The clinical impact of androgen deprivation therapy on SARS-CoV-2 infection rates and disease severity
et al., Türk Üroloji Dergisi/Turkish Journal of Urology, doi:10.5152/tud.2021.21278, Nov 2021
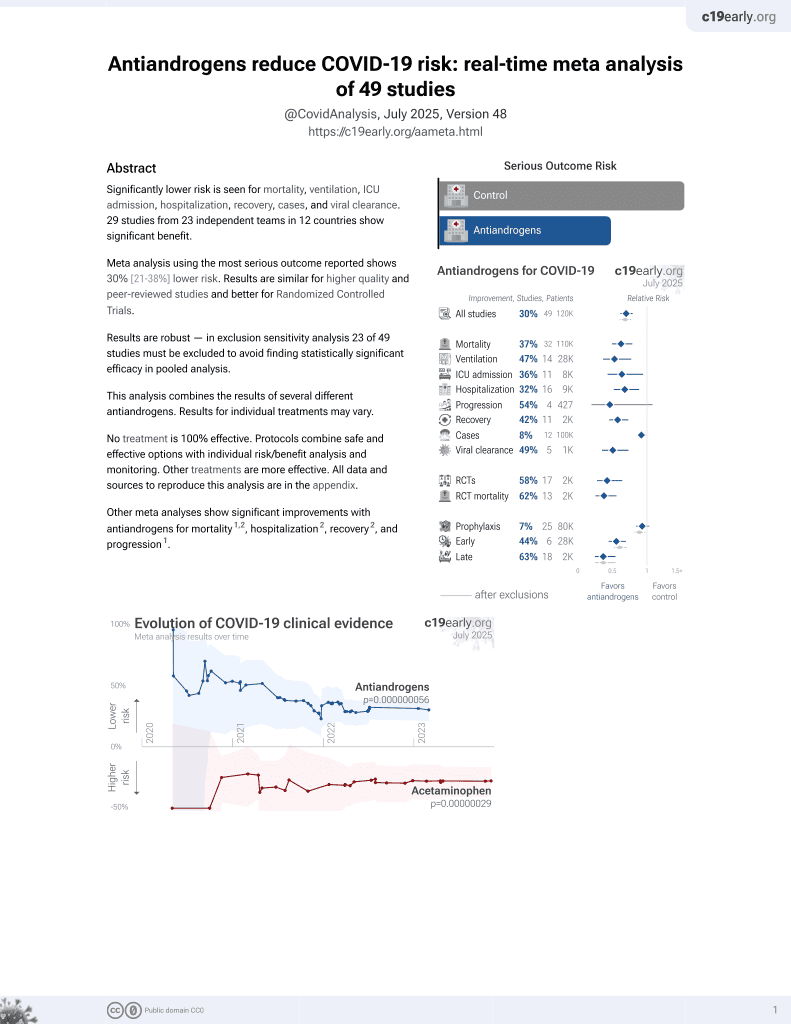
7th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000056 from 49 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
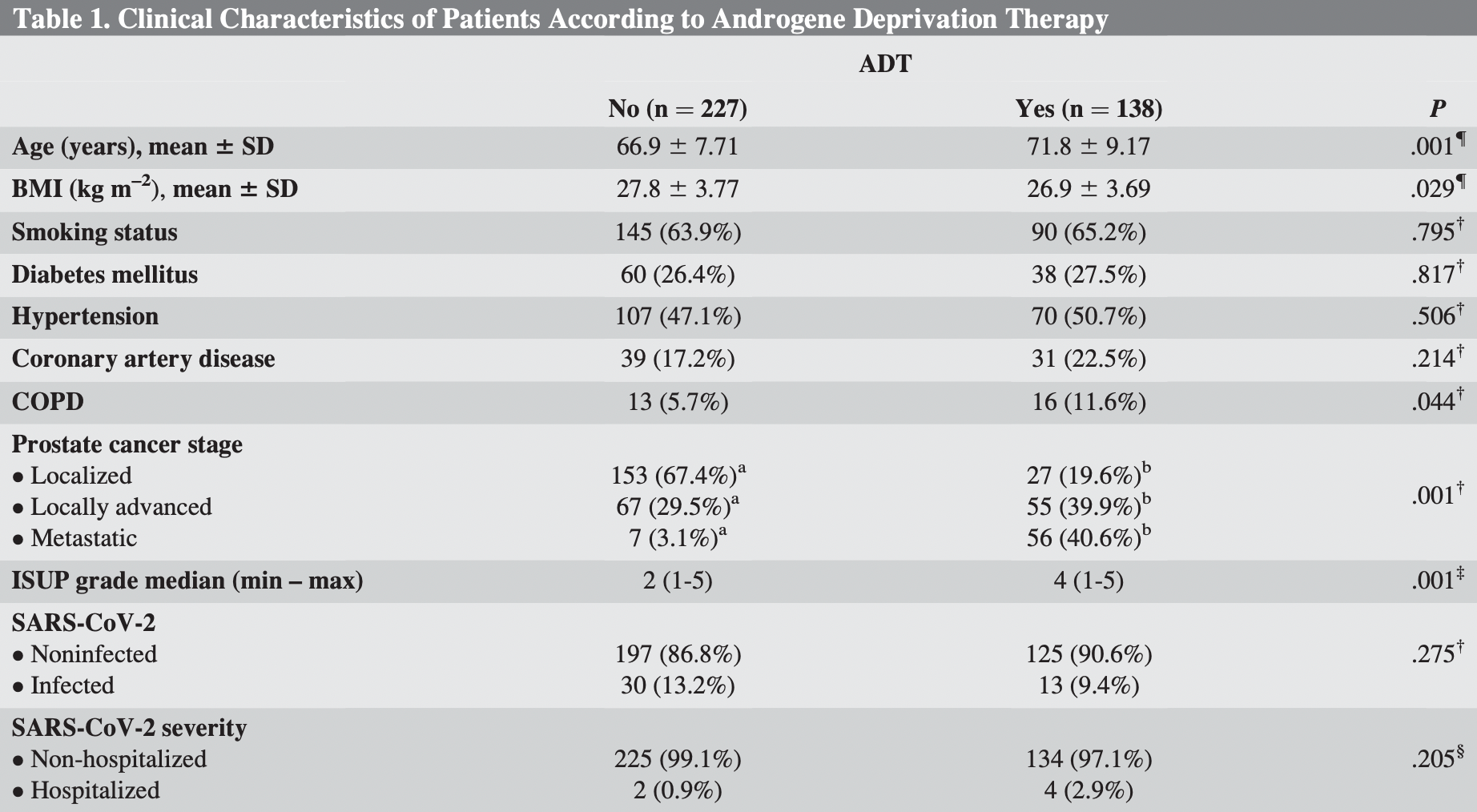
Retrospective 365 prostate cancer patients in Turkey, 138 treated with ADT, showing no significant differences with treatment.
This study is excluded in the after exclusion results of meta-analysis:
excessive unadjusted differences between groups.
|
risk of hospitalization, 229.0% higher, RR 3.29, p = 0.20, treatment 4 of 138 (2.9%), control 2 of 227 (0.9%).
|
|
risk of case, 28.7% lower, RR 0.71, p = 0.32, treatment 13 of 138 (9.4%), control 30 of 227 (13.2%), NNT 26.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Kazan et al., 1 Nov 2021, retrospective, Turkey, peer-reviewed, 10 authors, study period August 2020 - June 2021.
The clinical impact of androgen deprivation therapy on SARS-CoV-2 infection rates and disease severity
Türk Üroloji Dergisi/Turkish Journal of Urology, doi:10.5152/tud.2021.21278
Objective: The protective effect of androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is a novel hypothesis. ADT may protect patients with prostate cancer through the inhibition of androgen receptor-dependent transmembrane serine protease type 2. We analyzed the role of ADT on SARS-CoV-2 infection risk and disease severity. Material and methods: Between August 2020 and June 2021, patients with prostate cancer were included in our study. Patients were divided into two groups as men receiving ADT or not. Patients' characteristics such as prostate cancer grade and stage, comorbidities, SARS-CoV-2 infection status, and infection severity were assessed. SARS-CoV-2-infected close relatives and patients' compliance with the precautions against SARS-CoV-2 were also analyzed. Results: A total of 365 patients, 138 (37.8%) with ADT and 227 (62.2%) without ADT, were included in our analysis. Patients with ADT were older (71.8 vs 66.9 years, P ¼ .001) and had a higher rate of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (11.6% vs 5.7%, P ¼ .044). Patients receiving ADT were more often locally advanced and metastatic (80.4% vs 32.6%, P ¼ .001). SARS-CoV-2 infection rates were statistically similar between patients who received and did not receive ADT (9.4% vs 13.2%, P ¼ .275, respectively). There was no significant difference between two groups in terms of hospitalization rates (2.9% vs 0.9%, P ¼ .205). In multivariate analysis, the presence of SARS-CoV-2-infected close relatives and precautions score were only independent predictors for both risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection and infection severity.
Conclusion: We could not find any effect of ADT on risk and severity of SARS-CoV-2 infection. SARS-CoV-2 infection and hospitalization rates were similar between patients with and without ADT.
Ethics Committee Approval: Ethical committee approval was received from the _ Istanbul Medeniyet University (2021/440). Informed Consent: Written informed consent was obtained from all participants who participated in this study. Peer-review: Externally peer-reviewed. Author
References
Asselta, Paraboschi, Mantovani, Duga, ACE2 and TMPRSS2 variants and expression as candidates to sex and country differences in COVID-19 severity in Italy, Aging, doi:10.18632/aging.103415
Bennink, Foidart, Debruyne, Treatment of serious COVID-19 with testosterone suppression and highdose estrogen therapy, Eur Urol, doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2021.06.024
Caffo, Zagonel, Baldessari, On the relationship between androgen-deprivation therapy for prostate cancer and risk of infection by SARS-CoV-2, Ann Oncol, doi:10.1016/j.annonc.2020.06.005
Hoffmann, Kleine-Weber, Schroeder, SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052
Jin, Bai, He, Gender differences in patients with COVID-19: Focus on severity and mortality, Front Public Heal
Karimi, Nowroozi, Alilou, Amini, Effects of androgen deprivation therapy on COVID-19 in patients with prostate cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Urol J, doi:10.22037/uj.v18i.6691
Klein, Li, Milinovich, Androgen deprivation therapy in men with prostate cancer does not affect risk of infection with SARS-CoV-2, J Urol, doi:10.1097/JU.0000000000001338
Koskinen, Carpen, Honkanen, Androgen deprivation and SARS-CoV-2 in men with prostate cancer, Ann Oncol, doi:10.1016/j.annonc.2020.06.015
Kuderer, Choueiri, Shah, Clinical impact of COVID-19 on patients with cancer (CCC19): A cohort study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31187-9
Liang, Guan, Chen, Cancer patients in SARS-CoV-2 infection: A nationwide analysis in China, Lancet Oncol, doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30096-6
Liu, Zhao, Okwan-Duodu, Basho, Cui, COVID-19 in cancer patients: Risk, clinical features, and management, Cancer Biol Med, doi:10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2020.0289
Lucas, Heinlein, Kim, The androgen-regulated protease TMPRSS2 activates a proteolytic cascade involving components of the tumor microenvironment and promotes prostate cancer metastasis, Cancer Discov, doi:10.1158/2159-8290.CD-13-1010
Mikkonen, Pihlajamaa, Sahu, Zhang, Oa, Androgen receptor and androgen-dependent gene expression in lung, Mol Cell Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/j.mce.2009.12.022
Montopoli, Zumerle, Vettor, Androgen-deprivation therapies for prostate cancer and risk of infection by SARS-CoV-2: A population-based study (N ¼ 4532), Ann Oncol, doi:10.1016/j.annonc.2020.04.479
Patel, Zhong, Liaw, Does androgen deprivation therapy protect against severe complications from COVID-19?, Ann Oncol, doi:10.1016/j.annonc.2020.06.023
Shaw, Whitaker, Corcoran, The early effects of rapid androgen deprivation on human prostate cancer, Eur Urol, doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2015.10.042
Walls, Park, Tortorici, Wall, Mcguire et al., Structure, function, and antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.058
Xu, Wang, Xiao, Nuclear receptor ERRa and transcription factor ERG form a reciprocal loop in the regulation of TMPRSS2:ERG fusion gene in prostate cancer, Oncogene, doi:10.1038/s41388-018-0409-7
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.5152/tud.2021.21278",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.5152/tud.2021.21278",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kazan",
"given": "Özgür",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"name": "Department of Urology, Kocaeli State Hospital, Kocaeli, Turkey",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Çulpan",
"given": "Meftun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Efiloğlu",
"given": "Özgür",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Atis",
"given": "Gökhan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yildirim",
"given": "Asıf",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"name": "Department of Urology, Istanbul Medeniyet University School of Medicine, Istanbul, Turkey",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"name": "Department of Urology, Istanbul Medeniyet University School of Medicine, Istanbul, Turkey",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"name": "Department of Urology, Istanbul Medeniyet University School of Medicine, Istanbul, Turkey",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"name": "Department of Urology, Istanbul Medeniyet University School of Medicine, Istanbul, Turkey",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Türk Üroloji Dergisi/Turkish Journal of Urology"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-03T08:13:50Z",
"timestamp": 1638519230000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-03T08:14:00Z",
"timestamp": 1638519240000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2022-03-25T22:49:52Z",
"timestamp": 1648248592171
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 1,
"issue": "6",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
3
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "6",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
3
]
]
}
},
"member": "3111",
"original-title": [],
"page": "495-500",
"prefix": "10.5152",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
3
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
3
]
]
},
"publisher": "AVES Publishing Co.",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"Turkish Journal of Urology"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"The clinical impact of androgen deprivation therapy on SARS-CoV-2 infection rates and disease severity"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "47"
}