Effect of Subcutaneous Casirivimab and Imdevimab Antibody Combination vs Placebo on Development of Symptomatic COVID-19 in Early Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Randomized Clinical Trial
et al., JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2021.24939768, Jan 2022
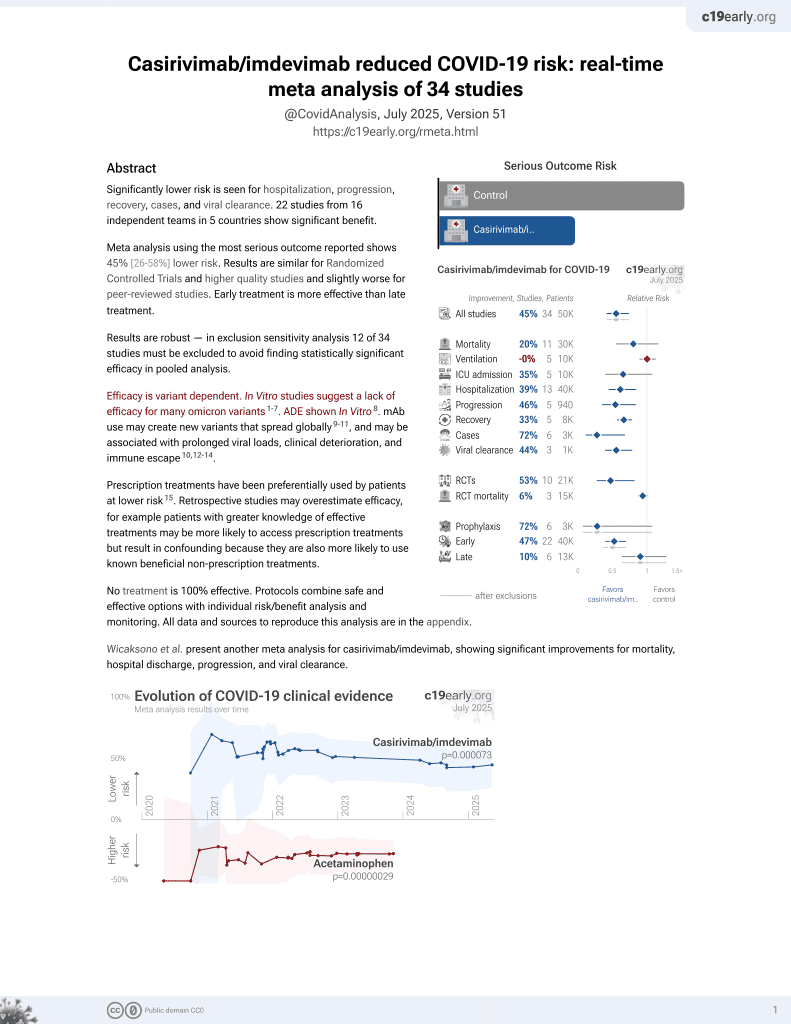
19th treatment shown to reduce risk in
March 2021, now with p = 0.000095 from 34 studies, recognized in 52 countries.
Efficacy is variant dependent.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
RCT 204 asymptomatic COVID+ patients, 100 treated with subcutaneous casirivimab/imdevimab, showing lower development of symptoms, lower hospitalization, and faster viral clearance with treatment. Study conducted prior to widespread circulation of delta and omicron in the study locations.
Efficacy is variant dependent. In Vitro research suggests a lack of efficacy for many omicron variants1-7.
|
risk of hospitalization, 85.5% lower, RR 0.15, p = 0.25, treatment 0 of 100 (0.0%), control 3 of 104 (2.9%), NNT 35, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
risk of hospitalization/ER, 92.2% lower, RR 0.08, p = 0.03, treatment 0 of 100 (0.0%), control 6 of 104 (5.8%), NNT 17, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
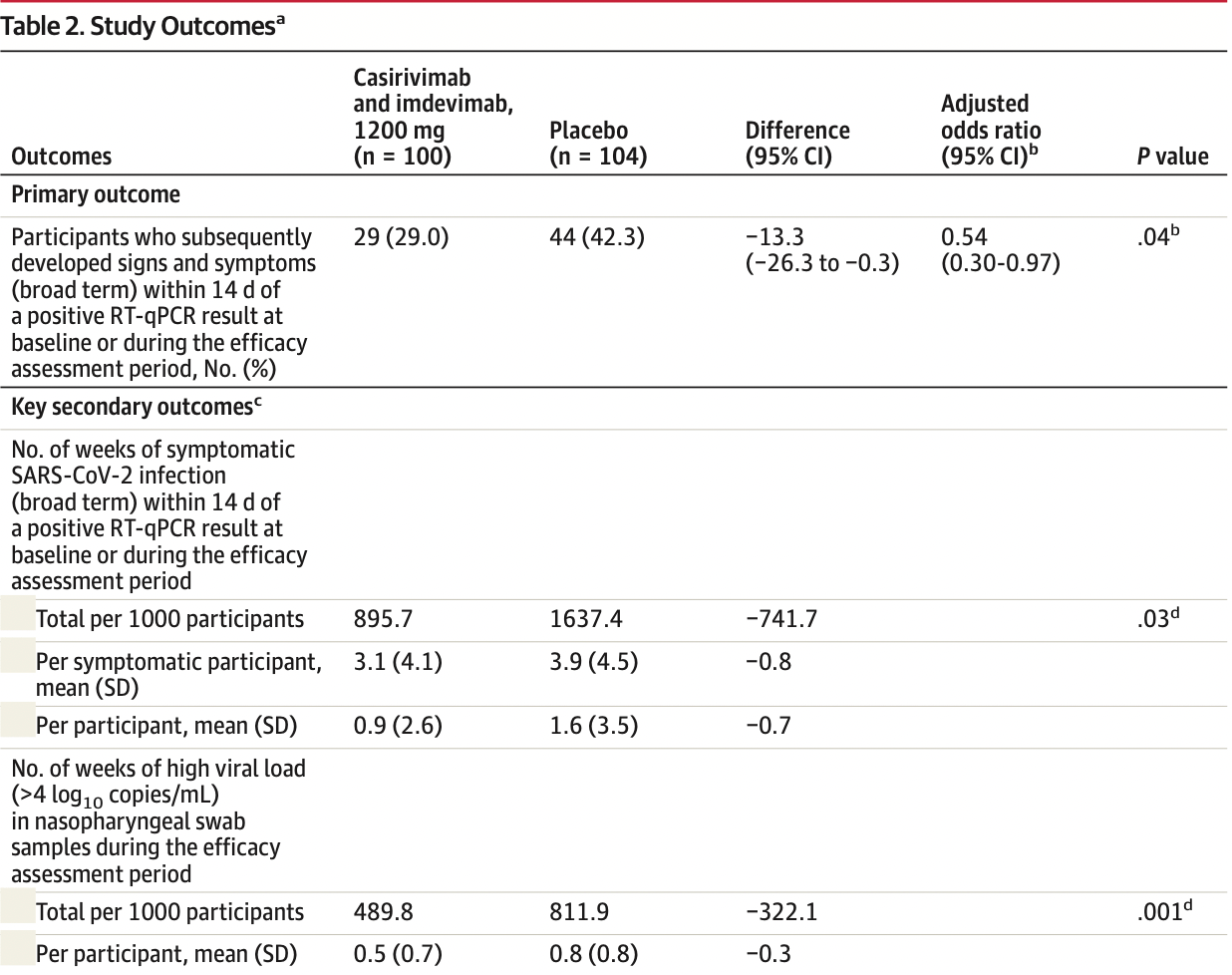
risk of symptomatic case, 33.0% lower, RR 0.67, p = 0.04, treatment 29 of 100 (29.0%), control 44 of 104 (42.3%), NNT 7.5, odds ratio converted to relative risk, day 14, primary outcome.
|
|
relative weeks with high viral load, 39.7% better, RR 0.60, p = 0.001, treatment 100, control 104.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Liu et al., Striking Antibody Evasion Manifested by the Omicron Variant of SARS-CoV-2, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.14.472719.
2.
Sheward et al., Variable loss of antibody potency against SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 (Omicron), bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.19.473354.
3.
VanBlargan et al., An infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 Omicron virus escapes neutralization by several therapeutic monoclonal antibodies, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.15.472828.
4.
Tatham et al., Lack of Ronapreve (REGN-CoV; casirivimab and imdevimab) virological efficacy against the SARS-CoV 2 Omicron variant (B.1.1.529) in K18-hACE2 mice, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.01.23.477397.
5.
Pochtovyi et al., In Vitro Efficacy of Antivirals and Monoclonal Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Lineages XBB.1.9.1, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5, XBB.1.16, XBB.2.4, BQ.1.1.45, CH.1.1, and CL.1, Vaccines, doi:10.3390/vaccines11101533.
O'Brien et al., 14 Jan 2022, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, multiple countries, peer-reviewed, 38 authors, study period 13 July, 2020 - 28 January, 2021.
Effect of Subcutaneous Casirivimab and Imdevimab Antibody Combination vs Placebo on Development of Symptomatic COVID-19 in Early Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infection
JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2021.24939
CoV-2 treatments may be used to prevent progression from asymptomatic infection to symptomatic disease and to reduce viral carriage. OBJECTIVE To evaluate the effect of combination subcutaneous casirivimab and imdevimab on progression from early asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection to symptomatic COVID-19. DESIGN, SETTING, AND PARTICIPANTS Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial of close household contacts of a SARS-CoV-2-infected index case at 112 sites in the US, Romania, and Moldova enrolled July 13, 2020-January 28, 2021; follow-up ended March 11, 2021. Asymptomatic individuals (aged Ն12 years) were eligible if identified within 96 hours of index case positive test collection. Results from 314 individuals positive on SARS-CoV-2 reverse transcriptase-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) testing are reported. INTERVENTIONS Individuals were randomized 1:1 to receive 1 dose of subcutaneous casirivimab and imdevimab, 1200 mg (600 mg of each; n = 158), or placebo (n = 156).
MAIN OUTCOMES AND MEASURES The primary end point was the proportion of seronegative participants who developed symptomatic COVID-19 during the 28-day efficacy assessment period. The key secondary efficacy end points were the number of weeks of symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection and the number of weeks of high viral load (>4 log 10 copies/mL). RESULTS Among 314 randomized participants (mean age, 41.0 years; 51.6% women), 310 (99.7%) completed the efficacy assessment period; 204 were asymptomatic and seronegative at baseline and included in the primary efficacy analysis. Subcutaneous casirivimab and imdevimab, 1200 mg, significantly prevented progression to symptomatic disease (29/100 [29.0%] vs 44/104 [42.3%] with placebo; odds ratio, 0.54 [95% CI, 0.30-0.97]; P = .04; absolute risk difference, −13.3% [95% CI, −26.3% to −0.3%]). Casirivimab and imdevimab reduced the number of symptomatic weeks per 1000 participants (895.7 weeks vs 1637.4 weeks with placebo; P = .03), an approximately 5.6-day reduction in symptom duration per symptomatic participant. Treatment with casirivimab and imdevimab also reduced the number of high viral load weeks per 1000 participants (489.8 weeks vs 811.9 weeks with placebo; P = .001). The proportion of participants receiving casirivimab and imdevimab who had 1 or more treatment-emergent adverse event was 33.5% vs 48.1% for placebo, including events related (25.8% vs 39.7%) or not related (11.0% vs 16.0%) to COVID-19. CONCLUSIONS AND RELEVANCE Among asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 RT-qPCR-positive individuals living with an infected household contact, treatment with subcutaneous casirivimab and imdevimab antibody combination vs placebo significantly reduced the incidence of symptomatic COVID-19 over 28 days.
Conflict of Interest Disclosures: Drs O'Brien, Isa, Turner, Hamilton, and Herman are Regeneron employees/stockholders and have a patent pending, which has been licensed and is receiving royalties, with Regeneron. Drs Forleo-Neto, Sarkar, Hou, Chan, Musser, Davis, Ramesh, Mahmood, Kim, DiCioccio, Lipsich, Braunstein, and Weinreich Role of the Funder/Sponsor: Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc in collaboration with the CoVPN and the NIAID were involved in the design and conduct of the study. Regeneron and CoVPN were involved in the collection and management of data. Regeneron analyzed the data. Regeneron, the NIAID, and the CoVPN were involved in interpretation of the data; were responsible for preparation, review, and approval of the manuscript; and were involved in the decision to submit the manuscript for publication. Regeneron did not have the right to veto publication. The trial sites were funded by Regeneron or were part of the CoVPN, funded by the NIAID.
Group Information: The members of the COVID-19 Phase 3 Prevention Trial Team are listed in Supplement 3.
Disclaimer: The content of this article is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the NIH. Data Sharing Statement: See Supplement 4.
Additional Contributions: We thank the study participants and their families; the investigational site members involved in this trial; the COVID-19 Phase 3 Prevention Trial Team; the members of the data and safety monitoring..
References
Baum, Ajithdoss, Copin, REGN-COV2 antibodies prevent and treat SARS-CoV-2 infection in rhesus macaques and hamsters, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abe2402
Baum, Fulton, Wloga, Antibody cocktail to SARS-CoV-2 spike protein prevents rapid mutational escape seen with individual antibodies, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abd0831
Boutron, Chaimani, Devane, Interventions for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: a living mapping of research and living network meta-analysis, Cochrane Database Syst Rev, doi:10.1002/14651858.CD013769
Boyarsky, Werbel, Avery, Antibody response to 2-dose SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine series in solid organ transplant recipients, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2021.7489?utm_campaign=articlePDF%26utm_medium=articlePDFlink%26utm_source=articlePDF%26utm_content=jama.2021.24939
Buitrago-Garcia, Egli-Gany, Counotte, Occurrence and transmission potential of asymptomatic and presymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infections: a living systematic review and meta-analysis, PLoS Med, doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1003346
Garcia-Beltran, Lam, Denis, Multiple SARS-CoV-2 variants escape neutralization by vaccine-induced humoral immunity, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2021.03.013
Gisaid, hCov19 Variants
Hansen, Baum, Pascal, The monoclonal antibody combination REGEN-COV protects against SARS-CoV-2 mutational escape in preclinical and human studies, Science, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2021.06.002
Higdon, Wahl, Jones, A systematic review of COVID-19 vaccine efficacy and effectiveness against SARS-CoV-2 infection and disease. medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.09.17.21263549
Isa, Hou, Chan, Musser, Bar et al., Statistical analysis: O
Kreuzberger, Hirsch, Chai, SARS-CoV-2-neutralising monoclonal antibodies for treatment of COVID-19, Cochrane Database Syst Rev, doi:10.1002/14651858.CD013825.pub2
Magesh, John, Li, Disparities in COVID-19 outcomes by race, ethnicity, and socioeconomic status: a systematic-review and meta-analysis, JAMA Netw Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.34147?utm_campaign=articlePDF%26utm_medium=articlePDFlink%26utm_source=articlePDF%26utm_content=jama.2021.24939
O'brien, Forleo-Neto, Musser, Covid-19 Phase 3 Prevention Trial Team. Subcutaneous REGEN-COV antibody combination to prevent Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2109682
Portal-Celhay, Forleo-Neto, Eagan, Dose-ranging virology study of the combination COVID-19 antibodies casirivimab and imdevimab in the outpatient setting-poster 04769
Weinreich, Sivapalasingam, Norton, Trial Investigators. REGEN-COV antibody combination and outcomes in outpatients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2108163
Weinreich, Sivapalasingam, Norton, Trial Investigators. REGN-COV2, a neutralizing antibody cocktail