Earlier clinical improvement in mild-moderate acute COVID patients treated with pharmacological-grade Curcumin
et al., Authorea Inc., doi:10.22541/au.174904567.74543434/v1, CURCOVID, Jun 2025
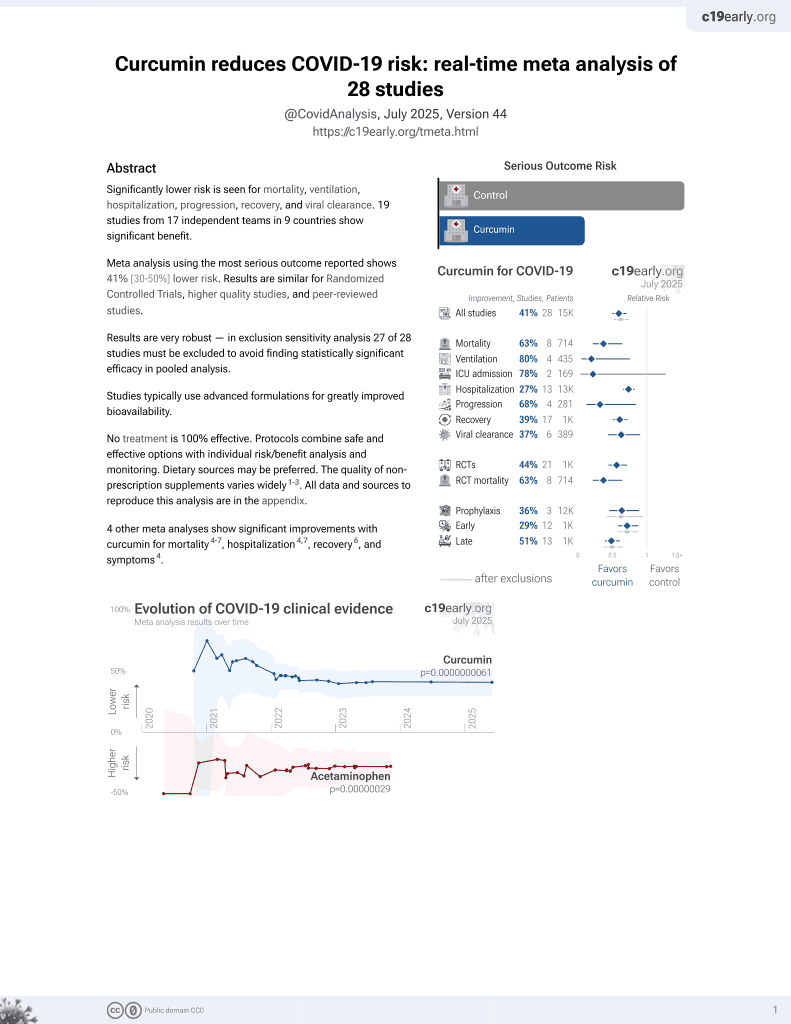
Curcumin for COVID-19
17th treatment shown to reduce risk in
February 2021, now with p = 0.0000000061 from 28 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
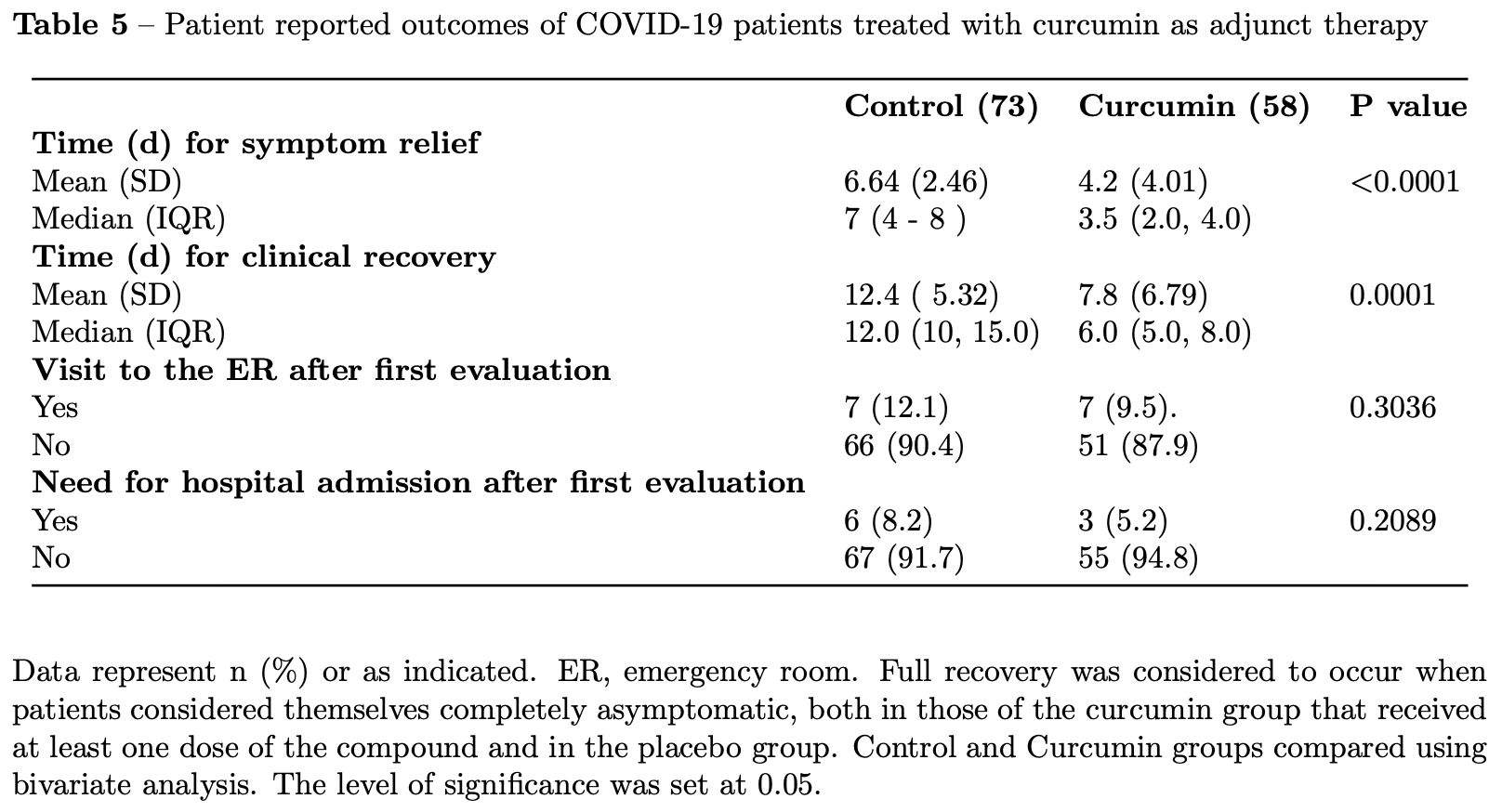
Prospective study of 131 mild-moderate COVID-19 patients showing significant reduction in time to symptom relief and complete recovery with pharmaceutical-grade curcumin.
This is the 28th COVID-19 controlled study for curcumin, which collectively show efficacy with p=0.0000000061.
21 studies are RCTs, which show efficacy with p=0.0000022.
|
risk of hospitalization, 37.1% lower, RR 0.63, p = 0.73, treatment 3 of 58 (5.2%), control 6 of 73 (8.2%), NNT 33.
|
|
ER visit, 25.9% higher, RR 1.26, p = 0.78, treatment 7 of 58 (12.1%), control 7 of 73 (9.6%).
|
|
clinical recovery, 37.1% lower, RR 0.63, p < 0.001, treatment mean 7.8 (±6.79) n=58, control mean 12.4 (±5.32) n=73.
|
|
symptom relief, 36.7% lower, RR 0.63, p < 0.001, treatment mean 4.2 (±4.01) n=58, control mean 6.64 (±2.46) n=73.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Alcântara et al., 4 Jun 2025, prospective, Brazil, preprint, mean age 44.9, 6 authors, study period 15 March, 2021 - 5 May, 2022, CURCOVID trial.
Contact: arocha@ufc.br.
Earlier clinical improvement in mild-moderate acute COVID patients treated with pharmacological-grade Curcumin
doi:10.22541/au.174904567.74543434/v1
Heavy curcumin consumers apparently had a lower-than-expected COVID-19 death rate. Curcumin modulates angiotensinconverting enzyme expression, which may impair SARS-CoV-2 entry into host cells. Our data show that curcumin provides earlier recovery in acute COVID-19. Curcovid was an observational study conducted from Mar21-May22. Individuals > 18 years, with [?]2 days of symptoms, seen at Emergency Room or Telehealth system with positive SARS-Cov-2 PCR and mild/moderate disease were invited to immediately add a pharmaceutical-grade curcumin formulation (1g/d/10 days) alongside usual care. Primary outcomes were self-reported time to symptom relief and judgement of full recovery. Patients who used curcumin were compared to those who did not add the compound to their treatment regimen (Control). There were 73 and 58 patients in usual care and curcumin groups, respectively; mean age was 44.9 ± 13.9 years-old with 52 (39.7%) male; 3 days after study entry, fewer patients using curcumin had dyspnea (p=0.0164); systolic BP and serum creatinine were lower in curcumin group (p=0.0035 and 0.038, respectively). Time for symptom relief was 6.6±2.4 and 4.2±4 days in control and curcumin groups, respectively (p<0.0001); time for complete recovery was 12.4±5.3 and 7.8±6.7 days in control and curcumin groups, respectively (p<0.0001). No serious adverse events reported in both groups. Early administration of curcumin reduced time for complete recovery in acute COVID-19.
Author Contributions statement: ACCA conceived, conducted, processed the data, and wrote the manuscript; DLCQ conducted and processed the data of the protocol; HALR statistical analysis; MRA and ACMDP analysed the data; FACR conceived, conducted, processed the data, and wrote the manuscript; all authors read, revised, and approved the final version of the manuscript.
References
Akinyemi, Effect of dietary supplementation of ginger and turmeric rhizomes on angiotensin-1 converting enzyme (ACE) and arginase activities in L-NAME induced hypertensive rats, Journal of Functional Foods
Alcantara, Ease in Emergency Hospital Visits Due to Covid-19 Following Implementation of a Telemedicine Service in Ceara, Brazil, Telemed J E Health
Amtaghri, Slaoui, Eddouks, Phytomedical compounds as promising therapeutic agents for COVID-19 targeting angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: a review, Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology
Belcaro, Efficacy and safety of Meriva (r), a curcumin-phosphatidylcholine complex, during extended administration in osteoarthritis patients, Altern Med Rev
Cuomo, Comparative absorption of a standardized curcuminoid mixture and its lecithin formulation, J Nat Prod
Esatbeyoglu, Huebbe, Ernst, Chin, Wagner et al., Curcumin-from molecule to biological function, Angew Chem Int Ed Engl
Fazal, Fatima, Shahid, Mahboob, Effects of curcumin on angiotensin-converting enzyme gene expression, oxidative stress and anti-oxidant status in thioacetamide-induced hepatotoxicity, Journal of the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System
Hammond, Fountaine, Yunis, Nirmatrelvir for Vaccinated or Unvaccinated Adult Outpatients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Menni, Symptom prevalence, duration, and risk of hospital admission in individuals infected with SARS-CoV-2 during periods of omicron and delta variant dominance: a prospective observational study from the ZOE COVID Study, Lancet
Pang, Attenuation of myocardial fibrosis with curcumin is mediated by modulating expression of angiotensin II AT1/AT2 receptors and ACE2 in rats, Drug Design, Development and Therapy
Paules, Fauci, COVID-19: the therapeutic landscape, Med (N Y)
Peters, COVID-19-related genes in sputum cells in asthma. Relationship to demographic features and corticosteroids, Am J Respir Crit Care Med
Pieralli, Real-world use of remdesivir for the treatment of patients admitted to Italian hospitals with COVID-19: the nationwide retrospective FADOI-RECOVER study, BMC Infect Dis
Qaseem, Outpatient Treatment of Confirmed COVID-19: Living, Rapid Practice Points From the American College of Physicians (Version 2, Update Alert), Ann Intern Med
Ramakrishnan, Inhaled budesonide in the treatment of early COVID-19 (STOIC): a phase 2, open-label, randomised controlled trial, Lancet Respir Med
Rocha, De Assis, Curcumin as a potential treatment for COVID-19, Phytother Res
Schilling, Antiviral efficacy of molnupiravir versus ritonavir-boosted nirmatrelvir in patients with early symptomatic COVID-19 (PLATCOV): an open-label, phase 2, randomised, controlled, adaptive trial, Lancet Infect Dis
Shanmugarajan, Kumar, Suresh, Curcumin to inhibit binding of spike glycoprotein to ACE2 receptors: computational modelling, simulations, and ADMET studies to explore curcuminoids against novel SARS-CoV-2 targets, RSC Adv
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.22541/au.174904567.74543434/v1",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.22541/au.174904567.74543434/v1",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
6,
4
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Universidade Federal do Ceara Faculdade de Medicina"
}
],
"family": "Alcântara",
"given": "Antonia Célia de Castro",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Universidade Federal do Ceara Faculdade de Medicina"
}
],
"family": "Queiroz",
"given": "Daniele Leite Cunha de",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Universidade Federal do Ceara Faculdade de Medicina"
}
],
"family": "Pinto",
"given": "Ana Carolina M. Dinelly",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6567-4570",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Fundacao Educacional do Municipio de Assis"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Assis",
"given": "Marcos Renato de",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Universidade Federal do Ceara Faculdade de Medicina"
}
],
"family": "Rocha",
"given": "Hermano Alexandre Lima",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4370-3294",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Universidade Federal do Ceara Faculdade de Medicina"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Rocha",
"given": "Francisco",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
6,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2025-06-04T14:01:17Z",
"timestamp": 1749045677000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
6,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2025-06-04T14:01:17Z",
"timestamp": 1749045677000
},
"group-title": "Preprints",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
6,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2025-06-05T04:13:23Z",
"timestamp": 1749096803365,
"version": "3.41.0"
},
"institution": [
{
"name": "Authorea Inc."
}
],
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
6,
4
]
]
},
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
6,
4
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.22541",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
6,
4
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.authorea.com/users/931296/articles/1302286-earlier-clinical-improvement-in-mild-moderate-acute-covid-patients-treated-with-pharmacological-grade-curcumin?commit=22dfef4f4d720252b1b9353e7a531de4ecd50562"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": "Earlier clinical improvement in mild-moderate acute COVID patients treated with pharmacological-grade Curcumin",
"type": "posted-content"
}