SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Induces Time-Dependent and Brain-Region-Specific Alterations in Ferroptosis Markers: A Preliminary Study in K18-hACE2 Mice
et al., International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms27031526, Feb 2026
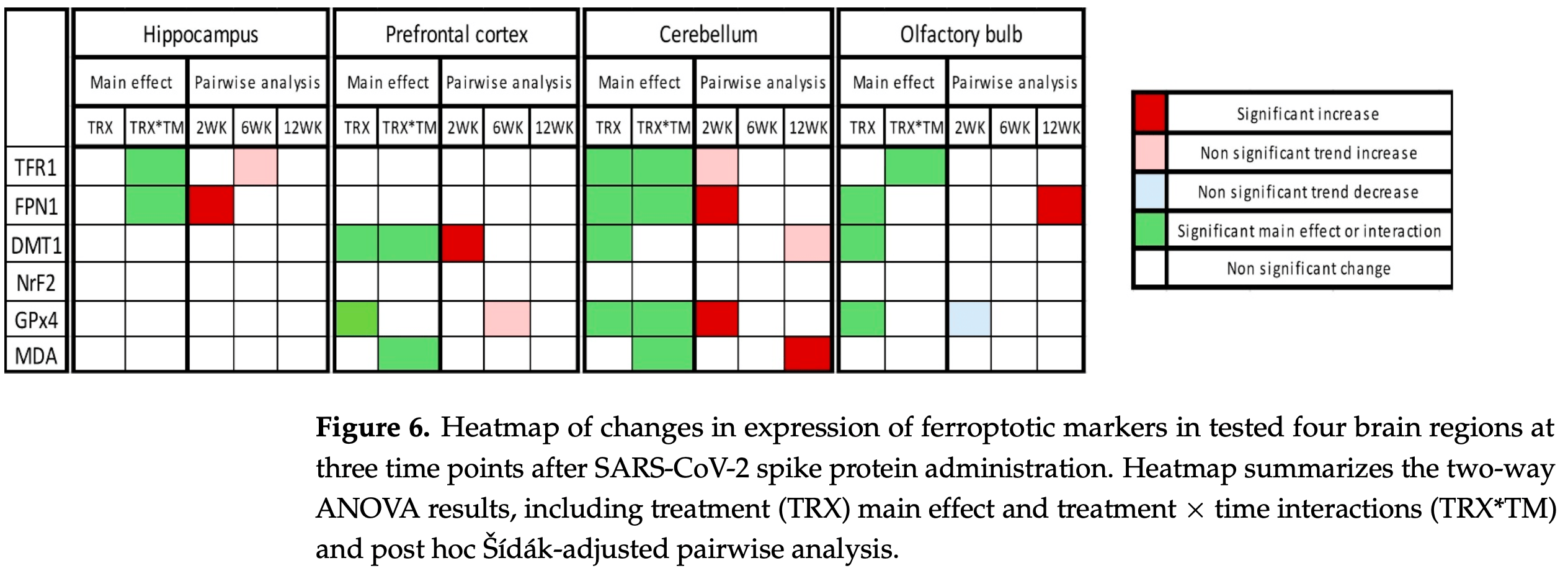
Mouse study showing potential harm from SARS-CoV-2 spike protein through ferroptosis induction in K18-hACE2 transgenic mice. The findings suggest spike protein exposure may contribute to persistent neurological manifestations seen in post-COVID syndrome through ferroptotic cell death mechanisms.
Yehia et al., 4 Feb 2026, peer-reviewed, 7 authors.
Contact: abulseoud.osama@mayo.edu (corresponding author), dalia.mr@mans.edu.eg, madel@mans.edu.eg, sara12@mans.edu.eg.
SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Induces Time-Dependent and Brain-Region-Specific Alterations in Ferroptosis Markers: A Preliminary Study in K18-hACE2 Mice
International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms27031526
Post-COVID syndrome comprises persistent neuropsychiatric manifestations for more than 12 weeks after recovery from acute SARS-CoV-2 infection, yet its underlying pathophysiology is unclear. Ferroptosis, an iron-dependent form of cell death with three hallmarks, iron dysregulation, antioxidant failure, and lipid peroxidation, seems to be involved in COVID-19/post-COVID-19 pathophysiology. Here, we administered the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein S1 subunit intranasally to K18-hACE2 transgenic mice and quantified ferroptotic marker protein expression in four brain regions (hippocampus, prefrontal cortex, cerebellum, and olfactory bulb) at 2, 6, and 12 weeks post-administration, alongside ultrastructural assessment by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) that was limited to the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex. Two-way ANOVA revealed region-and time-dependent modulation of iron-handling, antioxidant, and lipid peroxidation markers. In the hippocampus, FPN1 was significantly increased at 2 weeks, while TFR1 showed a time-dependent pattern without significant week-specific differences. In the prefrontal cortex, DMT1 significantly increased at 2 weeks, and GPx4 showed an overall treatment effect with a trend of increase at 6 weeks. The cerebellum exhibited early increases in FPN1 and GPx4 and a delayed increase in MDA-conjugated proteins. In the olfactory bulb, FPN1 increased at 12 weeks, with GPx4 showing an overall treatment effect and an early trend of decrease. TEM identified ferroptosis-consistent features in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex at all time points. These findings suggest that spike protein exposure may be associated with time-dependent and brain-region-specific alterations of ferroptosis-related markers. These preliminary findings are based on a limited sample size, which needs further research to elucidate the clinical implication and to study the mechanism in more depth as well as future validation with pharmacological inhibitors.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
Abudukeremu, Aikemu, Yang, Fang, Shanahati et al., Mechanism of ferroptosis in hypoxia-induced pulmonary vascular remodeling in hypoxia pulmonary hypertension: A study based on the ACE2-Ang-(1-7)-Mas axis, Chem. Biol. Interact, doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2025.111596
Abulseoud, Yehia, Egol, Nettey, Aly et al., Attenuated initial serum ferritin concentration in critically ill coronavirus disease 2019 geriatric patients with comorbid psychiatric conditions, Front. Psychiatry, doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2022.1035986
Al-Hakeim, Al-Rubaye, Al-Hadrawi, Almulla, Maes, Long-COVID post-viral chronic fatigue and affective symptoms are associated with oxidative damage, lowered antioxidant defenses and inflammation: A proof of concept and mechanism study, Mol. Psychiatry, doi:10.1038/s41380-022-01836-9
Anjana, Annie, Siba, Meenu, Chintha et al., Manifestations and risk factors of post COVID syndrome among COVID-19 patients presented with minimal symptoms-A study from Kerala, India, J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care
Bao, Pang, Zhou, Hu, Xiong et al., Loss of ferroportin induces memory impairment by promoting ferroptosis in Alzheimer's disease, Correction in Cell Death Differ, doi:10.1038/s41418-020-00685-9
Burnett, Coucha, Bolduc, Hermanns, Heath et al., SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Intensifies Cerebrovascular Complications in Diabetic hACE2 Mice through RAAS and TLR Signaling Activation, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms242216394
Cao, Zuo, Huang, Zhu, Zhao et al., Hippocampal proteomic analysis reveals activation of necroptosis and ferroptosis in a mouse model of chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depression, Behav. Brain Res, doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2021.113261
Carod-Artal, Post-COVID-19 syndrome: Epidemiology, diagnostic criteria and pathogenic mechanisms involved, Rev. Neurol
Caterino, Gelzo, Sol, Fedele, Annunziata et al., Dysregulation of lipid metabolism and pathological inflammation in patients with COVID-19, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-82426-7
Cheng, Li, Li, Liu, Yan et al., Ferritin in the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A systematic review and meta-analysis, J. Clin. Lab. Anal
Cosentino, Marino, Understanding the pharmacology of COVID-19 mRNA vaccines: Playing dice with the spike?, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms231810881
Cui, Zhang, Zhao, Shao, Liu et al., ACSL4 exacerbates ischemic stroke by promoting ferroptosis-induced brain injury and neuroinflammation, Brain Behav. Immun
Dai, Guo, Zhang, Chen, Ou et al., Lycium barbarum (Wolfberry) glycopeptide prevents stress-induced anxiety disorders by regulating oxidative stress and ferroptosis in the medial prefrontal cortex, Phytomedicine, doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154864
Davis, Mccorkell, Vogel, Topol, Long, Major findings, mechanisms and recommendations, Correction in Nat. Rev. Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41579-023-00896-0
De Melo, Da Silva, Rodrigues, Palmeira, Saldanha-Araujo et al., SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein and Long COVID-Part 1: Impact of Spike Protein in Pathophysiological Mechanisms of Long COVID Syndrome, Correction in Viruses, doi:10.3390/v17050617
Dedoni, Avdoshina, Camoglio, Siddi, Fratta et al., K18-and CAG-hACE2 Transgenic Mouse Models and SARS-CoV-2: Implications for Neurodegeneration Research, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules27134142
Dixon, Lemberg, Lamprecht, Skouta, Zaitsev et al., Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.042
Dixon, Stockwell, The hallmarks of ferroptosis, Annu. Rev. Cancer Biol, doi:10.1146/annurev-cancerbio-030518-055844
Feng, Schorpp, Jin, Yozwiak, Hoffstrom et al., Transferrin Receptor Is a Specific Ferroptosis Marker, Cell Rep, doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2020.02.049
Ferreira, Domingues, Oxidized phospholipid-protein adducts: The future targets of interest, Arch. Biochem. Biophys, doi:10.1016/j.abb.2024.109956
Fontes-Dantas, Fernandes, Gutman, De Lima, Antonio et al., SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein induces TLR4-mediated long-term cognitive dysfunction recapitulating post-COVID-19 syndrome in mice, Cell Rep
Fratta Pasini, Stranieri, Girelli, Busti, Cominacini, Is Ferroptosis a Key Component of the Process Leading to Multiorgan Damage in COVID-19?, Antioxidants, doi:10.3390/antiox10111677
Garrido, De, Castillo-Peinado, Priego-Capote, Barrio et al., Lipidomics signature in post-COVID patient sera and its influence on the prolonged inflammatory response, J. Infect. Public Health, doi:10.1016/j.jiph.2024.01.017
Golden, Cline, Zeng, Garrison, Carey et al., Human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 transgenic mice infected with SARS-CoV-2 develop severe and fatal respiratory disease, JCI Insight, doi:10.1172/jci.insight.142032
Hanson, Fine, Svitak, Faltesek, Intranasal administration of CNS therapeutics to awake mice, J. Vis. Exp. JoVE, doi:10.3791/4440
Hanson, Mulè, Ruffieux, Mescia, Bergamaschi et al., Iron dysregulation and inflammatory stress erythropoiesis associates with long-term outcome of COVID-19, Nat. Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41590-024-01754-8
Hastie, Lowe, Mcauley, Mills, Winter et al., True prevalence of long-COVID in a nationwide, population cohort study, Nat. Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-023-43661-w
He, Cong, Liang, Ma, Tian et al., Discovery and validation of Ferroptosis-related molecular patterns and immune characteristics in Alzheimer's disease, Front. Aging Neurosci
Hiromatsu, Toshida, Itoh, Harada, Kohashi et al., Transferrin Receptor is Associated with Sensitivity to Ferroptosis Inducers in Hepatocellular Carcinoma, Ann. Surg. Oncol
Hoffmann, Kleine-Weber, Pöhlmann, A multibasic cleavage site in the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 is essential for infection of human lung cells, Mol. Cell, doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2020.04.022
Ingold, Berndt, Schmitt, Doll, Poschmann et al., Selenium utilization by GPX4 is required to prevent hydroperoxide-induced ferroptosis, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2017.11.048
Jackson, Farzan, Chen, Choe, Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol, doi:10.1038/s41580-021-00418-x
Jennings, Monaghan, Xue, Mockler, Romero-Ortuno, A Systematic Review of Persistent Symptoms and Residual Abnormal Functioning following Acute COVID-19: Ongoing Symptomatic Phase vs. Post-COVID-19 Syndrome, J. Clin. Med, doi:10.3390/jcm10245913
Jia, Liu, Kang, NCOA4-mediated ferritinophagy: A vicious culprit in COVID-19 pathogenesis? Front, Mol. Biosci, doi:10.3389/fmolb.2021.761793
Jiang, Shi, Kong, Chen, Xu et al., Iron dysregulation and ferroptosis are associated with pulmonary fibrosis: Insight from idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, systemic sclerosis, and COVID-19 patients, J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jtemb.2025.127728
Kandemirli, Altundag, Yildirim, Tekcan Sanli, Saatci, Olfactory Bulb MRI and Paranasal Sinus CT Findings in Persistent COVID-19 Anosmia, Acad. Radiol, doi:10.1016/j.acra.2020.10.006
Karkhanei, Ghane, Mehri, Evaluation of oxidative stress level: Total antioxidant capacity, total oxidant status and glutathione activity in patients with COVID-19, New Microbes New Infect, doi:10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100897
Kaushal, Kaur, Sarma, Bhattacharyya, Sharma et al., Serum ferritin as a predictive biomarker in COVID-19. A systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression analysis, J. Crit. Care
Keklicek, Selçuk, Kurt, Ulukaya, Öztürk, Individuals with a COVID-19 history exhibit asymmetric gait patterns despite full recovery, J. Biomech, doi:10.1016/j.jbiomech.2022.111098
Kenny, Fidan, Yang, Anthonymuthu, New et al., Ferroptosis contributes to neuronal death and functional outcome after traumatic brain injury, Crit. Care Med, doi:10.1097/CCM.0000000000003555
Kumar, Osahon, Vides, Hanania, Minard et al., Severe glutathione deficiency, oxidative stress and oxidant damage in adults hospitalized with COVID-19: Implications for GlyNAC (Glycine and N-Acetylcysteine) supplementation, Antioxidants, doi:10.3390/antiox11010050
Li, Chen, Zhang, Heng, Yin et al., Praeruptorin A screened by a ferrous ion probe inhibited DMT1 and ferroptosis to attenuate Doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy, Eur. J. Med. Chem, doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2024.117108
Lin, Long, Yang, Chen, Xu et al., Serum ferritin as an independent risk factor for severity in COVID-19 patients, J. Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2020.06.053
López-Hernández, Oropeza-Valdez, García Lopez, Borrego, Murgu et al., Untargeted analysis in post-COVID-19 patients reveals dysregulated lipid pathways two years after recovery, Front. Mol. Biosci, doi:10.3389/fmolb.2023.1100486
Maio, Lafont, Sil, Li, Bollinger et al., Fe-S cofactors in the SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase are potential antiviral targets, Science
Martín-Fernández, Aller, Heredia-Rodríguez, Gómez-Sánchez, Martínez-Paz et al., Lipid peroxidation as a hallmark of severity in COVID-19 patients, Redox Biol, doi:10.1016/j.redox.2021.102181
Mccray, Jr, Pewe, Wohlford-Lenane, Hickey et al., Lethal infection of K18-hACE2 mice infected with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus, J. Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.02012-06
Meo, Abukhalaf, Alomar, Al-Hussain, Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and neurological manifestations in SARS-CoV-2 patients, Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci
Miyake, Murai, Kakuta, Uchiyama, Nakano, Identification of the hallmarks of necroptosis and ferroptosis by transmission electron microscopy, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun, doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.04.127
Moghaddam, Heller, Sun, Seelig, Cherkezov et al., Selenium deficiency is associated with mortality risk from COVID-19, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12072098
Muhammad, Kani, Iliya, Muhammad, Binji et al., Deficiency of antioxidants and increased oxidative stress in COVID-19 patients: A cross-sectional comparative study in Jigawa, Northwestern Nigeria, SAGE Open Med, doi:10.1177/2050312121991246
Nguyen, Zhang, Gao, Cao, Tian et al., The spike protein of sars-cov-2 impairs lipid metabolism and increases susceptibility to lipotoxicity: Implication for a role of nrf2, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells11121916
Nouraeinejad, Memory loss in patients with long COVID can be due to reduced hippocampal neurogenesis, Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci
Oh, Cho, Barcelon, Kim, Hong et al., SARS-CoV-2 spike protein induces cognitive deficit and anxiety-like behavior in mouse via non-cell autonomous hippocampal neuronal death, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-022-09410-7
Oladunni, Park, Pino, Gonzalez, Akhter et al., Lethality of SARS-CoV-2 infection in K18 human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 transgenic mice, Nat. Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-020-19891-7
Pandey, Acharya, Mohan, Ng, Reid et al., Animal models for SARS-CoV-2 research: A comprehensive literature review, Transbound. Emerg. Dis, doi:10.1111/tbed.13907
Park, Cha, Kim, Kim, Yang et al., NOX4 promotes ferroptosis of astrocytes by oxidative stress-induced lipid peroxidation via the impairment of mitochondrial metabolism in Alzheimer's diseases, Redox Biol
Park, Chung, ROS-mediated autophagy increases intracellular iron levels and ferroptosis by ferritin and transferrin receptor regulation, Cell Death Dis, doi:10.1038/s41419-019-2064-5
Peng, Chung, Lawrence, O'banion, Dirksen et al., DMT1 knockout abolishes ferroptosis induced mitochondrial dysfunction in C. elegans amyloid β proteotoxicity, Free Radic. Biol. Med
Pincemail, Cavalier, Charlier, Cheramy-Bien, Brevers et al., Oxidative stress status in COVID-19 patients hospitalized in intensive care unit for severe pneumonia. A pilot study, Antioxidants, doi:10.3390/antiox10020257
Poletti, Paolini, Mazza, Palladini, Furlan et al., Lower levels of glutathione in the anterior cingulate cortex associate with depressive symptoms and white matter hyperintensities in COVID-19 survivors, Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2022.06.008
Polonikov, Endogenous deficiency of glutathione as the most likely cause of serious manifestations and death in COVID-19 patients, ACS Infect. Dis, doi:10.1021/acsinfecdis.0c00288
Qeadan, Tingey, Gu, Packard, Erdei et al., Prognostic values of serum ferritin and D-dimer trajectory in patients with COVID-19, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v13030419
Raveendran, Jayadevan, Sashidharan, Long, An overview, Diabetes Metab. Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2021.04.007
Rhea, Logsdon, Hansen, Williams, Reed et al., The S1 protein of SARS-CoV-2 crosses the blood-brain barrier in mice, Nat. Neurosci, doi:10.1038/s41593-020-00771-8
Rodencal, Dixon, A tale of two lipids: Lipid unsaturation commands ferroptosis sensitivity, Proteomics, doi:10.1002/pmic.202100308
Saleh, Chang, Liang, Ryan, Cunningham et al., Ongoing oxidative stress in individuals with post-acute sequelae of COVID-19, Neuroimmune Pharmacol. Ther, doi:10.1515/nipt-2022-0006
Shi, Yang, Yang, Fan, Zheng et al., MaiJiTong granule attenuates atherosclerosis by reducing ferroptosis via activating STAT6-mediated inhibition of DMT1 and SOCS1/p53 pathways in LDLR(-/-) mice, Phytomedicine, doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155489
Song, Peng, Sun, Heng, Zhu, Temozolomide Drives Ferroptosis via a DMT1-Dependent Pathway in Glioblastoma Cells, Yonsei Med. J
Song, Wang, Tian, Wu, Zhou et al., Identification of Key Ferroptosis-Related Genes in the Peripheral Blood of Patients with Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis and Its Diagnostic Value, Int. J. Mol. Sci
Sousa, Yehia, Abulseoud, Attenuation of ferroptosis as a potential therapeutic target for neuropsychiatric manifestations of post-COVID syndrome, Front. Neurosci, doi:10.3389/fnins.2023.1237153
Stockwell, Ferroptosis turns 10: Emerging mechanisms, physiological functions, and therapeutic applications, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2022.06.003
Swank, Senussi, Manickas-Hill, Yu, Li et al., Persistent circulating severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 spike is associated with post-acute coronavirus disease 2019 sequelae, Clin. Infect. Dis
Taquet, Geddes, Husain, Luciano, Harrison, 6-month neurological and psychiatric outcomes in 236 379 survivors of COVID-19: A retrospective cohort study using electronic health records, Lancet Psychiatry, doi:10.1016/s2215-0366(21)00084-5
Tian, Lu, Hao, Li, Zhang et al., FTH1 inhibits ferroptosis through ferritinophagy in the 6-OHDA model of Parkinson's disease, Neurotherapeutics, doi:10.1007/s13311-020-00929-z
Ursini, Maiorino, Lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis: The role of GSH and GPx4. Free Radic, Biol. Med, doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.02.027
Van San, Debruyne, Veeckmans, Tyurina, Tyurin et al., Ferroptosis contributes to multiple sclerosis and its pharmacological targeting suppresses experimental disease progression, Cell Death Differ, doi:10.1038/s41418-023-01195-0
Van, Gouel, Jonneaux, Timmerman, Gelé et al., Ferroptosis, a newly characterized form of cell death in Parkinson's disease that is regulated by PKC, Neurobiol. Dis
Wang, Huang, Sun, Stubbs, He et al., SARS-CoV-2 suppresses mRNA expression of selenoproteins associated with ferroptosis, endoplasmic reticulum stress and DNA synthesis, Food Chem. Toxicol, doi:10.1016/j.fct.2021.112286
Wang, Liang, Huo, Wang, Wang et al., SPY1 inhibits neuronal ferroptosis in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis by reducing lipid peroxidation through regulation of GCH1 and TFR1, Cell Death Differ, doi:10.1038/s41418-022-01089-7
Wang, Tomas, Perera, Cuic, Luikinga et al., Ferroptosis mediates selective motor neuron death in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Cell Death Differ
Wang, Wen, Cao, Luo, Shuai et al., Transferrin receptor protein 1 cooperates with mGluR2 to mediate the internalization of rabies virus and SARS-CoV-2, J. Virol, doi:10.1128/jvi.01611-22
Winkler, Bailey, Kafai, Nair, Mccune et al., SARS-CoV-2 infection of human ACE2-transgenic mice causes severe lung inflammation and impaired function, Nat. Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41590-020-0794-2
Wu, Jiao, Yue, He, Jin et al., Ubiquitin ligase E3 HUWE1/MULE targets transferrin receptor for degradation and suppresses ferroptosis in acute liver injury, Cell Death Differ, doi:10.1038/s41418-022-00957-6
Wu, Ma, Xu, Chen, Chen et al., ACE2 mitigates Streptococcus uberis-induced ferroptosis in goat mammary epithelial cells by inhibiting ROS-chaperone-mediated autophagic degradation of GPX4, Microb. Pathog, doi:10.1016/j.micpath.2025.108141
Xie, Wang, Lin, Mao, Feng et al., Inhibition of ferroptosis attenuates tissue damage and improves long-term outcomes after traumatic brain injury in mice, CNS Neurosci. Ther
Xydakis, Albers, Holbrook, Lyon, Shih et al., Post-viral effects of COVID-19 in the olfactory system and their implications, Lancet Neurol, doi:10.1016/s1474-4422(21)00182-4
Yang, Stockwell, Ferroptosis: Death by lipid peroxidation, Trends Cell Biol, doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2015.10.014
Yang, Zeng, Yuan, Wang, Ge et al., The mechanism of ferroptosis regulating oxidative stress in ischemic stroke and the regulation mechanism of natural pharmacological active components, Biomed. Pharmacother, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113611
Yehia, Abulseoud, Melatonin: A ferroptosis inhibitor with potential therapeutic efficacy for the post-COVID-19 trajectory of accelerated brain aging and neurodegeneration, Mol. Neurodegener, doi:10.1186/s13024-024-00728-6
Yehia, Melhuish Beaupre, Ho, Biernnacka, Frye et al., Ferroptosis as a potential molecular mechanism of bipolar disorder, Transl. Psychiatry, doi:10.1038/s41398-025-03429-w
Youdim, Brain iron deficiency and excess; cognitive impairment and neurodegeneration with involvement of striatum and hippocampus, Neurotox. Res
Younesian, Khodabakhshi, Abdolahi, Norouzi, Behnampour et al., Decreased serum selenium levels of COVID-19 patients in comparison with healthy individuals, Biol. Trace Elem. Res, doi:10.1007/s12011-021-02797-w
Zarkovic, Jakovcevic, Mataic, Jaganjac, Vukovic et al., Post-mortem findings of inflammatory cells and the association of 4-hydroxynonenal with systemic vascular and oxidative stress in lethal COVID-19, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells11030444
Zhang, Ostrowski, Jiang, Zhao, Liang et al., Hepcidin Promoted Ferroptosis through Iron Metabolism which Is Associated with DMT1 Signaling Activation in Early Brain Injury following Subarachnoid Hemorrhage, Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev
Zhao, Huang, Dai, Feng, Liu et al., Serum iron level as a potential predictor of coronavirus disease 2019 severity and mortality: A retrospective study
Zhou, Meng, Li, Yao, Le et al., Ferroptosis in cancer: From molecular mechanisms to therapeutic strategies, Signal Transduct. Target. Ther, doi:10.1038/s41392-024-01769-5
Zhu, Li, Hao, Zhang, Gao, TIPE2 suppresses ferroptosis and pro-inflammatory polarization in macrophages triggered by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-025-14235-1
Çakırca, Damar Çakırca, Üstünel, Torun, Koyuncu, Thiol level and total oxidant/antioxidant status in patients with COVID-19 infection, Ir. J. Med. Sci, doi:10.1007/s11845-021-02743-8
Žarković, Orehovec, Milković, Baršić, Tatzber et al., Preliminary Findings on the Association of the Lipid Peroxidation Product 4-Hydroxynonenal with the Lethal Outcome of Aggressive COVID-19, Antioxidants, doi:10.3390/antiox10091341
Žarković, Łuczaj, Jarocka-Karpowicz, Orehovec, Baršić et al., Diversified Effects of COVID-19 as a Consequence of the Differential Metabolism of Phospholipids and Lipid Peroxidation Evaluated in the Plasma of Survivors and Deceased Patients upon Admission to the Hospital, Int. J. Mol. Sci
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms27031526",
"ISSN": [
"1422-0067"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/ijms27031526",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Post-COVID syndrome comprises persistent neuropsychiatric manifestations for more than 12 weeks after recovery from acute SARS-CoV-2 infection, yet its underlying pathophysiology is unclear. Ferroptosis, an iron-dependent form of cell death with three hallmarks, iron dysregulation, antioxidant failure, and lipid peroxidation, seems to be involved in COVID-19/post-COVID-19 pathophysiology. Here, we administered the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein S1 subunit intranasally to K18-hACE2 transgenic mice and quantified ferroptotic marker protein expression in four brain regions (hippocampus, prefrontal cortex, cerebellum, and olfactory bulb) at 2, 6, and 12 weeks post-administration, alongside ultrastructural assessment by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) that was limited to the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex. Two-way ANOVA revealed region- and time-dependent modulation of iron-handling, antioxidant, and lipid peroxidation markers. In the hippocampus, FPN1 was significantly increased at 2 weeks, while TFR1 showed a time-dependent pattern without significant week-specific differences. In the prefrontal cortex, DMT1 significantly increased at 2 weeks, and GPx4 showed an overall treatment effect with a trend of increase at 6 weeks. The cerebellum exhibited early increases in FPN1 and GPx4 and a delayed increase in MDA-conjugated proteins. In the olfactory bulb, FPN1 increased at 12 weeks, with GPx4 showing an overall treatment effect and an early trend of decrease. TEM identified ferroptosis-consistent features in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex at all time points. These findings suggest that spike protein exposure may be associated with time-dependent and brain-region-specific alterations of ferroptosis-related markers. These preliminary findings are based on a limited sample size, which needs further research to elucidate the clinical implication and to study the mechanism in more depth as well as future validation with pharmacological inhibitors.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"ijms27031526"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Neuroscience, Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences, Mayo Clinic College of Medicine, Phoenix, AZ 58054, USA"
},
{
"name": "Department of Medical Physiology, Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura University, Mansoura 35516, Egypt"
}
],
"family": "Yehia",
"given": "Asmaa",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6845-141X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Neuroscience, Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences, Mayo Clinic College of Medicine, Phoenix, AZ 58054, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Toufaily",
"given": "Chirine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8793-5356",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medical Physiology, Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura University, Mansoura 35516, Egypt"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Abdel Ghaffar",
"given": "Dalia M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medical Physiology, Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura University, Mansoura 35516, Egypt"
},
{
"name": "Department of Basic Dental Sciences, Faculty of Dentistry, The Hashemite University, Zarqa 13115, Jordan"
}
],
"family": "El Wakeel",
"given": "Gehan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0107-7320",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medical Physiology, Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura University, Mansoura 35516, Egypt"
},
{
"name": "Department of Medical Physiology, Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura National University, Gamasa 35712, Egypt"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Adel",
"given": "Mohamed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medical Physiology, Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura University, Mansoura 35516, Egypt"
}
],
"family": "Mostafa",
"given": "Abeer F.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0652-0862",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Neuroscience, Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences, Mayo Clinic College of Medicine, Phoenix, AZ 58054, USA"
},
{
"name": "Department of Psychiatry and Psychology, Mayo Clinic Arizona, Phoenix, AZ 85054, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Abulseoud",
"given": "Osama A.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "International Journal of Molecular Sciences",
"container-title-short": "IJMS",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
2,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2026-02-04T10:02:57Z",
"timestamp": 1770199377000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
2,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2026-02-04T10:03:45Z",
"timestamp": 1770199425000
},
"funder": [
{
"name": "Department of Psychiatry and Psychology at the Mayo Clinic, Arizona"
},
{
"name": "Edli Foundation"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
2,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2026-02-04T23:06:26Z",
"timestamp": 1770246386718,
"version": "3.49.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "3",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
2,
4
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "3",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
2
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
2,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2026-02-04T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1770163200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/27/3/1526/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1526",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
2,
4
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
2,
4
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.042",
"article-title": "Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death",
"author": "Dixon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1060",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_1",
"volume": "149",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev-cancerbio-030518-055844",
"article-title": "The hallmarks of ferroptosis",
"author": "Dixon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "35",
"journal-title": "Annu. Rev. Cancer Biol.",
"key": "ref_2",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2022.06.003",
"article-title": "Ferroptosis turns 10: Emerging mechanisms, physiological functions, and therapeutic applications",
"author": "Stockwell",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2401",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "185",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbr.2021.113261",
"article-title": "Hippocampal proteomic analysis reveals activation of necroptosis and ferroptosis in a mouse model of chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depression",
"author": "Cao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "113261",
"journal-title": "Behav. Brain Res.",
"key": "ref_4",
"volume": "407",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154864",
"article-title": "Lycium barbarum (Wolfberry) glycopeptide prevents stress-induced anxiety disorders by regulating oxidative stress and ferroptosis in the medial prefrontal cortex",
"author": "Dai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "154864",
"journal-title": "Phytomedicine",
"key": "ref_5",
"volume": "116",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41398-025-03429-w",
"article-title": "Ferroptosis as a potential molecular mechanism of bipolar disorder",
"author": "Yehia",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "205",
"journal-title": "Transl. Psychiatry",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2025"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbi.2021.01.003",
"article-title": "ACSL4 exacerbates ischemic stroke by promoting ferroptosis-induced brain injury and neuroinflammation",
"author": "Cui",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "312",
"journal-title": "Brain Behav. Immun.",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113611",
"article-title": "The mechanism of ferroptosis regulating oxidative stress in ischemic stroke and the regulation mechanism of natural pharmacological active components",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "113611",
"journal-title": "Biomed. Pharmacother.",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "154",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CCM.0000000000003555",
"article-title": "Ferroptosis contributes to neuronal death and functional outcome after traumatic brain injury",
"author": "Kenny",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "410",
"journal-title": "Crit. Care Med.",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/cns.13069",
"article-title": "Inhibition of ferroptosis attenuates tissue damage and improves long-term outcomes after traumatic brain injury in mice",
"author": "Xie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "465",
"journal-title": "CNS Neurosci. Ther.",
"key": "ref_10",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41418-020-00685-9",
"article-title": "Loss of ferroportin induces memory impairment by promoting ferroptosis in Alzheimer’s disease",
"author": "Bao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1548",
"journal-title": "Cell Death Differ.",
"key": "ref_11",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnagi.2022.1056312",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_12",
"unstructured": "He, Y.-J., Cong, L., Liang, S.-L., Ma, X., Tian, J.-N., Li, H., and Wu, Y. (2022). Discovery and validation of Ferroptosis-related molecular patterns and immune characteristics in Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Aging Neurosci., 14."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.redox.2021.101947",
"article-title": "NOX4 promotes ferroptosis of astrocytes by oxidative stress-induced lipid peroxidation via the impairment of mitochondrial metabolism in Alzheimer’s diseases",
"author": "Park",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "101947",
"journal-title": "Redox Biol.",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nbd.2016.05.011",
"article-title": "Ferroptosis, a newly characterized form of cell death in Parkinson’s disease that is regulated by PKC",
"author": "Gouel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "169",
"journal-title": "Neurobiol. Dis.",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s13311-020-00929-z",
"article-title": "FTH1 inhibits ferroptosis through ferritinophagy in the 6-OHDA model of Parkinson’s disease",
"author": "Tian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1796",
"journal-title": "Neurotherapeutics",
"key": "ref_15",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms24076399",
"article-title": "Identification of Key Ferroptosis-Related Genes in the Peripheral Blood of Patients with Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis and Its Diagnostic Value",
"author": "Song",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6399",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Mol. Sci.",
"key": "ref_16",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41418-023-01195-0",
"article-title": "Ferroptosis contributes to multiple sclerosis and its pharmacological targeting suppresses experimental disease progression",
"author": "Debruyne",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2092",
"journal-title": "Cell Death Differ.",
"key": "ref_17",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41418-022-01089-7",
"article-title": "SPY1 inhibits neuronal ferroptosis in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis by reducing lipid peroxidation through regulation of GCH1 and TFR1",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "369",
"journal-title": "Cell Death Differ.",
"key": "ref_18",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41418-021-00910-z",
"article-title": "Ferroptosis mediates selective motor neuron death in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1187",
"journal-title": "Cell Death Differ.",
"key": "ref_19",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13024-024-00728-6",
"article-title": "Melatonin: A ferroptosis inhibitor with potential therapeutic efficacy for the post-COVID-19 trajectory of accelerated brain aging and neurodegeneration",
"author": "Yehia",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "36",
"journal-title": "Mol. Neurodegener.",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.06.25.21259372",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_21",
"unstructured": "Jennings, G., Monaghan, A., Xue, F., Mockler, D., and Romero-Ortuno, R. (2021). A Systematic Review of Persistent Symptoms and Residual Abnormal Functioning following Acute COVID-19: Ongoing Symptomatic Phase vs. Post-COVID-19 Syndrome. J. Clin. Med., 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.33588/rn.7211.2021230",
"article-title": "Post-COVID-19 syndrome: Epidemiology, diagnostic criteria and pathogenic mechanisms involved",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "384",
"journal-title": "Rev. Neurol.",
"key": "ref_22",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2021.04.007",
"article-title": "Long COVID: An overview",
"author": "Raveendran",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "869",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab. Syndr.",
"key": "ref_23",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and neurological manifestations in SARS-CoV-2 patients",
"author": "Meo",
"first-page": "1101",
"journal-title": "Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci.",
"key": "ref_24",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_851_21",
"article-title": "Manifestations and risk factors of post COVID syndrome among COVID-19 patients presented with minimal symptoms—A study from Kerala, India",
"author": "Anjana",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4023",
"journal-title": "J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care",
"key": "ref_25",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2215-0366(21)00084-5",
"article-title": "6-month neurological and psychiatric outcomes in 236 379 survivors of COVID-19: A retrospective cohort study using electronic health records",
"author": "Taquet",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "416",
"journal-title": "Lancet Psychiatry",
"key": "ref_26",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-023-43661-w",
"article-title": "True prevalence of long-COVID in a nationwide, population cohort study",
"author": "Hastie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "7892",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "ref_27",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-022-00846-2",
"article-title": "Long COVID: Major findings, mechanisms and recommendations",
"author": "Davis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "133",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Microbiol.",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnins.2023.1237153",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_29",
"unstructured": "Sousa, R.A., Yehia, A., and Abulseoud, O.A. (2023). Attenuation of ferroptosis as a potential therapeutic target for neuropsychiatric manifestations of post-COVID syndrome. Front. Neurosci., 17."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abi5224",
"article-title": "Fe-S cofactors in the SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase are potential antiviral targets",
"author": "Maio",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "236",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "ref_30",
"volume": "373",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fpsyt.2022.1035986",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_31",
"unstructured": "Abulseoud, O.A., Yehia, A., Egol, C.J., Nettey, V.N., Aly, M., Qu, Y., Skolnik, A.B., Grill, M.F., Sen, A., and Schneekloth, T.D. (2022). Attenuated initial serum ferritin concentration in critically ill coronavirus disease 2019 geriatric patients with comorbid psychiatric conditions. Front. Psychiatry, 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmolb.2021.761793",
"article-title": "NCOA4-mediated ferritinophagy: A vicious culprit in COVID-19 pathogenesis?",
"author": "Jia",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "761793",
"journal-title": "Front. Mol. Biosci.",
"key": "ref_32",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcrc.2021.09.023",
"article-title": "Serum ferritin as a predictive biomarker in COVID-19. A systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression analysis",
"author": "Kaushal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "172",
"journal-title": "J. Crit. Care",
"key": "ref_33",
"volume": "67",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2020.06.053",
"article-title": "Serum ferritin as an independent risk factor for severity in COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Lin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "647",
"journal-title": "J. Infect.",
"key": "ref_34",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v13030419",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_35",
"unstructured": "Qeadan, F., Tingey, B., Gu, L.Y., Packard, A.H., Erdei, E., and Saeed, A.I. (2021). Prognostic values of serum ferritin and D-dimer trajectory in patients with COVID-19. Viruses, 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcla.23618",
"article-title": "Ferritin in the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Cheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e23618",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Lab. Anal.",
"key": "ref_36",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofaa250",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_37",
"unstructured": "Zhao, K., Huang, J., Dai, D., Feng, Y., Liu, L., and Nie, S. (2020). Serum iron level as a potential predictor of coronavirus disease 2019 severity and mortality: A retrospective study. Proceedings of the Open Forum Infectious Diseases, Oxford University Press."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41590-024-01754-8",
"article-title": "Iron dysregulation and inflammatory stress erythropoiesis associates with long-term outcome of COVID-19",
"author": "Hanson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "471",
"journal-title": "Nat. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_38",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100897",
"article-title": "Evaluation of oxidative stress level: Total antioxidant capacity, total oxidant status and glutathione activity in patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Karkhanei",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100897",
"journal-title": "New Microbes New Infect.",
"key": "ref_39",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antiox11010050",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_40",
"unstructured": "Kumar, P., Osahon, O., Vides, D.B., Hanania, N., Minard, C.G., and Sekhar, R.V. (2021). Severe glutathione deficiency, oxidative stress and oxidant damage in adults hospitalized with COVID-19: Implications for GlyNAC (Glycine and N-Acetylcysteine) supplementation. Antioxidants, 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/2050312121991246",
"article-title": "Deficiency of antioxidants and increased oxidative stress in COVID-19 patients: A cross-sectional comparative study in Jigawa, Northwestern Nigeria",
"author": "Muhammad",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2050312121991246",
"journal-title": "SAGE Open Med.",
"key": "ref_41",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antiox10020257",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_42",
"unstructured": "Pincemail, J., Cavalier, E., Charlier, C., Cheramy–Bien, J.-P., Brevers, E., Courtois, A., Fadeur, M., Meziane, S., Goff, C.L., and Misset, B. (2021). Oxidative stress status in COVID-19 patients hospitalized in intensive care unit for severe pneumonia. A pilot study. Antioxidants, 10."
},
{
"article-title": "Thiol level and total oxidant/antioxidant status in patients with COVID-19 infection",
"author": "Torun",
"first-page": "1925",
"journal-title": "Ir. J. Med. Sci. (1971-)",
"key": "ref_43",
"volume": "191",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acsinfecdis.0c00288",
"article-title": "Endogenous deficiency of glutathione as the most likely cause of serious manifestations and death in COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Polonikov",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1558",
"journal-title": "ACS Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_44",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.fct.2021.112286",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 suppresses mRNA expression of selenoproteins associated with ferroptosis, endoplasmic reticulum stress and DNA synthesis",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "112286",
"journal-title": "Food Chem. Toxicol.",
"key": "ref_45",
"volume": "153",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.20944/preprints202007.0113.v1",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_46",
"unstructured": "Moghaddam, A., Heller, R.A., Sun, Q., Seelig, J., Cherkezov, A., Seibert, L., Hackler, J., Seemann, P., Diegmann, J., and Pilz, M. (2020). Selenium deficiency is associated with mortality risk from COVID-19. Nutrients, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12011-021-02797-w",
"article-title": "Decreased serum selenium levels of COVID-19 patients in comparison with healthy individuals",
"author": "Younesian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1562",
"journal-title": "Biol. Trace Elem. Res.",
"key": "ref_47",
"volume": "200",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2017.11.048",
"article-title": "Selenium utilization by GPX4 is required to prevent hydroperoxide-induced ferroptosis",
"author": "Ingold",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "409",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_48",
"volume": "172",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.02.027",
"article-title": "Lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis: The role of GSH and GPx4",
"author": "Ursini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "175",
"journal-title": "Free Radic. Biol. Med.",
"key": "ref_49",
"volume": "152",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41380-022-01836-9",
"article-title": "Long-COVID post-viral chronic fatigue and affective symptoms are associated with oxidative damage, lowered antioxidant defenses and inflammation: A proof of concept and mechanism study",
"author": "Almulla",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "564",
"journal-title": "Mol. Psychiatry",
"key": "ref_50",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1515/nipt-2022-0006",
"article-title": "Ongoing oxidative stress in individuals with post-acute sequelae of COVID-19",
"author": "Saleh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "89",
"journal-title": "Neuroimmune Pharmacol. Ther.",
"key": "ref_51",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.euroneuro.2022.06.008",
"article-title": "Lower levels of glutathione in the anterior cingulate cortex associate with depressive symptoms and white matter hyperintensities in COVID-19 survivors",
"author": "Poletti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "71",
"journal-title": "Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol.",
"key": "ref_52",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.redox.2021.102181",
"article-title": "Lipid peroxidation as a hallmark of severity in COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Aller",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "102181",
"journal-title": "Redox Biol.",
"key": "ref_53",
"volume": "48",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antiox10091341",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_54",
"unstructured": "Žarković, N., Orehovec, B., Milković, L., Baršić, B., Tatzber, F., Wonisch, W., Tarle, M., Kmet, M., Mataić, A., and Jakovčević, A. (2021). Preliminary Findings on the Association of the Lipid Peroxidation Product 4-Hydroxynonenal with the Lethal Outcome of Aggressive COVID-19. Antioxidants, 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cells11030444",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_55",
"unstructured": "Zarkovic, N., Jakovcevic, A., Mataic, A., Jaganjac, M., Vukovic, T., Waeg, G., and Zarkovic, K. (2022). Post-mortem findings of inflammatory cells and the association of 4-hydroxynonenal with systemic vascular and oxidative stress in lethal COVID-19. Cells, 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-82426-7",
"article-title": "Dysregulation of lipid metabolism and pathological inflammation in patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Caterino",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2941",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "ref_56",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms231911810",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_57",
"unstructured": "Žarković, N., Łuczaj, W., Jarocka-Karpowicz, I., Orehovec, B., Baršić, B., Tarle, M., Kmet, M., Lukšić, I., Biernacki, M., and Skrzydlewska, E. (2022). Diversified Effects of COVID-19 as a Consequence of the Differential Metabolism of Phospholipids and Lipid Peroxidation Evaluated in the Plasma of Survivors and Deceased Patients upon Admission to the Hospital. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 23."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmolb.2023.1100486",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_58",
"unstructured": "López-Hernández, Y., Oropeza-Valdez, J.J., García Lopez, D.A., Borrego, J.C., Murgu, M., Valdez, J., López, J.A., and Monárrez-Espino, J. (2023). Untargeted analysis in post-COVID-19 patients reveals dysregulated lipid pathways two years after recovery. Front. Mol. Biosci., 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiph.2024.01.017",
"article-title": "Lipidomics signature in post-COVID patient sera and its influence on the prolonged inflammatory response",
"author": "Garrido",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "588",
"journal-title": "J. Infect. Public Health",
"key": "ref_59",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tcb.2015.10.014",
"article-title": "Ferroptosis: Death by lipid peroxidation",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "165",
"journal-title": "Trends Cell Biol.",
"key": "ref_60",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/pmic.202100308",
"article-title": "A tale of two lipids: Lipid unsaturation commands ferroptosis sensitivity",
"author": "Rodencal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2100308",
"journal-title": "Proteomics",
"key": "ref_61",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41590-020-0778-2",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 infection of human ACE2-transgenic mice causes severe lung inflammation and impaired function",
"author": "Winkler",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1327",
"journal-title": "Nat. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_62",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms231810881",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_63",
"unstructured": "Cosentino, M., and Marino, F. (2022). Understanding the pharmacology of COVID-19 mRNA vaccines: Playing dice with the spike?. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 23."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciac722",
"article-title": "Persistent circulating severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 spike is associated with post-acute coronavirus disease 2019 sequelae",
"author": "Swank",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e487",
"journal-title": "Clin. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_64",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112189",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein induces TLR4-mediated long-term cognitive dysfunction recapitulating post-COVID-19 syndrome in mice",
"author": "Fernandes",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "112189",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep.",
"key": "ref_65",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms242216394",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_66",
"unstructured": "Burnett, F.N., Coucha, M., Bolduc, D.R., Hermanns, V.C., Heath, S.P., Abdelghani, M., Macias-Moriarity, L.Z., and Abdelsaid, M. (2023). SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Intensifies Cerebrovascular Complications in Diabetic hACE2 Mice through RAAS and TLR Signaling Activation. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 24."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.04.127",
"article-title": "Identification of the hallmarks of necroptosis and ferroptosis by transmission electron microscopy",
"author": "Miyake",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "839",
"journal-title": "Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.",
"key": "ref_67",
"volume": "527",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/BF03033574",
"article-title": "Brain iron deficiency and excess; cognitive impairment and neurodegeneration with involvement of striatum and hippocampus",
"author": "Youdim",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "45",
"journal-title": "Neurotox. Res.",
"key": "ref_68",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00406-023-01610-0",
"article-title": "Memory loss in patients with long COVID can be due to reduced hippocampal neurogenesis",
"author": "Nouraeinejad",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "267",
"journal-title": "Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci.",
"key": "ref_69",
"volume": "275",
"year": "2025"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jbiomech.2022.111098",
"article-title": "Individuals with a COVID-19 history exhibit asymmetric gait patterns despite full recovery",
"author": "Keklicek",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "111098",
"journal-title": "J. Biomech.",
"key": "ref_70",
"volume": "137",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1474-4422(21)00182-4",
"article-title": "Post-viral effects of COVID-19 in the olfactory system and their implications",
"author": "Xydakis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "753",
"journal-title": "Lancet Neurol.",
"key": "ref_71",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.acra.2020.10.006",
"article-title": "Olfactory Bulb MRI and Paranasal Sinus CT Findings in Persistent COVID-19 Anosmia",
"author": "Kandemirli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "28",
"journal-title": "Acad. Radiol.",
"key": "ref_72",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2020.02.049",
"article-title": "Transferrin Receptor Is a Specific Ferroptosis Marker",
"author": "Feng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3411",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep.",
"key": "ref_73",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41419-019-2064-5",
"article-title": "ROS-mediated autophagy increases intracellular iron levels and ferroptosis by ferritin and transferrin receptor regulation",
"author": "Park",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "822",
"journal-title": "Cell Death Dis.",
"key": "ref_74",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41418-022-00957-6",
"article-title": "Ubiquitin ligase E3 HUWE1/MULE targets transferrin receptor for degradation and suppresses ferroptosis in acute liver injury",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1705",
"journal-title": "Cell Death Differ.",
"key": "ref_75",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1245/s10434-023-14053-7",
"article-title": "Transferrin Receptor is Associated with Sensitivity to Ferroptosis Inducers in Hepatocellular Carcinoma",
"author": "Hiromatsu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "8675",
"journal-title": "Ann. Surg. Oncol.",
"key": "ref_76",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/jvi.01611-22",
"article-title": "Transferrin receptor protein 1 cooperates with mGluR2 to mediate the internalization of rabies virus and SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e01611-22",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "ref_77",
"volume": "97",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2021/9800794",
"article-title": "Hepcidin Promoted Ferroptosis through Iron Metabolism which Is Associated with DMT1 Signaling Activation in Early Brain Injury following Subarachnoid Hemorrhage",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "9800794",
"journal-title": "Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev.",
"key": "ref_78",
"volume": "2021",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3349/ymj.2021.62.9.843",
"article-title": "Temozolomide Drives Ferroptosis via a DMT1-Dependent Pathway in Glioblastoma Cells",
"author": "Song",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "843",
"journal-title": "Yonsei Med. J.",
"key": "ref_79",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2024.09.034",
"article-title": "DMT1 knockout abolishes ferroptosis induced mitochondrial dysfunction in C. elegans amyloid β proteotoxicity",
"author": "Peng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "785",
"journal-title": "Free Radic. Biol. Med.",
"key": "ref_80",
"volume": "224",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejmech.2024.117108",
"article-title": "Praeruptorin A screened by a ferrous ion probe inhibited DMT1 and ferroptosis to attenuate Doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "117108",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Med. Chem.",
"key": "ref_81",
"volume": "283",
"year": "2025"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155489",
"article-title": "MaiJiTong granule attenuates atherosclerosis by reducing ferroptosis via activating STAT6-mediated inhibition of DMT1 and SOCS1/p53 pathways in LDLR(-/-) mice",
"author": "Shi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "155489",
"journal-title": "Phytomedicine",
"key": "ref_82",
"volume": "128",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jtemb.2025.127728",
"article-title": "Iron dysregulation and ferroptosis are associated with pulmonary fibrosis: Insight from idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, systemic sclerosis, and COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Jiang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "127728",
"journal-title": "J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol.",
"key": "ref_83",
"volume": "91",
"year": "2025"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.abb.2024.109956",
"article-title": "Oxidized phospholipid-protein adducts: The future targets of interest",
"author": "Ferreira",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "109956",
"journal-title": "Arch. Biochem. Biophys.",
"key": "ref_84",
"volume": "754",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-025-14235-1",
"article-title": "TIPE2 suppresses ferroptosis and pro-inflammatory polarization in macrophages triggered by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein",
"author": "Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "30246",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "ref_85",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2025"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2022.04.19.488806",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_86",
"unstructured": "Nguyen, V., Zhang, Y., Gao, C., Cao, X., Tian, Y., Carver, W., Kiaris, H., Cui, T., and Tan, W. (2022). The spike protein of sars-cov-2 impairs lipid metabolism and increases susceptibility to lipotoxicity: Implication for a role of nrf2. Cells, 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules27134142",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_87",
"unstructured": "Dedoni, S., Avdoshina, V., Camoglio, C., Siddi, C., Fratta, W., Scherma, M., and Fadda, P. (2022). K18-and CAG-hACE2 Transgenic Mouse Models and SARS-CoV-2: Implications for Neurodegeneration Research. Molecules, 27."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/tbed.13907",
"article-title": "Animal models for SARS-CoV-2 research: A comprehensive literature review",
"author": "Pandey",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1868",
"journal-title": "Transbound. Emerg. Dis.",
"key": "ref_88",
"volume": "68",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.02012-06",
"article-title": "Lethal infection of K18-hACE2 mice infected with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus",
"author": "McCray",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "813",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "ref_89",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-19891-7",
"article-title": "Lethality of SARS-CoV-2 infection in K18 human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 transgenic mice",
"author": "Oladunni",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6122",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "ref_90",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/jci.insight.142032",
"article-title": "Human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 transgenic mice infected with SARS-CoV-2 develop severe and fatal respiratory disease",
"author": "Golden",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e142032",
"journal-title": "JCI Insight",
"key": "ref_91",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41593-020-00771-8",
"article-title": "The S1 protein of SARS-CoV-2 crosses the blood–brain barrier in mice",
"author": "Rhea",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "368",
"journal-title": "Nat. Neurosci.",
"key": "ref_92",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v18010002",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_93",
"unstructured": "de Melo, B.P., da Silva, J.A.M., Rodrigues, M.A., Palmeira, J.d.F., Saldanha-Araujo, F., Argañaraz, G.A., and Argañaraz, E.R. (2025). SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein and Long COVID—Part 1: Impact of Spike Protein in Pathophysiological Mechanisms of Long COVID Syndrome. Viruses, 17, Correction in Viruses 2026, 18, 2."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.molcel.2020.04.022",
"article-title": "A multibasic cleavage site in the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 is essential for infection of human lung cells",
"author": "Hoffmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "779",
"journal-title": "Mol. Cell",
"key": "ref_94",
"volume": "78",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41580-021-00418-x",
"article-title": "Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells",
"author": "Jackson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol.",
"key": "ref_95",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antiox10111677",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_96",
"unstructured": "Fratta Pasini, A.M., Stranieri, C., Girelli, D., Busti, F., and Cominacini, L. (2021). Is Ferroptosis a Key Component of the Process Leading to Multiorgan Damage in COVID-19?. Antioxidants, 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cbi.2025.111596",
"article-title": "Mechanism of ferroptosis in hypoxia-induced pulmonary vascular remodeling in hypoxia pulmonary hypertension: A study based on the ACE2-Ang-(1-7)-Mas axis",
"author": "Abudukeremu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "111596",
"journal-title": "Chem. Biol. Interact.",
"key": "ref_97",
"volume": "418",
"year": "2025"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.micpath.2025.108141",
"article-title": "ACE2 mitigates Streptococcus uberis-induced ferroptosis in goat mammary epithelial cells by inhibiting ROS-chaperone-mediated autophagic degradation of GPX4",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "108141",
"journal-title": "Microb. Pathog.",
"key": "ref_98",
"volume": "210",
"year": "2026"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-022-09410-7",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 spike protein induces cognitive deficit and anxiety-like behavior in mouse via non-cell autonomous hippocampal neuronal death",
"author": "Oh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5496",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "ref_99",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3791/4440-v",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_100",
"unstructured": "Hanson, L.R., Fine, J.M., Svitak, A.L., and Faltesek, K.A. (2013). Intranasal administration of CNS therapeutics to awake mice. J. Vis. Exp. JoVE, 4440."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-024-01769-5",
"article-title": "Ferroptosis in cancer: From molecular mechanisms to therapeutic strategies",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "55",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct. Target. Ther.",
"key": "ref_101",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2024"
}
],
"reference-count": 101,
"references-count": 101,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/27/3/1526"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Induces Time-Dependent and Brain-Region-Specific Alterations in Ferroptosis Markers: A Preliminary Study in K18-hACE2 Mice",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.3390/mdpi_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "27"
}