Response to Intravenous N-Acetylcysteine Supplementation in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19
et al., Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15092235, May 2023
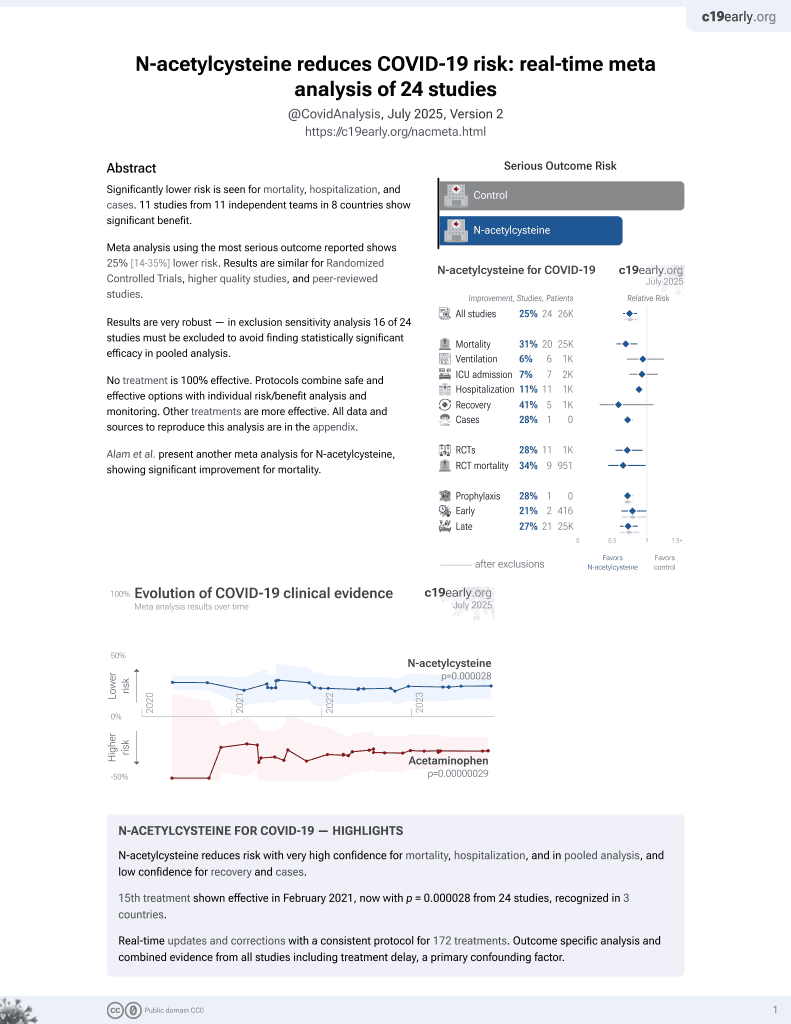
16th treatment shown to reduce risk in
February 2021, now with p = 0.0000032 from 25 studies, recognized in 3 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
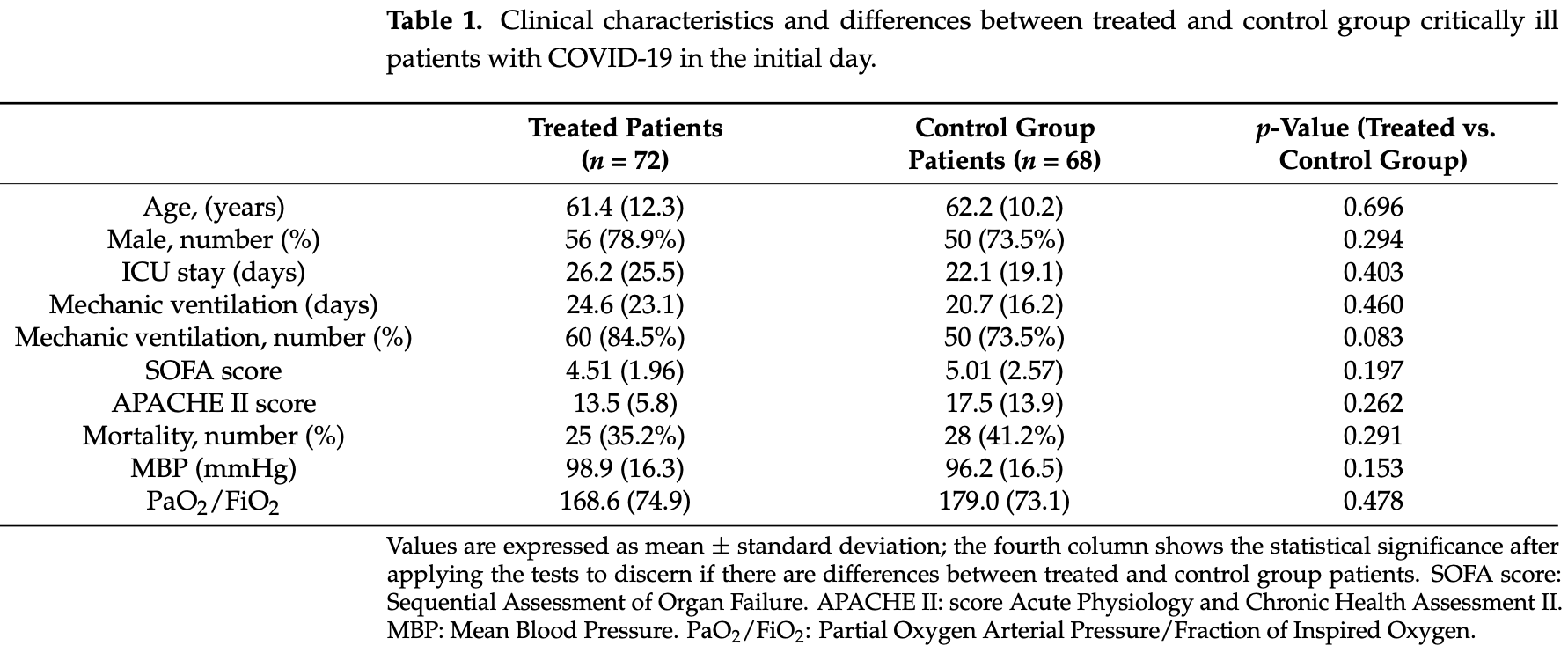
RCT 140 ICU patients in Spain, 72 treated with N-acetylcysteine (NAC). NAC patients showed improved PaO2/FiO2, CRP, D-dimer, and LDH, and there were associations between glutathione and clinical outcomes and severity biomarkers in NAC-treated patients. There was no significant difference in mortality.
|
risk of death, 15.7% lower, RR 0.84, p = 0.49, treatment 25 of 72 (34.7%), control 28 of 68 (41.2%), NNT 15.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Gamarra-Morales et al., 8 May 2023, Randomized Controlled Trial, Spain, peer-reviewed, 8 authors, study period 1 March, 2020 - 1 June, 2020.
Contact: jennifer_gamo@hotmail.com (corresponding author), jorge.molina@ddi.uhu.es.
Response to Intravenous N-Acetylcysteine Supplementation in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19
Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15092235
Administering N-acetylcysteine (NAC) could counteract the effect of free radicals, improving the clinical evolution of patients admitted to the Intensive Care Unit (ICU). This study aimed to investigate the clinical and biochemical effects of administering NAC to critically ill patients with COVID-19. A randomized controlled clinical trial was conducted on ICU patients (n = 140) with COVID-19 and divided into two groups: patients treated with NAC (NAC-treated group) and patients without NAC treatment (control group). NAC was administered as a continuous infusion with a loading dose and a maintenance dose during the study period (from admission until the third day of ICU stay). NAC-treated patients showed higher PaO 2 /FiO 2 (p ≤ 0.014) after 3 days in ICU than their control group counterparts. Moreover, C-reactive protein (p ≤ 0.001), D-dimer (p ≤ 0.042), and lactate dehydrogenase (p ≤ 0.001) levels decreased on the third day in NAC-treated patients. Glutathione concentrations decreased in both NAC-treated (p ≤ 0.004) and control (p ≤ 0.047) groups after 3 days in ICU; whereas glutathione peroxidase did not change during the ICU stay. The administration of NAC manages to improve the clinical and analytical response of seriously ill patients with COVID-19 compared to the control group. NAC is able to stop the decrease in glutathione concentrations.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Alamdari, Moghaddam, Amini, Keramati, Zarmehri et al., Application of Methylene Blue-Vitamin C-N-Acetyl Cysteine for Treatment of Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients, Eur. J. Pharm, doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173494
Assimakopoulos, Aretha, Komninos, Dimitropoulou, Lagadinou et al., N-Acetyl-Cysteine Reduces the Risk for Mechanical Ventilation and Mortality in Patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Two-Center Retrospective Cohort Study, Infect. Dis, doi:10.1080/23744235.2021.1945675
Barazzoni, Bischoff, Breda, Wickramasinghe, Krznaric et al., ESPEN Expert Statements and Practical Guidance for Nutritional Management of Individuals with SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2020.03.022
Behr, Degenkolb, Krombach, Vogelmeier, Intracellular Glutathione and Bronchoalveolar Cells in Fibrosing Alveolitis: Effects of N-Acetylcysteine, Eur. Respir. J, doi:10.1183/09031936.02.00204902
Bernard, N-Acetylcysteine in Experimental and Clinical Acute Lung Injury, Am. J. Med, doi:10.1016/0002-9343(91)90284-5
Bernhard, Junker, Hettinger, Lauterburg, Time Course of Total Cysteine, Glutathione and Homocysteine in Plasma of Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C Treated with Interferon-Alpha with and without Supplementation with N-Acetylcysteine, J. Hepatol, doi:10.1016/S0168-8278(98)80223-7
Betteridge, What Is Oxidative Stress? Metabolism, doi:10.1016/S0026-0495(00)80077-3
Borges Do Nascimento, Cacic, Abdulazeem, Von Groote, Jayarajah et al., Novel Coronavirus Infection (COVID-19) in Humans: A Scoping Review and Meta-Analysis, J. Clin. Med, doi:10.3390/jcm9040941
Chen, Wu, Guo, Cao, Huang et al., Clinical and Immunological Features of Severe and Moderate Coronavirus Disease, J. Clin. Investig, doi:10.1172/JCI137244
Connors, Levy, COVID-19 and Its Implications for Thrombosis and Anticoagulation, Blood, doi:10.1182/blood.2020006000
Darmaun, Smith, Sweeten, Hartman, Welch et al., Poorly Controlled Type 1 Diabetes Is Associated with Altered Glutathione Homeostasis in Adolescents: Apparent Resistance to N-Acetylcysteine Supplementation, Pediatr. Diabetes, doi:10.1111/j.1399-5448.2008.00436.x
De Alencar, Moreira, Müller, Chaves, Fukuhara et al., Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial With N-Acetylcysteine for Treatment of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Caused by Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19), Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa1443
De Flora, Balansky, La Maestra, Rationale for the Use of N-Acetylcysteine in Both Prevention and Adjuvant Therapy of COVID-19, FASEB J, doi:10.1096/fj.202001807
De Rosa, Zaretsky, Dubs, Roederer, Anderson et al., N-Acetylcysteine Replenishes Glutathione in HIV Infection, Eur. J. Clin. Investig, doi:10.1046/j.1365-2362.2000.00736.x
Du, Liang, Dong, Lu, Fu et al., Glutathione-Capped Ag2S Nanoclusters Inhibit Coronavirus Proliferation through Blockage of Viral RNA Synthesis and Budding, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, doi:10.1021/acsami.7b13811
Esalatmanesh, Jamali, Esalatmanesh, Soleimani, Khabbazi et al., Effects of N-Acetylcysteine Supplementation on Disease Activity, Oxidative Stress, and Inflammatory and Metabolic Parameters in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: A Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Trial, Amino Acids, doi:10.1007/s00726-022-03134-8
Fajgenbaum, Langan, Japp, Partridge, Pierson et al., Identifying and Targeting Pathogenic PI3K/AKT/MTOR Signaling in IL-6-Blockade-Refractory Idiopathic Multicentric Castleman Disease, J. Clin. Investig, doi:10.1172/JCI126091
Forman, Zhang, Rinna, Glutathione: Overview of Its Protective Roles, Measurement, and Biosynthesis. Mol. Asp. Med, doi:10.1016/j.mam.2008.08.006
Gamarra, Santiago, Molina-López, Castaño, Herrera-Quintana et al., Pyroglutamic Acidosis by Glutathione Regeneration Blockage in Critical Patients with Septic Shock, Crit. Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-019-2450-5
Gaynitdinova, Avdeev, Merzhoeva, Berikkhanov, Medvedeva et al., N-acetylcysteine as a part of complex treatment of moderate COVID-associated pneumonia, PULMONOLOGIYA, doi:10.18093/0869-0189-2021-31-1-21-29
Geiler, Michaelis, Naczk, Leutz, Langer et al., Inhibits Virus Replication and Expression of pro-Inflammatory Molecules in A549 Cells Infected with Highly Pathogenic H5N1 Influenza A Virus, Biochem. Pharm, doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2009.08.025
Girgis, Baker, Mao, Gil, Javitt et al., Effects of Acute N-Acetylcysteine Challenge on Cortical Glutathione and Glutamate in Schizophrenia: A Pilot in Vivo Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Study, Psychiatry Res, doi:10.1016/j.psychres.2019.03.018
Gordon, Jang, Bouhaddou, Xu, Obernier et al., A SARS-CoV-2 Protein Interaction Map Reveals Targets for Drug Repurposing, Nature
Gu, Gong, Zhang, Zheng, Gao et al., Multiple Organ Infection and the Pathogenesis of SARS, J. Exp. Med, doi:10.1084/jem.20050828
Gusdon, Faraday, Aita, Kumar, Mehta et al., Dendrimer Nanotherapy for Severe COVID-19 Attenuates Inflammation and Neurological Injury Markers and Improves Outcomes in a Phase2a Clinical Trial, Sci. Transl. Med, doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.abo2652
Hirai, Jones, Zelt, Da Silva, Bentley et al., Oral N-Acetylcysteine and Exercise Tolerance in Mild Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, J. Appl. Physiol, doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00990.2016
Horowitz, Freeman, Bruzzese, Efficacy of Glutathione Therapy in Relieving Dyspnea Associated with COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Report of 2 Cases, Respir. Med. Case Rep, doi:10.1016/j.rmcr.2020.101063
Ibrahim, Perl, Smith, Lewis, Kon et al., Therapeutic Blockade of Inflammation in Severe COVID-19 Infection with Intravenous N-Acetylcysteine, Clin. Immunol, doi:10.1016/j.clim.2020.108544
Ishii, Doi, Okamoto, Imamura, Dohi et al., Neutrophil Elastase Contributes to Acute Lung Injury Induced by Bilateral Nephrectomy, Am. J. Pathol, doi:10.2353/ajpath.2010.090793
Kirchner, Hermann, Möller, Klinger, Solbach et al., Flavonoids and 5-Aminosalicylic Acid Inhibit the Formation of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps, Mediat. Inflamm, doi:10.1155/2013/710239
Knaus, Draper, Wagner, Zimmerman, APACHE II: A Severity of Disease Classification System, Crit. Care Med, doi:10.1097/00003246-198510000-00009
Lai, Hanczko, Bonilla, Caza, Clair et al., Acetylcysteine Reduces Disease Activity by Blocking Mammalian Target of Rapamycin in T Cells from Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial, doi:10.1002/art.34502
Lai, Ng, Osburga Chan, Wong, Cheng, High-Dose N-Acetylcysteine Therapy for Novel H1N1 Influenza Pneumonia, Ann. Intern. Med, doi:10.7326/0003-4819-152-10-201005180-00017
Levi, Thachil, Iba, Levy, Coagulation Abnormalities and Thrombosis in Patients with COVID-19, Lancet Haematol, doi:10.1016/S2352-3026(20)30145-9
Li, Geng, Peng, Meng, Lu, Molecular Immune Pathogenesis and Diagnosis of COVID-19, J. Pharm. Anal, doi:10.1016/j.jpha.2020.03.001
Liang, Jahraus, Balta, Ziegler, Hübner et al., Sulforaphane Inhibits Inflammatory Responses of Primary Human T-Cells by Increasing ROS and Depleting Glutathione, Front. Immunol
Liu, Wang, Luo, Qian, Wu et al., Experience of N-Acetylcysteine Airway Management in the Successful Treatment of One Case of Critical Condition with COVID-19: A Case Report, Medicine, doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000022577
Madu, Belouzard, Whittaker, SARS-Coronavirus Spike S2 Domain Flanked by Cysteine Residues C822 and C833 Is Important for Activation of Membrane Fusion, Virology, doi:10.1016/j.virol.2009.07.038
Meyer, Buhl, Magnussen, The Effect of Oral N-Acetylcysteine on Lung Glutathione Levels in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis, Eur. Respir. J, doi:10.1183/09031936.94.07030431
Moradi, Mojtahedzadeh, Mandegari, Soltan-Sharifi, Najafi et al., The Role of Glutathione-S-Transferase Polymorphisms on Clinical Outcome of ALI/ARDS Patient Treated with N-Acetylcysteine, Respir. Med, doi:10.1016/j.rmed.2008.09.013
Pastore, Federici, Bertini, Piemonte, Analysis of Glutathione: Implication in Redox and Detoxification, Clin. Chim. Acta, doi:10.1016/S0009-8981(03)00200-6
Pirabbasi, Shahar, Manaf, Rajab, Manap, Efficacy of Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C) and/N-Acetylcysteine (NAC) Supplementation on Nutritional and Antioxidant Status of Male Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Patients, J. Nutr. Sci. Vitam, doi:10.3177/jnsv.62.54
Pisoschi, Pop, The Role of Antioxidants in the Chemistry of Oxidative Stress: A Review, Eur. J. Med. Chem, doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2015.04.040
Polonikov, Endogenous Deficiency of Glutathione as the Most Likely Cause of Serious Manifestations and Death in COVID-19 Patients, ACS Infect. Dis, doi:10.1021/acsinfecdis.0c00288
Porcu, Urbano, Verri, Barbosa, Baracat et al., Effects of Adjunctive N-Acetylcysteine on Depressive Symptoms: Modulation by Baseline High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein, doi:10.1016/j.psychres.2018.02.056
Prescott, Illingworth, Critchley, Stewart, Adam et al., Intravenous N-Acetylcystine: The Treatment of Choice for Paracetamol Poisoning, Br. Med. J, doi:10.1136/bmj.2.6198.1097
Qin, Zhou, Hu, Zhang, Yang et al., Dysregulation of Immune Response in Patients With Coronavirus, Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa248
Rostami, Mansouritorghabeh, Dimer Level in COVID-19 Infection: A Systematic Review, Expert. Rev. Hematol, doi:10.1080/17474086.2020.1831383
Ruan, Yang, Wang, Jiang, Song, Clinical Predictors of Mortality Due to COVID-19 Based on an Analysis of Data of 150 Patients from Wuhan, China, Intensive Care Med, doi:10.1007/s00134-020-05991-x
Rubio, Martin-Mosquero, Ortega, Peces-Barba, González-Mangado, Oral N-Acetylcysteine Attenuates Elastase-Induced Pulmonary Emphysema in Rats, Chest, doi:10.1378/chest.125.4.1500
Rushworth, Megson, Existing and Potential Therapeutic Uses for N-Acetylcysteine: The Need for Conversion to Intracellular Glutathione for Antioxidant Benefits, Pharmacol. Ther, doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.09.006
Sadowska, Manuel-Y-Keenoy, Vertongen, Schippers, Radomska-Lesniewska et al., Effect of N-Acetylcysteine on Neutrophil Activation Markers in Healthy Volunteers: In Vivo and In Vitro Study, Pharm. Res, doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2005.11.003
Safe, Amaral, Araújo-Pereira, Lacerda, Printes et al., Adjunct N-Acetylcysteine Treatment in Hospitalized Patients with HIV-Associated Tuberculosis Dampens the Oxidative Stress in Peripheral Blood: Results From the RIPENACTB Study Trial, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.602589
Schönrich, Raftery, Samstag, Devilishly Radical NETwork in COVID-19: Oxidative Stress, Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (NETs), and T Cell Suppression, Adv. Biol. Regul, doi:10.1016/j.jbior.2020.100741
Seitz, Lerch, Immel, Egbring, D-Dimer, Tests Detect Both Plasmin and Neutrophil Elastase Derived Split Products, Ann. Clin. Biochem, doi:10.1177/000456329503200211
Singer, Blaser, Berger, Alhazzani, Calder et al., ESPEN Guideline on Clinical Nutrition in the Intensive Care Unit, Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2018.08.037
Singh, Schwartz, Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation: A Devastating Systemic Disorder of Special Concern with COVID-19, Dermatol. Ther, doi:10.1111/dth.14053
Singhal, A Review of Coronavirus Disease-2019 (COVID-19), Indian. J. Pediatr, doi:10.1007/s12098-020-03263-6
Soltan-Sharifi, Mojtahedzadeh, Najafi, Reza Khajavi, Reza Rouini et al., Improvement by N-Acetylcysteine of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome through Increasing Intracellular Glutathione, and Extracellular Thiol Molecules and Anti-Oxidant Power: Evidence for Underlying Toxicological Mechanisms, Hum. Exp. Toxicol, doi:10.1177/0960327107083452
Szkudlinska, Von Frankenberg, Utzschneider, The Antioxidant N-Acetylcysteine Does Not Improve Glucose Tolerance or β-Cell Function in Type 2 Diabetes, J. Diabetes Complicat, doi:10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2016.02.003
Taher, Lashgari, Sedighi, Rahimi-Bashar, Poorolajal et al., A Pilot Study on Intravenous N-Acetylcysteine Treatment in Patients with Mild-to-Moderate COVID19-Associated Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome, doi:10.1007/s43440-021-00296-2
Takeuchi, Akira, Innate Immunity to Virus Infection, Immunol. Rev, doi:10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00737.x
Tirouvanziam, Conrad, Bottiglieri, Herzenberg, Moss et al., High-Dose Oral N-Acetylcysteine, a Glutathione Prodrug, Modulates Inflammation in Cystic Fibrosis, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.0511304103
Vincent, Moreno, Takala, Willatts, De Mendonça et al., The SOFA (Sepsis-Related Organ Failure Assessment) Score to Describe Organ Dysfunction/Failure. On Behalf of the Working Group on Sepsis-Related Problems of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine, Intensive Care Med, doi:10.1007/BF01709751
Wong, Lam, Wu, Ip, Lee et al., Plasma Inflammatory Cytokines and Chemokines in Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome, Clin. Exp. Immunol, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2249.2004.02415.x
Wool, Miller, The Impact of COVID-19 Disease on Platelets and Coagulation, Pathobiology, doi:10.1159/000512007
Xu, Shi, Wang, Zhang, Huang et al., Pathological Findings of COVID-19 Associated with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome, Lancet Respir. Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30076-X
Yang, Yu, Xu, Shu, Xia et al., A Single-Centered, Retrospective, Observational Study, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30079-5
Zhang, Li, Zhan, Wu, Yu et al., Analysis of Serum Cytokines in Patients with Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome, Infect. Immun, doi:10.1128/IAI.72.8.4410-4415.2004
Zhou, Yu, Du, Fan, Liu et al., Clinical Course and Risk Factors for Mortality of Adult Inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A Retrospective Cohort Study, Lancet
Zuin, Palamidese, Negrin, Catozzo, Scarda et al., High-Dose N-Acetylcysteine in Patients with Exacerbations of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, Clin. Drug. Investig, doi:10.2165/00044011-200525060-00005
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu15092235",
"ISSN": [
"2072-6643"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/nu15092235",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Administering N-acetylcysteine (NAC) could counteract the effect of free radicals, improving the clinical evolution of patients admitted to the Intensive Care Unit (ICU). This study aimed to investigate the clinical and biochemical effects of administering NAC to critically ill patients with COVID-19. A randomized controlled clinical trial was conducted on ICU patients (n = 140) with COVID-19 and divided into two groups: patients treated with NAC (NAC-treated group) and patients without NAC treatment (control group). NAC was administered as a continuous infusion with a loading dose and a maintenance dose during the study period (from admission until the third day of ICU stay). NAC-treated patients showed higher PaO2/FiO2 (p ≤ 0.014) after 3 days in ICU than their control group counterparts. Moreover, C-reactive protein (p ≤ 0.001), D-dimer (p ≤ 0.042), and lactate dehydrogenase (p ≤ 0.001) levels decreased on the third day in NAC-treated patients. Glutathione concentrations decreased in both NAC-treated (p ≤ 0.004) and control (p ≤ 0.047) groups after 3 days in ICU; whereas glutathione peroxidase did not change during the ICU stay. The administration of NAC manages to improve the clinical and analytical response of seriously ill patients with COVID-19 compared to the control group. NAC is able to stop the decrease in glutathione concentrations.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"nu15092235"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-0921-2168",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinical Analysis Unit, Valle de los Pedroches Hospital, Pozoblanco, 14400 Córdoba, Spain"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Gamarra-Morales",
"given": "Yenifer",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1407-322X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Physiology, School of Pharmacy, Institute of Nutrition and Food Technology “José Mataix”, University of Granada, 18071 Granada, Spain"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Herrera-Quintana",
"given": "Lourdes",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2516-5226",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Faculty of Education, Psychology and Sports Sciences, University of Huelva, 21007 Huelva, Spain"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Molina-López",
"given": "Jorge",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-0183-6902",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Physiology, School of Pharmacy, Institute of Nutrition and Food Technology “José Mataix”, University of Granada, 18071 Granada, Spain"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Vázquez-Lorente",
"given": "Héctor",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7852-6553",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Intensive Care Unit, Virgen de las Nieves Hospital, Fuerzas Armadas Avenue, 18014 Granada, Spain"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Machado-Casas",
"given": "Juan Francisco",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Intensive Care Unit, Virgen de las Nieves Hospital, Fuerzas Armadas Avenue, 18014 Granada, Spain"
}
],
"family": "Castaño-Pérez",
"given": "José",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Intensive Care Unit, Virgen de las Nieves Hospital, Fuerzas Armadas Avenue, 18014 Granada, Spain"
}
],
"family": "Pérez-Villares",
"given": "José Miguel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Physiology, School of Pharmacy, Institute of Nutrition and Food Technology “José Mataix”, University of Granada, 18071 Granada, Spain"
}
],
"family": "Planells",
"given": "Elena",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Nutrients",
"container-title-short": "Nutrients",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-09T05:06:28Z",
"timestamp": 1683608788000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-09T07:16:55Z",
"timestamp": 1683616615000
},
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"FIS PI10/1993"
],
"name": "Spanish Carlos III Health Institute"
},
{
"award": [
"REF. A-CTS-708-UGR20"
],
"name": "Consejería de Educación"
},
{
"award": [
"REF. FPU18/03702"
],
"name": "Spanish Ministry of Education"
},
{
"award": [
"REF. FPU18/03655"
],
"name": "Spanish Ministry of Education"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-10T04:42:08Z",
"timestamp": 1683693728855
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "9",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
8
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "9",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-08T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1683504000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/15/9/2235/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "2235",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
8
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
8
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00737.x",
"article-title": "Innate Immunity to Virus Infection",
"author": "Takeuchi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "75",
"journal-title": "Immunol. Rev.",
"key": "ref_1",
"volume": "227",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/IAI.72.8.4410-4415.2004",
"article-title": "Analysis of Serum Cytokines in Patients with Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4410",
"journal-title": "Infect. Immun.",
"key": "ref_2",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1365-2249.2004.02415.x",
"article-title": "Plasma Inflammatory Cytokines and Chemokines in Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome",
"author": "Wong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "95",
"journal-title": "Clin. Exp. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "136",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jpha.2020.03.001",
"article-title": "Molecular Immune Pathogenesis and Diagnosis of COVID-19",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "102",
"journal-title": "J. Pharm. Anal.",
"key": "ref_4",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0026-0495(00)80077-3",
"article-title": "What Is Oxidative Stress?",
"author": "Betteridge",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3",
"journal-title": "Metabolism",
"key": "ref_5",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00134-020-05991-x",
"article-title": "Clinical Predictors of Mortality Due to COVID-19 Based on an Analysis of Data of 150 Patients from Wuhan, China",
"author": "Ruan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "846",
"journal-title": "Intensive Care Med.",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12098-020-03263-6",
"article-title": "A Review of Coronavirus Disease-2019 (COVID-19)",
"author": "Singhal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "281",
"journal-title": "Indian. J. Pediatr.",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "87",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1084/jem.20050828",
"article-title": "Multiple Organ Infection and the Pathogenesis of SARS",
"author": "Gu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "415",
"journal-title": "J. Exp. Med.",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "202",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30079-5",
"article-title": "Clinical Course and Outcomes of Critically Ill Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A Single-Centered, Retrospective, Observational Study",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "475",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir. Med.",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mam.2008.08.006",
"article-title": "Glutathione: Overview of Its Protective Roles, Measurement, and Biosynthesis",
"author": "Forman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Mol. Asp. Med.",
"key": "ref_10",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"article-title": "Efficacy of Glutathione Therapy in Relieving Dyspnea Associated with COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Report of 2 Cases",
"author": "Horowitz",
"first-page": "101063",
"journal-title": "Respir. Med. Case Rep.",
"key": "ref_11",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acsinfecdis.0c00288",
"article-title": "Endogenous Deficiency of Glutathione as the Most Likely Cause of Serious Manifestations and Death in COVID-19 Patients",
"author": "Polonikov",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1558",
"journal-title": "ACS Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_12",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1096/fj.202001807",
"article-title": "Rationale for the Use of N-Acetylcysteine in Both Prevention and Adjuvant Therapy of COVID-19",
"author": "Balansky",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "13185",
"journal-title": "FASEB J.",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"article-title": "Clinical Course and Risk Factors for Mortality of Adult Inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A Retrospective Cohort Study",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1054",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejmech.2015.04.040",
"article-title": "The Role of Antioxidants in the Chemistry of Oxidative Stress: A Review",
"author": "Pisoschi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "55",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Med. Chem.",
"key": "ref_15",
"volume": "97",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm9040941",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_16",
"unstructured": "Borges do Nascimento, I.J., Cacic, N., Abdulazeem, H.M., von Groote, T.C., Jayarajah, U., Weerasekara, I., Esfahani, M.A., Civile, V.T., Marusic, A., and Jeroncic, A. (2020). Novel Coronavirus Infection (COVID-19) in Humans: A Scoping Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med., 9."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jbior.2020.100741",
"article-title": "Devilishly Radical NETwork in COVID-19: Oxidative Stress, Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (NETs), and T Cell Suppression",
"author": "Raftery",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100741",
"journal-title": "Adv. Biol. Regul.",
"key": "ref_17",
"volume": "77",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2013/710239",
"article-title": "Flavonoids and 5-Aminosalicylic Acid Inhibit the Formation of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps",
"author": "Kirchner",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "710239",
"journal-title": "Mediat. Inflamm.",
"key": "ref_18",
"volume": "2013",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2018.02584",
"article-title": "Sulforaphane Inhibits Inflammatory Responses of Primary Human T-Cells by Increasing ROS and Depleting Glutathione",
"author": "Liang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2584",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_19",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clim.2020.108544",
"article-title": "Therapeutic Blockade of Inflammation in Severe COVID-19 Infection with Intravenous N-Acetylcysteine",
"author": "Ibrahim",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "108544",
"journal-title": "Clin. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "219",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MD.0000000000022577",
"article-title": "Experience of N-Acetylcysteine Airway Management in the Successful Treatment of One Case of Critical Condition with COVID-19: A Case Report",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e22577",
"journal-title": "Medicine (Baltim.)",
"key": "ref_21",
"volume": "99",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173494",
"article-title": "Application of Methylene Blue-Vitamin C-N-Acetyl Cysteine for Treatment of Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients, Report of a Phase-I Clinical Trial",
"author": "Alamdari",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "173494",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Pharm.",
"key": "ref_22",
"volume": "885",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa1443",
"article-title": "Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial With N-Acetylcysteine for Treatment of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Caused by Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)",
"author": "Moreira",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e736",
"journal-title": "Clin. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_23",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s43440-021-00296-2",
"article-title": "A Pilot Study on Intravenous N-Acetylcysteine Treatment in Patients with Mild-to-Moderate COVID19-Associated Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome",
"author": "Taher",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1650",
"journal-title": "Pharm. Rep.",
"key": "ref_24",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CM9.0000000000000819",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_25",
"unstructured": "National Health Commission & National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine (2020). Diagnosis and treatment protocol for novel coronavirus pneumonia (Trial Version 7). Chin. Med. J., 133, 1087–1095."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2013.281053",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_26",
"unstructured": "World Medical Association (2013). World Medical Association World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects. JAMA, 310, 2191–2194."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clnu.2018.08.037",
"article-title": "ESPEN Guideline on Clinical Nutrition in the Intensive Care Unit",
"author": "Singer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "48",
"journal-title": "Clin. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_27",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clnu.2020.03.022",
"article-title": "ESPEN Expert Statements and Practical Guidance for Nutritional Management of Individuals with SARS-CoV-2 Infection",
"author": "Barazzoni",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1631",
"journal-title": "Clin. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.2.6198.1097",
"article-title": "Intravenous N-Acetylcystine: The Treatment of Choice for Paracetamol Poisoning",
"author": "Prescott",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1097",
"journal-title": "Br. Med. J.",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "2",
"year": "1979"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/00003246-198510000-00009",
"article-title": "APACHE II: A Severity of Disease Classification System",
"author": "Knaus",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "818",
"journal-title": "Crit. Care Med.",
"key": "ref_30",
"volume": "13",
"year": "1985"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/BF01709751",
"article-title": "The SOFA (Sepsis-Related Organ Failure Assessment) Score to Describe Organ Dysfunction/Failure. On Behalf of the Working Group on Sepsis-Related Problems of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine",
"author": "Vincent",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "707",
"journal-title": "Intensive Care Med.",
"key": "ref_31",
"volume": "22",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/23744235.2021.1945675",
"article-title": "N-Acetyl-Cysteine Reduces the Risk for Mechanical Ventilation and Mortality in Patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Two-Center Retrospective Cohort Study",
"author": "Assimakopoulos",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "847",
"journal-title": "Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_32",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18093/0869-0189-2021-31-1-21-29",
"article-title": "N-acetylcysteine as a part of complex treatment of moderate COVID-associated pneumonia",
"author": "Gaynitdinova",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "21",
"journal-title": "PULMONOLOGIYA",
"key": "ref_33",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood.2020006000",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and Its Implications for Thrombosis and Anticoagulation",
"author": "Connors",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2033",
"journal-title": "Blood",
"key": "ref_34",
"volume": "135",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2352-3026(20)30145-9",
"article-title": "Coagulation Abnormalities and Thrombosis in Patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Levi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e438",
"journal-title": "Lancet Haematol.",
"key": "ref_35",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/17474086.2020.1831383",
"article-title": "D-Dimer Level in COVID-19 Infection: A Systematic Review",
"author": "Rostami",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1265",
"journal-title": "Expert. Rev. Hematol.",
"key": "ref_36",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000512007",
"article-title": "The Impact of COVID-19 Disease on Platelets and Coagulation",
"author": "Wool",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "15",
"journal-title": "Pathobiology",
"key": "ref_37",
"volume": "88",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/000456329503200211",
"article-title": "D-Dimer Tests Detect Both Plasmin and Neutrophil Elastase Derived Split Products",
"author": "Seitz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "193",
"journal-title": "Ann. Clin. Biochem.",
"key": "ref_38",
"volume": "32",
"year": "1995"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2353/ajpath.2010.090793",
"article-title": "Neutrophil Elastase Contributes to Acute Lung Injury Induced by Bilateral Nephrectomy",
"author": "Ishii",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1665",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Pathol.",
"key": "ref_39",
"volume": "177",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/dth.14053",
"article-title": "Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation: A Devastating Systemic Disorder of Special Concern with COVID-19",
"author": "Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e14053",
"journal-title": "Dermatol. Ther.",
"key": "ref_40",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.phrs.2005.11.003",
"article-title": "Effect of N-Acetylcysteine on Neutrophil Activation Markers in Healthy Volunteers: In Vivo and In Vitro Study",
"author": "Sadowska",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "216",
"journal-title": "Pharm. Res.",
"key": "ref_41",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.0511304103",
"article-title": "High-Dose Oral N-Acetylcysteine, a Glutathione Prodrug, Modulates Inflammation in Cystic Fibrosis",
"author": "Tirouvanziam",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4628",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "ref_42",
"volume": "103",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1378/chest.125.4.1500",
"article-title": "Oral N-Acetylcysteine Attenuates Elastase-Induced Pulmonary Emphysema in Rats",
"author": "Rubio",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1500",
"journal-title": "Chest",
"key": "ref_43",
"volume": "125",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acsami.7b13811",
"article-title": "Glutathione-Capped Ag2S Nanoclusters Inhibit Coronavirus Proliferation through Blockage of Viral RNA Synthesis and Budding",
"author": "Du",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4369",
"journal-title": "ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces",
"key": "ref_44",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bcp.2009.08.025",
"article-title": "N-Acetyl-L-Cysteine (NAC) Inhibits Virus Replication and Expression of pro-Inflammatory Molecules in A549 Cells Infected with Highly Pathogenic H5N1 Influenza A Virus",
"author": "Geiler",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "413",
"journal-title": "Biochem. Pharm.",
"key": "ref_45",
"volume": "79",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/art.34502",
"article-title": "N-Acetylcysteine Reduces Disease Activity by Blocking Mammalian Target of Rapamycin in T Cells from Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial",
"author": "Lai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2937",
"journal-title": "Arthritis Rheum.",
"key": "ref_46",
"volume": "64",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2165/00044011-200525060-00005",
"article-title": "High-Dose N-Acetylcysteine in Patients with Exacerbations of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease",
"author": "Zuin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "401",
"journal-title": "Clin. Drug. Investig.",
"key": "ref_47",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.psychres.2018.02.056",
"article-title": "Effects of Adjunctive N-Acetylcysteine on Depressive Symptoms: Modulation by Baseline High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein",
"author": "Porcu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "268",
"journal-title": "Psychiatry Res.",
"key": "ref_48",
"volume": "263",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa248",
"article-title": "Dysregulation of Immune Response in Patients With Coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Qin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "762",
"journal-title": "Clin. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_49",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30076-X",
"article-title": "Pathological Findings of COVID-19 Associated with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome",
"author": "Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "420",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir. Med.",
"key": "ref_50",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI137244",
"article-title": "Clinical and Immunological Features of Severe and Moderate Coronavirus Disease 2019",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2620",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Investig.",
"key": "ref_51",
"volume": "130",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/0003-4819-152-10-201005180-00017",
"article-title": "High-Dose N-Acetylcysteine Therapy for Novel H1N1 Influenza Pneumonia",
"author": "Lai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "687",
"journal-title": "Ann. Intern. Med.",
"key": "ref_52",
"volume": "152",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virol.2009.07.038",
"article-title": "SARS-Coronavirus Spike S2 Domain Flanked by Cysteine Residues C822 and C833 Is Important for Activation of Membrane Fusion",
"author": "Madu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "265",
"journal-title": "Virology",
"key": "ref_53",
"volume": "393",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI126091",
"article-title": "Identifying and Targeting Pathogenic PI3K/AKT/MTOR Signaling in IL-6-Blockade-Refractory Idiopathic Multicentric Castleman Disease",
"author": "Fajgenbaum",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4451",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Investig.",
"key": "ref_54",
"volume": "129",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2286-9",
"article-title": "A SARS-CoV-2 Protein Interaction Map Reveals Targets for Drug Repurposing",
"author": "Gordon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "459",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_55",
"volume": "583",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-019-2450-5",
"article-title": "Pyroglutamic Acidosis by Glutathione Regeneration Blockage in Critical Patients with Septic Shock",
"author": "Gamarra",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "162",
"journal-title": "Crit. Care",
"key": "ref_56",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0009-8981(03)00200-6",
"article-title": "Analysis of Glutathione: Implication in Redox and Detoxification",
"author": "Pastore",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "19",
"journal-title": "Clin. Chim. Acta",
"key": "ref_57",
"volume": "333",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.psychres.2019.03.018",
"article-title": "Effects of Acute N-Acetylcysteine Challenge on Cortical Glutathione and Glutamate in Schizophrenia: A Pilot in Vivo Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Study",
"author": "Girgis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "78",
"journal-title": "Psychiatry Res.",
"key": "ref_58",
"volume": "275",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0168-8278(98)80223-7",
"article-title": "Time Course of Total Cysteine, Glutathione and Homocysteine in Plasma of Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C Treated with Interferon-Alpha with and without Supplementation with N-Acetylcysteine",
"author": "Bernhard",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "751",
"journal-title": "J. Hepatol.",
"key": "ref_59",
"volume": "28",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1399-5448.2008.00436.x",
"article-title": "Poorly Controlled Type 1 Diabetes Is Associated with Altered Glutathione Homeostasis in Adolescents: Apparent Resistance to N-Acetylcysteine Supplementation",
"author": "Darmaun",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "577",
"journal-title": "Pediatr. Diabetes",
"key": "ref_60",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2016.02.003",
"article-title": "The Antioxidant N-Acetylcysteine Does Not Improve Glucose Tolerance or β-Cell Function in Type 2 Diabetes",
"author": "Szkudlinska",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "618",
"journal-title": "J. Diabetes Complicat.",
"key": "ref_61",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0002-9343(91)90284-5",
"article-title": "N-Acetylcysteine in Experimental and Clinical Acute Lung Injury",
"author": "Bernard",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "54S",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_62",
"volume": "91",
"year": "1991"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0960327107083452",
"article-title": "Improvement by N-Acetylcysteine of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome through Increasing Intracellular Glutathione, and Extracellular Thiol Molecules and Anti-Oxidant Power: Evidence for Underlying Toxicological Mechanisms",
"author": "Mojtahedzadeh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "697",
"journal-title": "Hum. Exp. Toxicol.",
"key": "ref_63",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/09031936.94.07030431",
"article-title": "The Effect of Oral N-Acetylcysteine on Lung Glutathione Levels in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis",
"author": "Meyer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "431",
"journal-title": "Eur. Respir. J.",
"key": "ref_64",
"volume": "7",
"year": "1994"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/09031936.02.00204902",
"article-title": "Intracellular Glutathione and Bronchoalveolar Cells in Fibrosing Alveolitis: Effects of N-Acetylcysteine",
"author": "Behr",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "906",
"journal-title": "Eur. Respir. J.",
"key": "ref_65",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1046/j.1365-2362.2000.00736.x",
"article-title": "N-Acetylcysteine Replenishes Glutathione in HIV Infection",
"author": "Zaretsky",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "915",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Clin. Investig.",
"key": "ref_66",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.602589",
"article-title": "Adjunct N-Acetylcysteine Treatment in Hospitalized Patients with HIV-Associated Tuberculosis Dampens the Oxidative Stress in Peripheral Blood: Results From the RIPENACTB Study Trial",
"author": "Safe",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "602589",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_67",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3177/jnsv.62.54",
"article-title": "Efficacy of Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C) and/N-Acetylcysteine (NAC) Supplementation on Nutritional and Antioxidant Status of Male Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Patients",
"author": "Pirabbasi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "54",
"journal-title": "J. Nutr. Sci. Vitam.",
"key": "ref_68",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/japplphysiol.00990.2016",
"article-title": "Oral N-Acetylcysteine and Exercise Tolerance in Mild Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease",
"author": "Hirai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1351",
"journal-title": "J. Appl. Physiol. (1985)",
"key": "ref_69",
"volume": "122",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00726-022-03134-8",
"article-title": "Effects of N-Acetylcysteine Supplementation on Disease Activity, Oxidative Stress, and Inflammatory and Metabolic Parameters in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: A Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Trial",
"author": "Esalatmanesh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "433",
"journal-title": "Amino Acids",
"key": "ref_70",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.09.006",
"article-title": "Existing and Potential Therapeutic Uses for N-Acetylcysteine: The Need for Conversion to Intracellular Glutathione for Antioxidant Benefits",
"author": "Rushworth",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "150",
"journal-title": "Pharmacol. Ther.",
"key": "ref_71",
"volume": "141",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.rmed.2008.09.013",
"article-title": "The Role of Glutathione-S-Transferase Polymorphisms on Clinical Outcome of ALI/ARDS Patient Treated with N-Acetylcysteine",
"author": "Moradi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "434",
"journal-title": "Respir. Med.",
"key": "ref_72",
"volume": "103",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.abo2652",
"article-title": "Dendrimer Nanotherapy for Severe COVID-19 Attenuates Inflammation and Neurological Injury Markers and Improves Outcomes in a Phase2a Clinical Trial",
"author": "Gusdon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "eabo2652",
"journal-title": "Sci. Transl. Med.",
"key": "ref_73",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 73,
"references-count": 73,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/15/9/2235"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Food Science",
"Nutrition and Dietetics"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Response to Intravenous N-Acetylcysteine Supplementation in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "15"
}