera, Morales, Osuna-Ramos et al., Cholesterol-rich lipid rafts as platforms for SARS-CoV-2 entry, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.796855
Paraiso, Revel, Stevens, Ubani, Agwom et al., Molecular docking analysis of some phytochemicals on two SARS-CoV-2 targets, Curr Opin Food Sci, doi:10.1101/2020.03.31.017657
Pellegrini, Valtueña, Ardigò, Brighenti, Franzini et al., Intake of the plant lignans matairesinol, secoisolariciresinol, pinoresinol, and lariciresinol in relation to vascular inflammation and endothelial dysfunction in middle age-elderly men and post-menopausal women living in northern Italy, Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis, doi:10.1016/j.numecd.2009.02.003
Plat, Nichols, Mensink, Plant sterols and stanols: effects on mixed micellar composition and LXR (target gene) activation, J Lipid Res, doi:10.1194/jlr.M500272-JLR200
Plösch, Kruit, Bloks, Huijkman, Havinga et al., Reduction of cholesterol absorption by dietary plant sterols and stanols in mice is independent of the Abcg5/8 transporter, J Nutr, doi:10.1093/jn/136.8.2135
Pounis, Bonaccio, Castelnuovo, Costanzo, De Curtis et al., Polyphenol intake is associated with low-grade inflammation, using a novel data analysis from the Moli-sani study, Thromb Haemost, doi:10.1160/TH15-06-0487
Queipo-Ortuño, Boto-Ordóñez, Murri, Gomez-Zumaquero, Clemente-Postigo et al., Influence of red wine polyphenols and ethanol on the gut microbiota ecology and biochemical biomarkers, Am J Clin Nutr, doi:10.3945/ajcn.111.027847
Salehi, Quispe, Sharifi-Rad, Martins, Nigam et al., Phytosterols: from preclinical evidence to potential clinical applications, Front Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.599959
Shakoor, Feehan, Apostolopoulos, Platat, Dhaheri et al., Immunomodulatory effects of dietary polyphenols, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13030728
Shokry, Hegazy, Abbas, Mostafa, Eissa et al., Phytoestrogen β-sitosterol exhibits potent in vitro antiviral activity against influenza a viruses. Vaccines (Basel), doi:10.3390/vaccines11020228
Stromsnes, Lagzdina, Olaso-Gonzalez, Gimeno-Mallench, Gambini, Pharmacological properties of polyphenols: bioavailability, mechanisms of action, and biological effects in in vitro studies, animal models, and humans, Biomedicine, doi:10.3390/biomedicines9081074
Sureja, Shah, Gajjar, Jadeja, Bodiwala et al., -silico computational investigations of AntiViral lignan derivatives as potent inhibitors of SARS CoV-2, doi:10.1002/slct.202202069
Testino, Pellicano, COVID-19 and alcohol consumption: recommendations in the omicron era, Minerva Gastroenterol (Torino), doi:10.23736/S2724-5985.22.03194-1
Utomo, Ikawati, Meiyanto, Revealing the potency of citrus and galangal constituents to halt SARS-CoV-2 infection, Biology, doi:10.20944/preprints202003.0214.v1
Van Laren, Drießen, Rasa, Massar, Hoor, Nutritional changes during the COVID-19 pandemic: a rapid scoping review on the impact of psychological factors, Int J Food Sci Nutr, doi:10.1080/09637486.2023.2180613
Venzon, Bernard-Raichon, Klein, Axelrad, Zhang et al., Gut microbiome dysbiosis during COVID-19 is associated with increased risk for bacteremia and microbial translocation, BioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.07.15.452246
Vezza, Canet, De Marañón, Bañuls, Rocha et al., Phytosterols: nutritional health players in the management of obesity and its related disorders. Antioxidants (Basel), doi:10.3390/antiox9121266
Vijay, Valdes, Role of the gut microbiome in chronic diseases: a narrative review, Eur J Clin Nutr, doi:10.1038/s41430-021-00991-6
Vu, Rydland, Achenbach, Van Horn, Cornelis, Dietary Behaviors and incident COVID-19 in the UK biobank, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13062114
Wang, Qi, Zheng, Dietary polyphenol, gut microbiota, and health benefits. Antioxidants (Basel), doi:10.3390/antiox11061212
Waśkiewicz, Zujko, Szcześniewska, Tykarski, Kwaśniewska et al., Polyphenols and dietary antioxidant potential, and their relationship with arterial hypertension: a cross-sectional study of the adult population in Poland (WOBASZ II), Adv Clin Exp Med, doi:10.17219/acem/91487
Willett, Howe, Kushi, Adjustment for total energy intake in epidemiologic studies, Am J Clin Nutr, doi:10.1093/ajcn/65.4.1220S
Witkowska, Waśkiewicz, Zujko, Mirończuk-Chodakowska, Cicha-Mikołajczyk et al., Assessment of plant sterols in the diet of adult polish population with the use of a newly developed database, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13082722
Witkowska, Waśkiewicz, Zujko, Szcześniewska, Stepaniak et al., Are total and individual dietary lignans related to cardiovascular disease and its risk factors in postmenopausal women? A nationwide study, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu10070865
Wu, Liu, Wang, β-Sitosterol inhibits trimethylamine production by regulating the gut microbiota and attenuates atherosclerosis in ApoE-/-mice, Front Cardiovasc Med, doi:10.3389/fcvm.2022.986905
Wu, Pegan, Crich, Desrochers, Starling et al., Polyphenols as alternative treatments of COVID-19, Comput Struct Biotechnol J, doi:10.1016/j.csbj.2021.09.022
Wu, Wang, Li, Matairesinol exerts anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects in sepsis-mediated brain injury by repressing the MAPK and NF-κB pathways through up-regulating AMPK, Aging (Albany NY, doi:10.18632/aging.203649
Yan, Chu, Yang, Sze, Lai et al., Characterization of the lipidomic profile of human coronavirus-infected cells: implications for lipid metabolism Remodeling upon coronavirus replication, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v11010073
Yanagisawa, He, Asai, Hellwig, Henle et al., The impacts of cholesterol, oxysterols, and cholesterol lowering dietary compounds on the immune system, Int J Mol Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms232012236
Yang, Mcdonald, Patel, Zhang, Umetani et al., Sterol intermediates from cholesterol biosynthetic pathway as liver X receptor ligands, J Biol Chem, doi:10.1074/jbc.M603781200
Yang, Yu, Li, Xu, Cohen et al., Disruption of cholesterol homeostasis by plant sterols, J Clin Invest, doi:10.1172/JCI22186
Yu, Rohli, Yang, Jia, Impact of obesity on COVID-19 patients, J Diabetes Complicat, doi:10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2020.107817
Yuan, Zhang, Shen, Jia, Xie, Phytosterols suppress phagocytosis and inhibit inflammatory mediators via ERK pathway on LPS-triggered inflammatory responses in RAW264.7 macrophages and the correlation with their structure. Foods, doi:10.3390/foods8110582
Zhang, Balasooriya, Sirisena, Ng, The effectiveness of dietary polyphenols in obesity management: a systematic review and meta-analysis of human clinical trials, Food Chem, doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.134668
Zhang, Cheng, Wang, Liu, Ren et al., Secoisolariciresinol Diglucoside exerts anti-inflammatory and antiapoptotic effects through inhibiting the Akt/IκB/NF-κB pathway on human umbilical vein endothelial cells, Mediat Inflamm, doi:10.1155/2020/3621261
Zhuang, Zhong, Zhang, Chen, Huang et al., Exploring the potential mechanism of Shufeng Jiedu capsule for treating COVID-19 by comprehensive network pharmacological approaches and molecular docking validation, Comb Chem High Throughput Screen, doi:10.1016/j.jff.2020.104146
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnut.2023.1241016",
"ISSN": [
"2296-861X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2023.1241016",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Objectives</jats:title><jats:p>Devastating consequences of COVID-19 disease enhanced the role of promoting prevention-focused practices. Among targeted efforts, diet is regarded as one of the potential factors which can affect immune function and optimal nutrition is postulated as the method of augmentation of people’s viral resistance. As epidemiological evidence is scarce, the present study aimed to explore the association between dietary intake of total polyphenols, lignans and plant sterols and the abundance of immunomodulatory gut microbiota such as Enterococcus spp. and <jats:italic>Escherichia coli</jats:italic> and the risk of developing COVID-19 disease.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods</jats:title><jats:p>Demographic data, dietary habits, physical activity as well as the composition of body and gut microbiota were analyzed in a sample of 95 young healthy individuals. Dietary polyphenol, lignan and plant sterol intakes have been retrieved based on the amount of food consumed by the participants, the phytochemical content was assessed in laboratory analysis and using available databases.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>For all investigated polyphenols and phytosterols, except campesterol, every unit increase in the tertile of intake category was associated with a decrease in the odds of contracting COVID-19. The risk reduction ranged from several dozen percent to 70 %, depending on the individual plant-based chemical, and after controlling for basic covariates it was statistically significant for secoisolariciresinol (OR = 0.28, 95% CI: 0.11–0.61), total phytosterols (OR = 0.47, 95% CI: 0.22–0.95) and for stigmasterols (OR = 0.34, 95% CI: 0.14–0.72). We found an inverse association between increased β-sitosterol intake and phytosterols in total and the occurrence of <jats:italic>Escherichia coli</jats:italic> in stool samples outside reference values, with 72% (OR = 0.28, 95% CI: 0.08–0.86) and 66% (OR = 0.34, 95% CI: 0.10–1.08) reduced odds of abnormal level of bacteria for the highest compared with the lowest tertile of phytochemical consumption. Additionally, there was a trend of more frequent presence of Enterococcus spp. at relevant level in people with a higher intake of lariciresinol.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title><jats:p>The beneficial effects of polyphenols and phytosterols should be emphasized and these plant-based compounds should be regarded in the context of their utility as antiviral agents preventing influenza-type infections.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.3389/fnut.2023.1241016"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Micek",
"given": "Agnieszka",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bolesławska",
"given": "Izabela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jagielski",
"given": "Paweł",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Konopka",
"given": "Kamil",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Waśkiewicz",
"given": "Anna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Witkowska",
"given": "Anna Maria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Przysławski",
"given": "Juliusz",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Godos",
"given": "Justyna",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Frontiers in Nutrition",
"container-title-short": "Front. Nutr.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"frontiersin.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2023-08-03T12:12:00Z",
"timestamp": 1691064720000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2023-08-03T12:12:04Z",
"timestamp": 1691064724000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2023-08-04T04:27:03Z",
"timestamp": 1691123223844
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
3
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2023-08-03T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1691020800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2023.1241016/full",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1965",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.3389",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
3
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
3
]
]
},
"publisher": "Frontiers Media SA",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.34172/hpp.2021.17",
"article-title": "Nutritional approach for increasing public health during pandemic of COVID-19: a comprehensive review of antiviral nutrients and nutraceuticals",
"author": "Ebrahimzadeh-Attari",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "119",
"journal-title": "Health Promot Perspect",
"key": "ref1",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/mnfr.201600930",
"article-title": "A comprehensive meta-analysis on dietary flavonoid and lignan intake and cancer risk: level of evidence and limitations",
"author": "Grosso",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "930",
"journal-title": "Mol Nutr Food Res",
"key": "ref2",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nutrit/nuaa043",
"article-title": "Dietary phytoestrogens and biomarkers of their intake in relation to cancer survival and recurrence: a comprehensive systematic review with meta-analysis",
"author": "Micek",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "42",
"journal-title": "Nutr Rev",
"key": "ref3",
"volume": "79",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/aje/kww207",
"article-title": "Dietary flavonoid and lignan intake and mortality in prospective cohort studies: systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis",
"author": "Grosso",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1304",
"journal-title": "Am J Epidemiol",
"key": "ref4",
"volume": "185",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antiox8060152",
"article-title": "Dietary polyphenol intake, blood pressure, and hypertension: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies",
"author": "Godos",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "152",
"journal-title": "Antioxidants (Basel)",
"key": "ref5",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13030728",
"article-title": "Immunomodulatory effects of dietary polyphenols",
"author": "Shakoor",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "728",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "ref6",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antiox9121266",
"article-title": "Phytosterols: nutritional health players in the management of obesity and its related disorders",
"author": "Vezza",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "266",
"journal-title": "Antioxidants (Basel)",
"key": "ref7",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v11010073",
"article-title": "Characterization of the lipidomic profile of human coronavirus-infected cells: implications for lipid metabolism Remodeling upon coronavirus replication",
"author": "Yan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "73",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "ref8",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnut.2021.772700",
"article-title": "COVID-19 risk appears to vary across different alcoholic beverages",
"author": "Dai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "772700",
"journal-title": "Front Nutr",
"key": "ref9",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnut.2020.606398",
"article-title": "Zinc, vitamin D and vitamin C: perspectives for COVID-19 with a focus on physical tissue barrier integrity",
"author": "Name",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "606398",
"journal-title": "Front Nutr",
"key": "ref10",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14020350",
"article-title": "Associations of nutritional behavior and gut microbiota with the risk of COVID-19 in healthy young adults in Poland",
"author": "Jagielski",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "350",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "ref11",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu10070865",
"article-title": "Are total and individual dietary lignans related to cardiovascular disease and its risk factors in postmenopausal women? A nationwide study",
"author": "Witkowska",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "865",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "ref12",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.17219/acem/91487",
"article-title": "Polyphenols and dietary antioxidant potential, and their relationship with arterial hypertension: a cross-sectional study of the adult population in Poland (WOBASZ II)",
"author": "Waśkiewicz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "797",
"journal-title": "Adv Clin Exp Med",
"key": "ref13",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13082722",
"article-title": "Assessment of plant sterols in the diet of adult polish population with the use of a newly developed database",
"author": "Witkowska",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2722",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "ref14",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/65.4.1220S",
"article-title": "Adjustment for total energy intake in epidemiologic studies",
"author": "Willett",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1220S",
"journal-title": "Am J Clin Nutr",
"key": "ref15",
"volume": "65",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/72.3.694",
"article-title": "Healthy percentage body fat ranges: an approach for developing guidelines based on body mass index",
"author": "Gallagher",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "694",
"journal-title": "Am J Clin Nutr",
"key": "ref16",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14204227",
"article-title": "Proposition of a new POLA index to assess the immunomodulatory properties of the diet and its relationship with the gut microbiota, using the example of the incidence of COVID-19 in a Group of People without comorbidities",
"author": "Jagielski",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4227",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "ref17",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2020.00240",
"article-title": "May polyphenols have a role against coronavirus infection? An overview of in vitro evidence",
"author": "Annunziata",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "240",
"journal-title": "Front Med (Lausanne)",
"key": "ref18",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2022/1688826",
"article-title": "Lignans from Mosla scabra ameliorated influenza a virus-induced pneumonia via inhibiting macrophage activation",
"author": "Cai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1688826",
"journal-title": "Evid Based Complement Alternat Med",
"key": "ref19",
"volume": "2022",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/vaccines11020228",
"article-title": "Phytoestrogen β-sitosterol exhibits potent in vitro antiviral activity against influenza a viruses",
"author": "Shokry",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "228",
"journal-title": "Vaccines (Basel)",
"key": "ref20",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cells10071619",
"article-title": "Man-specific lectins from plants, fungi, algae and cyanobacteria, as potential blockers for SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) coronaviruses: biomedical perspectives",
"author": "Barre",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1619",
"journal-title": "Cells",
"key": "ref21",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11356-022-21125-w",
"article-title": "A new perspective to improve the treatment of Lianhuaqingwen on COVID-19 and prevent the environmental health risk of medication",
"author": "Gu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "74208",
"journal-title": "Environ Sci Pollut Res Int",
"key": "ref22",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.csbj.2021.09.022",
"article-title": "Polyphenols as alternative treatments of COVID-19",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "5371",
"journal-title": "Comput Struct Biotechnol J",
"key": "ref23",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1386207323999201029122301",
"article-title": "Exploring the potential mechanism of Shufeng Jiedu capsule for treating COVID-19 by comprehensive network pharmacological approaches and molecular docking validation",
"author": "Zhuang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1377",
"journal-title": "Comb Chem High Throughput Screen",
"key": "ref24",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jff.2020.104146",
"article-title": "Phytochemicals containing biologically active polyphenols as an effective agent against COVID-19-inducing coronavirus",
"author": "Chojnacka",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "104146",
"journal-title": "J Funct Foods",
"key": "ref25",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules25112707",
"article-title": "Potential of flavonoid-inspired phytomedicines against COVID-19",
"author": "Ngwa",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2707",
"journal-title": "Molecules",
"key": "ref26",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1039/d1ra03937g",
"article-title": "In silico study of natural compounds from sesame against COVID-19 by targeting Mpro, PLpro and RdRp",
"author": "Allam",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "22398",
"journal-title": "RSC Adv",
"key": "ref27",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cofs.2020.08.004",
"article-title": "Potential use of polyphenols in the battle against COVID-19",
"author": "Paraiso",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "149",
"journal-title": "Curr Opin Food Sci",
"key": "ref28",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.03.31.017657",
"article-title": "Molecular docking analysis of some phytochemicals on two SARS-CoV-2 targets",
"author": "Ubani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "BioRxiv",
"key": "ref29",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.20944/preprints202003.0214.v1",
"article-title": "Revealing the potency of citrus and galangal constituents to halt SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Utomo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Biology",
"key": "ref30",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3233/MNM-211521",
"article-title": "The difference in the dietary inflammatory index, functional food, and antioxidants intake between COVID -19 patients and healthy persons",
"author": "Mohajeri",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "219",
"journal-title": "Med J Nutrition Metab",
"key": "ref31",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/09637486.2023.2180613",
"article-title": "Nutritional changes during the COVID-19 pandemic: a rapid scoping review on the impact of psychological factors",
"author": "Van Laren",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "124",
"journal-title": "Int J Food Sci Nutr",
"key": "ref32",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/09637486.2022.2040009",
"article-title": "Changes in a Mediterranean lifestyle during the COVID-19 pandemic among elderly Italians: an analysis of gender and socioeconomic inequalities in the “LOST in Lombardia” study",
"author": "Bonaccio",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "683",
"journal-title": "Int J Food Sci Nutr",
"key": "ref33",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3233/MNM-210006",
"article-title": "COVID-19 pandemic: changes in the emotions, body weights and nutrition habits of individuals during social intervention measures",
"author": "Akkuş",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "11",
"journal-title": "Med J Nutrition Metab",
"key": "ref34",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cbi.2022.110117",
"article-title": "Multifunctional roles and pharmacological potential of β-sitosterol: emerging evidence toward clinical applications",
"author": "Khan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "110117",
"journal-title": "Chem Biol Interact",
"key": "ref35",
"volume": "365",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ph15101225",
"article-title": "Polyphenols, saponins and phytosterols in lentils and their health benefits: an overview",
"author": "Mustafa",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1225",
"journal-title": "Pharmaceuticals (Basel)",
"key": "ref36",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1515/jbcpp-2021-0172",
"article-title": "Phytocompounds and their molecular targets in immunomodulation: a review",
"author": "Cherian",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol",
"key": "ref37",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules24010041",
"article-title": "A review of lignan metabolism, milk enterolactone concentration, and antioxidant status of dairy cows fed flaxseed",
"author": "Brito",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "41",
"journal-title": "Molecules",
"key": "ref38",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules25245888",
"article-title": "Can natural polyphenols help in reducing cytokine storm in COVID-19 patients?",
"author": "Giovinazzo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "5888",
"journal-title": "Molecules",
"key": "ref39",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jafc.9b03025",
"article-title": "Anti-inflammatory and cytoprotective effect of plant sterol and Galactooligosaccharides-enriched beverages in Caco-2 cells",
"author": "López-García",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1862",
"journal-title": "J Agric Food Chem",
"key": "ref40",
"volume": "68",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2020/3621261",
"article-title": "Secoisolariciresinol Diglucoside exerts anti-inflammatory and antiapoptotic effects through inhibiting the Akt/IκB/NF-κB pathway on human umbilical vein endothelial cells",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3621261",
"journal-title": "Mediat Inflamm",
"key": "ref41",
"volume": "2020",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/138161213804805793",
"article-title": "The interplay between the gut immune system and microbiota in health and disease: nutraceutical intervention for restoring intestinal homeostasis",
"author": "Magrone",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1329",
"journal-title": "Curr Pharm Des",
"key": "ref42",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2019.00729",
"article-title": "Polyphenols: immunomodulatory and therapeutic implication in colorectal cancer",
"author": "Mileo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "729",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "ref43",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2020.599959",
"article-title": "Phytosterols: from preclinical evidence to potential clinical applications",
"author": "Salehi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "599959",
"journal-title": "Front Pharmacol",
"key": "ref44",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18632/aging.203649",
"article-title": "Matairesinol exerts anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects in sepsis-mediated brain injury by repressing the MAPK and NF-κB pathways through up-regulating AMPK",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "23780",
"journal-title": "Aging (Albany NY)",
"key": "ref45",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2018/1264074",
"article-title": "Regulation of immune function by polyphenols",
"author": "Ding",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1264074",
"journal-title": "J Immunol Res",
"key": "ref46",
"volume": "2018",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/foods8110582",
"article-title": "Phytosterols suppress phagocytosis and inhibit inflammatory mediators via ERK pathway on LPS-triggered inflammatory responses in RAW264.7 macrophages and the correlation with their structure",
"author": "Yuan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "582",
"journal-title": "Foods",
"key": "ref47",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcvm.2022.986905",
"article-title": "β-Sitosterol inhibits trimethylamine production by regulating the gut microbiota and attenuates atherosclerosis in ApoE−/− mice",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "986905",
"journal-title": "Front Cardiovasc Med",
"key": "ref48",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.796855",
"article-title": "Cholesterol-rich lipid rafts as platforms for SARS-CoV-2 entry",
"author": "Palacios-Rápalo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "796855",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "ref49",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms232012236",
"article-title": "The impacts of cholesterol, oxysterols, and cholesterol lowering dietary compounds on the immune system",
"author": "Yanagisawa",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "12236",
"journal-title": "Int J Mol Sci",
"key": "ref50",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules27020523",
"article-title": "The bioavailability and biological activities of phytosterols as modulators of cholesterol metabolism",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "27",
"journal-title": "Molecules",
"key": "ref51",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1194/jlr.M500272-JLR200",
"article-title": "Plant sterols and stanols: effects on mixed micellar composition and LXR (target gene) activation",
"author": "Plat",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2468",
"journal-title": "J Lipid Res",
"key": "ref52",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jn/136.8.2135",
"article-title": "Reduction of cholesterol absorption by dietary plant sterols and stanols in mice is independent of the Abcg5/8 transporter",
"author": "Plösch",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2135",
"journal-title": "J Nutr",
"key": "ref53",
"volume": "136",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M603781200",
"article-title": "Sterol intermediates from cholesterol biosynthetic pathway as liver X receptor ligands",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "27816",
"journal-title": "J Biol Chem",
"key": "ref54",
"volume": "281",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI22186",
"article-title": "Disruption of cholesterol homeostasis by plant sterols",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "813",
"journal-title": "J Clin Invest",
"key": "ref55",
"volume": "114",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijcard.2013.08.125",
"article-title": "Bergamot polyphenolic fraction enhances rosuvastatin-induced effect on LDL-cholesterol, LOX-1 expression and protein kinase B phosphorylation in patients with hyperlipidemia",
"author": "Gliozzi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "140",
"journal-title": "Int J Cardiol",
"key": "ref56",
"volume": "170",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbalip.2020.158849",
"article-title": "Cholesterol, lipoproteins, and COVID-19: basic concepts and clinical applications",
"author": "Kočar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "158849",
"journal-title": "Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids",
"key": "ref57",
"volume": "1866",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/mnfr.202001019",
"article-title": "Dietary flavonoids and cardiovascular disease: a comprehensive dose-response meta-analysis",
"author": "Micek",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e2001019",
"journal-title": "Mol Nutr Food Res",
"key": "ref58",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14030545",
"article-title": "The effect of dietary polyphenols on vascular health and hypertension: current evidence and mechanisms of action",
"author": "Grosso",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "545",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "ref59",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/10408398.2018.1492900",
"article-title": "Dietary polyphenols and type 2 diabetes: human study and clinical trial",
"author": "Cao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3371",
"journal-title": "Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr",
"key": "ref60",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1039/c8fo01997e",
"article-title": "The effects of polyphenols and other bioactives on human health",
"author": "Fraga",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "514",
"journal-title": "Food Funct",
"key": "ref61",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.134668",
"article-title": "The effectiveness of dietary polyphenols in obesity management: a systematic review and meta-analysis of human clinical trials",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "134668",
"journal-title": "Food Chem",
"key": "ref62",
"volume": "404",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110702",
"article-title": "An update on β-sitosterol: a potential herbal nutraceutical for diabetic management",
"author": "Babu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "110702",
"journal-title": "Biomed Pharmacother",
"key": "ref63",
"volume": "131",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gutjnl-2021-325353",
"article-title": "Diet quality and risk and severity of COVID-19: a prospective cohort study",
"author": "Merino",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2096",
"journal-title": "Gut",
"key": "ref64",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13062114",
"article-title": "Dietary Behaviors and incident COVID-19 in the UK biobank",
"author": "Vu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2114",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "ref65",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bcp.12924",
"article-title": "Mediterranean diet, dietary polyphenols and low grade inflammation: results from the MOLI-SANI study",
"author": "Bonaccio",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "107",
"journal-title": "Br J Clin Pharmacol",
"key": "ref66",
"volume": "83",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3233/MNM-200597",
"article-title": "The Mediterranean diet: healthy and sustainable dietary pattern in the time of Sars-Cov-2",
"author": "Bagnato",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "365",
"journal-title": "Med J Nutrition Metab",
"key": "ref67",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1160/TH15-06-0487",
"article-title": "Polyphenol intake is associated with low-grade inflammation, using a novel data analysis from the Moli-sani study",
"author": "Pounis",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "344",
"journal-title": "Thromb Haemost",
"key": "ref68",
"volume": "115",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41538-020-00081-0",
"article-title": "Side-stream products of malting: a neglected source of phytochemicals",
"author": "Koistinen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "21",
"journal-title": "NPJ Sci Food",
"key": "ref69",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/j.2050-0416.2007.tb00263.x",
"article-title": "Does beer contain compounds that might interfere with cholesterol metabolism?",
"author": "Muller",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "102",
"journal-title": "J Inst Brew",
"key": "ref70",
"volume": "113",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cells11091499",
"article-title": "A phase II study on the effect of Taurisolo® administered via AEROsol in hospitalized patients with mild to moderate COVID-19 pneumonia: the TAEROVID-19 study",
"author": "Sanduzzi Zamparelli",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1499",
"journal-title": "Cells",
"key": "ref71",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.33696/Pharmacol.2.014",
"article-title": "Beta-sitosterol: as immunostimulant, antioxidant and inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein",
"author": "Khan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "12",
"journal-title": "Arch Pharmacol Ther",
"key": "ref72",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/slct.202202069",
"article-title": "In-silico computational investigations of AntiViral lignan derivatives as potent inhibitors of SARS CoV-2",
"author": "Sureja",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e202202069",
"journal-title": "Chemistry Select",
"key": "ref73",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.numecd.2009.02.003",
"article-title": "Intake of the plant lignans matairesinol, secoisolariciresinol, pinoresinol, and lariciresinol in relation to vascular inflammation and endothelial dysfunction in middle age-elderly men and post-menopausal women living in northern Italy",
"author": "Pellegrini",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "64",
"journal-title": "Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis",
"key": "ref74",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2918-0",
"article-title": "Age-specific mortality and immunity patterns of SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "O’Driscoll",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "140",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref75",
"volume": "590",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.2223",
"article-title": "Sex-based differences in severity and mortality in COVID-19",
"author": "Alwani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e2223",
"journal-title": "Rev Med Virol",
"key": "ref76",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2020.107817",
"article-title": "Impact of obesity on COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Yu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "107817",
"journal-title": "J Diabetes Complicat",
"key": "ref77",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.23736/S2724-5985.22.03194-1",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and alcohol consumption: recommendations in the omicron era",
"author": "Testino",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Minerva Gastroenterol (Torino)",
"key": "ref78",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ph14100946",
"article-title": "Novel delivery systems of polyphenols and their potential health benefits",
"author": "Enaru",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "946",
"journal-title": "Pharmaceuticals (Basel)",
"key": "ref79",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biomedicines9081074",
"article-title": "Pharmacological properties of polyphenols: bioavailability, mechanisms of action, and biological effects in in vitro studies, animal models, and humans",
"author": "Stromsnes",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1074",
"journal-title": "Biomedicine",
"key": "ref80",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41430-021-00991-6",
"article-title": "Role of the gut microbiome in chronic diseases: a narrative review",
"author": "Vijay",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "489",
"journal-title": "Eur J Clin Nutr",
"key": "ref81",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.07.15.452246",
"article-title": "Gut microbiome dysbiosis during COVID-19 is associated with increased risk for bacteremia and microbial translocation",
"author": "Venzon",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "BioRxiv",
"key": "ref82",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/09637486.2020.1807475",
"article-title": "Probiotics and COVID-19",
"author": "Bottari",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "293",
"journal-title": "Int J Food Sci Nutr",
"key": "ref83",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Znaczenie mikrobioty jelitowej w kształtowaniu zdrowia człowieka—implikacje w praktyce lekarza rodzinnego",
"author": "Gałecka",
"first-page": "50",
"journal-title": "Forum Medycyny Rodzinnej",
"key": "ref84",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2022.04.007",
"article-title": "Nutrition as a key to boost immunity against COVID-19",
"author": "Calcuttawala",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "17",
"journal-title": "Clin Nutr ESPEN",
"key": "ref85",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antiox11061212",
"article-title": "Dietary polyphenol, gut microbiota, and health benefits",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1212",
"journal-title": "Antioxidants (Basel)",
"key": "ref86",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmicb.2017.00804",
"article-title": "Efficacy of (+)-Lariciresinol to control bacterial growth of Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli O157:H7",
"author": "Bajpai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "804",
"journal-title": "Front Microbiol",
"key": "ref87",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000177548",
"article-title": "Effects of stigmasterol-supplemented diets on fecal neutral sterols and bile acid excretion in rats",
"author": "Andriamiarina",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "297",
"journal-title": "Ann Nutr Metab",
"key": "ref88",
"volume": "33",
"year": "1989"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3945/ajcn.111.027847",
"article-title": "Influence of red wine polyphenols and ethanol on the gut microbiota ecology and biochemical biomarkers",
"author": "Queipo-Ortuño",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1323",
"journal-title": "Am J Clin Nutr",
"key": "ref89",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1039/c4fo00029c",
"article-title": "High levels of Bifidobacteria are associated with increased levels of anthocyanin microbial metabolites: a randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Boto-Ordóñez",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1932",
"journal-title": "Food Funct",
"key": "ref90",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2014"
}
],
"reference-count": 90,
"references-count": 90,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2023.1241016/full"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Nutrition and Dietetics",
"Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism",
"Food Science"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Association of dietary intake of polyphenols, lignans, and phytosterols with immune-stimulating microbiota and COVID-19 risk in a group of Polish men and women",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/crossmark-policy",
"volume": "10"
}