Impact of uricosurics on mortality outcomes in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
et al., International Journal of Pharmacy Practice, doi:10.1093/ijpp/riae003, Mar 2024
Vitamin C for COVID-19
6th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000076 from 73 studies, recognized in 22 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
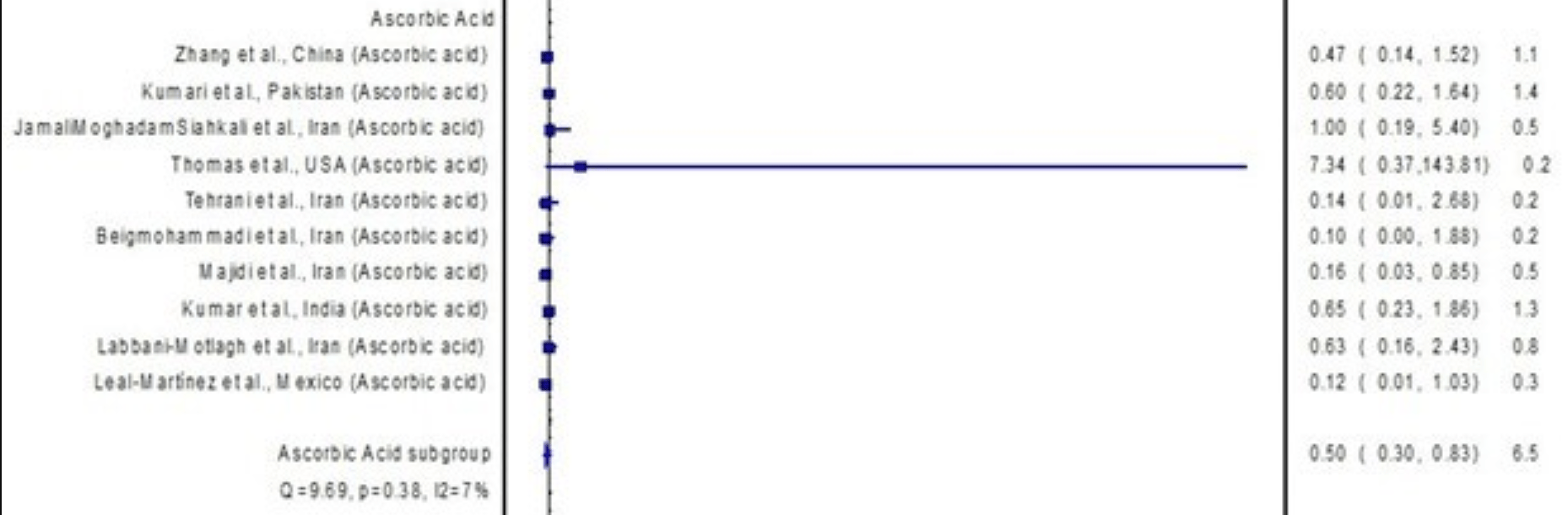
Systematic review and meta analysis of 27 RCTs investigating the impact of uricosuric drugs on mortality in COVID-19 patients. The pooled analysis found no significant association between uricosuric use and mortality risk. However, a subgroup analysis of 10 trials showed lower mortality with vitamin C.
7 meta-analyses show significant improvements with vitamin C for mortality1-5,
progression6,
severity1,5, and
cases7.
Currently there are 73 vitamin C for COVID-19 studies, showing 18% lower mortality [9‑27%], 9% lower ventilation [-12‑27%], 23% lower ICU admission [10‑34%], 19% lower hospitalization [7‑30%], and 3% fewer cases [-16‑19%].
|
risk of death, 50.0% lower, OR 0.50, p = 0.008, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Bhowmik et al., Impact of high-dose vitamin C on the mortality, severity, and duration of hospital stay in COVID-19 patients: A meta-analysis, Health Science Reports, doi:10.1002/hsr2.762.
2.
Olczak-Pruc et al., Vitamin C Supplementation for the Treatment of COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14194217.
3.
Kow et al., The effect of vitamin C on the risk of mortality in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-023-01200-5.
4.
Kow (B) et al., Impact of uricosurics on mortality outcomes in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, International Journal of Pharmacy Practice, doi:10.1093/ijpp/riae003.
5.
Qin et al., Effects of Vitamin C Supplements on Clinical Outcomes and Hospitalization Duration for Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Nutrition Reviews, doi:10.1093/nutrit/nuae154.
Kow et al., 4 Mar 2024, peer-reviewed, 4 authors.
Contact: kaeshaelya@gmail.com.
Impact of uricosurics on mortality outcomes in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Objectives: To determine risks associated with uricosurics in COVID-19 patients.
Methods: A systematic review and meta-analysis was conducted by systematically searching electronic databases.
Key findings: The pooled analysis of the included trials revealed that the use of uricosurics was not associated with the risk of mortality (pooled odds ratio [OR] = 1.03, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.94-1.12). However, there is a potential mortality benefit associated with the use of ascorbic acid (pooled OR = 0.78, 95% CI: 0.65-0.94).
Conclusions: The findings confirmed the safety of uricosurics in COVID-19 patients, despite their potential to cause uric acid excretion, which may possess antioxidant properties.
Supplementary material Supplementary data are available at International journal of Pharmacy Practice online. validation; roles/writing-original draft; writing-review & editing; final approval of the version to be published. All authors are accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved. The manuscript has been seen and approved by all authors. We confirm that this work is original and has not been published elsewhere, nor is it currently under consideration for publication elsewhere. All authors had complete access to the study data that support the publication.
Author contributions
Conflict of interest The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
References
Dufour, Werion, Belkhir, Serum uric acid, disease seeverity and outcomes in COVID-19, Crit Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-021-03616-3
Kow, Hasan, Ramachandram, The effect of vitamin C on the risk of mortality in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1093/ijpp/riae003/7619074bygueston05
Kurajoh, Hiura, Numaguchi, Inflammation related to asssociation of low uric acid and progression to severe disease in patients hospitalized for non-severe Coronavirus disease 2019, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines11030854
Sautin, Johnson, Uric acid: the oxidant-antioxidant parRadox, Nucleos Nucleot Nucl Acids, doi:10.1080/15257770802138558
Topless, Gaffo, Stamp, Gout and the risk of COVID-19 diagnosis and death in the UK Biobank: a population-based study, Lancet Rheumatol, doi:10.1016/S2665-9913(21)00401-X
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ijpp/riae003",
"ISSN": [
"0961-7671",
"2042-7174"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/ijpp/riae003",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Objectives</jats:title>\n <jats:p>To determine risks associated with uricosurics in COVID-19 patients.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>A systematic review and meta-analysis was conducted by systematically searching electronic databases.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Key findings</jats:title>\n <jats:p>The pooled analysis of the included trials revealed that the use of uricosurics was not associated with the risk of mortality (pooled odds ratio [OR] = 1.03, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.94–1.12). However, there is a potential mortality benefit associated with the use of ascorbic acid (pooled OR = 0.78, 95% CI: 0.65–0.94).</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title>\n <jats:p>The findings confirmed the safety of uricosurics in COVID-19 patients, despite their potential to cause uric acid excretion, which may possess antioxidant properties.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8186-2926",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Pharmacy, International Medical University , Kuala Lumpur , Malaysia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kow",
"given": "Chia Siang",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5390-7026",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Pharmacy, Monash University Malaysia , Bandar Sunway , Selangor , Malaysia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ramachandram",
"given": "Dinesh Sangarran",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4058-2215",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Applied Sciences, University of Huddersfield , United Kingdom"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Hasan",
"given": "Syed Shahzad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3754-1690",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Pharmacy, International Medical University , Kuala Lumpur , Malaysia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Thiruchelvam",
"given": "Kaeshaelya",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "International Journal of Pharmacy Practice",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-25T13:42:45Z",
"timestamp": 1706190165000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-05T03:14:43Z",
"timestamp": 1709608483000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-05T03:43:20Z",
"timestamp": 1709610200304
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
4
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-04T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1709510400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/ijpp/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/ijpp/riae003/56832744/riae003.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/ijpp/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/ijpp/riae003/56832744/riae003.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "286",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1093",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
4
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
4
]
]
},
"publisher": "Oxford University Press (OUP)",
"reference": [
{
"article-title": "Inflammation related to association of low uric acid and progression to severe disease in patients hospitalized for non-severe Coronavirus disease 2019",
"author": "Kurajoh",
"first-page": "854",
"key": "2024030503142663800_CIT0001",
"volume-title": "Biomedicines",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"article-title": "Uric acid: the oxidant-antioxidant paradox",
"author": "Sautin",
"first-page": "608",
"key": "2024030503142663800_CIT0002",
"volume-title": "Nucleos Nucleot Nucl Acids",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-021-03616-3",
"article-title": "Serum uric acid, disease severity and outcomes in COVID-19",
"author": "Dufour",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "212",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "2024030503142663800_CIT0003",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Gout and the risk of COVID-19 diagnosis and death in the UK Biobank: a population-based study",
"author": "Topless",
"first-page": "e274",
"key": "2024030503142663800_CIT0004",
"volume-title": "Lancet Rheumatol",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10787-023-01200-5",
"article-title": "The effect of vitamin C on the risk of mortality in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials",
"author": "Kow",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3357",
"journal-title": "Inflammopharmacology",
"key": "2024030503142663800_CIT0005",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2023"
}
],
"reference-count": 5,
"references-count": 5,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/ijpp/advance-article/doi/10.1093/ijpp/riae003/7619074"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Public Health, Environmental and Occupational Health",
"Health Policy",
"Pharmaceutical Science",
"Pharmacy"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Impact of uricosurics on mortality outcomes in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials",
"type": "journal-article"
}
