N-acetylcysteine as a part of complex treatment of moderate COVID-associated pneumonia
et al., Pulmonologiya, doi:10.18093/0869-0189-2021-31-1-21-29, Feb 2021
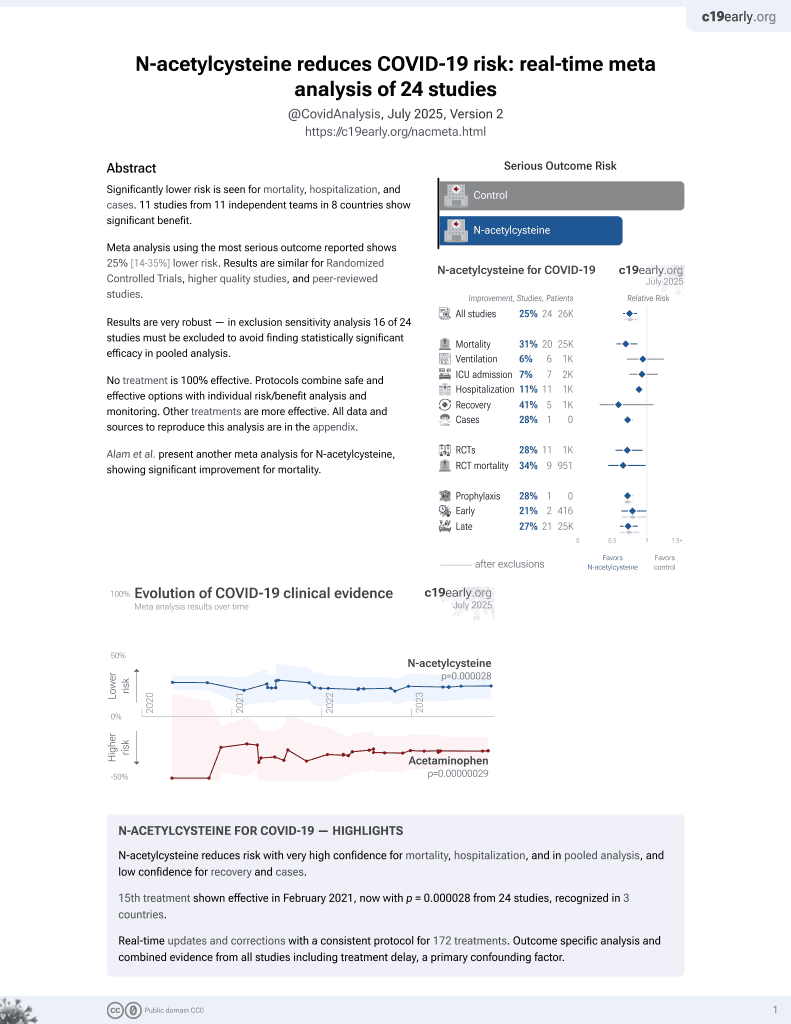
16th treatment shown to reduce risk in
February 2021, now with p = 0.0000032 from 25 studies, recognized in 3 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
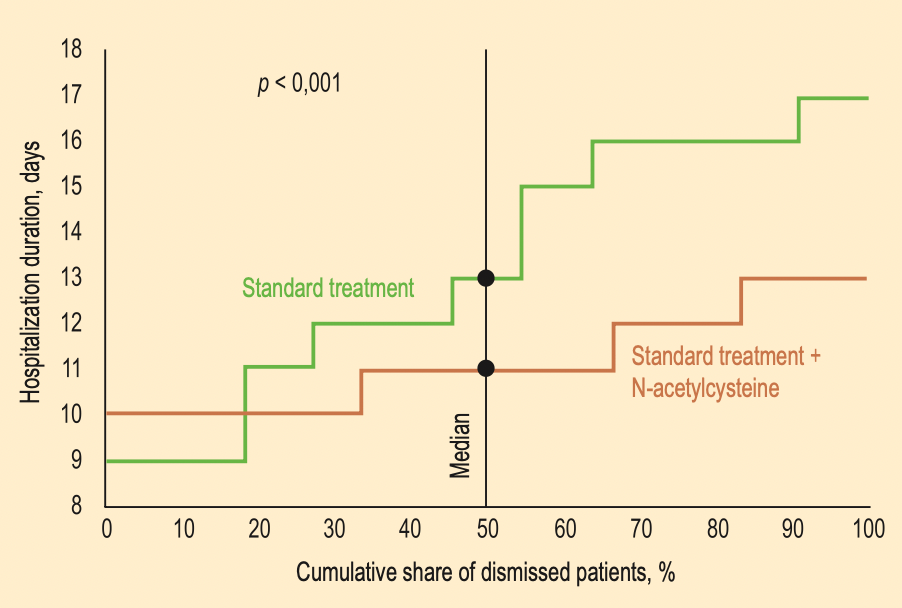
RCT 46 hospitalized patients with moderate COVID-19 pneumonia, 24 treated with N-acetylcysteine, showing significantly shorter hospitalization with treatment. NAC 1,200 - 1,500mg/day intravenously.
|
hospitalization time, 15.4% lower, relative time 0.85, p < 0.001, treatment 24, control 22.
|
|
relative improvement in lung Ct, 50.7% better, RR 0.49, p < 0.001, treatment 24, control 22.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Gaynitdinova et al., 19 Feb 2021, Randomized Controlled Trial, Russia, peer-reviewed, 6 authors, average treatment delay 7.0 days.
N-acetylcysteine as a part of complex treatment of moderate COVID-associated pneumonia
PULMONOLOGIYA, doi:10.18093/0869-0189-2021-31-1-21-29
The need for safe and effective treatment is becoming increasingly urgent due to the high COVID-19 mortality rates observed worldwide. The choice of drug products for COVID-19 treatment regimens is based on the efficacy and safety data, the mechanism of action, and potential interactions. N-acetylcysteine's (NAC) pharmacological activity and its potential to suppress the progression of COVID-19 make it a promising therapeutic agent for COVID-19. Aim of the study was to evaluate the efficacy of NAC in the complex treatment of moderate COVID-associated pneumonia. Methods. The study included adult patients (n = 46) with moderate COVID-associated (the 2 nd -3 rd degree on CT) pneumonia (age 57 (51; 71) years, body mass index -30 (27.1; 32.3) kg/m 2 , duration of the disease before hospitalization -7 (6; 8) days, body temperature at the admission -37.5 (37.1; 37.8) °С). The patients were randomized into two study groups. The 1 st group (n = 22) received standard COVID-19 treatment [1]. The 2 nd group (n = 24) additionally received NAC 1,200 -1,500 mg/day intravenously. Treatment with NAC was started together with the standard therapy. Results. Our study showed that the inclusion of NAC in the complex treatment of moderate COVID-associated pneumonia led to a statistically significant increase in blood oxygen saturation, oxygenation index, the difference in delta increase in oxygenation index, a quicker reduction in the volume of lung damage, and the difference between the groups in delta reduction of this index. Also, the rate of reduction of C-reactive protein and reduction of the duration of hospitalization in the group of patients who received NAC was statistically significantly more profound than in the standard treatment group.
Conclusion. The study confirmed the effectiveness of NAC as a part of the complex treatment of moderate COVID-associated pneumonia.
References
Abaturov, Volosovets, Borysova, Drug management of oxidation-reduction state of the body in respiratory tract diseases (part 2
Adhikari, Burns, Meade, Pharmacologic therapies for adults with acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome, Cochrane Database Syst. Rev, doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004477.pub2
Adhikari, Burns, Meade, Pharmacologic therapies for adults with acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome, Cochrane Database Syst. Rev, doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004477.pub2
Atmosfera, Pul'monologiya i allergologiya
Avdeev, Batyn, Merzhoeva, Chuchalin, High doses of N-acetylcysteine in acute respiratory distress syndrome
Avdeev, Effect of prolonged N-acetylcysteine administration on COPD exacerbation rates
Bernard, Lucht, Niedermeyer, Effect of N-acetylcysteine on the pulmonary response to endotoxin in the awake sheep and upon in vitro granulocyte function, J. Clin. Invest, doi:10.1172/JCI111386
Bernard, Lucht, Niedermeyer, Effect of N-acetylcysteine on the pulmonary response to endotoxin in the awake sheep and upon in vitro granulocyte function, J. Clin. Invest, doi:10.1172/JCI111386
Cao, Zhang, Wang, Clinical features of patients infected with the 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19)
Cao, Zhang, Wang, Clinical features of patients infected with the 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19), doi:10.1101/2020.03.04.20030395
Cascella, Rajnik, Cuomo, Features, evaluation, and treatment of coronavirus (COVID-19
Cascella, Rajnik, Cuomo, Features, evaluation, and treatment of coronavirus (COVID-19
Chousterman, Swirski, Weber, Cytokine storm and sepsis disease pathogenesis, Semin. Immunopathol, doi:10.1007/s00281-017-0639-8
Chousterman, Swirski, Weber, Cytokine storm and sepsis disease pathogenesis, Semin. Immunopathol, doi:10.1007/s00281-017-0639-8
Conti, Ronconi, Caraffa, Induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1 and IL-6) and lung inflammation by Coronavirus-19 (COVI-19 or SARS-CoV-2): anti-inflammatory strategies, J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents, doi:10.23812/CONTI-E
Conti, Ronconi, Caraffa, Induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1 and IL-6) and lung inflammation by Coronavirus-19 (COVI-19 or SARS-CoV-2): anti-inflammatory strategies, J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents, doi:10.23812/CONTI-E
Davreux, Soric, Nathens, N-acetyl cysteine attenuates acute lung injury in the rat, Shock
Davreux, Soric, Nathens, N-acetyl cysteine attenuates acute lung injury in the rat, Shock
De Alencar, Moreira, Müller, Double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial with N-acetylcysteine for treatment of severe acute respiratory syndrome caused by Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19), Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa1443
De Alencar, Moreira, Müller, Double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial with N-acetylcysteine for treatment of severe acute respiratory syndrome caused by Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19), Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa1443.Поступила12.03.20
Gaynitdinova, N-acetylcysteine as a part of complex treatment of moderately severe COVID-associated pneumonia
Guglielmetti, Quaglia, Sainaghi, War to the knife" against thromboinflammation to protect endothelial function of COVID-19 patients, Crit. Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-020-03060-9
Guglielmetti, Quaglia, Sainaghi, War to the knife" against thromboinflammation to protect endothelial function of COVID-19 patients, Crit. Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-020-03060-9
Ibrahim, Perl, Smith, Therapeutic blockade of inflammation in severe COVID-19 infection with intravenous N-acetylcysteine, Clin. Immunol, doi:10.1016/j.clim.2020.108544
Ibrahim, Perl, Smith, Therapeutic blockade of inflammation in severe COVID-19 infection with intravenous N-acetylcysteine, Clin. Immunol, doi:10.1016/j.clim.2020.108544
Island, Stat-Pearls Publishing
Island, Stat-Pearls Publishing
Kelly, Clinical application of N acetylcysteine, Altern. Med. Rev
Kelly, Clinical application of N acetylcysteine, Altern. Med. Rev
Lai, Ng, Osburga Chan, High-dose N-acetylcysteine therapy for novel H1N1 influenza pneumonia Ann, Intern. Med, doi:10.7326/0003-4819-152-10-201005180-00017
Lai, Ng, Osburga Chan, High-dose N-acetylcysteine therapy for novel H1N1 influenza pneumonia Ann, Intern. Med, doi:10.7326/0003-4819-152-10-201005180-00017
Luo, Liu, Liu, Li, Perspectives for the use of N-acetylcysteine as a candidate drug to treat COVID-19, Med. Chem, doi:10.2174/1389557520666201027160833
Luo, Liu, Liu, Li, Perspectives for the use of N-acetylcysteine as a candidate drug to treat COVID-19, Med. Chem, doi:10.2174/1389557520666201027160833
Mehta, Mcauley, Brown, COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0
Mehta, Mcauley, Brown, COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0
Olsson, Johansson, Gabrielsson, Bolme, Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of reduced and oxidized N-acetylcysteine, Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol, doi:10.1007/BF01061422
Olsson, Johansson, Gabrielsson, Bolme, Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of reduced and oxidized N-acetylcysteine, Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol, doi:10.1007/BF01061422
Pandharipande, Shintani, Hagerman, Derivation and validation of SpO 2 /FiO 2 ratio to impute for PaO 2 /FiO 2 ratio in the respiratory component of the Sequential Organ Failure Assessment score, Crit. Care Med, doi:10.1097/CCM.0b013e31819cefa9
Pandharipande, Shintani, Hagerman, Derivation and validation of SpO 2 /FiO 2 ratio to impute for PaO 2 /FiO 2 ratio in the respiratory component of the Sequential Organ Failure Assessment score, Crit. Care Med, doi:10.1097/CCM.0b013e31819cefa9
Pedersen, Ho, SARS-CoV-2: a storm is raging, J. Clin. Invest, doi:10.1172/JCI137647
Pedersen, Ho, SARS-CoV-2: a storm is raging, J. Clin. Invest, doi:10.1172/JCI137647
Poe, Corn, N-acetylcysteine: A potential therapeutic agent for SARS-CoV-2, Med. Hypotheses, doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2020.109862
Poe, Corn, N-acetylcysteine: A potential therapeutic agent for SARS-CoV-2, Med. Hypotheses, doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2020.109862
Polonikov, Endogenous deficiency of glutathione as the most likely cause of serious manifestations and death in COVID-19 patients, ACS Infect. Dis, doi:10.1021/acsin
Polonikov, Endogenous deficiency of glutathione as the most likely cause of serious manifestations and death in COVID-19 patients, ACS Infect. Dis, doi:10.1021/acsin
Rahman, Macnee, Oxidative stress and regulation of glutathione in lung inflammation, Eur. Respir. J, doi:10.1034/j.1399-3003.2000.016003534
Rahman, Macnee, Oxidative stress and regulation of glutathione in lung inflammation, Eur. Respir. J, doi:10.1034/j.1399-3003.2000.016003534
Rivellese, Prediletto, ACE2 at the centre of COVID-19 from paucisymptomatic infections to severe pneumonia, Autoimmun. Rev, doi:10.1016/j.au-trev.2020.102536
Rivellese, Prediletto, ACE2 at the centre of COVID-19 from paucisymptomatic infections to severe pneumonia, Autoimmun. Rev, doi:10.1016/j.au-trev.2020.102536
Sadowska, Manuel-Y-Keenoy, Backer, Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory efficacy of NAC in the treat-The article is licensed by CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 International Licensee, Pharmacol. Ther, doi:10.1016/j.pupt.2005.12.007
Sadowska, Manuel-Y-Keenoy, Backer, Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory efficacy of NAC in the treatment of COPD: discordant in vitro and in vivo dose-effects: A review, Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther, doi:10.1016/j.pupt.2005.12.007
Todd, Luzina, Atamas, Molecular and cellular mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis, Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair, doi:10.1186/1755-1536-5-11
Todd, Luzina, Atamas, Molecular and cellular mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis, Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair, doi:10.1186/1755-1536-5-11
Zafarullah, Li, Sylvester, Ahmad, Molecular mechanisms of N-acetylcysteine actions, Cell. Mol. Life Sci, doi:10.1007/s000180300001
Zafarullah, Li, Sylvester, Ahmad, Molecular mechanisms of N-acetylcysteine actions, Cell. Mol. Life Sci, doi:10.1007/s000180300001
Zhang, Ju, Ma, Wang, N-acetylcysteine improves oxidative stress and inflammatory response in patients with community acquired pneumonia: A randomized controlled trial, Medicine, doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000013087
Zhang, Ju, Ma, Wang, N-acetylcysteine improves oxidative stress and inflammatory response in patients with community acquired pneumonia: A randomized controlled trial, Medicine, doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000013087
Абатуров, Волосовец, Борисова, П. Медикаментозное управление окислительно-восстановительным состоянием организма при заболеваниях органов дыхания (часть 2), Здоровье ребенка, doi:10.22141/2224-0551.13.3.2018.132918
Авдеев, Батын, Мержоева, Чучалин, .Г. Высокие дозы N-ацетилцистеина при остром респираторном дистресс-синдроме, Пульмонология
Авдеев, Влияние длительного приема N-ацетилцистеина на частоту обострений ХОБЛ. Атмосфера. Пульмонология, и аллергология
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.18093/0869-0189-2021-31-1-21-29",
"ISSN": [
"2541-9617",
"0869-0189"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.18093/0869-0189-2021-31-1-21-29",
"abstract": "<jats:p>The need for safe and effective treatment is becoming increasingly urgent due to the high COVID-19 mortality rates observed worldwide. The choice of drug products for COVID-19 treatment regimens is based on the efficacy and safety data, the mechanism of action, and potential interactions. N-acetylcysteine's (NAC) pharmacological activity and its potential to suppress the progression of COVID-19 make it a promising therapeutic agent for COVID-19.<jats:bold> Aim</jats:bold> of the study was to evaluate the efficacy of NAC in the complex treatment of moderate COVID-associated pneumonia. <jats:bold>Methods</jats:bold>. The study included adult patients (<jats:italic>n</jats:italic> = 46) with moderate COVID-associated (the 2<jats:sup>nd</jats:sup> degree on CT) pneumonia (age 57 (51; 71) years, body mass index - 30 (27.1; 32.3) kg/m<jats:sup>2</jats:sup>, duration of the disease before hospitalization - 7 (6; 8) days, body temperature at the admission - 37.5 (37.1; 37.8)°С). The patients were randomized into two study groups. The 1<jats:sup>st</jats:sup> group (<jats:italic>n</jats:italic>= 22) received standard COVID-19 treatment [1]. The 2<jats:sup>nd</jats:sup> group (<jats:italic>n</jats:italic>= 24) additionally received NAC 1,200 - 1,500 mg/day intravenously. Treatment with NAC was started together with the standard therapy. <jats:bold>Results</jats:bold>. Our study showed that the inclusion of NAC in the complex treatment of moderate COVID-associated pneumonia led to a statistically significant increase in blood oxygen saturation, oxygenation index, the difference in delta increase in oxygenation index, a quicker reduction in the volume of lung damage and the difference between the groups in delta reduction of this index. Also, the rate of reduction of C-reactive protein and reduction of the duration of hospitalization in the group of patients who received NAC was statistically significantly more profound than in the standard treatment group. <jats:bold>Conclusion</jats:bold>. The study confirmed the effectiveness of NAC as a part of the complex treatment of moderate COVID-associated pneumonia.</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "I.M.Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University (Sechenov University), Healthcare Ministry of Russia"
}
],
"family": "Gaynitdinova",
"given": "V. V.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5999-2150",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "I.M.Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University (Sechenov University), Healthcare Ministry of Russia; Federal Pulmonology Research Institute, Federal Medical and Biological Agency of Russia"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Avdeev",
"given": "S. N.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "I.M.Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University (Sechenov University), Healthcare Ministry of Russia; University Clinical Hospital No.4, I.M.Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University (Sechenov University), Healthcare Ministry of Russia"
}
],
"family": "Merzhoeva",
"given": "Z. M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University Clinical Hospital No.4, I.M.Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University (Sechenov University), Healthcare Ministry of Russia"
}
],
"family": "Berikkhanov",
"given": "Z. G.-M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University Clinical Hospital No.4, I.M.Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University (Sechenov University), Healthcare Ministry of Russia"
}
],
"family": "Medvedeva",
"given": "I. V.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University Clinical Hospital No.4, I.M.Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University (Sechenov University), Healthcare Ministry of Russia"
}
],
"family": "Gorbacheva",
"given": "T. L.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"PULMONOLOGIYA"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"journal.pulmonology.ru"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2021-02-20T08:21:20Z",
"timestamp": 1613809280000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2021-02-20T08:22:52Z",
"timestamp": 1613809372000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-11T03:35:01Z",
"timestamp": 1639193701737
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 1,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "2541-9617"
},
{
"type": "print",
"value": "0869-0189"
}
],
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
19
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
19
]
]
}
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://journal.pulmonology.ru/pulm/about/editorialPolicies#openAccessPolicy",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2021-02-19T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1613692800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://journal.pulmonology.ru/pulm/article/viewFile/2263/1813",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "7431",
"original-title": [],
"page": "21-29",
"prefix": "10.18093",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
19
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
19
]
]
},
"publisher": "Scientific and Practical Reviewed Journal Pulmonology",
"reference-count": 29,
"references-count": 29,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"Pulʹmonologiâ (Mosk.)"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Pulmonary and Respiratory Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"N-acetylcysteine as a part of complex treatment of moderate COVID-associated pneumonia"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.18093/0869-0189-crossmark",
"volume": "31"
}