Evaluation of the Serum Zinc Level in Patients Followed in Hospital with the Diagnosis of COVID-19 in Samsun Province, Türkiye
et al., Life and Medical Sciences, doi:10.54584/lms.2023.39, Jul 2023
Zinc for COVID-19
2nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p = 0.00000028 from 47 studies, recognized in 23 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 51 COVID-19 patients and 26 healthy controls in Turkey, showing significantly lower zinc levels in COVID-19 patients, and zinc deficiency associated with COVID-19 in unadjusted results.
This study is excluded in the after exclusion results of meta-analysis:
unadjusted results with significant differences between groups.
|
risk of case, 88.3% lower, OR 0.12, p = 0.04, high zinc levels (≥70µg/dl) 38 of 51 (74.5%) cases,
25 of 26 (96.2%) controls, NNT 3.1, case control OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
İşler et al., 18 Jul 2023, retrospective, Turkey, peer-reviewed, 7 authors.
Contact: ilkay.bahceci@erdogan.edu.tr.
Evaluation of the Serum Zinc Level in Patients Followed in Hospital with the Diagnosis of COVID-19 in Samsun Province, Türkiye
Life and Medical Sciences, doi:10.54584/lms.2023.39
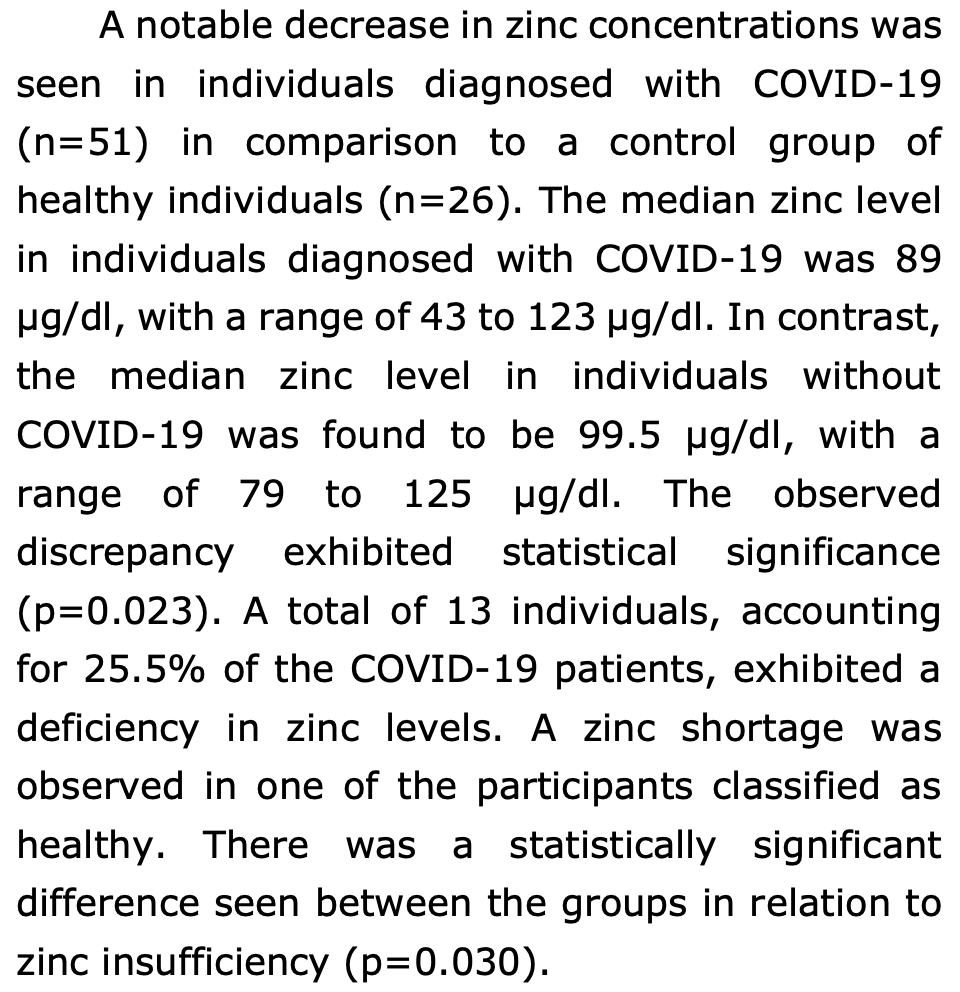
The COVID-19 (Coronavirus Disease 2019) outbreak has not yet ended and poses a persistent hazard to individuals, communities, and healthcare systems globally. Similar to numerous other diseases, the immune system of the patient is intricately associated with the advancement and mortality rates of COVID-19. In general, the immune system plays a crucial role in protecting the host against infections and neoplastic cells, and a well-balanced diet can enhance the immune system's ability to effectively defend against infectious agents. There have been suggestions that the administration of zinc supplements may decrease the occurrence of lower respiratory tract infections in children who are deficient in zinc. This study will thus examine the potential of zinc as a preventive and therapeutic agent, either on its own or in conjunction with other techniques, as zinc fulfills all the requirements outlined above. The study cohort was stratified into three distinct groups, namely critical care patients, service patients, and a healthy control group; a total of 24 COVID-19 patients in critical care, 27 ward-treated COVID-19 patients, and 26 healthy individuals. The groups exhibited a notable disparity in age distribution (p<0.001). A statistically significant difference was seen among the groups in relation to the survey results, presence of chronic disease, and length of hospital stay (p<0.001, p<0.001, and p=0.007, respectively). COVID-19 patients (n=51) exhibited markedly reduced zinc levels in comparison to a control group of healthy individuals (n=26). It was observed that the average zinc level in patients diagnosed with COVID-19 was 89 μg/dl (range: 43-123 μg/dl). In comparison, the median zinc level in individuals without COVID-19 was found to be 99.5 μg/dl (range: 79-125 μg/dl). A statistically significant difference was observed between the groups (p=0.023). The study revealed that a total of 13 individuals, accounting for 25.5% of the COVID-19 patients, exhibited a deficiency in zinc levels. The findings of our study ©Copyright LMS.
Conflict of interest: The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of the paper. Financial disclosure: There is no financial support for this study.
References
Akdeniz, Kınık, Yerlikaya, Akan, Importance of Zinc in Human Health and Nutrition Physiology, Academic Food Journal
Barocas, So-Armah, Cheng, Lioznov, Baum et al., Zinc deficiency and advanced liver fibrosis among HIV and hepatitis C co-infected antiretroviral naïve persons with alcohol use in Russia, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0218852
Boyraz, Alataş, Toğuç, Delen, Çavdar et al., The Effect of Mediterranean Diet Compliance on COVID-19 Symptoms and Disease Severity, J Mol Virol Immunol, doi:10.46683/jmvi.2022.55
Brown, Ojha, Fricke, Sa, Imarogbe et al., Innate and Adaptive Immunity during SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Biomolecular Cellular Markers and Mechanisms, Vaccines, doi:10.3390/vaccines11020408
Childs, Calder, Miles, Diet and Immune Function, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu11081933
Devaux, Rolain, Raoult, ACE2 receptor polymorphism: Susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2, hypertension, multi-organ failure, and COVID-19 disease outcome, J Microbiol Immunol Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jmii.2020.04.015
Gupta, Read, Shackel, Hebbard, George et al., The Role of Micronutrients in the Infection and Subsequent Response to Hepatitis C Virus, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells8060603
Jothimani, Kailasam, Danielraj, Nallathambi, Ramachandran et al., COVID-19: Poor outcomes in patients with zinc deficiency, Int J Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.014
Karakuş, Innate Immune Response and Immune Evasion in Viral Infections, J Mol Virol Immunol, doi:10.46683/jmvi.2022.44
Keleş, Çiftdoğan, Çolak, Aksay, Üstündag et al., Serum zinc levels in pediatric patients with COVID-19, Eur J Pediatr, doi:10.1007/s00431-021-04348-w
Lassi, Moin, Bhutta, Zinc supplementation for the prevention of pneumonia in children aged 2 months to 59 months, Cochrane Database Syst Rev, doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005978.pub3
Maret, Zinc and the zinc proteome, Met Ions Life Sci, doi:10.1007/978-94-007-5561-1_14
Patel, Chinni, El-Khoury, Perera, Neto et al., A pilot double-blind safety and feasibility randomized controlled trial of high-dose intravenous zinc in hospitalized COVID-19 patients, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.26895
Prasad, Zinc: role in immunity, oxidative stress and chronic inflammation, Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care, doi:10.1097/MCO.0b013e3283312956
Singh, Das, Zinc for the common cold, Cochrane Database Syst Rev, doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001364.pub3
Yasui, Yasui, Suzuki, Saitou, Yamamoto et al., Analysis of the predictive factors for a critical illness of COVID-19 during treatment -relationship between serum zinc level and critical illness of COVID-19, Int J Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.008
Şenol, Şakul, COVID-19 and Support Products: The Effects of Nutritional Immunity, J Mol Virol Immunol, doi:10.46683/jmvi.2023.66
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.54584/lms.2023.39",
"ISSN": [
"2791-9145"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.54584/lms.2023.39",
"abstract": "<jats:p xml:lang=\"tr\">The COVID-19 (Coronavirus Disease 2019) outbreak has not yet ended and poses a persistent hazard to individuals, communities, and healthcare systems globally. Similar to numerous other diseases, the immune system of the patient is intricately associated with the advancement and mortality rates of COVID-19. In general, the immune system plays a crucial role in protecting the host against infections and neoplastic cells, and a well-balanced diet can enhance the immune system's ability to effectively defend against infectious agents. There have been suggestions that the administration of zinc supplements may decrease the occurrence of lower respiratory tract infections in children who are deficient in zinc. This study will thus examine the potential of zinc as a preventive and therapeutic agent, either on its own or in conjunction with other techniques, as zinc fulfills all the requirements outlined above. The study cohort was stratified into three distinct groups, namely critical care patients, service patients, and a healthy control group; a total of 24 COVID-19 patients in critical care, 27 ward-treated COVID-19 patients, and 26 healthy individuals. The groups exhibited a notable disparity in age distribution (p<0.001). A statistically significant difference was seen among the groups in relation to the survey results, presence of chronic disease, and length of hospital stay (p<0.001, p<0.001, and p=0.007, respectively). COVID-19 patients (n=51) exhibited markedly reduced zinc levels in comparison to a control group of healthy individuals (n=26). It was observed that the average zinc level in patients diagnosed with COVID-19 was 89 μg/dl (range: 43-123 μg/dl). In comparison, the median zinc level in individuals without COVID-19 was found to be 99.5 μg/dl (range: 79-125 μg/dl). A statistically significant difference was observed between the groups (p=0.023). The study revealed that a total of 13 individuals, accounting for 25.5% of the COVID-19 patients, exhibited a deficiency in zinc levels. The findings of our study indicate that zinc potentially plays a significant role in the context of COVID-19. However, additional research is required to get a comprehensive understanding of the association between COVID-19 and zinc.</jats:p>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
18
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0722-8425",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "İşler",
"given": "Hacer",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3662-1629",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Bahçeci",
"given": "İlkay",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6318-1238",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Güdül Havuz",
"given": "Seda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4271-4960",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Aydoğan",
"given": "Seher",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2581-6001",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Ünlügüzel Üstün",
"given": "Göksenin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6959-1695",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Öztürk",
"given": "Çağatay Erman",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8235-9524",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Başbulut",
"given": "Eşe",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Life and Medical Sciences",
"container-title-short": "lms",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2023-10-03T08:15:01Z",
"timestamp": 1696320901000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2023-10-03T08:15:08Z",
"timestamp": 1696320908000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2023-10-04T05:18:13Z",
"timestamp": 1696396693841
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
18
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"member": "33105",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.54584",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
18
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
18
]
]
},
"publisher": "Life and Medical Sciences",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://lifemedsci.com/a/2023/3/oz/39.htm"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Evaluation of the Serum Zinc Level in Patients Followed in Hospital with the Diagnosis of COVID-19 in Samsun Province, Türkiye",
"type": "journal-article"
}
