RNA Polymerase Inhibitor Enisamium for Treatment of Moderate COVID-19 Patients: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Multicenter, Double-Blind Phase 3 Clinical Trial
et al., Advances in Respiratory Medicine, doi:10.3390/arm92030021, NCT04682873, May 2024
RCT 592 hospitalized moderate COVID-19 patients in Ukraine showing improved recovery and lower progression with enisamium. The trial initially included patients with moderate COVID-19 not requiring oxygen, but a mid-trial change was made to exclude this group due to a lack of benefit. This paper reports results only for the subgroup of patients requiring oxygen. Only very limited results have been reported for all patients as of the interim analysis1.
|
recovery time, no change, relative time 1.00, treatment 186, control 186, all patients, interim analysis, 373 total patients, group counts not reported.
|
|
risk of death, 85.7% lower, RR 0.14, p = 0.25, treatment 0 of 142 (0.0%), control 3 of 143 (2.1%), NNT 48, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), SR=4.
|
|
risk of progression, 74.8% lower, RR 0.25, p = 0.03, treatment 3 of 142 (2.1%), control 12 of 143 (8.4%), NNT 16, SR=4.
|
|
time to improvement, 9.1% lower, relative time 0.91, p = 0.01, treatment 142, control 143, SR=4, post-hoc primary outcome.
|
|
risk of no hospital discharge, 88.9% lower, RR 0.11, p = 0.12, treatment 0 of 142 (0.0%), control 4 of 143 (2.8%), NNT 36, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), SR=4, day 29.
|
|
risk of no hospital discharge, 94.1% lower, RR 0.06, p = 0.007, treatment 0 of 142 (0.0%), control 8 of 143 (5.6%), NNT 18, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), SR=4, day 22.
|
|
risk of no hospital discharge, 60.8% lower, RR 0.39, p = 0.03, treatment 7 of 142 (4.9%), control 18 of 143 (12.6%), NNT 13, SR=4, day 15.
|
|
risk of no hospital discharge, 11.3% lower, RR 0.89, p = 0.23, treatment 81 of 142 (57.0%), control 92 of 143 (64.3%), NNT 14, SR=4, day 8.
|
|
risk of no viral clearance, 66.6% lower, RR 0.33, p = 1.00, treatment 0 of 142 (0.0%), control 1 of 143 (0.7%), NNT 143, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), SR=4, day 29.
|
|
risk of no viral clearance, 79.9% lower, RR 0.20, p = 0.50, treatment 0 of 142 (0.0%), control 2 of 143 (1.4%), NNT 72, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), SR=4, day 22.
|
|
risk of no viral clearance, 37.1% lower, RR 0.63, p = 0.57, treatment 5 of 142 (3.5%), control 8 of 143 (5.6%), NNT 48, SR=4, day 15.
|
|
risk of no viral clearance, 12.7% lower, RR 0.87, p = 0.40, treatment 52 of 142 (36.6%), control 60 of 143 (42.0%), NNT 19, SR=4, day 8.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Holubovska et al., 6 May 2024, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, Ukraine, peer-reviewed, median age 59.0, 10 authors, study period 15 May, 2020 - 26 March, 2021, trial NCT04682873 (history).
Contact: aj.te.velthuis@princeton.edu (corresponding author), ogolubovska@gmail.com, babich@gmail.com, miralla@ukr.net, milde@pharmalog.com, stammer@pharmalog.com, lebed@pharmaxi.com.ua, lutz.mueller@regenold.com, v.margitich@farmak.ua, a.goy@farmak.ua.
RNA Polymerase Inhibitor Enisamium for Treatment of Moderate COVID-19 Patients: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Multicenter, Double-Blind Phase 3 Clinical Trial
Advances in Respiratory Medicine, doi:10.3390/arm92030021
Enisamium is an orally available therapeutic that inhibits influenza A virus and SARS-CoV-2 replication. We evaluated the clinical efficacy of enisamium treatment combined with standard care in adult, hospitalized patients with moderate COVID-19 requiring external oxygen. Hospitalized patients with laboratory-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection were randomly assigned to receive either enisamium (500 mg per dose, four times a day) or a placebo. The primary outcome was an improvement of at least two points on an eight-point severity rating (SR) scale within 29 days of randomization. We initially set out to study the effect of enisamium on patients with a baseline SR of 4 or 5. However, because the study was started early in the COVID-19 pandemic, and COVID-19 had been insufficiently studied at the start of our study, an interim analysis was performed alongside a conditional power analysis in order to ensure patient safety and assess whether the treatment was likely to be beneficial for one or both groups. Following this analysis, a beneficial effect was observed
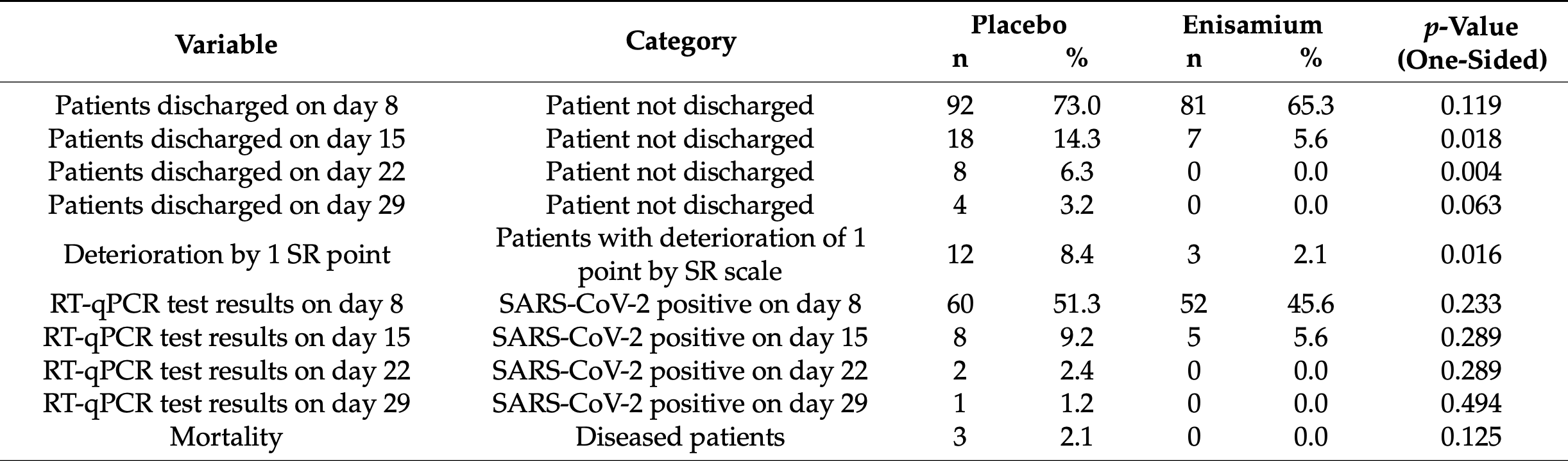
randomization". We observed that on day 15, significantly fewer patients remained in the hospital in the enisamium-treated group compared to the placebo group (5.65% vs. 14.29%; one-sided p = 0.018) (Table 4 , Figure 4A ). On day 22, there were 0% hospitalized patients in the enisamium group compared to 6.3% in the placebo group (0.0% vs. 6.3%; one-sided p = 0.004).
References
Arman, Brun, Hill, Zitzmann, Von Delft, An Update on SARS-CoV-2 Clinical Trial Results-What We Can Learn for the Next Pandemic, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms25010354
Azam, Sulistiana, Ratnawati, Fibriana, Bahrudin et al., Recurrent SARS-CoV-2 RNA Positivity after COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-020-77739-y
Bansode, Singh, Tellis, Chugh, Deshmukh et al., A Comprehensive Molecular and Clinical Investigation of Approved Anti-HCV Drugs Repurposing against SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Glaring Gap between Benchside and Bedside Medicine, Vaccines, doi:10.3390/vaccines11030515
Bauer, Koenig, The Reassessment of Trial Perspectives from Interim Data--a Critical View, Stat. Med, doi:10.1002/sim.2180
Bauer, Köhne, Evaluation of Experiments with Adaptive Interim Analyses, Biometrics, doi:10.2307/2533441
Bege, Borbás, The Design, Synthesis and Mechanism of Action of Paxlovid, a Protease Inhibitor Drug Combination for the Treatment of COVID-19, Pharmaceutics, doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics16020217
Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, Mehta, Zingman et al., Remdesivir for the Treatment of Covid-19-Final Report, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2007764
Boltz, Peng, Muzzio, Dash, Thomas et al., Activity of Enisamium, an Isonicotinic Acid Derivative, against Influenza Viruses in Differentiated Normal Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells, Antivir. Chem. Chemother, doi:10.1177/2040206618811416
Broberg, Sample Size Re-Assessment Leading to a Raised Sample Size Does Not Inflate Type I Error Rate under Mild Conditions, BMC Med. Res. Methodol, doi:10.1186/1471-2288-13-94
Cocking, Cinatl, Boltz, Peng, Johnson et al., Antiviral Effect of a Derivative of Isonicotinic Acid Enisamium Iodide (FAV00A) against Influenza Virus, Acta Virol, doi:10.4149/av_2018_211
Dutta, Naiyer, Mansuri, Soni, Singh et al., COVID-19 Diagnosis: A Comprehensive Review of the RT-qPCR Method for Detection of SARS-CoV-2, Diagnostics, doi:10.3390/diagnostics12061503
Elli, Bojkova, Bechtel, Vial, Boltz et al., Enisamium Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 RNA Synthesis, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines9091254
Gorbalenya, Baker, Baric, De Groot, Drosten et al., The Species Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-Related Coronavirus: Classifying 2019-nCoV and Naming It SARS-CoV-2, Nat. Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41564-020-0695-z
Kalil, Patterson, Mehta, Tomashek, Wolfe et al., Baricitinib plus Remdesivir for Hospitalized Adults with Covid-19, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2031994
Liu, Zhang, Hu, Song, Mei et al., Remdesivir Derivative VV116 Is a Potential Broad-Spectrum Inhibitor of Both Human and Animal Coronaviruses, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v15122295
Moshawih, Jarrar, Bahrin, Lim, Ming et al., Evaluating NSAIDs in SARS-CoV-2: Immunomodulatory Mechanisms and Future Therapeutic Strategies, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e25734
Posthuma, Te, Velthuis, Snijder, Nidovirus RNA Polymerases: Complex Enzymes Handling Exceptional RNA Genomes, Virus Res, doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2017.01.023
Russell, Fairfield, Drake, Turtle, Seaton et al., Secondary Infections, and Antimicrobial Use in Patients Hospitalised with COVID-19 during the First Pandemic Wave from the ISARIC WHO CCP-UK Study: A Multicentre, Prospective Cohort Study, Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/S2666-5247(21)00090-2
Snijder, Decroly, Ziebuhr, The Nonstructural Proteins Directing Coronavirus RNA Synthesis and Processing, Adv. Virus Res, doi:10.1016/bs.aivir.2016.08.008
Snijder, Limpens, De Wilde, Jong, Zevenhoven-Dobbe et al., A Unifying Structural and Functional Model of the Coronavirus Replication Organelle: Tracking down RNA Synthesis, PLoS Biol, doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.3000715
Tanino, Nishioka, Yamamoto, Watanabe, Daidoji et al., Emergence of SARS-CoV-2 with Dual-Drug Resistant Mutations During a Long-Term Infection in a Kidney Transplant Recipient, Infect. Drug Resist, doi:10.2147/IDR.S438915
Urena Neme, Tran, Victoria Guerrero, Roa Gomez, Rodriguez Guerra, A Successful Treatment of COVID-Induced Acute Idiopathic Pancreatitis with an RNA-Polymerase Inhibitor Agent, Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.51992
Velthuis, Arnold, Cameron, Van Den Worm, Snijder, The RNA Polymerase Activity of SARS-Coronavirus Nsp12 Is Primer Dependent, Nucleic Acids Res, doi:10.1093/nar/gkp904
Velthuis, Common and Unique Features of Viral RNA-Dependent Polymerases, Cell Mol. Life Sci, doi:10.1007/s00018-014-1695-z
Velthuis, Zubkova, Shaw, Mehle, Boltz et al., Enisamium Reduces Influenza Virus Shedding and Improves Patient Recovery by Inhibiting Viral RNA Polymerase Activity, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother, doi:10.1128/AAC.02605-20
Velásquez, Hernandez, Galeano, Hincapié-García, Rugeles et al., Effectiveness of Drug Repurposing and Natural Products Against SARS-CoV-2: A Comprehensive Review, Clin. Pharmacol, doi:10.2147/CPAA.S429064
Walker, Fan, Keown, Margitich, Grimes et al., Enisamium Is a Small Molecule Inhibitor of the Influenza A Virus and SARS-CoV-2 RNA Polymerases, BioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.04.21.053017
Yamato, Kinoshita, Miyazawa, Seki, Mizuno et al., Ensitrelvir in Patients with SARS-CoV-2: A Retrospective Chart Review, J. Infect. Chemother, doi:10.1016/j.jiac.2024.02.015
Zhang, Bisht, Flamier, Barrasa, Friesen et al., LINE1-Mediated Reverse Transcription and Genomic Integration of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA Detected in Virus-Infected but Not in Viral mRNA-Transfected Cells, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v15030629
Zhang, Richards, Barrasa, Hughes, Young et al., Reverse-Transcribed SARS-CoV-2 RNA Can Integrate into the Genome of Cultured Human Cells and Can Be Expressed in Patient-Derived Tissues, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.2105968118
Zhou, Yang, Wang, Hu, Zhang et al., A Pneumonia Outbreak Associated with a New Coronavirus of Probable Bat Origin, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/arm92030021",
"ISSN": [
"2543-6031"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/arm92030021",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Enisamium is an orally available therapeutic that inhibits influenza A virus and SARS-CoV-2 replication. We evaluated the clinical efficacy of enisamium treatment combined with standard care in adult, hospitalized patients with moderate COVID-19 requiring external oxygen. Hospitalized patients with laboratory-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection were randomly assigned to receive either enisamium (500 mg per dose, four times a day) or a placebo. The primary outcome was an improvement of at least two points on an eight-point severity rating (SR) scale within 29 days of randomization. We initially set out to study the effect of enisamium on patients with a baseline SR of 4 or 5. However, because the study was started early in the COVID-19 pandemic, and COVID-19 had been insufficiently studied at the start of our study, an interim analysis was performed alongside a conditional power analysis in order to ensure patient safety and assess whether the treatment was likely to be beneficial for one or both groups. Following this analysis, a beneficial effect was observed for patients with an SR of 4 only, i.e., patients with moderate COVID-19 requiring supplementary oxygen. The study was continued for these COVID-19 patients. Overall, a total of 592 patients were enrolled and randomized between May 2020 and March 2021. Patients with a baseline SR of 4 were divided into two groups: 142 (49.8%) were assigned to the enisamium group and 143 (50.2%) to the placebo group. An analysis of the population showed that if patients were treated within 4 days of the onset of COVID-19 symptoms (n = 33), the median time to improvement was 8 days for the enisamium group and 13 days for the placebo group (p = 0.005). For patients treated within 10 days of the onset of COVID-19 symptoms (n = 154), the median time to improvement was 10 days for the enisamium group and 12 days for the placebo group (p = 0.002). Our findings suggest that enisamium is safe to use with COVID-19 patients, and that the observed clinical benefit of enisamium is worth reporting and studying in detail.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"arm92030021"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases, O.O. Bogomolets National Medical University, T. Shevchenko Blvd. 13, 01601 Kyiv, Ukraine"
}
],
"family": "Holubovska",
"given": "Olga",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "State Expert Center, Smolenska Str. 10, 03057 Kyiv, Ukraine"
}
],
"family": "Babich",
"given": "Pavlo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2630-1827",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Respiratory and Other Viral Infections, L.V. Gromashevsky Institute of Epidemiology and Infectious Diseases of the NAMS of Ukraine, Amosova Str. 5a, 03083 Kyiv, Ukraine"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Mironenko",
"given": "Alla",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pharmalog Institut für Klinische Forschung GmbH, Oskar-Messter-Str. 29, 85737 Ismaning, Germany"
}
],
"family": "Milde",
"given": "Jens",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pharmaxi LLC, Filatova Str. 10A, 01042 Kyiv, Ukraine"
}
],
"family": "Lebed",
"given": "Yuriy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pharmalog Institut für Klinische Forschung GmbH, Oskar-Messter-Str. 29, 85737 Ismaning, Germany"
}
],
"family": "Stammer",
"given": "Holger",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3633-1309",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regenold GmbH, Zöllinplatz 4, 79410 Badenweiler, Germany"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Mueller",
"given": "Lutz",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Molecular Biology, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544, USA"
},
{
"name": "Division of Virology, Department of Pathology, University of Cambridge Addenbrooke’s Hospital, Cambridge CB2 2QQ, UK"
}
],
"family": "te Velthuis",
"given": "Aartjan J. W.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Farmak Joint Stock Company, Kyrylivska Str., 04080 Kyiv, Ukraine"
}
],
"family": "Margitich",
"given": "Victor",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Farmak Joint Stock Company, Kyrylivska Str., 04080 Kyiv, Ukraine"
}
],
"family": "Goy",
"given": "Andrew",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Advances in Respiratory Medicine",
"container-title-short": "ARM",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-06T19:09:36Z",
"timestamp": 1715022576000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-06T20:35:20Z",
"timestamp": 1715027720000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100004440",
"award": [
"206579/Z/17/Z"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "joint Welcome Trust and Royal Society"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-07T00:33:18Z",
"timestamp": 1715041998627
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "3",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
6
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "3",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-06T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1714953600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2543-6031/92/3/21/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "202-217",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
6
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
6
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41564-020-0695-z",
"article-title": "The Species Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-Related Coronavirus: Classifying 2019-nCoV and Naming It SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Gorbalenya",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "536",
"journal-title": "Nat. Microbiol.",
"key": "ref_1",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7",
"article-title": "A Pneumonia Outbreak Associated with a New Coronavirus of Probable Bat Origin",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "270",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_2",
"volume": "579",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Effectiveness of Drug Repurposing and Natural Products Against SARS-CoV-2: A Comprehensive Review",
"author": "Hernandez",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Clin. Pharmacol.",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms25010354",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_4",
"unstructured": "Arman, B.Y., Brun, J., Hill, M.L., Zitzmann, N., and von Delft, A. (2023). An Update on SARS-CoV-2 Clinical Trial Results-What We Can Learn for the Next Pandemic. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 25."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiac.2024.02.015",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_5",
"unstructured": "Yamato, M., Kinoshita, M., Miyazawa, S., Seki, M., Mizuno, T., and Sonoyama, T. (2024). Ensitrelvir in Patients with SARS-CoV-2: A Retrospective Chart Review. J. Infect. Chemother., in press."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v15122295",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_6",
"unstructured": "Liu, W., Zhang, M., Hu, C., Song, H., Mei, Y., Liu, Y., and Zhang, Q. (2023). Remdesivir Derivative VV116 Is a Potential Broad-Spectrum Inhibitor of Both Human and Animal Coronaviruses. Viruses, 15."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e25734",
"article-title": "Evaluating NSAIDs in SARS-CoV-2: Immunomodulatory Mechanisms and Future Therapeutic Strategies",
"author": "Moshawih",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e25734",
"journal-title": "Heliyon",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/IDR.S438915",
"article-title": "Emergence of SARS-CoV-2 with Dual-Drug Resistant Mutations During a Long-Term Infection in a Kidney Transplant Recipient",
"author": "Tanino",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "531",
"journal-title": "Infect. Drug Resist.",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/bs.aivir.2016.08.008",
"article-title": "The Nonstructural Proteins Directing Coronavirus RNA Synthesis and Processing",
"author": "Snijder",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "59",
"journal-title": "Adv. Virus Res.",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.03.24.005298",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_10",
"unstructured": "Snijder, E.J., Limpens, R., de Wilde, A.H., de Jong, A.W.M., Zevenhoven-Dobbe, J.C., Maier, H.J., Faas, F., Koster, A.J., and Barcena, M. (2020). A Unifying Structural and Functional Model of the Coronavirus Replication Organelle: Tracking down RNA Synthesis. PLoS Biol., 18."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virusres.2017.01.023",
"article-title": "Nidovirus RNA Polymerases: Complex Enzymes Handling Exceptional RNA Genomes",
"author": "Posthuma",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "58",
"journal-title": "Virus Res.",
"key": "ref_11",
"volume": "234",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00018-014-1695-z",
"article-title": "Common and Unique Features of Viral RNA-Dependent Polymerases",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4403",
"journal-title": "Cell Mol. Life Sci.",
"key": "ref_12",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gkp904",
"article-title": "The RNA Polymerase Activity of SARS-Coronavirus Nsp12 Is Primer Dependent",
"author": "Arnold",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "203",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res.",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/2040206618811416",
"article-title": "Activity of Enisamium, an Isonicotinic Acid Derivative, against Influenza Viruses in Differentiated Normal Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells",
"author": "Boltz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2040206618811416",
"journal-title": "Antivir. Chem. Chemother.",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.02605-20",
"article-title": "Enisamium Reduces Influenza Virus Shedding and Improves Patient Recovery by Inhibiting Viral RNA Polymerase Activity",
"author": "Zubkova",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e02605-20",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob. Agents Chemother.",
"key": "ref_15",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4149/av_2018_211",
"article-title": "Antiviral Effect of a Derivative of Isonicotinic Acid Enisamium Iodide (FAV00A) against Influenza Virus",
"author": "Cocking",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "191",
"journal-title": "Acta Virol.",
"key": "ref_16",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.04.21.053017",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_17",
"unstructured": "Walker, A.P., Fan, H., Keown, J.R., Margitich, V., Grimes, J.M., Fodor, E., and Te Velthuis, A.J.W. (2020). Enisamium Is a Small Molecule Inhibitor of the Influenza A Virus and SARS-CoV-2 RNA Polymerases. BioRxiv."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biomedicines9091254",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_18",
"unstructured": "Elli, S., Bojkova, D., Bechtel, M., Vial, T., Boltz, D., Muzzio, M., Peng, X., Sala, F., Cosentino, C., and Goy, A. (2021). Enisamium Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 RNA Synthesis. Biomedicines, 9."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/sim.2180",
"article-title": "The Reassessment of Trial Perspectives from Interim Data--a Critical View",
"author": "Bauer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "23",
"journal-title": "Stat. Med.",
"key": "ref_19",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2307/2533441",
"article-title": "Evaluation of Experiments with Adaptive Interim Analyses",
"author": "Bauer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1029",
"journal-title": "Biometrics",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "50",
"year": "1994"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2007764",
"article-title": "Remdesivir for the Treatment of Covid-19-Final Report",
"author": "Beigel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1813",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_21",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/diagnostics12061503",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_22",
"unstructured": "Dutta, D., Naiyer, S., Mansuri, S., Soni, N., Singh, V., Bhat, K.H., Singh, N., Arora, G., and Mansuri, M.S. (2022). COVID-19 Diagnosis: A Comprehensive Review of the RT-qPCR Method for Detection of SARS-CoV-2. Diagnostics, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1471-2288-13-94",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_23",
"unstructured": "Broberg, P. (2013). Sample Size Re-Assessment Leading to a Raised Sample Size Does Not Inflate Type I Error Rate under Mild Conditions. BMC Med. Res. Methodol., 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/pharmaceutics16020217",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_24",
"unstructured": "Bege, M., and Borbás, A. (2024). The Design, Synthesis and Mechanism of Action of Paxlovid, a Protease Inhibitor Drug Combination for the Treatment of COVID-19. Pharmaceutics, 16."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/vaccines11030515",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_25",
"unstructured": "Bansode, S., Singh, P.K., Tellis, M., Chugh, A., Deshmukh, N., Gupta, M., Verma, S., Giri, A., Kulkarni, M., and Joshi, R. (2023). A Comprehensive Molecular and Clinical Investigation of Approved Anti-HCV Drugs Repurposing against SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Glaring Gap between Benchside and Bedside Medicine. Vaccines, 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2023.02.10.527906",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_26",
"unstructured": "Zhang, L., Bisht, P., Flamier, A., Barrasa, M.I., Friesen, M., Richards, A., Hughes, S.H., and Jaenisch, R. (2023). LINE1-Mediated Reverse Transcription and Genomic Integration of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA Detected in Virus-Infected but Not in Viral mRNA-Transfected Cells. Viruses, 15."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2105968118",
"article-title": "Reverse-Transcribed SARS-CoV-2 RNA Can Integrate into the Genome of Cultured Human Cells and Can Be Expressed in Patient-Derived Tissues",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e2105968118",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "ref_27",
"volume": "118",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-020-77739-y",
"article-title": "Recurrent SARS-CoV-2 RNA Positivity after COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis",
"author": "Azam",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "20692",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2031994",
"article-title": "Baricitinib plus Remdesivir for Hospitalized Adults with Covid-19",
"author": "Kalil",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "795",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "A Successful Treatment of COVID-Induced Acute Idiopathic Pancreatitis with an RNA-Polymerase Inhibitor Agent",
"author": "Tran",
"first-page": "e51992",
"journal-title": "Cureus",
"key": "ref_30",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2666-5247(21)00090-2",
"article-title": "Co-Infections, Secondary Infections, and Antimicrobial Use in Patients Hospitalised with COVID-19 during the First Pandemic Wave from the ISARIC WHO CCP-UK Study: A Multicentre, Prospective Cohort Study",
"author": "Russell",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e354",
"journal-title": "Lancet Microbe",
"key": "ref_31",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 31,
"references-count": 31,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2543-6031/92/3/21"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "RNA Polymerase Inhibitor Enisamium for Treatment of Moderate COVID-19 Patients: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Multicenter, Double-Blind Phase 3 Clinical Trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "92"
}