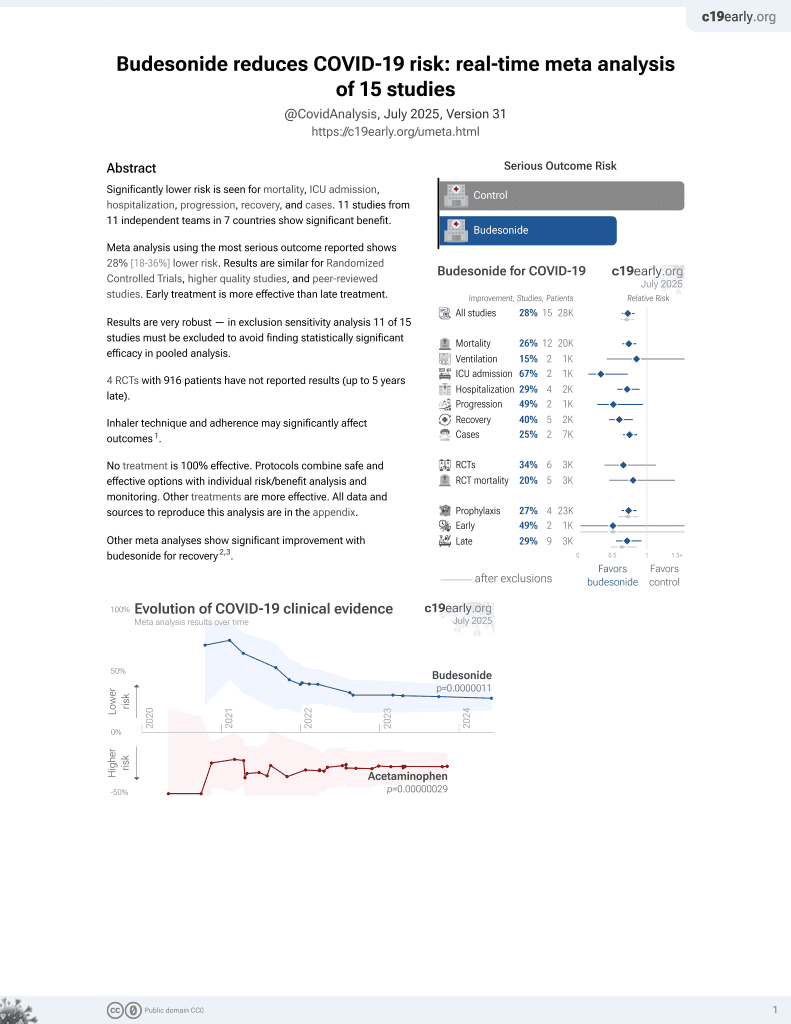
Budesonide for COVID-19
28th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2021, now with p = 0.0000042 from 14 studies, recognized in 10 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
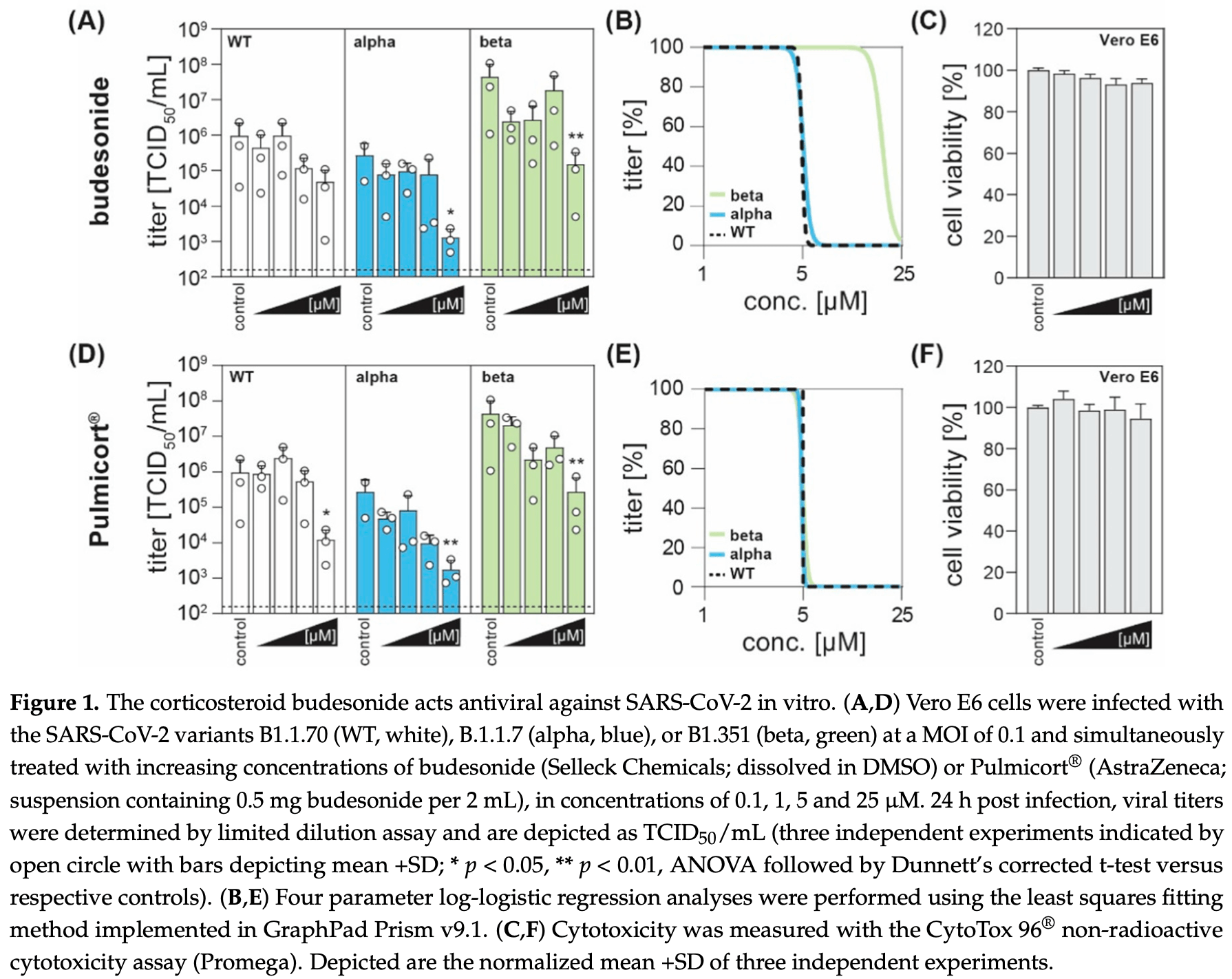
In vitro study showing dose-dependent inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 with budesonide.
3 preclinical studies support the efficacy of budesonide for COVID-19:
Heinen et al., 20 Jul 2021, peer-reviewed, 6 authors.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Antiviral Effect of Budesonide against SARS-CoV-2
Viruses, doi:10.3390/v13071411
Treatment options for COVID-19, a disease caused by Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection, are currently severely limited. Therefore, antiviral drugs that efficiently reduce SARS-CoV-2 replication or alleviate COVID-19 symptoms are urgently needed. Inhaled glucocorticoids are currently being discussed in the context of treatment for COVID-19, partly based on a previous study that reported reduced recovery times in cases of mild COVID-19 after inhalative administration of the glucocorticoid budesonide. Given various reports that describe the potential antiviral activity of glucocorticoids against respiratory viruses, we aimed to analyze a potential antiviral activity of budesonide against SARS-CoV-2 and circulating variants of concern (VOC) B.1.1.7 (alpha) and B.1.351 (beta). We demonstrate a dose-dependent inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 that was comparable between all viral variants tested while cell viability remains unaffected. Our results are encouraging as they could indicate a multimodal mode of action of budesonide against SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19, which could contribute to an improved clinical performance.
Author Contributions: S.P. designed the project; N.H. and T.L.M. performed the experiments; N.H., S.P. and M.K. wrote the manuscript; D.T. evaluated the data; E.S. and S.P. supervised the study. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript. Funding: This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement: Not applicable. Informed Consent Statement: Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement: The data generated and analyzed in this study are included in the article. Viruses 2021, 13, 1411 Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Arabi, Mandourah, Al-Hameed, Sindi, Almekhlafi et al., Corticosteroid Therapy for Critically Ill Patients with Middle East Respiratory Syndrome, Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med, doi:10.1164/rccm.201706-1172OC
Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, Mehta, Zingman et al., Remdesivir for the Treatment of Covid-19-Final Report, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2007764
Chen, Li, Influence of Corticosteroid Dose on Viral Shedding Duration in Patients With COVID-19, Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa832
Davies, Carroll, Li, Poh, Kirkegard et al., Budesonide and formoterol reduce early innate anti-viral immune responses in vitro, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0027898
Deliloglu, Tuzun, Cengiz, Ozkan, Duman, Endotracheal Surfactant Combined With Budesonide for Neonatal ARDS, Front. Pediatr, doi:10.3389/fped.2020.00210
Ding, Feng, Chen, Yuan, Yi et al., Effect of Corticosteroid Therapy on the Duration of SARS-CoV-2 Clearance in Patients with Mild COVID-19: A Retrospective Cohort Study, Infect. Dis. Ther, doi:10.1007/s40121-020-00337-y
Gibson, Saltos, Fakes, Acute anti-inflammatory effects of inhaled budesonide in asthma: A randomized controlled trial, Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med, doi:10.1164/ajrccm.163.1.9807061
Halpin, Faner, Sibila, Badia, Agusti, Do chronic respiratory diseases or their treatment affect the risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection?, Lancet Respir. Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30167-3
Horby, Lim, Emberson, Mafham, Bell et al., Dexamethasone in Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2021436
Kelly, Busse, Jarjour, Inhaled budesonide decreases airway inflammatory response to allergen, Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med, doi:10.1164/ajrccm.162.3.9910077
Kim, Song, Ahn, Lee, Ahn et al., Antiviral and anti-inflammatory activity of budesonide against human rhinovirus infection mediated via autophagy activation, Antiviral Res, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2018.01.012
Li, Hu, Song, High-dose but Not Low-dose Corticosteroids Potentially Delay Viral Shedding of Patients With COVID-19, Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa829
Matsuyama, Kawase, Nao, Shirato, Ujike et al., The Inhaled Steroid Ciclesonide Blocks SARS-CoV-2 RNA Replication by Targeting the Viral Replication-Transcription Complex in Cultured Cells, J. Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.01648-20
Mendes, Rebolledo, Campos, Wanner, Immediate antiinflammatory effects of inhaled budesonide in patients with asthma, Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc, doi:10.1513/AnnalsATS.201307-220OC
Mohamed, Meguid, Effect of nebulized budesonide on respiratory mechanics and oxygenation in acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome: Randomized controlled study, Saudi J. Anaesth, doi:10.4103/1658-354X.197369
Ramakrishnan, Nicolau, Langford, Mahdi, Jeffers et al., Inhaled budesonide in the treatment of early COVID-19 (STOIC): A phase 2, open-label, randomised controlled trial, Lancet Respir. Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00160-0
Sterne, Murthy, Diaz, Slutsky, Villar et al., Association Between Administration of Systemic Corticosteroids and Mortality Among Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19: A Meta-analysis, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.17023
Szafranski, Cukier, Ramirez, Menga, Sansores et al., Efficacy and safety of budesonide/formoterol in the management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, Eur. Respir. J, doi:10.1183/09031936.03.00031402
Torres Acosta, Singer, Pathogenesis of COVID-19-induced ARDS: Implications for an ageing population, Eur. Respir. J, doi:10.1183/13993003.02049-2020
Wang, Zhang, Du, Du, Zhao et al., Remdesivir in adults with severe COVID-19: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31022-9
Yamaya, Nishimura, Deng, Sugawara, Watanabe et al., Inhibitory effects of glycopyrronium, formoterol, and budesonide on coronavirus HCoV-229E replication and cytokine production by primary cultures of human nasal and tracheal epithelial cells, Respir. Investig, doi:10.1016/j.resinv.2019.12.005
Zetterström, Buhl, Mellem, Perpiñá, Hedman et al., Improved asthma control with budesonide/formoterol in a single inhaler, compared with budesonide alone, Eur. Respir. J, doi:10.1183/09031936.01.00065801
Zhou, Dejnirattisai, Supasa, Liu, Mentzer et al., Evidence of escape of SARS-CoV-2 variant B.1.351 from natural and vaccine-induced sera, Cell
Zhu, Zhang, Wang, Li, Yang et al., A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2001017
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v13071411",
"ISSN": [
"1999-4915"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/v13071411",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Treatment options for COVID-19, a disease caused by Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection, are currently severely limited. Therefore, antiviral drugs that efficiently reduce SARS-CoV-2 replication or alleviate COVID-19 symptoms are urgently needed. Inhaled glucocorticoids are currently being discussed in the context of treatment for COVID-19, partly based on a previous study that reported reduced recovery times in cases of mild COVID-19 after inhalative administration of the glucocorticoid budesonide. Given various reports that describe the potential antiviral activity of glucocorticoids against respiratory viruses, we aimed to analyze a potential antiviral activity of budesonide against SARS-CoV-2 and circulating variants of concern (VOC) B.1.1.7 (alpha) and B.1.351 (beta). We demonstrate a dose-dependent inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 that was comparable between all viral variants tested while cell viability remains unaffected. Our results are encouraging as they could indicate a multimodal mode of action of budesonide against SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19, which could contribute to an improved clinical performance.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"v13071411"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-0906-5073",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Heinen",
"given": "Natalie",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8962-9443",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Meister",
"given": "Toni Luise",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7707-2040",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Klöhn",
"given": "Mara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Steinmann",
"given": "Eike",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3564-1014",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Todt",
"given": "Daniel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pfaender",
"given": "Stephanie",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Viruses",
"container-title-short": "Viruses",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-20T15:26:10Z",
"timestamp": 1626794770000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-20T17:18:23Z",
"timestamp": 1626801503000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-06T22:35:51Z",
"timestamp": 1715034951723
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 14,
"issue": "7",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
20
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "7",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-20T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1626739200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1999-4915/13/7/1411/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1411",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
20
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
20
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001017",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref1"
},
{
"key": "ref2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31022-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref3"
},
{
"key": "ref4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2007764",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2021.02.037",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref6"
},
{
"key": "ref7",
"unstructured": "COG-UK report on SARS-CoV-2 Spike mutations of interestin the UK\nhttps://www.cogconsortium.uk/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/Report-2_COG-UK_SARS-CoV-2-Mutations.pdf"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00160-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30167-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/09031936.01.00065801",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref10"
},
{
"key": "ref11",
"unstructured": "Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention\nhttps://ginasthma.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/04/GINA-2021-Main-Report_FINAL_21_04_28-WMS.pdf"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/09031936.03.00031402",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref12"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2018.01.012",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.01648-20",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.resinv.2019.12.005",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref15"
},
{
"key": "ref16",
"unstructured": "Therapeutics and COVID-19\nhttps://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/336729/WHO-2019-nCov-remdesivir-2020.1-eng.pdf"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40121-020-00337-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa832",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref18"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.201706-1172OC",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref19"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa829",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.17023",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref21"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021436",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref22"
},
{
"key": "ref23"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.02049-2020",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref24"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fped.2020.00210",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref25"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/1658-354X.197369",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref26"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0027898",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref27"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/ajrccm.163.1.9807061",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref28"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/ajrccm.162.3.9910077",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref29"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1513/AnnalsATS.201307-220OC",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref30"
}
],
"reference-count": 30,
"references-count": 30,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1999-4915/13/7/1411"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Antiviral Effect of Budesonide against SARS-CoV-2",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "13"
}