Does androgen deprivation therapy protect against severe complications from COVID-19?
et al., Annals of Oncology, doi:10.1016/j.annonc.2020.06.023, Jul 2020
7th treatment shown to reduce risk in
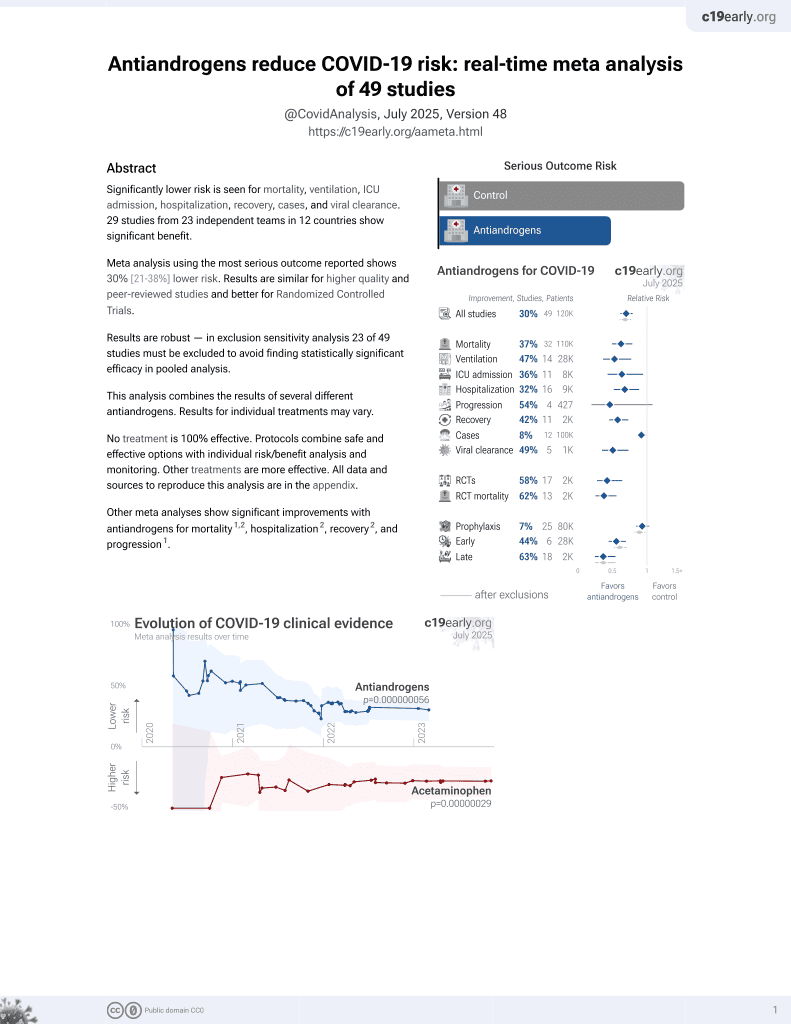
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000056 from 49 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
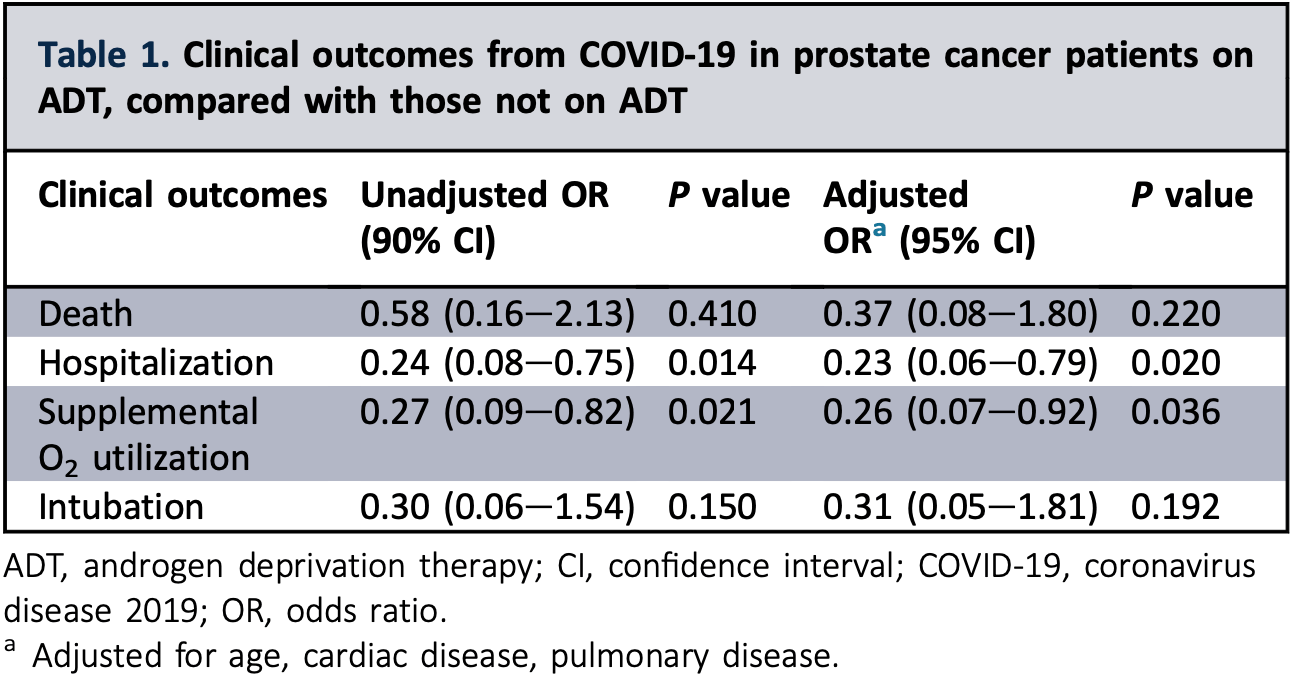
Retrospective 58 prostate cancer patients in the USA, showing lower risk of hospitalization with ADT.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
This may explain in part the very high mortality seen in this study.
Results may differ in countries with improved SOC.
|
risk of death, 55.2% lower, RR 0.45, p = 0.22, treatment 4 of 22 (18.2%), control 10 of 36 (27.8%), adjusted per study, odds ratio converted to relative risk, multivariable.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 69.0% lower, OR 0.31, p = 0.19, treatment 22, control 36, adjusted per study, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 77.0% lower, OR 0.23, p = 0.02, treatment 22, control 36, adjusted per study, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Patel et al., 9 Jul 2020, retrospective, USA, peer-reviewed, 7 authors, study period 1 March, 2020 - 4 June, 2020.
Abstract: Annals of Oncology
Letters to the Editor
investigation, including antiviral drugs, we suggest that
convalescent plasma could be useful in patients with COVID19 infection and concurrent persistent B-cell immunodeficiency; we will consider this approach for our patient.3e5
N. Issa1*, F. Lacassin2 & F. Camou1
Medical Intensive Care and Infectious Diseases Unit, SaintAndre Hospital, CHU Bordeaux, Bordeaux;
2
Infectious Disease Department, Mont de Marsan Hospital,
Mont de Marsan, France
(*E-mail: nahema.issa@chu-bordeaux.fr).
1
Available online 29 June 2020
© 2020 European Society for Medical Oncology. Published
by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annonc.2020.06.016
FUNDING
None declared.
DISCLOSURE
The authors have declared no conflicts of interest.
REFERENCES
1. Berlin DA, Gulick RM, Martinez FJ. Severe Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020.
https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMcp2009575.
2. Gao Y, Chen Y, Liu M, Shi S, Tian J. Impacts of immunosuppression and
immunodeficiency on COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
J Infect. 2020;81(2):e93ee95.
3. Valk SJ, Piechotta V, Chai KL, et al. Convalescent plasma or hyperimmune
immunoglobulin for people with COVID-19: a rapid review. Cochrane
Database Syst Rev. 2020;5:CD013600.
4. Franchini M. Why should we use convalescent plasma for COVID-19? Eur
J Intern Med. 2020;77:150e151.
5. Pinto D, Park YJ, Beltramello M, et al. Cross-neutralization of SARS-CoV-2
by a human monoclonal SARS-CoV antibody. Nature. 2020;583(7815):
290e295.
Does androgen deprivation therapy protect
against severe complications from COVID-19?
Currently, there is a paucity of effective treatments to
address the remarkably high morbidity and mortality
associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19).
This letter highlights a potential therapeutic strategy based
on known biology of SARS-CoV-2 cellular entry and
replication.
SARS-CoV-2 relies on surface expression of angiotensinconverting enzyme 2 (ACE2) and transmembrane serine
proteases 2 (TMPRSS2) for cellular entry and replication in
the respiratory epithelium.1,2 In in vitro and mouse models,
Volume 31 - Issue 10 - 2020
TMPRSS2 inhibition limits respiratory cell damage and
reduces severity of infection.1,3 TMPRSS2 is commonly
expressed in prostate cancer cells and is known to be
regulated by androgens.4 Hence, androgen deprivation
therapy (ADT) may theoretically reduce TMPRSS2 expression limiting SARS-CoV-2 cellular entry and preventing
severe complications from COVID-19. In fact, a recent
report from Alimonti and colleagues demonstrated a lower
rate of infection in prostate cancer patients on ADT,
compared with those not on ADT.5 Herein, we report our
observational study of all patients in a single New York City
health system with COVID-19 and prostate cancer to
determine the impact of ADT on COVID-19 clinical outcomes. To our best knowledge, this is the largest study to
report severity of COVID-19 in patients receiving ADT.
This study was approved by the Mount Sinai School of
Medicine Institutional Review Board. We identified all
Mount Sinai Health System (MSHS) patients with prostate
cancer and SARS-CoV-2 viral detection by PCR (based on
testing within and outside MSHS) from 1 March 2020 to
4 June 2020. We collected clinical information including
demographics, medical history, and medications including
ADT use. ADT use was defined as a gonadotropin-releasing
hormone (GnRH) analog or..
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.annonc.2020.06.023",
"ISSN": [
"0923-7534"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.annonc.2020.06.023",
"alternative-id": [
"S0923753420399336"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Does androgen deprivation therapy protect against severe complications from COVID-19?"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Annals of Oncology"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annonc.2020.06.023"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to the associated document",
"name": "associatedlink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annonc.2020.04.479"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "simple-article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2020 European Society for Medical Oncology. Published by Elsevier Ltd."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Patel",
"given": "V.G.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhong",
"given": "X.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liaw",
"given": "B.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tremblay",
"given": "D.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tsao",
"given": "C.-K.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Galsky",
"given": "M.D.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Oh",
"given": "W.K.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Annals of Oncology"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"annalsofoncology.org",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2020-07-09T22:48:59Z",
"timestamp": 1594334939000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2021-10-05T07:21:00Z",
"timestamp": 1633418460000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100005565",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Janssen Biotech"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100007659",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Bayer Corporation"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100004702",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Baxter International"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100004325",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "AstraZeneca"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2022-03-25T19:27:11Z",
"timestamp": 1648236431935
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 37,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "0923-7534"
}
],
"issue": "10",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "10",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2020-10-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1601510400000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://www.elsevier.com/open-access/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 365,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-10-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1633046400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0923753420399336?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0923753420399336?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1419-1420",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor",
"author": "Hoffmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "271",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "10.1016/j.annonc.2020.06.023_bib1",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7",
"article-title": "A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "270",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.annonc.2020.06.023_bib2",
"volume": "579",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.01815-18",
"article-title": "TMPRSS2 contributes to virus spread and immunopathology in the airways of murine models after coronavirus infection",
"author": "Iwata-Yoshikawa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e01815",
"journal-title": "J Virol",
"key": "10.1016/j.annonc.2020.06.023_bib3",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"article-title": "Prostate-localized and androgen-regulated expression of the membrane-bound serine protease TMPRSS2",
"author": "Lin",
"first-page": "4180",
"journal-title": "Cancer Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.annonc.2020.06.023_bib4",
"volume": "59",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.annonc.2020.04.479",
"article-title": "Androgen-deprivation therapies for prostate cancer and risk of infection by SARS-CoV-2: a population-based study (N = 4532)",
"author": "Montopoli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1040",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Ann Oncol",
"key": "10.1016/j.annonc.2020.06.023_bib5",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1530/ERC-20-0133",
"article-title": "Androgen hazards with COVID-19",
"author": "Sharifi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "E1",
"journal-title": "Endocr Relat Cancer",
"key": "10.1016/j.annonc.2020.06.023_bib6",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 6,
"references-count": 6,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"Annals of Oncology"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Oncology",
"Hematology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Does androgen deprivation therapy protect against severe complications from COVID-19?"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "31"
}