Association between population vitamin D status and SARS-CoV-2 related serious-critical illness and deaths: An ecological integrative approach
et al., World J. Virology, doi:10.5501/wjv.v10.i3.111], May 2021
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 136 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
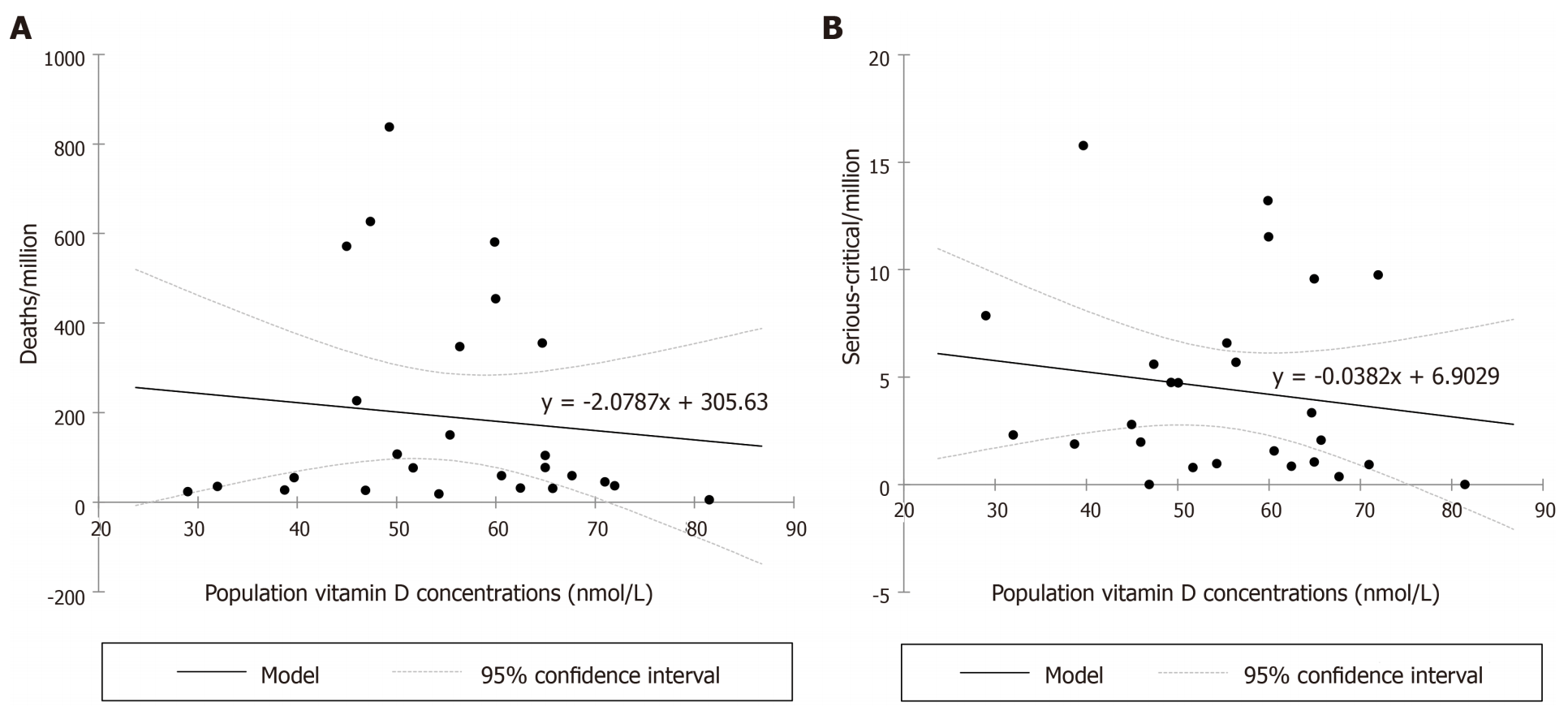
Country analysis showing negative correlations between population vitamin D level and severe cases and death (but not with cases overall). Authors conclude that higher vitamin D levels may protect from severe cases and death, even more so in the elderly.
Papadimitriou et al., 25 May 2021, peer-reviewed, 3 authors.
Association between population vitamin D status and SARS-CoV-2 related serious-critical illness and deaths: An ecological integrative approach
World Journal of Virology, doi:10.5501/wjv.v10.i3.111
BACKGROUND Vitamin D population status may have possible unappreciated consequences to the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. Α significant association between vitamin D sufficiency and reduction in clinical severity and inpatient mortality from COVID-19 disease has recently been shown, while a recent study has claimed lower COVID-19 cases in European countries with a better vitamin D status. Low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin-D [25(OH)D] was identified as an independent risk factor for COVID-19 infection and hospitalization, and administration of 0.532 mg (21280 IU) of calcifediol or 25(OH)D, followed by 0.266 mg on days 3 and 7 and then weekly until discharge or intensive care unit admission significantly reduced the need for intensive care unit treatment. AIM To elucidate the role of vitamin D European population status in the COVID-19 pandemic, data from the Worldometer were analyzed.
Research motivation Vitamin D population status may indeed have possible unappreciated consequences to the COVID-19 pandemic, a hypothesis that needed to be further elucidated.
Research objectives Following an ecological integrative approach, we examined the associations between published representative and standardized European population vitamin D data and the Worldometer COVID-19 data at two completely different time points of the first wave of this pandemic. If any sustained correlations were to be found, they would be an indication of a truthful association, even though they could not prove causality.
Research methods Using linear regression, we explored the correlation between published representative and standardized population vitamin D concentrations and the number of total cases/million (M), recovered/M, deaths/M and serious-critically ill/M from COVID-19 for 26 European countries populated > 4 M. Life expectancy (LE) was also analyzed with semi-parametric regression. Weighted analysis of variance/analysis of covariance evaluated serious-critical/M and deaths/M by the vitamin D population status: deficient < 50, insufficient: 50-62.5, mildly insufficient > 62.5-75 and sufficient > 75 nmol/L, while controlling for LE for deaths/M. Statistical analyses were performed in XLSTAT LIFE SCIENCE and R (SemiPar library).
Research results No correlation was found between population vitamin D concentrations and the total cases-recovered/M, but negative..
References
Alipio, Do latitude and ozone concentration predict Covid-2019 cases in 34 countries? medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.04.09.20060202
Avenell, Mak, Connell, Vitamin D and vitamin D analogues for preventing fractures in post-menopausal women and older men, Cochrane Database Syst Rev, doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000227.pub4
Bettencourt, Boleixa, Reis, Oliveira, Mendonça et al., Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels in a healthy population from the North of Portugal, J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2016.11.005
Bolland, Grey, Avenell, Effects of vitamin D supplementation on musculoskeletal health: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and trial sequential analysis, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(18)30265-1
Bone, Society, Vitamin D and health in adults in Australia and New Zealand: a position statement, Med J Aust, doi:10.5694/mja11.10301
Borissova, Shinkov, Vlahov, Dakovska, Todorov et al., Vitamin D status in Bulgaria--winter data, Arch Osteoporos, doi:10.1007/s11657-013-0133-4
Caccialanza, Laviano, Lobascio, Montagna, Bruno et al., Early nutritional supplementation in non-critically ill patients hospitalized for the 2019 novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19): Rationale and feasibility of a shared pragmatic protocol, Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.nut.2020.110835
Calder, Carr, Gombart, Eggersdorfer, Optimal Nutritional Status for a Well-Functioning Immune System Is an Important Factor to Protect against Viral Infections, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12041181
Carlberg, Haq, The concept of the personal vitamin D response index, J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2016.12.011
Cashman, Dowling, Škrabáková, Gonzalez-Gross, Valtueña et al., Vitamin D deficiency in Europe: pandemic?, Am J Clin Nutr, doi:10.3945/ajcn.115.120873
Castillo, Costa, Barrios, Díaz, Miranda et al., Effect of calcifediol treatment and best available therapy vs best available therapy on intensive care unit admission and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: A pilot randomized clinical study, J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105751
Cesareo, Iozzino, 'onofrio, Terrinoni, Maddaloni et al., Effectiveness and safety of calcium and vitamin D treatment for postmenopausal osteoporosis, Minerva Endocrinol
D'avolio, Avataneo, Manca, Cusato, Nicolò et al., 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Concentrations Are Lower in Patients with Positive PCR for SARS-CoV-2, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12051359
Dancer, Parekh, Lax, Souza, Zheng et al., Vitamin D deficiency contributes directly to the acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), Thorax, doi:10.1136/thoraxjnl-2014-206680
Daneshkhah, Agrawal, Eshein, Subramanian, Roy et al., The Role of Vitamin D in Suppressing Cytokine Storm and Associated Mortality in COVID-19 Patients, MedRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.04.08.20058578
Darbeheshti, Rezaei, Genetic predisposition models to COVID-19 infection, Med Hypotheses, doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2020.109818
De Groot, Verheijden, De Henauw, Schroll, Van Staveren et al., Lifestyle, nutritional status, health, and mortality in elderly people across Europe: a review of the longitudinal results of the SENECA study, J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci, doi:10.1093/gerona/59.12.1277
Devaux, Rolain, Raoult, ACE2 receptor polymorphism: Susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2, hypertension, multi-organ failure, and COVID-19 disease outcome, J Microbiol Immunol Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jmii.2020.04.015
Egro, Why is type 1 diabetes increasing?, J Mol Endocrinol, doi:10.1530/JME-13-0067
Ekwaru, Zwicker, Holick, Giovannucci, Veugelers, The importance of body weight for the dose response relationship of oral vitamin D supplementation and serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D in healthy volunteers, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0111265
Elmadfa, Meyer, Wottawa, Wagner, Hasenegger, Vitamin D intake and status in Austria and its effects on some health indicators, Austin J Nutr Metab
Garland, Kim, Mohr, Gorham, Grant et al., Meta-analysis of all-cause mortality according to serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D, Am J Public Health, doi:10.2105/AJPH.2014.302034
Ginde, Brower, Caterino, Finck, Banner-Goodspeed et al., and Blood Institute PETAL Clinical Trials Network. Early High-Dose Vitamin D 3 for Critically Ill, Vitamin D-Deficient Patients, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1911124
Gomez, Nomellini, Faunce, Kovacs, Innate immunity and aging, Exp Gerontol, doi:10.1016/j.exger.2008.05.016
Grant, Giovannucci, The possible roles of solar ultraviolet-B radiation and vitamin D in reducing case-fatality rates from the 1918-1919 influenza pandemic in the United States, Dermatoendocrinol, doi:10.4161/derm.1.4.9063
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Baggerly, French et al., Evidence that Vitamin D Supplementation Could Reduce Risk of Influenza and COVID-19 Infections and Deaths, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12040988
Heaney, Garland, Baggerly, French, Gorham et al., A statistical error in the estimation of the recommended dietary allowance for vitamin D, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu7031688
Hilger, Friedel, Herr, Rausch, Roos et al., A systematic review of vitamin D status in populations worldwide, Br J Nutr, doi:10.1017/S0007114513001840
Ilie, Stefanescu, Smith, The role of vitamin D in the prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 infection and mortality, Aging Clin Exp Res, doi:10.1007/s40520-020-01570-8
Kara, Ekiz, Ricci, Kara, Chang et al., Scientific Strabismus' or two related pandemics: coronavirus disease and vitamin D deficiency, Br J Nutr, doi:10.1017/S0007114520001749
Koivisto, Hanel, Carlberg, Key Vitamin D Target Genes with Functions in the Immune System, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12041140
Lips, Cashman, Lamberg-Allardt, Bischoff-Ferrari, Obermayer-Pietsch et al., Current vitamin D status in European and Middle East countries and strategies to prevent vitamin D deficiency: a position statement of the European Calcified Tissue Society, Eur J Endocrinol, doi:10.1530/EJE-18-0736
Madden, Feldman, Chun, Smith, Sullivan et al., Critically Ill Children Have Low Vitamin D-Binding Protein, Influencing Bioavailability of Vitamin D, Ann Am Thorac Soc, doi:10.1513/AnnalsATS.201503-160OC
Maghbooli, Sahraian, Ebrahimi, Pazoki, Kafan et al., Vitamin D sufficiency, a serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D at least 30 ng/mL reduced risk for adverse clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19 infection, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0239799
Manios, Moschonis, Lambrinou, Tsoutsoulopoulou, Binou et al., A systematic review of vitamin D status in southern European countries, Eur J Nutr, doi:10.1007/s00394-017-1564-2
Manson, Brannon, Rosen, Taylor, Vitamin D Deficiency -Is There Really a Pandemic?, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMp1608005
Manson, Cook, Lee, Bassuk, Mora et al., Vitamin D Supplements and Prevention of Cancer and Cardiovascular Disease, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1809944
Martens, Gysemans, Verstuyf, Mathieu, Vitamin D's Effect on Immune Function, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12051248
Martineau, Jolliffe, Hooper, Greenberg, Aloia et al., Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.i6583
Mccartney, Byrne, Optimisation of Vitamin D Status for Enhanced Immuno-protection Against Covid-19, Ir Med J
Mead, Benefits of sunlight: a bright spot for human health, Environ Health Perspect, doi:10.1289/ehp.116-a160
Meehan, Penckofer, The Role of Vitamin D in the Aging Adult, J Aging Gerontol, doi:10.12974/2309-6128.2014.02.02.1
Meltzer, Best, Zhang, Vokes, Arora et al., Association of Vitamin D Status and Other Clinical Characteristics With COVID-19 Test Results, JAMA Netw Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.19722
Merzon, Tworowski, Gorohovski, Vinker, Cohen et al., Low plasma 25(OH) vitamin D level is associated with increased risk of COVID-19 infection: an Israeli population-based study, FEBS J, doi:10.1111/febs.15495
Munns, Shaw, Kiely, Specker, Thacher et al., Global Consensus Recommendations on Prevention and Management of Nutritional Rickets, J Clin Endocrinol Metab, doi:10.1210/jc.2015-2175
Napoli, Strollo, Sprini, Maddaloni, Rini, Serum 25-OH Vitamin D in relation to Bone Mineral Density and Bone Turnover, Int J Endocrinol, doi:10.1155/2014/487463
Nowson, Mcgrath, Ebeling, Haikerwal, Daly et al., None
Pairo-Castineira, Clohisey, Klaric, Bretherick, Rawlik et al., 's, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-03065-y
Papadimitriou, The Big Vitamin D Mistake, J Prev Med Public Health, doi:10.3961/jpmph.16.111
Plos One Editors, Expression of Concern: Vitamin D sufficiency, a serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D at least 30 ng/mL reduced risk for adverse clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19 infection, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0240965
Rhodes, Subramanian, Laird, Kenny, Editorial: low population mortality from COVID-19 in countries south of latitude 35 degrees North supports vitamin D as a factor determining severity, Aliment Pharmacol Ther, doi:10.1111/apt.15777
Rondanelli, Miccono, Lamburghini, Avanzato, Riva et al., Self-Care for Common Colds: The Pivotal Role of Vitamin D, Vitamin C, Zinc, and Echinacea in Three Main Immune Interactive Clusters (Physical Barriers, Innate and Adaptive Immunity) Involved during an Episode of Common Colds-Practical Advice on Dosages and on the Time to Take These Nutrients/Botanicals in order to Prevent or Treat Common Colds, Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, doi:10.1155/2018/5813095
Sempos, Heijboer, Bikle, Bollerslev, Bouillon et al., Vitamin D assays and the definition of hypovitaminosis D: results from the First International Conference on Controversies in Vitamin D, Br J Clin Pharmacol, doi:10.1111/bcp.13652
Shirvani, Kalajian, Song, Holick, Disassociation of Vitamin D's Calcemic Activity and Non-calcemic Genomic Activity and Individual Responsiveness: A Randomized Controlled Double-Blind Clinical Trial, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-019-53864-1
Somasundaram, Ranathunga, Ratnasamy, Wijewickrama, Dissanayake et al., The Impact of SARS-Cov-2 Virus Infection on the Endocrine System, J Endocr Soc, doi:10.1210/jendso/bvaa082
Telcian, Zdrenghea, Edwards, Laza-Stanca, Mallia et al., Vitamin D increases the antiviral activity of bronchial epithelial cells in vitro, Antiviral Res, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2016.11.004
Tramontana, Napoli, El-Hajj Fuleihan, Strollo, The D-side of COVID-19: musculoskeletal benefits of vitamin D and beyond, Endocrine, doi:10.1007/s12020-020-02407-0
Van Der Wielen, Löwik, Van Den Berg, De Groot, Haller et al., Serum vitamin D concentrations among elderly people in Europe, Lancet, doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(95)91266-5
Veugelers, Ekwaru, A statistical error in the estimation of the recommended dietary allowance for vitamin D, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu6104472
Vidovic, Faid, Pantovic, Nikolic, Debeljak-Martacic et al., Vitamin D and cardio-metabolic biomarkers: small-scale comparative study between Libyan migrants and resident women in Serbia, Libyan J Med, doi:10.1080/19932820.2019.1622364
Vieth, Holick, The IOM-Endocrine Society Controversy on Recommended Vitamin D Targets, doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-809965-0.00059-8
Vieth, Vitamin D toxicity, policy, and science, J Bone Miner Res, doi:10.1359/jbmr.07s221
Vojdeman, Madsen, Frederiksen, Durup, Olsen et al., Vitamin D levels and cancer incidence in 217,244 individuals from primary health care in Denmark, Int J Cancer, doi:10.1002/ijc.32105
Wacker, Holick, Vitamin D -effects on skeletal and extraskeletal health and the need for supplementation, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu5010111
Wang, Hu, Hu, Zhu, Liu et al., Clinical Characteristics of 138 Hospitalized Patients With 2019 Novel Coronavirus-Infected Pneumonia in Wuhan, China, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.1585
Weaver, Alexander, Boushey, Dawson-Hughes, Lappe et al., Calcium plus vitamin D supplementation and risk of fractures: an updated meta-analysis from the National Osteoporosis Foundation, Osteoporos Int, doi:10.1007/s00198-015-3386-5
Zhang, Fang, Tang, Jia, Feng et al., Association between vitamin D supplementation and mortality: systematic review and meta-analysis, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.l4673
Zhou, Dong, Kim, Choi, Sun et al., Vitamin D Receptor Activation in Liver Macrophages Protects Against Hepatic Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Mice, Hepatology, doi:10.1002/hep.30887
