Leisure Time Physical Activity and SARS-CoV-2 Infection among ELSA-Brasil Participants
et al., International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, doi:10.3390/ijerph192114155, Oct 2022
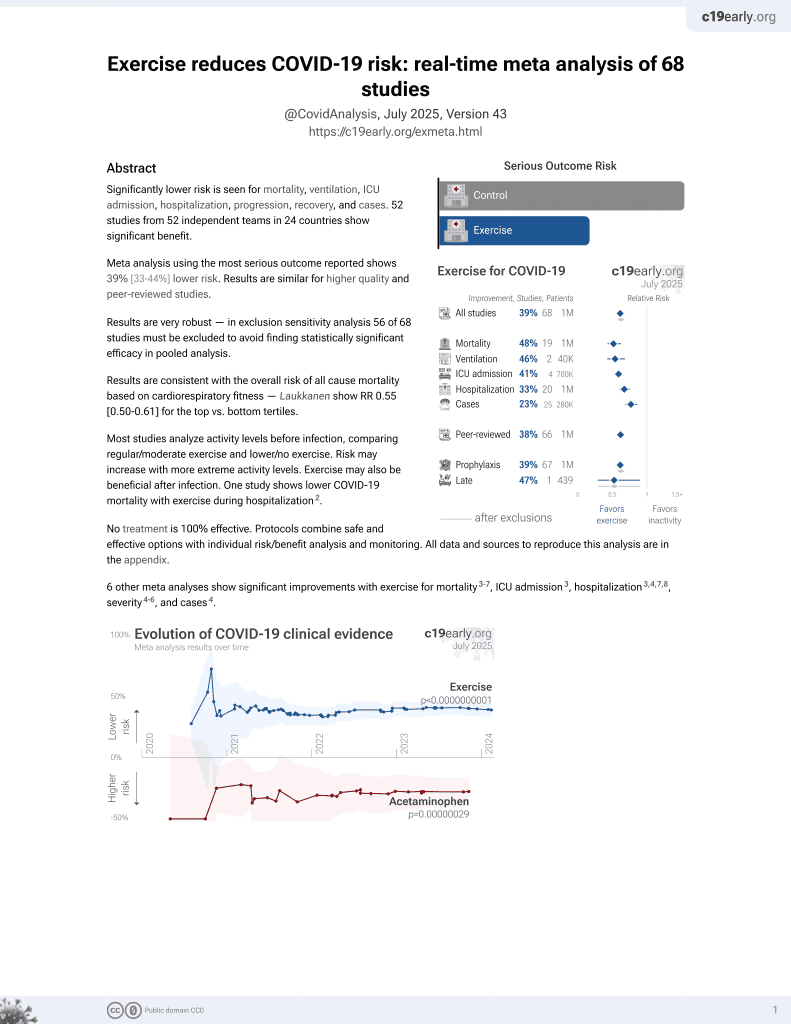
Exercise for COVID-19
9th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 68 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
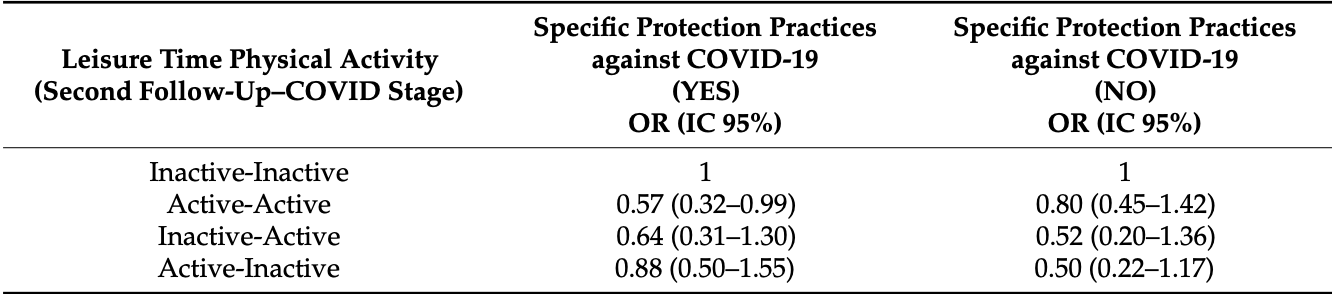
Retrospective 4,476 participants in Brazil, showing lower risk of COVID-19 cases with a history of physical activity, statistically significant only for those following specific practices to protect against COVID-19.
|
risk of case, 33.0% lower, OR 0.67, p = 0.05, high activity levels 1,469, low activity levels 1,552, combined results with and without protection practices, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of case, 43.0% lower, OR 0.57, p = 0.05, with protection practices, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of case, 20.0% lower, OR 0.80, p = 0.46, without protection practices, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Pitanga et al., 29 Oct 2022, retrospective, Brazil, peer-reviewed, survey, 11 authors.
Contact: pitanga@lognet.com.br (corresponding author).
Leisure Time Physical Activity and SARS-CoV-2 Infection among ELSA-Brasil Participants
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, doi:10.3390/ijerph192114155
The regular practice of physical activity (PA) can reduce the chance of aggravation of the disease and lower rates of hospitalization and mortality from COVID-19, but few studies have analyzed the association of PA with the risk of infection by SARS-CoV-2. The aim of the study was to analyze the association between PA and self-reported SARS-CoV-2 infection. A longitudinal study was conducted with data from 4476 ELSA-Brasil participants who had their PA analyzed twice, once in 2016-2018 and again in 2020. PA was identified using the IPAQ at both follow-up moments and categorized into four groups: (a) remained physically inactive (reference); (b) remained physically active; (c) became physically active in the second moment; and (d) became physically inactive in the second moment. The variables of age, sex, obesity, hypertension, diabetes and specific protective practices against COVID-19 were tested as possible confounders. Data were analyzed by logistic regression. A 95% confidence interval (CI) was used. Remaining physically active was associated with a 43% reduction in the risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection only among those who used specific practices to protect against COVID-19, OR = 0.57 and CI = 0.32-0.99. The results suggested that regular practice of PA can reduce the risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection, especially among those who have used specific practices to protect against COVID-19 during the pandemic.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript or in the decision to publish the results.
References
Aquino, Barreto, Bensenor, Carvalho, Chor et al., Brazilian Longitudinal Study of Adult Health (ELSA-Brasil): Objectives and design, Am. J. Epidemiol, doi:10.1093/aje/kwr294
Chastin, Abaraogu, Bourgois, Dall, Darnborough et al., Effects of Regular Physical Activity on the Immune System, Vaccination and Risk of Community-Acquired Infectious Disease in the General Population: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Sports Med, doi:10.1007/s40279-021-01466-1
Cho, Lee, Jae, Kim, Ha et al., Physical Activity and the Risk of COVID-19 Infection and Mortality: A Nationwide Population-Based Case-Control Study, J. Clin. Med, doi:10.3390/jcm10071539
Cuervo, Grandvaux, ACE2: Evidence of role as entry receptor for SARS-CoV-2 and implications in comorbidities, Elife, doi:10.7554/eLife.61390
Ezzatvar, Ramírez-Vélez, Izquierdo, Garcia-Hermoso, Physical activity and risk of infection, severity and mortality of COVID-19: A systematic review and non-linear dose-response meta-analysis of data from 1 853 610 adults, Br. J. Sports Med, doi:10.1136/bjsports-2022-105733
Hosmer, Lemeshow, Appled Logistic Regression
Klentrou, Cieslak, Macneil, Vintinner, Plyley, Effect of moderate exercise on salivary immunoglobulin A and infection risk in humans, Eur. J. Appl. Physiol, doi:10.1007/s00421-002-0609-1
Kohut, Cooper, Nickolaus, Russell, Cunnick, Exercise and psychosocial factors modulate immunity to influenza vaccine in elderly individuals, J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci, doi:10.1093/gerona/57.9.M557
Lee, Lee, Moon, Jin, Yang et al., Physical activity and the risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection, severe COVID-19 illness and COVID-19 related mortality in South Korea: A nationwide cohort study, Br. J. Sports Med, doi:10.1136/bjsports-2021-104203
Lotufo, Construction of the Longitudinal Study of Adult Health (ELSA-Brazil), Rev. Saude Publica, doi:10.1590/S0034-8910.2013047S20002
Matsudo, Araújo, Matsudo, Questionário internacional de atividade física (IPAQ): Estudo de validade e reprodutibilidade no Brasil, Rev. Bras. Ativ. Fís. Saude, doi:10.12820/rbafs.v.6n2p5-18
Pitanga, Beck, Pitanga, Pinho Cscortez, Guedes et al., Association between leisure time physical activity and mortality by COVID-19 in the brazilian capitals: An ecological analysis, Rev. Bras. Med. Esporte, doi:10.1590/1517-8692202127062021_0071
Salgado-Aranda, Pérez-Castellano, Núñez-Gil, Orozco, Torres-Esquivel et al., Influence of Baseline Physical Activity as a Modifying Factor on COVID-19 Mortality: A Single-Center, Retrospective Study, Infect. Dis. Ther, doi:10.1007/s40121-021-00418-6
Sallis, Young, Tartof, Sallis, Sall et al., Physical inactivity is associated with a higher risk for severe COVID-19 outcomes: A study in 48 440 adult patients, Br. J. Sports Med, doi:10.1136/bjsports-2021-104080
Schmidt, Griep, Passos, Luft, Goulart et al., Strategies and development of quality assurance and control in the ELSA-Brasil, Rev. Saude Publica, doi:10.1590/S0034-8910.2013047003889
Shimizu, Kimura, Akimoto, Akama, Otsuki et al., Effects of exercise, age and gender on salivary secretory immunoglobulin A in elderly individuals, Exerc. Immunol. Rev
Siu, Campitelli, Kwong, Physical activity and influenza-coded outpatient visits, a population-based cohort study, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0039518
Tada, Senpuku, The Impact of Oral Health on Respiratory Viral Infection, Dent. J, doi:10.3390/dj9040043
Talic, Shah, Wild, Gasevic, Maharaj et al., Effectiveness of public health measures in reducing the incidence of COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2 transmission, and COVID-19 mortality: Systematic review and meta-analysis, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj-2021-068302
Zbinden-Foncea, Francaux, Deldicque, Hawley, Does High Cardiorespiratory Fitness Confer Some Protection against Proinflammatory Responses after Infection by SARS-CoV-2?, Obesity, doi:10.1002/oby.22849
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijerph192114155",
"ISSN": [
"1660-4601"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192114155",
"abstract": "<jats:p>The regular practice of physical activity (PA) can reduce the chance of aggravation of the disease and lower rates of hospitalization and mortality from COVID-19, but few studies have analyzed the association of PA with the risk of infection by SARS-CoV-2. The aim of the study was to analyze the association between PA and self-reported SARS-CoV-2 infection. A longitudinal study was conducted with data from 4476 ELSA-Brasil participants who had their PA analyzed twice, once in 2016–2018 and again in 2020. PA was identified using the IPAQ at both follow-up moments and categorized into four groups: (a) remained physically inactive (reference); (b) remained physically active; (c) became physically active in the second moment; and (d) became physically inactive in the second moment. The variables of age, sex, obesity, hypertension, diabetes and specific protective practices against COVID-19 were tested as possible confounders. Data were analyzed by logistic regression. A 95% confidence interval (CI) was used. Remaining physically active was associated with a 43% reduction in the risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection only among those who used specific practices to protect against COVID-19, OR = 0.57 and CI = 0.32-0.99. The results suggested that regular practice of PA can reduce the risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection, especially among those who have used specific practices to protect against COVID-19 during the pandemic.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"ijerph192114155"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1033-8684",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Pitanga",
"given": "Francisco José Gondim",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Almeida",
"given": "Maria da Conceição",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Duncan",
"given": "Bruce B.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0987-368X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Mill",
"given": "José Geraldo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Giatti",
"given": "Luana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8614-988X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Molina",
"given": "Maria del Carmen B.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fonseca",
"given": "Maria de Jesus Mendes da",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Schmidt",
"given": "Maria Inês",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6250-2036",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Griep",
"given": "Rosane Harter",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7383-7811",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Barreto",
"given": "Sandhi Maria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Matos",
"given": "Sheila Maria Alvim de",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health",
"container-title-short": "IJERPH",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2022-10-30T08:57:34Z",
"timestamp": 1667120254000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2022-10-30T09:25:13Z",
"timestamp": 1667121913000
},
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"405551/2015-0 BA",
"405544/2015-4 RJ",
"405552/2015-7 MG",
"405543/2015-8 ES",
"405545/2015-0 RS"
],
"name": "Brazilian Ministry of Health"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2022-10-31T04:54:30Z",
"timestamp": 1667192070109
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "21",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
29
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "21",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2022-10-29T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1667001600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1660-4601/19/21/14155/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "14155",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
29
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
29
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"key": "ref1",
"unstructured": "Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV): Situation Report-19"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0039518",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/gerona/57.9.M557",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/oby.22849",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40121-021-00418-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bjsports-2021-104080",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1590/1517-8692202127062021_0071",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref7"
},
{
"article-title": "Coronavirus Disease",
"author": "Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)",
"key": "ref8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40279-021-01466-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm10071539",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref10"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bjsports-2021-104203",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7554/eLife.61390",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref12"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00421-002-0609-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj-2021-068302",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/aje/kwr294",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1590/S0034-8910.2013047003889",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref16"
},
{
"DOI": "10.12820/rbafs.v.6n2p5-18",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1590/S0034-8910.2013047S20002",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref18"
},
{
"author": "Hosmer",
"key": "ref19",
"series-title": "Appled Logistic Regression",
"year": "1989"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bjsports-2022-105733",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref20"
},
{
"article-title": "Effects of exercise, age and gender on salivary secretory immunoglobulin A in elderly individuals",
"author": "Shimizu",
"first-page": "55",
"journal-title": "Exerc. Immunol. Rev.",
"key": "ref21",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/dj9040043",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref22"
}
],
"reference-count": 22,
"references-count": 22,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1660-4601/19/21/14155"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Health, Toxicology and Mutagenesis",
"Public Health, Environmental and Occupational Health"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Leisure Time Physical Activity and SARS-CoV-2 Infection among ELSA-Brasil Participants",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "19"
}