Efficacy of Andrographis paniculata extract treatment in mild to moderate COVID-19 patients being treated with favipiravir: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study (APFaVi trial)
et al., Phytomedicine, doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018, APFaVi, TCTR20210609001, Aug 2023
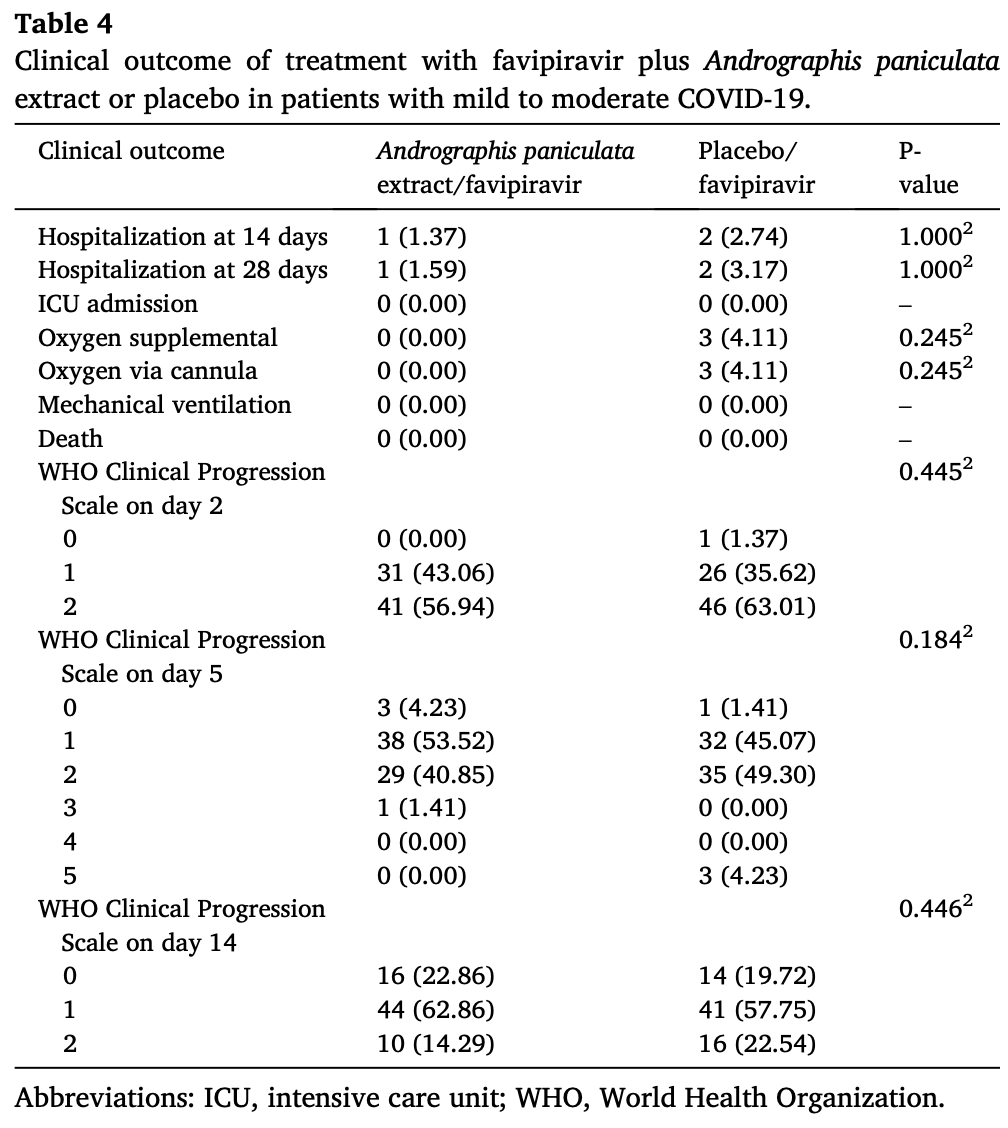
RCT 146 mild/moderate COVID-19 patients in Thailand, showing no significant difference in clinical outcomes. There were very few serious outcomes.
|
risk of hospitalization, 50.0% lower, RR 0.50, p = 1.00, treatment 1 of 73 (1.4%), control 2 of 73 (2.7%), NNT 73, day 28.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 50.0% lower, RR 0.50, p = 1.00, treatment 1 of 73 (1.4%), control 2 of 73 (2.7%), NNT 73, day 14.
|
|
risk of oxygen therapy, 85.7% lower, RR 0.14, p = 0.24, treatment 0 of 73 (0.0%), control 3 of 73 (4.1%), NNT 24, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
risk of progression, 49.3% lower, RR 0.51, p = 1.00, treatment 1 of 71 (1.4%), control 2 of 72 (2.8%), NNT 73, day 4.
|
|
WHO scale ≥2, 36.6% lower, RR 0.63, p = 0.28, treatment 10 of 71 (14.1%), control 16 of 72 (22.2%), NNT 12, day 14.
|
|
WHO scale ≥1, 3.9% lower, RR 0.96, p = 0.69, treatment 54 of 71 (76.1%), control 57 of 72 (79.2%), NNT 32, day 14.
|
|
CT severity, 33.3% lower, RR 0.67, p = 0.24, treatment 71, control 72, day 5.
|
|
relative Ct improvement, 5.0% worse, RR 1.05, p = 0.46, treatment 71, control 72, E gene, day 5.
|
|
relative Ct improvement, 13.3% worse, RR 1.13, p = 0.34, treatment 71, control 72, ORF, day 5.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Siripongboonsitti et al., 12 Aug 2023, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, Thailand, peer-reviewed, 10 authors, study period 11 June, 2021 - 15 September, 2021, average treatment delay 2.0 days, trial TCTR20210609001 (APFaVi).
Contact: nithimahanonda.cra@gmail.com.
Efficacy of Andrographis paniculata extract treatment in mild to moderate COVID-19 patients being treated with favipiravir: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study (APFaVi trial)
Phytomedicine, doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018
Background: While favipiravir had been the standard anti-SARS-CoV-3 drug for COVID-19 treatment in Thailand, the efficacy of favipiravir treatment is controversial. Andrographis paniculata extract (APE) inhibits viral entry, exhibits immunomodulatory effects, and proposes to have the potential for early-stage COVID-19 treatment. Methods: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial was performed in Thailand during June -September 2021. Non-severe COVID-19 patients were randomized 1:1 to groups receiving 180 mg/day of APE plus favipiravir (APE-FPV group) or placebo plus favipiravir (placebo-FPV group). Efficacy in preventing disease progression to severe COVID-19 was assessed on day 4, using World Health Organization Clinical Progression Scale (WHO-CPS) score and visual analog scale (VAS) for acute respiratory tract infection symptoms. Results: Of 146 patients, there were 73 patients in each group. Non-deterioration of WHO -CPS scores on day 4 was 98.63% versus 97.26% of patients in the APE-FPV and placebo-FPV groups (p = 1.000). No difference in supplemental oxygen, hospitalization, and death was shown in both groups. The oxygen supplemental was 4.11% in the placebo-FPV group. The interleukin (IL)-1β was significantly lower in the APE than in the placebo-FPV group throughout the study. We found no difference in virologic outcomes between groups and no substantial adverse events. Conclusions: APE treatment did not demonstrate additional clinical and virological benefits in patients with mild to moderate COVID-19 being treated with favipiravir. Early reduction of IL-1β with APE may be advantageous in preventing cytokine storms in severe COVID-19 and requires further study.
Authors' contributions T.S. and N.M. had full access to all the data in this study and took responsibility for data integrity and accuracy. C.M., N.M., C.A., K.T., T. S., T.U., W.C., T.J., R.J., and K.S. contributed equally to the study.
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Taweegrit Siripongboonsitti reports financial support, administrative support, article publishing charges, equipment, drugs, or supplies, and statistical analysis were provided by Chulabhorn Royal Academy.
Supplementary materials Supplementary material associated with this article can be found, in the online version, at doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018.
References
Bast, Tang, Dahn, Palacio, Increased risk of hospitalisation and death with the delta variant in the USA, Lancet Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/s1473-3099(21)00685-x
Benjaponpitak, Visithanon, Sawaengtham, Thaneerat, Wanaratna, Short Communication on Use of Andrographis Herb (FA THALAI CHON) for the Treatment of COVID-19 Patients, J. Thai Tradit. Alternat. Med
Bernal, Gomes Da Silva, Musungaie, Kovalchuk, Gonzalez et al., Molnupiravir for oral treatment of Covid-19 in nonhospitalized patients, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2116044
Caceres, Hancke, Burgos, Wikman, Prevention of common colds with Andrographis paniculata dried extract. A pilot double blind trial, Phytomedicine
Cai, Yang, Liu, Chen, Shu et al., Experimental treatment with favipiravir for COVID-19: an open-label control study, Engineering (Beijing), doi:10.1016/j.eng.2020.03.007
Chen, Huang, Cheng, Wu, Chen et al., Favipiravir versus arbidol for COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, MedRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.03.17.20037432
Chuah, Chow, Hor, Cheng, Ker et al., Efficacy of early treatment with favipiravir on disease progression among high-risk patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a randomized, open-label clinical trial, Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciab962
Coon, Ernst, Andrographis paniculata in the treatment of upper respiratory tract infections: a systematic review of safety and efficacy, Planta Med
Dabbous, Abd-Elsalam, El-Sayed, Sherief, Ebeid et al., Efficacy of favipiravir in COVID-19 treatment: a multi-center randomized study, Arch. Virol, doi:10.1007/s00705-021-04956-9
Deng, Nie, Liu, Comparison of pharmacological effect of four andrographolides, Chinese Pharmaceut. Bull
Dey, Khanal, Patil, Wanjari, Srivast et al., The role of andrographolide and its derivative in COVID-19 associated proteins and immune system
Doi, Ando, Kuwatsuka, Ishihara, Favipiravir, Favipiravir observational study interim report 3
Du, Chen, Favipiravir: pharmacokinetics and concerns about clinical trials for 2019-nCoV infection, Clin. Pharmacol. Therapeut, doi:10.1002/cpt.1844
Fajgenbaum, June, Cytokine storm, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMra2026131
Francone, Iafrate, Masci, Coco, Cilia et al., Chest CT score in COVID-19 patients: correlation with disease severity and short-term prognosis, Eur. Radiol, doi:10.1007/s00330-020-07033-y
Furuta, Komeno, Nakamura, Favipiravir (T-705), a broad spectrum inhibitor of viral RNA polymerase, Proc. Jpn. Acad., Ser. B, doi:10.2183/pjab.93.027
Gabrielian, Shukarian, Goukasova, Chandanian, Panossian et al., A double blind, placebo-controlled study of Andrographis paniculata fixed combination Kan Jang in the treatment of acute upper respiratory tract infections including sinusitis, Phytomedicine
Golan, Campos, Woolson, Cilla, Hanabergh et al., Favipiravir in patients with early mild-tomoderate COVID-19: a randomized controlled trial, Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciac712
Hammond, Leister-Tebbe, Gardner, Abreu, Bao et al., Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk
Hassanipour, Arab-Zozani, Amani, Heidarzad, Fathalipour et al., The efficacy and safety of Favipiravir in treatment of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-90551-6
Hsu, Chang, Shen, Chuang, Andrographolide and its derivatives as TNF-alpha antagonists
Ivashchenko, Dmitriev, Vostokova, Azarova, Blinow et al., AVIFAVIR for treatment of patients with moderate coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): interim results of a phase II/III multicenter randomized clinical trial, Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa1176
Joshi, Parkar, Ansari, Vora, Talwar et al., Role of favipiravir in the treatment of COVID-19, Int. J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.10.069
Joshi, Vora, Venugopal, Dadhich, Daxini et al., Real-world experience with favipiravir for the treatment of mild-to-moderate COVID-19 in India, Pragmat Obs Res
Kligler, Ulbricht, Basch, Kirkwood, Abrams et al., Andrographis paniculata for the treatment of upper respiratory infection: a systematic review by the natural standard research collaboration, Explore: J. Sci. Heal
Lim, Chan, Tan, Teh, Mohd Abd Razak et al., Andrographis paniculata (Burm. F.) Wall. Ex Nees, andrographolide, and andrographolide analogues as SARS-CoV-2 antivirals? A rapid review, doi:10.1177/1934578X211016610
Madav, Tandan, Lal, Tripathi, Anti-inflammatory activity of andrographolide, Fitoterapia (Milano)
Madav, Tripathi, Mishra, Analgesic, antipyretic and antiulcerogenic effects of andrographolide, Indian J. Pharm. Sci
Mcmahon, Lau, Coldham, Roney, Hagenauer et al., Favipiravir in early symptomatic COVID-19, a randomised placebo-controlled trial, EClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101703
Mousavizadeh, Ghasemi, Genotype and phenotype of COVID-19: their roles in pathogenesis, J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jmii.2020.03.022
Nguyen, Corre, Honsel, Curac, Zarrouk et al., Applicability of the CURB-65 pneumonia severity score for outpatient treatment of COVID-19, J. Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2020.05.049
Poolsup, Suthisisang, Prathanturarug, Asawamekin, Chanchareon, Andrographis paniculata in the symptomatic treatment of uncomplicated upper respiratory tract infection: systematic review of randomized controlled trials, J Clin. Pharm. Ther
Qin, Kong, Shi, Wang, Ge, Andrographolide inhibits the production of TNF-α and interleukin-12 in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages: role of mitogen-activated protein kinases, Biol. Pharmaceut. Bull
Rehan, Ahmed, Howladar, Refai, Baeissa et al., A computational approach identified andrographolide as a potential drug for suppressing COVID-19-induced cytokine storm, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.648250
Romano, Ruggiero, Squeglia, Maga, Berisio, A structural view of SARS-CoV-2 RNA replication machinery: RNA synthesis, proofreading and final capping, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells9051267
Sa-Ngiamsuntorn, Suksatu, Pewkliang, Thongsri, Kanjanasirirat et al., Anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity of andrographis paniculata extract and its major component andrographolide in human lung epithelial cells and cytotoxicity evaluation in major organ cell representatives, J. Nat. Prod, doi:10.1021/acs.jnatprod.0c01324
Shen, Chen, Chiou, Andrographolide prevents oxygen radical production by human neutrophils: possible mechanism (s) involved in its antiinflammatory effect, Br. J. Pharmacol
Shrestha, Budhathoki, Khadka, Shah, Pokharel et al., Favipiravir versus other antiviral or standard of care for COVID-19 treatment: a rapid systematic review and meta-analysis, Virol. J, doi:10.1186/s12985-020-01412-z
Thamaree, Rugrungtham, Ruangrungsi, Thaworn, Kemsri, The inhibitory effects of extracts of some herbal medicines on the production of proinflammatory cytokines by in vitro stimulated human blood cells, Thai J. Pharmacol. S
Udwadia, Singh, Barkate, Patil, Rangwala et al., Efficacy and safety of favipiravir, an oral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase inhibitor, in mild-to-moderate COVID-19: a randomized, comparative, open-label, multicenter, phase 3 clinical trial, Int. J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.11.142
V'kovski, Kratzel, Steiner, Stalder, Thiel, Coronavirus biology and replication: implications for SARS-CoV-2, Nat. Rev. Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41579-020-00468-6
Wagner, Cramer, Klose, Lauche, Gass et al., Herbal medicine for cough: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Compl. Med. Res
Wanaratna, Leethong, Inchai, Chueawiang, Sriraksa et al., Efficacy and safety of Andrographis paniculata extract in patients with mild COVID-19: a randomized controlled trial
Weiss, Jellingsø, Sommer, WHO Working Group on the Clinical Characterisation and Management of COVID-19 infection, 2020. A minimal common outcome measure set for COVID-19 clinical research, Lancet Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/s1473-3099(20)30483-7
Wu, Mcgoogan, Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.2648
Yearsley, Thailand approves asian herb Andrographis to treat COVID-19, HerbalGram
Zhang, Lv, Zhou, Xie, Xu et al., Efficacy and safety of Xiyanping injection in the treatment of COVID-19: a multicenter, prospective, open-label and randomized controlled trial, Phytother. Res, doi:10.1002/ptr.7141
Zhu, Zhang, Wang, Li, Yang et al., A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/nejmoa2001017
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018",
"ISSN": [
"0944-7113"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018",
"alternative-id": [
"S0944711323003793"
],
"article-number": "155018",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Efficacy of Andrographis paniculata extract treatment in mild to moderate COVID-19 patients being treated with favipiravir: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study (APFaVi trial)"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Phytomedicine"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier GmbH."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7256-9982",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Siripongboonsitti",
"given": "Taweegrit",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0140-9866",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ungtrakul",
"given": "Teerapat",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tawinprai",
"given": "Kriangkrai",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Auewarakul",
"given": "Chirayu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chartisathian",
"given": "Wipada",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jansala",
"given": "Thitikan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Julsawad",
"given": "Rattana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8053-2984",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Soonklang",
"given": "Kamonwan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6383-6580",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Mahanonda",
"given": "Nithi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mahidol",
"given": "Chulabhorn",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Phytomedicine",
"container-title-short": "Phytomedicine",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2023-08-12T05:58:43Z",
"timestamp": 1691819923000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2023-08-23T19:07:08Z",
"timestamp": 1692817628000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100016175",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Chulabhorn Royal Academy"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2023-08-24T19:47:22Z",
"timestamp": 1692906442316
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-10-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1696118400000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2023-08-11T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1691712000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0944711323003793?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0944711323003793?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "155018",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00685-X",
"article-title": "Increased risk of hospitalisation and death with the delta variant in the USA",
"author": "Bast",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1629",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect. Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib0001",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Short Communication on Use of Andrographis Herb (FA THALAI CHON) for the Treatment of COVID-19 Patients",
"author": "Benjaponpitak",
"first-page": "229",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Thai Tradit. Alternat. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib0002",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0944-7113(97)80051-7",
"article-title": "Prevention of common colds with Andrographis paniculata dried extract. A pilot double blind trial",
"author": "Caceres",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "101",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Phytomedicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib0003",
"volume": "4",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"article-title": "Experimental treatment with favipiravir for COVID-19: an open-label control study",
"author": "Cai",
"first-page": "1192",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Engineering (Beijing)",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib0004",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Favipiravir versus arbidol for COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Chen",
"journal-title": "MedRxiv",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib0005",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciab962",
"article-title": "Efficacy of early treatment with favipiravir on disease progression among high-risk patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a randomized, open-label clinical trial",
"author": "Chuah",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e432",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Clin. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib0006",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1055/s-2004-818938",
"article-title": "Andrographis paniculata in the treatment of upper respiratory tract infections: a systematic review of safety and efficacy",
"author": "Coon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "293",
"issue": "04",
"journal-title": "Planta Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib0007",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00705-021-04956-9",
"article-title": "Efficacy of favipiravir in COVID-19 treatment: a multi-center randomized study",
"author": "Dabbous",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "949",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Arch. Virol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib0008",
"volume": "166",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Comparison of pharmacological effect of four andrographolides",
"author": "Deng",
"first-page": "195",
"journal-title": "Chinese Pharmaceut. Bull.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib0009",
"volume": "17",
"year": "1982"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib0010",
"unstructured": "Department of Medical Service. (2021). Clinical practice guideline to diagnosis, treatment and prevention COVID-19 for physicain and health care provider, 21 July 2021. Retrieved 16 December 2022 from https://covid19.dms.go.th/Content/Select_Landding_page?contentId=139."
},
{
"DOI": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-35800/v1",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib0011",
"unstructured": "Dey, Y.N., Khanal, P., Patil, B., Wanjari, M.M., Srivast, B., Gurav, S.S., & Gaidhani, S.N. (2020). The role of andrographolide and its derivative in COVID-19 associated proteins and immune system."
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib0012",
"unstructured": "Doi, Y.K., M. Ando, M. Kuwatsuka, Y. Ishihara, T Favipiravir Observational Study Group, Fujita Health University. (2021). Favipiravir observational study interim report 3 https://www.kansensho.or.jp/uploads/files/topics/2019ncov/covid19_favip_210419_eng.pdf."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cpt.1844",
"article-title": "Favipiravir: pharmacokinetics and concerns about clinical trials for 2019-nCoV infection",
"author": "Du",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "242",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Clin. Pharmacol. Therapeut.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib0013",
"volume": "108",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMra2026131",
"article-title": "Cytokine storm",
"author": "Fajgenbaum",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2255",
"issue": "23",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib0014",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00330-020-07033-y",
"article-title": "Chest CT score in COVID-19 patients: correlation with disease severity and short-term prognosis",
"author": "Francone",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6808",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Eur. Radiol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib0015",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2183/pjab.93.027",
"article-title": "Favipiravir (T-705), a broad spectrum inhibitor of viral RNA polymerase",
"author": "Furuta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "449",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Proc. Jpn. Acad., Ser. B",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib0016",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1078/094471102321616391",
"article-title": "A double blind, placebo-controlled study of Andrographis paniculata fixed combination Kan Jang in the treatment of acute upper respiratory tract infections including sinusitis",
"author": "Gabrielian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "589",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Phytomedicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib0017",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"article-title": "Favipiravir in patients with early mild-to-moderate COVID-19: a randomized controlled trial",
"author": "Golan",
"journal-title": "Clin. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib0018",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2118542",
"article-title": "Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with Covid-19",
"author": "Hammond",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1397",
"issue": "15",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib0019",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-90551-6",
"article-title": "The efficacy and safety of Favipiravir in treatment of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials",
"author": "Hassanipour",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib0020",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib0021",
"unstructured": "Hsu, L.-W., Chang, S.-C., Shen, C.-H., & Chuang, K.-S. (2006). Andrographolide and its derivatives as TNF-alpha antagonists. In: Google Patents."
},
{
"article-title": "AVIFAVIR for treatment of patients with moderate coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): interim results of a phase II/III multicenter randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Ivashchenko",
"journal-title": "Clin. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib0022",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2116044",
"article-title": "Molnupiravir for oral treatment of Covid-19 in nonhospitalized patients",
"author": "Jayk Bernal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "509",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib0023",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Role of favipiravir in the treatment of COVID-19",
"author": "Joshi",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib0024",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Real-world experience with favipiravir for the treatment of mild-to-moderate COVID-19 in India",
"author": "Joshi",
"first-page": "33",
"journal-title": "Pragmat Obs Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib49",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.explore.2005.08.008",
"article-title": "Andrographis paniculata for the treatment of upper respiratory infection: a systematic review by the natural standard research collaboration",
"author": "Kligler",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "25",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Explore: J. Sci. Heal.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib0025",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"article-title": "Andrographis paniculata (Burm. F.) Wall. Ex Nees, andrographolide, and andrographolide analogues as SARS-CoV-2 antivirals? A rapid review",
"author": "Lim",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Nat. Prod. Commun.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib0026",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Analgesic, antipyretic and antiulcerogenic effects of andrographolide",
"author": "Madav",
"first-page": "121",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Indian J. Pharm. Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib50",
"volume": "57",
"year": "1995"
},
{
"article-title": "Anti-inflammatory activity of andrographolide",
"author": "Madav",
"first-page": "452",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Fitoterapia (Milano)",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib0027",
"volume": "67",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101703",
"article-title": "Favipiravir in early symptomatic COVID-19, a randomised placebo-controlled trial",
"author": "McMahon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "EClinicalMedicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib0028",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jmii.2020.03.022",
"article-title": "Genotype and phenotype of COVID-19: their roles in pathogenesis",
"author": "Mousavizadeh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "159",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib0029",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2020.05.049",
"article-title": "Applicability of the CURB-65 pneumonia severity score for outpatient treatment of COVID-19",
"author": "Nguyen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e96",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "J. Infect.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib0030",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1046/j.1365-2710.2003.00534.x",
"article-title": "Andrographis paniculata in the symptomatic treatment of uncomplicated upper respiratory tract infection: systematic review of randomized controlled trials",
"author": "Poolsup",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "37",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Clin. Pharm. Ther.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib0031",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1248/bpb.29.220",
"article-title": "Andrographolide inhibits the production of TNF-α and interleukin-12 in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages: role of mitogen-activated protein kinases",
"author": "Qin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "220",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Biol. Pharmaceut. Bull.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib0032",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.648250",
"article-title": "A computational approach identified andrographolide as a potential drug for suppressing COVID-19-induced cytokine storm",
"author": "Rehan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib0033",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cells9051267",
"article-title": "A structural view of SARS-CoV-2 RNA replication machinery: RNA synthesis, proofreading and final capping",
"author": "Romano",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Cells",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib0034",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jnatprod.0c01324",
"article-title": "Anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity of andrographis paniculata extract and its major component andrographolide in human lung epithelial cells and cytotoxicity evaluation in major organ cell representatives",
"author": "Sa-Ngiamsuntorn",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1261",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "J. Nat. Prod.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib0035",
"volume": "84",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/sj.bjp.0704493",
"article-title": "Andrographolide prevents oxygen radical production by human neutrophils: possible mechanism (s) involved in its anti-inflammatory effect",
"author": "Shen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "399",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Br. J. Pharmacol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib0036",
"volume": "135",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12985-020-01412-z",
"article-title": "Favipiravir versus other antiviral or standard of care for COVID-19 treatment: a rapid systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Shrestha",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Virol. J.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib0037",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "The inhibitory effects of extracts of some herbal medicines on the production of proinflammatory cytokines by in vitro stimulated human blood cells",
"author": "Thamaree",
"journal-title": "Thai J. Pharmacol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib0038",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.11.142",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of favipiravir, an oral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase inhibitor, in mild-to-moderate COVID-19: a randomized, comparative, open-label, multicenter, phase 3 clinical trial",
"author": "Udwadia",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "62",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib0039",
"volume": "103",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-020-00468-6",
"article-title": "Coronavirus biology and replication: implications for SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "V'Kovski",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "155",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Microbiol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib0040",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Herbal medicine for cough: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Wagner",
"first-page": "359",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Compl. Med. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib0041",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of Andrographis paniculata extract in patients with mild COVID-19: a randomized controlled trial",
"author": "Wanaratna",
"journal-title": "MedRxiv",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib0042",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102916",
"article-title": "Spatial and temporal dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Weiss",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "EBioMedicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib0043",
"volume": "58",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30483-7",
"article-title": "A minimal common outcome measure set for COVID-19 clinical research",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e192",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect. Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib0044",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.2648",
"article-title": "Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1239",
"issue": "13",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib0045",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Thailand approves asian herb Andrographis to treat COVID-19",
"author": "Yearsley",
"first-page": "35",
"issue": "129",
"journal-title": "HerbalGram",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib0046",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.7141",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of Xiyanping injection in the treatment of COVID-19: a multicenter, prospective, open-label and randomized controlled trial",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4401",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Phytother. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib0047",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001017",
"article-title": "A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019",
"author": "Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155018_bib0048",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 50,
"references-count": 50,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0944711323003793"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Complementary and alternative medicine",
"Drug Discovery",
"Pharmaceutical Science",
"Pharmacology",
"Molecular Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Efficacy of Andrographis paniculata extract treatment in mild to moderate COVID-19 patients being treated with favipiravir: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study (APFaVi trial)",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "119"
}