Efficacy comparison of 3CL protease inhibitors ensitrelvir and nirmatrelvir against SARS-CoV-2 in vitro and in vivo
et al., Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, doi:10.1093/jac/dkad027, Feb 2023
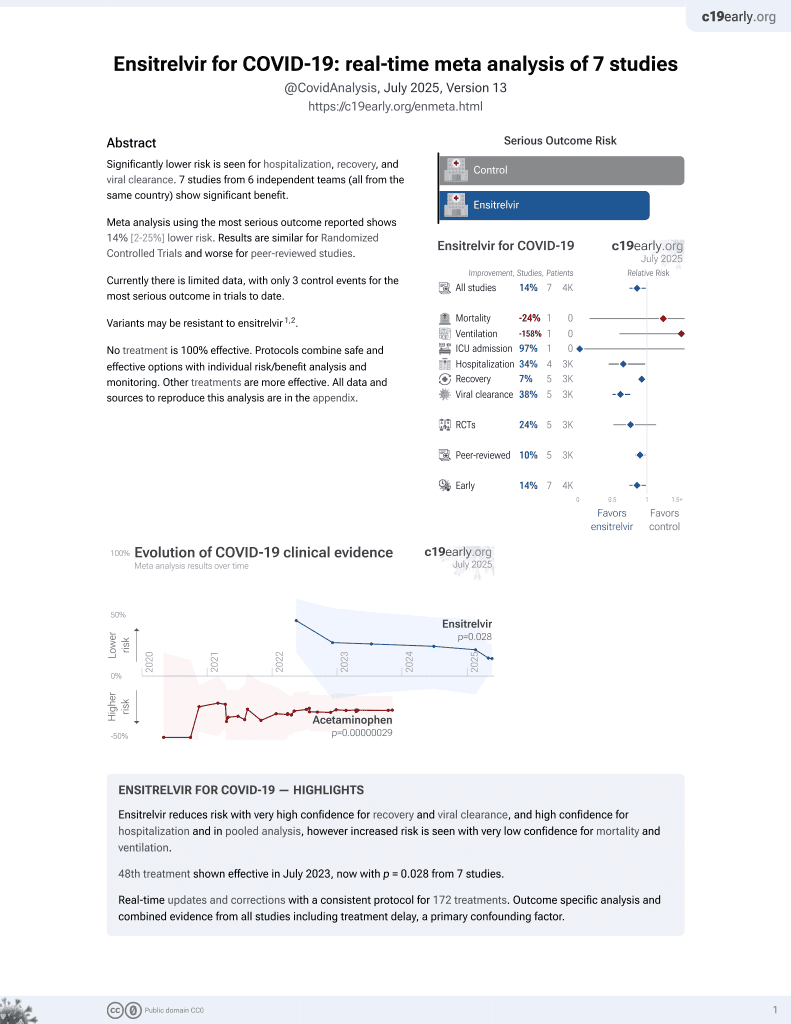
50th treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2023, now with p = 0.015 from 8 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
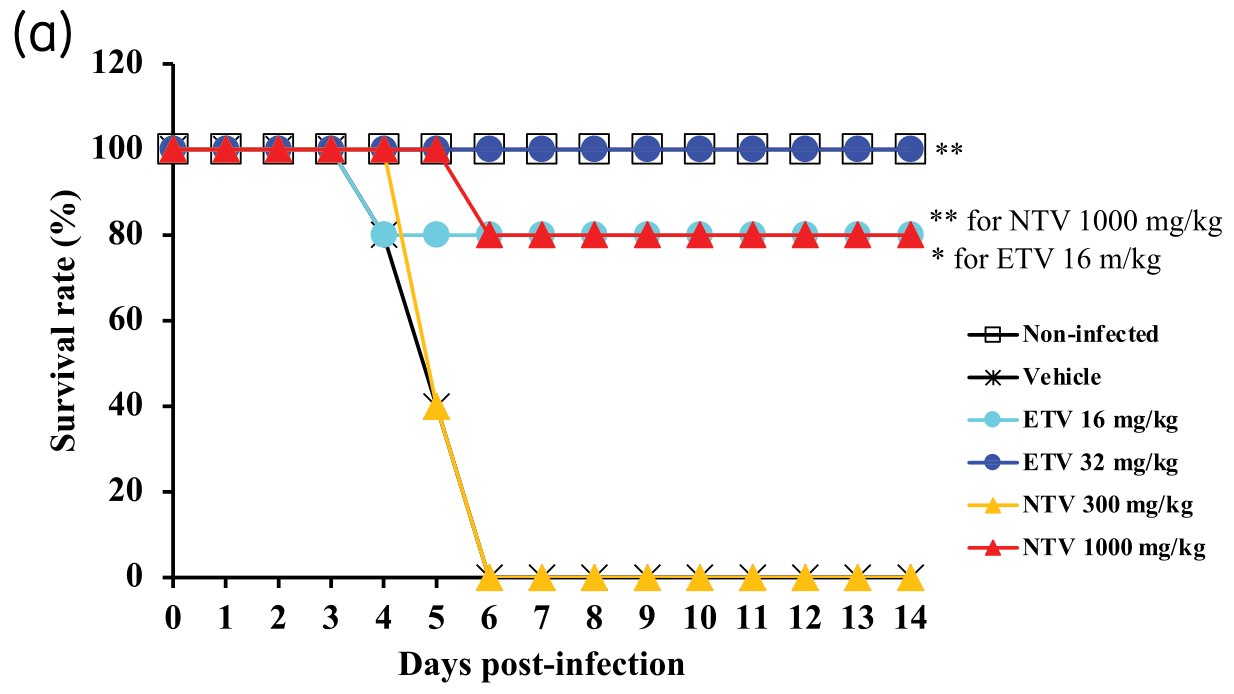
In vitro and animal study comparing nirmatrelvir and ensitrelvir, showing similar efficacy in vitro, and equal or better efficacy of ensitrelvir in vivo (with similar unbound-drug plasma concentrations).
5 preclinical studies support the efficacy of ensitrelvir for COVID-19:
Study covers paxlovid and ensitrelvir.
1.
Nair et al., Persistence of an infectious form of SARS-CoV-2 post protease inhibitor treatment of permissive cells in vitro, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiae385.
2.
Moghadasi et al., Transmissible SARS-CoV-2 variants with resistance to clinical protease inhibitors, Science Advances, doi:10.1126/sciadv.ade8778.
a.
VeroE6/TMPRSS2 is a Vero E6 cell line engineered to express the human serine protease TMPRSS2, enabling SARS-CoV-2 S protein priming and entry.
b.
HEK293T/ACE2-TMPRSS2 is a human embryonic kidney cell line engineered to express human ACE2 and TMPRSS2, making it highly susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 infection.
c.
MucilAir cells are primary human nasal epithelial cells that mimic the structure and physiology of the human airway epithelium.
d.
A mouse model commonly used in infectious disease and cancer research due to higher immune response and susceptibility to infection.
e.
A rodent model used in SARS-CoV-2 research that replicates key aspects of human infection including efficient replication in the upper and lower respiratory tract.
f.
The original SARS-CoV-2 strain that emerged in Wuhan, China in late 2019. Also referred to as wild-type.
g.
A variant of concern first identified in India in late 2020, delta (B.1.617.2) transmitted more efficiently than previous variants. It contains spike mutations including L452R which increases binding to the ACE2 receptor.
h.
A highly transmissible variant of concern first detected in South Africa in late 2021. Omicron possesses many spike mutations which confer partial immune evasion, including deletions near the furin cleavage site.
Kuroda et al., 10 Feb 2023, Japan, peer-reviewed, 19 authors.
Contact: takao.shishido@shionogi.co.jp.
Efficacy comparison of 3CL protease inhibitors ensitrelvir and nirmatrelvir against SARS-CoV-2 in vitro and in vivo
Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, doi:10.1093/jac/dkad027
Objectives: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has become established in the human population, making the need to develop safe and effective treatments critical. We have developed the small-molecule antiviral ensitrelvir, which targets the 3C-like (3CL) protease of SARS-CoV-2. This study evaluated the in vitro and in vivo efficacy of ensitrelvir compared with that of another SARS-CoV-2 3CL PI, nirmatrelvir. Methods: Cultured cells, BALB/cAJcl mice and Syrian hamsters were infected with various SARS-CoV-2 strains, including the ancestral strain WK-521, mouse-adapted SARS-CoV-2 (MA-P10) strain, Delta strain and Omicron strain. Ensitrelvir efficacy was compared with that of nirmatrelvir. Effective concentrations were determined in vitro based on virus-induced cytopathic effects, viral titres and RNA levels. Lung viral titres, nasal turbinate titres, body-weight changes, and animal survival were also monitored. Results: Ensitrelvir and nirmatrelvir showed comparable antiviral activity in multiple cell lines. Both ensitrelvir and nirmatrelvir reduced virus levels in the lungs of mice and the nasal turbinates and lungs of hamsters. However, ensitrelvir demonstrated comparable or better in vivo efficacy than that of nirmatrelvir when present at similar or slightly lower unbound-drug plasma concentrations. Conclusions: Direct in vitro and in vivo efficacy comparisons of 3CL PIs revealed that ensitrelvir demonstrated comparable in vitro efficacy to that of nirmatrelvir in cell culture and exhibited equal to or greater in vivo efficacy in terms of unbound-drug plasma concentration in both animal models evaluated. The results suggest that ensitrelvir may become an important resource for treating individuals infected with SARS-CoV-2.
Supplementary data Supplementary Methods and Figure S1 are available as Supplementary data at JAC Online.
References
Abdelnabi, Foo, Jochmans, The oral protease inhibitor (PF-07321332) protects Syrian hamsters against infection with SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-022-28354-0
Boras, Jones, Bj, Preclinical characterization of an intravenous coronavirus 3CL protease inhibitor for the potential treatment of COVID19, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-021-26239-2
Gu, Chen, Yang, Adaptation of SARS-CoV-2 in BALB/c mice for testing vaccine efficacy, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abc4730
Hammond, Leister-Tebbe, Gardner, Oral nirmatrelvir for highrisk, nonhospitalized adults with Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2118542
Harrison, Lin, Wang, Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 transmission and pathogenesis, Trends Immunol, doi:10.1016/j.it.2020.10.004
Haynes, Corey, Fernandes, Prospects for a safe COVID-19 vaccine, Sci Transl Med, doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.abe0948
Imai, Iwatsuki-Horimoto, Hatta, Syrian hamsters as a small animal model for SARS-CoV-2 infection and countermeasure development, Proc Nat Acad Sci U S A, doi:10.1073/pnas.2009799117
Imran, Arora, Asdaq, Discovery, development, and patent trends on molnupiravir: a prospective oral treatment for COVID-19, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules26195795
Lamb, Nirmatrelvir plus ritonavir: first approval, Drugs, doi:10.1007/s40265-022-01692-5
Matsuyama, Nao, Shirato, Enhanced isolation of SARS-CoV-2 by TMPRSS2-expressing cells, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, doi:10.1073/pnas.2002589117
Mukae, Yotsuyanagi, Ohmagari, A randomized phase 2/3 study of ensitrelvir, a novel oral SARS-CoV-2 3C-like protease inhibitor, in Japanese patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19 or asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection: results of the phase 2a part, Antimicrob Agents Chemother, doi:10.1128/aac.00697-22
Mukae, Yotsuyanagi, Ohmagari, Efficacy and safety of ensitrelvir in patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19: the phase 2b part of a randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 2/3 study, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciac933
Owen, Allerton, Anderson, An oral SARS-CoV-2 M pro inhibitor clinical candidate for the treatment of COVID-19, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abl4784
Sasaki, Tabata, Kishimoto, Oral administration of S-217622, a SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitor, decreases viral load and accelerates recovery from clinical aspects of COVID-19, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.02.14.480338
Sendi, Razonable, Nelson, First-generation oral antivirals against SARS-CoV-2, Clin Microbiol Infect, doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2022.04.015
Sia, Yan, Chin, Pathogenesis and transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in golden hamsters, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2342-5
Smith, Di, Kerns, The effect of plasma protein binding on in vivo efficacy: misconceptions in drug discovery, Nat Rev Drug Discov, doi:10.1038/nrd3287
Sun, Gu, Cao, Characterization and structural basis of a lethal mouse-adapted SARS-CoV-2, Nat Comm, doi:10.1038/s41467-021-25903-x
Uemura, Nobori, Sato, 2-Thiouridine is a broad-spectrum antiviral nucleoside analogue against positive-strand RNA viruses, BioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.12.14.520006
Ullrich, Nitsche, The SARS-CoV-2 main protease as drug target, Bioorg Med Chem Lett, doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2020.127377
Unoh, Uehara, Nakahara, Discovery of S-217622, a noncovalent oral SARS-CoV-2 3CL protease inhibitor clinical candidate for treating COVID-19, J Med Chem, doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c00117
Uraki, Kiso, Iida, Characterization and antiviral susceptibility of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.2, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04856-1
Vangeel, Chiu, Jonghe, Remdesivir, molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir remain active against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron and other variants of concern, Antiviral Res, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2022.105252
Zhang, Xiao, Cai, Structure of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, Curr Opin Virol, doi:10.1016/j.coviro.2021.08.010
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jac/dkad027",
"ISSN": [
"0305-7453",
"1460-2091"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkad027",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Objectives</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has become established in the human population, making the need to develop safe and effective treatments critical. We have developed the small-molecule antiviral ensitrelvir, which targets the 3C-like (3CL) protease of SARS-CoV-2. This study evaluated the in vitro and in vivo efficacy of ensitrelvir compared with that of another SARS-CoV-2 3CL PI, nirmatrelvir.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Cultured cells, BALB/cAJcl mice and Syrian hamsters were infected with various SARS-CoV-2 strains, including the ancestral strain WK-521, mouse-adapted SARS-CoV-2 (MA-P10) strain, Delta strain and Omicron strain. Ensitrelvir efficacy was compared with that of nirmatrelvir. Effective concentrations were determined in vitro based on virus-induced cytopathic effects, viral titres and RNA levels. Lung viral titres, nasal turbinate titres, body-weight changes, and animal survival were also monitored.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Ensitrelvir and nirmatrelvir showed comparable antiviral activity in multiple cell lines. Both ensitrelvir and nirmatrelvir reduced virus levels in the lungs of mice and the nasal turbinates and lungs of hamsters. However, ensitrelvir demonstrated comparable or better in vivo efficacy than that of nirmatrelvir when present at similar or slightly lower unbound-drug plasma concentrations.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Direct in vitro and in vivo efficacy comparisons of 3CL PIs revealed that ensitrelvir demonstrated comparable in vitro efficacy to that of nirmatrelvir in cell culture and exhibited equal to or greater in vivo efficacy in terms of unbound-drug plasma concentration in both animal models evaluated. The results suggest that ensitrelvir may become an important resource for treating individuals infected with SARS-CoV-2.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pharmaceutical Research Division, Shionogi & Co., Ltd. , 1-1, Futaba-cho 3-chome, Toyonaka, Osaka 561-0825 , Japan"
}
],
"family": "Kuroda",
"given": "Takayuki",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5735-0843",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pharmaceutical Research Division, Shionogi & Co., Ltd. , 1-1, Futaba-cho 3-chome, Toyonaka, Osaka 561-0825 , Japan"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Nobori",
"given": "Haruaki",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pharmaceutical Research Division, Shionogi & Co., Ltd. , 1-1, Futaba-cho 3-chome, Toyonaka, Osaka 561-0825 , Japan"
}
],
"family": "Fukao",
"given": "Keita",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Research Area for Drug Candidate Generation II, Shionogi TechnoAdvance Research Co., Ltd. , 1-1, Futaba-cho 3-chome, Toyonaka, Osaka 561-0825 , Japan"
}
],
"family": "Baba",
"given": "Kaoru",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Research Area for Drug Candidate Generation II, Shionogi TechnoAdvance Research Co., Ltd. , 1-1, Futaba-cho 3-chome, Toyonaka, Osaka 561-0825 , Japan"
}
],
"family": "Matsumoto",
"given": "Kazumi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pharmaceutical Research Division, Shionogi & Co., Ltd. , 1-1, Futaba-cho 3-chome, Toyonaka, Osaka 561-0825 , Japan"
}
],
"family": "Yoshida",
"given": "Shinpei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pharmaceutical Research Division, Shionogi & Co., Ltd. , 1-1, Futaba-cho 3-chome, Toyonaka, Osaka 561-0825 , Japan"
}
],
"family": "Tanaka",
"given": "Yukari",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pharmaceutical Research Division, Shionogi & Co., Ltd. , 1-1, Futaba-cho 3-chome, Toyonaka, Osaka 561-0825 , Japan"
}
],
"family": "Watari",
"given": "Ryosuke",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pharmaceutical Research Division, Shionogi & Co., Ltd. , 1-1, Futaba-cho 3-chome, Toyonaka, Osaka 561-0825 , Japan"
}
],
"family": "Oka",
"given": "Ryoko",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pharmaceutical Research Division, Shionogi & Co., Ltd. , 1-1, Futaba-cho 3-chome, Toyonaka, Osaka 561-0825 , Japan"
}
],
"family": "Kasai",
"given": "Yasuyuki",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Research Area for Drug Candidate Generation II, Shionogi TechnoAdvance Research Co., Ltd. , 1-1, Futaba-cho 3-chome, Toyonaka, Osaka 561-0825 , Japan"
}
],
"family": "Inoue",
"given": "Kae",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pharmaceutical Research Division, Shionogi & Co., Ltd. , 1-1, Futaba-cho 3-chome, Toyonaka, Osaka 561-0825 , Japan"
}
],
"family": "Kawashima",
"given": "Sho",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pharmaceutical Research Division, Shionogi & Co., Ltd. , 1-1, Futaba-cho 3-chome, Toyonaka, Osaka 561-0825 , Japan"
}
],
"family": "Shimba",
"given": "Alice",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pharmaceutical Research Division, Shionogi & Co., Ltd. , 1-1, Futaba-cho 3-chome, Toyonaka, Osaka 561-0825 , Japan"
}
],
"family": "Hayasaki-Kajiwara",
"given": "Yoko",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pharmaceutical Research Division, Shionogi & Co., Ltd. , 1-1, Futaba-cho 3-chome, Toyonaka, Osaka 561-0825 , Japan"
}
],
"family": "Tanimura",
"given": "Miki",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pharmaceutical Research Division, Shionogi & Co., Ltd. , 1-1, Futaba-cho 3-chome, Toyonaka, Osaka 561-0825 , Japan"
}
],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Qianhui",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6845-4453",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pharmaceutical Research Division, Shionogi & Co., Ltd. , 1-1, Futaba-cho 3-chome, Toyonaka, Osaka 561-0825 , Japan"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Tachibana",
"given": "Yuki",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5041-0110",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pharmaceutical Research Division, Shionogi & Co., Ltd. , 1-1, Futaba-cho 3-chome, Toyonaka, Osaka 561-0825 , Japan"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kato",
"given": "Teruhisa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pharmaceutical Research Division, Shionogi & Co., Ltd. , 1-1, Futaba-cho 3-chome, Toyonaka, Osaka 561-0825 , Japan"
}
],
"family": "Shishido",
"given": "Takao",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-10T06:02:01Z",
"timestamp": 1676008921000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-10T06:02:24Z",
"timestamp": 1676008944000
},
"funder": [
{
"name": "Shionogi & Co., Ltd"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-11T05:29:44Z",
"timestamp": 1676093384879
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
10
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-10T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1675987200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/jac/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/jac/dkad027/49151594/dkad027.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/jac/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/jac/dkad027/49151594/dkad027.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "286",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1093",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
10
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
10
]
]
},
"publisher": "Oxford University Press (OUP)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.it.2020.10.004",
"article-title": "Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 transmission and pathogenesis",
"author": "Harrison",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1100",
"journal-title": "Trends Immunol",
"key": "2023021006005803300_dkad027-B1",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.abe0948",
"article-title": "Prospects for a safe COVID-19 vaccine",
"author": "Haynes",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Sci Transl Med",
"key": "2023021006005803300_dkad027-B2",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.coviro.2021.08.010",
"article-title": "Structure of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "173",
"journal-title": "Curr Opin Virol",
"key": "2023021006005803300_dkad027-B3",
"volume": "50",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2022.105252",
"article-title": "Remdesivir, molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir remain active against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron and other variants of concern",
"author": "Vangeel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Antiviral Res",
"key": "2023021006005803300_dkad027-B4",
"volume": "198",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2118542",
"article-title": "Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with Covid-19",
"author": "Hammond",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1397",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2023021006005803300_dkad027-B5",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules26195795",
"article-title": "Discovery, development, and patent trends on molnupiravir: a prospective oral treatment for COVID-19",
"author": "Imran",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5795",
"journal-title": "Molecules",
"key": "2023021006005803300_dkad027-B6",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40265-022-01692-5",
"article-title": "Nirmatrelvir plus ritonavir: first approval",
"author": "Lamb",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "585",
"journal-title": "Drugs",
"key": "2023021006005803300_dkad027-B7",
"volume": "82",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmi.2022.04.015",
"article-title": "First-generation oral antivirals against SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Sendi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1230",
"journal-title": "Clin Microbiol Infect",
"key": "2023021006005803300_dkad027-B8",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bmcl.2020.127377",
"article-title": "The SARS-CoV-2 main protease as drug target",
"author": "Ullrich",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Bioorg Med Chem Lett",
"key": "2023021006005803300_dkad027-B9",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "2-Thiouridine is a broad-spectrum antiviral nucleoside analogue against positive-strand RNA viruses",
"author": "Uemura",
"journal-title": "BioRxiv",
"key": "2023021006005803300_dkad027-B10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/aac.00697-22",
"article-title": "A randomized phase 2/3 study of ensitrelvir, a novel oral SARS-CoV-2 3C-like protease inhibitor, in Japanese patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19 or asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection: results of the phase 2a part",
"author": "Mukae",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob Agents Chemother",
"key": "2023021006005803300_dkad027-B11",
"volume": "66",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciac933",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of ensitrelvir in patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19: the phase 2b part of a randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 2/3 study",
"author": "Mukae",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "2023021006005803300_dkad027-B12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2002589117",
"article-title": "Enhanced isolation of SARS-CoV-2 by TMPRSS2-expressing cells",
"author": "Matsuyama",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "7001",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A",
"key": "2023021006005803300_dkad027-B13",
"volume": "117",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c00117",
"article-title": "Discovery of S-217622, a noncovalent oral SARS-CoV-2 3CL protease inhibitor clinical candidate for treating COVID-19",
"author": "Unoh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6499",
"journal-title": "J Med Chem",
"key": "2023021006005803300_dkad027-B14",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abl4784",
"article-title": "An oral SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor clinical candidate for the treatment of COVID-19",
"author": "Owen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1586",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "2023021006005803300_dkad027-B15",
"volume": "374",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2342-5",
"article-title": "Pathogenesis and transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in golden hamsters",
"author": "Sia",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "834",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "2023021006005803300_dkad027-B16",
"volume": "583",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2009799117",
"article-title": "Syrian hamsters as a small animal model for SARS-CoV-2 infection and countermeasure development",
"author": "Imai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "16587",
"journal-title": "Proc Nat Acad Sci U S A",
"key": "2023021006005803300_dkad027-B17",
"volume": "117",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Oral administration of S-217622, a SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitor, decreases viral load and accelerates recovery from clinical aspects of COVID-19",
"author": "Sasaki",
"journal-title": "bioRxiv",
"key": "2023021006005803300_dkad027-B18",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-04856-1",
"article-title": "Characterization and antiviral susceptibility of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.2",
"author": "Uraki",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "119",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "2023021006005803300_dkad027-B19",
"volume": "607",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-26239-2",
"article-title": "Preclinical characterization of an intravenous coronavirus 3CL protease inhibitor for the potential treatment of COVID19",
"author": "Boras",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6055",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "2023021006005803300_dkad027-B20",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrd3287",
"article-title": "The effect of plasma protein binding on in vivo efficacy: misconceptions in drug discovery",
"author": "Smith",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "929",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Drug Discov",
"key": "2023021006005803300_dkad027-B21",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abc4730",
"article-title": "Adaptation of SARS-CoV-2 in BALB/c mice for testing vaccine efficacy",
"author": "Gu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1603",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "2023021006005803300_dkad027-B22",
"volume": "369",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-25903-x",
"article-title": "Characterization and structural basis of a lethal mouse-adapted SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Sun",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5654",
"journal-title": "Nat Comm",
"key": "2023021006005803300_dkad027-B23",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-022-28354-0",
"article-title": "The oral protease inhibitor (PF-07321332) protects Syrian hamsters against infection with SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern",
"author": "Abdelnabi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "719",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "2023021006005803300_dkad027-B24",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 24,
"references-count": 24,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/jac/advance-article/doi/10.1093/jac/dkad027/7033725"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Pharmacology (medical)",
"Pharmacology",
"Microbiology (medical)"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Efficacy comparison of 3CL protease inhibitors ensitrelvir and nirmatrelvir against SARS-CoV-2 <i>in vitro</i> and <i>in vivo</i>",
"type": "journal-article"
}