Double-blinded, randomised, placebo-controlled trial of convalescent plasma for COVID-19: analyses by neutralising antibodies homologous to donors’ variants
et al., Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1080/23744235.2024.2329957, CP_COVID-19, NCT04730401, Mar 2024
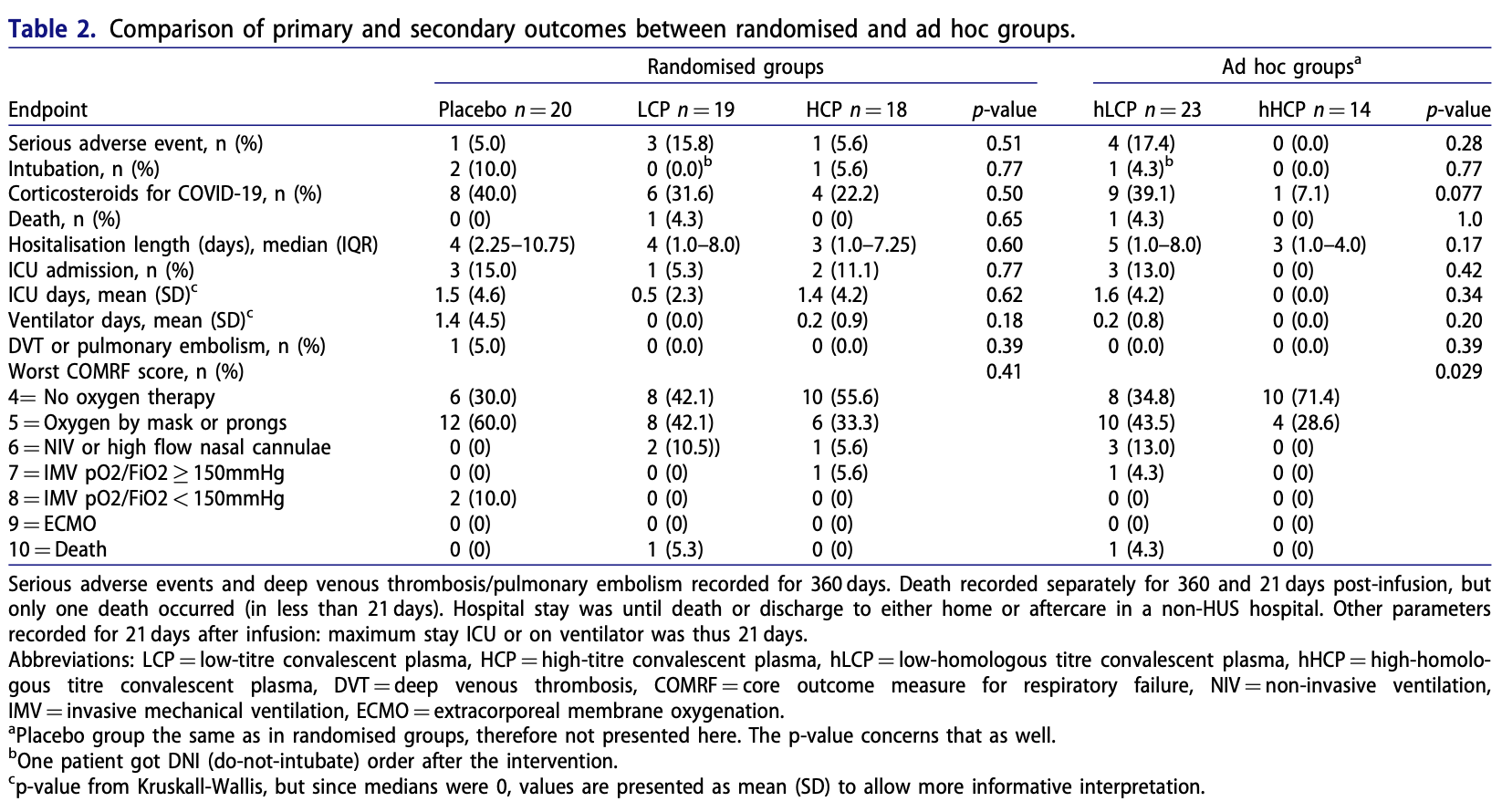
RCT 57 hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing no significant difference in outcomes with convalescent plasma treatment.
|
risk of death, 154.1% higher, RR 2.54, p = 1.00, treatment 1 of 37 (2.7%), control 0 of 20 (0.0%), continuity correction due to zero event (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 73.0% lower, RR 0.27, p = 0.28, treatment 1 of 37 (2.7%), control 2 of 20 (10.0%), NNT 14.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 45.9% lower, RR 0.54, p = 0.65, treatment 3 of 37 (8.1%), control 3 of 20 (15.0%), NNT 15.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Khawaja et al., 21 Mar 2024, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, Finland, peer-reviewed, mean age 51.7, 23 authors, study period 2 February, 2021 - 19 January, 2022, average treatment delay 8.0 days, trial NCT04730401 (history) (CP_COVID-19).
Contact: anu.kantele@helsinki.fi.
Double-blinded, randomised, placebo-controlled trial of convalescent plasma for COVID-19: analyses by neutralising antibodies homologous to donors’ variants
Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1080/23744235.2024.2329957
Introduction: Convalescent plasma (CP) emerged as potential treatment for COVID-19 early in the pandemic. While efficacy in hospitalised patients has been lacklustre, CP may be beneficial at the first stages of disease. Despite multiple new variants emerging, no trials have involved analyses on variant-specific antibody titres of CP. Methods: We recruited hospitalised COVID-19 patients within 10 days of symptom onset and, employing a doubleblinded approach, randomised them to receive 200 ml convalescent plasma with high (HCP) or low (LCP) neutralising antibody (NAb) titre against the ancestral strain (Wuhan-like variant) or placebo in 1:1:1 ratio. Primary endpoints comprised intubation, corticosteroids for symptom aggravation, and safety assessed as serious adverse events. For a preplanned ad hoc analysis, the patients were regrouped by infused CP's NAb titers to variants infecting the recipients i.e. by titres of homologous HCP (hHCP) or LCP (hLCP). Results: Of the 57 patients, 18 received HCP, 19 LCP and 20 placebo, all groups smaller than planned. No significant differences were found for primary endpoints. In ad hoc analysis, hHCPrecipients needed significantly less respiratory support, and appeared to be given corticosteroids less frequently (1/14; 7.1%) than those receiving hLCP (9/23; 39.1%) or placebo (8/20; 40%), (p ¼ 0.077). Discussion: Our double-blinded, placebo-controlled CP therapy trial remained underpowered and does not allow any firm conclusions for early-stage hospitalised COVID-19 patients. Interestingly, however, regrouping by homologous -recipients' variantspecific -CP titres suggested benefits for hHCP. We encourage similar re-analysis of ongoing/previous larger CP studies.
Disclosure statement The authors report there are no competing interests to declare.
References
Abani, Abbas, Abbas, Convalescent plasma in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised controlled, open-label, platform trial, The Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00897-7
Agarwal, Mukherjee, Kumar, Convalescent plasma in the management of moderate covid-19 in adults in India: open label phase II multicentre randomised controlled trial (PLACID trial), BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.m3939
Bar, Shaw, Choi, A randomized controlled study of convalescent plasma for individuals hospitalized with COVID-19 pneumonia, J Clin Investig, doi:10.1172/JCI155114
Bartelt, Markmann, Nelson, Outcomes of convalescent plasma with defined high versus lower neutralizing antibody titers against SARS-CoV-2 among hospitalized patients: CoronaVirus inactivating plasma (CoVIP) study, mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.01751-22
Bastard, Rosen, Zhang, Autoantibodies against type I IFNs in patients with life-threatening COVID-19, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abd4585
Bhimraj, Shumaker, Baden, Infectious Diseases Society of America Guidelines on the Treatment and Management of Patients with COVID-19, Infectious Diseases Society of America
Burnouf, Yazer, International forum on the collection and use of COVID-19 convalescent plasma: protocols, challenges and lessons learned: summary, Vox Sang, doi:10.1111/vox.13113
Cabrera, Pekkarinen, Alander, Characterization of low-density granulocytes in COVID-19, PLoS Pathog, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1009721
Cantoni, Wilkie, Bentley, Correlation between pseudotyped virus and authentic virus neutralisation assays, a systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1184362
Casadevall, Joyner, Pirofski, Convalescent plasma therapy in COVID-19: unravelling the data using the principles of antibody therapy, Expert Rev Respir Med
Corman, Landt, Kaiser, Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR. Euro Surveillance: bulletin Europeen, Sur Les Maladies Transmissibles ¼ Eur Commun Dis Bull
Focosi, Franchini, Pirofski, COVID-19 convalescent plasma and clinical trials: understanding conflicting outcomes, Clin Microbiol Rev, doi:10.1128/cmr.00200-21
Franchini, Cruciani, Casadevall, Safety of COVID-19 convalescent plasma: a definitive systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Transfusion, doi:10.1111/trf.17701
Franchini, Focosi, Percivalle, Variant of concern-Matched COVID-19 convalescent plasma usage in seronegative hospitalized patients, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v14071443
Fred, Kuivanen, Ugurlu, Antidepressant and antipsychotic drugs reduce viral infection by SARS-CoV-2 and fluoxetine shows antiviral activity against the novel variants in vitro, Front Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.755600
Haveri, Smura, Kuivanen, Serological and molecular findings during SARS-CoV-2 infection: the first case study in Finland, january to february 2020. Euro Surveillance: bulletin Europeen Sur Les, Maladies Transmissibles ¼ Eur Commun Dis Bull
Horby, Lim, Emberson, Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with covid-19, N Engl J Med
Iannizzi, Chai, Piechotta, Convalescent plasma for people with COVID-19: a living systematic review, Cochrane Database Syst Rev, doi:10.1002/14651858.CD013600.pub5
Jacobs, Haidar, Mellors, COVID-19: Challenges of viral variants, Annu Rev Med, doi:10.1146/annurev-med-042921-020956
Jalkanen, Kolehmainen, H€ Akkinen, Hk, COVID-19 mRNA vaccine induced antibody responses against three SARS-CoV-2 variants, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-021-24285-4
Jokinen, Edelman, Krohn, Neutralizing natural anti-IL-17F autoantibodies protect autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1 (APS-1) patients from asthma, Clin Immunol, doi:10.1016/j.clim.2020.108512
Joyner, Bruno, Klassen, Safety update: COVID-19 convalescent plasma in 20,000 hospitalized patients, Mayo Clin Proc, doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.06.028
Joyner, Senefeld, Klassen, Effect of convalescent plasma on mortality among hospitalized patients with COVID-19: initial three-Month experience, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.08.12.20169359
Kant, Nguyen, Blomqvist, Incidence trends for SARS-CoV-2 alpha and beta variants, Finland, spring 2021, Emerg Infect Dis, doi:10.3201/eid2712.211631
Kantele, Kareinen, SARS-CoV-2 infections among healthcare workers at helsinki university hospital, Finland, spring 2020: serosurvey, symptoms and risk factors, Travel Med Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/j.tmaid.2020.101949
Knip, Parviainen, Turtinen, SARS-CoV-2 and type 1 diabetes in children in Finland: an observational study, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(23)00041-4
Kurki, Kantonen, Kaivola, APOE epsilon4 associates with increased risk of severe COVID-19, cerebral microhaemorrhages and post-COVID mental fatigue: a finnish biobank, autopsy and clinical study, Acta Neuropathol Commun, doi:10.1186/s40478-021-01302-7
Levine, Fukuta, Huaman, Coronavirus disease 2019 convalescent plasma outpatient therapy to prevent outpatient hospitalization: a meta-analysis of individual participant data from 5 randomized trials, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciad088
Li, Zhang, Hu, Effect of convalescent plasma therapy on time to clinical improvement in patients with severe and life-threatening COVID-19, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.10044
Libster, P� Erez Marc, Wappner, Early high-titer plasma therapy to prevent severe covid-19 in older adults, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2033700
Luke, Kilbane, Jackson, Meta-analysis: convalescent blood products for Spanish influenza pneumonia: a future H5N1 treatment?, Ann Intern Med, doi:10.7326/0003-4819-145-8-200610170-00139
Mair-Jenkins, Saavedra-Campos, Baillie, The effectiveness of convalescent plasma and hyperimmune immunoglobulin for the treatment of severe acute respiratory infections of viral etiology: a systematic review and exploratory meta-analysis, J Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiu396
Marshall, Murthy, Diaz, A minimal common outcome measure set for COVID-19 clinical research, The Lancet Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30483-7
Misset, Piagnerelli, Hoste, Convalescent plasma for covid-19-induced ARDS in mechanically ventilated patients, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2209502
Nguyen, Plyusnin, Sironen, a bioinformatic pipeline for reference-based consensus assembly and lineage assignment for SARS-CoV-2 sequences, BMC Bioinformatics, doi:10.1186/s12859-021-04294-2
R€ Ossler, Riepler, Bante, SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant neutralization in serum from vaccinated and convalescent persons, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMc2119236
Senefeld, Gorman, Johnson, Mortality rates among hospitalized patients with COVID-19 treated with convalescent plasma: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Mayo Clin Proc Innov Qual Outcomes, doi:10.1016/j.mayocpiqo.2023.09.001
Simonovich, Pratx, Scibona, A randomized trial of convalescent plasma in covid-19 severe pneumonia, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2031304
Sullivan, Franchini, Joyner, Analysis of anti-SARS-CoV-2 omicron-neutralizing antibody titers in different vaccinated and unvaccinated convalescent plasma sources, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-022-33864-y
Sullivan, Gebo, Shoham, Early outpatient treatment for covid-19 with convalescent plasma, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2119657
Tong, Baumgart, Evangelidis, Core outcome measures for trials in people with coronavirus disease 2019: respiratory failure, multiorgan failure, shortness of breath, and recovery, Crit Care Med, doi:10.1097/CCM.0000000000004817
Vauhkonen, Nguyen, Kant, Introduction and rapid spread of SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant and dynamics of BA.1 and BA.1.1 sublineages, Finland, december 2021, Emerg Infect Dis, doi:10.3201/eid2806.220515
Virtanen, Uusitalo, Korhonen, Kinetics of neutralizing antibodies of COVID-19 patients tested using clinical D614G, B.1.1.7, and B 1.351 isolates in microneutralization assays, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v13060996
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1080/23744235.2024.2329957",
"ISSN": [
"2374-4235",
"2374-4243"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/23744235.2024.2329957",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1080/23744235.2024.2329957"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "Peer Review Statement",
"name": "peerreview_statement",
"order": 1,
"value": "The publishing and review policy for this title is described in its Aims & Scope."
},
{
"URL": "http://www.tandfonline.com/action/journalInformation?show=aimsScope&journalCode=infd20",
"label": "Aim & Scope",
"name": "aims_and_scope_url",
"order": 2,
"value": "http://www.tandfonline.com/action/journalInformation?show=aimsScope&journalCode=infd20"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2023-12-18"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 1,
"value": "2024-03-08"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 2,
"value": "2024-03-21"
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Meilahti Vaccine Research Center, MeVac, Department of Infectious Diseases, University of Helsinki and Helsinki University Hospital, Helsinki, Finland"
},
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases, University of Helsinki and Helsinki University Hospital, Helsinki, Finland"
},
{
"name": "Human Microbiome Research Program, Faculty of Medicine, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland"
},
{
"name": "FIMAR, Multidisciplinary Center of Excellence in Antimicrobial Resistance Research, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland"
}
],
"family": "Khawaja",
"given": "T.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Meilahti Vaccine Research Center, MeVac, Department of Infectious Diseases, University of Helsinki and Helsinki University Hospital, Helsinki, Finland"
},
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases, University of Helsinki and Helsinki University Hospital, Helsinki, Finland"
},
{
"name": "Human Microbiome Research Program, Faculty of Medicine, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland"
},
{
"name": "FIMAR, Multidisciplinary Center of Excellence in Antimicrobial Resistance Research, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland"
}
],
"family": "Kajova",
"given": "M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Meilahti Vaccine Research Center, MeVac, Department of Infectious Diseases, University of Helsinki and Helsinki University Hospital, Helsinki, Finland"
},
{
"name": "Human Microbiome Research Program, Faculty of Medicine, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland"
}
],
"family": "Levonen",
"given": "I.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Meilahti Vaccine Research Center, MeVac, Department of Infectious Diseases, University of Helsinki and Helsinki University Hospital, Helsinki, Finland"
},
{
"name": "Human Microbiome Research Program, Faculty of Medicine, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland"
},
{
"name": "FIMAR, Multidisciplinary Center of Excellence in Antimicrobial Resistance Research, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland"
}
],
"family": "Pietilä",
"given": "J. P.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Meilahti Vaccine Research Center, MeVac, Department of Infectious Diseases, University of Helsinki and Helsinki University Hospital, Helsinki, Finland"
},
{
"name": "Department of Virology, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland"
}
],
"family": "Välimaa",
"given": "H.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Meilahti Vaccine Research Center, MeVac, Department of Infectious Diseases, University of Helsinki and Helsinki University Hospital, Helsinki, Finland"
},
{
"name": "Department of Pulmonary Medicine, Heart and Lung Center, University of Helsinki and Helsinki University Hospital, Helsinki, Finland"
}
],
"family": "Paajanen",
"given": "J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Meilahti Vaccine Research Center, MeVac, Department of Infectious Diseases, University of Helsinki and Helsinki University Hospital, Helsinki, Finland"
},
{
"name": "Human Microbiome Research Program, Faculty of Medicine, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland"
},
{
"name": "FIMAR, Multidisciplinary Center of Excellence in Antimicrobial Resistance Research, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland"
}
],
"family": "Pakkanen",
"given": "S. H.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Meilahti Vaccine Research Center, MeVac, Department of Infectious Diseases, University of Helsinki and Helsinki University Hospital, Helsinki, Finland"
},
{
"name": "Human Microbiome Research Program, Faculty of Medicine, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland"
},
{
"name": "FIMAR, Multidisciplinary Center of Excellence in Antimicrobial Resistance Research, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland"
}
],
"family": "Patjas",
"given": "A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Virology, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland"
}
],
"family": "Montonen",
"given": "R.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Virology, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland"
},
{
"name": "Department of Veterinary Biosciences, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland"
}
],
"family": "Miettinen",
"given": "S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Virology, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland"
},
{
"name": "Department of Veterinary Biosciences, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland"
}
],
"family": "Virtanen",
"given": "J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Virology, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland"
}
],
"family": "Smura",
"given": "T.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Virology, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland"
},
{
"name": "Department of Veterinary Biosciences, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland"
}
],
"family": "Sironen",
"given": "T.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Virology, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland"
}
],
"family": "Fagerlund",
"given": "R.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Virology, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland"
}
],
"family": "Ugurlu",
"given": "H.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Virology, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland"
},
{
"name": "Department of Veterinary Biosciences, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland"
}
],
"family": "Iheozor-Ejiofor",
"given": "R.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Virology, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland"
},
{
"name": "HUS Diagnostic Centre, HUSLAB, Clinical Microbiology, Helsinki University Hospital, Helsinki, Finland"
}
],
"family": "Saksela",
"given": "K.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Biostatistics, University of Turku and Turku University Hospital, Turku, Finland"
}
],
"family": "Vahlberg",
"given": "T.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Dermatology, Allergology and Venereology, University of Helsinki and Helsinki University Hospital, Helsinki, Finland"
}
],
"family": "Ranki",
"given": "A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Finnish Red Cross Blood Service, Helsinki, Finland"
}
],
"family": "Vierikko",
"given": "A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Finnish Red Cross Blood Service, Helsinki, Finland"
}
],
"family": "Ihalainen",
"given": "J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Virology, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland"
},
{
"name": "Department of Veterinary Biosciences, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland"
},
{
"name": "HUS Diagnostic Centre, HUSLAB, Clinical Microbiology, Helsinki University Hospital, Helsinki, Finland"
}
],
"family": "Vapalahti",
"given": "O.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Meilahti Vaccine Research Center, MeVac, Department of Infectious Diseases, University of Helsinki and Helsinki University Hospital, Helsinki, Finland"
},
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases, University of Helsinki and Helsinki University Hospital, Helsinki, Finland"
},
{
"name": "Human Microbiome Research Program, Faculty of Medicine, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland"
},
{
"name": "FIMAR, Multidisciplinary Center of Excellence in Antimicrobial Resistance Research, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland"
}
],
"family": "Kantele",
"given": "A.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Infectious Diseases",
"container-title-short": "Infectious Diseases",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"www.tandfonline.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-21T18:41:53Z",
"timestamp": 1711046513000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-21T18:42:09Z",
"timestamp": 1711046529000
},
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"TYH 2021315"
],
"name": "Finnish Government Subsidy for Health Science Research"
},
{
"award": [
"335527"
],
"name": "Finnish Medical Foundationand the Academy of Finland"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-22T01:30:27Z",
"timestamp": 1711071027504
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
21
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-21T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1710979200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/23744235.2024.2329957",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "301",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1-11",
"prefix": "10.1080",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
21
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
21
]
]
},
"publisher": "Informa UK Limited",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.7326/0003-4819-145-8-200610170-00139",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_2_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiu396",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_3_1"
},
{
"key": "e_1_3_3_4_1",
"unstructured": "Directorate-General for Health and Food Safety An EU programme of COVID-19 convalescent plasma collection and transfusion: guidance on collection testing processing storage distribution and monitored use. Brussels: european Comission; 2021."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.06.028",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_5_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/trf.17701",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_6_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m3939",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_7_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.10044",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_8_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2031304",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_9_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.08.12.20169359",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_10_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00897-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_11_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1009721",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_12_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-24285-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_13_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tmaid.2020.101949",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_14_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40478-021-01302-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_15_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/vox.13113",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_16_1"
},
{
"author": "European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines & HealthCare (EDQM)",
"edition": "20",
"key": "e_1_3_3_17_1",
"unstructured": "European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines & HealthCare (EDQM). Guide to the preparation, use and quality assurance of blood components. 20th ed. Strasbourg: Council of Europe; 2020.",
"volume-title": "Guide to the preparation, use and quality assurance of blood components",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CCM.0000000000004817",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_18_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30483-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_19_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR",
"author": "Corman VM",
"first-page": "23",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Euro Surveillance: bulletin Europeen Sur Les Maladies Transmissibles = Eur Commun Dis Bull",
"key": "e_1_3_3_20_1",
"unstructured": "Corman VM, Landt O, Kaiser M, et al. Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR. Euro Surveillance: bulletin Europeen Sur Les Maladies Transmissibles = Eur Commun Dis Bull. 2020;25(3):23–30.",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3201/eid2806.220515",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_21_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12859-021-04294-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_22_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Serological and molecular findings during SARS-CoV-2 infection: the first case study in Finland, january to february 2020",
"author": "Haveri A",
"first-page": "16",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Euro Surveillance: bulletin Europeen Sur Les Maladies Transmissibles = Eur Commun Dis Bull",
"key": "e_1_3_3_23_1",
"unstructured": "Haveri A, Smura T, Kuivanen S, et al. Serological and molecular findings during SARS-CoV-2 infection: the first case study in Finland, january to february 2020. Euro Surveillance: bulletin Europeen Sur Les Maladies Transmissibles = Eur Commun Dis Bull. 2020;25(11):16–21.",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v13060996",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_24_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3201/eid2712.211631",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_25_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2021.755600",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_26_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(23)00041-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_27_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clim.2020.108512",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_28_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/cmr.00200-21",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_29_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev-med-042921-020956",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_30_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2119236",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_31_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/14651858.CD013600.pub5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_32_1"
},
{
"key": "e_1_3_3_33_1",
"unstructured": "Bhimraj AMR Shumaker AH Baden L et al. Infectious Diseases Society of America Guidelines on the Treatment and Management of Patients with COVID-19.: Infectious Diseases Society of America; 2023 [cited 2024 25th Jan]. Available from: https://www.idsociety.org/practice-guideline/covid-19-guideline-treatment-and-management/."
},
{
"key": "e_1_3_3_34_1",
"unstructured": "National Institutes of Health. COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines Panel. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Treatment Guidelines. [cited 2024 25th Jan]. Available from: https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciad088",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_35_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2033700",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_36_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2119657",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_37_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI155114",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_38_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2209502",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_39_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021436",
"article-title": "Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with covid-19",
"author": "Horby P",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "693",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "e_1_3_3_40_1",
"unstructured": "Horby P, Lim WS, Emberson JR, Recovery Collaborative Group., et al. Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(8):693–704.",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mayocpiqo.2023.09.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_41_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mbio.01751-22",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_42_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/17476348.2023.2208349",
"article-title": "Convalescent plasma therapy in COVID-19: unravelling the data using the principles of antibody therapy",
"author": "Casadevall A",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "381",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Expert Rev Respir Med",
"key": "e_1_3_3_43_1",
"unstructured": "Casadevall A, Joyner MJ, Pirofski LA, et al. Convalescent plasma therapy in COVID-19: unravelling the data using the principles of antibody therapy. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2023;17(5):381–395.",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-022-33864-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_44_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2023.1184362",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_45_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v14071443",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_46_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abd4585",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_3_47_1"
}
],
"reference-count": 46,
"references-count": 46,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/23744235.2024.2329957"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Microbiology (medical)",
"General Immunology and Microbiology",
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Double-blinded, randomised, placebo-controlled trial of convalescent plasma for COVID-19: analyses by neutralising antibodies homologous to donors’ variants",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/tandf_crossmark_01"
}