Peginterferon lambda for the treatment of hospitalized patients with mild COVID-19: A pilot phase 2 randomized placebo-controlled trial
et al., Frontiers in Medicine, doi:10.3389/fmed.2023.1095828, NCT04343976, Feb 2023
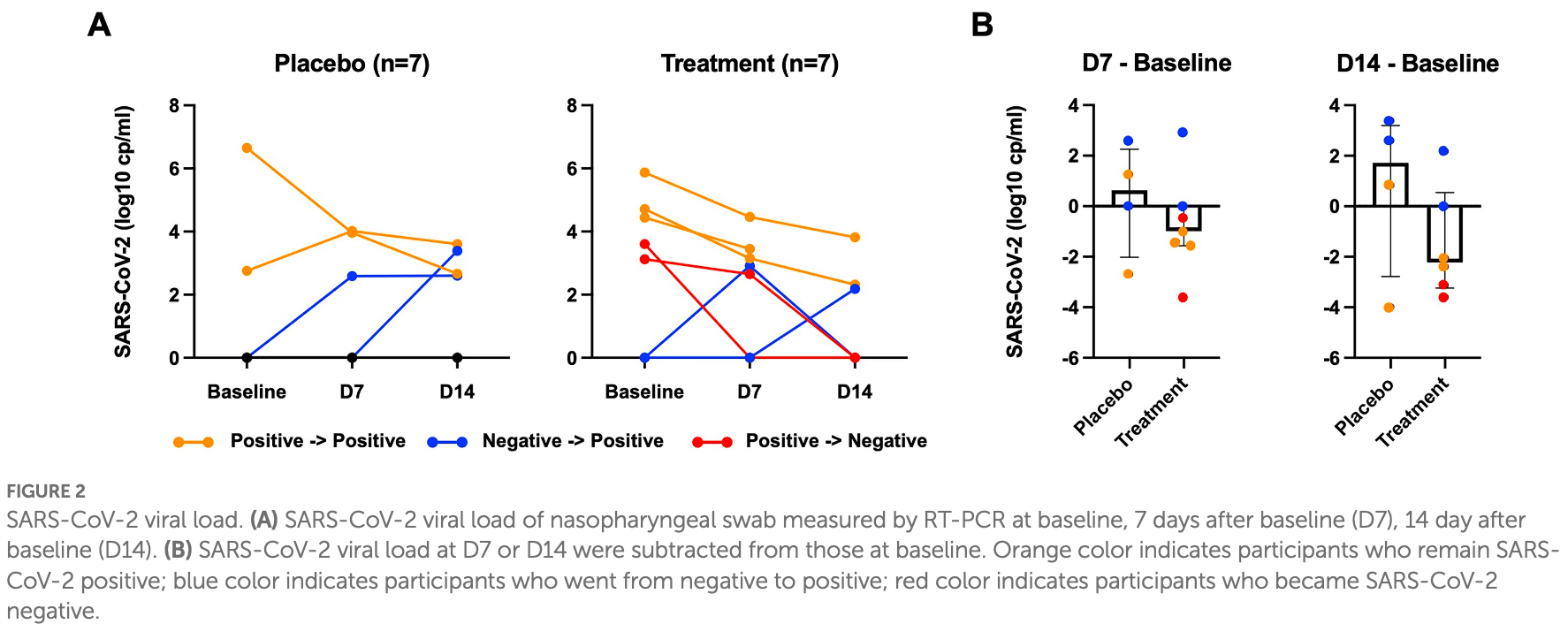
Very small RCT with 14 hospitalized patients in the USA showing no significant differences with peginterferon lambda. Viral load was improved, however 86% of treatment versus 14% of control patients received remdesivir, and the median baseline viral load for treatment patients was 3.6 log10 copies/ml versus 0 for control.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
risk of ICU admission, 200.0% higher, RR 3.00, p = 1.00, treatment 1 of 7 (14.3%), control 0 of 7 (0.0%), continuity correction due to zero event (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
hospitalization time, 25.0% higher, relative time 1.25, p = 0.59, treatment median 5.0 IQR 4.0 n=7, control median 4.0 IQR 5.0 n=7.
|
|
risk of no viral clearance, 12.5% lower, RR 0.88, p = 1.00, treatment 3 of 6 (50.0%), control 4 of 7 (57.1%), NNT 14, day 14.
|
|
risk of no viral clearance, 66.7% higher, RR 1.67, p = 0.59, treatment 5 of 7 (71.4%), control 3 of 7 (42.9%), day 7.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Kim et al., 24 Feb 2023, Single Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, USA, peer-reviewed, median age 54.0, 9 authors, study period 14 July, 2020 - 16 July, 2021, trial NCT04343976 (history).
Contact: chung.raymond@mgh.harvard.edu.
Peginterferon lambda for the treatment of hospitalized patients with mild COVID-19: A pilot phase 2 randomized placebo-controlled trial
Frontiers in Medicine, doi:10.3389/fmed.2023.1095828
Background: This study aimed to investigate the efficacy and safety of subcutaneous injection of peginterferon lambda in patients hospitalized with COVID-19. Methods: In this study (NCT04343976), patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 confirmed by RT-PCR from nasopharyngeal swab were randomly assigned within 48 h to receive peginterferon lambda or placebo in a 1:1 ratio. Participants were subcutaneously injected with a peginterferon lambda or saline placebo at baseline and day 7 and were followed up until day 14. Results: We enrolled 14 participants; 6 participants (85.7%) in the peginterferon lambda group and 1 participant (14.3%) in the placebo group were treated with remdesivir prior to enrollment. Fifty percent of participants were SARS-CoV-2 RNA negative at baseline although they tested SARS-CoV-2 RNA positive within 48 h of randomization. Among participants who were SARS-CoV-2 positive at baseline, 2 out of 5 participants (40%) in the peginterferon lambda group became negative at day 14, while 0 out of 2 participants (0%) in the placebo group achieved negativity for SARS-CoV-2 by day 14 (p > 0.05). The median change in viral load (log copies per ml) was +1.72 (IQR −2.78 to 3.19) in the placebo group and −2.22 (IQR −3.24 to 0.55) in the peginterferon lambda group at day 14 (p = 0.24). Symptomatic changes did not differ between the two groups. Peginterferon lambda was well tolerated with a few treatment-related adverse effects.
Conclusion: Peginterferon lambda appears to accelerate SARS-CoV-2 viral load decline and improve plasma disease progression markers in hospitalized patients with COVID-19.
Results We enrolled 14 participants admitted to the Massachusetts General Hospital and with COVID-19 between July 14, 2020 and July 16, 2021. The median age was 54.0 (IQR 45.50 to 58.50), 11 participants (78.6%) were male, and 9 (64.3%) were Hispanic (Table 1 ; Supplementary Table 1 ). All 14 randomly assigned participants were initially injected with a placebo or peginterferon lambda within a median of 43.1 h (IQR 35.8 to 48.4) after testing SARS-CoV-2 positive. Thirteen participants (92.9%) completed 14 days of follow up with 1 participant in the placebo group lost to follow up after day 7 (Figure 1 ). The median baseline SARS-CoV-2 viral load was 1.38 log copies per ml (IQR 0.00 to 4.23), with 5 participants (71.4%) in the placebo group and 2 participants (28.6%) in the peginterferon lambda group having undetectable viral load on the day of randomization although they were tested SARS-CoV-2 RNA positive within 48 h of randomization. The median sum of symptom scores was 2.00 (IQR 0.00 to 4.00) in the placebo group and 5.50 (IQR 2.75 to 7.50) in the peginterferon lambda group. Six participants (85.7%) in the peginterferon lambda group and
Ethics statement The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by Massachusetts General Hospital. The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions MHK, NJ, AK, and RC contributed to study conception and design. MHK, JE, JG, and EN contributed to..
References
Akinbolade, Coughlan, Fairbairn, Mcconkey, Powell et al., Combination therapies for COVID-19: an overview of the clinical trials landscape, Br J Clin Pharmacol, doi:10.1111/bcp.15089
Barratt-Due, Olsen, Ic, Nezvalova-Henriksen, Kåsine et al., Evaluation of the effects of remdesivir and hydroxychloroquine on viral clearance in COVID-19: a randomized trial, Ann Intern Med, doi:10.7326/M21-0653
Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, Mehta, Zingman et al., Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19-final report, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2007764
Chan, Ahn, Sh, Chang, Peng et al., Peginterferon lambda for the treatment of HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B: a randomized phase 2b study (LIRA-B), J Hepatol, doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2015.12.018
Cochrane Haematology Groupansems, Grundeis, Dahms, Mikolajewska, Thieme, Remdesivir for the treatment of COVID-19, Cochrane Database Syst Rev, doi:10.1002/14651858.CD014962
Feld, Kandel, Biondi, Mj, Kozak et al., Peginterferon lambda for the treatment of outpatients with COVID-19: a phase 2, placebo-controlled randomised trial, Lancet Respir Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30566-X
Forero, Ozarkar, Li, Lee, Ch et al., Differential activation of the transcription factor IRF1 underlies the distinct immune responses elicited by type I and type III Interferons, Immunity, doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2019.07.007
Hruska, Adamczyk, Colston, Hesney, Stonier et al., The pharmacokinetics of peginterferon lambda-1a following single dose administration to subjects with impaired renal function, Br J Clin Pharmacol, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2708-8
Jagannathan, Andrews, Bonilla, Hedlin, Jacobson et al., Peginterferon lambda-1a for treatment of outpatients with uncomplicated COVID-19: a randomized placebo-controlled trial, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-021-22177-1
Lingas, Néant, Gaymard, Belhadi, Peytavin et al., Effect of remdesivir on viral dynamics in COVID-19 hospitalized patients: a modelling analysis the randomized, controlled, open-label DisCoVeRy trial, J Antimicrob Chemother, doi:10.1093/jac/dkac048
Muir, Arora, Everson, Flisiak, George et al., A randomized phase 2b study of peginterferon lambda-1a for the treatment of chronic HCV infection, J Hepatol, doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2014.07.022
Nair, Jacob, Hung, If, Lung et al., Triple combination of interferon beta-1b, lopinavir-ritonavir, and ribavirin in the treatment of patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19: an open-label, randomised, phase 2 trial, J Basic Clin Pharm, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31042-4
Park, Iwasaki, Type I and type III Interferons -induction, signaling, evasion, and application to combat COVID-19, Cell Host Microbe, doi:10.1016/j.chom.2020.05.008
Sims, Krishnan, Chang, Engle, Casalini et al., Characterization of the cytokine storm reflects hyperinflammatory endothelial dysfunction in COVID-19, J Allergy Clin Immunol, doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2020.08.031
Yang, Shen, Li, Yuan, Wei et al., Observational cohort study of IP-10's potential as a biomarker to aid in inflammation regulation within a clinical decision support protocol for patients with severe COVID-19, J Allergy Clin Immunol, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0245296
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2023.1095828",
"ISSN": [
"2296-858X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2023.1095828",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Background</jats:title><jats:p>This study aimed to investigate the efficacy and safety of subcutaneous injection of peginterferon lambda in patients hospitalized with COVID-19.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods</jats:title><jats:p>In this study (NCT04343976), patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 confirmed by RT-PCR from nasopharyngeal swab were randomly assigned within 48 h to receive peginterferon lambda or placebo in a 1:1 ratio. Participants were subcutaneously injected with a peginterferon lambda or saline placebo at baseline and day 7 and were followed up until day 14.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>We enrolled 14 participants; 6 participants (85.7%) in the peginterferon lambda group and 1 participant (14.3%) in the placebo group were treated with remdesivir prior to enrollment. Fifty percent of participants were SARS-CoV-2 RNA negative at baseline although they tested SARS-CoV-2 RNA positive within 48 h of randomization. Among participants who were SARS-CoV-2 positive at baseline, 2 out of 5 participants (40%) in the peginterferon lambda group became negative at day 14, while 0 out of 2 participants (0%) in the placebo group achieved negativity for SARS-CoV-2 by day 14 (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic> &gt; 0.05). The median change in viral load (log copies per ml) was +1.72 (IQR −2.78 to 3.19) in the placebo group and −2.22 (IQR −3.24 to 0.55) in the peginterferon lambda group at day 14 (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.24). Symptomatic changes did not differ between the two groups. Peginterferon lambda was well tolerated with a few treatment-related adverse effects.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title><jats:p>Peginterferon lambda appears to accelerate SARS-CoV-2 viral load decline and improve plasma disease progression markers in hospitalized patients with COVID-19.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.3389/fmed.2023.1095828"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kim",
"given": "Myung-Ho",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Elbaz",
"given": "Josh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jilg",
"given": "Nikolaus",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gustafson",
"given": "Jenna L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Xu",
"given": "Min",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hatipoglu",
"given": "Dilara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nohelty",
"given": "Eric",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kim",
"given": "Arthur Y.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chung",
"given": "Raymond T.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Frontiers in Medicine",
"container-title-short": "Front. Med.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"frontiersin.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-24T05:59:26Z",
"timestamp": 1677218366000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-24T05:59:28Z",
"timestamp": 1677218368000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-25T05:10:22Z",
"timestamp": 1677301822331
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
24
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-24T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1677196800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2023.1095828/full",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1965",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.3389",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
24
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
24
]
]
},
"publisher": "Frontiers Media SA",
"reference": [
{
"key": "ref1",
"year": ""
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chom.2020.05.008",
"article-title": "Type I and type III Interferons - induction, signaling, evasion, and application to combat COVID-19",
"author": "Park",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "870",
"journal-title": "Cell Host Microbe",
"key": "ref2",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.immuni.2019.07.007",
"article-title": "Differential activation of the transcription factor IRF1 underlies the distinct immune responses elicited by type I and type III Interferons",
"author": "Forero",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "451",
"journal-title": "Immunity",
"key": "ref3",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jhep.2014.07.022",
"article-title": "A randomized phase 2b study of peginterferon lambda-1a for the treatment of chronic HCV infection",
"author": "Muir",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1238",
"journal-title": "J Hepatol",
"key": "ref4",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jhep.2015.12.018",
"article-title": "Peginterferon lambda for the treatment of HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B: a randomized phase 2b study (LIRA-B)",
"author": "Chan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1011",
"journal-title": "J Hepatol",
"key": "ref5",
"volume": "64",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30566-X",
"article-title": "Peginterferon lambda for the treatment of outpatients with COVID-19: a phase 2, placebo-controlled randomised trial",
"author": "Feld",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "498",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "ref6",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-22177-1",
"article-title": "Peginterferon lambda-1a for treatment of outpatients with uncomplicated COVID-19: a randomized placebo-controlled trial",
"author": "Jagannathan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1967",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "ref7",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/14651858.CD014962",
"article-title": "Remdesivir for the treatment of COVID-19",
"author": "Ansems",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Cochrane Database Syst Rev",
"key": "ref8",
"volume": "2021",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M21-0653",
"article-title": "Evaluation of the effects of remdesivir and hydroxychloroquine on viral clearance in COVID-19: a randomized trial",
"author": "Barratt-Due",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1261",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "ref9",
"volume": "174",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jac/dkac048",
"article-title": "Effect of remdesivir on viral dynamics in COVID-19 hospitalized patients: a modelling analysis of the randomized, controlled, open-label DisCoVeRy trial",
"author": "Lingas",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1404",
"journal-title": "J Antimicrob Chemother",
"key": "ref10",
"volume": "77",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2007764",
"article-title": "Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19—final report",
"author": "Beigel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1813",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "ref11",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bcp.15089",
"article-title": "Combination therapies for COVID-19: an overview of the clinical trials landscape",
"author": "Akinbolade",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1590",
"journal-title": "Br J Clin Pharmacol",
"key": "ref12",
"volume": "88",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bcp.12634",
"article-title": "The pharmacokinetics of peginterferon lambda-1a following single dose administration to subjects with impaired renal function",
"author": "Hruska",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "515",
"journal-title": "Br J Clin Pharmacol",
"key": "ref13",
"volume": "80",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2708-8",
"article-title": "A mouse-adapted model of SARS-CoV-2 to test COVID-19 countermeasures",
"author": "Dinnon",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "560",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref14",
"volume": "586",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/0976-0105.177703",
"article-title": "A simple practice guide for dose conversion between animals and human",
"author": "Nair",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "27",
"journal-title": "J Basic Clin Pharm",
"key": "ref15",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31042-4",
"article-title": "Triple combination of interferon beta-1b, lopinavir-ritonavir, and ribavirin in the treatment of patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19: an open-label, randomised, phase 2 trial",
"author": "Hung",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1695",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref16",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaci.2020.08.031",
"article-title": "Characterization of the cytokine storm reflects hyperinflammatory endothelial dysfunction in COVID-19",
"author": "Sims",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "107",
"journal-title": "J Allergy Clin Immunol",
"key": "ref17",
"volume": "147",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaci.2020.04.027",
"article-title": "Plasma IP-10 and MCP-3 levels are highly associated with disease severity and predict the progression of COVID-19",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "119",
"journal-title": "J Allergy Clin Immunol",
"key": "ref18",
"volume": "146",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0245296",
"article-title": "Observational cohort study of IP-10's potential as a biomarker to aid in inflammation regulation within a clinical decision support protocol for patients with severe COVID-19",
"author": "Lev",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e0245296",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "ref19",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "ref20",
"year": ""
}
],
"reference-count": 20,
"references-count": 20,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2023.1095828/full"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Peginterferon lambda for the treatment of hospitalized patients with mild COVID-19: A pilot phase 2 randomized placebo-controlled trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/crossmark-policy",
"volume": "10"
}