Potential Beneficial Role of Nitric Oxide in SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Beyond Spike-Binding Inhibition
et al., Antioxidants, doi:10.3390/antiox13111301, Oct 2024
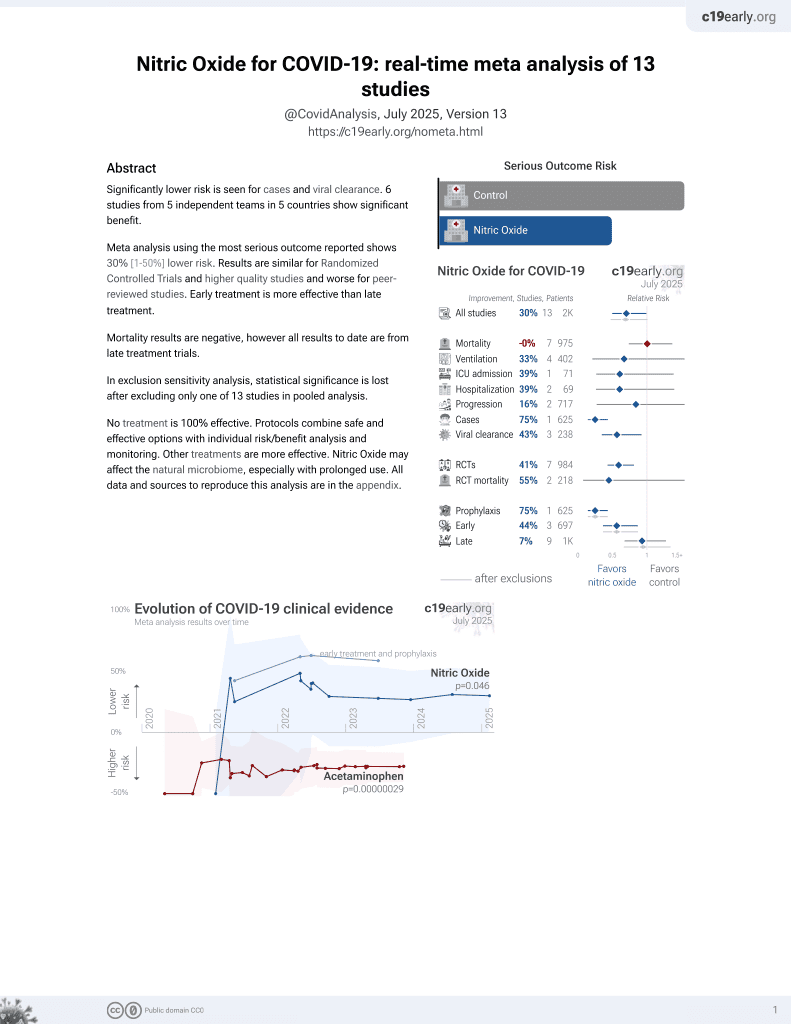
43rd treatment shown to reduce risk in
June 2022, now with p = 0.012 from 12 studies, recognized in 10 countries.
Lower risk for cases and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
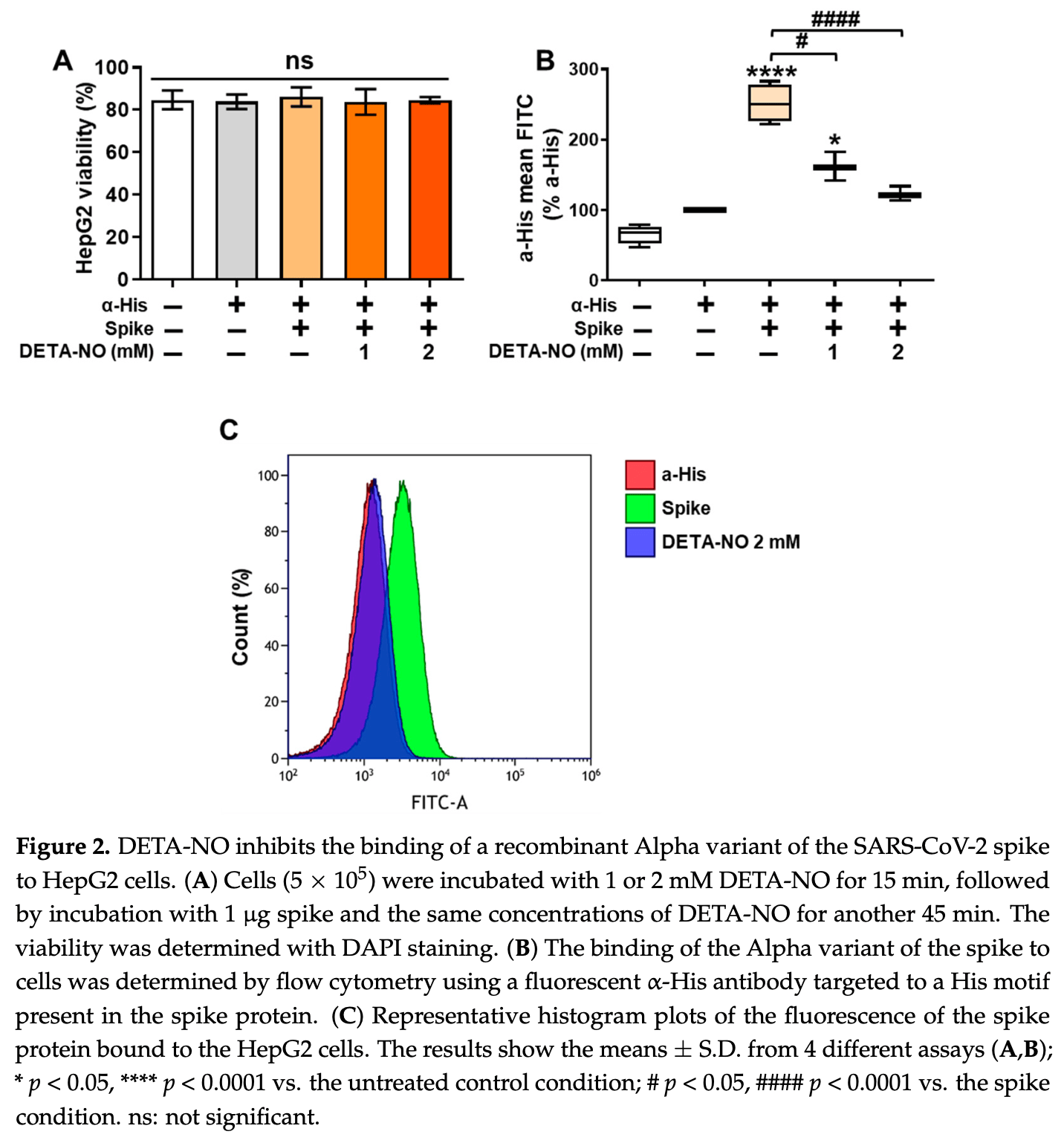
In vitro study showing that nitric oxide (NO) inhibits SARS-CoV-2 spike protein binding to ACE2 and reduces ACE2 enzymatic activity. Authors showed that NO donors DETA-NONOate (DETA-NO) and S-nitrosoglutathione (GSNO) significantly decreased ACE2 activity, with GSNO showing stronger inhibition comparable to the specific ACE2 inhibitor MLN-4760. The binding of both alpha and gamma variants of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein was reduced by NO donors in HepG2 cells and ACE2-transfected A549 lung epithelial cells, without affecting cell viability. Using a co-culture system with murine peritoneal macrophages stimulated to produce NO, authors confirmed that endogenous NO production also inhibited spike protein binding to ACE2. The study utilized multiple experimental approaches to validate NO's effects: recombinant protein assays for ACE2 activity, flow cytometry for spike binding, and immunofluorescence for ACE2 expression. NO's dual action of inhibiting both ACE2 activity and spike protein binding suggests potential therapeutic applications for COVID-19.
3 preclinical studies support the efficacy of nitric oxide for COVID-19:
1.
Martins et al., Broad-Spectrum Virucidal Activity of Nitric Oxide Nasal Spray (NONS) Against SARS-CoV-2 Variants and Major Respiratory Viruses, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v18010091.
Sánchez-García et al., 26 Oct 2024, peer-reviewed, 4 authors.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Potential Beneficial Role of Nitric Oxide in SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Beyond Spike-Binding Inhibition
Antioxidants, doi:10.3390/antiox13111301
SARS-CoV-2, the causative virus for the COVID-19 disease, uses its spike glycoprotein to bind to human ACE2 as a first step for viral entry into the cell. For this reason, great efforts have been made to find mechanisms that disrupt this interaction, avoiding the infection. Nitric oxide (NO) is a soluble endogenous gas with known antiviral and immunomodulatory properties. In this study, we aimed to test whether NO could inhibit the binding of the viral spike to ACE2 in human cells and its effects on ACE2 enzymatic activity. Our results show that ACE2 activity was decreased by the NO donors DETA-NONOate and GSNO and by the NO byproduct peroxynitrite. Furthermore, we found that DETA-NONOate could break the spike-ACE2 interaction using the spike from two different variants (Alpha and Gamma) and in two different human cell types. Moreover, the same result was obtained when using NO-producing murine macrophages, while no significant changes were observed in ACE2 expression or distribution within the cell. These results support that it is worth considering NO as a therapeutic agent for COVID-19, as previous reports have suggested.
Supplementary Materials: The following supporting information can be downloaded at https: //www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/antiox13111301/s1 , Figure S1 : NO donors and peroxynitrite inhibit the activity of recombinant human ACE2 (extended); Figure S2 : A549-ACE2 and HepG2 cells express ACE2 protein; Figure S3 : GSNO inhibits the binding of the recombinant Gamma variant of the SARS-CoV-2 spike to A549-ACE2 cells; Figure S4 Funding: This research was funded by PID2023-148933OB-I00 and PID2022-137696OB-I00 from MICIN/AEI 13039/501100011033 and the Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red en Enfermedades Cardiovasculares (CB16/11/00222) from the Instituto de Salud Carlos III (co-financed by the European Development Regional Fund "A Way to Achieve Europe", by the "European Union" and by the "European Union NextGeneration EU/PRTR"), Comunidad de Madrid, Programa Biociencias (S2022-BMD-7223). We acknowledge support of the publication fee by the CSIC Open Access Publication Support Initiative through its Unit of Information Resources for Research (URICI).
Institutional Review Board
References
Ackermann, Fernández-Alfonso, Sánchez De Rojas, Ortega, Paul et al., Modulation of Angiotensinconverting Enzyme by Nitric Oxide, Br. J. Pharmacol, doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0701836
Akaike, Maeda, Nitric Oxide and Virus Infection, Immunology, doi:10.1046/j.1365-2567.2000.00142.x
Albina, On the Expression of Nitric Oxide Synthase by Human Macrophages. Why No NO?, J. Leukoc. Biol, doi:10.1002/jlb.58.6.643
Alvarez, Berra, Gladwin, Home Nitric Oxide Therapy for COVID-19, Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med, doi:10.1164/rccm.202005-1906ED
Andrabi, Sharma, Karan, Shahriar, Cordon et al., Nitric Oxide: Physiological Functions, Delivery, and Biomedical Applications, Adv. Sci, doi:10.1002/advs.202303259
Ascenzi, Di Masi, Sciorati, Clementi, Peroxynitrite-An Ugly Biofactor?, BioFactors, doi:10.1002/biof.103
Bartesaghi, Radi, Fundamentals on the Biochemistry of Peroxynitrite and Protein Tyrosine Nitration, Redox Biol, doi:10.1016/j.redox.2017.09.009
Bastos, Lima, Neto, Maryam; Yousaf, Cruz et al., Design and Identification of Inhibitors for the Spike-ACE2 Target of SARS-CoV-2, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms24108814
Ben-Avraham, Muzumdar, Atzmon, Epigenetic Genome-Wide Association Methylation in Aging and Longevity, Epigenomics, doi:10.2217/epi.12.41
Beyerstedt, Casaro, Rangel, COVID-19: Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) Expression and Tissue Susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1007/s10096-020-04138-6
Bosca, Zeini, Traves, Hortelano, Boscá et al., Nitric Oxide and Cell Viability in Inflammatory Cells: A Role for NO in Macrophage Function and Fate, Toxicology, doi:10.1016/j.tox.2004.11.035
Castrillo, Pennington, Otto, Parker, Owen et al., Protein Kinase Cepsilon Is Required for Macrophage Activation and Defense against Bacterial Infection, J. Exp. Med, doi:10.1084/jem.194.9.1231
Cherian, Kumar, Akasapu, Ashton, Aparnath et al., Salvage Therapies for Refractory Hypoxemia in ARDS, Respir. Med, doi:10.1016/j.rmed.2018.06.030
Choi, Rai, Chu, Cool, Chan, Analysis of Nitric Oxide Synthase and Nitrotyrosine Expression in Human Pulmonary Tuberculosis, Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med, doi:10.1164/rccm.2201023
Choudhary, Gupta, Sharma, Parmar, Therapeutically Effective Covalent Spike Protein Inhibitors in Treatment of SARS-CoV-2, J. Proteins Proteom, doi:10.1007/s42485-021-00074-x
Ciaglia, Vecchione, Puca, COVID-19 Infection and Circulating ACE2 Levels: Protective Role in Women and Children, Front. Pediatr, doi:10.3389/fped.2020.00206
Colasanti, Persichini, Venturini, Ascenzi, S-Nitrosylation of Viral Proteins: Molecular Bases for Antiviral Effect of Nitric Oxide, IUBMB Life, doi:10.1080/713803459
Crassous, Couloubaly, Huang, Zhou, Baskaran et al., Soluble Guanylyl Cyclase Is a Target of Angiotensin II-Induced Nitrosative Stress in a Hypertensive Rat Model, Am. J. Physiol.-Heart Circ. Physiol, doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00138.2012
Croen, Evidence for Antiviral Effect of Nitric Oxide. Inhibition of Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 Replication, J. Clin. Investig, doi:10.1172/JCI116479
De Simone, Di Masi, Ascenzi, Strategies of Pathogens to Escape from NO-Based Host Defense, Antioxidants, doi:10.3390/antiox11112176
De Vera, Shapiro, Nussler, Mudgett, Simmons et al., Transcriptional Regulation of Human Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase (NOS2) Gene by Cytokines: Initial Analysis of the Human NOS2 Promoter, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.93.3.1054
Esteban, Heringer-Walther, Sterner-Kock, De Bruin, Van Den Engel et al., Angiotensin-(1-7) and the G Protein-Coupled Receptor Mas Are Key Players in Renal Inflammation, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0005406
Foo, Bellot, Pervaiz, Alonso, Mitochondria-Mediated Oxidative Stress during Viral Infection, Trends Microbiol, doi:10.1016/j.tim.2021.12.011
González-Rayas, Rayas-Gómez, García-González, González-Yáñez, Hernández-Hernández et al., COVID-19 and ACE-Inhibitors and Angiotensin Receptor Blockers-: The Need to Differentiate between Early Infection and Acute Lung Injury, Rev. Colomb. Cardiol, doi:10.1016/j.rccar.2020.04.005
Gross, Kremens, Powers, Brink, Knutson et al., Epigenetic Silencing of the Human NOS2 Gene: Rethinking the Role of Nitric Oxide in Human Macrophage Inflammatory Responses, J. Immunol, doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1301758
Grunst, Qin, Dodero-Rojas, Ding, Prévost et al., Structure and Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Refolding in Membranes, Science, doi:10.1126/science.adn5658
Guo, Shao, Zheng, Du, Li et al., MiRNA-939 Regulates Human Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase Posttranscriptional Gene Expression in Human Hepatocytes, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci
Guo, Zhao, Jia, Li, Huang et al., Efficient Inactivation of the Contamination with Pathogenic Microorganisms by a Combination of Water Spray and Plasma-Activated Air, J. Hazard. Mater, doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.130686
Gómez, Amado, Roca, Torres, Nicolas et al., Effect of Nitric Oxide Inhalation on Gas Exchange in Acute Severe Pneumonia, Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol, doi:10.1016/j.resp.2013.03.006
Harvey, Carabelli, Jackson, Gupta, Thomson et al., SARS-CoV-2 Variants, Spike Mutations and Immune Escape, Nat. Rev. Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41579-021-00573-0
Hortelano, Alvarez, Boscá, Nitric Oxide Induces Tyrosine Nitration and Release of Cytochrome c Preceding an Increase of Mitochondrial Transmembrane Potential in Macrophages, FASEB J, doi:10.1096/fasebj.13.15.2311
Hortelano, Través, Zeini, Alvarez, Boscá, Sustained Nitric Oxide Delivery Delays Nitric Oxide-Dependent Apoptosis in Macrophages: Contribution to the Physiological Function of Activated Macrophages, J. Immunol, doi:10.4049/jimmunol.171.11.6059
Hu, Guo, Zhou, Shi, Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19, Nat. Rev. Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41579-020-00459-7
Ichiki, Usui, Kato, Funakoshi, Ito et al., Downregulation of Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor Gene Transcription by Nitric Oxide, Hypertension, doi:10.1161/01.HYP.31.1.342
Ichinose, Roberts, Zapol, Inhaled Nitric Oxide: A Selective Pulmonary Vasodilator: Current Uses and Therapeutic Potential, Circulation, doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000134595.80170.62
Jaén, Povo-Retana, Rosales-Mendoza, Capillas-Herrero, Sánchez-García et al., Functional Crosstalk between PCSK9 Internalization and Pro-Inflammatory Activation in Human Macrophages: Role of Reactive Oxygen Species Release, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms23169114
Jiang, Yang, Zhang, Dong, Wang et al., Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 and Angiotensin 1-7: Novel Therapeutic Targets, Nat. Rev. Cardiol, doi:10.1038/nrcardio.2014.59
Kaplish, Vagha, Meshram, Lohiya, A Comprehensive Review of Inhaled Nitric Oxide Therapy: Current Trends, Challenges, and Future Directions, Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.53558
Karupiah, Xie, Buller, Nathan, Duarte et al., Inhibition of Viral Replication by Interferon-γ-Induced Nitric Oxide Synthase, Science, doi:10.1126/science.7690156
Keyaerts, Vijgen, Chen, Maes, Hedenstierna et al., Inhibition of SARS-Coronavirus Infection in Vitro by S-Nitroso-N-Acetylpenicillamine, a Nitric Oxide Donor Compound, Int. J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2004.04.012
Konings, Perkins, Kuhn, Pallen, Alm et al., SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Interest and Concern Naming Scheme Conducive for Global Discourse, Nat. Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41564-021-00932-w
Lan, Ge, Yu, Shan, Zhou et al., Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Receptor-Binding Domain Bound to the ACE2 Receptor, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2180-5
Lei, Chen, Wu, Duan, Men, Small Molecules in the Treatment of COVID-19, Signal Transduct. Target. Ther, doi:10.1038/s41392-022-01249-8
Li, Ming, Liu, Xing, Fu et al., Recent Developments in Pharmacological Effect, Mechanism and Application Prospect of Diazeniumdiolates, Front. Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.00923
Lisi, Zelikin, Chandrawati, Nitric Oxide to Fight Viral Infections, Adv. Sci, doi:10.1002/advs.202003895
Liu, Miller, Joshi, Sadowska-Krowicka, Clark et al., Diffusion-Limited Reaction of Free Nitric Oxide with Erythrocytes, J. Biol. Chem, doi:10.1074/jbc.273.30.18709
Lu, Sun, High Affinity Binding of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Enhances ACE2 Carboxypeptidase Activity, J. Biol. Chem, doi:10.1074/jbc.RA120.015303
López-Collazo, Hortelano, Rojas, Boscá, Triggering of Peritoneal Macrophages with IFN-α/β Attenuates the Expression of Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase through a Decrease in NF-kB Activation, J. Immunol, doi:10.4049/jimmunol.160.6.2889
Mannick, Asano, Izumi, Kieff, Stamler, Nitric Oxide Produced by Human B Lymphocytes Inhibits Apoptosis and Epstein-Barr Virus Reactivation, Cell, doi:10.1016/0092-8674(94)90005-1
Martel, Ko, Young, Ojcius, Could Nasal Nitric Oxide Help to Mitigate the Severity of COVID-19?, Microbes Infect, doi:10.1016/j.micinf.2020.05.002
Martin, Edwards, Interferon-Gamma Enhances Monocyte Cytotoxicity via Enhanced Reactive Oxygen Intermediate Production. Absence of an Effect on Macrophage Cytotoxicity Is Due to Failure to Enhance Reactive Nitrogen Intermediate Production, Immunology
Nicholson, Bonecini-Almeida, Lapa E Silva, Nathan, Xie et al., Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase in Pulmonary Alveolar Macrophages from Patients with Tuberculosis, J. Exp. Med, doi:10.1084/jem.183.5.2293
Oh, Nakamura, Beutler, Zhang, Piña-Crespo et al., Targeted Protein S-Nitrosylation of ACE2 Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Nat. Chem. Biol, doi:10.1038/s41589-022-01149-6
Parasher, COVID-19: Current Understanding of Its Pathophysiology, Clinical Presentation and Treatment, Postgrad. Med. J, doi:10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-138577
Povo-Retana, Landauro-Vera, Fariñas, Sánchez-García, Alvarez-Lucena et al., Defining the Metabolic Signatures Associated with Human Macrophage Polarisation, Biochem. Soc. Trans, doi:10.1042/BST20220504
Redaelli, Magliocca, Malhotra, Ristagno, Citerio et al., Nitric Oxide: Clinical Applications in Critically Ill Patients, Nitric Oxide, doi:10.1016/j.niox.2022.01.007
Rico, Vaquerizas, Dopazo, Boscá, Identification of Conserved Domains in the Promoter Regions of Nitric Oxide Synthase 2: Implications for the Species-Specific Transcription and Evolutionary Differences, BMC Genom, doi:10.1186/1471-2164-8-271
Sama, Ravera, Santema, Van Goor, Ter Maaten et al., Circulating Plasma Concentrations of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 in Men and Women with Heart Failure and Effects of Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Inhibitors, Eur. Heart J, doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa373
Samavati, Uhal, ACE2, Much More Than Just a Receptor for SARS-COV-2, Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2020.00317
Sander, Fourie, Sabiu, O'neill, Pohl et al., Reactive Oxygen Species as Potential Antiviral Targets, Rev. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/rmv.2240
Saura, Zaragoza, Mcmillan, Quick, Hohenadl et al., An Antiviral Mechanism of Nitric Oxide, Immunity, doi:10.1016/S1074-7613(00)80003-5
Shanmugam, Venkattappan, Gromiha, Structure Based Drug Designing Approaches in SARS-CoV-2 Spike Inhibitor Design, Curr. Top. Med. Chem, doi:10.2174/1568026623666221103091658
Sherlock, Wright, Kinsella, Delaney, Inhaled Nitric Oxide Use in Neonates: Balancing What Is Evidence-Based and What Is Physiologically Sound, Nitric Oxide, doi:10.1016/j.niox.2019.12.001
Shu, Shi, Huang, Yu, Sun, Transcription Tuned by S-Nitrosylation Underlies a Mechanism for Staphylococcus Aureus to Circumvent Vancomycin Killing, Nat. Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-023-37949-0
Silva, Krogstad, Teles, Andrade, Rajfer et al., IFN-γ-Mediated Control of SARS-CoV-2 Infection through Nitric Oxide, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1284148
Singh, Wishnok, Keshive, Deen, Tannenbaum, The Chemistry of the S-Nitrosoglutathione/Glutathione System, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.93.25.14428
Sodano, Gazzano, Fruttero, Lazzarato, NO in Viral Infections: Role and Development of Antiviral Therapies, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules27072337
Tandon, Wu, Moore, Winchester, Tu et al., SARS-CoV-2 Accelerated Clearance Using a Novel Nitric Oxide Nasal Spray (NONS) Treatment: A Randomized Trial, Lancet Reg. Health-Southeast Asia, doi:10.1016/j.lansea.2022.100036
V'kovski, Kratzel, Steiner, Stalder, Thiel, Coronavirus Biology and Replication: Implications for SARS-CoV-2, Nat. Rev. Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41579-020-00468-6
Velkoska, Dean, Griggs, Burchill, Burrell, Angiotensin-(1-7) Infusion Is Associated with Increased Blood Pressure and Adverse Cardiac Remodelling in Rats with Subtotal Nephrectomy, Clin. Sci, doi:10.1042/CS20100280
Virág, Jaén, Regdon, Boscá, Prieto, Self-Defense of Macrophages against Oxidative Injury: Fighting for Their Own Survival, Redox Biol, doi:10.1016/j.redox.2019.101261
Winchester, John, Jabbar, John, Clinical Efficacy of Nitric Oxide Nasal Spray (NONS) for the Treatment of Mild COVID-19 Infection, J. Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2021.05.009
Wolak, Dicker, Shifer, Grossman, Rokach et al., A Safety Evaluation of Intermittent High-Dose Inhaled Nitric Oxide in Viral Pneumonia Due to COVID-19: A Randomised Clinical Study, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-024-68055-w
Wu, Gaucher, Diab, Fries, Xiao et al., Time Lasting S-Nitrosoglutathione Polymeric Nanoparticles Delay Cellular Protein S-Nitrosation, Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm, doi:10.1016/j.ejpb.2014.11.005
Xu, Humphries, Tomita, Okuyama, Matsuki et al., Survey of the Allelic Frequency of a NOS2A Promoter Microsatellite in Human Populations: Assessment of the NOS2A Gene and Predisposition to Infectious Disease, Nitric Oxide, doi:10.1006/niox.2000.0290
Yamamoto, Chappell, Brosnihan, Ferrario, In Vivo Metabolism of Angiotensin I by Neutral Endopeptidase (EC 3.4.24.11) in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats, Hypertension, doi:10.1161/01.HYP.19.6.692
Yan, Zhang, Li, Xia, Guo et al., Structural Basis for the Recognition of SARS-CoV-2 by Full-Length Human ACE2, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abb2762
Yang, Petitjean, Koehler, Zhang, Dumitru et al., Molecular Interaction and Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Binding to the ACE2 Receptor, Nat. Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-020-18319-6
Yeung, Teng, Jia, Zhang, Huang et al., Soluble ACE2-Mediated Cell Entry of SARS-CoV-2 via Interaction with Proteins Related to the Renin-Angiotensin System, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2021.02.053
Zamai, The Yin and Yang of ACE/ACE2 Pathways: The Rationale for the Use of Renin-Angiotensin System Inhibitors in COVID-19 Patients, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells9071704
Zhang, Zhang, Hua, Chen, Saying No to SARS-CoV-2: The Potential of Nitric Oxide in the Treatment of COVID-19 Pneumonia, Med. Gas Res, doi:10.4103/2045-9912.385414
Zhou, Yang, Wang, Hu, Zhang et al., A Pneumonia Outbreak Associated with a New Coronavirus of Probable Bat Origin, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7
Åkerström, Gunalan, Keng, Tan, Mirazimi, Dual Effect of Nitric Oxide on SARS-CoV Replication: Viral RNA Production and Palmitoylation of the S Protein Are Affected, Virology, doi:10.1016/j.virol.2009.09.007
Åkerström, Mousavi-Jazi, Klingström, Leijon, Lundkvist et al., Nitric Oxide Inhibits the Replication Cycle of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus, J. Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.79.3.1966-1969.2005
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antiox13111301",
"ISSN": [
"2076-3921"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/antiox13111301",
"abstract": "<jats:p>SARS-CoV-2, the causative virus for the COVID-19 disease, uses its spike glycoprotein to bind to human ACE2 as a first step for viral entry into the cell. For this reason, great efforts have been made to find mechanisms that disrupt this interaction, avoiding the infection. Nitric oxide (NO) is a soluble endogenous gas with known antiviral and immunomodulatory properties. In this study, we aimed to test whether NO could inhibit the binding of the viral spike to ACE2 in human cells and its effects on ACE2 enzymatic activity. Our results show that ACE2 activity was decreased by the NO donors DETA-NONOate and GSNO and by the NO byproduct peroxynitrite. Furthermore, we found that DETA-NONOate could break the spike–ACE2 interaction using the spike from two different variants (Alpha and Gamma) and in two different human cell types. Moreover, the same result was obtained when using NO-producing murine macrophages, while no significant changes were observed in ACE2 expression or distribution within the cell. These results support that it is worth considering NO as a therapeutic agent for COVID-19, as previous reports have suggested.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"antiox13111301"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3332-7603",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Instituto de Investigaciones Biomédicas Sols-Morreale, CSIC-UAM, Arturo Duperier 4, 28029 Madrid, Spain"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Sánchez-García",
"given": "Sergio",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Instituto de Investigaciones Biomédicas Sols-Morreale, CSIC-UAM, Arturo Duperier 4, 28029 Madrid, Spain"
},
{
"name": "Unidad de Biomedicina (Unidad Asociada al CSIC), Universidad de Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, 35016 Las Palmas, Spain"
}
],
"family": "Castrillo",
"given": "Antonio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0253-5469",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Instituto de Investigaciones Biomédicas Sols-Morreale, CSIC-UAM, Arturo Duperier 4, 28029 Madrid, Spain"
},
{
"name": "Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red de Enfermedades Cardiovasculares (CIBERCV), Av. Monforte de Lemos 3-5, P-11, 28029 Madrid, Spain"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Boscá",
"given": "Lisardo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6943-7663",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red de Enfermedades Cardiovasculares (CIBERCV), Av. Monforte de Lemos 3-5, P-11, 28029 Madrid, Spain"
},
{
"name": "Departamento de Farmacología, Farmacognosia y Botánica, Facultad de Farmacia, Universidad Complutense de Madrid, Plaza Ramón y Cajal, 28040 Madrid, Spain"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Prieto",
"given": "Patricia",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Antioxidants",
"container-title-short": "Antioxidants",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2024-10-28T08:15:02Z",
"timestamp": 1730103302000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2024-10-28T09:29:11Z",
"timestamp": 1730107751000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2024-10-28T10:40:39Z",
"timestamp": 1730112039887,
"version": "3.28.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "11",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
26
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "11",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2024-10-26T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1729900800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3921/13/11/1301/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1301",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
26
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
26
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-020-00459-7",
"article-title": "Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19",
"author": "Hu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "141",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Microbiol.",
"key": "ref_1",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-138577",
"article-title": "COVID-19: Current Understanding of Its Pathophysiology, Clinical Presentation and Treatment",
"author": "Parasher",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "312",
"journal-title": "Postgrad. Med. J.",
"key": "ref_2",
"volume": "97",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Structural Basis for the Recognition of SARS-CoV-2 by Full-Length Human ACE2",
"author": "Yan",
"first-page": "1444",
"journal-title": "Science (1979)",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "367",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Structure and Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Refolding in Membranes",
"author": "Grunst",
"first-page": "757",
"journal-title": "Science (1979)",
"key": "ref_4",
"volume": "385",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-021-00573-0",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Variants, Spike Mutations and Immune Escape",
"author": "Harvey",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "409",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Microbiol.",
"key": "ref_5",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41564-021-00932-w",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Interest and Concern Naming Scheme Conducive for Global Discourse",
"author": "Konings",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "821",
"journal-title": "Nat. Microbiol.",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa373",
"article-title": "Circulating Plasma Concentrations of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 in Men and Women with Heart Failure and Effects of Renin–Angiotensin–Aldosterone Inhibitors",
"author": "Sama",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1810",
"journal-title": "Eur. Heart J.",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fped.2020.00206",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_8",
"unstructured": "Ciaglia, E., Vecchione, C., and Puca, A.A. (2020). COVID-19 Infection and Circulating ACE2 Levels: Protective Role in Women and Children. Front. Pediatr., 8."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcimb.2020.00317",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_9",
"unstructured": "Samavati, L., and Uhal, B.D. (2020). ACE2, Much More Than Just a Receptor for SARS-COV-2. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol., 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrcardio.2014.59",
"article-title": "Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 and Angiotensin 1–7: Novel Therapeutic Targets",
"author": "Jiang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "413",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Cardiol.",
"key": "ref_10",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7",
"article-title": "A Pneumonia Outbreak Associated with a New Coronavirus of Probable Bat Origin",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "270",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_11",
"volume": "579",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-18319-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_12",
"unstructured": "Yang, J., Petitjean, S.J.L., Koehler, M., Zhang, Q., Dumitru, A.C., Chen, W., Derclaye, S., Vincent, S.P., Soumillion, P., and Alsteens, D. (2020). Molecular Interaction and Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Binding to the ACE2 Receptor. Nat. Commun., 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tim.2021.12.011",
"article-title": "Mitochondria-Mediated Oxidative Stress during Viral Infection",
"author": "Foo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "679",
"journal-title": "Trends Microbiol.",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.2240",
"article-title": "Reactive Oxygen Species as Potential Antiviral Targets",
"author": "Sander",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Rev. Med. Virol.",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.redox.2019.101261",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_15",
"unstructured": "Virág, L., Jaén, R.I.R.I., Regdon, Z., Boscá, L., and Prieto, P. (2019). Self-Defense of Macrophages against Oxidative Injury: Fighting for Their Own Survival. Redox Biol., 26."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/BST20220504",
"article-title": "Defining the Metabolic Signatures Associated with Human Macrophage Polarisation",
"author": "Marin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1429",
"journal-title": "Biochem. Soc. Trans.",
"key": "ref_16",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1471-2164-8-271",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_17",
"unstructured": "Rico, D., Vaquerizas, J.M., Dopazo, H., and Boscá, L. (2007). Identification of Conserved Domains in the Promoter Regions of Nitric Oxide Synthase 2: Implications for the Species-Specific Transcription and Evolutionary Differences. BMC Genom., 8."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.93.3.1054",
"article-title": "Transcriptional Regulation of Human Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase (NOS2) Gene by Cytokines: Initial Analysis of the Human NOS2 Promoter",
"author": "Shapiro",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1054",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "ref_18",
"volume": "93",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/biof.103",
"article-title": "Peroxynitrite—An Ugly Biofactor?",
"author": "Ascenzi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "264",
"journal-title": "BioFactors",
"key": "ref_19",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/advs.202003895",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_20",
"unstructured": "Lisi, F., Zelikin, A.N., and Chandrawati, R. (2021). Nitric Oxide to Fight Viral Infections. Adv. Sci., 8."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-023-37949-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_21",
"unstructured": "Shu, X., Shi, Y., Huang, Y., Yu, D., and Sun, B. (2023). Transcription Tuned by S-Nitrosylation Underlies a Mechanism for Staphylococcus Aureus to Circumvent Vancomycin Killing. Nat. Commun., 14."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antiox11112176",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_22",
"unstructured": "De Simone, G., di Masi, A., and Ascenzi, P. (2022). Strategies of Pathogens to Escape from NO-Based Host Defense. Antioxidants, 11."
},
{
"article-title": "S-Nitrosylation of Viral Proteins: Molecular Bases for Antiviral Effect of Nitric Oxide",
"author": "Colasanti",
"first-page": "25",
"journal-title": "IUBMB Life",
"key": "ref_23",
"volume": "48",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"article-title": "Inhibition of Viral Replication by Interferon-γ-Induced Nitric Oxide Synthase",
"author": "Karupiah",
"first-page": "1445",
"journal-title": "Science (1979)",
"key": "ref_24",
"volume": "261",
"year": "1993"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI116479",
"article-title": "Evidence for Antiviral Effect of Nitric Oxide. Inhibition of Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 Replication",
"author": "Croen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2446",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Investig.",
"key": "ref_25",
"volume": "91",
"year": "1993"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0092-8674(94)90005-1",
"article-title": "Nitric Oxide Produced by Human B Lymphocytes Inhibits Apoptosis and Epstein-Barr Virus Reactivation",
"author": "Mannick",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1137",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_26",
"volume": "79",
"year": "1994"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1074-7613(00)80003-5",
"article-title": "An Antiviral Mechanism of Nitric Oxide",
"author": "Saura",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "21",
"journal-title": "Immunity",
"key": "ref_27",
"volume": "10",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virol.2009.09.007",
"article-title": "Dual Effect of Nitric Oxide on SARS-CoV Replication: Viral RNA Production and Palmitoylation of the S Protein Are Affected",
"author": "Gunalan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Virology",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.79.3.1966-1969.2005",
"article-title": "Nitric Oxide Inhibits the Replication Cycle of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus",
"author": "Leijon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1966",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "79",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2004.04.012",
"article-title": "Inhibition of SARS-Coronavirus Infection in Vitro by S-Nitroso-N-Acetylpenicillamine, a Nitric Oxide Donor Compound",
"author": "Keyaerts",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "223",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_30",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/2045-9912.385414",
"article-title": "Saying No to SARS-CoV-2: The Potential of Nitric Oxide in the Treatment of COVID-19 Pneumonia",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "39",
"journal-title": "Med. Gas Res.",
"key": "ref_31",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules27072337",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_32",
"unstructured": "Sodano, F., Gazzano, E., Fruttero, R., and Lazzarato, L. (2022). NO in Viral Infections: Role and Development of Antiviral Therapies. Molecules, 27."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.273.30.18709",
"article-title": "Diffusion-Limited Reaction of Free Nitric Oxide with Erythrocytes",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "18709",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "ref_33",
"volume": "273",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2020.00923",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_34",
"unstructured": "Li, B., Ming, Y., Liu, Y., Xing, H., Fu, R., Li, Z., Ni, R., Li, L., Duan, D., and Xu, J. (2020). Recent Developments in Pharmacological Effect, Mechanism and Application Prospect of Diazeniumdiolates. Front. Pharmacol., 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejpb.2014.11.005",
"article-title": "Time Lasting S-Nitrosoglutathione Polymeric Nanoparticles Delay Cellular Protein S-Nitrosation",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm.",
"key": "ref_35",
"volume": "89",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jlb.58.6.643",
"article-title": "On the Expression of Nitric Oxide Synthase by Human Macrophages. Why No NO?",
"author": "Albina",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "643",
"journal-title": "J. Leukoc. Biol.",
"key": "ref_36",
"volume": "58",
"year": "1995"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2217/epi.12.41",
"article-title": "Epigenetic Genome-Wide Association Methylation in Aging and Longevity",
"author": "Muzumdar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "503",
"journal-title": "Epigenomics",
"key": "ref_37",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1118118109",
"article-title": "MiRNA-939 Regulates Human Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase Posttranscriptional Gene Expression in Human Hepatocytes",
"author": "Guo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5826",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "ref_38",
"volume": "109",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1006/niox.2000.0290",
"article-title": "Survey of the Allelic Frequency of a NOS2A Promoter Microsatellite in Human Populations: Assessment of the NOS2A Gene and Predisposition to Infectious Disease",
"author": "Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "379",
"journal-title": "Nitric Oxide",
"key": "ref_39",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7759/cureus.53558",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_40",
"unstructured": "Kaplish, D., Vagha, J.D., Meshram, R.J., and Lohiya, S. (2024). A Comprehensive Review of Inhaled Nitric Oxide Therapy: Current Trends, Challenges, and Future Directions. Cureus, 16."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.niox.2022.01.007",
"article-title": "Nitric Oxide: Clinical Applications in Critically Ill Patients",
"author": "Redaelli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "20",
"journal-title": "Nitric Oxide",
"key": "ref_41",
"volume": "121",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms23169114",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_42",
"unstructured": "Jaén, R.I., Povo-Retana, A., Rosales-Mendoza, C., Capillas-Herrero, P., Sánchez-García, S., Martín-Sanz, P., Mojena, M., Prieto, P., and Boscá, L. (2022). Functional Crosstalk between PCSK9 Internalization and Pro-Inflammatory Activation in Human Macrophages: Role of Reactive Oxygen Species Release. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 23."
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.160.6.2889",
"article-title": "Triggering of Peritoneal Macrophages with IFN-α/β Attenuates the Expression of Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase through a Decrease in NF-kB Activation",
"author": "Hortelano",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2889",
"journal-title": "J. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_43",
"volume": "160",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/sj.bjp.0701836",
"article-title": "Modulation of Angiotensin-converting Enzyme by Nitric Oxide",
"author": "Ackermann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "291",
"journal-title": "Br. J. Pharmacol.",
"key": "ref_44",
"volume": "124",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.93.25.14428",
"article-title": "The Chemistry of the S-Nitrosoglutathione/Glutathione System",
"author": "Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "14428",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "ref_45",
"volume": "93",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1096/fasebj.13.15.2311",
"article-title": "Nitric Oxide Induces Tyrosine Nitration and Release of Cytochrome c Preceding an Increase of Mitochondrial Transmembrane Potential in Macrophages",
"author": "Hortelano",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2311",
"journal-title": "FASEB J.",
"key": "ref_46",
"volume": "13",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tox.2004.11.035",
"article-title": "Nitric Oxide and Cell Viability in Inflammatory Cells: A Role for NO in Macrophage Function and Fate",
"author": "Bosca",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "249",
"journal-title": "Toxicology",
"key": "ref_47",
"volume": "208",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.redox.2017.09.009",
"article-title": "Fundamentals on the Biochemistry of Peroxynitrite and Protein Tyrosine Nitration",
"author": "Bartesaghi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "618",
"journal-title": "Redox Biol.",
"key": "ref_48",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1084/jem.194.9.1231",
"article-title": "Protein Kinase Cepsilon Is Required for Macrophage Activation and Defense against Bacterial Infection",
"author": "Castrillo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1231",
"journal-title": "J. Exp. Med.",
"key": "ref_49",
"volume": "194",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.171.11.6059",
"article-title": "Sustained Nitric Oxide Delivery Delays Nitric Oxide-Dependent Apoptosis in Macrophages: Contribution to the Physiological Function of Activated Macrophages",
"author": "Hortelano",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6059",
"journal-title": "J. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_50",
"volume": "171",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2180-5",
"article-title": "Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Receptor-Binding Domain Bound to the ACE2 Receptor",
"author": "Lan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "215",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_51",
"volume": "581",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-020-00468-6",
"article-title": "Coronavirus Biology and Replication: Implications for SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Kratzel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "155",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Microbiol.",
"key": "ref_52",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1568026623666221103091658",
"article-title": "Structure Based Drug Designing Approaches in SARS-CoV-2 Spike Inhibitor Design",
"author": "Shanmugam",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2396",
"journal-title": "Curr. Top. Med. Chem.",
"key": "ref_53",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s42485-021-00074-x",
"article-title": "Therapeutically Effective Covalent Spike Protein Inhibitors in Treatment of SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Choudhary",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "257",
"journal-title": "J. Proteins Proteom.",
"key": "ref_54",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/advs.202303259",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_55",
"unstructured": "Andrabi, S.M., Sharma, N.S., Karan, A., Shahriar, S.M.S., Cordon, B., Ma, B., and Xie, J. (2023). Nitric Oxide: Physiological Functions, Delivery, and Biomedical Applications. Adv. Sci., 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.niox.2019.12.001",
"article-title": "Inhaled Nitric Oxide Use in Neonates: Balancing What Is Evidence-Based and What Is Physiologically Sound",
"author": "Sherlock",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "12",
"journal-title": "Nitric Oxide",
"key": "ref_56",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.rmed.2018.06.030",
"article-title": "Salvage Therapies for Refractory Hypoxemia in ARDS",
"author": "Cherian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "150",
"journal-title": "Respir. Med.",
"key": "ref_57",
"volume": "141",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.resp.2013.03.006",
"article-title": "Effect of Nitric Oxide Inhalation on Gas Exchange in Acute Severe Pneumonia",
"author": "Amado",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "157",
"journal-title": "Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol.",
"key": "ref_58",
"volume": "187",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2021.05.009",
"article-title": "Clinical Efficacy of Nitric Oxide Nasal Spray (NONS) for the Treatment of Mild COVID-19 Infection",
"author": "Winchester",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "237",
"journal-title": "J. Infect.",
"key": "ref_59",
"volume": "83",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-024-68055-w",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_60",
"unstructured": "Wolak, T., Dicker, D., Shifer, Y., Grossman, A., Rokach, A., Shitrit, M., and Tal, A. (2024). A Safety Evaluation of Intermittent High-Dose Inhaled Nitric Oxide in Viral Pneumonia Due to COVID-19: A Randomised Clinical Study. Sci. Rep., 14."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lansea.2022.100036",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_61",
"unstructured": "Tandon, M., Wu, W., Moore, K., Winchester, S., Tu, Y.-P., Miller, C., Kodgule, R., Pendse, A., Rangwala, S., and Joshi, S. (2022). SARS-CoV-2 Accelerated Clearance Using a Novel Nitric Oxide Nasal Spray (NONS) Treatment: A Randomized Trial. Lancet Reg. Health—Southeast Asia, 3."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.micinf.2020.05.002",
"article-title": "Could Nasal Nitric Oxide Help to Mitigate the Severity of COVID-19?",
"author": "Martel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "168",
"journal-title": "Microbes Infect.",
"key": "ref_62",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.202005-1906ED",
"article-title": "Home Nitric Oxide Therapy for COVID-19",
"author": "Alvarez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "16",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med.",
"key": "ref_63",
"volume": "202",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2023.1284148",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_64",
"unstructured": "Silva, B.J.d.A., Krogstad, P.A., Teles, R.M.B., Andrade, P.R., Rajfer, J., Ferrini, M.G., Yang, O.O., Bloom, B.R., and Modlin, R.L. (2023). IFN-γ-Mediated Control of SARS-CoV-2 Infection through Nitric Oxide. Front. Immunol., 14."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1046/j.1365-2567.2000.00142.x",
"article-title": "Nitric Oxide and Virus Infection",
"author": "Akaike",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "300",
"journal-title": "Immunology",
"key": "ref_65",
"volume": "101",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1084/jem.183.5.2293",
"article-title": "Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase in Pulmonary Alveolar Macrophages from Patients with Tuberculosis",
"author": "Nicholson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2293",
"journal-title": "J. Exp. Med.",
"key": "ref_66",
"volume": "183",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.2201023",
"article-title": "Analysis of Nitric Oxide Synthase and Nitrotyrosine Expression in Human Pulmonary Tuberculosis",
"author": "Choi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "178",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med.",
"key": "ref_67",
"volume": "166",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.1301758",
"article-title": "Epigenetic Silencing of the Human NOS2 Gene: Rethinking the Role of Nitric Oxide in Human Macrophage Inflammatory Responses",
"author": "Gross",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2326",
"journal-title": "J. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_68",
"volume": "192",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"article-title": "Interferon-Gamma Enhances Monocyte Cytotoxicity via Enhanced Reactive Oxygen Intermediate Production. Absence of an Effect on Macrophage Cytotoxicity Is Due to Failure to Enhance Reactive Nitrogen Intermediate Production",
"author": "Martin",
"first-page": "592",
"journal-title": "Immunology",
"key": "ref_69",
"volume": "81",
"year": "1994"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/01.HYP.31.1.342",
"article-title": "Downregulation of Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor Gene Transcription by Nitric Oxide",
"author": "Ichiki",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "342",
"journal-title": "Hypertension",
"key": "ref_70",
"volume": "31",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10096-020-04138-6",
"article-title": "COVID-19: Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2) Expression and Tissue Susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 Infection",
"author": "Beyerstedt",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "905",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_71",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajpheart.00138.2012",
"article-title": "Soluble Guanylyl Cyclase Is a Target of Angiotensin II-Induced Nitrosative Stress in a Hypertensive Rat Model",
"author": "Crassous",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "H597",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Physiol.-Heart Circ. Physiol.",
"key": "ref_72",
"volume": "303",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/01.HYP.19.6.692",
"article-title": "In Vivo Metabolism of Angiotensin I by Neutral Endopeptidase (EC 3.4.24.11) in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats",
"author": "Yamamoto",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "692",
"journal-title": "Hypertension",
"key": "ref_73",
"volume": "19",
"year": "1992"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2021.02.053",
"article-title": "Soluble ACE2-Mediated Cell Entry of SARS-CoV-2 via Interaction with Proteins Related to the Renin-Angiotensin System",
"author": "Yeung",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2212",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_74",
"volume": "184",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cells9071704",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_75",
"unstructured": "Zamai, L. (2020). The Yin and Yang of ACE/ACE2 Pathways: The Rationale for the Use of Renin-Angiotensin System Inhibitors in COVID-19 Patients. Cells, 9."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/CS20100280",
"article-title": "Angiotensin-(1–7) Infusion Is Associated with Increased Blood Pressure and Adverse Cardiac Remodelling in Rats with Subtotal Nephrectomy",
"author": "Velkoska",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "335",
"journal-title": "Clin. Sci.",
"key": "ref_76",
"volume": "120",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0005406",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_77",
"unstructured": "Esteban, V., Heringer-Walther, S., Sterner-Kock, A., de Bruin, R., van den Engel, S., Wang, Y., Mezzano, S., Egido, J., Schultheiss, H.-P., and Ruiz-Ortega, M. (2009). Angiotensin-(1–7) and the G Protein-Coupled Receptor Mas Are Key Players in Renal Inflammation. PLoS ONE, 4."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.RA120.015303",
"article-title": "High Affinity Binding of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Enhances ACE2 Carboxypeptidase Activity",
"author": "Lu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "18579",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "ref_78",
"volume": "295",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41589-022-01149-6",
"article-title": "Targeted Protein S-Nitrosylation of ACE2 Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Infection",
"author": "Oh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "275",
"journal-title": "Nat. Chem. Biol.",
"key": "ref_79",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.130686",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_80",
"unstructured": "Guo, L., Zhao, P., Jia, Y., Li, T., Huang, L., Wang, Z., Liu, D., Hou, Z., Zhao, Y., and Zhang, L. (2023). Efficient Inactivation of the Contamination with Pathogenic Microorganisms by a Combination of Water Spray and Plasma-Activated Air. J. Hazard. Mater., 446."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-022-01249-8",
"article-title": "Small Molecules in the Treatment of COVID-19",
"author": "Lei",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "387",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct. Target. Ther.",
"key": "ref_81",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms24108814",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_82",
"unstructured": "Bastos, R.S., Lima, L.R.d., Neto, M.F.A., Yousaf, N., Cruz, J.N., Campos, J.M., Kimani, N.M., Ramos, R.S., and Santos, C.B.R. (2023). Design and Identification of Inhibitors for the Spike-ACE2 Target of SARS-CoV-2. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 24."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/01.CIR.0000134595.80170.62",
"article-title": "Inhaled Nitric Oxide: A Selective Pulmonary Vasodilator: Current Uses and Therapeutic Potential",
"author": "Ichinose",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3106",
"journal-title": "Circulation",
"key": "ref_83",
"volume": "109",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"article-title": "COVID-19 and ACE-Inhibitors and Angiotensin Receptor Blockers-: The Need to Differentiate between Early Infection and Acute Lung Injury",
"first-page": "129",
"journal-title": "Rev. Colomb. Cardiol.",
"key": "ref_84",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 84,
"references-count": 84,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3921/13/11/1301"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Potential Beneficial Role of Nitric Oxide in SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Beyond Spike-Binding Inhibition",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "13"
}