Ursodeoxycholic acid relieves clinical severity of COVID-19 in patients with chronic liver diseases
et al., Frontiers in Medicine, doi:10.3389/fmed.2025.1494248, Feb 2025
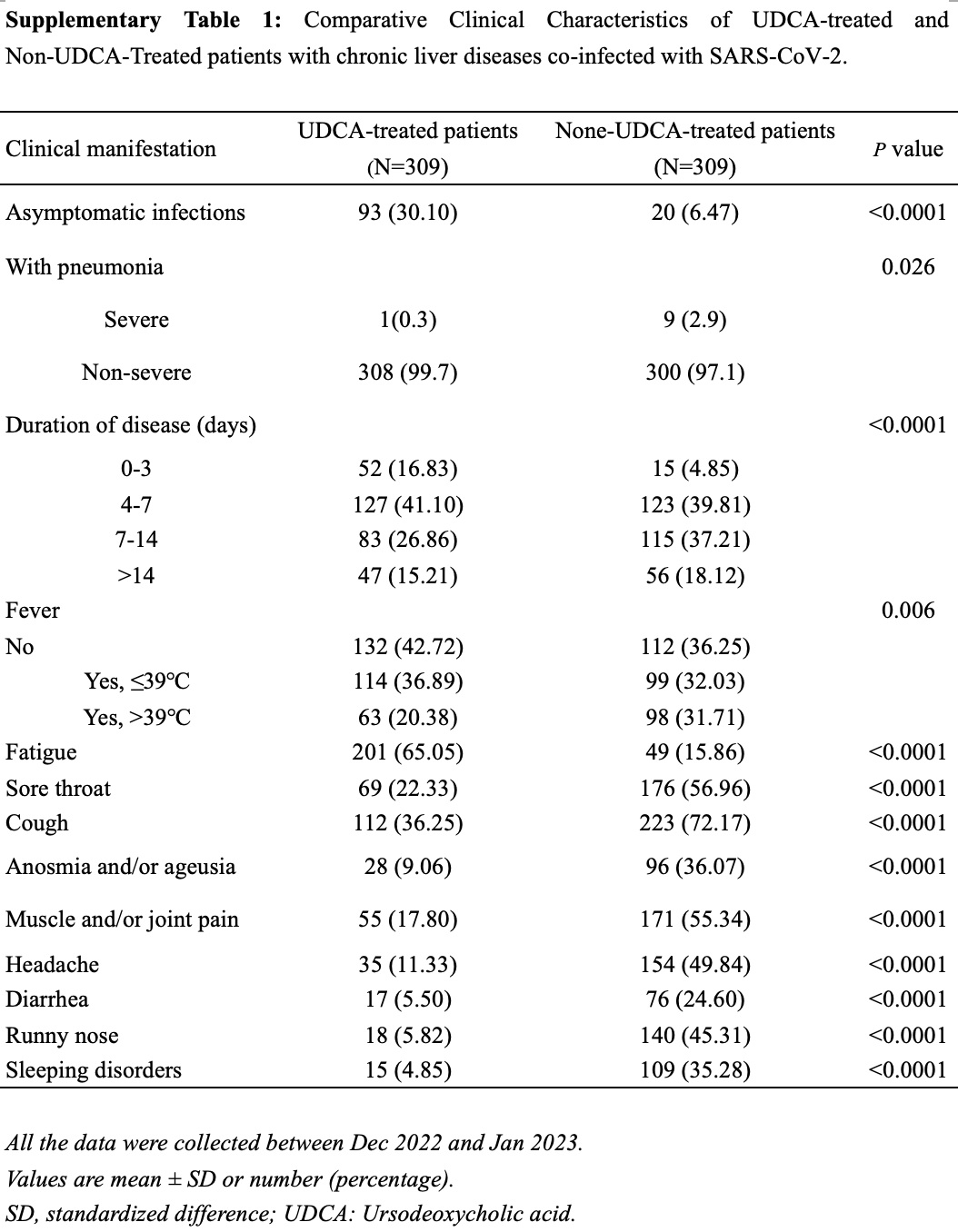
Retrospective 926 outpatients with chronic liver diseases in China showing lower incidence of symptomatic COVID-19 and milder symptoms with ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) treatment.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments1.
|
risk of severe case, 88.9% lower, RR 0.11, p = 0.02, treatment 1 of 309 (0.3%), control 9 of 309 (2.9%), NNT 39.
|
|
risk of symptomatic case, 25.3% lower, RR 0.75, p < 0.001, treatment 216 of 309 (69.9%), control 289 of 309 (93.5%), NNT 4.2.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Hu et al., 6 Feb 2025, retrospective, China, peer-reviewed, median age 62.0, 6 authors, study period 7 December, 2022 - 23 January, 2023.
Contact: jmzhang@fudan.edu.cn, jinyuwang77@163.com.
Ursodeoxycholic acid relieves clinical severity of COVID-19 in patients with chronic liver diseases
Frontiers in Medicine, doi:10.3389/fmed.2025.1494248
Background: The potential effect of ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) on the clinical outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 in patients with chronic liver diseases has been a subject of ongoing debate since the onset of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic in 2019. This study aims to investigate the effect of UDCA on the prognosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection in patients with chronic liver diseases. Methods: A total of 926 patients with chronic liver diseases who contracted their first SARS-CoV-2 infection during December 2022 to January 2023, were included in this study. Participants were divided into two groups based on the use of UDCA: the UDCA cohort (n = 329) and the non-UDCA cohort (n = 597). After performing a 1:1 age-and sex-matching, the analysis proceeded with 309 patients from each group for further evaluation. Results: In the UDCA-treated cohort, the incidence of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infections was significantly higher, with 30.1% of patients affected, compared to 6.47% in the non-UDCA group (p < 0.0001). Multivariable analysis identified UDCA as a protective factor against symptomatic infections, yielding an odds ratio (OR) of 4.77 (95% CI: 2.70-8.44, p < 0.001). Furthermore, age over 50 was found to be a risk factor for asymptomatic infections in the UDCA cohort, with an adjusted OR of 1.51 (95% CI: 1.01-2.24, p = 0.05).
Conclusion: The study suggests that UDCA therapy may improve clinical outcomes in patients with chronic liver diseases patients who are infected with SARS-CoV-2, highlighting its potential role in improving prognosis within this vulnerable population. However, further research is required to validate these findings and to elucidate the mechanisms underlying UDCA's protective effect.
Ethics statement The studies involving humans were approved by Huashan Hospital of Fudan University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
Conflict of interest The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2025.1494248/ full#supplementary-material
References
Abenavoli, Aquila, Sacco, Procopio, Cinaglia et al., Liver injury associated with high value of D-dimer plasmatic level in COVID-19 patients, Minerva Gastroenterol, doi:10.23736/S2724-5985.22.03189-8
Aby, Moafa, Latt, Sultan, Cacioppo et al., Long-term clinical outcomes of patients with COVID-19 and chronic liver disease: US multicenter COLD study, Hepatol Commun, doi:10.1097/01.HC9.0000897224.68874.de
Alsharif, Qurashi, Effectiveness of COVID-19 diagnosis and management tools: A review, Radiography, doi:10.1016/j.radi.2020.09.010
Batiha, Gareeb, Youssef, El-Sherbeni, Negm, A perspective study of the possible impact of obeticholic acid against SARS-CoV-2 infection, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-022-01111-x
Bedossa, Poynard, An algorithm for the grading of activity in chronic hepatitis C, Hepatology, doi:10.1002/hep.510240201
Brevini, Maes, Webb, John, Fuchs et al., FXR inhibition may protect from SARS-CoV-2 infection by reducing ACE2, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-022-05594-0
Buryova, Chalupsky, Zbodakova, Kanchev, Jirouskova et al., Liver protective effect of ursodeoxycholic acid includes regulation of ADAM17 activity, BMC Gastroenterol, doi:10.1186/1471-230X-13-155
Cabrera, Arab, Arrese, UDCA, NorUDCA, and TUDCA in liver diseases: a review of their mechanisms of action and clinical applications, Handb Exp Pharmacol, doi:10.1007/164_2019_241
Cascella, Features, evaluation, and treatment of coronavirus (COVID-19)
Chen, Zhu, Zhang, UDCA, a novel strategy for preventing SARS-CoV-2 infection via FXR-mediated ACE2 downregulation: UDCA and SARS-CoV-2 infection, Acta Biochim Biophys Sin, doi:10.3724/abbs.2023075
Colapietro, Angelotti, Masetti, Shiffer, Pugliese et al., Ursodeoxycholic acid does not improve COVID-19 outcome in hospitalized patients, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v15081738
El Hakim, Abdou, Abou Donia, Saad Khaled, COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy, protective behaviors, and risk perception among university students in Alexandria, Egyptian J Health Care, doi:10.21608/ejhc.2021.195790
Gao, Lv, He, Zhao, Liu et al., Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on liver disease-related mortality rates in the United States, J Hepatol, doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2022.07.028
Gulick, Pau, Daar, Evans, Gandhi et al., National Institutes of Health COVID-19 treatment guidelines panel: perspectives and lessons learned, Ann Intern Med, doi:10.7326/ANNALS-24-00464
Hu, Ni, Fan, Men, Yang, Past hepatitis B virus infection was not associated with poorer response or the UK-PBC risk score in ursodeoxycholic acid-treated patients with primary biliary cirrhosis, Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, doi:10.1097/MEG.0000000000001320
Işık, Karaman, Micili, Çağlayan-Sözmen, Bağrıyanık et al., Beneficial effects of ursodeoxycholic acid via inhibition of airway remodelling, apoptosis of airway epithelial cells, and Th2 immune response in murine model of chronic asthma, Allergol Immunopathol, doi:10.1016/j.aller.2016.12.003
Janik, Niemcewicz, Podogrocki, Majsterek, Bijak, The emerging concern and interest SARS-CoV-2 variants, Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens10060633
Lai, Ma, Wang, Cai, Hu et al., Factors associated with mental health outcomes among health care workers exposed to coronavirus disease 2019, JAMA Netw Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.3976
Li, Zhang, Wu, Xu, Li et al., Tauroursodeoxycholic acid (TUDCA) inhibits influenza A viral infection by disrupting viral proton channel M2, Sci Bulletin, doi:10.1016/j.scib.2018.08.013
Li, Zhu, Cui, Lin, Li, Protective effect of ursodeoxycholic acid on COVID-19 in patients with chronic liver disease, Front Cell Infect Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2023.1178590
Lirussi, Beccarello, Bortolato, Morselli-Labate, Crovatto et al., Long-term treatment of chronic hepatitis C with ursodeoxycholic acid: influence of HCV genotypes and severity of liver disease, Liver, doi:10.1111/j.1478-3231.1999.tb00066.x
Liu, Qureshi, Secondary treatment of primary biliary cholangitis: early prediction of inadequate response to Ursodeoxycholic acid in patients with PBC, Dig Dis Sci, doi:10.1007/s10620-022-07661-y
Lu, Zhang, Zhang, He, Yuan, Geriatric risk and protective factors for serious COVID-19 outcomes among older adults in Shanghai omicron wave, Emerg Microbes Infect, doi:10.1080/22221751.2022.2109517
Luo, Chen, Du, Mei, Wang et al., Immunogenicity ofCOVID-19 vaccines in chronic liver disease patients and liver transplant recipients: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Liver Int, doi:10.1111/liv.15403
Luo, Han, Du, Yang, Duan et al., Chenodeoxycholic acid from bile inhibits influenza A virus replication via blocking nuclear export of viral ribonucleoprotein complexes, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules23123315
Marjot, Webb, Barritt, Iv, Moon et al., COVID-19 and liver disease: mechanistic and clinical perspectives, Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, doi:10.1038/s41575-021-00426-4
Marrone, Covino, Merra, Piccioni, Amodeo et al., Ursodeoxycholic acid does not affect the clinical outcome of SARS-CoV-2 infection: A retrospective study of propensity score-matched cohorts, Liver Int, doi:10.1111/liv.15736
Miura, Ouchida, Yoshikawa, Okamoto, Makino et al., Functional modulation of the glucocorticoid receptor and suppression of NF-κBdependent transcription by ursodeoxycholic acid, J Biol Chem, doi:10.1074/jbc.M107098200
Nojiri, Nakao, Sugauchi, Miyaki, Senda et al., Effect of ursodeoxycholic acid on serum liver enzymes and bile acid metabolism in chronic active hepatitis C virus infection, Hepatol Res, doi:10.1111/j.1872-034X.2008.00406.x
Qiao, Yacoub, Studer, Gupta, Pei et al., Inhibition of the MAPK and PI3K pathways enhances UDCA-induced apoptosis in primary rodent hepatocytes, Hepatology, doi:10.1053/jhep.2002.32533
Salzberger, Buder, Lampl, Ehrenstein, Hitzenbichler et al., Epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2, Infection, doi:10.1007/s15010-020-01531-3
Sarin, Choudhury, Lau, Zheng, Ji et al., Preexisting liver disease is associated with poor outcome in patients with SARS CoV2 infection; the APCOLIS study (APASL COVID-19 liver injury Spectrum study), Hepatol Int, doi:10.1007/s12072-020-10072-8
Sherman, Smith, Sim, Amlôt, Cutts et al., COVID-19 vaccination intention in the UK: results from the COVID-19 vaccination acceptability study (CoVAccS), a nationally representative cross-sectional survey, Hum Vaccin Immunother, doi:10.1080/21645515.2020.1846397
Shi, Li, Zeng, Lin, Xie, Ursodeoxycholic acid in primary sclerosing cholangitis: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Hepatol Res, doi:10.1111/j.1872-034X.2009.00527.x
Song, Li, Geng, Guo, Yang et al., Uncovering key molecules and immune landscape in cholestatic liver injury: implications for pathogenesis and drug therapy, Front Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1171512
Stan, Biciușcă, Clenciu, Mitrea, Boldeanu et al., The therapeutic mechanisms and beneficial effects of ursodeoxycholic acid in the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review, Med Pharmacy Rep, doi:10.15386/mpr-2629
Thuy, Bao, Moon, Ursodeoxycholic acid ameliorates cell migration retarded by the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in BEAS-2B human bronchial epithelial cells, Biomed Pharmacother, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113021
Walensky, Walke, Fauci, SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern in the United States-challenges and opportunities, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2021.2294
Winston, Rivera, Cai, Thanissery, Montgomery et al., Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) mitigates the host inflammatory response during Clostridioides difficile infection by altering gut bile acids, Infect Immun, doi:10.1128/IAI.00045-20
Yoshikawa, Tsujii, Matsumura, Yamao, Matsumura et al., Immunomodulatory effects of ursodeoxycholic acid on immune responses, Hepatology, doi:10.1002/hep.1840160213
Zhao, Xiao, Xu, Liu, Jiang et al., Glycyrrhizic acid nanoparticles as antiviral and anti-inflammatory agents for COVID-19 treatment, ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, doi:10.1021/acsami.1c02755
Zhu, Boucheron, Müller, Májek, Claudel et al., 24-Norursodeoxycholic acid reshapes immunometabolism in CD8+ T cells and alleviates hepatic inflammation, J Hepatol, doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2021.06.036
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2025.1494248",
"ISSN": [
"2296-858X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2025.1494248",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Background</jats:title><jats:p>The potential effect of ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) on the clinical outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 in patients with chronic liver diseases has been a subject of ongoing debate since the onset of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic in 2019. This study aims to investigate the effect of UDCA on the prognosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection in patients with chronic liver diseases.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods</jats:title><jats:p>A total of 926 patients with chronic liver diseases who contracted their first SARS-CoV-2 infection during December 2022 to January 2023, were included in this study. Participants were divided into two groups based on the use of UDCA: the UDCA cohort (<jats:italic>n</jats:italic> = 329) and the non-UDCA cohort (<jats:italic>n</jats:italic> = 597). After performing a 1:1 age-and sex-matching, the analysis proceeded with 309 patients from each group for further evaluation.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>In the UDCA-treated cohort, the incidence of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infections was significantly higher, with 30.1% of patients affected, compared to 6.47% in the non-UDCA group (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic> &lt; 0.0001). Multivariable analysis identified UDCA as a protective factor against symptomatic infections, yielding an odds ratio (OR) of 4.77 (95% CI: 2.70–8.44, <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> &lt; 0.001). Furthermore, age over 50 was found to be a risk factor for asymptomatic infections in the UDCA cohort, with an adjusted OR of 1.51 (95% CI: 1.01–2.24, <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.05).</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title><jats:p>The study suggests that UDCA therapy may improve clinical outcomes in patients with chronic liver diseases patients who are infected with SARS-CoV-2, highlighting its potential role in improving prognosis within this vulnerable population. However, further research is required to validate these findings and to elucidate the mechanisms underlying UDCA’s protective effect.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.3389/fmed.2025.1494248"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hu",
"given": "Tiantian",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tong",
"given": "Jie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Yunhui",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yuan",
"given": "Changrong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Jiming",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Jinyu",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Frontiers in Medicine",
"container-title-short": "Front. Med.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"frontiersin.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-06T07:13:38Z",
"timestamp": 1738826018000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-06T07:13:42Z",
"timestamp": 1738826022000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-07T05:08:25Z",
"timestamp": 1738904905109,
"version": "3.37.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
6
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-06T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1738800000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2025.1494248/full",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1965",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.3389",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
6
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
6
]
]
},
"publisher": "Frontiers Media SA",
"reference": [
{
"first-page": "2023",
"key": "ref1",
"volume-title": "COVID-19 weekly epidemiological update, edition 158, 2023",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.3976",
"article-title": "Factors associated with mental health outcomes among health care workers exposed to coronavirus disease 2019",
"author": "Lai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e203976",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "ref2",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2022.2109517",
"article-title": "Geriatric risk and protective factors for serious COVID-19 outcomes among older adults in Shanghai omicron wave",
"author": "Lu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2045",
"journal-title": "Emerg Microbes Infect",
"key": "ref3",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "ref4",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "ref5",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/liv.15403",
"article-title": "Immunogenicity ofCOVID‐19 vaccines in chronic liver disease patients and liver transplant recipients: a systematic review and meta‐analysis",
"author": "Luo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "34",
"journal-title": "Liver Int",
"key": "ref6",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jhep.2022.07.028",
"article-title": "Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on liver disease-related mortality rates in the United States",
"author": "Gao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "16",
"journal-title": "J Hepatol",
"key": "ref7",
"volume": "78",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/01.HC9.0000897224.68874.de",
"article-title": "Long-term clinical outcomes of patients with COVID-19 and chronic liver disease: US multicenter COLD study",
"author": "Aby",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e8874",
"journal-title": "Hepatol Commun",
"key": "ref8",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MEG.0000000000001320",
"article-title": "Past hepatitis B virus infection was not associated with poorer response or the UK-PBC risk score in ursodeoxycholic acid-treated patients with primary biliary cirrhosis",
"author": "Hu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "277",
"journal-title": "Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol",
"key": "ref9",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15386/mpr-2629",
"article-title": "The therapeutic mechanisms and beneficial effects of ursodeoxycholic acid in the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review",
"author": "Stan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "12",
"journal-title": "Med Pharmacy Rep",
"key": "ref10",
"volume": "97",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2023.1171512",
"article-title": "Uncovering key molecules and immune landscape in cholestatic liver injury: implications for pathogenesis and drug therapy",
"author": "Song",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1171512",
"journal-title": "Front Pharmacol",
"key": "ref11",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10620-022-07661-y",
"article-title": "Secondary treatment of primary biliary cholangitis: early prediction of inadequate response to Ursodeoxycholic acid in patients with PBC",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "346",
"journal-title": "Dig Dis Sci",
"key": "ref12",
"volume": "68",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1872-034X.2009.00527.x",
"article-title": "Ursodeoxycholic acid in primary sclerosing cholangitis: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials",
"author": "Shi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "865",
"journal-title": "Hepatol Res",
"key": "ref13",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/164_2019_241",
"article-title": "UDCA, NorUDCA, and TUDCA in liver diseases: a review of their mechanisms of action and clinical applications",
"author": "Cabrera",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "237",
"journal-title": "Handb Exp Pharmacol",
"key": "ref14",
"volume": "256",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1471-230X-13-155",
"article-title": "Liver protective effect of ursodeoxycholic acid includes regulation of ADAM17 activity",
"author": "Buryova",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC Gastroenterol",
"key": "ref15",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1478-3231.1999.tb00066.x",
"article-title": "Long-term treatment of chronic hepatitis C with ursodeoxycholic acid: influence of HCV genotypes and severity of liver disease",
"author": "Lirussi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "381",
"journal-title": "Liver",
"key": "ref16",
"volume": "19",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.scib.2018.08.013",
"article-title": "Tauroursodeoxycholic acid (TUDCA) inhibits influenza A viral infection by disrupting viral proton channel M2",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "180",
"journal-title": "Sci Bulletin",
"key": "ref17",
"volume": "64",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules23123315",
"article-title": "Chenodeoxycholic acid from bile inhibits influenza A virus replication via blocking nuclear export of viral ribonucleoprotein complexes",
"author": "Luo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3315",
"journal-title": "Molecules",
"key": "ref18",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-05594-0",
"article-title": "FXR inhibition may protect from SARS-CoV-2 infection by reducing ACE2",
"author": "Brevini",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "134",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref19",
"volume": "615",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcimb.2023.1178590",
"article-title": "Protective effect of ursodeoxycholic acid on COVID-19 in patients with chronic liver disease",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1178590",
"journal-title": "Front Cell Infect Microbiol",
"key": "ref20",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v15081738",
"article-title": "Ursodeoxycholic acid does not improve COVID-19 outcome in hospitalized patients",
"author": "Colapietro",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1738",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "ref21",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/liv.15736",
"article-title": "Ursodeoxycholic acid does not affect the clinical outcome of SARS-CoV-2 infection: A retrospective study of propensity score-matched cohorts",
"author": "Marrone",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "83",
"journal-title": "Liver Int",
"key": "ref22",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/hep.510240201",
"article-title": "An algorithm for the grading of activity in chronic hepatitis C",
"author": "Bedossa",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "289",
"journal-title": "Hepatology",
"key": "ref23",
"volume": "24",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.radi.2020.09.010",
"article-title": "Effectiveness of COVID-19 diagnosis and management tools: A review",
"author": "Alsharif",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "682",
"journal-title": "Radiography",
"key": "ref24",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s15010-020-01531-3",
"article-title": "Epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Salzberger",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "233",
"journal-title": "Infection",
"key": "ref25",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/pathogens10060633",
"article-title": "The emerging concern and interest SARS-CoV-2 variants",
"author": "Janik",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "633",
"journal-title": "Pathogens",
"key": "ref26",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2021.2294",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern in the United States—challenges and opportunities",
"author": "Walensky",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1037",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "ref27",
"volume": "325",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21608/ejhc.2021.195790",
"article-title": "COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy, protective behaviors, and risk perception among university students in Alexandria",
"author": "El Hakim",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "108",
"journal-title": "Egyptian J Health Care",
"key": "ref28",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/21645515.2020.1846397",
"article-title": "COVID-19 vaccination intention in the UK: results from the COVID-19 vaccination acceptability study (CoVAccS), a nationally representative cross-sectional survey",
"author": "Sherman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1612",
"journal-title": "Hum Vaccin Immunother",
"key": "ref29",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/hep.1840160213",
"article-title": "Immunomodulatory effects of ursodeoxycholic acid on immune responses",
"author": "Yoshikawa",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "358",
"journal-title": "Hepatology",
"key": "ref30",
"volume": "16",
"year": "1992"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.aller.2016.12.003",
"article-title": "Beneficial effects of ursodeoxycholic acid via inhibition of airway remodelling, apoptosis of airway epithelial cells, and Th2 immune response in murine model of chronic asthma",
"author": "Işık",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "339",
"journal-title": "Allergol Immunopathol",
"key": "ref31",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jhep.2021.06.036",
"article-title": "24-Norursodeoxycholic acid reshapes immunometabolism in CD8+ T cells and alleviates hepatic inflammation",
"author": "Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1164",
"journal-title": "J Hepatol",
"key": "ref32",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1872-034X.2008.00406.x",
"article-title": "Effect of ursodeoxycholic acid on serum liver enzymes and bile acid metabolism in chronic active hepatitis C virus infection",
"author": "Nojiri",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "21",
"journal-title": "Hepatol Res",
"key": "ref33",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/IAI.00045-20",
"article-title": "Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) mitigates the host inflammatory response during Clostridioides difficile infection by altering gut bile acids",
"author": "Winston",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "10.1128/iai. 00045-20",
"journal-title": "Infect Immun",
"key": "ref34",
"volume": "88",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/jhep.2002.32533",
"article-title": "Inhibition of the MAPK and PI3K pathways enhances UDCA-induced apoptosis in primary rodent hepatocytes",
"author": "Qiao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "779",
"journal-title": "Hepatology",
"key": "ref35",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M107098200",
"article-title": "Functional modulation of the glucocorticoid receptor and suppression of NF-κB-dependent transcription by ursodeoxycholic acid",
"author": "Miura",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "47371",
"journal-title": "J Biol Chem",
"key": "ref36",
"volume": "276",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113021",
"article-title": "Ursodeoxycholic acid ameliorates cell migration retarded by the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in BEAS-2B human bronchial epithelial cells",
"author": "Thuy",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "113021",
"journal-title": "Biomed Pharmacother",
"key": "ref37",
"volume": "150",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.23736/S2724-5985.22.03189-8",
"article-title": "Liver injury associated with high value of D-dimer plasmatic level in COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Abenavoli",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "141",
"journal-title": "Minerva Gastroenterol",
"key": "ref38",
"volume": "69",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"author": "Cascella",
"key": "ref39",
"volume-title": "Features, evaluation, and treatment of coronavirus (COVID-19)",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/ANNALS-24-00464",
"article-title": "National Institutes of Health COVID-19 treatment guidelines panel: perspectives and lessons learned",
"author": "Gulick",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1547",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "ref40",
"volume": "177",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3724/abbs.2023075",
"article-title": "UDCA, a novel strategy for preventing SARS-CoV-2 infection via FXR-mediated ACE2 downregulation: UDCA and SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "885",
"journal-title": "Acta Biochim Biophys Sin",
"key": "ref41",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10787-022-01111-x",
"article-title": "A perspective study of the possible impact of obeticholic acid against SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Batiha",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "9",
"journal-title": "Inflammopharmacology",
"key": "ref42",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acsami.1c02755",
"article-title": "Glycyrrhizic acid nanoparticles as antiviral and anti-inflammatory agents for COVID-19 treatment",
"author": "Zhao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "20995",
"journal-title": "ACS Appl Mater Interfaces",
"key": "ref43",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12072-020-10072-8",
"article-title": "Pre-existing liver disease is associated with poor outcome in patients with SARS CoV2 infection; the APCOLIS study (APASL COVID-19 liver injury Spectrum study)",
"author": "Sarin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "690",
"journal-title": "Hepatol Int",
"key": "ref44",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41575-021-00426-4",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and liver disease: mechanistic and clinical perspectives",
"author": "Marjot",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "348",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol",
"key": "ref45",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 45,
"references-count": 45,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2025.1494248/full"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Ursodeoxycholic acid relieves clinical severity of COVID-19 in patients with chronic liver diseases",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.3389/crossmark-policy",
"volume": "12"
}