SARS-CoV-2 virulence factor ORF3a blocks lysosome function by modulating TBC1D5-dependent Rab7 GTPase cycle
et al., Nature Communications, doi:10.1038/s41467-024-46417-2, Mar 2024
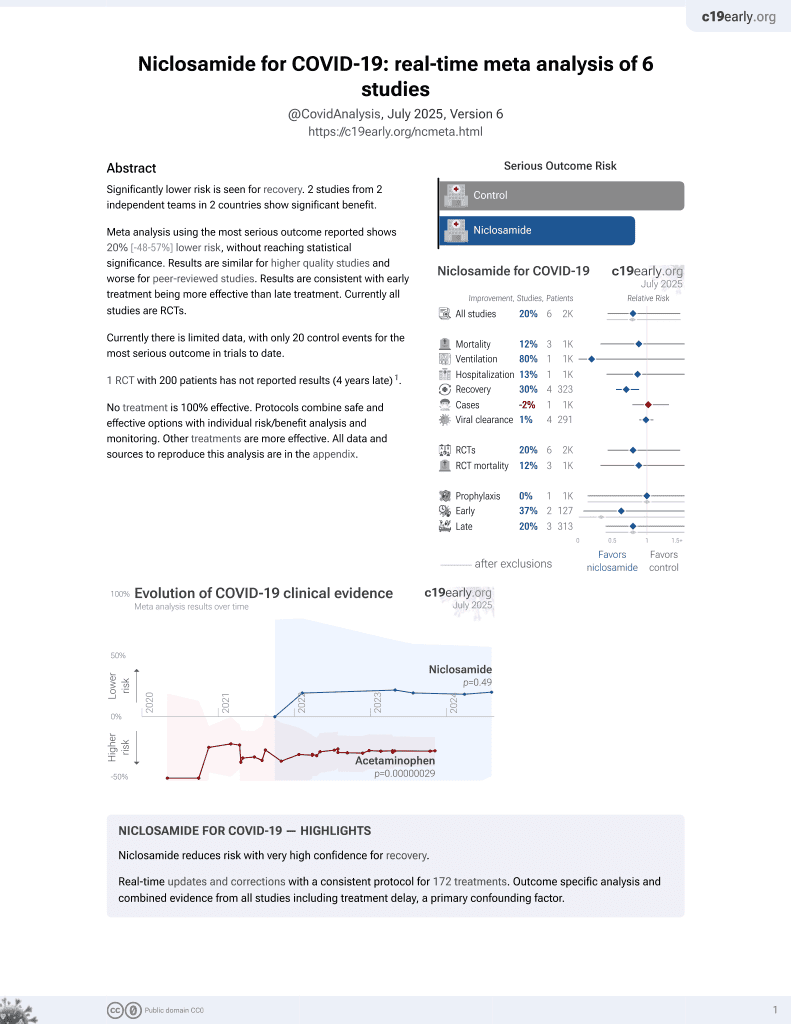
56th treatment shown to reduce risk in
August 2025, now with p = 0.0069 from 7 studies.
Lower risk for recovery.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
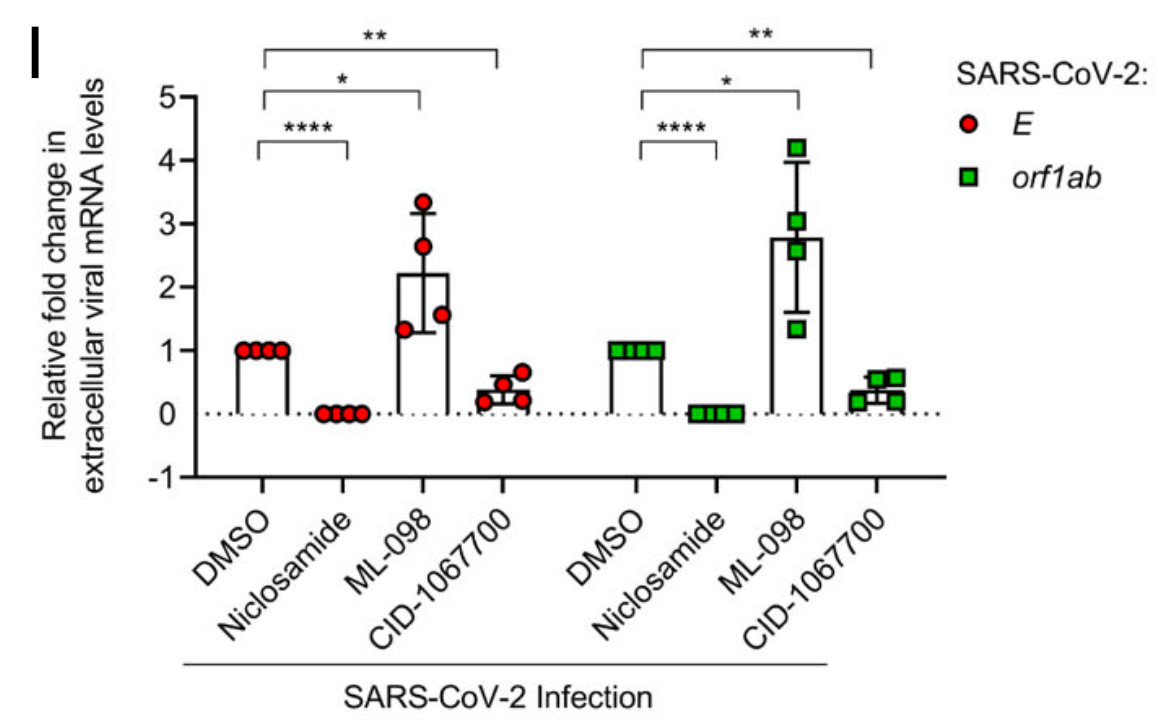
In vitro study showing that SARS-CoV-2 ORF3a protein hyperactivates the Rab7 GTPase to block lysosomal degradation and promote viral replication. Authors found that the chemical compound CID-1067700, a Rab7 inhibitor, reduced SARS-CoV-2 replication in infected Vero E6 cells, while the Rab7 activator ML-098 enhanced viral replication. The results suggest that Rab7 hyperactivation by the viral ORF3a protein is beneficial for SARS-CoV-2, likely by preventing the degradation of viral components in lysosomes. Inhibiting Rab7 with CID-1067700 impaired viral replication, indicating Rab7 could be a potential therapeutic target.
Niclosamide was used as a positive control and showed the most potent inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 replication in this study.
9 preclinical studies support the efficacy of niclosamide for COVID-19:
In silico studies predict inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 with niclosamide or metabolites via binding to the spikeA,1, MproB,1, RNA-dependent RNA polymeraseC,1, PLproD,1, nucleocapsidE,1, and helicaseF,1 proteins.
Niclosamide inhibits endolysosomal acidification and suppresses
TLR3-mediated pro-inflammatory signaling in human small airway
epithelial cells stimulated with TLR3 agonists mimicking viral RNA2, modulates host lipid metabolism and reduces
infectious SARS-CoV-2 virion production in Vero E6 cells4, reduces CD147 protein levels and inhibits
SARS-CoV-2-induced upregulation of CD147 in A549-ACE2 cells, including
the highly glycosylated form of CD147 which has been implicated in
COVID-19 disease progression and post-COVID-19 cardiac complications5, blocked the formation of syncytia mediated by
SARS-CoV-2 spike protein pseudovirus-producing cells6, may reduce inflammation, NLRP3 formation, and
caspase-1 activity9, may inhibit viral uncoating, replication, and
assembly via disruption of pH gradients and reduced ATP production in
host cells8, may counter immune evasion by reversing E-, ORF7a-, and ORF8-mediated down-regulation of MHC-I, preserving CD8⁺ T-cell recognition10, and shows strong synergy when combined with
ivermectin7.
1.
Haque et al., Exploring potential therapeutic candidates against COVID-19: a molecular docking study, Discover Molecules, doi:10.1007/s44345-024-00005-5.
2.
Pejler et al., Blockade of endolysosomal acidification suppresses TLR3-mediated pro-inflammatory signaling in airway epithelial cells, Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2024.05.031.
3.
Walia et al., SARS-CoV-2 virulence factor ORF3a blocks lysosome function by modulating TBC1D5-dependent Rab7 GTPase cycle, Nature Communications, doi:10.1038/s41467-024-46417-2.
4.
Garrett et al., Niclosamide as a chemical probe for analyzing SARS-CoV-2 modulation of host cell lipid metabolism, Frontiers in Microbiology, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2023.1251065.
5.
Yang et al., Repurposing Niclosamide as a Novel Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Drug by Restricting Entry Protein CD147, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines11072019.
6.
Sheng et al., A pseudovirus-based method to dynamically mimic SARS-CoV-2-associated cell-to-cell fusion and transmission, Acta Biochimica et Biophysica Sinica, doi:10.3724/abbs.2023129.
7.
Jitobaom et al., Synergistic anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity of repurposed anti-parasitic drug combinations, BMC Pharmacology and Toxicology, doi:10.1186/s40360-022-00580-8.
8.
Needham, D., The pH Dependence of Niclosamide Solubility, Dissolution, and Morphology: Motivation for Potentially Universal Mucin-Penetrating Nasal and Throat Sprays for COVID19, its Variants and other Viral Infections, Pharmaceutical Research, doi:10.1007/s11095-021-03112-x.
a.
The trimeric spike (S) protein is a glycoprotein that mediates viral entry by binding to the host ACE2 receptor, is critical for SARS-CoV-2's ability to infect host cells, and is a target of neutralizing antibodies. Inhibition of the spike protein prevents viral attachment, halting infection at the earliest stage.
b.
The main protease or Mpro, also known as 3CLpro or nsp5, is a cysteine protease that cleaves viral polyproteins into functional units needed for replication. Inhibiting Mpro disrupts the SARS-CoV-2 lifecycle within the host cell, preventing the creation of new copies.
c.
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp), also called nsp12, is the core enzyme of the viral replicase-transcriptase complex that copies the positive-sense viral RNA genome into negative-sense templates for progeny RNA synthesis. Inhibiting RdRp blocks viral genome replication and transcription.
d.
The papain-like protease (PLpro) has multiple functions including cleaving viral polyproteins and suppressing the host immune response by deubiquitination and deISGylation of host proteins. Inhibiting PLpro may block viral replication and help restore normal immune responses.
e.
The nucleocapsid (N) protein binds and encapsulates the viral genome by coating the viral RNA. N enables formation and release of infectious virions and plays additional roles in viral replication and pathogenesis. N is also an immunodominant antigen used in diagnostic assays.
f.
The helicase, or nsp13, protein unwinds the double-stranded viral RNA, a crucial step in replication and transcription. Inhibition may prevent viral genome replication and the creation of new virus components.
Walia et al., 6 Mar 2024, peer-reviewed, 8 authors.
Contact: atuli@imtech.res.in.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Abstract: Article
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-46417-2
SARS-CoV-2 virulence factor ORF3a blocks
lysosome function by modulating TBC1D5dependent Rab7 GTPase cycle
Received: 12 June 2023
Check for updates
1234567890():,;
1234567890():,;
Accepted: 26 February 2024
Kshitiz Walia1,2, Abhishek Sharma1, Sankalita Paul3, Priya Chouhan1,2,
Gaurav Kumar 1, Rajesh Ringe1, Mahak Sharma 3 & Amit Tuli 1,2
SARS-CoV-2, the causative agent of COVID-19, uses the host endolysosomal
system for entry, replication, and egress. Previous studies have shown that the
SARS-CoV-2 virulence factor ORF3a interacts with the lysosomal tethering
factor HOPS complex and blocks HOPS-mediated late endosome and autophagosome fusion with lysosomes. Here, we report that SARS-CoV-2 infection
leads to hyperactivation of the late endosomal and lysosomal small GTPbinding protein Rab7, which is dependent on ORF3a expression. We also
observed Rab7 hyperactivation in naturally occurring ORF3a variants encoded
by distinct SARS-CoV-2 variants. We found that ORF3a, in complex with Vps39,
sequesters the Rab7 GAP TBC1D5 and displaces Rab7 from this complex. Thus,
ORF3a disrupts the GTP hydrolysis cycle of Rab7, which is beneficial for viral
production, whereas the Rab7 GDP-locked mutant strongly reduces viral
replication. Hyperactivation of Rab7 in ORF3a-expressing cells impaired CIM6PR retrieval from late endosomes to the trans-Golgi network, disrupting the
biosynthetic transport of newly synthesized hydrolases to lysosomes. Furthermore, the tethering of the Rab7- and Arl8b-positive compartments was
strikingly reduced upon ORF3a expression. As SARS-CoV-2 egress requires
Arl8b, these findings suggest that ORF3a-mediated hyperactivation of Rab7
serves a multitude of functions, including blocking endolysosome formation,
interrupting the transport of lysosomal hydrolases, and promoting viral
egress.
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the
agent responsible for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), is a positive sense single-stranded RNA virus belonging to the beta-coronavirus
(β-CoV) genus. Positive-sense RNA viruses are known to modify
endomembrane compartments to produce replication compartments
(RCs). These RCs contain viral RNA and proteins, in addition to host
proteins and lipids, and provide a barrier between viral replication and
the host cytosol, which contains the viral RNA degradation machinery
and innate immune sensors1,2. The viral particles formed from
structural proteins assemble in the ER-Golgi intermediate compartment. Ultimately, virions transit in vesicles and undergo exocytosis via
the biosynthetic secretory pathway3. Interestingly, another mechanism
for extracellular release, in which virions reside in deacidified lysosomes that fuse with the plasma membrane has recently been reported
for β-CoVs, including SARS-CoV-24.
The genomic size of SARS-CoV-2 ranges from 29.8 kb to 29.9 kb,
encompassing eleven genes with open reading frames (ORFs)5,6. The 5’
genomic region constitutes more than two-thirds of the genome and
1
Division of Cell Biology and Immunology, CSIR-Institute of Microbial Technology (IMTECH), Chandigarh, India. 2Academy of Scientific and Innovative
Research (AcSIR), Ghaziabad, Uttar Pradesh, India. 3Department of Biological Sciences, Indian Institute of Science Education and Research (IISER), Mohali,
e-mail: atuli@imtech.res.in
Punjab, India.
Nature Communications | (2024)15:2053
1
Article
encodes the ORF1ab polyproteins. In..
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-024-46417-2",
"ISSN": [
"2041-1723"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-46417-2",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:p>SARS-CoV-2, the causative agent of COVID-19, uses the host endolysosomal system for entry, replication, and egress. Previous studies have shown that the SARS-CoV-2 virulence factor ORF3a interacts with the lysosomal tethering factor HOPS complex and blocks HOPS-mediated late endosome and autophagosome fusion with lysosomes. Here, we report that SARS-CoV-2 infection leads to hyperactivation of the late endosomal and lysosomal small GTP-binding protein Rab7, which is dependent on ORF3a expression. We also observed Rab7 hyperactivation in naturally occurring ORF3a variants encoded by distinct SARS-CoV-2 variants. We found that ORF3a, in complex with Vps39, sequesters the Rab7 GAP TBC1D5 and displaces Rab7 from this complex. Thus, ORF3a disrupts the GTP hydrolysis cycle of Rab7, which is beneficial for viral production, whereas the Rab7 GDP-locked mutant strongly reduces viral replication. Hyperactivation of Rab7 in ORF3a-expressing cells impaired CI-M6PR retrieval from late endosomes to the trans-Golgi network, disrupting the biosynthetic transport of newly synthesized hydrolases to lysosomes. Furthermore, the tethering of the Rab7- and Arl8b-positive compartments was strikingly reduced upon ORF3a expression. As SARS-CoV-2 egress requires Arl8b, these findings suggest that ORF3a-mediated hyperactivation of Rab7 serves a multitude of functions, including blocking endolysosome formation, interrupting the transport of lysosomal hydrolases, and promoting viral egress.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"46417"
],
"article-number": "2053",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "12 June 2023"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "26 February 2024"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "6 March 2024"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1,
"value": "The authors declare no competing interests."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Walia",
"given": "Kshitiz",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sharma",
"given": "Abhishek",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Paul",
"given": "Sankalita",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chouhan",
"given": "Priya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9614-1032",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kumar",
"given": "Gaurav",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ringe",
"given": "Rajesh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4117-4790",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Sharma",
"given": "Mahak",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5476-4127",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Tuli",
"given": "Amit",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Nature Communications",
"container-title-short": "Nat Commun",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-06T18:02:49Z",
"timestamp": 1709748169000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-06T19:04:20Z",
"timestamp": 1709751860000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100001843",
"award": [
"CRG/2022/003266",
"CVD/2020/000733",
"IPA/2020/000168"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "DST | Science and Engineering Research Board"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100009053",
"award": [
"IA/I/14/2/501543",
"IA/S/19/1/504270"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "DBT India Alliance"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100001407",
"award": [
"BT/HRD/NWBA/39/01/2018-19"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Department of Biotechnology, Ministry of Science and Technology"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-07T00:35:17Z",
"timestamp": 1709771717696
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
6
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-06T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1709683200000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-06T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1709683200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-46417-2.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-46417-2",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-46417-2.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1038",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
6
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
6
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mib.2016.05.003",
"author": "A Shulla",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "82",
"journal-title": "Curr. Opin. Microbiol.",
"key": "46417_CR1",
"unstructured": "Shulla, A. & Randall, G. (+) RNA virus replication compartments: a safe home for (most) viral replication. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 32, 82–88 (2016).",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/boc.202200073",
"author": "V Prasad",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Biol. Cell",
"key": "46417_CR2",
"unstructured": "Prasad, V. & Bartenschlager, R. A snapshot of protein trafficking in SARS-CoV-2 infection. Biol. Cell 115, e2200073 (2023).",
"volume": "115",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrmicro1890",
"author": "S Miller",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "363",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Microbiol.",
"key": "46417_CR3",
"unstructured": "Miller, S. & Krijnse-Locker, J. Modification of intracellular membrane structures for virus replication. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 6, 363–374 (2008).",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.10.039",
"author": "S Ghosh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1520",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "46417_CR4",
"unstructured": "Ghosh, S. et al. beta-coronaviruses use lysosomes for egress instead of the biosynthetic secretory pathway. Cell 183, 1520–1535.e1514 (2020).",
"volume": "183",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.genrep.2020.100682",
"author": "RA Khailany",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Gene Rep.",
"key": "46417_CR5",
"unstructured": "Khailany, R. A., Safdar, M. & Ozaslan, M. Genomic characterization of a novel SARS-CoV-2. Gene Rep. 19, 100682 (2020).",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10930-020-09947-4",
"author": "FK Yoshimoto",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "599",
"journal-title": "Protein J.",
"key": "46417_CR6",
"unstructured": "Yoshimoto, F. K. & Berliner, L. J. Editorial: proteins of SARS CoV-2, the Cause of COVID-19, and the proteins that interact with them. Protein J. 39, 599 (2020).",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmicb.2022.854567",
"author": "J Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front. Microbiol.",
"key": "46417_CR7",
"unstructured": "Zhang, J. et al. Understanding the role of SARS-CoV-2 ORF3a in viral pathogenesis and COVID-19. Front. Microbiol. 13, 854567 (2022).",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41594-021-00619-0",
"author": "DM Kern",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "573",
"journal-title": "Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol.",
"key": "46417_CR8",
"unstructured": "Kern, D. M. et al. Cryo-EM structure of SARS-CoV-2 ORF3a in lipid nanodiscs. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 28, 573–582 (2021).",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.0605402103",
"author": "W Lu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "12540",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "46417_CR9",
"unstructured": "Lu, W. et al. Severe acute respiratory syndrome-associated coronavirus 3a protein forms an ion channel and modulates virus release. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 12540–12545 (2006).",
"volume": "103",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mSystems.00266-20",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "46417_CR10",
"unstructured": "Issa, E., Merhi, G., Panossian, B., Salloum, T. & Tokajian, S. SARS-CoV-2 and ORF3a: Nonsynonymous Mutations, Functional Domains, and Viral Pathogenesis. mSystems 5, https://doi.org/10.1128/mSystems.00266-20 (2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.00402-21",
"author": "JA Silvas",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "46417_CR11",
"unstructured": "Silvas, J. A. et al. Contribution of SARS-CoV-2 accessory proteins to viral pathogenicity in K18 human ACE2 transgenic mice. J. Virol. 95, e0040221 (2021).",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2021.02.044",
"author": "X Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2229",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "46417_CR12",
"unstructured": "Zhang, X. et al. A trans-complementation system for SARS-CoV-2 recapitulates authentic viral replication without virulence. Cell 184, 2229–2238 e2213 (2021).",
"volume": "184",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.febslet.2004.03.086",
"author": "CJ Yu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "111",
"journal-title": "FEBS Lett.",
"key": "46417_CR13",
"unstructured": "Yu, C. J. et al. Identification of a novel protein 3a from severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus. FEBS Lett. 565, 111–116 (2004).",
"volume": "565",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s42003-021-02866-9",
"author": "TL Toft-Bertelsen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1347",
"journal-title": "Commun. Biol.",
"key": "46417_CR14",
"unstructured": "Toft-Bertelsen, T. L. et al. Amantadine has potential for the treatment of COVID-19 because it inhibits known and novel ion channels encoded by SARS-CoV-2. Commun. Biol. 4, 1347 (2021).",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7554/eLife.84477",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "46417_CR15",
"unstructured": "Miller, A. N. et al. The SARS-CoV-2 accessory protein Orf3a is not an ion channel, but does interact with trafficking proteins. Elife 12, https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.84477 (2023)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.devcel.2020.12.010",
"author": "G Miao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "427",
"journal-title": "Dev. Cell",
"key": "46417_CR16",
"unstructured": "Miao, G. et al. ORF3a of the COVID-19 virus SARS-CoV-2 blocks HOPS complex-mediated assembly of the SNARE complex required for autolysosome formation. Dev. Cell 56, 427–442.e425 (2021).",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.devcel.2021.10.006",
"author": "D Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3250",
"journal-title": "Dev. Cell",
"key": "46417_CR17",
"unstructured": "Chen, D. et al. ORF3a of SARS-CoV-2 promotes lysosomal exocytosis-mediated viral egress. Dev. Cell 56, 3250–3263.e3255 (2021).",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcell.2022.1011221",
"author": "R Cruz-Cosme",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front. Cell Dev. Biol.",
"key": "46417_CR18",
"unstructured": "Cruz-Cosme, R. et al. A novel diG motif in ORF3a protein of SARS-Cov-2 for intracellular transport. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 10, 1011221 (2022).",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1743-422X-11-75",
"author": "R Minakshi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "75",
"journal-title": "Virol. J.",
"key": "46417_CR19",
"unstructured": "Minakshi, R. & Padhan, K. The YXXPhi motif within the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) 3a protein is crucial for its intracellular transport. Virol. J. 11, 75 (2014).",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41421-021-00268-z",
"author": "Y Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "31",
"journal-title": "Cell Discov.",
"key": "46417_CR20",
"unstructured": "Zhang, Y. et al. The SARS-CoV-2 protein ORF3a inhibits fusion of autophagosomes with lysosomes. Cell Discov. 7, 31 (2021).",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1083/jcb.201607085",
"author": "R Marwaha",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1051",
"journal-title": "J. Cell Biol.",
"key": "46417_CR21",
"unstructured": "Marwaha, R. et al. The Rab7 effector PLEKHM1 binds Arl8b to promote cargo traffic to lysosomes. J. Cell Biol. 216, 1051–1070 (2017).",
"volume": "216",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-022-29077-y",
"author": "G Kumar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "46417_CR22",
"unstructured": "Kumar, G. et al. RUFY3 links Arl8b and JIP4-Dynein complex to regulate lysosome size and positioning. Nat. Commun. 13, 1540 (2022).",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.aan6298",
"author": "M Abu-Remaileh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "807",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "46417_CR23",
"unstructured": "Abu-Remaileh, M. et al. Lysosomal metabolomics reveals V-ATPase- and mTOR-dependent regulation of amino acid efflux from lysosomes. Science 358, 807–813 (2017).",
"volume": "358",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"author": "D Khatter",
"first-page": "1746",
"journal-title": "J. Cell Sci.",
"key": "46417_CR24",
"unstructured": "Khatter, D. et al. The small GTPase Arl8b regulates assembly of the mammalian HOPS complex on lysosomes. J. Cell Sci. 128, 1746–1761 (2015).",
"volume": "128",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1083/jcb.202108001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "46417_CR25",
"unstructured": "Rawat, S. et al. RUFY1 binds Arl8b and mediates endosome-to-TGN CI-M6PR retrieval for cargo sorting to lysosomes. J. Cell Biol. 222, https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.202108001 (2023)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.21769/BioProtoc.2571",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "46417_CR26",
"unstructured": "Marwaha, R. & Sharma, M. DQ-Red BSA Trafficking Assay in Cultured Cells to Assess Cargo Delivery to Lysosomes. Biol. Protoc. 7, https://doi.org/10.21769/BioProtoc.2571 (2017)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcell.2021.716208",
"author": "Y Qu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front. Cell Dev. Biol.",
"key": "46417_CR27",
"unstructured": "Qu, Y. et al. ORF3a-mediated incomplete autophagy facilitates severe acute respiratory syndrome Coronavirus-2 Replication. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 9, 716208 (2021).",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2286-9",
"author": "DE Gordon",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "459",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "46417_CR28",
"unstructured": "Gordon, D. E. et al. A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing. Nature 583, 459–468 (2020).",
"volume": "583",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.molcel.2014.11.006",
"author": "DG McEwan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "39",
"journal-title": "Mol. Cell",
"key": "46417_CR29",
"unstructured": "McEwan, D. G. et al. PLEKHM1 regulates autophagosome-lysosome fusion through HOPS complex and LC3/GABARAP proteins. Mol. Cell 57, 39–54 (2015).",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.0601617103",
"author": "BL Grosshans",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "11821",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "46417_CR30",
"unstructured": "Grosshans, B. L., Ortiz, D. & Novick, P. Rabs and their effectors: achieving specificity in membrane traffic. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 11821–11827 (2006).",
"volume": "103",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/15548627.2015.1034419",
"author": "DG McEwan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "720",
"journal-title": "Autophagy",
"key": "46417_CR31",
"unstructured": "McEwan, D. G. & Dikic, I. PLEKHM1: adapting to life at the lysosome. Autophagy 11, 720–722 (2015).",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chom.2014.11.011",
"author": "DG McEwan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "58",
"journal-title": "Cell Host Microbe.",
"key": "46417_CR32",
"unstructured": "McEwan, D. G. et al. PLEKHM1 regulates Salmonella-containing vacuole biogenesis and infection. Cell Host Microbe. 17, 58–71 (2015).",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1091/mbc.e08-09-0911",
"author": "K Romero Rosales",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2831",
"journal-title": "Mol. Biol. Cell",
"key": "46417_CR33",
"unstructured": "Romero Rosales, K., Peralta, E. R., Guenther, G. G., Wong, S. Y. & Edinger, A. L. Rab7 activation by growth factor withdrawal contributes to the induction of apoptosis. Mol. Biol. Cell 20, 2831–2840 (2009).",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0960-9822(01)00531-0",
"author": "I Jordens",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1680",
"journal-title": "Curr. Biol.",
"key": "46417_CR34",
"unstructured": "Jordens, I. et al. The Rab7 effector protein RILP controls lysosomal transport by inducing the recruitment of dynein-dynactin motors. Curr. Biol. 11, 1680–1685 (2001).",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1091/mbc.e05-03-0189",
"author": "M Johansson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "5480",
"journal-title": "Mol. Biol. Cell",
"key": "46417_CR35",
"unstructured": "Johansson, M., Lehto, M., Tanhuanpaa, K., Cover, T. L. & Olkkonen, V. M. The oxysterol-binding protein homologue ORP1L interacts with Rab7 and alters functional properties of late endocytic compartments. Mol. Biol. Cell 16, 5480–5492 (2005).",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ncomms13305",
"author": "D Jia",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "46417_CR36",
"unstructured": "Jia, D. et al. Structural and mechanistic insights into regulation of the retromer coat by TBC1d5. Nat. Commun. 7, 13305 (2016).",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/sj.embor.7401055",
"author": "A Mukhopadhyay",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "931",
"journal-title": "EMBO Rep.",
"key": "46417_CR37",
"unstructured": "Mukhopadhyay, A., Pan, X., Lambright, D. G. & Tissenbaum, H. A. An endocytic pathway as a target of tubby for regulation of fat storage. EMBO Rep. 8, 931–938 (2007).",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.07.070",
"author": "XM Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "154",
"journal-title": "Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.",
"key": "46417_CR38",
"unstructured": "Zhang, X. M., Walsh, B., Mitchell, C. A. & Rowe, T. TBC domain family, member 15 is a novel mammalian Rab GTPase-activating protein with substrate preference for Rab7. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 335, 154–161 (2005).",
"volume": "335",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M110.111633",
"author": "ER Peralta",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "16814",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "46417_CR39",
"unstructured": "Peralta, E. R., Martin, B. C. & Edinger, A. L. Differential effects of TBC1D15 and mammalian Vps39 on Rab7 activation state, lysosomal morphology, and growth factor dependence. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 16814–16821 (2010).",
"volume": "285",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/15548627.2021.1946739",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "46417_CR40",
"unstructured": "Jin, X. et al. RAB7 activity is required for the regulation of mitophagy in oocyte meiosis and oocyte quality control during ovarian aging. Autophagy. 18, 643–660 (2022)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/cb3001099",
"author": "JO Agola",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1095",
"journal-title": "ACS Chem. Biol.",
"key": "46417_CR41",
"unstructured": "Agola, J. O. et al. A competitive nucleotide binding inhibitor: in vitro characterization of Rab7 GTPase inhibition. ACS Chem. Biol. 7, 1095–1108 (2012).",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1083/jcb.202105120",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "46417_CR42",
"unstructured": "Borchers, A. C., Langemeyer, L. & Ungermann, C. Who’s in control? Principles of Rab GTPase activation in endolysosomal membrane trafficking and beyond. J. Cell Biol. 220, https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.202105120 (2021)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcell.2023.1140605",
"author": "DP Buser",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front. Cell Dev. Biol.",
"key": "46417_CR43",
"unstructured": "Buser, D. P. & Spang, A. Protein sorting from endosomes to the TGN. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 11, 1140605 (2023).",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/tra.12574",
"author": "J Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "578",
"journal-title": "Traffic",
"key": "46417_CR44",
"unstructured": "Wang, J. et al. Endosomal receptor trafficking: retromer and beyond. Traffic 19, 578–590 (2018).",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/tra.12136",
"author": "J Follett",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "230",
"journal-title": "Traffic",
"key": "46417_CR45",
"unstructured": "Follett, J. et al. The Vps35 D620N mutation linked to Parkinson’s disease disrupts the cargo sorting function of retromer. Traffic 15, 230–244 (2014).",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/tra.12237",
"author": "A Priya",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "68",
"journal-title": "Traffic",
"key": "46417_CR46",
"unstructured": "Priya, A., Kalaidzidis, I. V., Kalaidzidis, Y., Lambright, D. & Datta, S. Molecular insights into Rab7-mediated endosomal recruitment of core retromer: deciphering the role of Vps26 and Vps35. Traffic 16, 68–84 (2015).",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15252/embj.2019102301",
"author": "ML Jongsma",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "EMBO J.",
"key": "46417_CR47",
"unstructured": "Jongsma, M. L. et al. SKIP-HOPS recruits TBC1D15 for a Rab7-to-Arl8b identity switch to control late endosome transport. EMBO J. 39, e102301 (2020).",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1423456112",
"author": "A Jeschke",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4636",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "46417_CR48",
"unstructured": "Jeschke, A. et al. Phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate and phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate regulate phagolysosome biogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 112, 4636–4641 (2015).",
"volume": "112",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.immuni.2011.06.009",
"author": "S Garg",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "182",
"journal-title": "Immunity",
"key": "46417_CR49",
"unstructured": "Garg, S. et al. Lysosomal trafficking, antigen presentation, and microbial killing are controlled by the Arf-like GTPase Arl8b. Immunity 35, 182–193 (2011).",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcell.2021.648024",
"author": "X Yong",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front. Cell Dev. Biol.",
"key": "46417_CR50",
"unstructured": "Yong, X. et al. Targeting Endosomal Recycling Pathways by Bacterial and Viral Pathogens. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 9, 648024 (2021).",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virs.2022.04.014",
"author": "Y Lu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "321",
"journal-title": "Virol. Sin.",
"key": "46417_CR51",
"unstructured": "Lu, Y., He, P., Zhang, Y., Ren, Y. & Zhang, L. The emerging roles of retromer and sorting nexins in the life cycle of viruses. Virol. Sin. 37, 321–330 (2022).",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1515/hsz-2022-0294",
"author": "D Kummel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "441",
"journal-title": "Biol. Chem.",
"key": "46417_CR52",
"unstructured": "Kummel, D., Herrmann, E., Langemeyer, L. & Ungermann, C. Molecular insights into endolysosomal microcompartment formation and maintenance. Biol. Chem. 404, 441–454 (2023).",
"volume": "404",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"author": "MT Shi",
"first-page": "12",
"journal-title": "Yi Chuan",
"key": "46417_CR53",
"unstructured": "Shi, M. T., Zhang, Y. & Zhou, G. Q. The critical roles of TBC proteins in human diseases. Yi Chuan 40, 12–21 (2018).",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1083/jcb.201611027",
"author": "P Lorincz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1937",
"journal-title": "J. Cell Biol.",
"key": "46417_CR54",
"unstructured": "Lorincz, P. et al. Rab2 promotes autophagic and endocytic lysosomal degradation. J. Cell Biol. 216, 1937–1947 (2017).",
"volume": "216",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1091/mbc.e13-05-0259",
"author": "A Tuli",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3721",
"journal-title": "Mol. Biol. Cell",
"key": "46417_CR55",
"unstructured": "Tuli, A. et al. Arf-like GTPase Arl8b regulates lytic granule polarization and natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Mol. Biol. Cell 24, 3721–3735 (2013).",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112286",
"author": "X Tan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep.",
"key": "46417_CR56",
"unstructured": "Tan, X. et al. Coronavirus subverts ER-phagy by hijacking FAM134B and ATL3 into p62 condensates to facilitate viral replication. Cell Rep. 42, 112286 (2023).",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2016.05.078",
"author": "ML Jongsma",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "152",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "46417_CR57",
"unstructured": "Jongsma, M. L. et al. An ER-associated pathway defines endosomal architecture for controlled cargo transport. Cell 166, 152–166 (2016).",
"volume": "166",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/0471142956.cy0219s62",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "46417_CR58",
"unstructured": "Day, C. A., Kraft, L. J., Kang, M. & Kenworthy, A. K. Analysis of protein and lipid dynamics using confocal fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP). Curr. Protoc. Cytom Chapter 2, Unit2 19, https://doi.org/10.1002/0471142956.cy0219s62 (2012)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/bs.mcb.2021.06.003",
"author": "A Sharma",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "235",
"journal-title": "Methods Cell Biol.",
"key": "46417_CR59",
"unstructured": "Sharma, A. et al. Methods for binding analysis of small GTP-binding proteins with their effectors. Methods Cell Biol. 166, 235–250 (2021).",
"volume": "166",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3201/eid2606.200516",
"author": "J Harcourt",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1266",
"journal-title": "Emerg. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "46417_CR60",
"unstructured": "Harcourt, J. et al. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 from patient with coronavirus disease, United States. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 26, 1266–1273 (2020).",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcell.2017.00071",
"author": "L Ma",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "71",
"journal-title": "Front. Cell Dev. Biol.",
"key": "46417_CR61",
"unstructured": "Ma, L., Ouyang, Q., Werthmann, G. C., Thompson, H. M. & Morrow, E. M. Live-cell microscopy and fluorescence-based measurement of Luminal pH in intracellular organelles. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 5, 71 (2017).",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1006700",
"author": "A Sindhwani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e1006700",
"journal-title": "PLoS Pathog",
"key": "46417_CR62",
"unstructured": "Sindhwani, A. et al. Salmonella exploits the host endolysosomal tethering factor HOPS complex to promote its intravacuolar replication. PLoS Pathog 13, e1006700 (2017).",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1908409116",
"author": "L Niu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "14029",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "46417_CR63",
"unstructured": "Niu, L. et al. Atlastin-mediated membrane tethering is critical for cargo mobility and exit from the endoplasmic reticulum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 116, 14029–14038 (2019).",
"volume": "116",
"year": "2019"
}
],
"reference-count": 63,
"references-count": 63,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-024-46417-2"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Physics and Astronomy",
"General Biochemistry, Genetics and Molecular Biology",
"General Chemistry",
"Multidisciplinary"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "SARS-CoV-2 virulence factor ORF3a blocks lysosome function by modulating TBC1D5-dependent Rab7 GTPase cycle",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "15"
}