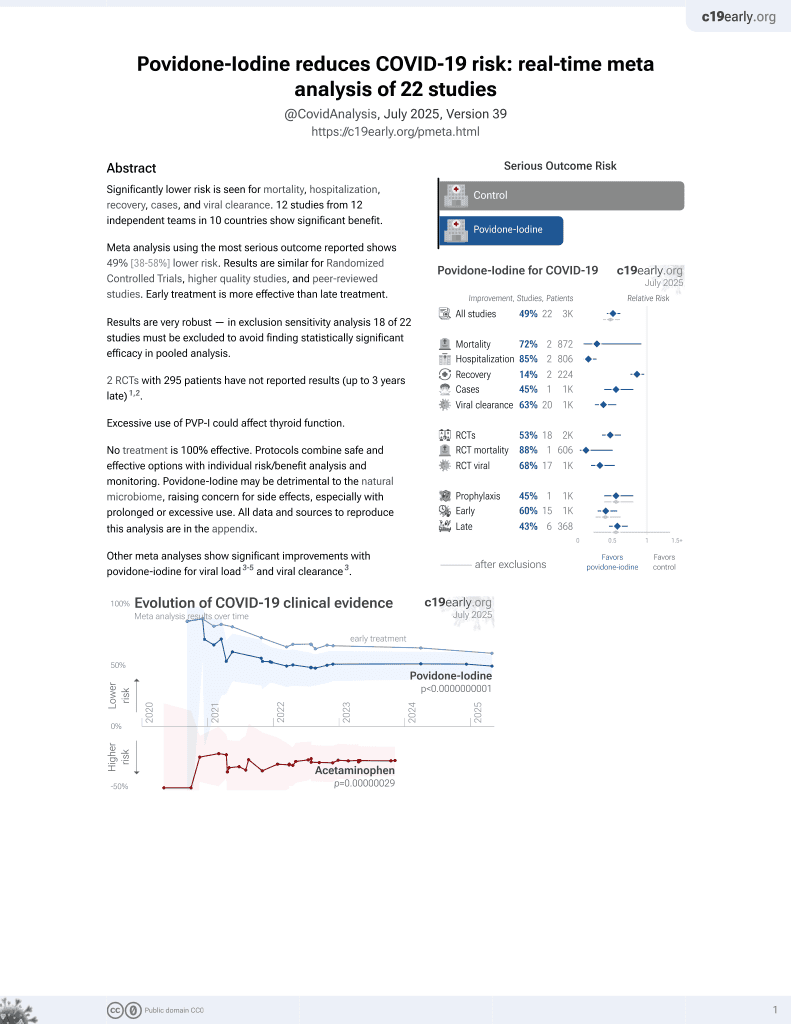
Povidone Iodine Mouthwash, Gargle, and Nasal Spray to Reduce Nasopharyngeal Viral Load in Patients With COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial
et al., JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg., doi:10.1001/jamaoto.2020.5490, NCT04371965, Feb 2021
PVP-I for COVID-19
15th treatment shown to reduce risk in
February 2021, now with p = 0.000000000016 from 22 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
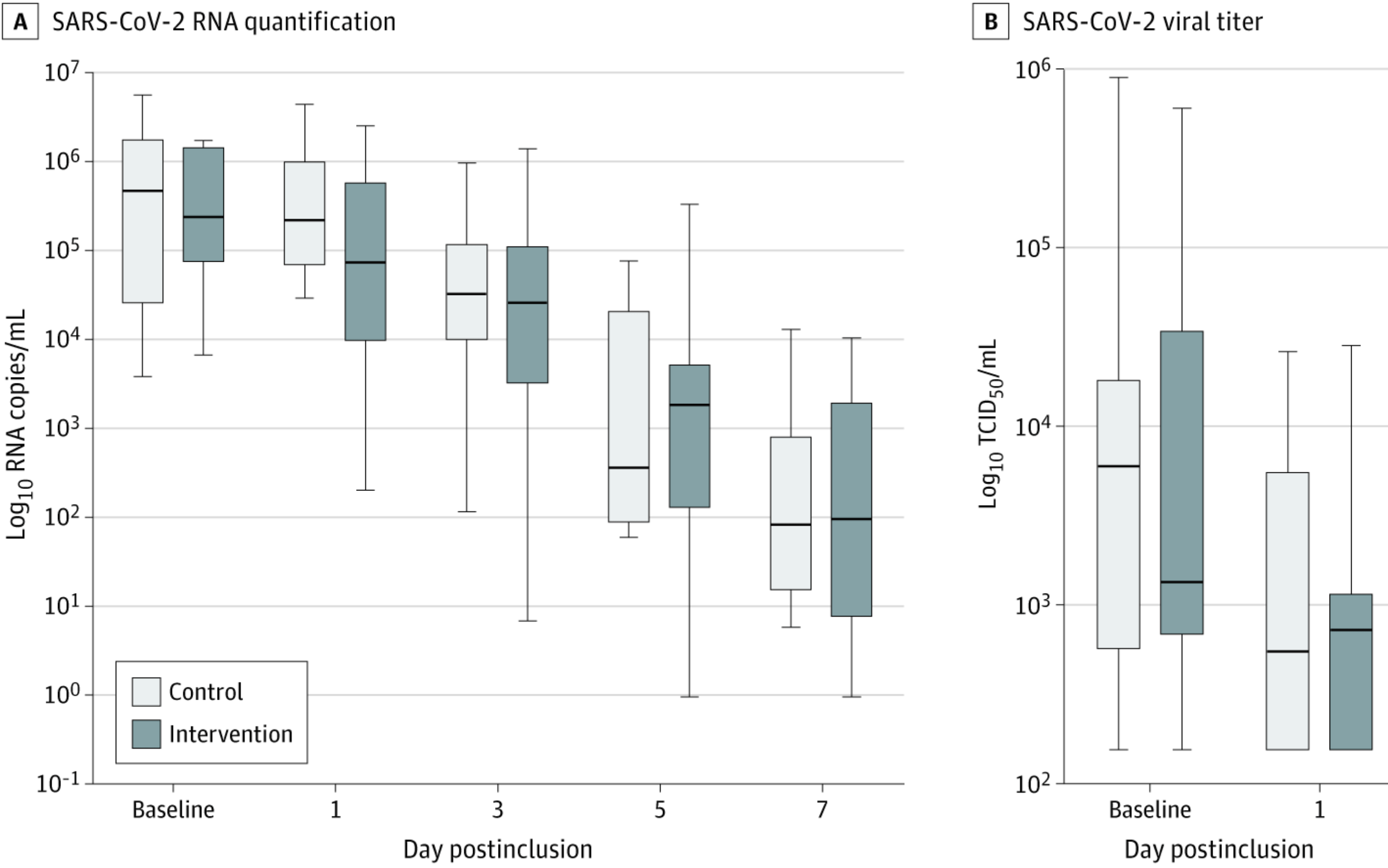
RCT of PCR+ patients with Ct ≤20 with 12 treatment and 12 control patients, concluding that nasopharyngeal decolonization may reduce the carriage of infectious SARS-CoV-2 in adults with mild to moderate COVID-19. All patients but 1 had negative viral titer by day 3 (group not specified). There was no significant difference in viral RNA quantification over time. The mean relative difference in viral titers between baseline and day 1 was 75% [43%-95%] in the intervention group and 32% [10%-65%] in the control group. Thyroid dysfunction occurred in 42% of treated patients, with spontaneous resolution after the end of treatment. Patients in the treatment group were younger.
Targeted administration to the respiratory tract provides treatment directly
to the typical source of initial SARS-CoV-2 infection and replication, and
allows for rapid onset of action, higher local drug concentration, and reduced systemic side effects.
|
relative improvement in viral titer reduction between baseline and day 1, 63.2% better, RR 0.37, p = 0.25, treatment 12, control 12.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Guenezan et al., 4 Feb 2021, Randomized Controlled Trial, France, peer-reviewed, 7 authors, study period 1 September, 2020 - 23 October, 2020, trial NCT04371965 (history).
Povidone Iodine Mouthwash, Gargle, and Nasal Spray to Reduce Nasopharyngeal Viral Load in Patients With COVID-19
JAMA Otolaryngology–Head & Neck Surgery, doi:10.1001/jamaoto.2020.5490
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is primarily transmitted person-to-person through the aerosolization of droplets containing contaminated nasopharyngeal secretions. 1 Povidone iodine (PI) solutions at concentrations as low as 0.5% rapidly inactivate SARS-CoV-2 in vitro with contact times as short as 15 seconds. 2 We investigated whether nasopharyngeal application of PI could reduce the viral load of patients with nonsevere coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) symptoms.
Conflict of Interest Funding/Support: This project was supported by the University Hospital of Poitiers, France. This study did not benefit from financial support. Role of the Funder/Sponsor: University Hospital of Poitiers, France, had no role in the design and conduct of the study; collection, management, analysis, and interpretation of the data; preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript; and decision to submit the manuscript for publication. Data Sharing Statement: See Supplement 2.
Additional Contributions: We acknowledge Cynthia Bordage, RN, Bertrand Drugeon, MD, Amélie Mabille, MD, Nicolas Marjanovic, MD, Severine Mousse, MSc, Alexandre Rahoui, MD and Camille Raynaud, MD, who assisted in data collection and patient follow-up, Pierre Dupuis, PharmD, who performed the biochemical tests, and Jeffrey Arsham for editing assistance, all from the University hospital of Poitiers, France. There was no financial compensation for these contributions.
OBSERVATION Adolescent Presentation of Nasal Chondromesenchymal Hamartoma: A Case Report and Literature Review Nasal chondromesenchymal hamartoma (NCMH) is a very rare benign tumor of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses that usually presents in infancy. These tumors may be expansile and locally destructive. The etiology has remained unclear, but it has been linked in the past to pleuropulmonary blastoma as
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamaoto.2020.5490",
"ISSN": [
"2168-6181"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jamaoto.2020.5490",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Emergency Department, University Hospital of Poitiers, Poitiers, France"
}
],
"family": "Guenezan",
"given": "Jeremy",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Virology laboratory, University Hospital of Poitiers, Poitiers, France"
}
],
"family": "Garcia",
"given": "Magali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Emergency Department, University Hospital of Poitiers, Poitiers, France"
}
],
"family": "Strasters",
"given": "Deidre",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Virology laboratory, University Hospital of Poitiers, Poitiers, France"
}
],
"family": "Jousselin",
"given": "Clément",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Virology laboratory, University Hospital of Poitiers, Poitiers, France"
}
],
"family": "Lévêque",
"given": "Nicolas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Anesthesia, Intensive Care and Perioperative Medicine, University Hospital of Poitiers, Poitiers, France"
}
],
"family": "Frasca",
"given": "Denis",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Emergency Department, University Hospital of Poitiers, Poitiers, France"
}
],
"family": "Mimoz",
"given": "Olivier",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "JAMA Otolaryngology–Head & Neck Surgery",
"container-title-short": "JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2021-02-06T02:55:47Z",
"timestamp": 1612580147000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-15T02:50:46Z",
"timestamp": 1671072646000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-30T12:27:24Z",
"timestamp": 1711801644140
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 63,
"issue": "4",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
1
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "4",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
1
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaotolaryngology/articlepdf/2775984/jamaotolaryngology_guenezan_2021_ld_200020_1617835427.97743.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "10",
"original-title": [],
"page": "400",
"prefix": "10.1001",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
1
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
1
]
]
},
"publisher": "American Medical Association (AMA)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.12839",
"article-title": "Pathophysiology, transmission, diagnosis, and treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Review.",
"author": "Wiersinga",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "782",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "old200020r1",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamaoto.2020.3053",
"article-title": "In vitro efficacy of a povidone-iodine nasal antiseptic for rapid inactivation of SARS-CoV-2.",
"author": "Frank",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg",
"key": "old200020r2",
"volume": "146",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm9061871",
"article-title": "Performance assessment of SARS-CoV-2 PCR assays developed by WHO referral laboratories.",
"author": "Etievant",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1871",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "J Clin Med",
"key": "old200020r3",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/BF01863914",
"article-title": "Beitrag zur kollektiven Behandlung pharmakologischer Reihenversuche.",
"author": "Kärber",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "480",
"journal-title": "Archiv f experiment Pathol u Pharmakol",
"key": "old200020r4",
"volume": "162",
"year": "1934"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamaoto.2020.1622",
"article-title": "Benefits and safety of nasal saline irrigations in a pandemic—washing COVID-19 away.",
"author": "Farrell",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "787",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg",
"key": "old200020r5",
"volume": "146",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0002-8223(21)01843-5",
"article-title": "A review of iodine toxicity reports.",
"author": "Pennington",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1571",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "J Am Diet Assoc",
"key": "old200020r6",
"volume": "90",
"year": "1990"
}
],
"reference-count": 6,
"references-count": 6,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaotolaryngology/fullarticle/2775984"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Otorhinolaryngology",
"Surgery"
],
"subtitle": [
"A Randomized Clinical Trial"
],
"title": "Povidone Iodine Mouthwash, Gargle, and Nasal Spray to Reduce Nasopharyngeal Viral Load in Patients With COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "147"
}