Challenges in the Management of SARS-CoV2 Infection: The Role of Oral Bacteriotherapy as Complementary Therapeutic Strategy to Avoid the Progression of COVID-19
et al., Frontiers in Medicine, doi:10.3389/fmed.2020.00389, Jul 2020
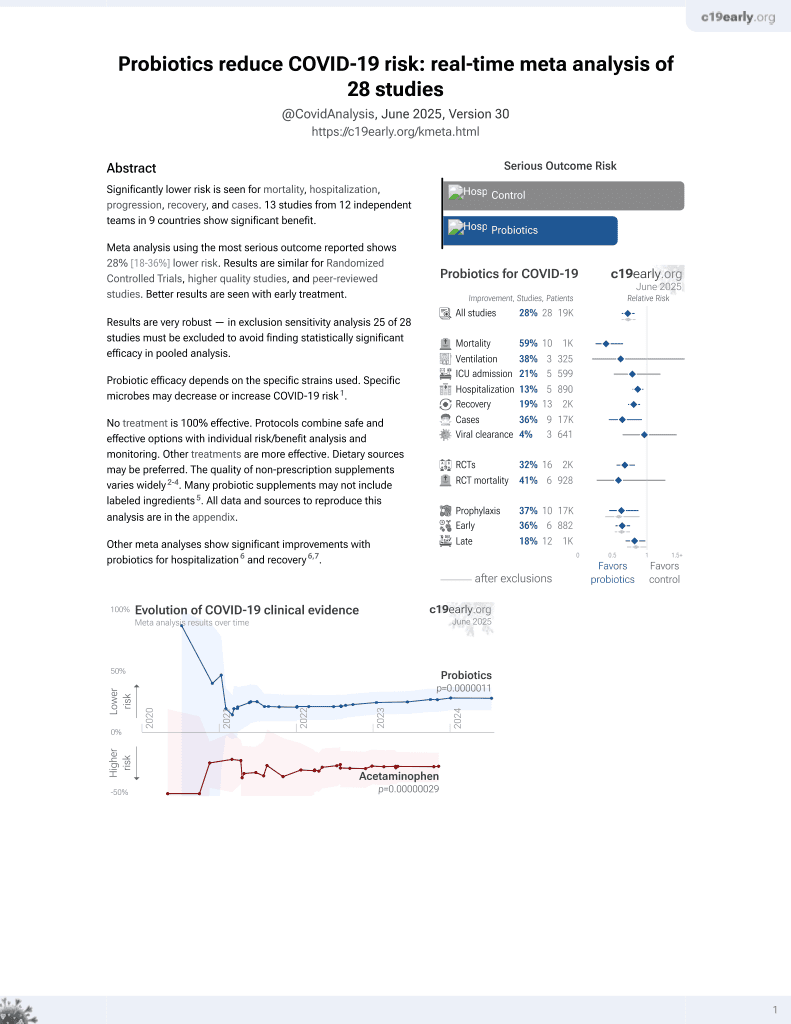
Probiotics for COVID-19
20th treatment shown to reduce risk in
March 2021, now with p = 0.00000044 from 29 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 70 hospitalized patients in Italy, 28 treated with probiotic Sivomixx, showing lower risk of respiratory failure and faster recovery with treatment.
Probiotic efficacy depends on the specific strains used. Specific microbes may decrease or increase COVID-19 risk1.
|
risk of death, 87.0% lower, RR 0.13, p = 0.14, treatment 0 of 28 (0.0%), control 4 of 42 (9.5%), NNT 10, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 76.9% lower, RR 0.23, p = 0.51, treatment 0 of 28 (0.0%), control 2 of 42 (4.8%), NNT 21, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
respiratory failure, 88.4% lower, OR 0.12, p = 0.01, treatment 28, control 42, inverted to make OR<1 favor treatment, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
d'Ettorre et al., 7 Jul 2020, retrospective, Italy, peer-reviewed, 17 authors.
Challenges in the Management of SARS-CoV2 Infection: The Role of Oral Bacteriotherapy as Complementary Therapeutic Strategy to Avoid the Progression of COVID-19
Frontiers in Medicine, doi:10.3389/fmed.2020.00389
Background: Gastrointestinal disorders are frequent in COVID-19 and SARS-CoV-2 has been hypothesized to impact on host microbial flora and gut inflammation, infecting intestinal epithelial cells. Since there are currently no coded therapies or guidelines for treatment of COVID-19, this study aimed to evaluate the possible role of a specific oral bacteriotherapy as complementary therapeutic strategy to avoid the progression of COVID-19. Methods: We provide a report of 70 patients positive for COVID-19, hospitalized between March 9th and April 4th, 2020. All the patients had fever, required non-invasive oxygen therapy and presented a CT lung involvement on imaging more than 50%. Forty-two patients received hydroxychloroquine, antibiotics, and tocilizumab, alone or in combination. A second group of 28 subjects received the same therapy added with oral bacteriotherapy, using a multistrain formulation.
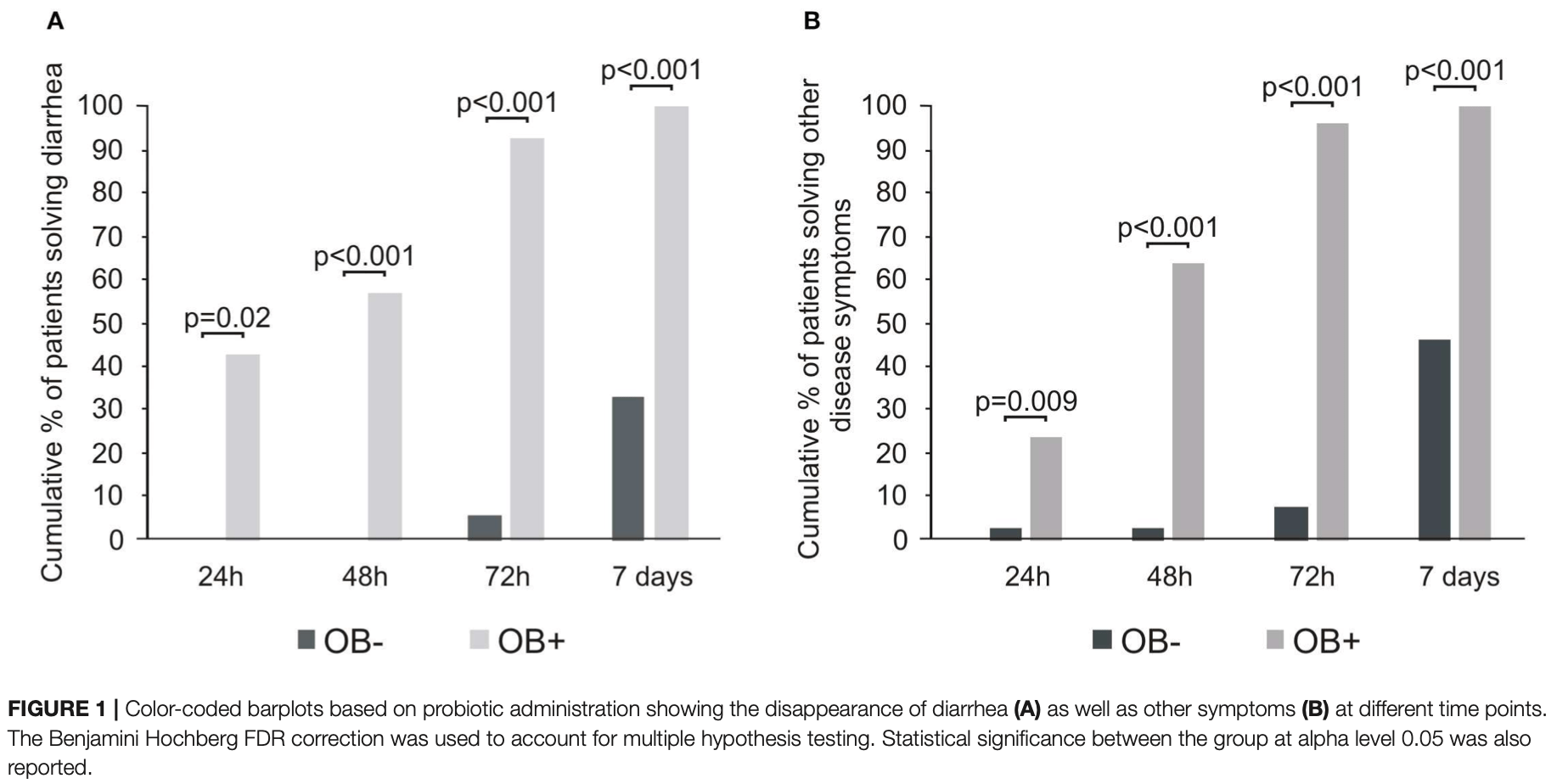
Results: The two cohorts of patients were comparable for age, sex, laboratory values, concomitant pathologies, and the modality of oxygen support. Within 72 h, nearly all patients treated with bacteriotherapy showed remission of diarrhea and other symptoms as compared to less than half of the not supplemented group. The estimated risk of developing respiratory failure was eight-fold lower in patients receiving oral bacteriotherapy. Both the prevalence of patients transferred to ICU and mortality were higher among the patients not treated with oral bacteriotherapy. d'Ettorre et al. Bacteriotherapy in Treating COVID-19 Conclusions: A specific bacterial formulation showed a significant ameliorating impact on the clinical conditions of patients positive for SARS-CoV-2 infection. These results also stress the importance of the gut-lung axis in controlling the COVID-19 disease.
ETHICS STATEMENT The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by Ethics Committee of Policlinico Umberto I. The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS Gd'E, GCe, and MM contributed substantially to the conception and design of the study and interpretation and wrote the manuscript. GCa, CP, FA, FR, GR, LC, CS, CM, VT, GER, and VM contributed substantially to the the acquisition of data and the analysis. GA, FP, and CMM drafted or provided critical revision of the article and provided final approval of the version to publish. GR contributed substantially to data interpretation.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS Authors wish to thank Prof. Claudio De Simone for suggesting the rationale of the study and the dosage of administered oral bacteriotherapy. We thank all those in the Intensive Care COVID-19 Study Group and in the Infectious Diseases COVID-19 Study Group of La Sapienza University of Rome who assisted in the care of the patients in this program. We express our solidarity with those who are or have been ill with COVID-19 the health care workers on the front lines of this pandemic.
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
Alhazzani, Moller, Arabi, Loeb, Gong et al., Surviving sepsis campaign: guidelines on the management of critically Ill adults with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Intensive Care Med, doi:10.1097/CCM.0000000000004363
Anand, Mande, Diet, microbiota and gut-lung connection, Front Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2018.02147
Angus, Optimizing the trade-off between learning and doing in a pandemic, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.4984
Barr, Smith, Acute diarrhea, Am Fam Physician
Bingula, Filaire, Radosevic-Robin, Bey, Berthon et al., Desired turbulence? Gut-lung axis, immunity, and lung cancer, J. Oncol, doi:10.1155/2017/5035371
Cait, Hughes, Antignano, Cait, Dimitriu et al., Microbiome-driven allergic lung inflammation is ameliorated by short-chain fatty acids, Mucosal Immunol, doi:10.1038/mi.2017.75
Castelli, Angelo, Lombardi, Alfonsetti, Antonosante, Effects of the probiotic formulation SLAB51 in in vitro and in vivo Parkinson's disease models, Aging, doi:10.18632/aging.102927
Charlson, Pompei, Ales, Mackenzie, A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation, J Chronic Dis, doi:10.1016/0021-9681(87)90171-8
Chiu, Bazin, Truchetet, Schaeverbeke, Delhaes et al., Protective microbiota: from localized to long-reaching co-immunity, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2017.01678
Devadas, Dhawan, Hemin activation ameliorates HIV-1 infection via heme oxygenase-1 induction, J Immunol, doi:10.4049/jimmunol.176.7.4252
Dumas, Bernard, Poquet, Lugo-Villarino, Neyrolles, The role of the lung microbiota and the gut-lung axis in respiratory infectious diseases, Cell Microbiol, doi:10.1111/cmi.12966
Enaud, Prevel, Ciarlo, Beaufils, Wieërs et al., The gut-lung axis in health and respiratory diseases: a place for interorgan and inter-kingdom crosstalks, Front Cell Infect Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2020.00009
Espinoza, León, Céspedes, Gómez, Canedo-Marroquín et al., Heme oxygenase-1 modulates human respiratory syncytial virus replication and lung pathogenesis during infection, J Immunol, doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1601414
Feng, Wang, Qi, The small intestine, an underestimated site of SARS-CoV-2 infection: from red queen effect to probiotics, Preprints, doi:10.20944/preprints202003.0161.v1
Freedman, Schnadower, Tarr, The probiotic conundrum: regulatory confusion, conflicting studies, and safety concerns, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2019.22268
Hashiba, Suzuki, Nagashima, Suzuki, Inoue et al., Adenovirus-mediated transfer of heme oxygenase-1 cDNA attenuates severe lung injury induced by the influenza virus in mice, Gene Ther, doi:10.1038/sj.gt.3301540
Hill-Batorski, Halfmann, Neumann, Kawaoka, The cytoprotective enzyme heme oxygenase-1 suppresses Ebola virus replication, J Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.02422-13
Hosakote, Jantzi, Esham, Spratt, Kurosky et al., Viral-mediated inhibition of antioxidant enzymes contributes to the pathogenesis of severe respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis, Am J Respir Crit Care Med, doi:10.1164/rccm.201010-1755OC
Infusino, Marazzato, Mancone, Fedele, Mastroianni et al., Diet supplementation, probiotics, and nutraceuticals in SARS-CoV-2 infection: a scoping review, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12061718
Laviolette, Laveneziana, Dyspnoea: a multidimensional and multidisciplinary approach, Eur Respir J, doi:10.1183/09031936.00092613
Leung, To, Chan, Chan, Wu et al., Enteric involvement of severe acute respiratory syndromeassociated coronavirus infection, Gastroenterology, doi:10.1016/S0016-5085(03)01215-0
Leyer, Li, Mubasher, Reifer, Ouwehand, Probiotic effects on cold and influenza-like symptom incidence and duration in children, Pediatrics Aug, doi:10.1542/peds.2008-2666
Li, Ma, Pang, Fan, Hua, The commensal microbiota and viral infection: a comprehensive review, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2019.01551
Mcaleer, Kolls, Contributions of the intestinal microbiome in lung immunity, Eur J Immunol, doi:10.1002/eji.201646721
Siaarti, Percorso assistenziale per il paziente affetto da COVID-19 Sezione 1 -Procedure area critica -versione 02
Trompette, Gollwitzer, Yadava, Sichelstiel, Sprenger et al., Gut microbiota metabolism of dietary fiber influences allergic airway disease and hematopoiesis, Nat Med, doi:10.1038/nm.3444
Tseng, Lin, Wu, Chen, Chen et al., Human heme oxygenase 1 is a potential host cell factor against dengue virus replication, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/srep32176
Wilson, Chotirmall, Bai, Rello, COVID-19: Interim Guidance on Management Pending Empirical Evidence
Ye, Zhang, Wang, Chest CT manifestations of new coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a pictorial review, Eur Radiol, doi:10.1007/s00330-020-06801-0
Yu, Tong, Shen, Fu, Lai et al., Immunodepletion with hypoxemia: a potential high-risk subtype of coronavirus disease, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.03.03.20030650
Zhang, Wang, Ni, Di, Ma et al., COVID-19: Melatonin as a potential adjuvant treatment, Life Sci, doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117583
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2020.00389",
"ISSN": [
"2296-858X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2020.00389",
"alternative-id": [
"10.3389/fmed.2020.00389"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "d'Ettorre",
"given": "Gabriella",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ceccarelli",
"given": "Giancarlo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marazzato",
"given": "Massimiliano",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Campagna",
"given": "Giuseppe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pinacchio",
"given": "Claudia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alessandri",
"given": "Francesco",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ruberto",
"given": "Franco",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rossi",
"given": "Giacomo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Celani",
"given": "Luigi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Scagnolari",
"given": "Carolina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mastropietro",
"given": "Cristina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Trinchieri",
"given": "Vito",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Recchia",
"given": "Gregorio Egidio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mauro",
"given": "Vera",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Antonelli",
"given": "Guido",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pugliese",
"given": "Francesco",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mastroianni",
"given": "Claudio Maria",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Frontiers in Medicine",
"container-title-short": "Front. Med.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"frontiersin.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2020-07-07T04:42:00Z",
"timestamp": 1594096920000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2020-07-07T04:42:04Z",
"timestamp": 1594096924000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-08T09:19:05Z",
"timestamp": 1712567945875
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 151,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7,
7
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2020-07-07T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1594080000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fmed.2020.00389/full",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1965",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.3389",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7,
7
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7,
7
]
]
},
"publisher": "Frontiers Media SA",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.20944/preprints202003.0161.v1",
"article-title": "The small intestine, an underestimated site of SARS-CoV-2 infection: from red queen effect to probiotics",
"author": "Feng",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Preprints.",
"key": "B1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.03.03.20030650",
"article-title": "Immunodepletion with hypoxemia: a potential high-risk subtype of coronavirus disease 2019",
"author": "Lilei",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "medRxiv.",
"key": "B2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2017.01678",
"article-title": "Protective microbiota: from localized to long-reaching co-immunity",
"author": "Chiu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1678",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol.",
"key": "B3",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1542/peds.2008-2666",
"article-title": "Probiotic effects on cold and influenza-like symptom incidence and duration in children",
"author": "Leyer",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e172",
"journal-title": "Pediatrics Aug.",
"key": "B4",
"volume": "124",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2019.01551",
"article-title": "The commensal microbiota and viral infection: a comprehensive review",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1551",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol.",
"key": "B5",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcimb.2020.00009",
"article-title": "The gut-lung axis in health and respiratory diseases: a place for inter-organ and inter-kingdom crosstalks",
"author": "Enaud",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "9",
"journal-title": "Front Cell Infect Microbiol.",
"key": "B6",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/cmi.12966",
"article-title": "The role of the lung microbiota and the gut–lung axis in respiratory infectious diseases",
"author": "Dumas",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e12966",
"journal-title": "Cell Microbiol.",
"key": "B7",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/09031936.00092613",
"article-title": "Dyspnoea: a multidimensional and multidisciplinary approach",
"author": "Laviolette",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1750",
"journal-title": "Eur Respir J.",
"key": "B8",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"article-title": "Acute diarrhea",
"author": "Barr",
"first-page": "180",
"journal-title": "Am Fam Physician.",
"key": "B9",
"volume": "89",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00330-020-06801-0.",
"article-title": "Chest CT manifestations of new coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a pictorial review",
"author": "Ye",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Eur Radiol.",
"key": "B10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0021-9681(87)90171-8",
"article-title": "A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation",
"author": "Charlson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "373",
"journal-title": "J Chronic Dis.",
"key": "B11",
"volume": "40",
"year": "1987"
},
{
"key": "B12",
"unstructured": "Percorso assistenziale per il paziente affetto da COVID-19 Sezione 1 - Procedure area critica - versione 022020"
},
{
"key": "B13",
"unstructured": "Source: Italian Civil Protection Department"
},
{
"key": "B14",
"unstructured": "WilsonKC\n ChotirmallSH\n BaiC\n RelloJ\n COVID-19: Interim Guidance on Management Pending Empirical Evidence"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CCM.0000000000004363",
"article-title": "Surviving sepsis campaign: guidelines on the management of critically Ill adults with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)",
"author": "Alhazzani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Intensive Care Med",
"key": "B15",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.4984",
"article-title": "Optimizing the trade-off between learning and doing in a pandemic",
"author": "Angus",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1895",
"journal-title": "JAMA.",
"key": "B16",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2017/5035371",
"article-title": "Desired turbulence? Gut-lung axis, immunity, and lung cancer",
"author": "Bingula",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "5035371",
"journal-title": "J. Oncol.",
"key": "B17",
"volume": "2017",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/eji.201646721",
"article-title": "Contributions of the intestinal microbiome in lung immunity",
"author": "McAleer",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "39",
"journal-title": "Eur J Immunol",
"key": "B18",
"volume": "48",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nm.3444",
"article-title": "Gut microbiota metabolism of dietary fiber influences allergic airway disease and hematopoiesis",
"author": "Trompette",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "159",
"journal-title": "Nat Med.",
"key": "B19",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/mi.2017.75",
"article-title": "Microbiome-driven allergic lung inflammation is ameliorated by short-chain fatty acids",
"author": "Cait",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "785",
"journal-title": "Mucosal Immunol.",
"key": "B20",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmicb.2018.02147",
"article-title": "Diet, microbiota and gut-lung connection",
"author": "Anand",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2147",
"journal-title": "Front Microbiol.",
"key": "B21",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.201010-1755OC",
"article-title": "Viral-mediated inhibition of antioxidant enzymes contributes to the pathogenesis of severe respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis",
"author": "Hosakote",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1550",
"journal-title": "Am J Respir Crit Care Med.",
"key": "B22",
"volume": "183",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117583",
"article-title": "COVID-19: Melatonin as a potential adjuvant treatment",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "117583",
"journal-title": "Life Sci.",
"key": "B23",
"volume": "250",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18632/aging.102927",
"article-title": "Effects of the probiotic formulation SLAB51 in in vitro and in vivo Parkinson's disease models",
"author": "Castelli",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4641",
"journal-title": "Aging (Albany NY).",
"key": "B24",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.176.7.4252",
"article-title": "Hemin activation ameliorates HIV-1 infection via heme oxygenase-1 induction",
"author": "Devadas",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4252",
"journal-title": "J Immunol.",
"key": "B25",
"volume": "176",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/sj.gt.3301540",
"article-title": "Adenovirus-mediated transfer of heme oxygenase-1 cDNA attenuates severe lung injury induced by the influenza virus in mice",
"author": "Hashiba",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1499",
"journal-title": "Gene Ther.",
"key": "B26",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.1601414",
"article-title": "Heme oxygenase-1 modulates human respiratory syncytial virus replication and lung pathogenesis during infection",
"author": "Espinoza",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "212",
"journal-title": "J Immunol.",
"key": "B27",
"volume": "199",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/srep32176",
"article-title": "Human heme oxygenase 1 is a potential host cell factor against dengue virus replication",
"author": "Tseng",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "32176",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep.",
"key": "B28",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.02422-13",
"article-title": "The cytoprotective enzyme heme oxygenase-1 suppresses Ebola virus replication",
"author": "Hill-Batorski",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "13795",
"journal-title": "J Virol.",
"key": "B29",
"volume": "87",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0016-5085(03)01215-0",
"article-title": "Enteric involvement of severe acute respiratory syndrome-associated coronavirus infection",
"author": "Leung",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1011",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology.",
"key": "B30",
"volume": "125",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12061718",
"article-title": "Diet supplementation, probiotics, and nutraceuticals in SARS-CoV-2 infection: a scoping review",
"author": "Infusino",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "E1718",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "B31",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2019.22268",
"article-title": "The probiotic conundrum: regulatory confusion, conflicting studies, and safety concerns",
"author": "Freedman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "823",
"journal-title": "JAMA.",
"key": "B32",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 32,
"references-count": 32,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fmed.2020.00389/full"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Challenges in the Management of SARS-CoV2 Infection: The Role of Oral Bacteriotherapy as Complementary Therapeutic Strategy to Avoid the Progression of COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/crossmark-policy",
"volume": "7"
}