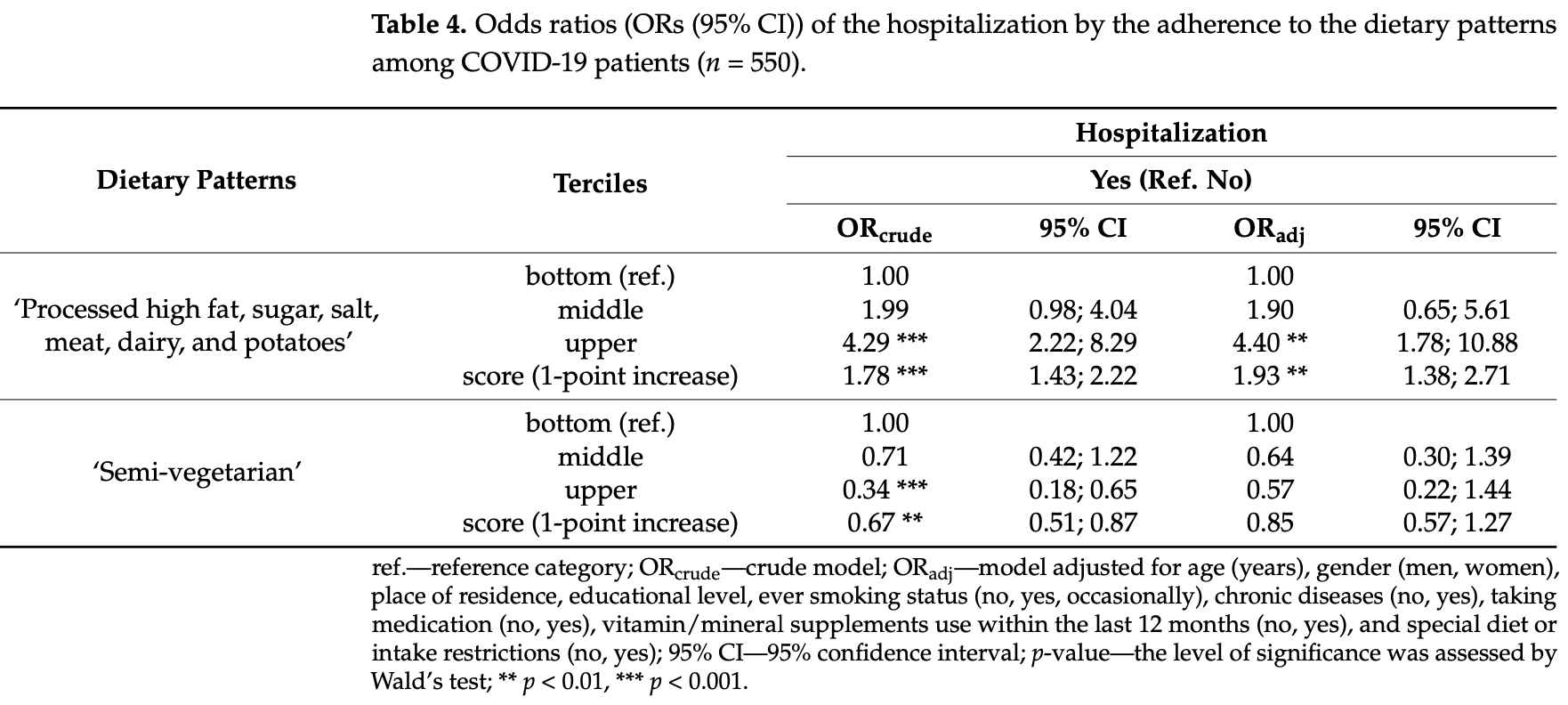
Associations Between Dietary Patterns and the Occurrence of Hospitalization and Gastrointestinal Disorders—A Retrospective Study of COVID-19 Patients
et al., Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu17050800, Feb 2025
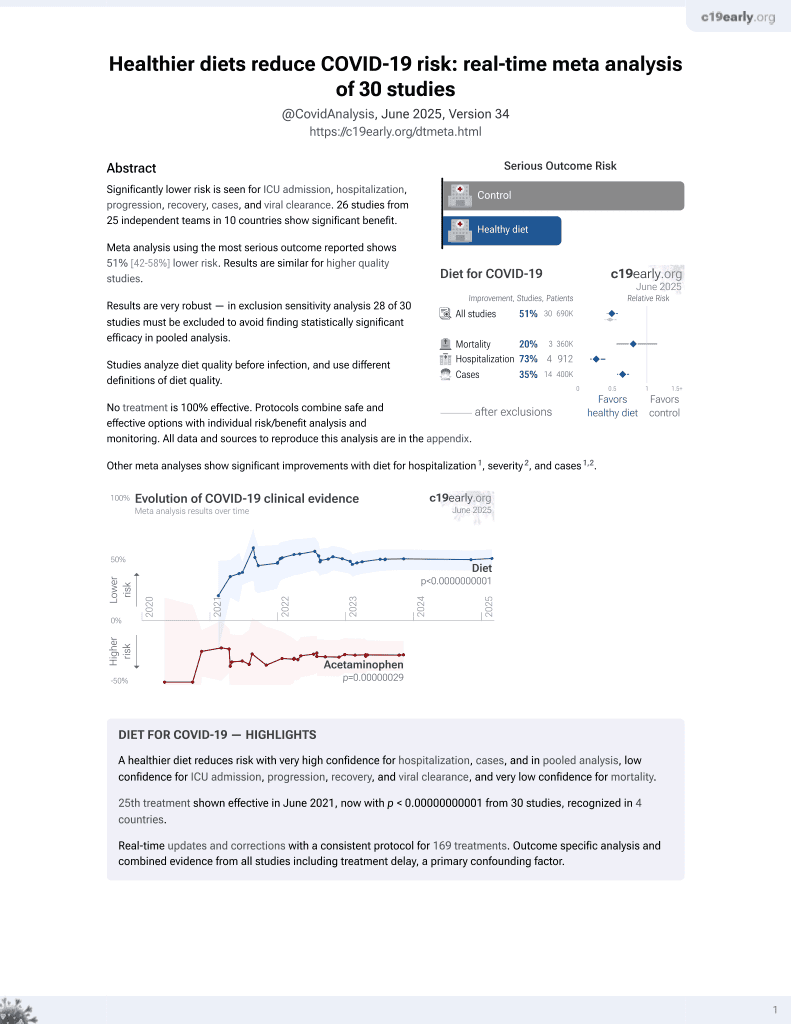
Diet for COVID-19
26th treatment shown to reduce risk in
June 2021, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 30 studies, recognized in 4 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 550 COVID-19 patients in Poland showing that higher adherence to a processed food dietary pattern was associated with 4.4 times higher odds of hospitalization.
|
risk of hospitalization, 77.3% lower, OR 0.23, p = 0.001, higher quality diet 183, lower quality diet 183, inverted to make OR<1 favor higher quality diet, lower vs. upper tertile processed high fat, sugar, salt, meat, dairy, and potatoes, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Hawryłkowicz et al., 26 Feb 2025, retrospective, Poland, peer-reviewed, mean age 41.2, 7 authors, study period December 2021 - June 2022.
Contact: beata.stasiewicz@uwm.edu.pl (corresponding author), viktoria.hawrylkowicz@pum.edu.pl, 67392@student.pum.edu.pl, wiktoria.krauze00@gmail.com, kamila.rachubinska@pum.edu.pl, elzbieta.grochans@pum.edu.pl, ewa.stachowska@pum.edu.pl.
Associations Between Dietary Patterns and the Occurrence of Hospitalization and Gastrointestinal Disorders—A Retrospective Study of COVID-19 Patients
Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu17050800
During the COVID-19 pandemic, dietary habits in the population changed and sometimes deviated from healthy eating patterns, such as the Mediterranean diet. Based on reports on the quality of the diet of respondents to studies conducted at the beginning of the pandemic, it could be concluded that these new dietary habits are unfavorable for a good prognosis and the course of any disease and its severity of symptoms. This study decided to confront these assumptions with the results of people who had COVID-19. Background/Objectives: This study aimed to assess the associations between dietary patterns and the occurrence of hospitalization and gastrointestinal disorders among patients diagnosed with COVID-19. Methods: This study included 550 respondents who completed a survey up to 8 months after being diagnosed with COVID-19. The survey included 62 items from the FFQ-6 ® , GSRS, PAC-SYM and FACT-G7 standardized questionnaires. Results: Two dietary patterns (DPs) were identified: 'Processed high fat/sugar/salt/meat/dairy/potatoes' and 'Semi-vegetarian'. Higher adherence to the 'Processed' DP was associated with higher odds of hospitalization due to COVID-19, a more severe course of the disease, and the highest intensity of gastrointestinal symptoms. Higher adherence to the 'Semi-vegetarian' DP was associated with lower odds of hospitalization due to COVID-19, a less severe course of the disease, and the lowest intensity of gastrointestinal symptoms. Conclusions: This study showed a strong harmful effect of high adherence to a processed dietary pattern on an increased incidence of hospitalization and gastrointestinal disorders among northwestern Polish adults during the COVID-19 pandemic, emphasizing the importance of a healthy diet.
consumption of highly processed foods and increase the quality of the diet by choosing mainly plant-based diets with added fish and a limited amount of meat. These dietary models are called Semi-vegetarian or Mediterranean, and they contain all nutrients, which makes them balanced and valuable.
Supplementary Materials: The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/nu17050800/s1 . Table S1 : Description of 23 food groups aggregated: data based on the 62-item FFQ-6 ® ; Table S2 : The mean (95% CI) of the frequency of food consumption by dietary patterns among the COVID-19 patients (times/day); Table S3 : The mean (SD) of the selected gastric scales by hospitalization among the COVID-19 patients; Table S4 : The sample characteristics by dietary patterns among the COVID-19 patients (%) or mean (SD); Table S5 Informed Consent Statement: All subjects gave their written informed consent for participation in this study.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
Armitage, Berry, Matthews, Statistical Methods in Medical Research
Balta, Papathanasiou, Christopoulos, Specialized Pro-Resolving Mediators as Potential Regulators of Inflammatory Macrophage Responses in COVID-19, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.632238
Barber, Mego, Sabater, Vallejo, Bendezu et al., Differential Effects of Western and Mediterranean-Type Diets on Gut Microbiota: A Metagenomics and Metabolomics Approach, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13082638
Barberio, Judge, Savarino, Ford, Global Prevalence of Functional Constipation According to the Rome Criteria: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol, doi:10.1016/S2468-1253(21)00111-4
Baroni, Bonetto, Solinas, Visaggi, Galchenko et al., Diets Including Animal Food Are Associated with Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease, Eur. J. Investig. Health Psychol. Educ, doi:10.3390/ejihpe13120189
Barrett, Youssef, Shah, Ioana, Lawati et al., Vitamin D Status and Mortality from SARS CoV-2: A Prospective Study of Unvaccinated Caucasian Adults, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14163252
Bo, Bernardi, Cherubini, Porrini, Gargari et al., A Polyphenol-Rich Dietary Pattern Improves Intestinal Permeability, Evaluated as Serum Zonulin Levels, in Older Subjects: The MaPLE Randomised Controlled Trial, Clin. Nutr. Edinb. Scotl, doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2020.12.014
Bonaccio, Costanzo, Ruggiero, Persichillo, Esposito et al., Changes in ultra-processed food consumption during the first Italian lockdown following the COVID-19 pandemic and major correlates: Results from two population-based cohorts, Public Health Nutr, doi:10.1017/S1368980021000999
Cagnina, Duvall, Nijmeh, Levy, Specialized Pro-Resolving Mediators in Respiratory Diseases, Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care, doi:10.1097/MCO.0000000000000805
Calder, Carr, Gombart, Eggersdorfer, Optimal Nutritional Status for a Well-Functioning Immune System Is an Important Factor to Protect against Viral Infections, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12041181
Chen, Lu, Shen, Xu, Chen et al., Associations between pre-infection serum vitamin D concentrations and Omicron COVID-19 incidence, severity and reoccurrence in elderly individuals, Public Health Nutr, doi:10.1017/S1368980024001873
Chey, Chey, Jackson, Eswaran, Exploratory Comparative Effectiveness Trial of Green Kiwifruit, Psyllium, or Prunes in US Patients with Chronic Constipation, Am. J. Gastroenterol, doi:10.14309/ajg.0000000000001149
Chooi, Zhang, Magkos, Ng, Michael et al., Effect of an Asian-Adapted Mediterranean Diet and Pentadecanoic Acid on Fatty Liver Disease: The TANGO Randomized Controlled Trial, Am. J. Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1016/j.ajcnut.2023.11.013
Cioboata, Vasile, Bălteanu, Georgescu, Toma et al., Evaluating Serum Calcium and Magnesium Levels as Predictive Biomarkers for Tuberculosis and COVID-19 Severity: A Romanian Prospective Study, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms25010418
Clemente-Suárez, Beltrán-Velasco, Redondo-Flórez, Martín-Rodríguez, Tornero-Aguilera, Global Impacts of Western Diet and Its Effects on Metabolism and Health: A Narrative Review, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15122749
Da Glı, Kalkan, The Role of Lifestyle Changes in Gastroesophageal Reflux Diseases Treatment, Turk. J. Gastroenterol. Off. J. Turk. Soc. Gastroenterol, doi:10.5152/tjg.2017.10
Da Silva Oliveira, Vieira, De Souza, Noll, Bezerra et al., Consumption of Ultra-Processed Foods in the Brazilian Amazon during COVID-19, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu16132117
Damayanthi, Prabani, Nutritional determinants and COVID-19 outcomes of older patients with COVID-19: A systematic review, Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr, doi:10.1016/j.archger.2021.104411
Di Giosia, Stamerra, Giorgini, Jamialahamdi, Butler et al., The Role of Nutrition in Inflammaging, Ageing Res. Rev, doi:10.1016/j.arr.2022.101596
Duncanson, Williams, Hoedt, Collins, Keely et al., Diet-Microbiota Associations in Gastrointestinal Research: A Systematic Review, Gut Microbes, doi:10.1080/19490976.2024.2350785
Eusurvey-Welcome, None
Fao, Dietary Assessment: A Resource Guide to Method Selection and Application in Low Resource Settings
Frank, Kleinman, Farup, Taylor, Miner, Psychometric Validation of a Constipation Symptom Assessment Questionnaire, Scand. J. Gastroenterol, doi:10.1080/003655299750025327
García-Montero, Fraile-Martínez, Gómez-Lahoz, Pekarek, Castellanos et al., Nutritional Components in Western Diet Versus Mediterranean Diet at the Gut Microbiota-Immune System Interplay. Implications for Health and Disease, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13020699
Gombart, Pierre, Maggini, A Review of Micronutrients and the Immune System-Working in Harmony to Reduce the Risk of Infection, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12010236
Gracia Aznar, Moreno Egea, Gracia Banzo, Gutierrez, Rizo et al., Pro-Resolving Inflammatory Effects of a Marine Oil Enriched in Specialized Pro-Resolving Mediators (SPMs) Supplement and Its Implication in Patients with Post-COVID Syndrome (PCS), Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines12102221
Gu, Han, Wang, COVID-19: Gastrointestinal Manifestations and Potential Fecal-Oral Transmission, Gastroenterology, doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.02.054
Guasch-Ferré, Willett, The Mediterranean Diet and Health: A Comprehensive Overview, J. Intern. Med, doi:10.1111/joim.13333
Han, Duan, Zhang, Spiegel, Shi et al., Digestive Symptoms in COVID-19 Patients With Mild Disease Severity: Clinical Presentation, Stool Viral RNA Testing, and Outcomes, Am. J. Gastroenterol, doi:10.14309/ajg.0000000000000664
Huang, Wang, Li, Ren, Zhao et al., Clinical Features of Patients Infected with 2019 Novel Coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet Lond. Engl, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5
Johnson, Clockston, Fremling, Clark, Lundeberg et al., Changes in Adults' Eating Behaviors During the Initial Months of the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Narrative Review, J. Acad. Nutr. Diet, doi:10.1016/j.jand.2022.08.132
Kami Ński, Łoniewski, Misera, Marlicz, Heartburn-Related Internet Searches and Trends of Interest across Six Western Countries: A Four-Year Retrospective Analysis Using Google Ads Keyword Planner, Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, doi:10.3390/ijerph16234591
Kariyawasam, Jayarajah, Riza, Abeysuriya, Seneviratne, Gastrointestinal Manifestations in COVID-19, Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg, doi:10.1093/trstmh/trab042
Khavandegar, Heidarzadeh, Angoorani, Hasani-Ranjbar, Ejtahed et al., Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet Can Beneficially Affect the Gut Microbiota Composition: A Systematic Review, BMC Med. Genom, doi:10.1186/s12920-024-01861-3
Kim, Complex Regulatory Effects of Gut Microbial Short-Chain Fatty Acids on Immune Tolerance and Autoimmunity, Cell. Mol. Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41423-023-00987-1
Kulich, Madisch, Pacini, Piqué, Regula et al., Reliability and Validity of the Gastrointestinal Symptom Rating Scale (GSRS) and Quality of Life in Reflux and Dyspepsia (QOLRAD) Questionnaire in Dyspepsia: A Six-Country Study, Health Qual. Life Outcomes, doi:10.1186/1477-7525-6-12
Lacy, Carter, Weiss, Crowell, The Effects of Intraduodenal Nutrient Infusion on Serum CCK, LES Pressure, and Gastroesophageal Reflux, Neurogastroenterol. Motil, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2982.2011.01701.x
Lai, Li, He, Chen, Mi et al., Effects of Dietary Fibers or Probiotics on Functional Constipation Symptoms and Roles of Gut Microbiota: A Double-Blinded Randomized Placebo Trial, Gut Microbes, doi:10.1080/19490976.2023.2197837
Lechien, Bobin, Mouawad, Zelenik, Calvo-Henriquez et al., Development of Scores Assessing the Refluxogenic Potential of Diet of Patients with Laryngopharyngeal Reflux, Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol, doi:10.1007/s00405-019-05631-1
Losno, Sieferle, Perez-Cueto, Ritz, Vegan Diet and the Gut Microbiota Composition in Healthy Adults, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13072402
Lu, Zhao, Li, Niu, Yang et al., Genomic Characterisation and Epidemiology of 2019 Novel Coronavirus: Implications for Virus Origins and Receptor Binding, Lancet Lond. Engl, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30251-8
López-Taboada, González-Pardo, Conejo, Western Diet: Implications for Brain Function and Behavior, Front. Psychol, doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2020.564413
Malesza, Malesza, Walkowiak, Mussin, Walkowiak et al., High-Fat, Western-Style Diet, Systemic Inflammation, and Gut Microbiota: A Narrative Review, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells10113164
Mardi, Kamran, Pourfarzi, Zare, Hajipour et al., Potential of Macronutrients and Probiotics to Boost Immunity in Patients with SARS-COV-2: A Narrative Review, Front. Nutr, doi:10.3389/fnut.2023.1161894
Mignogna, Costanzo, Ghulam, Cerletti, Donati et al., Impact of Nationwide Lockdowns Resulting from the First Wave of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Food Intake, Eating Behaviors, and Diet Quality: A Systematic Review, Adv. Nutr, doi:10.1093/advances/nmab130
Mitsou, Kakali, Antonopoulou, Mountzouris, Yannakoulia et al., Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet Is Associated with the Gut Microbiota Pattern and Gastrointestinal Characteristics in an Adult Population, Br. J. Nutr, doi:10.1017/S0007114517001593
Muscogiuri, Pugliese, Barrea, Savastano, Colao et al., Obesity: The "Achilles Heel" for COVID-19?, Metabolism, doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154251
Nag, Martin, Mladsi, Olayinka-Amao, Purser et al., The Humanistic and Economic Burden of Chronic Idiopathic Constipation in the USA: A Systematic Literature Review, Clin. Exp. Gastroenterol, doi:10.2147/CEG.S239205
Niedzwiedzka, Wadolowska, Kowalkowska, Reproducibility of A Non-Quantitative Food Frequency Questionnaire (62-Item FFQ-6) and PCA-Driven Dietary Pattern Identification in 13-21-Year-Old Females, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu11092183
Pan, Mu, Yang, Sun, Wang et al., Clinical Characteristics of COVID-19 Patients With Digestive Symptoms in Hubei, China: A Descriptive, Cross-Sectional, Multicenter Study, Am. J. Gastroenterol, doi:10.14309/ajg.0000000000000620
Perez-Araluce, Martinez-Gonzalez, Fernandez-Lazaro, Bes-Rastrollo, Gea et al., Mediterranean diet and the risk of COVID-19 in the 'Seguimiento Universidad de Navarra' cohort, Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2021.04.001
Rahmati, Fatemi, Yon, .; Won, Lee et al., The effect of adherence to high-quality dietary pattern on COVID-19 outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.28298
Rashidah, Lim, Neoh, Majeed, Tan et al., Differential Gut Microbiota and Intestinal Permeability between Frail and Healthy Older Adults: A Systematic Review, Ageing Res. Rev, doi:10.1016/j.arr.2022.101744
Ruiz-Roso, Knott-Torcal, Matilla-Escalante, Garcimartín, Sampedro-Nuñez et al., COVID-19 Lockdown and Changes of the Dietary Pattern and Physical Activity Habits in a Cohort of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12082327
Schloss, Nutritional Deficiencies That May Predispose to Long COVID, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-023-01183-3
Sedighiyan, Abdollahi, Karimi, Badeli, Erfanian et al., Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Supplementation Improve Clinical Symptoms in Patients with Covid-19: A Randomised Clinical Trial, Int. J. Clin. Pract, doi:10.1111/ijcp.14854
Sidor, Rzymski, Dietary Choices and Habits during COVID-19 Lockdown: Experience from Poland, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12061657
Singh, Chang, Yan, Lee, Ucmak et al., Influence of Diet on the Gut Microbiome and Implications for Human Health, J. Transl. Med, doi:10.1186/s12967-017-1175-y
Svedlund, Sjödin, Dotevall, GSRS--a Clinical Rating Scale for Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Peptic Ulcer Disease, Dig. Dis. Sci, doi:10.1007/BF01535722
Taha, Shaarawy, Omar, Abouelmagd, Shalma et al., Effect of Omega-3 Fatty Acids Supplementation on Serum Level of C-Reactive Protein in Patients with COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials, J. Transl. Med, doi:10.1186/s12967-022-03604-3
Taraszewska, Risk Factors for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Symptoms Related to Lifestyle and Diet, Rocz. Panstw. Zakl. Hig, doi:10.32394/rpzh.2021.0145
Tassakos, Kloppman, Chun, Louie, The Impact of Diet Quality on COVID-19 Severity and Outcomes-A Scoping Review, Curr. Nutr. Rep, doi:10.1007/s13668-025-00618-3
Thompson, Subar, Assessment Methods for Research and Practice, doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-802928-2.00001-1
Toubal, Kiaf, Beaudoin, Cagninacci, Rhimi et al., Mucosal-Associated Invariant T Cells Promote Inflammation and Intestinal Dysbiosis Leading to Metabolic Dysfunction during Obesity, Nat. Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-020-17307-0
Trujillo-Mayol, Guerra-Valle, Casas-Forero, Sobral, Viegas et al., Western Dietary Pattern Antioxidant Intakes and Oxidative Stress: Importance During the SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19 Pandemic, Adv. Nutr, doi:10.1093/advances/nmaa171
Vogel-González, Talló-Parra, Herrera-Fernández, Pérez-Vilaró, Chillón et al., Low Zinc Levels at Admission Associates with Poor Clinical Outcomes in SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13020562
Vriesman, Koppen, Camilleri, Di Lorenzo, Benninga, Management of Functional Constipation in Children and Adults, Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol, doi:10.1038/s41575-019-0222-y
Wang, Li, Zhang, Liu, Liu, Are Gastrointestinal Symptoms Associated with Higher Risk of Mortality in COVID-19 Patients? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, BMC Gastroenterol, doi:10.1186/s12876-022-02132-0
Who, Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard
Xiao, Tang, Zheng, Liu, Li et al., Evidence for Gastrointestinal Infection of SARS-CoV-2, Gastroenterology, doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.02.055
Yan, Zhang, Li, Xia, Guo et al., Structural Basis for the Recognition of SARS-CoV-2 by Full-Length Human ACE2, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abb2762
Yanez, Pearman, Lis, Beaumont, Cella, The FACT-G7: A Rapid Version of the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-General (FACT-G) for Monitoring Symptoms and Concerns in Oncology Practice and Research, Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol, doi:10.1093/annonc/mds539
Yiannakou, Tack, Piessevaux, Dubois, Quigley et al., The PAC-SYM Questionnaire for Chronic Constipation: Defining the Minimal Important Difference, Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther, doi:10.1111/apt.14349
Younesian, Khodabakhshi, Abdolahi, Norouzi, Behnampour et al., Decreased Serum Selenium Levels of COVID-19 Patients in Comparison with Healthy Individuals, Biol. Trace Elem. Res, doi:10.1007/s12011-021-02797-w
Zhang, Hou, Huang, Chen, Liu, Dietary and Lifestyle Factors Related to Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: A Systematic Review, Ther. Clin. Risk Manag, doi:10.2147/TCRM.S296680
Zhao, Zhan, Wang, Wang, The Relationship Between Plant-Based Diet and Risk of Digestive System Cancers: A Meta-Analysis Based on 3,059,009 Subjects, Front. Public Health, doi:10.3389/fpubh.2022.892153
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu17050800",
"ISSN": [
"2072-6643"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/nu17050800",
"abstract": "<jats:p>During the COVID-19 pandemic, dietary habits in the population changed and sometimes deviated from healthy eating patterns, such as the Mediterranean diet. Based on reports on the quality of the diet of respondents to studies conducted at the beginning of the pandemic, it could be concluded that these new dietary habits are unfavorable for a good prognosis and the course of any disease and its severity of symptoms. This study decided to confront these assumptions with the results of people who had COVID-19. Background/Objectives: This study aimed to assess the associations between dietary patterns and the occurrence of hospitalization and gastrointestinal disorders among patients diagnosed with COVID-19. Methods: This study included 550 respondents who completed a survey up to 8 months after being diagnosed with COVID-19. The survey included 62 items from the FFQ-6®, GSRS, PAC-SYM and FACT-G7 standardized questionnaires. Results: Two dietary patterns (DPs) were identified: ‘Processed high fat/sugar/salt/meat/dairy/potatoes’ and ‘Semi-vegetarian’. Higher adherence to the ‘Processed’ DP was associated with higher odds of hospitalization due to COVID-19, a more severe course of the disease, and the highest intensity of gastrointestinal symptoms. Higher adherence to the ‘Semi-vegetarian’ DP was associated with lower odds of hospitalization due to COVID-19, a less severe course of the disease, and the lowest intensity of gastrointestinal symptoms. Conclusions: This study showed a strong harmful effect of high adherence to a processed dietary pattern on an increased incidence of hospitalization and gastrointestinal disorders among northwestern Polish adults during the COVID-19 pandemic, emphasizing the importance of a healthy diet.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"nu17050800"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8975-8824",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Human Nutrition and Metabolomics, Faculty of Health Sciences, Pomeranian Medical University in Szczecin, Broniewskiego 24, 71-460 Szczecin, Poland"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Hawryłkowicz",
"given": "Viktoria",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0718-9101",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Human Nutrition, The Faculty of Food Science, University of Warmia and Mazury in Olsztyn, Sloneczna 45f, 10-718 Olsztyn, Poland"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Stasiewicz",
"given": "Beata",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Human Nutrition and Metabolomics, Faculty of Health Sciences, Pomeranian Medical University in Szczecin, Broniewskiego 24, 71-460 Szczecin, Poland"
}
],
"family": "Korus",
"given": "Sebastian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Human Nutrition and Metabolomics, Faculty of Health Sciences, Pomeranian Medical University in Szczecin, Broniewskiego 24, 71-460 Szczecin, Poland"
}
],
"family": "Krauze",
"given": "Wiktoria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2200-3766",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Nursing, Faculty of Health Sciences, Pomeranian Medical University in Szczecin, 71-210 Szczecin, Poland"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Rachubińska",
"given": "Kamila",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3679-7002",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Nursing, Faculty of Health Sciences, Pomeranian Medical University in Szczecin, 71-210 Szczecin, Poland"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Grochans",
"given": "Elżbieta",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4009-1977",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Human Nutrition and Metabolomics, Faculty of Health Sciences, Pomeranian Medical University in Szczecin, Broniewskiego 24, 71-460 Szczecin, Poland"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Stachowska",
"given": "Ewa",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Nutrients",
"container-title-short": "Nutrients",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-26T13:28:31Z",
"timestamp": 1740576511000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-26T13:46:48Z",
"timestamp": 1740577608000
},
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"WNoZ 330-05/S/2024"
],
"name": "Pomeranian Medical University in Szczecin, Poland"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-27T05:23:58Z",
"timestamp": 1740633838834,
"version": "3.38.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "5",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
26
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "5",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-26T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1740528000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/17/5/800/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "800",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
26
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
26
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"key": "ref_1",
"unstructured": "WHO (2023, November 26). Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"article-title": "Clinical Features of Patients Infected with 2019 Novel Coronavirus in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "497",
"journal-title": "Lancet Lond. Engl.",
"key": "ref_2",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2020.02.055",
"article-title": "Evidence for Gastrointestinal Infection of SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Xiao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1831",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "158",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2020.02.054",
"article-title": "COVID-19: Gastrointestinal Manifestations and Potential Fecal–Oral Transmission",
"author": "Gu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1518",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "ref_4",
"volume": "158",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.14309/ajg.0000000000000664",
"article-title": "Digestive Symptoms in COVID-19 Patients With Mild Disease Severity: Clinical Presentation, Stool Viral RNA Testing, and Outcomes",
"author": "Han",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "916",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Gastroenterol.",
"key": "ref_5",
"volume": "115",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.14309/ajg.0000000000000620",
"article-title": "Clinical Characteristics of COVID-19 Patients With Digestive Symptoms in Hubei, China: A Descriptive, Cross-Sectional, Multicenter Study",
"author": "Pan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "766",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Gastroenterol.",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "115",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12876-022-02132-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_7",
"unstructured": "Wang, Y., Li, Y., Zhang, Y., Liu, Y., and Liu, Y. (2022). Are Gastrointestinal Symptoms Associated with Higher Risk of Mortality in COVID-19 Patients? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Gastroenterol., 22."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30251-8",
"article-title": "Genomic Characterisation and Epidemiology of 2019 Novel Coronavirus: Implications for Virus Origins and Receptor Binding",
"author": "Lu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "565",
"journal-title": "Lancet Lond. Engl.",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abb2762",
"article-title": "Structural Basis for the Recognition of SARS-CoV-2 by Full-Length Human ACE2",
"author": "Yan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1444",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "367",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/trstmh/trab042",
"article-title": "Gastrointestinal Manifestations in COVID-19",
"author": "Kariyawasam",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1362",
"journal-title": "Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg.",
"key": "ref_10",
"volume": "115",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10787-023-01183-3",
"article-title": "Nutritional Deficiencies That May Predispose to Long COVID",
"author": "Schloss",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "573",
"journal-title": "Inflammopharmacology",
"key": "ref_11",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12010236",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_12",
"unstructured": "Gombart, A.F., Pierre, A., and Maggini, S. (2020). A Review of Micronutrients and the Immune System–Working in Harmony to Reduce the Risk of Infection. Nutrients, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.20944/preprints202407.2492.v1",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_13",
"unstructured": "Gracia Aznar, A., Moreno Egea, F., Gracia Banzo, R., Gutierrez, R., Rizo, J.M., Rodriguez-Ledo, P., Nerin, I., and Regidor, P.-A. (2024). Pro-Resolving Inflammatory Effects of a Marine Oil Enriched in Specialized Pro-Resolving Mediators (SPMs) Supplement and Its Implication in Patients with Post-COVID Syndrome (PCS). Biomedicines, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.632238",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_14",
"unstructured": "Balta, M.G., Papathanasiou, E., and Christopoulos, P.F. (2021). Specialized Pro-Resolving Mediators as Potential Regulators of Inflammatory Macrophage Responses in COVID-19. Front. Immunol., 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MCO.0000000000000805",
"article-title": "Specialized Pro-Resolving Mediators in Respiratory Diseases",
"author": "Cagnina",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "67",
"journal-title": "Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care",
"key": "ref_15",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12967-022-03604-3",
"article-title": "Effect of Omega-3 Fatty Acids Supplementation on Serum Level of C-Reactive Protein in Patients with COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials",
"author": "Taha",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "401",
"journal-title": "J. Transl. Med.",
"key": "ref_16",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/ijcp.14854",
"article-title": "Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Supplementation Improve Clinical Symptoms in Patients with Covid-19: A Randomised Clinical Trial",
"author": "Sedighiyan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e14854",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Clin. Pract.",
"key": "ref_17",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-17307-0",
"article-title": "Mucosal-Associated Invariant T Cells Promote Inflammation and Intestinal Dysbiosis Leading to Metabolic Dysfunction during Obesity",
"author": "Toubal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3755",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "ref_18",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12041181",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_19",
"unstructured": "Calder, P.C., Carr, A.C., Gombart, A.F., and Eggersdorfer, M. (2020). Optimal Nutritional Status for a Well-Functioning Immune System Is an Important Factor to Protect against Viral Infections. Nutrients, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13020699",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_20",
"unstructured": "García-Montero, C., Fraile-Martínez, O., Gómez-Lahoz, A.M., Pekarek, L., Castellanos, A.J., Noguerales-Fraguas, F., Coca, S., Guijarro, L.G., García-Honduvilla, N., and Asúnsolo, A. (2021). Nutritional Components in Western Diet Versus Mediterranean Diet at the Gut Microbiota–Immune System Interplay. Implications for Health and Disease. Nutrients, 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnut.2023.1161894",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_21",
"unstructured": "Mardi, A., Kamran, A., Pourfarzi, F., Zare, M., Hajipour, A., Doaei, S., Abediasl, N., and Hackett, D. (2023). Potential of Macronutrients and Probiotics to Boost Immunity in Patients with SARS-COV-2: A Narrative Review. Front. Nutr., 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12061657",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_22",
"unstructured": "Sidor, A., and Rzymski, P. (2020). Dietary Choices and Habits during COVID-19 Lockdown: Experience from Poland. Nutrients, 12."
},
{
"key": "ref_23",
"unstructured": "(2024, November 10). EUSurvey—Welcome. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eusurvey/home/welcome?language=en."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu11092183",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_24",
"unstructured": "Niedzwiedzka, E., Wadolowska, L., and Kowalkowska, J. (2019). Reproducibility of A Non-Quantitative Food Frequency Questionnaire (62-Item FFQ-6) and PCA-Driven Dietary Pattern Identification in 13–21-Year-Old Females. Nutrients, 11."
},
{
"key": "ref_25",
"unstructured": "Armitage, P., Berry, G., and Matthews, J.N.S. (2013). Statistical Methods in Medical Research, John Wiley & Sons."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/BF01535722",
"article-title": "GSRS--a Clinical Rating Scale for Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Peptic Ulcer Disease",
"author": "Svedlund",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "129",
"journal-title": "Dig. Dis. Sci.",
"key": "ref_26",
"volume": "33",
"year": "1988"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1477-7525-6-12",
"article-title": "Reliability and Validity of the Gastrointestinal Symptom Rating Scale (GSRS) and Quality of Life in Reflux and Dyspepsia (QOLRAD) Questionnaire in Dyspepsia: A Six-Country Study",
"author": "Kulich",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "12",
"journal-title": "Health Qual. Life Outcomes",
"key": "ref_27",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/apt.14349",
"article-title": "The PAC-SYM Questionnaire for Chronic Constipation: Defining the Minimal Important Difference",
"author": "Yiannakou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1103",
"journal-title": "Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther.",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/003655299750025327",
"article-title": "Psychometric Validation of a Constipation Symptom Assessment Questionnaire",
"author": "Frank",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "870",
"journal-title": "Scand. J. Gastroenterol.",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "34",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/annonc/mds539",
"article-title": "The FACT-G7: A Rapid Version of the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-General (FACT-G) for Monitoring Symptoms and Concerns in Oncology Practice and Research",
"author": "Yanez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1073",
"journal-title": "Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol.",
"key": "ref_30",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"key": "ref_31",
"unstructured": "(2024, November 11). FACT-G7. Available online: https://www.facit.org/measures/fact-g7."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/advances/nmaa171",
"article-title": "Western Dietary Pattern Antioxidant Intakes and Oxidative Stress: Importance During the SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19 Pandemic",
"author": "Sobral",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "670",
"journal-title": "Adv. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_32",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu16132117",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_33",
"unstructured": "da Silva Oliveira, E.K., Vieira, T.d.S., de Souza, O.F., Noll, P.R.e.S., Bezerra, I.M.P., Cavalcanti, M.P.E., de Abreu, L.C., and Riera, A.R.P. (2024). Consumption of Ultra-Processed Foods in the Brazilian Amazon during COVID-19. Nutrients, 16."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cells10113164",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_34",
"unstructured": "Malesza, I.J., Malesza, M., Walkowiak, J., Mussin, N., Walkowiak, D., Aringazina, R., Bartkowiak-Wieczorek, J., and Mądry, E. (2021). High-Fat, Western-Style Diet, Systemic Inflammation, and Gut Microbiota: A Narrative Review. Cells, 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu15122749",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_35",
"unstructured": "Clemente-Suárez, V.J., Beltrán-Velasco, A.I., Redondo-Flórez, L., Martín-Rodríguez, A., and Tornero-Aguilera, J.F. (2023). Global Impacts of Western Diet and Its Effects on Metabolism and Health: A Narrative Review. Nutrients, 15."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fpsyg.2020.564413",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_36",
"unstructured": "López-Taboada, I., González-Pardo, H., and Conejo, N.M. (2020). Western Diet: Implications for Brain Function and Behavior. Front. Psychol., 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.arr.2022.101596",
"article-title": "The Role of Nutrition in Inflammaging",
"author": "Stamerra",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "101596",
"journal-title": "Ageing Res. Rev.",
"key": "ref_37",
"volume": "77",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/advances/nmab130",
"article-title": "Impact of Nationwide Lockdowns Resulting from the First Wave of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Food Intake, Eating Behaviors, and Diet Quality: A Systematic Review",
"author": "Mignogna",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "388",
"journal-title": "Adv. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_38",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S1368980021000999",
"article-title": "Changes in ultra-processed food consumption during the first Italian lockdown following the COVID-19 pandemic and major correlates: Results from two population-based cohorts",
"author": "Bonaccio",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3905",
"journal-title": "Public Health Nutr.",
"key": "ref_39",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/joim.13333",
"article-title": "The Mediterranean Diet and Health: A Comprehensive Overview",
"author": "Willett",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "549",
"journal-title": "J. Intern. Med.",
"key": "ref_40",
"volume": "290",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.28298",
"article-title": "The effect of adherence to high-quality dietary pattern on COVID-19 outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Rahmati",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e28298",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "ref_41",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clnu.2021.04.001",
"article-title": "Mediterranean diet and the risk of COVID-19 in the ‘Seguimiento Universidad de Navarra’ cohort",
"author": "Gea",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3061",
"journal-title": "Clin. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_42",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s13668-025-00618-3",
"article-title": "The Impact of Diet Quality on COVID-19 Severity and Outcomes—A Scoping Review",
"author": "Tassakos",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "27",
"journal-title": "Curr. Nutr. Rep.",
"key": "ref_43",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2025"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S1368980024001873",
"article-title": "Associations between pre-infection serum vitamin D concentrations and Omicron COVID-19 incidence, severity and reoccurrence in elderly individuals",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e197",
"journal-title": "Public Health Nutr.",
"key": "ref_44",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.archger.2021.104411",
"article-title": "Nutritional determinants and COVID-19 outcomes of older patients with COVID-19: A systematic review",
"author": "Damayanthi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "104411",
"journal-title": "Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr.",
"key": "ref_45",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13020562",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_46",
"unstructured": "Vogel-González, M., Talló-Parra, M., Herrera-Fernández, V., Pérez-Vilaró, G., Chillón, M., Nogués, X., Gómez-Zorrilla, S., López-Montesinos, I., Arnau-Barrés, I., and Sorli-Redó, M.L. (2021). Low Zinc Levels at Admission Associates with Poor Clinical Outcomes in SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Nutrients, 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14163252",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_47",
"unstructured": "Barrett, R., Youssef, M., Shah, I., Ioana, J., Lawati, A.A., Bukhari, A., Hegarty, S., Cormican, L.J., Judge, E., and Burke, C.M. (2022). Vitamin D Status and Mortality from SARS CoV-2: A Prospective Study of Unvaccinated Caucasian Adults. Nutrients, 14."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12011-021-02797-w",
"article-title": "Decreased Serum Selenium Levels of COVID-19 Patients in Comparison with Healthy Individuals",
"author": "Younesian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1562",
"journal-title": "Biol. Trace Elem. Res.",
"key": "ref_48",
"volume": "200",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms25010418",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_49",
"unstructured": "Cioboata, R., Vasile, C.M., Bălteanu, M.A., Georgescu, D.E., Toma, C., Dracea, A.S., and Nicolosu, D. (2024). Evaluating Serum Calcium and Magnesium Levels as Predictive Biomarkers for Tuberculosis and COVID-19 Severity: A Romanian Prospective Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 25."
},
{
"article-title": "Risk Factors for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease Symptoms Related to Lifestyle and Diet",
"author": "Taraszewska",
"first-page": "21",
"journal-title": "Rocz. Panstw. Zakl. Hig.",
"key": "ref_50",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00405-019-05631-1",
"article-title": "Development of Scores Assessing the Refluxogenic Potential of Diet of Patients with Laryngopharyngeal Reflux",
"author": "Lechien",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3389",
"journal-title": "Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol.",
"key": "ref_51",
"volume": "276",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"article-title": "The Role of Lifestyle Changes in Gastroesophageal Reflux Diseases Treatment",
"author": "Kalkan",
"first-page": "S33",
"journal-title": "Turk. J. Gastroenterol. Off. J. Turk. Soc. Gastroenterol.",
"key": "ref_52",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijerph16234591",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_53",
"unstructured": "Kamiński, M., Łoniewski, I., Misera, A., and Marlicz, W. (2019). Heartburn-Related Internet Searches and Trends of Interest across Six Western Countries: A Four-Year Retrospective Analysis Using Google Ads Keyword Planner. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, 16."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1365-2982.2011.01701.x",
"article-title": "The Effects of Intraduodenal Nutrient Infusion on Serum CCK, LES Pressure, and Gastroesophageal Reflux",
"author": "Lacy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "631-e256",
"journal-title": "Neurogastroenterol. Motil.",
"key": "ref_54",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ejihpe13120189",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_55",
"unstructured": "Baroni, L., Bonetto, C., Solinas, I., Visaggi, P., Galchenko, A.V., Mariani, L., Bottari, A., Orazzini, M., Guidi, G., and Lambiase, C. (2023). Diets Including Animal Food Are Associated with Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Eur. J. Investig. Health Psychol. Educ., 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/TCRM.S296680",
"article-title": "Dietary and Lifestyle Factors Related to Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: A Systematic Review",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "305",
"journal-title": "Ther. Clin. Risk Manag.",
"key": "ref_56",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0007114517001593",
"article-title": "Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet Is Associated with the Gut Microbiota Pattern and Gastrointestinal Characteristics in an Adult Population",
"author": "Mitsou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1645",
"journal-title": "Br. J. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_57",
"volume": "117",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13082638",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_58",
"unstructured": "Barber, C., Mego, M., Sabater, C., Vallejo, F., Bendezu, R.A., Masihy, M., Guarner, F., Espín, J.C., Margolles, A., and Azpiroz, F. (2021). Differential Effects of Western and Mediterranean-Type Diets on Gut Microbiota: A Metagenomics and Metabolomics Approach. Nutrients, 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2468-1253(21)00111-4",
"article-title": "Global Prevalence of Functional Constipation According to the Rome Criteria: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis",
"author": "Barberio",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "638",
"journal-title": "Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol.",
"key": "ref_59",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/CEG.S239205",
"article-title": "The Humanistic and Economic Burden of Chronic Idiopathic Constipation in the USA: A Systematic Literature Review",
"author": "Nag",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "255",
"journal-title": "Clin. Exp. Gastroenterol.",
"key": "ref_60",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41575-019-0222-y",
"article-title": "Management of Functional Constipation in Children and Adults",
"author": "Vriesman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "21",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol.",
"key": "ref_61",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/19490976.2023.2197837",
"article-title": "Effects of Dietary Fibers or Probiotics on Functional Constipation Symptoms and Roles of Gut Microbiota: A Double-Blinded Randomized Placebo Trial",
"author": "Lai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2197837",
"journal-title": "Gut Microbes",
"key": "ref_62",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.14309/ajg.0000000000001149",
"article-title": "Exploratory Comparative Effectiveness Trial of Green Kiwifruit, Psyllium, or Prunes in US Patients with Chronic Constipation",
"author": "Chey",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1304",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Gastroenterol.",
"key": "ref_63",
"volume": "116",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12920-024-01861-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_64",
"unstructured": "Khavandegar, A., Heidarzadeh, A., Angoorani, P., Hasani-Ranjbar, S., Ejtahed, H.-S., Larijani, B., and Qorbani, M. (2024). Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet Can Beneficially Affect the Gut Microbiota Composition: A Systematic Review. BMC Med. Genom., 17."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/19490976.2024.2350785",
"article-title": "Diet-Microbiota Associations in Gastrointestinal Research: A Systematic Review",
"author": "Duncanson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2350785",
"journal-title": "Gut Microbes",
"key": "ref_65",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajcnut.2023.11.013",
"article-title": "Effect of an Asian-Adapted Mediterranean Diet and Pentadecanoic Acid on Fatty Liver Disease: The TANGO Randomized Controlled Trial",
"author": "Chooi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "788",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Clin. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_66",
"volume": "119",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fpubh.2022.892153",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_67",
"unstructured": "Zhao, Y., Zhan, J., Wang, Y., and Wang, D. (2022). The Relationship Between Plant-Based Diet and Risk of Digestive System Cancers: A Meta-Analysis Based on 3,059,009 Subjects. Front. Public Health, 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13072402",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_68",
"unstructured": "Losno, E.A., Sieferle, K., Perez-Cueto, F.J.A., and Ritz, C. (2021). Vegan Diet and the Gut Microbiota Composition in Healthy Adults. Nutrients, 13."
},
{
"article-title": "A Polyphenol-Rich Dietary Pattern Improves Intestinal Permeability, Evaluated as Serum Zonulin Levels, in Older Subjects: The MaPLE Randomised Controlled Trial",
"author": "Bernardi",
"first-page": "3006",
"journal-title": "Clin. Nutr. Edinb. Scotl.",
"key": "ref_69",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41423-023-00987-1",
"article-title": "Complex Regulatory Effects of Gut Microbial Short-Chain Fatty Acids on Immune Tolerance and Autoimmunity",
"author": "Kim",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "341",
"journal-title": "Cell. Mol. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_70",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12967-017-1175-y",
"article-title": "Influence of Diet on the Gut Microbiome and Implications for Human Health",
"author": "Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "73",
"journal-title": "J. Transl. Med.",
"key": "ref_71",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154251",
"article-title": "Commentary: Obesity: The “Achilles Heel” for COVID-19?",
"author": "Muscogiuri",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "154251",
"journal-title": "Metabolism",
"key": "ref_72",
"volume": "108",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12082327",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_73",
"unstructured": "Ruiz-Roso, M.B., Knott-Torcal, C., Matilla-Escalante, D.C., Garcimartín, A., Sampedro-Nuñez, M.A., Dávalos, A., and Marazuela, M. (2020). COVID-19 Lockdown and Changes of the Dietary Pattern and Physical Activity Habits in a Cohort of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Nutrients, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jand.2022.08.132",
"article-title": "Changes in Adults’ Eating Behaviors During the Initial Months of the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Narrative Review",
"author": "Johnson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "144",
"journal-title": "J. Acad. Nutr. Diet.",
"key": "ref_74",
"volume": "123",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.arr.2022.101744",
"article-title": "Differential Gut Microbiota and Intestinal Permeability between Frail and Healthy Older Adults: A Systematic Review",
"author": "Rashidah",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "101744",
"journal-title": "Ageing Res. Rev.",
"key": "ref_75",
"volume": "82",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "ref_76",
"unstructured": "Thompson, F.E., and Subar, A.F. (2025, February 16). Assessment Methods for Research and Practice. Nutrition in the Prevention and Treatment of Disease, Dietary Assessment Methodology, Available online: https://epi.grants.cancer.gov."
},
{
"key": "ref_77",
"unstructured": "FAO (2018). Dietary Assessment: A Resource Guide to Method Selection and Application in Low Resource Settings, Food & Agriculture Org."
}
],
"reference-count": 77,
"references-count": 77,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/17/5/800"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Associations Between Dietary Patterns and the Occurrence of Hospitalization and Gastrointestinal Disorders—A Retrospective Study of COVID-19 Patients",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "17"
}