Double-blind, Randomized, Placebo-controlled Trial With N-acetylcysteine for Treatment of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Caused by Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)
et al., Clinical Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa1443, Sep 2020
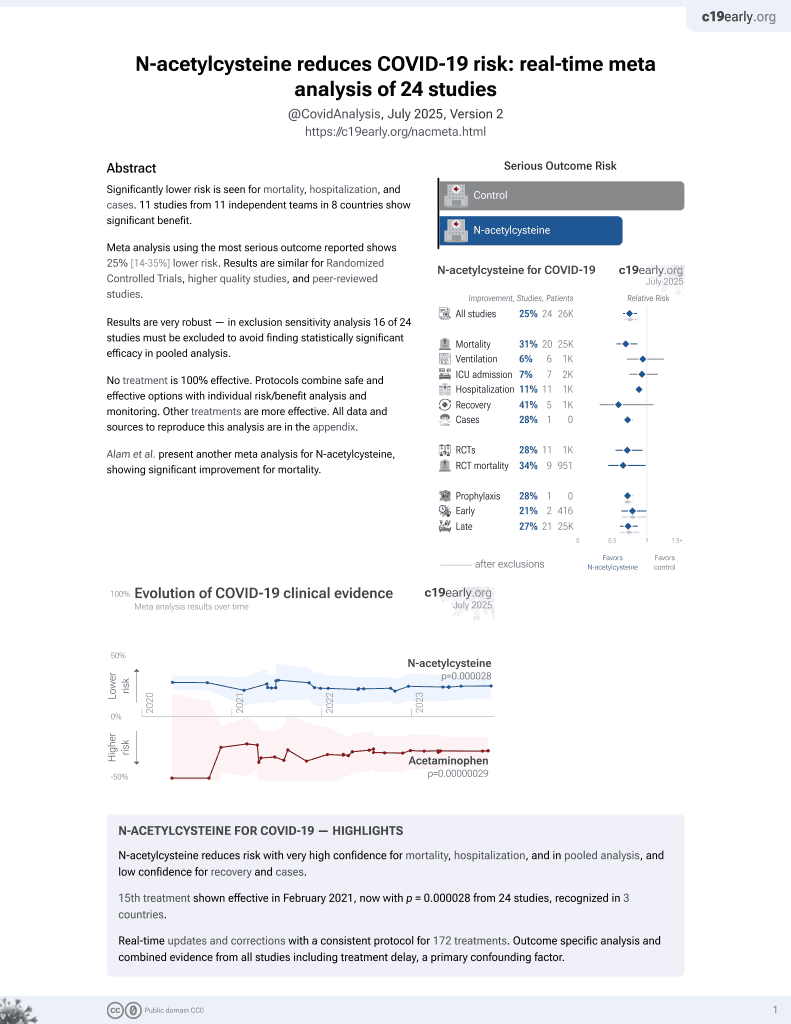
16th treatment shown to reduce risk in
February 2021, now with p = 0.0000032 from 25 studies, recognized in 3 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
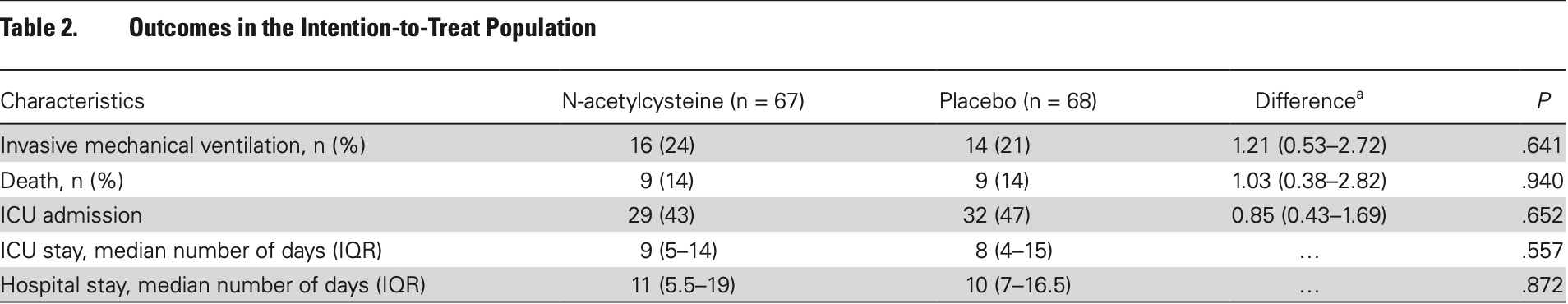
RCT 135 severe stage patients in Brazil, showing no significant differences. NAC 21g (~300mg/kg) for 20 hours. U1111-1250-3561.
|
risk of death, 2.6% higher, RR 1.03, p = 0.94, treatment 9 of 67 (13.4%), control 9 of 68 (13.2%), odds ratio converted to relative risk.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 16.0% higher, RR 1.16, p = 0.64, treatment 16 of 67 (23.9%), control 14 of 68 (20.6%), odds ratio converted to relative risk.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 8.5% lower, RR 0.91, p = 0.65, treatment 29 of 67 (43.3%), control 32 of 68 (47.1%), NNT 26, odds ratio converted to relative risk.
|
|
ICU time, 12.5% higher, relative time 1.12, p = 0.56, treatment 67, control 68.
|
|
hospitalization time, 10.0% higher, relative time 1.10, p = 0.87, treatment 67, control 68.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
de Alencar et al., 23 Sep 2020, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, Brazil, peer-reviewed, median age 59.0, 65 authors, study period 10 April, 2020 - 25 May, 2020, average treatment delay 7.0 days.
Double-blind, Randomized, Placebo-controlled Trial With N-acetylcysteine for Treatment of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Caused by Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)
Clinical Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa1443
Background. A local increase in angiotensin 2 after inactivation of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) may induce a redox imbalance in alveolar epithelium cells, causing apoptosis, increased inflammation and, consequently, impaired gas exchange. We hypothesized that N-acetylcysteine (NAC) administration could restore this redox homeostasis and suppress unfavorable evolution in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 . Methods. This was a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, single-center trial conducted at the Emergency Department of Hospital das Clínicas, São Paulo, Brazil, to determine whether NAC in high doses can avoid respiratory failure in patients with COVID-19. We enrolled 135 patients with severe COVID-19 (confirmed or suspected), with an oxyhemoglobin saturation <94% or respiratory rate >24 breaths/minute. Patients were randomized to receive NAC 21 g (~300 mg/kg) for 20 hours or dextrose 5%. The primary endpoint was the need for mechanical ventilation. Secondary endpoints were time of mechanical ventilation, admission to the intensive care unit (ICU), time in ICU, and mortality. Results. Baseline characteristics were similar between the 2 groups, with no significant differences in age, sex, comorbidities, medicines taken, and disease severity. Also, groups were similar in laboratory tests and chest computed tomography scan findings. Sixteen patients (23.9%) in the placebo group received endotracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation, compared with 14 patients (20.6%) in the NAC group (P = .675). No difference was observed in secondary endpoints. Conclusions. Administration of NAC in high doses did not affect the evolution of severe COVID-19. clinical Trials Registration. Brazilian Registry of Clinical Trials (REBEC): U1111-1250-356 (http://www.ensaiosclinicos.gov. br/rg/RBR-8969zg/).
References
Alnahdi, John, Raza, N-acetyl cysteine attenuates oxidative stress and glutathione-dependent redox imbalance caused by high glucose/high palmitic acid treatment in pancreatic Rin-5F cells, PLoS One
Atkuri, Mantovani, Herzenberg, Herzenberg, N-Acetylcysteine-a safe antidote for cysteine/glutathione deficiency, Curr Opin Pharmacol
Bunyavanich, Do, Vicencio, Nasal gene expression of angiotensinconverting enzyme 2 in children and adults, JAMA
Cao, Wang, Wen, A trial of lopinavir-ritonavir in adults hospitalized with severe Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Cazzola, Calzetta, Page, Rogliani, Matera, Thiol-based drugs in pulmonary medicine: much more than mucolytics, Trends Pharmacol Sci
Diamond, The renin-angiotensin system: an integrated view of lung disease and coagulopathy in COVID-19 and therapeutic implications, J Exp Med
Dikalov, Nazarewicz, Angiotensin II-induced production of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species: potential mechanisms and relevance for cardiovascular disease, Antioxid Redox Signal
Docherty, Harrison, Green, Features of 20 133 UK patients in hospital with covid-19 using the ISARIC WHO Clinical Characterisation Protocol: prospective observational cohort study, BMJ
Ehre, Rushton, Wang, An improved inhaled mucolytic to treat airway muco-obstructive diseases, Am J Respir Crit Care Med
Ershad, Wermuth, Vearrier, N acetylcysteine
Felice, Nardin, Tanna, Use of RAAS inhibitors and risk of clinical deterioration in COVID-19: results from an Italian cohort of 133 hypertensives, Am J Hypertens, doi:10.1093/ajh/hpaa096
Fiorentini, Falzano, Rivabene, Fabbri, Malorni, N-acetylcysteine protects epithelial cells against the oxidative imbalance due to Clostridium difficile toxins, FEBS Lett
Fisher, Curry, Evaluation and treatment of acetaminophen toxicity, Adv Pharmacol
Grasselli, Zangrillo, Zanella, Baseline characteristics and outcomes of 1591 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 admitted to ICUs of the Lombardy region, Italy, JAMA
Gurwitz, Angiotensin receptor blockers as tentative SARS-CoV-2 therapeutics, Drug Dev Res, doi:10.1002/ddr.21656
Harrison, Wendon, Gimson, Alexander, Williams, Improvement by acetylcysteine of hemodynamics and oxygen transport in fulminant hepatic failure, N Engl J Med
Hoffmann, Kleine-Weber, Schroeder, SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor, Cell
Lanza, Perez, Costa, Covid-19: the renin-angiotensin system imbalance hypothesis, Clin Sci
Laurindo, De Souza, Mde, Janiszewski, Redox aspects of vascular response to injury, Methods Enzymol
Lee, Hynan, Rossaro, Intravenous N-acetylcysteine improves transplant-free survival in early stage non-acetaminophen acute liver failure, Gastroenterology
Merad, Martin, Pathological inflammation in patients with COVID-19: a key role for monocytes and macrophages, Nat Rev Immunol
Oliveira, Laurindo, Implications of plasma thiol redox in disease, Clin Sci (Lond)
Pirola, Sookoian, Estimation of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone-system (RAAS)-inhibitor effect on COVID-19 outcome: a meta-analysis, J Infect
Redza-Dutordoir, Da, Activation of apoptosis signalling pathways by reactive oxygen species, Biochim Biophys Acta
Richardson, Hirsch, Narasimhan, Northwell COVID-19 Research Consortium. Presenting characteristics, comorbidities, and outcomes among 5700 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in the New York city area, JAMA
Smilkstein, Knapp, Kulig, Rumack, Efficacy of oral N-acetylcysteine in the treatment of acetaminophen overdose: analysis of the national multicenter study (1976 to 1985), N Engl J Med
Souza, Frediani, Cobra, Angiotensin II modulates CD40 expression in vascular smooth muscle cells, Clin Sci (Lond)
Sturrock, Milne, Chevassut, The renin-angiotensin system -a therapeutic target in COVID-19?, Clin Med (Lond), doi:10.7861/clinmed.2020-0146
Tay, Poh, Rénia, Macary, Ng, The trinity of COVID-19: immunity, inflammation and intervention, Nat Rev Immunol
Touyz, Li, Delles, ACE2 the Janus-faced protein-from cardiovascular protection to severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus and COVID-19, Clin Sci
Wang, Zhang, Bai, An anti-oxidative therapy for ameliorating cardiac injuries of critically ill COVID-19-infected patients, Int J Cardiol
Wong, Graudins, Simplification of the standard three-bag intravenous acetylcysteine regimen for paracetamol poisoning results in a lower incidence of adverse drug reactions, Clin Toxicol (Phila)
Wu, Hu, Zhang, Ren, Yu et al., Elevation of plasma angiotensin II level is a potential pathogenesis for the critically ill COVID-19 patients, Crit Care
Wu, Leung, Bushman, Estimating clinical severity of COVID-19 from the transmission dynamics in Wuhan, China, Nat Med
Zhang, Wang, Ni, COVID-19: melatonin as a potential adjuvant treatment, Life Sci
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa1443",
"ISSN": [
"1058-4838",
"1537-6591"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciaa1443",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Background</jats:title>\n <jats:p>A local increase in angiotensin 2 after inactivation of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) may induce a redox imbalance in alveolar epithelium cells, causing apoptosis, increased inflammation and, consequently, impaired gas exchange. We hypothesized that N-acetylcysteine (NAC) administration could restore this redox homeostasis and suppress unfavorable evolution in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>This was a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, single-center trial conducted at the Emergency Department of Hospital das Clínicas, São Paulo, Brazil, to determine whether NAC in high doses can avoid respiratory failure in patients with COVID-19. We enrolled 135 patients with severe COVID-19 (confirmed or suspected), with an oxyhemoglobin saturation &lt;94% or respiratory rate &gt;24 breaths/minute. Patients were randomized to receive NAC 21 g (~300 mg/kg) for 20 hours or dextrose 5%. The primary endpoint was the need for mechanical ventilation. Secondary endpoints were time of mechanical ventilation, admission to the intensive care unit (ICU), time in ICU, and mortality.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Baseline characteristics were similar between the 2 groups, with no significant differences in age, sex, comorbidities, medicines taken, and disease severity. Also, groups were similar in laboratory tests and chest computed tomography scan findings. Sixteen patients (23.9%) in the placebo group received endotracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation, compared with 14 patients (20.6%) in the NAC group (P = .675). No difference was observed in secondary endpoints.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Administration of NAC in high doses did not affect the evolution of severe COVID-19.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Clinical Trials Registration</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Brazilian Registry of Clinical Trials (REBEC): U1111-1250-356 (http://www.ensaiosclinicos.gov.br/rg/RBR-8969zg/).</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Emergency Medicine Department, Faculdade de Medicina da Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil"
}
],
"family": "de Alencar",
"given": "Julio Cesar Garcia",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Emergency Medicine Department, Faculdade de Medicina da Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil"
}
],
"family": "Moreira",
"given": "Claudia de Lucena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Emergency Medicine Department, Faculdade de Medicina da Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil"
}
],
"family": "Müller",
"given": "Alicia Dudy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pharmacy Division, Instituto Central do Hospital das Clínicas da Faculdade de Medicina da Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil"
}
],
"family": "Chaves",
"given": "Cleuber Esteves",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pharmacy Division, Instituto Central do Hospital das Clínicas da Faculdade de Medicina da Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil"
}
],
"family": "Fukuhara",
"given": "Marina Akemi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pharmacy Division, Instituto Central do Hospital das Clínicas da Faculdade de Medicina da Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil"
}
],
"family": "da Silva",
"given": "Elizabeth Aparecida",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pharmacy Division, Instituto Central do Hospital das Clínicas da Faculdade de Medicina da Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil"
}
],
"family": "Miyamoto",
"given": "Maria de Fátima Silva",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pharmacy Division, Instituto Central do Hospital das Clínicas da Faculdade de Medicina da Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil"
}
],
"family": "Pinto",
"given": "Vanusa Barbosa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Emergency Medicine Department, Faculdade de Medicina da Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil"
}
],
"family": "Bueno",
"given": "Cauê Gasparotto",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Emergency Medicine Department, Faculdade de Medicina da Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil"
}
],
"family": "Lazar Neto",
"given": "Felippe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Emergency Medicine Department, Faculdade de Medicina da Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil"
}
],
"family": "Gomez Gomez",
"given": "Luz Marina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Emergency Medicine Department, Faculdade de Medicina da Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil"
}
],
"family": "Menezes",
"given": "Maria Clara Saad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Emergency Medicine Department, Faculdade de Medicina da Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil"
}
],
"family": "Marchini",
"given": "Julio Flavio Meirelles",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Emergency Medicine Department, Faculdade de Medicina da Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil"
}
],
"family": "Marino",
"given": "Lucas Oliveira",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Emergency Medicine Department, Faculdade de Medicina da Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil"
}
],
"family": "Brandão Neto",
"given": "Rodrigo Antônio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2499-5674",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Emergency Medicine Department, Faculdade de Medicina da Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Souza",
"given": "Heraldo Possolo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Valente",
"given": "Fernando Salvetti",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rahhal",
"given": "Hassan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pereira",
"given": "Juliana Batista Rodrigues",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Padrão",
"given": "Eduardo Messias Hirano",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wanderley",
"given": "Annelise Passos Bispos",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marques",
"given": "Bruno",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gomez",
"given": "Luz Marina Gomez",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "D’Souza",
"given": "Edwin Albert",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bellintani",
"given": "Arthur Petrillo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Miléo",
"given": "Rodrigo Cezar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Toccoli",
"given": "Rodrigo Werner",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Silva",
"given": "Fernanda Máximo Fonseca e",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Baptista",
"given": "João Martelleto",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Silva",
"given": "Marcelo de Oliveira",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Costa",
"given": "Giovanna Babikian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Luna",
"given": "Rafael Berenguer",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "dos Santos",
"given": "Henrique Tibucheski",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "De Calasans",
"given": "Mariana Mendes Gonçalves Cimatti",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sanches",
"given": "Marcelo Petrof",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Takamune",
"given": "Diego Juniti",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Boscolo",
"given": "Luiza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Simões",
"given": "Pedro Antonio Araújo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pandolfi",
"given": "Manuela Cristina Adsuara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fantinatti",
"given": "Beatriz Larios",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Travessini",
"given": "Gabriel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "de Faria",
"given": "Matheus Finardi Lima",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lima",
"given": "Ligia Trombetta",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nicolao",
"given": "Bianca Ruiz",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Escudeiro",
"given": "Gabriel de Paula Maroni",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nascimento",
"given": "João Pedro Afonso",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Caldeira",
"given": "Bruna Tolentino",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Campos",
"given": "Laura de Góes",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Medeiros",
"given": "Vitor Macedo Brito",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Monsalvarga",
"given": "Tales Cabral",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Omori",
"given": "Isabela Harumi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Guidotte",
"given": "Diogo Visconti",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bortolotto",
"given": "Alexandre Lemos",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abreu",
"given": "Rodrigo de Souza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Martins",
"given": "Nilo Arthur Bezerra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Juck",
"given": "Carlos Eduardo Umehara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Utiyama",
"given": "Lucas de Oliveira",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bortoleto",
"given": "Felipe Mouzo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tinel",
"given": "Renan Dourado",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Andreola",
"given": "Gabriel Martinez",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cardoso",
"given": "Natalia Paula",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Claure",
"given": "Osvaldo Santistevan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lopes",
"given": "João Vitor Ziroldo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "da Costa Ribeiro",
"given": "Sabrina Correa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"name": "COVID Register Group",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Clinical Infectious Diseases"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2020-09-21T19:23:22Z",
"timestamp": 1600716202000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-06-01T07:58:46Z",
"timestamp": 1622534326000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100001807",
"award": [
"2016/14566-4",
"2020/04738-8"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-06T10:48:10Z",
"timestamp": 1641466090252
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 20,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "1058-4838"
},
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "1537-6591"
}
],
"issue": "11",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9,
23
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "11",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9,
23
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
1
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/journals/pages/open_access/funder_policies/chorus/standard_publication_model",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2020-09-23T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1600819200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "http://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/cid/ciaa1443/34124822/ciaa1443.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "am",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "http://academic.oup.com/cid/article-pdf/72/11/e736/38389463/ciaa1443.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "http://academic.oup.com/cid/article-pdf/72/11/e736/38389463/ciaa1443.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "286",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e736-e741",
"prefix": "10.1093",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9,
23
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
9,
23
]
]
},
"published-other": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
1
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
1
]
]
},
"publisher": "Oxford University Press (OUP)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.6775",
"article-title": "Presenting characteristics, comorbidities, and outcomes among 5700 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in the New York city area",
"author": "Richardson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2052",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "2021060106120827900_CIT0001",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m1985",
"article-title": "Features of 20 133 UK patients in hospital with covid-19 using the ISARIC WHO Clinical Characterisation Protocol: prospective observational cohort study",
"author": "Docherty",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "m1985",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "2021060106120827900_CIT0002",
"volume": "369",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.5394",
"article-title": "Baseline characteristics and outcomes of 1591 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 admitted to ICUs of the Lombardy region, Italy",
"author": "Grasselli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1574",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "2021060106120827900_CIT0003",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-020-0311-8",
"article-title": "The trinity of COVID-19: immunity, inflammation and intervention",
"author": "Tay",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "363",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Immunol",
"key": "2021060106120827900_CIT0004",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor",
"author": "Hoffmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "271",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "2021060106120827900_CIT0005",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/CS20200363",
"article-title": "ACE2 the Janus-faced protein—from cardiovascular protection to severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus and COVID-19",
"author": "Touyz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "747",
"journal-title": "Clin Sci",
"key": "2021060106120827900_CIT0006",
"volume": "134",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-03015-0",
"article-title": "Elevation of plasma angiotensin II level is a potential pathogenesis for the critically ill COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "290",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "2021060106120827900_CIT0007",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.8707",
"article-title": "Nasal gene expression of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in children and adults",
"author": "Bunyavanich",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2427",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "2021060106120827900_CIT0008",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0076-6879(02)52039-5",
"article-title": "Redox aspects of vascular response to injury",
"author": "Laurindo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "432",
"journal-title": "Methods Enzymol",
"key": "2021060106120827900_CIT0009",
"volume": "352",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/ars.2012.4604",
"article-title": "Angiotensin II-induced production of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species: potential mechanisms and relevance for cardiovascular disease",
"author": "Dikalov",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1085",
"journal-title": "Antioxid Redox Signal",
"key": "2021060106120827900_CIT0010",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbamcr.2016.09.012",
"article-title": "Activation of apoptosis signalling pathways by reactive oxygen species",
"author": "Redza-Dutordoir",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2977",
"journal-title": "Biochim Biophys Acta",
"key": "2021060106120827900_CIT0011",
"volume": "1863",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/CS20080155",
"article-title": "Angiotensin II modulates CD40 expression in vascular smooth muscle cells",
"author": "Souza",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "423",
"journal-title": "Clin Sci (Lond)",
"key": "2021060106120827900_CIT0012",
"volume": "116",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.201802-0245OC",
"article-title": "An improved inhaled mucolytic to treat airway muco-obstructive diseases",
"author": "Ehre",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "171",
"journal-title": "Am J Respir Crit Care Med",
"key": "2021060106120827900_CIT0013",
"volume": "199",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2009.06.006",
"article-title": "Intravenous N-acetylcysteine improves transplant-free survival in early stage non-acetaminophen acute liver failure",
"author": "Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "856",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "2021060106120827900_CIT0014",
"volume": "137",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/bs.apha.2018.12.004",
"article-title": "Evaluation and treatment of acetaminophen toxicity",
"author": "Fisher",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "263",
"journal-title": "Adv Pharmacol",
"key": "2021060106120827900_CIT0015",
"volume": "85",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tips.2019.04.015",
"article-title": "Thiol-based drugs in pulmonary medicine: much more than mucolytics",
"author": "Cazzola",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "452",
"journal-title": "Trends Pharmacol Sci",
"key": "2021060106120827900_CIT0016",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"author": "Ershad",
"key": "2021060106120827900_CIT0017",
"volume-title": "N acetylcysteine",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/CS20180157",
"article-title": "Implications of plasma thiol redox in disease",
"author": "Oliveira",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1257",
"journal-title": "Clin Sci (Lond)",
"key": "2021060106120827900_CIT0018",
"volume": "132",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/CS20200492",
"article-title": "Covid-19: the renin–angiotensin system imbalance hypothesis",
"author": "Lanza",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1259",
"journal-title": "Clin Sci",
"key": "2021060106120827900_CIT0019",
"volume": "134",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3109/15563650.2015.1115055",
"article-title": "Simplification of the standard three-bag intravenous acetylcysteine regimen for paracetamol poisoning results in a lower incidence of adverse drug reactions",
"author": "Wong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "115",
"journal-title": "Clin Toxicol (Phila)",
"key": "2021060106120827900_CIT0020",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001282",
"article-title": "A trial of lopinavir-ritonavir in adults hospitalized with severe Covid-19",
"author": "Cao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1787",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2021060106120827900_CIT0021",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1084/jem.20201000",
"article-title": "The renin–angiotensin system: an integrated view of lung disease and coagulopathy in COVID-19 and therapeutic implications",
"author": "Diamond",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e20201000",
"journal-title": "J Exp Med",
"key": "2021060106120827900_CIT0022",
"volume": "217",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7861/clinmed.2020-0146",
"article-title": "The renin-angiotensin system - a therapeutic target in COVID-19?",
"author": "Sturrock",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e72",
"journal-title": "Clin Med (Lond)",
"key": "2021060106120827900_CIT0023",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.coph.2007.04.005",
"article-title": "N-Acetylcysteine–a safe antidote for cysteine/glutathione deficiency",
"author": "Atkuri",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "355",
"journal-title": "Curr Opin Pharmacol",
"key": "2021060106120827900_CIT0024",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0226696",
"article-title": "N-acetyl cysteine attenuates oxidative stress and glutathione-dependent redox imbalance caused by high glucose/high palmitic acid treatment in pancreatic Rin-5F cells",
"author": "Alnahdi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e0226696",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "2021060106120827900_CIT0025",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0014-5793(99)00706-1",
"article-title": "N-acetylcysteine protects epithelial cells against the oxidative imbalance due to Clostridium difficile toxins",
"author": "Fiorentini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "124",
"journal-title": "FEBS Lett",
"key": "2021060106120827900_CIT0026",
"volume": "453",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJM199106273242604",
"article-title": "Improvement by acetylcysteine of hemodynamics and oxygen transport in fulminant hepatic failure",
"author": "Harrison",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1852",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2021060106120827900_CIT0027",
"volume": "324",
"year": "1991"
},
{
"article-title": "Efficacy of oral N-acetylcysteine in the treatment of acetaminophen overdose: analysis of the national multicenter study (1976 to 1985)",
"author": "Smilkstein",
"first-page": "319",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2021060106120827900_CIT0028",
"year": "1988"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-020-0331-4",
"article-title": "Pathological inflammation in patients with COVID-19: a key role for monocytes and macrophages",
"author": "Merad",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "355",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Immunol",
"key": "2021060106120827900_CIT0029",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-0822-7",
"article-title": "Estimating clinical severity of COVID-19 from the transmission dynamics in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "506",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "2021060106120827900_CIT0030",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2020.05.052",
"article-title": "Estimation of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone-system (RAAS)-inhibitor effect on COVID-19 outcome: a meta-analysis",
"author": "Pirola",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "276",
"journal-title": "J Infect",
"key": "2021060106120827900_CIT0031",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajh/hpaa096",
"article-title": "Use of RAAS inhibitors and risk of clinical deterioration in COVID-19: results from an Italian cohort of 133 hypertensives",
"author": "Felice",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Am J Hypertens",
"key": "2021060106120827900_CIT0032",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ddr.21656",
"article-title": "Angiotensin receptor blockers as tentative SARS-CoV-2 therapeutics",
"author": "Gurwitz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "537",
"journal-title": "Drug Dev Res",
"key": "2021060106120827900_CIT0033",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijcard.2020.04.009",
"article-title": "An anti-oxidative therapy for ameliorating cardiac injuries of critically ill COVID-19-infected patients",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "137",
"journal-title": "Int J Cardiol",
"key": "2021060106120827900_CIT0034",
"volume": "312",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117583",
"article-title": "COVID-19: melatonin as a potential adjuvant treatment",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "117583",
"journal-title": "Life Sci",
"key": "2021060106120827900_CIT0035",
"volume": "250",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 35,
"references-count": 35,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Microbiology (medical)"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Double-blind, Randomized, Placebo-controlled Trial With N-acetylcysteine for Treatment of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Caused by Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "72"
}