Association Between Androgen Deprivation Therapy and Mortality Among Patients With Prostate Cancer and COVID-19
et al., JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.34330, Nov 2021
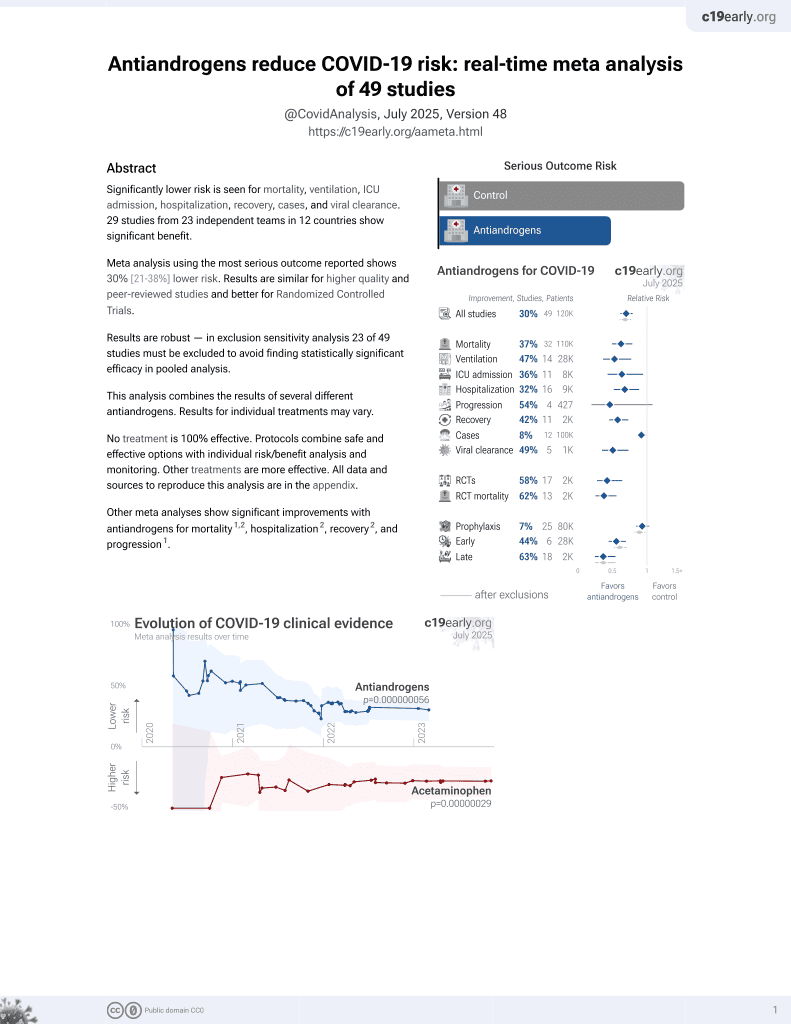
7th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000056 from 49 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 1,106 prostate cancer patients, showing no significant differences in COVID-19 outcomes with ADT.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
Study covers HCQ and remdesivir.
|
risk of death, 20.4% lower, RR 0.80, p = 0.41, treatment 25 of 169 (14.8%), control 44 of 308 (14.3%), adjusted per study, odds ratio converted to relative risk, propensity score matching, multivariable.
|
|
risk of severe case, 2.0% lower, OR 0.98, p = 0.94, treatment 169, control 308, adjusted per study, propensity score matching, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Schmidt et al., 12 Nov 2021, retrospective, USA, peer-reviewed, 42 authors, study period 17 March, 2020 - 11 February, 2021.
Association Between Androgen Deprivation Therapy and Mortality Among Patients With Prostate Cancer and COVID-19
JAMA Network Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.34330
IMPORTANCE Androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) has been theorized to decrease the severity of SARS-CoV-2 infection in patients with prostate cancer owing to a potential decrease in the tissuebased expression of the SARS-CoV-2 coreceptor transmembrane protease, serine 2 (TMPRSS2). OBJECTIVE To examine whether ADT is associated with a decreased rate of 30-day mortality from SARS-CoV-2 infection among patients with prostate cancer.
Conflict of Interest Disclosures: Dr Bakouny reported grants from Genentech/imCORE; nonfinancial support from Bristol Myers Squibb; and personal fees from UpToDate outside the submitted work. Dr Shyr reported grants from the National Cancer Institute during the conduct of the study. Dr Armstrong reported grants from Bayer, Janssen, and Pfizer/Astellas; and personal fees from Bayer, Janssen, and Pfizer/Astellas outside the submitted work. Dr Beer reported grants paid to his institution from Alliance Foundation Trials, Astellas Pharma, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Corcept Therapeutics, Endocyte Inc, Freenome, Grail Inc, Harpoon Therapeutics, Janssen Research and Development, Medivation Inc, Sotio, Theraclone Sciences/OncoResponse, and Zenith Epigenetics; personal fees from Arvinas, Astellas Pharma, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squib, Clovis Oncology, Constellation, GlaxoSmithKline, Grail Inc, Janssen, Merck & Co, Myovant Sciences, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi, and Tolero; and stock ownership in Arvinas Inc and Salarius Pharmaceuticals outside the submitted work. Dr Bilen reported grants to his institution from AAA, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Genentech/Roche, Genome and Company, Incyte, Nektar, Peloton Therapeutics, Pfizer, SeaGen, Tricon Pharmaceuticals, and Xencor outside the submitted work; and personal fees from AstraZeneca, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Calithera Biosciences, Eisai, EMD Serono, Exelixis, Genomic Health, Janssen, Nektar, Pfizer, Sanofi,..
References
Abidi, Aboulafia, Accordino, 19 and Cancer Consortium. A systematic framework to rapidly obtain data on patients with cancer and COVID-19: CCC19 governance, protocol, and quality assurance, Cancer Cell, doi:10.1016/j.ccell.2020.10.022
Acquisition, Schmidt, Tucker, Bakouny, Labaki et al., Critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content
Administrative, Tucker, Labaki, Armstrong, Dawsey et al., None
Author, Shyr, Schmidt, Tucker, Bakouny et al., access to all of the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis
Baratchian, Mcmanus, Berk, Androgen regulation of pulmonary AR, TMPRSS2 and ACE2 with implications for sex-discordant COVID-19 outcomes, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-90491-1
Bhopal, Bhopal, Sex differential in COVID-19 mortality varies markedly by age, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31748-7
Butterworth, Mcclellan, Allansmith, Influence of sex in immunoglobulin levels, Nature, doi:10.1038/2141224a0
Chalmers, Burns, Ebot, Early-onset metastatic and clinically advanced prostate cancer is a distinct clinical and molecular entity characterized by increased TMPRSS2-ERG fusions, Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis, doi:10.1038/s41391-020-00314-z
Crawford, Heidenreich, Lawrentschuk, Androgen-targeted therapy in men with prostate cancer: evolving practice and future considerations, Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis, doi:10.1038/s41391-018-0079-0
Dai, Liu, Liu, Patients with cancer appear more vulnerable to SARS-CoV-2: a multicenter study during the COVID-19 outbreak, Cancer Discov
Deng, Rasool, Russell, Natesan, Asangani, Targeting androgen regulation of TMPRSS2 and ACE2 as a therapeutic strategy to combat COVID-19, iScience, doi:10.1016/j.isci.2021.102254
Dhindsa, Zhang, Mcphaul, Association of circulating sex hormones with inflammation and disease severity in patients with COVID-19, JAMA Netw Open, doi:https://jama.jamanetwork.com/article.aspx?doi=10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.11398&utm_campaign=articlePDF%26utm_medium=articlePDFlink%26utm_source=articlePDF%26utm_content=jamanetworkopen.2021.34330
Grivas, Khaki, Wise-Draper, Association of clinical factors and recent anticancer therapy with COVID-19 severity among patients with cancer: a report from the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium, Ann Oncol, doi:10.1016/j.annonc.2021.02.024
Harris, Taylor, Minor, The REDCap Consortium: building an international community of software platform partners, J Biomed Inform, doi:10.1016/j.jbi.2019.103208
Harris, Taylor, Thielke, Payne, Gonzalez et al., Research electronic data capture (REDCap)-a metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support, J Biomed Inform, doi:10.1016/j.jbi.2008.08.010
Hoffmann, Kleine-Weber, Schroeder, SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052
Klein, Li, Milinovich, Androgen deprivation therapy in men with prostate cancer does not affect risk of infection with SARS-CoV-2, J Urol, doi:10.1097/JU.0000000000001338
Kuderer, Choueiri, Shah, Clinical impact of COVID-19 on patients with cancer (CCC19): a cohort study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31187-9
Lee, Cazier, Angelis, UK Coronavirus Monitoring Project Team. COVID-19 mortality in patients with cancer on chemotherapy or other anticancer treatments: a prospective cohort study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31173-9
Li, Han, Dai, Distinct mechanisms for TMPRSS2 expression explain organ-specific inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 infection by enzalutamide, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-021-21171-x
Lin, Ferguson, White, Prostate-localized and androgen-regulated expression of the membranebound serine protease TMPRSS2, Cancer Res
Lucas, Heinlein, Kim, The androgen-regulated protease TMPRSS2 activates a proteolytic cascade involving components of the tumor microenvironment and promotes prostate cancer metastasis, Cancer Discov, doi:10.1158/2159-8290.CD-13-1010
Ming, Rosenbaum, Substantial gains in bias reduction from matching with a variable number of controls, Biometrics, doi:10.1111/j.0006-341X.2000.00118.x
Montopoli, Zumerle, Vettor, Androgen-deprivation therapies for prostate cancer and risk of infection by SARS-CoV-2: a population-based study (N = 4532), Ann Oncol, doi:10.1016/j.annonc.2020.04.479
Patel, Zhong, Liaw, Does androgen deprivation therapy protect against severe complications from COVID-19?, Ann Oncol, doi:10.1016/j.annonc.2020.06.023
Peckham, De Gruijter, Raine, Male sex identified by global COVID-19 meta-analysis as a risk factor for death and ITU admission, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-020-19741-6
Pettersson, Graff, Bauer, The TMPRSS2:ERG rearrangement, ERG expression, and prostate cancer outcomes: a cohort study and meta-analysis, Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev, doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-12-0042
Qiao, Wang, Mannan, Targeting transcriptional regulation of SARS-CoV-2 entry factors ACE2 and TMPRSS2, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, doi:10.1073/pnas.2021450118
Samuel, Majd, Richter, Androgen signaling regulates SARS-CoV-2 receptor levels and is associated with severe COVID-19 symptoms in men, Cell Stem Cell, doi:10.1016/j.stem.2020.11.009
Von Elm, Altman, Egger, Pocock, Gøtzsche et al., The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies, Ann Intern Med, doi:10.7326/0003-4819-147-8-200710160-00010
Westblade, Brar, Pinheiro, SARS-CoV-2 viral load predicts mortality in patients with and without cancer who are hospitalized with COVID-19, Cancer Cell, doi:10.1016/j.ccell.2020.09.007
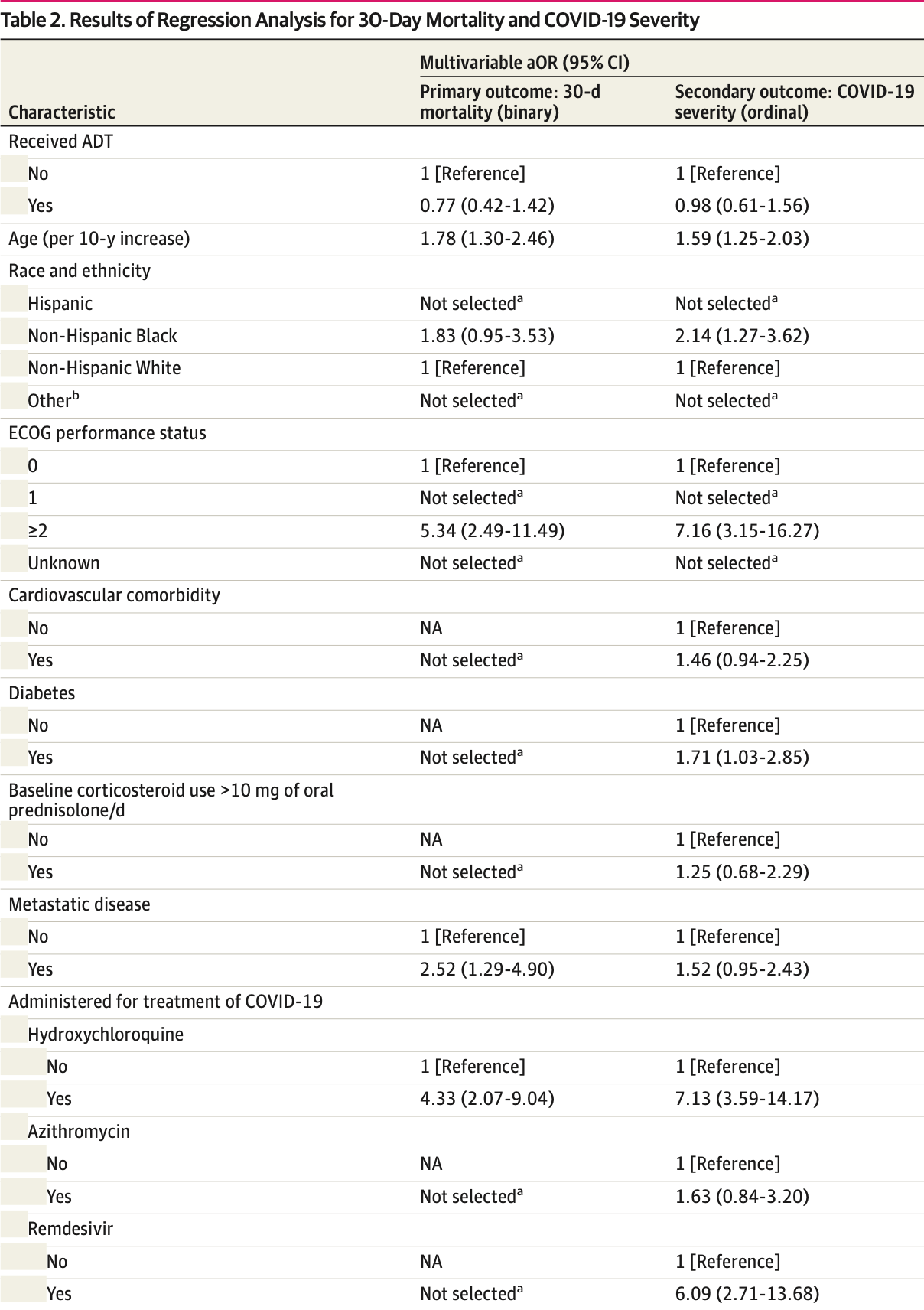
Wise-Draper, Desai, Elkrief, Rini, Flora et al., Mixing Parameter of 1 (LASSO) eTable 6. Results of Regression Analysis for 30-Day Mortality Between ADT + Chemotherapy Compared to ADT, Adjusting for the Variables Selected by the Elastic-Net Regularization With a Mixing Parameter of 1 (LASSO) eFigure 1. Patient Selection eFigure 2. Loss of Dead30 Events (All Cause 30-Day Mortality) and Standardized Mean Difference of Propensity Scores Between the 2 ADT Groups (on ADT and Not on ADT) eFigure 3. Distributions of Propensity Scores of Patients on ADT and Not on ADT Before and After Matching SUPPLEMENT 2, doi:10.1016/j.annonc.2020.08.2312
Zhu, Zhang, Wang, China Novel Coronavirus Investigating and Research Team. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2001017
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.34330",
"ISSN": [
"2574-3805"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.34330",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Lank Center for Genitourinary Oncology, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, Massachusetts"
}
],
"family": "Schmidt",
"given": "Andrew L.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee"
}
],
"family": "Tucker",
"given": "Matthew D.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Lank Center for Genitourinary Oncology, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, Massachusetts"
}
],
"family": "Bakouny",
"given": "Ziad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Lank Center for Genitourinary Oncology, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, Massachusetts"
}
],
"family": "Labaki",
"given": "Chris",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee"
}
],
"family": "Hsu",
"given": "Chih-Yuan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee"
}
],
"family": "Shyr",
"given": "Yu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Duke Cancer Institute Center for Prostate and Urologic Cancer, Duke University, Durham, North Carolina"
}
],
"family": "Armstrong",
"given": "Andrew J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Oregon Health and Science University Knight Cancer Institute, Portland"
}
],
"family": "Beer",
"given": "Tomasz M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "UPMC Western Maryland, Cumberland"
}
],
"family": "Bijjula",
"given": "Ragneel R.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University, Atlanta, Georgia"
}
],
"family": "Bilen",
"given": "Mehmet A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Penn State Cancer Institute, Hershey, Pennsylvania"
}
],
"family": "Connell",
"given": "Cindy F.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Cleveland Clinic Taussig Cancer Institute, Cleveland, Ohio"
}
],
"family": "Dawsey",
"given": "Scott Joseph",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Missouri Baptist Medical Center, St Louis"
}
],
"family": "Faller",
"given": "Bryan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston"
}
],
"family": "Gao",
"given": "Xin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Montefiore Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, New York"
}
],
"family": "Gartrell",
"given": "Benjamin A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Intermountain Healthcare, Salt Lake City, Utah"
}
],
"family": "Gill",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University of Cincinnati College of Medicine, Cincinnati, Ohio"
}
],
"family": "Gulati",
"given": "Shuchi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Duke Cancer Institute Center for Prostate and Urologic Cancer, Duke University, Durham, North Carolina"
}
],
"family": "Halabi",
"given": "Susan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Henry Ford Cancer Institute, Henry Ford Hospital, Detroit, Michigan"
}
],
"family": "Hwang",
"given": "Clara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Cleveland Clinic Taussig Cancer Institute, Cleveland, Ohio"
}
],
"family": "Joshi",
"given": "Monika",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University of Washington, Seattle Cancer Care Alliance, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, Seattle"
},
{
"name": "Stanford University, Stanford, California"
}
],
"family": "Khaki",
"given": "Ali Raza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Cleveland Clinic Taussig Cancer Institute, Cleveland, Ohio"
}
],
"family": "Menon",
"given": "Harry",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, New York"
}
],
"family": "Morris",
"given": "Michael J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Virtua Health Network, Marlton, New Jersey"
}
],
"family": "Puc",
"given": "Matthew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Tallahassee Memorial Healthcare, Tallahassee, Florida"
}
],
"family": "Russell",
"given": "Karen B.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio, San Antonio"
}
],
"family": "Shah",
"given": "Dimpy P.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, New York"
}
],
"family": "Shah",
"given": "Neil J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Cleveland Clinic Taussig Cancer Institute, Cleveland, Ohio"
}
],
"family": "Sharifi",
"given": "Nima",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Moores Cancer Center, University of California, San Diego"
}
],
"family": "Shaya",
"given": "Justin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University of Washington, Seattle Cancer Care Alliance, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, Seattle"
}
],
"family": "Schweizer",
"given": "Michael T.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Lank Center for Genitourinary Oncology, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, Massachusetts"
}
],
"family": "Steinharter",
"given": "John",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University of Kansas Medical Center, Westwood"
}
],
"family": "Wulff-Burchfield",
"given": "Elizabeth M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Lank Center for Genitourinary Oncology, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, Massachusetts"
}
],
"family": "Xu",
"given": "Wenxin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Penn State Cancer Institute, Hershey, Pennsylvania"
}
],
"family": "Zhu",
"given": "Jay",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee"
}
],
"family": "Mishra",
"given": "Sanjay",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University of Washington, Seattle Cancer Care Alliance, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, Seattle"
}
],
"family": "Grivas",
"given": "Petros",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee"
}
],
"family": "Rini",
"given": "Brian I.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee"
}
],
"family": "Warner",
"given": "Jeremy Lyle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Duke Cancer Institute Center for Prostate and Urologic Cancer, Duke University, Durham, North Carolina"
}
],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Tian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Lank Center for Genitourinary Oncology, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, Massachusetts"
}
],
"family": "Choueiri",
"given": "Toni K.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Cleveland Clinic Taussig Cancer Institute, Cleveland, Ohio"
}
],
"family": "Gupta",
"given": "Shilpa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Moores Cancer Center, University of California, San Diego"
}
],
"family": "McKay",
"given": "Rana R.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Desai",
"given": "Aakash",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Cohen",
"given": "Aaron M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Olszewski",
"given": "Adam J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Bardia",
"given": "Aditya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Daher",
"given": "Ahmad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Brown",
"given": "Alaina J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Yeh",
"given": "Albert",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Hsiao",
"given": "Albert",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Cheng",
"given": "Alex",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Zhou",
"given": "Alice Y.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Beeghly-Fadiel",
"given": "Alicia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Morgans",
"given": "Alicia K.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Jha",
"given": "Alokkumar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Menendez",
"given": "Alvaro G.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Fazio",
"given": "Alyson",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Nizam",
"given": "Amanda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Ramirez",
"given": "Amelie G.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Kulkarni",
"given": "Amit A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Verma",
"given": "Amit K.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Elshoury",
"given": "Amro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Rivera",
"given": "Andrea Verghese",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Walden",
"given": "Andrew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Piper-Vallillo",
"given": "Andrew J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Cook",
"given": "Andrew L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Ang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Cantrell",
"given": "Angela Shaw",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Cabal",
"given": "Angelo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Nohria",
"given": "Anju",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Angevine",
"given": "Anne H.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Gulati",
"given": "Anthony P.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Giordano",
"given": "Antonio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Kasi",
"given": "Anup",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Ajmera",
"given": "Archana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Elkrief",
"given": "Arielle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Kariapper",
"given": "Ariffa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Loaiza-Bonilla",
"given": "Arturo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Jayaraj",
"given": "Asha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Thakkar",
"given": "Astha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Russ",
"given": "Atlantis D.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Bashir",
"given": "Babar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Halmos",
"given": "Balazs",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Logan",
"given": "Barbara B.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Wood",
"given": "Barbara R.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Slawik",
"given": "Becky",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Dixon",
"given": "Becky",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "French",
"given": "Benjamin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Routy",
"given": "Bertrand",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Mavromatis",
"given": "Blanche H.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Hayes-Lattin",
"given": "Brandon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Barrow McCollough",
"given": "Briana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Fleissner",
"given": "Bridget",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Stith",
"given": "Brittany",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Wicher",
"given": "Camille P.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Schwartz",
"given": "Candice",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Thomson",
"given": "Carey C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Solorzano",
"given": "Carmen C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Granada",
"given": "Carolina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Brown",
"given": "CarrieAnn",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Hennessy",
"given": "Cassandra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Stratton",
"given": "Catherine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Castellano",
"given": "Cecilia A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Ang",
"given": "Celina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Mandapakala",
"given": "Chaitanya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Chen-Pin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Jani",
"given": "Chinmay",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Su",
"given": "Chris",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Misdary",
"given": "Christian F.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Chapman",
"given": "Christina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "McNair",
"given": "Christopher",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Lemmon",
"given": "Christopher A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Geiger",
"given": "Christopher L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Friese",
"given": "Christopher R.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Su",
"given": "Christopher T.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "McKeown",
"given": "Cindy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Hoppenot",
"given": "Claire",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Low",
"given": "Clarke A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Pillainayagam",
"given": "Clement",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Ferrario",
"given": "Cristiano",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Rock",
"given": "Crosby D.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Gonzalez Gomez",
"given": "Cyndi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Masson",
"given": "Cynthia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Mundt",
"given": "Daniel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Addison",
"given": "Daniel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Flora",
"given": "Daniel B.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Stover",
"given": "Daniel G.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Kwon",
"given": "Daniel H.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Hausrath",
"given": "Daniel J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Bowles",
"given": "Daniel W.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Reuben",
"given": "Daniel Y.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Shafer",
"given": "Danielle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Bitterman",
"given": "Danielle S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "O' Sullivan",
"given": "Darciann",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Mahadevan",
"given": "Daruka",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Sohal",
"given": "Davendra P. S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Whaley",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Slosky",
"given": "David A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Chism",
"given": "David D.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Hershman",
"given": "Dawn L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Doroshow",
"given": "Deborah B.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Ravindranathan",
"given": "Deepak",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Farmakiotis",
"given": "Dimitrios",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Bhutani",
"given": "Divaya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Vinh",
"given": "Donald C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Freeman",
"given": "Dory A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Johnson",
"given": "Douglas B.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Hatton",
"given": "Edward",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Van Allen",
"given": "Eliezer M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Griffiths",
"given": "Elizabeth A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Davis",
"given": "Elizabeth J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Nakasone",
"given": "Elizabeth S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Loggers",
"given": "Elizabeth T.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Robilotti",
"given": "Elizabeth V.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Levine",
"given": "Ellis",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Cabebe",
"given": "Elwyn C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Hsu",
"given": "Emily",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Powell",
"given": "Emily",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Nemecek",
"given": "Eneida R.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Lau",
"given": "Eric",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Durbin",
"given": "Eric B.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Bernicker",
"given": "Eric H.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Small",
"given": "Eric J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Cook",
"given": "Erin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Gillaspie",
"given": "Erin A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Reid",
"given": "Erin G.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Papadopoulos",
"given": "Esperanza B.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Tadesse",
"given": "Eyob",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Wehbe",
"given": "Firas H.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Lyman",
"given": "Gary H.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Schwartz",
"given": "Gary K.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Nagaraj",
"given": "Gayathri",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Boland",
"given": "Genevieve",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Demetri",
"given": "George D.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Batist",
"given": "Gerald",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Gantt Jr.",
"given": "Gerald",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Kloecker",
"given": "Goetz",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Shaw",
"given": "Grace",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Riely",
"given": "Gregory J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Borno",
"given": "Hala T.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Saker",
"given": "Haneen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Dzimitrowicz",
"given": "Hannah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Nelson",
"given": "Heather H.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Khan",
"given": "Hina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Shaikh",
"given": "Hira G.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Polimera",
"given": "Hyma V.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "James L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Stratton",
"given": "Jamie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Acoba",
"given": "Jared D.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Patel",
"given": "Jaymin M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Connors",
"given": "Jean M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Mather",
"given": "Jeff",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Henderson",
"given": "Jeffrey P.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Dill",
"given": "Jennifer",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Girard",
"given": "Jennifer",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Warner",
"given": "Jeremy L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Graber",
"given": "Jerome J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Papenburg",
"given": "Jesse",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Altman",
"given": "Jessica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Hawley",
"given": "Jessica E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Clement",
"given": "Jessica M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Park",
"given": "Ji (Janie)",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Campian",
"given": "Jian Li",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Philip",
"given": "John",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Deeken",
"given": "John F.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Riess",
"given": "Jonathan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Rosenberg",
"given": "Jonathan E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Loree",
"given": "Jonathan M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Senefeld",
"given": "Jonathon (Jack) W.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Kharofa",
"given": "Jordan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Garcia",
"given": "Jorge A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Palmer",
"given": "Joshua D.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Lewis",
"given": "Judy T.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Guido",
"given": "Julie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Fu",
"given": "Julie C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Wu",
"given": "Julie Tsu-Yu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Jiang",
"given": "Jun Yang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Gainor",
"given": "Justin F.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Klamerus",
"given": "Justin F.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Steve Lo",
"given": "K. M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Patel",
"given": "Kanishka G.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "de Cardenas",
"given": "Karen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Vega-Luna",
"given": "Karen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Goldsmith",
"given": "Karen J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Hansen",
"given": "Karla",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Huber",
"given": "Kathryn E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Stockerl-Goldstein",
"given": "Keith E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Jeffords",
"given": "Kelly J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Hoskins",
"given": "Kent F.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Reynolds",
"given": "Kerry L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Cerrone",
"given": "Kim",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Cortez",
"given": "Kimberly",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Enriquez",
"given": "Kyle T.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Rosen",
"given": "Lane R.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Lashley",
"given": "Latoya N.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Pomerantz",
"given": "Lauren D.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Smith",
"given": "Laurie J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Feldman",
"given": "Lawrence E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Fecher",
"given": "Leslie A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Zubiri",
"given": "Leyre",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Li C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Schapira",
"given": "Lidia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Tachiki",
"given": "Lisa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Weissmann",
"given": "Lisa B.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Rosenstein",
"given": "Lori J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Lucy L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Tomasini",
"given": "Maggie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Abidi",
"given": "Maheen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Khan",
"given": "Mahir",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Shah",
"given": "Mansi R.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Rovito",
"given": "Marc A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Gatti-Mays",
"given": "Margaret E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Escobedo",
"given": "Maria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Alexander",
"given": "Mariam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Bonnen",
"given": "Mark",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Fiala",
"given": "Mark A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Lewis",
"given": "Mark A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Dailey",
"given": "Mark E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Reeves",
"given": "Mark E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Sueyoshi",
"given": "Mark H.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Portes",
"given": "Mary",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Salazar",
"given": "Mary",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Mulcahy",
"given": "Mary F.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Pasquinelli",
"given": "Mary M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Lustberg",
"given": "Maryam B.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Fiebach",
"given": "Maryann Z.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Luders",
"given": "Matt",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Galsky",
"given": "Matthew D.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Weiss",
"given": "Matthias",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Clark",
"given": "Melanie J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Smits",
"given": "Melissa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Accordino",
"given": "Melissa K.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Markham",
"given": "Merry-Jennifer",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Gurley",
"given": "Michael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Thompson",
"given": "Michael A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Bar",
"given": "Michael H.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Wagner",
"given": "Michael J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Joyner",
"given": "Michael J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Glover",
"given": "Michael J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Wotman",
"given": "Michael T.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Braccioforte",
"given": "Michelle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Marcum",
"given": "Michelle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Seletyn",
"given": "Mildred E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Huynh-Le",
"given": "Minh-Phuong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Santos Dutra",
"given": "Miriam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Streckfuss",
"given": "Mitrianna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Akhtari",
"given": "Mojtaba",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Gatson",
"given": "Na Tosha N.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Bahadur",
"given": "Nadia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Knox",
"given": "Natalie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Edwin",
"given": "Natasha C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Pennell",
"given": "Nathan A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Bouganim",
"given": "Nathaniel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Hafez",
"given": "Navid",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Venepalli",
"given": "Neeta K.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Williams",
"given": "Nicole O.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Balanchivadze",
"given": "Nino",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Ohri",
"given": "Nitin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Butt",
"given": "Omar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Panagiotou",
"given": "Orestis A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Serrano",
"given": "Oscar K.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Bohachek",
"given": "Pamela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Egan",
"given": "Pamela C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Shah",
"given": "Pankil K.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Caimi",
"given": "Paolo F.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "LoRusso",
"given": "Patricia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Weinstein",
"given": "Paul L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Yu",
"given": "Peter Paul",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Lammers",
"given": "Philip E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Nuzzo",
"given": "Pier Vitale",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Bindal",
"given": "Poorva",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Peddi",
"given": "Prakash",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Grover",
"given": "Punita",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Zaman",
"given": "Qamar U.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Sica",
"given": "R. Alejandro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Rosovsky",
"given": "Rachel P.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Elias",
"given": "Rawad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Zon",
"given": "Rebecca L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Gandhi",
"given": "Rikin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Belenkaya",
"given": "Rimma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Rice",
"given": "Robert L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Buerki",
"given": "Robin A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Herbst",
"given": "Roy S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Mesa",
"given": "Ruben A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Lynch",
"given": "Ryan C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Nguyen",
"given": "Ryan H.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Monahan",
"given": "Ryan S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Jhawar",
"given": "Sachin R.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Alimohamed",
"given": "Saif I.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Jabbour",
"given": "Salma K.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Del Prete",
"given": "Salvatore A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Mahmood",
"given": "Sana Z.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Goel",
"given": "Sanjay",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Revankar",
"given": "Sanjay G.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Matar",
"given": "Sara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Saif",
"given": "Sara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Mushtaq",
"given": "Sarah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Wall",
"given": "Sarah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Croessman",
"given": "Sarah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Kligerman",
"given": "Seth",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "McWeeney",
"given": "Shannon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Goyal",
"given": "Sharad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Choi",
"given": "Sharon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Brouha",
"given": "Sharon S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Taylor",
"given": "Sharona",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Vinayak",
"given": "Shaveta",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Gadgeel",
"given": "Shirish M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Blau",
"given": "Sibel H.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Hallmeyer",
"given": "Sigrun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Reid",
"given": "Sonya A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Williamson",
"given": "Staci P.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Fry",
"given": "Stacy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "May",
"given": "Stephanie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Berg",
"given": "Stephanie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Duda",
"given": "Stephany N.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Greenland",
"given": "Steven",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Murdock",
"given": "Sue",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Subbiah",
"given": "Suki",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Shah",
"given": "Sumit A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Shah",
"given": "Surbhi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Van Loon",
"given": "Susan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Ayre",
"given": "Susan K.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Owenby",
"given": "Susie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Rose",
"given": "Suzanne J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Ahmad",
"given": "Syed A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Sylvia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Latif",
"given": "Tahir",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Bekaii-Saab",
"given": "Tanios S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Cronin",
"given": "Tara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Nonato",
"given": "Taylor K.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Rhodes",
"given": "Terence D.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Carducci",
"given": "Theresa M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Halfdanarson",
"given": "Thorvardur R.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Sun",
"given": "Tianyi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Wise-Draper",
"given": "Trisha M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Masters",
"given": "Tyler",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Topaloglu",
"given": "Umit",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Koshkin",
"given": "Vadim S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Mico",
"given": "Vasil",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Karivedu",
"given": "Vidhya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Walters",
"given": "Wendy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Miller Jr.",
"given": "Wilson H.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Xuanyi (Lexi)",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Rho",
"given": "Young Soo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Xie",
"given": "Zhuoer",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "for the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium"
}
],
"family": "Sachs",
"given": "Zohar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"name": "COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"JAMA Network Open"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-12T16:32:09Z",
"timestamp": 1636734729000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-28T16:15:45Z",
"timestamp": 1640708145000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2022-03-02T22:29:55Z",
"timestamp": 1646260195383
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 6,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "2574-3805"
}
],
"issue": "11",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
12
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "11",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
1
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/articlepdf/2786026/schmidt_2021_oi_210972_1640021628.64851.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "10",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e2134330",
"prefix": "10.1001",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
12
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
12
]
]
},
"publisher": "American Medical Association (AMA)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001017",
"article-title": "A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019.",
"author": "Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "727",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "zoi210972r1",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31748-7",
"article-title": "Sex differential in COVID-19 mortality varies markedly by age.",
"author": "Bhopal",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "532",
"issue": "10250",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "zoi210972r2",
"volume": "396",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1158/2159-8290.CD-13-1010",
"article-title": "The androgen-regulated protease TMPRSS2 activates a proteolytic cascade involving components of the tumor microenvironment and promotes prostate cancer metastasis.",
"author": "Lucas",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1310",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Cancer Discov",
"key": "zoi210972r3",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "zoi210972r4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41391-020-00314-z",
"article-title": "Early-onset metastatic and clinically advanced prostate cancer is a distinct clinical and molecular entity characterized by increased TMPRSS2–ERG fusions.",
"author": "Chalmers",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "558",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis",
"key": "zoi210972r5",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Prostate-localized and androgen-regulated expression of the membrane-bound serine protease TMPRSS2.",
"author": "Lin",
"first-page": "4180",
"issue": "17",
"journal-title": "Cancer Res",
"key": "zoi210972r6",
"volume": "59",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-12-0042",
"article-title": "The TMPRSS2:ERG rearrangement, ERG expression, and prostate cancer outcomes: a cohort study and meta-analysis.",
"author": "Pettersson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1497",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev",
"key": "zoi210972r7",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor.",
"author": "Hoffmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "271",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "zoi210972r8",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.stem.2020.11.009",
"article-title": "Androgen signaling regulates SARS-CoV-2 receptor levels and is associated with severe COVID-19 symptoms in men.",
"author": "Samuel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "876",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Cell Stem Cell",
"key": "zoi210972r9",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.annonc.2020.04.479",
"article-title": "Androgen-deprivation therapies for prostate cancer and risk of infection by SARS-CoV-2: a population-based study (N?=?4532).",
"author": "Montopoli",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1040",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Ann Oncol",
"key": "zoi210972r10",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.annonc.2020.06.023",
"article-title": "Does androgen deprivation therapy protect against severe complications from COVID-19?",
"author": "Patel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1419",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Ann Oncol",
"key": "zoi210972r11",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"journal-title": "J Urol",
"key": "zoi210972r12"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.11398",
"article-title": "Association of circulating sex hormones with inflammation and disease severity in patients with COVID-19.",
"author": "Dhindsa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "zoi210972r13",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.annonc.2021.02.024",
"article-title": "Association of clinical factors and recent anticancer therapy with COVID-19 severity among patients with cancer: a report from the COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium.",
"author": "Grivas",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "787",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Ann Oncol",
"key": "zoi210972r14",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Patients with cancer appear more vulnerable to SARS-CoV-2: a multicenter study during the COVID-19 outbreak.",
"author": "Dai",
"first-page": "783",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Cancer Discov",
"key": "zoi210972r15",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ccell.2020.09.007",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 viral load predicts mortality in patients with and without cancer who are hospitalized with COVID-19.",
"author": "Westblade",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "661",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Cancer Cell",
"key": "zoi210972r16",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31187-9",
"article-title": "Clinical impact of COVID-19 on patients with cancer (CCC19): a cohort study.",
"author": "Kuderer",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1907",
"issue": "10241",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "zoi210972r17",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31173-9",
"article-title": "COVID-19 mortality in patients with cancer on chemotherapy or other anticancer treatments: a prospective cohort study.",
"author": "Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1919",
"issue": "10241",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "zoi210972r18",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.isci.2021.102254",
"article-title": "Targeting androgen regulation of TMPRSS2 and ACE2 as a therapeutic strategy to combat COVID-19.",
"author": "Deng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "iScience",
"key": "zoi210972r19",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Targeting transcriptional regulation of SARS-CoV-2 entry factors ACE2 and TMPRSS2.",
"author": "Qiao",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A",
"key": "zoi210972r20",
"volume": "118",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jbi.2008.08.010",
"article-title": "Research electronic data capture (REDCap)—a metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support.",
"author": "Harris",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "377",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Biomed Inform",
"key": "zoi210972r21",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jbi.2019.103208",
"article-title": "The REDCap Consortium: building an international community of software platform partners.",
"author": "Harris",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Biomed Inform",
"key": "zoi210972r22",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ccell.2020.10.022",
"article-title": "A systematic framework to rapidly obtain data on patients with cancer and COVID-19: CCC19 governance, protocol, and quality assurance.",
"author": "Abidi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "761",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Cancer Cell",
"key": "zoi210972r23",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/0003-4819-147-8-200710160-00010",
"article-title": "The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies.",
"author": "von Elm",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "573",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "zoi210972r24",
"volume": "147",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41391-018-0079-0",
"article-title": "Androgen-targeted therapy in men with prostate cancer: evolving practice and future considerations.",
"author": "Crawford",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "24",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis",
"key": "zoi210972r26",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.0006-341X.2000.00118.x",
"article-title": "Substantial gains in bias reduction from matching with a variable number of controls.",
"author": "Ming",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "118",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Biometrics",
"key": "zoi210972r27",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/2141224a0",
"article-title": "Influence of sex in immunoglobulin levels.",
"author": "Butterworth",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1224",
"issue": "5094",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "zoi210972r28",
"volume": "214",
"year": "1967"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-21171-x",
"article-title": "Distinct mechanisms for TMPRSS2 expression explain organ-specific inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 infection by enzalutamide.",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "866",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "zoi210972r29",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-90491-1",
"article-title": "Androgen regulation of pulmonary AR, TMPRSS2 and ACE2 with implications for sex-discordant COVID-19 outcomes.",
"author": "Baratchian",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "11130",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "zoi210972r30",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.annonc.2020.08.2312",
"article-title": "LBA71 systemic cancer treatment-related outcomes in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: a CCC19 registry analysis.",
"author": "Wise-Draper",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "S1201",
"journal-title": "Ann Oncol",
"key": "zoi210972r31",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "zoi210972r25",
"unstructured": "The COVID-19 and Cancer Consortium (CCC19) Registry. ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT04354701. Updated September 9, 2021. Accessed September 27, 2021. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04354701"
}
],
"reference-count": 31,
"references-count": 31,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"JAMA Netw Open"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Association Between Androgen Deprivation Therapy and Mortality Among Patients With Prostate Cancer and COVID-19"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "4"
}