Oxygen Sparing Effect of Bacteriotherapy in COVID-19
et al., Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13082898, Aug 2021
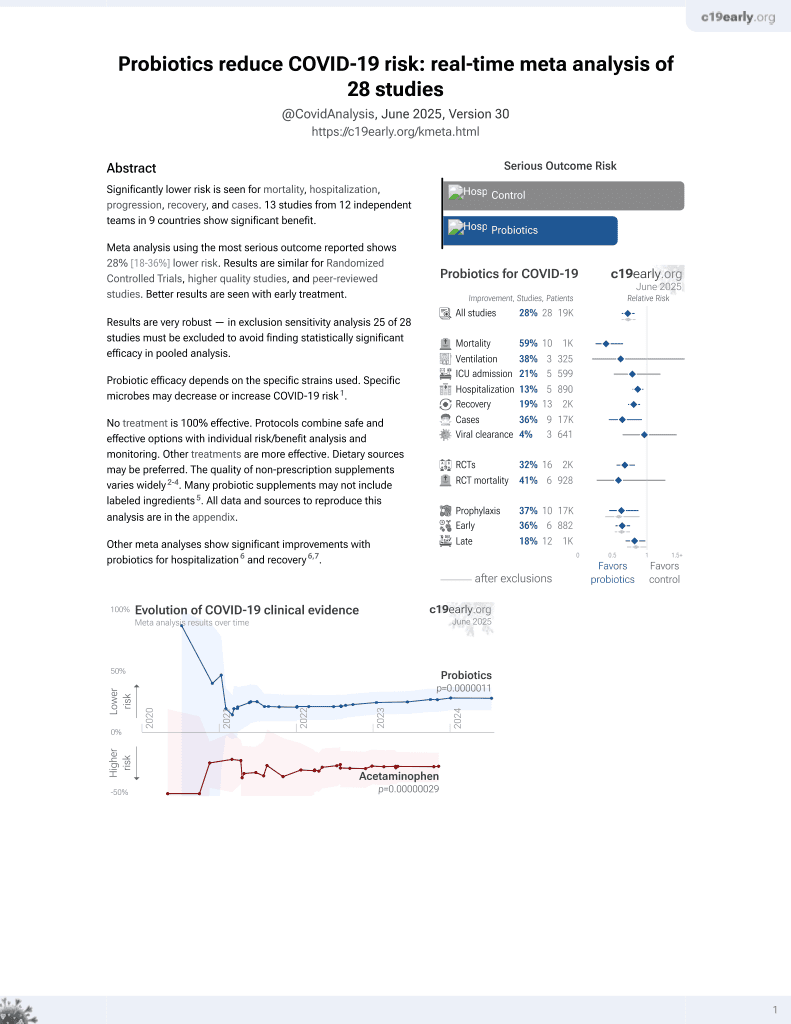
Probiotics for COVID-19
20th treatment shown to reduce risk in
March 2021, now with p = 0.00000044 from 29 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
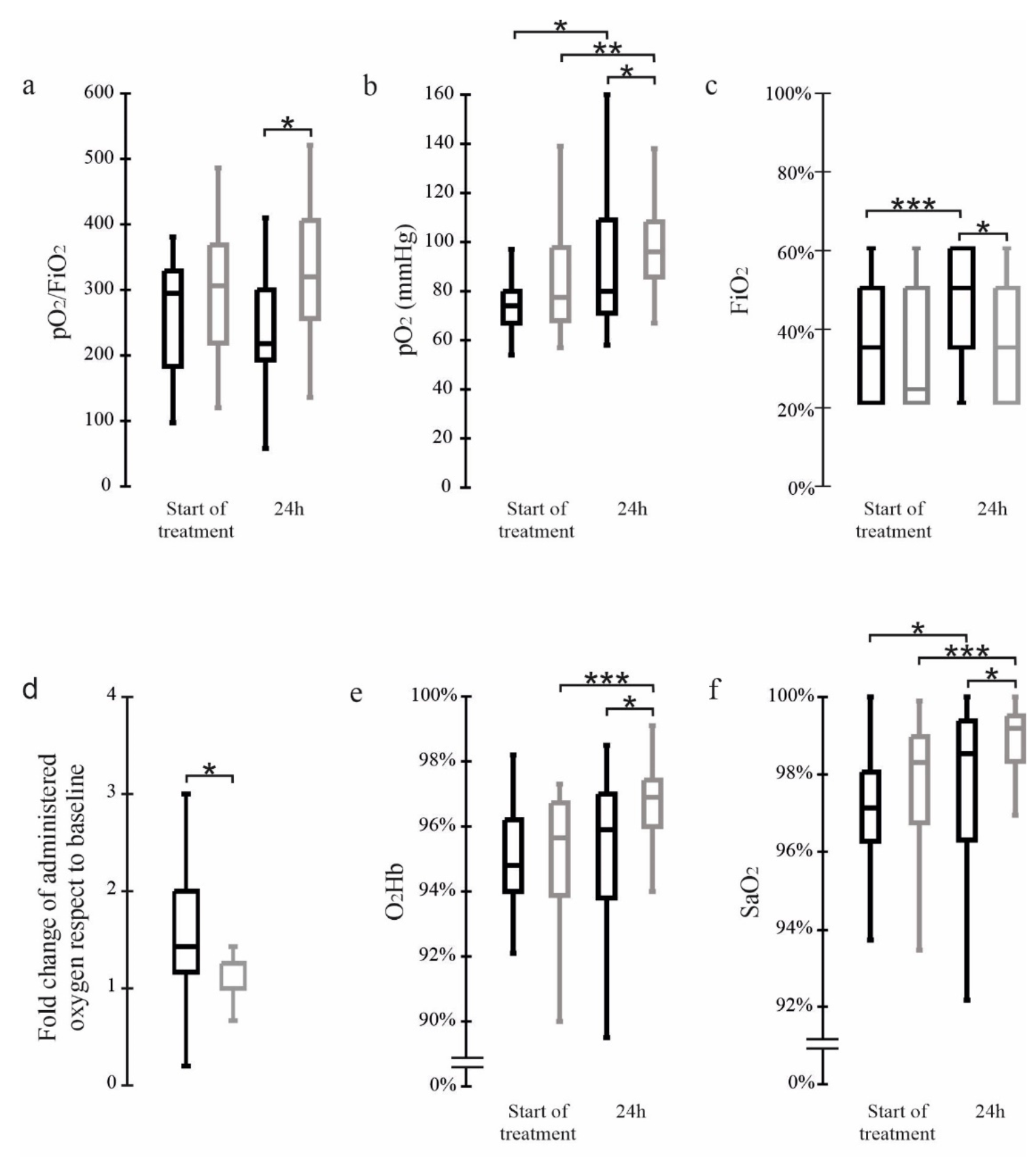
Prospective analysis of 69 severe COVID-19 patients requiring non-invasive oxygen therapy, 40 treated with probiotic formulation SLAB51, showing lower oxygen requirements and higher blood levels of pO2, O2Hb and SaO2 with treatment. Authors suggest that enzymes in SLAB51 could reduce oxygen requirements in intestinal cells, resulting in more oxygen available for other organs.
Probiotic efficacy depends on the specific strains used. Specific microbes may decrease or increase COVID-19 risk1.
|
risk of death, 70.4% lower, RR 0.30, p = 0.42, treatment 0 of 40 (0.0%), control 1 of 29 (3.4%), NNT 29, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 81.9% lower, RR 0.18, p = 0.15, treatment 1 of 40 (2.5%), control 4 of 29 (13.8%), NNT 8.9.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Ceccarelli et al., 23 Aug 2021, prospective, Italy, peer-reviewed, 10 authors.
Oxygen Sparing Effect of Bacteriotherapy in COVID-19
Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13082898
Background: We previously reported that severe COVID-19 patients had higher chances of survival and a reduced risk of developing respiratory failure when administered with the probiotic formulation SLAB51. This study aimed to investigate further bacteriotherapy mechanisms and how early they are activated. Methods: We performed an analysis on the blood oxygenation parameters collected in sixty-nine severe COVID-19 patients requiring non-invasive oxygen therapy and presenting a CT lung involvement ≥50%. Twenty-nine patients received low-molecular-weight heparin, azithromycin and Remdesivir. In addition, forty subjects received SLAB51. Blood gas analyses were performed before the beginning of treatments and at 24 h. Results: The patients receiving only standard therapy needed significantly increased oxygen amounts during the 24 h observation period. Furthermore, they presented lower blood levels of pO 2 , O 2 Hb and SaO 2 than the group also supplemented with oral bacteriotherapy. In vitro data suggest that SLAB51 can reduce nitric oxide synthesis in intestinal cells. Conclusions: SARS-CoV-2 infected patients may present lesions in the lungs compromising their gas exchange capability. The functionality of the organs essential for these patients' survival depends mainly on the levels of pO 2 , O 2 Hb and SaO 2 . SLAB51 contains enzymes that could reduce oxygen consumption in the intestine, making it available for the other organs.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Abruzzo, Vitali, Lombardi, Guerrini, Cinque et al., Mucoadhesive Buccal Films for Local Delivery of Lactobacillus brevis, Pharmaceutics, doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics12030241
Baud, Dimopoulou Agri, Gibson, Reid, Giannoni, Using Probiotics to Flatten the Curve of Coronavirus Disease COVID-2019 Pandemic, Front. Public Health, doi:10.3389/fpubh.2020.00186
Bellan, Soddu, Balbo, Baricich, Zeppegno et al., Respiratory and Psychophysical Sequelae Among Patients with COVID-19 Four Months after Hospital Discharge, JAMA Netw. Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.36142
Ceccarelli, Borrazzo, Pinacchio, Santinelli, Innocenti et al., Oral Bacteriotherapy in Patients With COVID-19: A Retrospective Cohort Study, Front. Nutr
Ceccarelli, Scagnolari, Pugliese, Mastroianni, ; D'ettorre, Probiotics and COVID-19, Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol, doi:10.1016/S2468-1253(20)30196-5
Core, R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing
D'ettorre, Ceccarelli, Marazzato, Campagna, Pinacchio et al., Challenges in the Management of SARS-CoV2 Infection: The Role of Oral Bacteriotherapy as Complementary Therapeutic Strategy to Avoid the Progression of COVID-19, Front. Med, doi:10.3389/fmed.2020.00389
Giannoni, Baud, Agri, Gibson, Reid, Probiotics and COVID-19, Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol
Grimes, Khan, Badeaux, Rao, Rowlinson et al., Arginine depletion as a therapeutic approach for patients with COVID-19, Int J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.10.100
Huang, Huang, Wang, Li, Ren et al., 6-month consequences of COVID-19 in patients discharged from hospital: A cohort study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32656-8
Ignarro, Nitric oxide as a unique signaling molecule in the vascular system: A historical overview, J. Physiol. Pharmacol
Izzo, Marra, Beneduce, Castello, Vallone et al., Pegylated arginine deiminase treatment of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: Results from phase I/II studies, J. Clin. Oncol, doi:10.1200/JCO.2004.11.120
Lundquist, Artursson, Oral absorption of peptides and nanoparticles across the human intestine: Opportunities, limitations and studies in human tissues, Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev, doi:10.1016/j.addr.2016.07.007
Mach, Thimmesch, Pierce, Pierce, Consequences of hyperoxia and the toxicity of oxygen in the lung, Nurs Res. Pract, doi:10.1155/2011/260482
Moncada, Palmer, Higgs, The discovery of nitric oxide as the endogenous nitrovasodilator, Hypertension, doi:10.1161/01.HYP.12.4.365
Palumbo, Lombardi, Augello, Giusti, Luzzi et al., NOS2 inhibitor 1400 W Induces Autophagic Flux and Influences Extracellular Vesicle Profile in Human Glioblastoma U87MG Cell Line, Int J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms20123010
Palumbo, Miconi, Cinque, Lombardi, La Torre et al., NOS2 expression in glioma cell lines and glioma primary cell cultures: Correlation with neurosphere generation and SOX-2 expression, Oncotarget, doi:10.18632/oncotarget.16106
Panaro, Carofiglio, Acquafredda, Cavallo, Cianciulli, Anti-inflammatory effects of resveratrol occur via inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-induced NF-κB activation in Caco-2 and SW480 human colon cancer cells, Br. J. Nutr, doi:10.1017/S0007114511007227
Perrone, Belser, Wadford, Katz, Tumpey, Inducible nitric oxide contributes to viral pathogenesis following highly pathogenic influenza virus infection in mice, J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/infdis/jit062
Rabi, Al Zoubi, Kasasbeh, Salameh, Al-Nasser, SARS-CoV-2 and Coronavirus Disease 2019: What We Know So Far, Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens9030231
Riccia, Bizzini, Perilli, Polimeni, Trinchieri et al., Anti-inflammatory effects of Lactobacillus brevis (CD2) on periodontal disease, Oral Dis, doi:10.1111/j.1601-0825.2006.01291.x
Sekirov, Russell, Antunes, Finlay, Gut microbiota in health and disease, Physiol. Rev, doi:10.1152/physrev.00045.2009
Singhal, Shah, Oxygen battle in the gut: Hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factors in metabolic and inflammatory responses in the intestine, J. Biol. Chem, doi:10.1074/jbc.REV120.011188
Sundararaman, Ray, Ravindra, Halami, Role of probiotics to combat viral infections with emphasis on COVID-19, Appl Microbiol. Biotechnol, doi:10.1007/s00253-020-10832-4
Xu, Shi, Wang, Zhang, Huang et al., Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome, Lancet Respir Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30076-X
Zuo, Zhang, Lui, Yeoh, Li et al., Alterations in Gut Microbiota of Patients With COVID-19 During Time of Hospitalization, Gastroenterology, doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.048
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13082898",
"ISSN": [
"2072-6643"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/nu13082898",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Background: We previously reported that severe COVID-19 patients had higher chances of survival and a reduced risk of developing respiratory failure when administered with the probiotic formulation SLAB51. This study aimed to investigate further bacteriotherapy mechanisms and how early they are activated. Methods: We performed an analysis on the blood oxygenation parameters collected in sixty-nine severe COVID-19 patients requiring non-invasive oxygen therapy and presenting a CT lung involvement ≥50%. Twenty-nine patients received low-molecular-weight heparin, azithromycin and Remdesivir. In addition, forty subjects received SLAB51. Blood gas analyses were performed before the beginning of treatments and at 24 h. Results: The patients receiving only standard therapy needed significantly increased oxygen amounts during the 24 h observation period. Furthermore, they presented lower blood levels of pO2, O2Hb and SaO2 than the group also supplemented with oral bacteriotherapy. In vitro data suggest that SLAB51 can reduce nitric oxide synthesis in intestinal cells. Conclusions: SARS-CoV-2 infected patients may present lesions in the lungs compromising their gas exchange capability. The functionality of the organs essential for these patients’ survival depends mainly on the levels of pO2, O2Hb and SaO2. SLAB51 contains enzymes that could reduce oxygen consumption in the intestine, making it available for the other organs.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"nu13082898"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5921-3180",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ceccarelli",
"given": "Giancarlo",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marazzato",
"given": "Massimiliano",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Celani",
"given": "Luigi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0551-5076",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Lombardi",
"given": "Francesca",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Piccirilli",
"given": "Alessandra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mancone",
"given": "Massimo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Trinchieri",
"given": "Vito",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pugliese",
"given": "Francesco",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mastroianni",
"given": "Claudio M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3571-5677",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "d’Ettorre",
"given": "Gabriella",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Nutrients",
"container-title-short": "Nutrients",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2021-08-23T14:24:17Z",
"timestamp": 1629728657000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2021-08-24T09:25:28Z",
"timestamp": 1629797128000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-05T13:35:44Z",
"timestamp": 1712324144762
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 10,
"issue": "8",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
23
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "8",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2021-08-23T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1629676800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/13/8/2898/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "2898",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
23
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
23
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00253-020-10832-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2468-1253(20)30195-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fpubh.2020.00186",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnut.2020.613928",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2020.00389",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.10.100",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30076-X",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/pharmaceutics12030241",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18632/oncotarget.16106",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref9"
},
{
"key": "ref10",
"series-title": "R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0007114511007227",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms20123010",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref12"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1601-0825.2006.01291.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/pathogens9030231",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2011/260482",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32656-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref16"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.36142",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.addr.2016.07.007",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref18"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/01.HYP.12.4.365",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref19"
},
{
"article-title": "Nitric oxide as a unique signaling molecule in the vascular system: A historical overview",
"author": "Ignarro",
"first-page": "503",
"journal-title": "J. Physiol. Pharmacol.",
"key": "ref20",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.REV120.011188",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref21"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.048",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref22"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jit062",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref23"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1200/JCO.2004.11.120",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref24"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/physrev.00045.2009",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref25"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2468-1253(20)30196-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref26"
}
],
"reference-count": 26,
"references-count": 26,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/13/8/2898"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Food Science",
"Nutrition and Dietetics"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Oxygen Sparing Effect of Bacteriotherapy in COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "13"
}