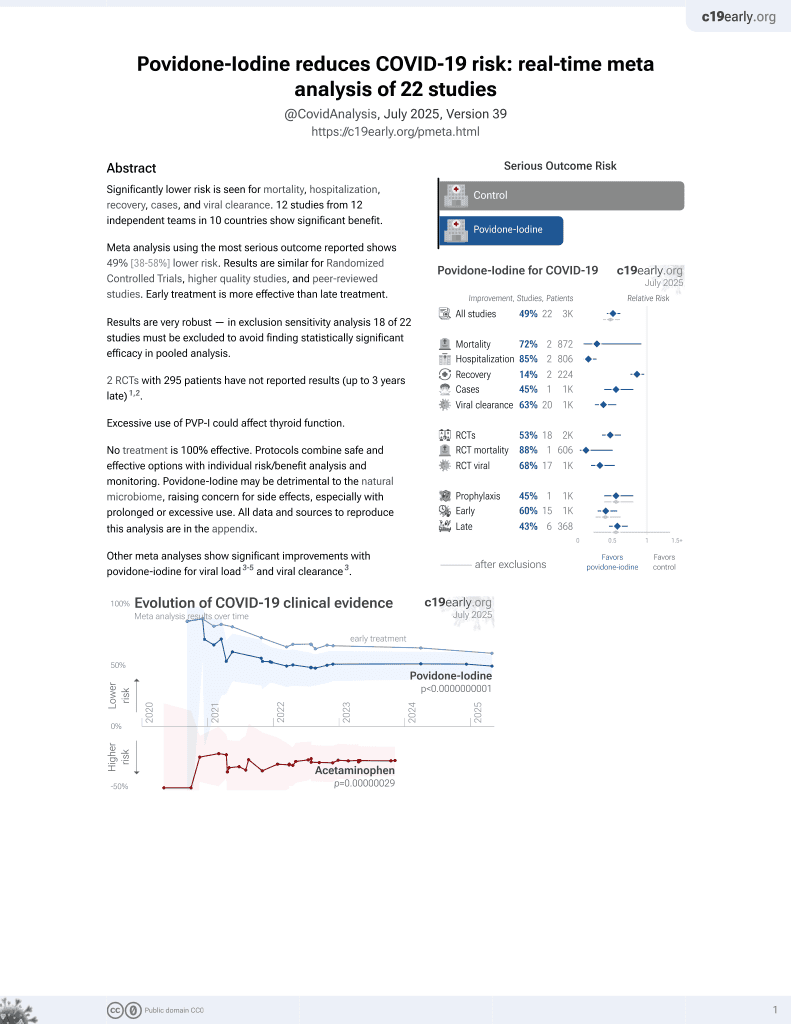
Virucidal effect of povidone iodine on COVID-19 in the nasopharynx: an open-label randomized clinical trial
et al., Indian Journal of Otolaryngology and Head & Neck Surgery, doi:10.1007/s12070-021-02616-7, NCT04549376, May 2021
PVP-I for COVID-19
15th treatment shown to reduce risk in
February 2021, now with p = 0.000000000016 from 22 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
RCT with 189 patients showing significantly greater viral clearance with a single application of PVP-I. Authors recommend using PVP-I prophylactically in the nasopharynx and oropharynx. NCT04549376 (history)1.
Analysis of short-term changes in viral load using PCR may not detect
effective treatments because PCR is unable to differentiate between intact
infectious virus and non-infectious or destroyed virus particles. For example
Tarragó-Gil, Alemany perform RCTs with cetylpyridinium chloride
(CPC) mouthwash that show no difference in PCR viral load, however there was
significantly increased detection of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein,
indicating viral lysis. CPC inactivates SARS-CoV-2 by degrading its membrane,
exposing the nucleocapsid of the virus. To better estimate changes in viral
load and infectivity, methods like viral culture that can
differentiate intact vs. degraded virus are preferred.
This study is excluded in the after exclusion results of meta-analysis:
study only provides short-term viral load results.
|
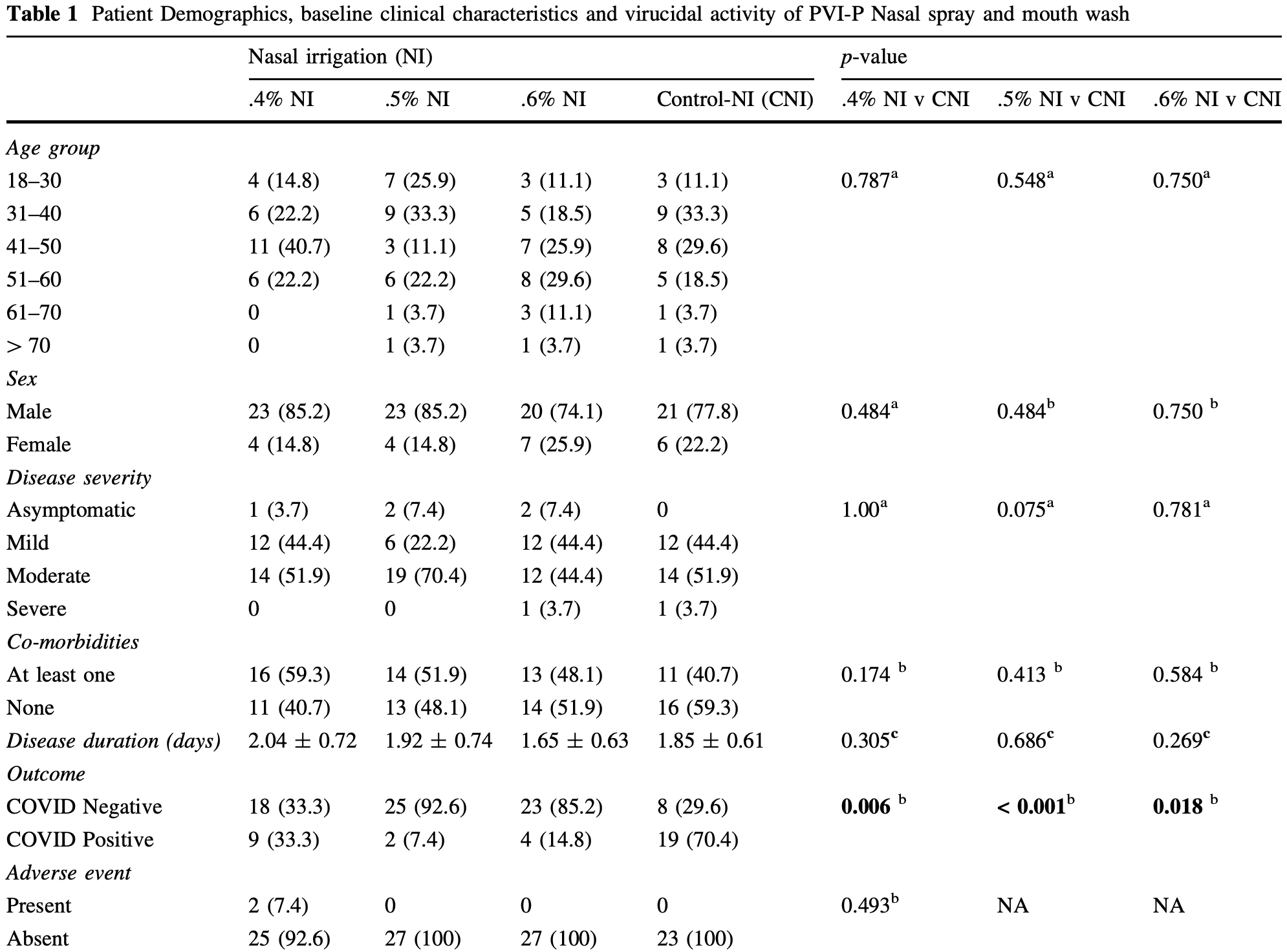
risk of no viral clearance, 78.9% lower, RR 0.21, p = 0.02, treatment 4 of 27 (14.8%), control 19 of 27 (70.4%), NNT 1.8, 0.6% nasal irrigation.
|
|
risk of no viral clearance, 89.5% lower, RR 0.11, p < 0.001, treatment 2 of 27 (7.4%), control 19 of 27 (70.4%), NNT 1.6, 0.5% nasal irrigation.
|
|
risk of no viral clearance, 52.6% lower, RR 0.47, p = 0.006, treatment 9 of 27 (33.3%), control 19 of 27 (70.4%), NNT 2.7, 0.4% nasal irrigation.
|
|
risk of no viral clearance, 80.0% lower, RR 0.20, p < 0.001, treatment 5 of 27 (18.5%), control 25 of 27 (92.6%), NNT 1.4, 0.6% nasal spray.
|
|
risk of no viral clearance, 64.0% lower, RR 0.36, p < 0.001, treatment 9 of 27 (33.3%), control 25 of 27 (92.6%), NNT 1.7, 0.5% nasal spray.
|
|
risk of no viral clearance, 73.6% lower, RR 0.26, p < 0.001, treatment 29 of 135 (21.5%), control 44 of 54 (81.5%), NNT 1.7, all treatment vs. all control.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
trialsjournal.biomedcentral.com, trialsjournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13063-020-04963-2.
Arefin et al., 18 May 2021, Randomized Controlled Trial, Bangladesh, peer-reviewed, 9 authors, study period 1 July, 2020 - 30 October, 2020, trial NCT04549376 (history).
Virucidal effect of povidone iodine on COVID-19 in the nasopharynx: an open-label randomized clinical trial
Indian Journal of Otolaryngology and Head & Neck Surgery, doi:10.1007/s12070-021-02616-7
Povidone-iodine (PVP-I) is a time-tested antiseptic agent with excellent virucidal (99.99%) properties. Repurposing it against coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19) is a relatively newer concept and has been sparsely tested in vivo. The most common route of entry of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS CoV-2) is the nasopharynx. Averting colonization of the virus could be one of the best options to reduce the incidence of infection. PVP-I gargle and mouthwash were found to be effective in vitro rapid inactivation against SARS-CoV-2 on a smaller scale (Hassandarvish et al. in BDJ 1-4, 2020, Pelletier et al. in ENTJ 1-5, 2020). However, efficacy in humans is lacking. To assess the virucidal effect of PVP-I against SARS-CoV-2 located in the nasopharynx was the objective of this parallel armed randomized clinical trial. We screened all RT-PCR-confirmed COVID-19 cases aged 18 years and above with symptoms. Written informed consent was obtained before randomization. Nasopharyngeal clearance of SARS-CoV-2 was tested after single time application of PVP-I nasal irrigation (NI) at diluted concentrations of .4%, .5% and .6% and PVP-I nasal spray (NS) at diluted concentrations of .5% and .6%. All groups were compared to the corresponding controls (distilled water). The primary outcome was viral clearance in a repeat RT-PCR (qualitative), and the secondary outcome was the number of adverse events. Final data analysis was performed using the statistical software SPSS (Version 20). A total of 189 confirmed COVID-19 cases were randomized into seven groups: 27 patients in each group. Of all, 159 (84.1%) were male, and 30 (15.9%) were female. We observed a statistically significant proportion of nasopharyngeal clearance with all strengths of PVP-I NI and PVP-I NS compared to the corresponding controls. Additionally, 0.5% NI was significantly better than 0.5% NS for viral clearance (p = 0.018) and had the highest nasopharyngeal clearance among all & Mostafa Kamal Arefin
Author contributions MKA had full access to all of the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. Conception of the research idea: MKA. Research design: MKA and MJH. Acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data: All authors. Drafting of the manuscript: All authors. Critical revision of the manuscript: All authors. Statistical analysis: ASK, MKA and MJH. Administrative, technical, or material support: AKMNU, MK and SSB. Supervision: MKA, SKNFR, and MJH. The authors read and approved the final manuscript. Funding The trial received research partial grant from BRICM.
Data Availability The corresponding author has access to the alltrial information, and the data will be available on reasonable request (contact: dr.jahid61@gmail.com or arefin61dmc@gmail.com).
Declarations Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval
References
Guenezan, Garcia, Strasters, Povidone iodine mouthwash, gargle, and nasal spray to reduce nasopharyngeal viral load in patients with COVID-19, JAMA-Otolaryngol Neck Surg, doi:10.1001/jamaoto.2020.5490
Hasan, Rumi, Banu, Uddin, Islam et al., Virucidal effect of povidone iodine on COVID-19 in the nasopharynx: a structured summary of a study protocol for an open-label randomized clinical trial, Trials, doi:10.1186/s13063-020-04963-2
Hassandarvish, Tiong, Mohamed, In vitro virucidal activity of povidone iodine gargle and mouthwash against SARS-CoV-2: implications for dental practice, Br Dent J, doi:10.1038/s41415-020-2402-0
Juszczak, Altman, Hopewell, Schulz, Reporting of multi-arm parallel-group randomized trials: extension of the CONSORT 2010 statement, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2019.3087
Lamas, Dios, Rodrı, Is povidone iodine mouthwash effective against SARS-CoV-2? First in vivo Tests Oral Dis, doi:10.1111/odi.13526
Pelletier, Tessema, Frank, Westover, Brown et al., Efficacy of povidone-iodine nasal and oral antiseptic preparations against severe acute respiratory syndromecoronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), Ear Nose Throat J, doi:10.1177/0145561320957237
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12070-021-02616-7",
"ISSN": [
"2231-3796",
"0973-7707"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12070-021-02616-7",
"alternative-id": [
"2616"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "14 April 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "10 May 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "18 May 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Declarations",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Conflict of interest",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "The authors declare that they have no competing interests."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Ethics approval",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 3,
"value": "The RCT protocol was approved by the Ethical Review Committee of Dhaka Medical College (Memo No: ERC-DMC/ECC/2020/93) on 23 May 2020."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Trial registration",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 4,
"value": "The trial protocol has been registered at ClinicalTrials.gov on September 16, 2020. NCT Identifier Number: NCT04549376. (ExternalRef removed)."
},
{
"label": "Free to read",
"name": "free",
"value": "This content has been made available to all."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6822-7418",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Arefin",
"given": "Mostafa Kamal",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rumi",
"given": "S. K. Nurul Fattah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Uddin",
"given": "A. K. M. Nasir",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Banu",
"given": "Sultana Sahana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khan",
"given": "Mala",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kaiser",
"given": "Ahsanul",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chowdhury",
"given": "Joybaer Anam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khan",
"given": "Md. Abdullah Saeed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hasan",
"given": "Mohammad Jahid",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Indian Journal of Otolaryngology and Head & Neck Surgery",
"container-title-short": "Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2021-05-18T18:02:41Z",
"timestamp": 1621360961000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-27T21:33:59Z",
"timestamp": 1669584839000
},
"funder": [
{
"name": "Bangladesh Reference Institute for Chemical Measurements"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-30T12:28:23Z",
"timestamp": 1711801703609
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 7,
"issue": "S2",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
18
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "S2",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.springer.com/tdm",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2021-05-18T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1621296000000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.springer.com/tdm",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2021-05-18T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1621296000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s12070-021-02616-7.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12070-021-02616-7/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s12070-021-02616-7.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"page": "2963-2967",
"prefix": "10.1007",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
18
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
18
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41415-020-2402-0",
"author": "P Hassandarvish",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Br Dent J",
"key": "2616_CR1",
"unstructured": "Hassandarvish P, Tiong V, Mohamed NA et al (2020) In vitro virucidal activity of povidone iodine gargle and mouthwash against SARS-CoV-2: implications for dental practice. Br Dent J. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41415-020-2402-0",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0145561320957237",
"author": "JS Pelletier",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Ear Nose Throat J",
"key": "2616_CR2",
"unstructured": "Pelletier JS, Tessema B, Frank S, Westover JB, Brown SM, Capriotti JA (2020) Efficacy of povidone-iodine nasal and oral antiseptic preparations against severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Ear Nose Throat J. https://doi.org/10.1177/0145561320957237",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2019.3087",
"author": "E Juszczak",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1610",
"issue": "16",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "2616_CR3",
"unstructured": "Juszczak E, Altman DG, Hopewell S, Schulz K (2019) Reporting of multi-arm parallel-group randomized trials: extension of the CONSORT 2010 statement. JAMA 321(16):1610–1620. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2019.3087",
"volume": "321",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13063-020-04963-2",
"author": "MJ Hasan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2",
"journal-title": "Trials",
"key": "2616_CR4",
"unstructured": "Hasan MJ, Rumi SKNF, Banu SS, Uddin AKMN, Islam MS, Arefin MK (2021) Virucidal effect of povidone iodine on COVID-19 in the nasopharynx: a structured summary of a study protocol for an open-label randomized clinical trial. Trials 22:2. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-020-04963-2",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/odi.13526",
"author": "LM Lamas",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "First in vivo Tests Oral Dis",
"key": "2616_CR5",
"unstructured": "Lamas LM, Dios PD, Rodríguez MTP et al (2020) Is povidone iodine mouthwash effective against SARS-CoV-2? First in vivo Tests Oral Dis. https://doi.org/10.1111/odi.13526",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamaoto.2020.5490",
"author": "J Guenezan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1871",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "JAMA-Otolaryngol Neck Surg",
"key": "2616_CR6",
"unstructured": "Guenezan J, Garcia M, Strasters D et al (2021) Povidone iodine mouthwash, gargle, and nasal spray to reduce nasopharyngeal viral load in patients with COVID-19. JAMA-Otolaryngol Neck Surg 9(6):1871. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoto.2020.5490",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 6,
"references-count": 6,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s12070-021-02616-7"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Otorhinolaryngology",
"Surgery"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Virucidal effect of povidone iodine on COVID-19 in the nasopharynx: an open-label randomized clinical trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "74"
}