Intravenous Vitamin C for Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19 Two Harmonized Randomized Clinical Trials
et al., JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2023.21407, LOVIT-COVID, NCT04401150, Oct 2023
Vitamin C for COVID-19
6th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000068 from 74 studies, recognized in 22 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
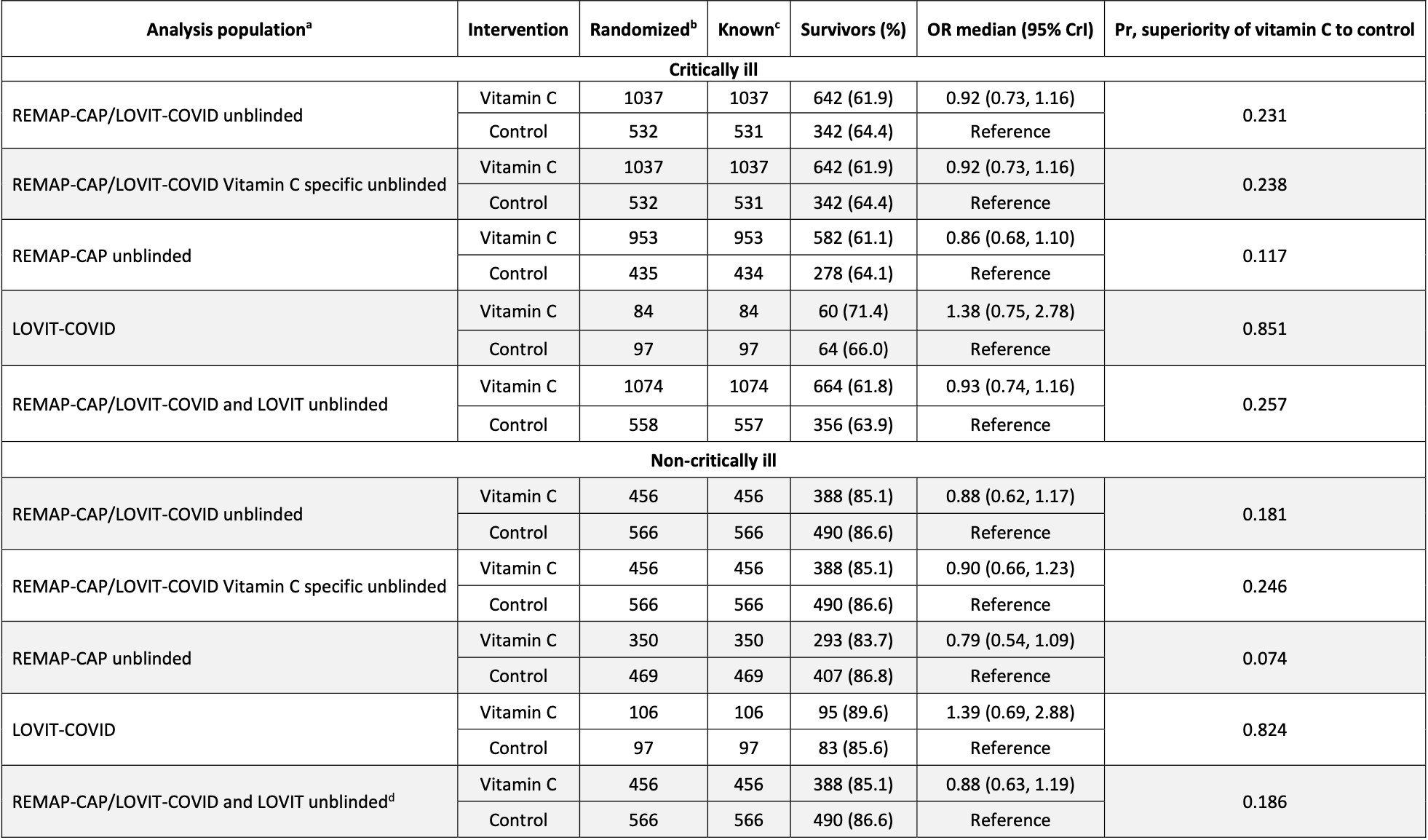
Very late stage (APACHE II 8 and 12 for non-critical and critical) RCT with publication delayed over a year showing higher ventilation and no significant difference in mortality with vitamin C.
Authors have combined what was to be two separate trials into one trial, however there are very large differences between the trials. The results for each source trial are shown separately here1,2.
eTable 15 shows that results in LOVIT-COVID were substantially better than those in REMAP-CAP. eTable 13 shows improved survival for LOVIT-COVID and worse survival for REMAP-CAP (authors provide mortality breakdown only for hospital survival):
LOVIT-COVID shows 85% and 82% probability of superiority of vitamin C (critical and non-critical).
REMAP-CAP shows 12% and 7% probability of superiority of vitamin C.
REMAP-CAP shows 12% and 7% probability of superiority of vitamin C.
Notably, LOVIT-COVID patients were blinded, while REMAP-CAP was open-label, introducing additional opportunity for bias on this highly politicized treatment. REMAP-CAP had more patients and dominates the combined results.
eFigure 8b also shows that the REMAP-CAP results were initially positive, switching to negative around September 2021. Authors note that they were unable to explain this reversal. The overall negative result is only due to the larger number of patients in the REMAP-CAP later time period.
Results for intubation are much worse than mortality, with statistically significant higher intubation for the treatment group. Hypothetically, if the actual risk matched other trials (~20% lower risk in meta analysis of 18 RCTs at the time), and there was something causing biased intubation of treatment patients in this mostly open-label trial, we may get the observed results whereby intubation is significantly worse due to the bias, but this has a muted effect on mortality which may reflect the change in risk due to intubation combined with that due to treatment.
Results varied dramatically over time. For example, during 22 Jan - 21 Apr 2021, the probability of superiority for vitamin C was 1.0 for critical and 0.97 for non-critical (eTable 17).
There were dramatic changes in randomization proportions and in overall clinical outcomes over time, leading to potential issues and inaccuracies in the attempted adjustment for confounding by time.
The very long delay between the end of the trial and publication also raises questions.
See also Hemilä et al. which shows that the poor results may be explained by a rebound effect due to the abrupt termination of treatment after 4 days.
NCT04401150 (history) (LOVIT-COVID) and NCT02735707 (history) (REMAP-CAP). 50mg/kg vitamin C administered intravenously over 30-60 minutes every 6 hours for 4 days.
Although the 28% lower mortality is not statistically significant, it is consistent with the significant 18% lower mortality [9‑27%] from meta-analysis of the 45 mortality results to date.
This is the 20th of 21 COVID-19 RCTs for vitamin C, which collectively show efficacy with p=0.0012.
This is the 66th of 74 COVID-19 controlled studies for vitamin C, which collectively show efficacy with p=0.000000068.
|
risk of death, 27.8% lower, HR 0.72, p = 0.19, treatment 190, control 194, combined.
|
|
risk of death, 27.5% lower, HR 0.72, p = 0.34, treatment 84, control 97, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, LOVIT-COVID critical.
|
|
risk of death, 28.1% lower, HR 0.72, p = 0.37, treatment 106, control 97, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, LOVIT-COVID non-critical.
|
|
risk of death, 16.3% higher, HR 1.16, p = 0.22, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, REMAP-CAP critical.
|
|
risk of death, 26.6% higher, HR 1.27, p = 0.19, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, REMAP-CAP non-critical.
|
|
risk of death, 6.4% higher, HR 1.06, p = 0.47, treatment 1,032, control 528, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, combined trials, critical, day 90.
|
|
risk of death, 7.5% higher, HR 1.08, p = 0.56, treatment 454, control 563, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, combined trials, non-critical, day 90.
|
|
risk of death, 6.4% higher, HR 1.06, p = 0.61, treatment 1,032, control 528, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, combined trials, critical, day 28.
|
|
risk of death, 6.4% higher, HR 1.06, p = 0.71, treatment 454, control 563, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, non-critical, day 28.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 35.1% higher, HR 1.35, p = 0.04, treatment 1,032, control 528, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, combined trials, critical.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 69.5% higher, HR 1.69, p = 0.008, treatment 454, control 563, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, combined trials, non-critical.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Adhikari et al., Intravenous Vitamin C for Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19 Two Harmonized Randomized Clinical Trials, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2023.21407.
Adhikari et al., 25 Oct 2023, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, multiple countries, peer-reviewed, 82 authors, dosage 50mg/kg qid days 1-4, trial NCT04401150 (history) (LOVIT-COVID).
Intravenous Vitamin C for Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19
JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2023.21407
The efficacy of vitamin C for hospitalized patients with COVID-19 is uncertain. OBJECTIVE To determine whether vitamin C improves outcomes for patients with COVID-19.
Additional Information: This article was written with gratitude to and in memory of our friend and colleague, Wilma van Bentum-Puijk, MSc.
References
Abraham, Reinhart, Opal, Efficacy and safety of tifacogin (recombinant tissue factor pathway inhibitor) in severe sepsis: a randomized controlled trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.290.2.238?utm_campaign=articlePDF%26utm_medium=articlePDFlink%26utm_source=articlePDF%26utm_content=jama.2023.21407
Angus, Berry, Lewis, The REMAP-CAP (Randomized Embedded Multifactorial Adaptive Platform for Community-acquired Pneumonia) study: rationale and design, Ann Am Thorac Soc, doi:10.1513/AnnalsATS.202003-192SD
Attacc, ACTIV-4a Investigators, and REMAP-CAP Investigators. Therapeutic anticoagulation with heparin in noncritically ill patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2105911
Bhatt, Mehta, Adaptive designs for clinical trials, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMra1510061
Canner, The Coronary Drug Project: monitoring of the data for evidence of adverse or beneficial treatment effects, Control Clin Trials, doi:10.1016/0197-2456(83)90029-6
Carr, Rowe, The emerging role of vitamin C in the prevention and treatment of COVID-19, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12113286
Chiscano-Camón, Ruiz-Rodriguez, Ruiz-Sanmartin, Roca, Ferrer, Vitamin C levels in patients with SARS-CoV-2-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome, Crit Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-020-03249-y
Dechartres, Trinquart, Boutron, Ravaud, Influence of trial sample size on treatment effect estimates: meta-epidemiological study, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.f2304
Fish, Rynne, Jennings, REMAP-CAP Immunoglobulin Domain UK Investigators. Coronavirus disease 2019 subphenotypes and differential treatment response to convalescent plasma in critically ill adults: secondary analyses of a randomized clinical trial, Intensive Care Med, doi:10.1007/s00134-022-06869-w
Fowler, Iii, Syed, Knowlson, Unit Nursing. Phase I safety trial of intravenous ascorbic acid in patients with severe sepsis, J Transl Med, doi:10.1186/1479-5876-12-32
Fowler, Iii, Truwit, Hite, Effect of vitamin C infusion on organ failure and biomarkers Research Original Investigation Intravenous Vitamin C for Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19 of inflammation and vascular injury in patients with sepsis and severe acute respiratory failure: the CITRIS-ALI randomized clinical trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2019.11825?utm_campaign=articlePDF%26utm_medium=articlePDFlink%26utm_source=articlePDF%26utm_content=jama.2023.21407
Fujii, Luethi, Young, Effect of vitamin C, hydrocortisone, and thiamine vs hydrocortisone alone on time alive and free of vasopressor support among patients with septic shock: the VITAMINS randomized clinical trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2019.22176?utm_campaign=articlePDF%26utm_medium=articlePDFlink%26utm_source=articlePDF%26utm_content=jama.2023.21407
Glasziou, Sanders, Hoffmann, Waste in COVID-19 research, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.m1847
Granholm, Kaas-Hansen, Lange, An overview of methodological considerations regarding adaptive stopping, arm dropping, and randomization in clinical trials, J Clin Epidemiol, doi:10.1016/j.jclinepi.2022.11.002
Heyland, Muscedere, Drover, Jiang, Day et al., Persistent organ dysfunction plus death: a novel, composite outcome measure for critical care trials, Crit Care, doi:10.1186/cc10110
Higgins, Berry, Lorenzi, Writing Committee for the REMAP-CAP Investigators. Long-term (180-day) outcomes in critically ill patients with COVID-19 in the REMAP-CAP randomized clinical trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2022.23257?utm_campaign=articlePDF%26utm_medium=articlePDFlink%26utm_source=articlePDF%26utm_content=jama.2023.21407
Horby, Lim, Emberson, Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2021436
Lamontagne, Agarwal, Rochwerg, A living WHO guideline on drugs for COVID-19, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.m3379
Lamontagne, Masse, Menard, Intravenous vitamin C in adults with sepsis in the intensive care unit, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2200644
Laterre, Berry, Blemings, Effect of selepressin vs placebo on ventilator-and vasopressor-free days in patients with septic shock: the SEPSIS-ACT randomized clinical trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2019.14607?utm_campaign=articlePDF%26utm_medium=articlePDFlink%26utm_source=articlePDF%26utm_content=jama.2023.21407
Olczak-Pruc, Swieczkowski, Ladny, Vitamin C supplementation for the treatment of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14194217
Ramanan, Tong, Kumar, Venkatesh, Geographical representation of low-and middle-income countries in randomized clinical trials for COVID-19, JAMA Netw Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.0444?utm_campaign=articlePDF%26utm_medium=articlePDFlink%26utm_source=articlePDF%26utm_content=jama.2023.21407
Sevransky, Rothman, Hager, Effect of vitamin C, thiamine, and hydrocortisone on ventilator-and vasopressor-free days in patients with sepsis: the VICTAS randomized clinical trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.24505?utm_campaign=articlePDF%26utm_medium=articlePDFlink%26utm_source=articlePDF%26utm_content=jama.2023.21407
Usher, The global COVID-19 treatment divide, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00372-5
Vail, Wunsch, Pinto, Use of hydrocortisone, ascorbic acid, and thiamine in adults with septic shock, Am J Respir Crit Care Med, doi:10.1164/rccm.202005-1829OC
Vijayaraghavan, Md; Rashan, Haniffa, Beane, Phd et al., None
Wheatley, Clayton, Be skeptical about unexpected large apparent treatment effects: the case of an MRC AML12 randomization, Control Clin Trials, doi:10.1016/S0197-2456(02)00273-8
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2023.21407",
"ISSN": [
"0098-7484"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/jama.2023.21407",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Importance</jats:title><jats:p>The efficacy of vitamin C for hospitalized patients with COVID-19 is uncertain.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Objective</jats:title><jats:p>To determine whether vitamin C improves outcomes for patients with COVID-19.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Design, Setting, and Participants</jats:title><jats:p>Two prospectively harmonized randomized clinical trials enrolled critically ill patients receiving organ support in intensive care units (90 sites) and patients who were not critically ill (40 sites) between July 23, 2020, and July 15, 2022, on 4 continents.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Interventions</jats:title><jats:p>Patients were randomized to receive vitamin C administered intravenously or control (placebo or no vitamin C) every 6 hours for 96 hours (maximum of 16 doses).</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Main Outcomes and Measures</jats:title><jats:p>The primary outcome was a composite of organ support–free days defined as days alive and free of respiratory and cardiovascular organ support in the intensive care unit up to day 21 and survival to hospital discharge. Values ranged from –1 organ support–free days for patients experiencing in-hospital death to 22 organ support–free days for those who survived without needing organ support. The primary analysis used a bayesian cumulative logistic model. An odds ratio (OR) greater than 1 represented efficacy (improved survival, more organ support–free days, or both), an OR less than 1 represented harm, and an OR less than 1.2 represented futility.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>Enrollment was terminated after statistical triggers for harm and futility were met. The trials had primary outcome data for 1568 critically ill patients (1037 in the vitamin C group and 531 in the control group; median age, 60 years [IQR, 50-70 years]; 35.9% were female) and 1022 patients who were not critically ill (456 in the vitamin C group and 566 in the control group; median age, 62 years [IQR, 51-72 years]; 39.6% were female). Among critically ill patients, the median number of organ support–free days was 7 (IQR, −1 to 17 days) for the vitamin C group vs 10 (IQR, −1 to 17 days) for the control group (adjusted proportional OR, 0.88 [95% credible interval {CrI}, 0.73 to 1.06]) and the posterior probabilities were 8.6% (efficacy), 91.4% (harm), and 99.9% (futility). Among patients who were not critically ill, the median number of organ support–free days was 22 (IQR, 18 to 22 days) for the vitamin C group vs 22 (IQR, 21 to 22 days) for the control group (adjusted proportional OR, 0.80 [95% CrI, 0.60 to 1.01]) and the posterior probabilities were 2.9% (efficacy), 97.1% (harm), and greater than 99.9% (futility). Among critically ill patients, survival to hospital discharge was 61.9% (642/1037) for the vitamin C group vs 64.6% (343/531) for the control group (adjusted OR, 0.92 [95% CrI, 0.73 to 1.17]) and the posterior probability was 24.0% for efficacy. Among patients who were not critically ill, survival to hospital discharge was 85.1% (388/456) for the vitamin C group vs 86.6% (490/566) for the control group (adjusted OR, 0.86 [95% CrI, 0.61 to 1.17]) and the posterior probability was 17.8% for efficacy.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusions and Relevance</jats:title><jats:p>In hospitalized patients with COVID-19, vitamin C had low probability of improving the primary composite outcome of organ support–free days and hospital survival.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Trial Registration</jats:title><jats:p>ClinicalTrials.gov Identifiers: <jats:ext-link xmlns:xlink=\"http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink\" ext-link-type=\"uri\" xlink:href=\"https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04401150?id=NCT04401150&amp;amp;rank=1\">NCT04401150</jats:ext-link> (LOVIT-COVID) and <jats:ext-link xmlns:xlink=\"http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink\" ext-link-type=\"uri\" xlink:href=\"https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02735707?id=NCT02735707&amp;amp;rank=1\">NCT02735707</jats:ext-link> (REMAP-CAP)</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Florescu",
"given": "Simin ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Stanciu",
"given": "Delia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Zaharia",
"given": "Mihaela ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": " Kosa",
"given": "Alma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Codreanu",
"given": "Daniel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Fareed",
"given": "Komal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kidwai",
"given": "Aneela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kaye",
"given": "Callum",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Coutts",
"given": "Amanda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "MacKay",
"given": "Lynn",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Summers",
"given": "Charlotte",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Polgarova",
"given": "Petra ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Farahi",
"given": "Neda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Fox",
"given": "Eleonore",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sapsford",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bongaerts",
"given": "Katherine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Featherstone",
"given": "Peter",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ng",
"given": "Anthony",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McWilliam",
"given": "Stephen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hawcutt",
"given": "Daniel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rad",
"given": "Laura",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "O’Malley",
"given": "Laura",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Whitbread",
"given": "Jennifer",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "Dawn",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Dore",
"given": "Rachael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Saunderson",
"given": "Paula ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kelsall",
"given": "Olivia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cowley",
"given": "Nicholas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wild",
"given": "Laura",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Thrush",
"given": "Jessica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wood",
"given": "Hannah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Austin",
"given": "Karen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Donnelly",
"given": "Adrian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kelly",
"given": "Martin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Smyth",
"given": "Naoise",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "O’Kane",
"given": "Sinéad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McClintock",
"given": "Declan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Warnock",
"given": "Majella",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Campbell",
"given": "Ryan ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McCallion",
"given": "Edmund",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": " Azaiz",
"given": "Amine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Charron",
"given": "Cyril",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Godement",
"given": "Mathieu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Geri",
"given": "Guillaume",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vieillard-Baron",
"given": "Antoine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Johnson",
"given": "Paul",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McKenna",
"given": "Shirley",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hanley",
"given": "Joanne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Currie",
"given": "Andrew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Allen",
"given": "Barbara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McGoldrick",
"given": "Clare ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McMaster",
"given": "Moyra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mani",
"given": "Ashwin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mathew",
"given": "Meghena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kandeepan",
"given": "Revathi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vignesh",
"given": "Chandrashekar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ramakrishnan",
"given": "Nagarajan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "James",
"given": "Augustian ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Elvira ",
"given": "Evangeline",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pratheema",
"given": "Ramachandran",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Babu",
"given": "Suresh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ebenezer",
"given": "Rabindrarajan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Krishnamoorthy",
"given": "S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ranganathan",
"given": "Lakshmi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ganesan",
"given": "Manisha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Shree",
"given": "Madhu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Piva",
"given": "Simone",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Focà",
"given": "Emanuele",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rizzoni",
"given": "Damiano",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Boari",
"given": "Gianluca",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Marchesi",
"given": "Mattia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Butler",
"given": "Magdalena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cowdrey",
"given": "Keri-Anne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mason",
"given": "Brittany",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Woolett",
"given": "Melissa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Duffy",
"given": "Eamon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Yan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Nakamuro",
"given": "Hiromi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "O’Connor",
"given": "Caroline",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "West",
"given": "Lauren",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "El-Khawas",
"given": "Khaled",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Richardson",
"given": "Angus",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hill",
"given": "Dianne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Commons",
"given": "Robert",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Abdelkharim",
"given": "Hussam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Saxena",
"given": "Manoj",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Muteithia",
"given": "Margaret",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Dobell-Brown",
"given": "Kelsey",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jha",
"given": "Rajeev",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kalogirou",
"given": "Michael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ellis",
"given": "Christine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Krishnamurthy",
"given": "Vinodh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "O’Connor",
"given": "Aibhilin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Thurairatnam",
"given": "Saranya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mukherjee",
"given": "Dipak",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kaliappan",
"given": "Agilan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vertue",
"given": "Mark",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Nicholson",
"given": "Anne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Riches",
"given": "Joanne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Maloney",
"given": "Gracie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kittridge",
"given": "Lauren",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Solesbury",
"given": "Amanda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ramos",
"given": "Angelo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Collins",
"given": "Daniel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Brickell",
"given": "Kathy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Reid",
"given": "Liadain",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Smyth",
"given": "Michelle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Breen",
"given": "Patrick",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Spain",
"given": "Sandra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Curley",
"given": "Gerard",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McEvoy",
"given": "Natalie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Geoghegan",
"given": "Pierce",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Clarke ",
"given": "Jennifer",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Silversides",
"given": "Jon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McGuigan",
"given": "Peter",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ward",
"given": "Kathryn",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "O’Neill",
"given": "Aisling",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Finn",
"given": "Stephanie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wright",
"given": "Chris",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Green",
"given": "Jackie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Collins",
"given": "Érin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Major",
"given": "Emmet",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McAuley",
"given": "Julie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Carter",
"given": "Angus",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Smith",
"given": "Julie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Boschert",
"given": "Catherine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Slieker",
"given": "Kitty",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ewalds",
"given": "Esther",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sanders",
"given": "Arnate",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wittenberg",
"given": "Wendy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Geurts",
"given": "Heidi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Poojara",
"given": "Latesh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sara",
"given": "Treena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Nand",
"given": "Kiran",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Reeve",
"given": "Brenda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Dechert ",
"given": "William",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Phillips",
"given": "Barbara ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Oritz-Ruiz de Gordoa",
"given": "Laura",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Campbell",
"given": "Marion",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Dos Santos",
"given": "Filipa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hansen",
"given": "Dan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mullan",
"given": "Dee",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Affleck",
"given": "Julia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Shaikh",
"given": "Arif",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Murray",
"given": "Andrew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ramanan",
"given": "Mahesh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Frakking",
"given": "Thuy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pinnell",
"given": "Jez",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Robinson",
"given": "Matt ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gledhill",
"given": "Lisa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wood",
"given": "Tracy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sanghavi",
"given": "Ritesh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bhonagiri",
"given": "Deepak",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ford",
"given": "Megan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Parikh",
"given": "Harshel G.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Avard",
"given": "Bronwyn",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Nourse",
"given": "Mary",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McDonald",
"given": "Bree",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Edmunds",
"given": "Natasha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hoiting",
"given": "Oscar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Peters",
"given": "Marco",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rengers",
"given": "Els",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bindels",
"given": "Manon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Evers",
"given": "Mirjam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Prinssen",
"given": "Anton",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Morgan",
"given": "Matt",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cole",
"given": "Jade ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hill",
"given": "Helen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Davies",
"given": "Michelle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Williams",
"given": "Angharad ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Thomas",
"given": "Emma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Davies",
"given": "Rhys",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wise",
"given": "Matt",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Law",
"given": "Daniel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Grimm",
"given": "Patrick",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Soukup",
"given": "Jens",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wetzold",
"given": "Richard",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Löbel",
"given": "Madlen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Starke",
"given": "Lisa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lellouche",
"given": "Francois ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lizotte",
"given": "Patricia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Auvet",
"given": "Adrien",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ravry",
"given": "Celine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Creange",
"given": "Vanessa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Boivin",
"given": "Anne-Helene",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Barreau",
"given": "Amélie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vandewoestyne",
"given": "Sophie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Declercq",
"given": "Pierre-Louis",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Marchalot ",
"given": "Antoine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Saladin",
"given": "Cecile",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gelinotte",
"given": "Stephanie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Eraldi",
"given": "Jean-Pierre",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bourgerol ",
"given": "François",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Beuzelin ",
"given": "Marion",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jean-Philippe",
"given": "Rigaud",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pourcine",
"given": "Franck",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Monchi",
"given": "Mehran",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pradel",
"given": "Gael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hausermann",
"given": "Marie-Helene",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Boudineau",
"given": "Michel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Nguyen-Valat",
"given": "Thi-My-Hue",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Guitton",
"given": "Christophe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Marnai",
"given": "Remy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Leroyer",
"given": "Marie-Helene",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Landais",
"given": "Michaël",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Darreau",
"given": "Cedric",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Saint Martin",
"given": "Marjorie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Tirot",
"given": "Patrice",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Chudeau",
"given": "Nicolas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Brasselet",
"given": "Aurélie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Volkov",
"given": "Lev",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Callahan",
"given": "Jean-Christophe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Meunier",
"given": "Juliette",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Douillard",
"given": "Thomas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Le Basnier",
"given": "Elliot",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Veillard",
"given": "Marion",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vivier",
"given": "Dominique",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Luis",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mercier",
"given": "Romain",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sagnier",
"given": "Anne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Verrier",
"given": "Nathalie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Caplin",
"given": "Cecile",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Richecoeur",
"given": "Jack",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Combaux",
"given": "Daniele",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Siami",
"given": "Shidasp",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Aparicio",
"given": "Christelle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vautier",
"given": "Sarah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jeblaoui",
"given": "Asma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lemaire-Brunel",
"given": "Delphine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "D’Aragon",
"given": "Frédérick",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bérard",
"given": "Dominique",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Grondin-Beaudoin",
"given": "Brian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Leclair",
"given": "Marc-André",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lesur",
"given": "Olivier",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mayette",
"given": "Michaël",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Poulin",
"given": "Yannick",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Quiroz-Martinez",
"given": "Hector",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "St-Arnaud",
"given": "Charles",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Carbonneau",
"given": "Elaine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bolduc",
"given": "Brigitte",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bélisle",
"given": "Julie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bouchard",
"given": "Marie-Pier",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Côté",
"given": "Line",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Martineau",
"given": "Joannie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Naisby",
"given": "Alexandra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Robert-Petit",
"given": "Louise",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Thibault",
"given": "Marie-Ève",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Leblond",
"given": "Julie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Plantefeve",
"given": "Gaetan ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Leparco",
"given": "Cécile",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Contou",
"given": "Damien",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Fartoukh",
"given": "Muriel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Courtin",
"given": "Laura",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Labbe",
"given": "Vincent",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Voiriot",
"given": "Guillaume",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Salhi",
"given": "Sara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Chassé",
"given": "Michaël",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pierre",
"given": "Aslanian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bélisle",
"given": "Sylvain",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Carrier",
"given": "François Martin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Charbonney",
"given": "Emmanuel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Girard",
"given": "Martin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Guimond",
"given": "Jean-Gilles",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Halwagi",
"given": "Antoine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kolan",
"given": "Christophe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Robillard",
"given": "Nicholas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Boumahni",
"given": "Dounia ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Benettaib",
"given": "Fatna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cantin",
"given": "Marie-Ève",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Coutu-Beaudry",
"given": "Katherine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ghamraoui",
"given": "Ali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lamothe",
"given": "Francesca",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lebrasseur",
"given": "Martine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Prie",
"given": "Cindy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Salamé",
"given": "Maya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Archambault",
"given": "Patrick",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Côté",
"given": "Émilie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Beaudoin",
"given": "Rosalie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Noel-Hunter",
"given": "Monia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Boutin",
"given": "Mireille",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Couture",
"given": "Laurie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sement",
"given": "Arnaud",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gachet",
"given": "Alexandre",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hanisch",
"given": "Alexis",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Haffiane",
"given": "Abdelmagid",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Boivin",
"given": "Anne-Hélène",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Barreau",
"given": "Amelie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Guerineau",
"given": "Elodie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Poupblanc",
"given": "Séverine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Egreteau",
"given": "Pierre-Yves",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lefevre",
"given": "Montaine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bocher",
"given": "Simon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Le Loup",
"given": "Guillaume",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Le Guen",
"given": "Lenaïg",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Carn",
"given": "Vanessa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bertel",
"given": "Melanie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Antcliffe",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Templeton",
"given": "Maie ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rojo",
"given": "Roceld",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Coghlan",
"given": "Phoebe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Smee",
"given": "Joanna ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Barker",
"given": "Gareth",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Finn",
"given": "André",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kreß",
"given": "Gabriele",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hoff",
"given": "Uwe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hinrichs",
"given": "Carl",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Nee",
"given": "Jens",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mackay",
"given": "Euan ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cort",
"given": "Jon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Whileman",
"given": "Amanda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Spencer",
"given": "Thomas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Spittle",
"given": "Nick",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Beavis",
"given": "Sarah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Padmakumar",
"given": "Anand",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Dale",
"given": "Katie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hawes",
"given": "Joanne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Moakes",
"given": "Emma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gascoyne",
"given": "Rachel ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pritchard",
"given": "Kelly",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Stevenson",
"given": "Lesley",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cooke",
"given": "Justin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Nemeth-Roszpopa",
"given": "Karolina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Adhikari",
"given": "Sheetal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gauli",
"given": "Basanta",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kunwar",
"given": "Puja",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Muller",
"given": "Grégoire",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Nay",
"given": "Mai-Anh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kamel",
"given": "Toufik",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Benzekri",
"given": "Dalila",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jacquier",
"given": "Sophie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Runge",
"given": "Isabelle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mathonnet",
"given": "Armelle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Barbier",
"given": "François",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bretagnol",
"given": "Anne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Carter",
"given": "Jay",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Van Der Heyden",
"given": "Kymbalee",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mehrtens",
"given": "Jan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Morris",
"given": "Anna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Morgan",
"given": "Stacey",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Burke",
"given": "Tara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mercier",
"given": "Emmanuelle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Chartier",
"given": "Delphine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Salmon",
"given": "Charlotte",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Dequin",
"given": "Pierre-François",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Garot",
"given": "Denis",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Quenot",
"given": "Jean Pierre",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Garrier",
"given": "Ludivine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Villot",
"given": "Solenne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Audry",
"given": "Mathilde",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Brassard",
"given": "Eric",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Francoeur ",
"given": "Charles",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lauzier",
"given": "François",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Leblanc",
"given": "Guillaume",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "St-Onge",
"given": "Maude",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bellemare",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cloutier",
"given": "Ève ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Daher",
"given": "Rana ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Costerousse",
"given": "Olivier",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Boulanger",
"given": "Marie-Claude",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Couillard-Chénard",
"given": "Émilie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mallard",
"given": "Louis-Charles",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Thibeault",
"given": "Frédérique",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Tremblay",
"given": "Antoine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Francois",
"given": "Bruno",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gay",
"given": "Alexandra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Anne-Laure",
"given": "Fedou",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ramali",
"given": "Mohamed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "HC",
"given": "Ooi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ghosh",
"given": "Alison",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Osagie",
"given": "Rawlings",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Arachchige",
"given": "Malka",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hartley",
"given": "Melissa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Shu Ki Lok",
"given": "Jennifer",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Plummer",
"given": "Bethany",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hin Lui",
"given": "Lok",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bloomfield",
"given": "Jack",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Balls-Burgess",
"given": "Sam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Seigne",
"given": "Patick",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Philip",
"given": "Annlin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cleary",
"given": "Joanne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "O'Neill",
"given": "Lorraine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kelly",
"given": "Niamh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bamford",
"given": "Peter",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Reid",
"given": "Andrew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cawley",
"given": "Kathryn",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Faulkner",
"given": "Maria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pickering",
"given": "Charlotte",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Raj",
"given": "Ashok ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Tsinaslanidis",
"given": "Georgios",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Khade",
"given": "Reena ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Agha",
"given": "Gloria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sekiwala",
"given": "Rose",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Smith",
"given": "Tim",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Brewer",
"given": "Chris",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gregory",
"given": "Jane",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Limb",
"given": "James",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cowton",
"given": "Amanda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "O’Brien",
"given": "Julie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Postlethwaite",
"given": "Kelly",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Malakouti ",
"given": "Salim",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Music",
"given": "Edvin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ricketts",
"given": "Dan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "King",
"given": "Andrew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Clermont",
"given": "Gilles",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bart",
"given": "Robert",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mayr",
"given": "Florian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Schoenling",
"given": "Andrew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Andreae",
"given": "Mark",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Shetty",
"given": "Varun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Brant",
"given": "Emily",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Malley",
"given": "Brian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Donadee",
"given": "Chenell",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Horvat",
"given": "Christopher",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Girard",
"given": "Timothy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sackrowitz",
"given": "Rachel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Weissman",
"given": "Alexandra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Yealy",
"given": "Donald",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Barton",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Talia",
"given": "Nadine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Nikitas",
"given": "Nikitas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wells",
"given": "Colin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McMillan",
"given": "Helen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Stowe",
"given": "Bethan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Spencer",
"given": "Kayleigh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Stapleton",
"given": "Liana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "van den Oever",
"given": "Huub",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kruisdijk-Gerritsen",
"given": "Arriette",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Haidar",
"given": "Ghady ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bain",
"given": "William",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Barbash",
"given": "Ian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Fitzpatrick",
"given": "Meghan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kitsios",
"given": "Georgios",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Moghbeli",
"given": "Kaveh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rosborough",
"given": "Brian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Shah",
"given": "Faraaz",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Suber",
"given": "Tomeka",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Stanley",
"given": "Timothy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Castle",
"given": "James",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Carr",
"given": "Zoe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Alegria",
"given": "Ana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Turki",
"given": "Salah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Elsefi",
"given": "Tarek",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Crisp",
"given": "Nikki",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Allen",
"given": "Louise",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Truman",
"given": "Nicholas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Smith",
"given": "Matthew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Chukkambotla",
"given": "Sri",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Goddard",
"given": "Wendy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Duberley",
"given": "Stephen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Khan",
"given": "Meherunnisa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kazi",
"given": "Aayesha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Simpson",
"given": "Joanna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Duke",
"given": "Graeme",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Chan",
"given": "Peter",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Carter",
"given": "Brittney",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hunter",
"given": "Stephanie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Voigt",
"given": "Ingo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Schueler",
"given": "Robert",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Blank",
"given": "Elisabeth",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hüning",
"given": "Vanessa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Steffen",
"given": "Melanie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Goralski",
"given": "Patricia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Regli",
"given": "Adrian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pellicano",
"given": "Susan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Palermo",
"given": "Annamaria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Eroglu ",
"given": "Ege",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bihari",
"given": "Shailesh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Laver",
"given": "Russell D.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Shrestha",
"given": "Tapaswi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jin ",
"given": "Xia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McIntyre",
"given": "Joanne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McCullagh",
"given": "Iain",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cairns",
"given": "Tom",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hanson",
"given": "Helen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Patel",
"given": "Bijal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Clement",
"given": "Ian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Evetts",
"given": "George",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Touma",
"given": "Omar ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Holland",
"given": "Susan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hodge",
"given": "Christopher",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Taylor",
"given": "Holly",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Alderman",
"given": "Meera",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Barnes",
"given": "Nicky",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Da Rocha",
"given": "Joana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Smith",
"given": "Catherine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Brooks",
"given": "Nicole",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Weerasinghe",
"given": "Thanuja",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sinclair",
"given": "Julie-Ann",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Abusamra",
"given": "Yousuf",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Doherty",
"given": "Ronan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cudlipp",
"given": "Joanna ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Singh",
"given": "Rajeev",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Yu",
"given": "Haili",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Daebis",
"given": "Admad ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "NG",
"given": "Christopher",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kendrick",
"given": "Sara ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Saran",
"given": "Anita",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Makky",
"given": "Ahmed ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Greener",
"given": "Danni",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rowe-Leete",
"given": "Louise",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Edwards",
"given": "Alexandra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bland",
"given": "Yvonne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Dolman",
"given": "Rozzie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Foster",
"given": "Tracy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Conway",
"given": "Robert",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Csabi",
"given": "Peter",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Szawarski",
"given": "Piotr",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hajdu",
"given": "Bence",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Tamm",
"given": "Tina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bryden",
"given": "Emma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Glynou",
"given": "Loukia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Graniewski",
"given": "Jaroslaw",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kuybida",
"given": "Yuriy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "Samantha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kavanagh",
"given": "Lisa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Singler",
"given": "Karen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Laffey",
"given": "John",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McNicholas",
"given": "Bairbre",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Scully",
"given": "Michael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Casey",
"given": "Siobhan ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kernan",
"given": "Maeve",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Brennan",
"given": "Aoife",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rangan",
"given": "Ritika",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Tully",
"given": "Riona",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Corbett",
"given": "Sarah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McCarthy",
"given": "Aine ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Duffy",
"given": "Oscar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Burke",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Linnett",
"given": "Vanessa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sanderson",
"given": "Amanda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ritzema",
"given": "Jenny",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wild",
"given": "Helen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lucas",
"given": "Rachael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Marriott",
"given": "Yvonne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Khare",
"given": "Divya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pinder",
"given": "Meredith",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gopinath",
"given": "Amitha ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kannan",
"given": "Thogulava",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Dean",
"given": "Steven",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vanmali",
"given": "Piyush",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Depuydt",
"given": "Pieter",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "De Waele",
"given": "Jan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "De Bus",
"given": "Liesbet",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Fierens",
"given": "Jan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bracke",
"given": "Stephanie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vermassen",
"given": "Joris",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vermeiren",
"given": "Daisy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Van Hecke",
"given": "Jolien",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "De Smeytere",
"given": "Anouska",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pugh",
"given": "Richard",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lean",
"given": "Richard",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Qiu",
"given": "Xinyi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Scanlan",
"given": "Jeremy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Evans",
"given": "Andrew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Davies",
"given": "Gwyneth",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lewis",
"given": "Joanne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rees",
"given": "Stephanie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "MacKay",
"given": "Callum",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Craddock",
"given": "Richard",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Davies",
"given": "Jennifer",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Williams",
"given": "Hannah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Manley",
"given": "Rachel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Garrod",
"given": "Esther",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Tee",
"given": "Ameilia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Plesnikova",
"given": "Yvonna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Khoud",
"given": "Ahmed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Coetzee",
"given": "Samantha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Puxty",
"given": "Kathryn",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cathcart",
"given": "Susanne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rimmer",
"given": "Dominic",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bagot",
"given": "Catherine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Scott",
"given": "Kathryn",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Martin",
"given": "Laila",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "MacTavish",
"given": "Pamela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Murphy",
"given": "Ryan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Carmichael",
"given": "Samantha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Tait",
"given": "Jennifer",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Nygren",
"given": "Maria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Yusuff",
"given": "Hakeem",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Isgro",
"given": "Graziella",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Brightling",
"given": "Chris",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bourne",
"given": "Michelle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Craner",
"given": "Michelle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Boyles",
"given": "Rebecca",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Alexander",
"given": "Brian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Roberts",
"given": "Tracey",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Nelli",
"given": "Apoorva",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rosenstein-Sisson",
"given": "Rachel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Speyer",
"given": "Rebecca",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pech",
"given": "Yadira",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McCullough",
"given": "James",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Tallott",
"given": "Mandy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vazquez-Grande",
"given": "Gloria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Marten",
"given": "Nicole",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Theresa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Siddiqui",
"given": "Atif",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Khanal",
"given": "Sushil",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Amatya ",
"given": "Sameena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Shrestha",
"given": "Sabita",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pathak",
"given": "Shreya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mali",
"given": "Sharmila",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bhattarai",
"given": "Bina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Szakmany",
"given": "Tamas ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cherian",
"given": "Shiney",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Williams",
"given": "Gemma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "James",
"given": "Christie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Waters",
"given": "Abby",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Duric",
"given": "Natalie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Almeshhedani",
"given": "Hasham",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jesty",
"given": "Robert",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Spiers",
"given": "Catriona",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Prout",
"given": "Rachel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Stedman",
"given": "Roger",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Davies",
"given": "Louisa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pegler",
"given": "Suzannah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kyeremeh",
"given": "Lynsey",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Moorhouse",
"given": "Louise",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Watters",
"given": "Malcolm",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Arbane",
"given": "Gill",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bociek",
"given": "Aneta",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ostermann",
"given": "Marlies",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "D’Amato",
"given": "Fabiola",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "GrauNovellas",
"given": "Neus",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mathew",
"given": "Moncy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lim",
"given": "Rosario",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "van Nieuwkoop",
"given": "Kees",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ottens",
"given": "Thomas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Visser",
"given": "Yorik",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "van den Berg",
"given": "Lettie ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "van der Kraan-Donker ",
"given": "Annemarie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Meade",
"given": "Maureen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Belley-Côté",
"given": "Émilie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hand",
"given": "Lori",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Brett",
"given": "Stephen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Arias",
"given": "Sonia ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hall",
"given": "Rebecca",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Paneru",
"given": "Hem",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Koirala",
"given": "Sabin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Paudel",
"given": "Pratibha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Shakya",
"given": "Roshni",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kayastha",
"given": "Srijana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Karki",
"given": "Rakshya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wilson",
"given": "Maggie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vaara",
"given": "Suvi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pettilä",
"given": "Leena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Heinonen",
"given": "Jonna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pettilä",
"given": "Ville",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jain",
"given": "Susan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gupta",
"given": "Abhinav",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Holbrook",
"given": "Catherine ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Antoine",
"given": "Pierre",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Meziani",
"given": "Ferhat",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Allam",
"given": "Hayat",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cattelan",
"given": "Jessy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Clere-Jehl",
"given": "Raphael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Helms",
"given": "Julie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kummerlen",
"given": "Christine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Merdji",
"given": "Hamid",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Monnier",
"given": "Alexandra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rahmani",
"given": "Hassene",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Antoine",
"given": "Studer",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Schneider",
"given": "Francis",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Castelain",
"given": "Vincent",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Morel",
"given": "Guillaume",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "L’Hotellier",
"given": "Sylvie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ochin",
"given": "Evelina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vanjak",
"given": "Christian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rouge",
"given": "Patrick",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bendjemar",
"given": "Lynda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Albert",
"given": "Martin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Serri",
"given": "Karim",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cavayas",
"given": "Alexandros",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Duplaix",
"given": "Mathilde",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Williams",
"given": "Virginie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Catorze",
"given": "Nuno José Teodoro Amaro dos Santos",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pereira",
"given": "Tiago Nuno Alfaro Lima",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ferreira",
"given": "Ricardo Manuel Castro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bastos",
"given": "Joana Margarida Pereira Sousa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Batista ",
"given": "Teresa Margarida Oliveira",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Badie",
"given": "Julio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Berdaguer",
"given": "Fernando",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Malfroy",
"given": "Sylvain",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mezher",
"given": "Chaouki",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bourgoin",
"given": "Charlotte",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Moneger",
"given": "Guy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bouvier",
"given": "Elodie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Muñoz-Bermúdez",
"given": "Rosana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Marin-Corral",
"given": "Judith",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Degracia",
"given": "Anna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gómez",
"given": "Francisco",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "López ",
"given": "Maria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pérez-Terán",
"given": "Purificación",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vilá",
"given": "Clara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bigas",
"given": "Judit",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Roche-Campo",
"given": "Ferran",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Franch-LLasat",
"given": "Diego",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Concha",
"given": "Pablo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Domingo-Marco",
"given": "Joana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Reverté-Villarroya",
"given": "Silvia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sauras-Colón",
"given": "Esther",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Masdeu-Eixarch",
"given": "Gaspar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Aceto",
"given": "Romina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Aghemo",
"given": "Alessio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Badalamenti",
"given": "Salvatore",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Brunetta",
"given": "Enrico",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ciccarelli",
"given": "Michele",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Constantini",
"given": "Elena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Greco",
"given": "Massimiliano",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Folci",
"given": "Marco",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Selmi",
"given": "Carlo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Voza",
"given": "Antonio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Occhipinti",
"given": "Giovanna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Constantino",
"given": "Claudia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cuffaro",
"given": "Raffaele",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Russelli",
"given": "Giovanna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Martucci",
"given": "Gennaro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Landoni",
"given": "Giovanni",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Aldo Bonizzoni",
"given": "Matteo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Galbiati",
"given": "Carola",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Nakhnoukh",
"given": "Cristina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lembo",
"given": "Rosalba",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mascherpa",
"given": "Glenda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Giardina",
"given": "Giuseppe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Belletti",
"given": "Alessandro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ripa",
"given": "Marco",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rovere-Querini",
"given": "Patrizia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Di Lucca",
"given": "Giuseppe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bonaccorso",
"given": "Alessandra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Alessandro Carà",
"given": "Gianmarco",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Russo",
"given": "Giada",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Salvati",
"given": "Stefano",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Tomasi",
"given": "Enrico",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Henning",
"given": "Jeremy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bonner",
"given": "Stephen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hugill",
"given": "Keith",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cirstea",
"given": "Emanuel ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wilkinson",
"given": "Dean",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "Jessica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Altomy",
"given": "Mohammed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Headlam",
"given": "Evie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Karlikowski",
"given": "Michal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sutherland",
"given": "Helen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wilhelmsen",
"given": "Elva",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Woods",
"given": "Jane",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "North",
"given": "Julie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Brodbeck",
"given": "Andreas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mackintosh",
"given": "Katherine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Garvey",
"given": "James",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bothma",
"given": "Pieter",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Tupper-Carey",
"given": "Daryl",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ikhena",
"given": "Ikhuemose",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Osborne",
"given": "Jason",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Waugh",
"given": "Victoria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pletz",
"given": "Mathias",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hagel",
"given": "Stefan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ankert",
"given": "Juliane",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kolanos",
"given": "Steffi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bloos",
"given": "Frank",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Simons",
"given": "Koen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "van Zuylen",
"given": "Tamara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bouman",
"given": "Angela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kumar",
"given": "Nikhil",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Panwar",
"given": "Rakshit",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Poulter",
"given": "Amber-Louise",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sunkara",
"given": "Krishna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rochwerg",
"given": "Bram",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Karachi",
"given": "Tim",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Oczkowski",
"given": "Simon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Centofanti",
"given": "John",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Millen",
"given": "Tina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Camargo",
"given": "Mercedes",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Khaled",
"given": "Alia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sundaran",
"given": "Dhinesh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hollos",
"given": "Laszlo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Williams",
"given": "Anna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Turns",
"given": "Margaret ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Walsh",
"given": "Joanne ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Al Qasim",
"given": "Eman",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Alswaidan",
"given": "Lolowa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hegazy",
"given": "Mohamed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Arishi",
"given": "Hatim",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Al Amri",
"given": "Ali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "AlQahtani",
"given": "Samah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Naidu",
"given": "Brintha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Tlayjeh",
"given": "Haytham",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hussain",
"given": "Sajid",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Al Enezi",
"given": "Farhan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Abdukahil ",
"given": "Sheryl Ann",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hopkins",
"given": "Phil",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Smith",
"given": "John",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Noble",
"given": "Harriet ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "O’Reilly",
"given": "Kevin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mehta",
"given": "Reena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wong",
"given": "Onyee ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Makanju",
"given": "Esther",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rao",
"given": "Deepak",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sikondari",
"given": "Nyma ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Saha",
"given": "Sian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Corcoran",
"given": "Ele",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pappa",
"given": "Evita",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cockrell",
"given": "Maeve",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Donegan",
"given": "Clare",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Balaie",
"given": "Morteza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Depante",
"given": "Maria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Nickoleit-Bitzenberger",
"given": "Daniela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Schaaf",
"given": "Bernhard",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Meermeier",
"given": "Werner",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Prebeg",
"given": "Katharina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Azzaui",
"given": "Harun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hower",
"given": "Martin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Brieger",
"given": "Klaus-Gerd",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Elender",
"given": "Corinna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sabelhaus",
"given": "Timo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Riepe",
"given": "Ansgar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Akamp",
"given": "Ceren",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kremling",
"given": "Julius",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Klein",
"given": "Daniela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Landsiedel-Mechenbier",
"given": "Elke",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Laha",
"given": "Shondipon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Verlander",
"given": "Mark",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Williams",
"given": "Alexandra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jha",
"given": "Avinash",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Megarbane",
"given": "Bruno",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Voicu",
"given": "Sebastian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Deye",
"given": "Nicolas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Malissin",
"given": "Isabelle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sutterlin",
"given": "Laetitia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mrad",
"given": "Aymen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lehalleur",
"given": "Adrien",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Naim",
"given": "Giulia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Nguyen",
"given": "Philippe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ekhérian",
"given": "Jean-Michel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Boué",
"given": "Yvonnick",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sidéris",
"given": "Georgios",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vodovar",
"given": "Dominique",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Guérin",
"given": "Emmanuelle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Grant",
"given": "Caroline",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Brain",
"given": "Matthew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mckeon",
"given": "Laurie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Lixian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Tresize",
"given": "Tarnya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Unwin",
"given": "Maria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Laugs",
"given": "Fabian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lunde",
"given": "Ragnar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Blanck",
"given": "Wendy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Paramasivam",
"given": "Elankumaran",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wilby",
"given": "Elizabeth",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ogg",
"given": "Bethan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Howcroft",
"given": "Clare",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Aspinwall",
"given": "Angelique",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Charlton",
"given": "Sam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gould",
"given": "Richard",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mistry",
"given": "Deena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Awan",
"given": "Sidra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bedford",
"given": "Caroline",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Carr-Wilkinson",
"given": "Joanne ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hall",
"given": "Andrew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cooke",
"given": "Jill",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gardiner-Hill",
"given": "Caroline",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Maloney",
"given": "Carolyn",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Brunskill",
"given": "Nigel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Watchorn",
"given": "Olivia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hardy",
"given": "Chloe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Qureshi",
"given": "Hafiz",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Flint",
"given": "Neil",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Nicholson",
"given": "Sarah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Southin",
"given": "Sara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Nicholson",
"given": "Andrew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ghattaoraya",
"given": "Amardeep",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Harding",
"given": "Daniel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "O’Halloran",
"given": "Sinead",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Collins",
"given": "Amy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Smith",
"given": "Emma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Trues",
"given": "Estefania",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Borgatta",
"given": "Barbara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Turner-Bone",
"given": "Ian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Reddy",
"given": "Amie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wilding",
"given": "Laura",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wilson",
"given": "Craig",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Surti",
"given": "Zuhra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Aneman",
"given": "Anders",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Dugan",
"given": "Christopher",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Chin",
"given": "Edison",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Miller",
"given": "Jennene",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "White",
"given": "Hayden",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Estensen",
"given": "Kristen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Morrison",
"given": "Lynette",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sutton",
"given": "Joanne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cooper",
"given": "Melanie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Warnapura",
"given": "Loku",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Agno",
"given": "Ronan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sathianathan",
"given": "Prasannakumari ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Shaw",
"given": "Deborah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ijaz",
"given": "Nazia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Spong",
"given": "Adam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sabaretnam",
"given": "Suganya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Burns",
"given": "Dean",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lang",
"given": "Eva",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Tate",
"given": "Margaret",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Fischer",
"given": "Roy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Biradar",
"given": "Vishwanath",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Soar",
"given": "Natalie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Golden",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Davey",
"given": "Miriam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Seaman",
"given": "Rebecca",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Osborne",
"given": "Alexander",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bannard-Smith",
"given": "Jonathan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Clark",
"given": "Richard",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Birchall",
"given": "Kathrine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Henry",
"given": "Joanne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pomeroy",
"given": "Fiona",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Quayle",
"given": "Rachael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wylie",
"given": "Katharine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sukuraman",
"given": "Anila",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "John",
"given": "Maya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sibin",
"given": "Sindhu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Leditschke",
"given": "Anne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Finnis",
"given": "Mackenzie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jongebloed",
"given": "Katherine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Roumen",
"given": "Rudy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "de Groot",
"given": "Klaas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Khwaja",
"given": "Kosar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Campisi",
"given": "Josie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "van Vonderen",
"given": "Marit",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Stienstra",
"given": "Riejanne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kampschreur ",
"given": "Linda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pietersma",
"given": "Mario",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "van Gulik",
"given": "Laura",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Makowski",
"given": "Arystarch",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Misztal",
"given": "Beata",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Haider",
"given": "Syeda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Liao",
"given": "Angela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Squires",
"given": "Rebecca",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Oborska",
"given": "Aneta",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kayani",
"given": "Abdul",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kalchko-Veyssal",
"given": "Selver",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Prabakaran",
"given": "Rajalakshmi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hadebe",
"given": "Bernard",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Williams",
"given": "Tony",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Song",
"given": "Rima",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Girijadevi",
"given": "Dinuraj",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lai",
"given": "Vivian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Morpeth",
"given": "Susan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mwembani",
"given": "Tina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Stewart",
"given": "Richard",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mwaura",
"given": "Esther",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mew",
"given": "Louise",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wren",
"given": "Lynn",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Willams",
"given": "Felicity",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sutherland",
"given": "Sara-Beth",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rebello",
"given": "Rashmi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rehman",
"given": "Atique",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bharaj",
"given": "Kiranjit",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Shehabi",
"given": "Yahya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Al-Bassam",
"given": "Wisam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hulley",
"given": "Amanda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kadam",
"given": "Umesh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sathianathan",
"given": "Kushaharan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Burgess",
"given": "Richard",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Doble",
"given": "Patricia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Graham",
"given": "Libby",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Shovelton",
"given": "Charmaine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Dean",
"given": "Tessa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Purnell",
"given": "Rebecca",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Thomas",
"given": "Ashly",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Masood",
"given": "Sobia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Salahuddin",
"given": "Nawal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Khanal",
"given": "Kishor",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Dheke",
"given": "Krishan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rai",
"given": "Namrata",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Maharjan",
"given": "Mili",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Aryal",
"given": "Diptesh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Koirala",
"given": "Kanchan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Luitel",
"given": "Subekshya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Seppelt",
"given": "Ian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Whitehead",
"given": "Christina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lowrey",
"given": "Julie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gresham",
"given": "Rebecca",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Masters",
"given": "Kristy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hamlyn",
"given": "Vincent",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hawkins",
"given": "Nancy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Roynon-Reed",
"given": "Anna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cutler",
"given": "Sean",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lewis",
"given": "Sarah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Martin-Lazaro",
"given": "Juan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Newman",
"given": "Tabitha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Zdanavidiene",
"given": "Ausra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Smallshaw",
"given": "Karen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hand",
"given": "James",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Aravindan",
"given": "Latha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Asghar",
"given": "Adeeba",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bartholomew",
"given": "Jazz",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bayne",
"given": "Madeleine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Beddows",
"given": "Seonaid",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Birch",
"given": "Catherine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Brend",
"given": "Morwenna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Byrne",
"given": "Rahim",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Campbell",
"given": "Debbie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Campbell",
"given": "Hilary",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Chambers",
"given": "Emma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Clinton",
"given": "Alison",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Collins",
"given": "Joanne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Crawshaw",
"given": "Sarah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Dawson",
"given": "Laura Ann",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Donaldson",
"given": "Kate",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Drake",
"given": "Chelsea",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Dyas",
"given": "Sarah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ellis",
"given": "Yvette",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gilmour",
"given": "Kate",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Goodwin",
"given": "Jayne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Halden",
"given": "Sandra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hall",
"given": "Alistair S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hanson",
"given": "Jane",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Harper",
"given": "Heather",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Harrison",
"given": "Susan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hayes",
"given": "Amber",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hodgson",
"given": "Helen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hurford",
"given": "Sally-Anne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jackson",
"given": "Shane",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Levett",
"given": "Chris",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lock",
"given": "Stephen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lockett",
"given": "Teresa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Logan",
"given": "Meg",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lomme",
"given": "Kaatje",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Luo",
"given": "Ji",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Marsh",
"given": "Emma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McKenna",
"given": "Sonia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mguni",
"given": "Nhlanhla",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Monaghan",
"given": "Holly",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Murphy",
"given": "Sheenagh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Muzengi",
"given": "Natasha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Naz",
"given": "Mobeena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "O'Kell",
"given": "Eleanor",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Oliver",
"given": "Anne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "O'Reilly",
"given": "Joanna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pearson",
"given": "Karen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Porter",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Potter",
"given": "Alison",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rook",
"given": "Clare",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rounds",
"given": "Charles",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sheffield",
"given": "Jonathan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Shirley",
"given": "Kim",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Siewerski",
"given": "Chris",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Skinner",
"given": "Tabitha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Speight",
"given": "Holly",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sutu",
"given": "Mihaela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Unsworth",
"given": "Adam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Van’t Hoff",
"given": "William",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Walker",
"given": "Susan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Williams",
"given": "Penny",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Williamson",
"given": "Dawn",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Williamson",
"given": "James D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Tsang",
"given": "Jennifer",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Duan",
"given": "Erick",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ali",
"given": "Karim",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Farjou",
"given": "George",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Chung",
"given": "Han-Oh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jensen",
"given": "Lorraine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Patterson",
"given": "Lisa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Nielsen-Smith",
"given": "Diane",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Becevel",
"given": "Julia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cavers",
"given": "Christine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ding",
"given": "Josephine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "irish",
"given": "Jamie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jomy",
"given": "Jane",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Austin",
"given": "Pauline",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Chapman",
"given": "Susan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cabrelli",
"given": "Louise",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Fletcher",
"given": "Simon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Nortje",
"given": "Jurgens",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Fottrell-Gould",
"given": "Deirdre",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Randell",
"given": "Georgina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Stammers",
"given": "Katie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Healey",
"given": "Gail",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pinto",
"given": "Marta",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Woodward",
"given": "Robert",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Oliver",
"given": "Martyn",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Harvey",
"given": "James",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Convery",
"given": "Karen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Brown",
"given": "Zarah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Taylor",
"given": "Sian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Fraser",
"given": "Catherine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Glister",
"given": "Georgina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hindle",
"given": "Grace",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "O Rourke",
"given": "Kate",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Borrill",
"given": "Zoe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Duncan",
"given": "Tracy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ustianowski",
"given": "Andrew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Uriel",
"given": "Alison",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Eltayeb",
"given": "Ayaa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Alfonso",
"given": "Jordan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hey",
"given": "Samuel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Shaw",
"given": "Joanne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Fox",
"given": "Claire",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lindergard",
"given": "Gabriella",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Charles",
"given": "Bethan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Blackledge",
"given": "Bethany",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Connolly",
"given": "Karen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Harris",
"given": "Jade",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cuesta",
"given": "Jeronimo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Xavier",
"given": "Kugan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Purohit",
"given": "Dharam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Elhassan",
"given": "Munzir",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Haldeos",
"given": "Anne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vincent",
"given": "Rachel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Abdelrazik",
"given": "Marwa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jenkins",
"given": "Samuel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ganesan",
"given": "Arunkumar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kumar",
"given": "Rohit",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Carter",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bakthavatsalam",
"given": "Dhanalakshmi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Frater",
"given": "Alasdair",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Saleem",
"given": "Malik",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Madarbukus",
"given": "Daanyaal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Everitt",
"given": "Robert",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bridges",
"given": "Sarah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Karim",
"given": "Hina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Zaman",
"given": "Mohsin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Elmahi",
"given": "Einas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "Andrea",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hall",
"given": "Kathryn",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Phillips",
"given": "Matt",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Terrill",
"given": "Lenae",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mills",
"given": "Gary",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Raithatha",
"given": "Ajay",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bauchmuller",
"given": "Kris",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ryalls",
"given": "Kim",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Harrington",
"given": "Kate",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bowler",
"given": "Helen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sall",
"given": "Jas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bourne",
"given": "Richard",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Howell",
"given": "Alice",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lye",
"given": "Alison",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kirk",
"given": "Rosemary",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jarman",
"given": "Claire",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Yates",
"given": "Bryan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kilner",
"given": "Mari",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bomken",
"given": "Charlotte",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Reynolds",
"given": "Jessica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gross",
"given": "Jamie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Massey",
"given": "Natalie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Adebambo",
"given": "Olumide",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Long",
"given": "Matilda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Tony",
"given": "Kiran",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kohli",
"given": "Sonny",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cui",
"given": "Fulan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Khera",
"given": "Vikas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rehsia",
"given": "Sachdeep",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Perez",
"given": "Adic",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bharti",
"given": "Dalisha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Handa",
"given": "Surbhi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Shields",
"given": "Fiona",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Henschke",
"given": "Alice",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Juffermans",
"given": "Nicole",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Koopmans",
"given": "Matty",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rowland",
"given": "Matthew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hutton",
"given": "Paula",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bashyal",
"given": "Archana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Davidson",
"given": "Neil",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hird",
"given": "Clare",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Beer",
"given": "Sally",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wilson",
"given": "Jean",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Polley",
"given": "Grace",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Chhablani",
"given": "Manish",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Phalod",
"given": "Gunjan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kirkby",
"given": "Amy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Archer",
"given": "Simon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Netherton",
"given": "Kimberley ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Reschreiter",
"given": "Henrik",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Camsooksai",
"given": "Julie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Patch",
"given": "Sarah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jenkins",
"given": "Sarah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Humphrey",
"given": "Charlotte",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Langridge",
"given": "Emma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Flynn",
"given": "Gordon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Harrington",
"given": "Claire",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kruger",
"given": "Peter",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Walsham",
"given": "James",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Meyer",
"given": "Jason",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Harward",
"given": "Meg",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mackay",
"given": "Josephine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "Cassie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sathe",
"given": "Sonia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Roche",
"given": "Lisa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Davies",
"given": "Ellie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Skinner",
"given": "Denise",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gaylard",
"given": "Jane",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Newman",
"given": "Julie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pogson",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rose",
"given": "Steve",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Daly",
"given": "Zoe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Brimfield",
"given": "Lutece",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Nown",
"given": "Angie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Parekh",
"given": "Dhruv",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bergin",
"given": "Colin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bates",
"given": "Michelle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McGhee",
"given": "Christopher",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lynch",
"given": "Daniella",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bhandal",
"given": "Khushpreet",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Tsakiridou",
"given": "Kyriaki",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bamford",
"given": "Amy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cooper",
"given": "Lauren",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Whitehouse",
"given": "Tony",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Veenith",
"given": "Tonny",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Forster",
"given": "Elliot",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "O'Connell",
"given": "Martin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Page",
"given": "Shannon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Haider",
"given": "Nafeesah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Adams",
"given": "Nick",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sim",
"given": "Malcolm",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hay",
"given": "Sophie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Henderson",
"given": "Steven",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Valentine",
"given": "Eliza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ralston",
"given": "Maximillian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McCreath",
"given": "Gordan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Arnott",
"given": "Andrew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Orlikowska",
"given": "Izabela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Parker",
"given": "Natasha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Katary",
"given": "Amro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bell",
"given": "Gillian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wilcox",
"given": "Louise",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mataliotakis",
"given": "Michail",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Smith",
"given": "Paul",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ali",
"given": "Murtaza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Isguzar",
"given": "Agah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Phull",
"given": "Mandeep-Kaur",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Zaidi",
"given": "Abbas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pogreban",
"given": "Tatiana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rosaroso",
"given": "Lace",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "O’Brien",
"given": "Neale",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Visentin",
"given": "Elisa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Harvey",
"given": "Daniel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lowe",
"given": "Benjamin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Meredith",
"given": "Megan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ryan",
"given": "Lucy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Clark",
"given": "Amy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Peters",
"given": "Cecilia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Walton",
"given": "Catherine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Joseph",
"given": "Treesa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gibbins",
"given": "Alexandra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sampson",
"given": "Julia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Morris",
"given": "Lucy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Dent",
"given": "Martin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Haghi",
"given": "Theerata",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Schouten",
"given": "Jeroen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pickkers",
"given": "Peter",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Roovers",
"given": "Noortje",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Klop-Riehl",
"given": "Margreet",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "van der Eng",
"given": "Hetty",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "van de Veerdonk",
"given": "Frank",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sloots-Cuppen",
"given": "Sonja",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Preijers",
"given": "Lieke",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Polfliet",
"given": "Margot",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Heming",
"given": "Nicholas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Moine",
"given": "Pierre",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Maxime",
"given": "Virginie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bossard",
"given": "Isabelle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Nicholier",
"given": "Tiphaine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Clair",
"given": "Bernard",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Orlikowski",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bounab",
"given": "Rania",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Abdeladim",
"given": "Lilia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Baker",
"given": "Stuart",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Tabah",
"given": "Alexis",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Duroux",
"given": "Maree",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ratcliffe",
"given": "Megan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sy",
"given": "Eric",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mailman",
"given": "Jonathan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lee",
"given": "Stephen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kassir",
"given": "Sandy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "England",
"given": "Jenna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "López",
"given": "Rafael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rodríguez-Gómez",
"given": "Jorge",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cárcel",
"given": "Sheila",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Carmona",
"given": "Rosario",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "de la Fuente",
"given": "Carmen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rodriguez",
"given": "Marina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "de la Torre Cisneros",
"given": "Julian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jan Hassing",
"given": "Robert ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Greven",
"given": "Frances",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Huijbens",
"given": "Danique",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Verheij",
"given": "Harald",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Roebers",
"given": "L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Miles",
"given": "Helen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Attokaran",
"given": "Antony",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Buehner",
"given": "Ulrike",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Williams",
"given": "Erin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Plummer",
"given": "Mark",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "O’Connor",
"given": "Stephanie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Glasby",
"given": "Kathleen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rivett",
"given": "Justine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Brown",
"given": "Nerissa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kutsogiannis",
"given": "Demetrios",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Chowdhury",
"given": "Raiyan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Davidow",
"given": "Jon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Johnston",
"given": "Curtis",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kim",
"given": "Michael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Macala",
"given": "Kimberley ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Markland",
"given": "Darren",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Matheson",
"given": "Doug",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Parker",
"given": "Arabesque",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Paton-Gay",
"given": "Damian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Robinson",
"given": "Andrea",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Thompson",
"given": "Patrica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hewer",
"given": "Tayne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rooney",
"given": "Kevin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rodden",
"given": "Natalie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Thomson",
"given": "Nicola",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McGlynn",
"given": "Deborah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Abel",
"given": "Lynn",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gemmell",
"given": "Lisa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sundaram",
"given": "Radha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hornsby",
"given": "James",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Walden",
"given": "Andrew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Keating",
"given": "Liza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Frise",
"given": "Matthew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rai",
"given": "Sabi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bartley",
"given": "Shauna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Schuster-Bruce",
"given": "Martin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pitts",
"given": "Sally",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Miln",
"given": "Rebecca",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Purandare",
"given": "Laura",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vamplew",
"given": "Luke",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Patel",
"given": "Brijesh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Dempster",
"given": "Debra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gummadi",
"given": "Mahitha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Dormand",
"given": "Natalie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Shu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Spivey",
"given": "Michael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bean",
"given": "Sarah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Burt",
"given": "Karen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Moore",
"given": "Lorraine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hammonds",
"given": "Fiona",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Richards",
"given": "Carol",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Chapman",
"given": "Rachel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cornell",
"given": "Thomas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Campbell",
"given": "Lewis",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Smyth",
"given": "Kirsty",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ross",
"given": "Elizabeth",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mackenzie",
"given": "Brittney",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Day",
"given": "Christopher",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Zitter",
"given": "Letizia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Benyon",
"given": "Sarah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Singh",
"given": "Jayaprakash",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lynch",
"given": "Ceri ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mikusek",
"given": "Justyna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Deacon",
"given": "Bethan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Turner",
"given": "Keri",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Baker",
"given": "Evelyn",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hickey",
"given": "John",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Champanerkar",
"given": "Shreekant",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Aitken",
"given": "Lindianne ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "LewisProsser",
"given": "Lorraine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ahmad",
"given": "Norfaizan ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wiles",
"given": "Matt",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Willson",
"given": "Jayne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Grecu",
"given": "Irina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Martin",
"given": "Jane",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wrey Brown",
"given": "Caroline",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Arias",
"given": "Ana-Marie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bevan",
"given": "Emily",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Westlake",
"given": "Samantha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Craven",
"given": "Thomas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hope",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Singleton",
"given": "Jo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Clark",
"given": "Sarah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McCulloch",
"given": "Corrienne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Biddie",
"given": "Simon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Marshall",
"given": "Lucy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Birch",
"given": "Sophie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Britton",
"given": "Kate",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Welters",
"given": "Ingeborg",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hamilton",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Williams",
"given": "Karen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Shaw",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mulla",
"given": "Suleman",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Waite",
"given": "Alicia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Roman",
"given": "Jaime",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Martinez",
"given": "Maria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Johnston",
"given": "Brian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Medhurst",
"given": "Laura",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Beresford",
"given": "Stephanie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ayee",
"given": "Robert",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Puthucheary",
"given": "Zudin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Martin",
"given": "Timothy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Santos",
"given": "Filipa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Uddin",
"given": "Ruzena ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Fernandez",
"given": "Maria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Seidu",
"given": "Fatima",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Somerville",
"given": "Alastair",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pakats",
"given": "Mari-Liis",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Begum",
"given": "Salma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Shahid",
"given": "Tasnin ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Dias",
"given": "Priya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Presneill",
"given": "Jeffrey",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Barge",
"given": "Deborah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Byrne",
"given": "Kathleen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vuylsteke",
"given": "Alain",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Chan",
"given": "Charles",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Victor",
"given": "Saji",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Waterson",
"given": "Sharon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McNamara",
"given": "Robert",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Boardman",
"given": "Melanie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gattas",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Buhr",
"given": "Heidi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Coles",
"given": "Jennifer",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Matsa",
"given": "Ramprasad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gellamucho",
"given": "Minerva",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sernicola",
"given": "Elisa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bailey",
"given": "Lucy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Creagh-Brown",
"given": "Ben",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Marriot",
"given": "Cheryl",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Salberg",
"given": "Armorel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Zouita",
"given": "Louisa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Stone",
"given": "Sarah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Michalak-Glinska",
"given": "Natalia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Donlon",
"given": "Sinead",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mtuwa",
"given": "Shelia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mayangao",
"given": "Irving",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Verula",
"given": "Jerik",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Burda",
"given": "Dorota",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Harris",
"given": "Celia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "Emily",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bradley",
"given": "Paul",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Tarr",
"given": "Esther",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Harden",
"given": "Lesley",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Piercy",
"given": "Charlie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Smith",
"given": "Eleanor",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Nolan",
"given": "Jerry",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kerslake",
"given": "Ian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cook",
"given": "Tim",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Simpson",
"given": "Tom",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Dalton",
"given": "James",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Demetriou",
"given": "Carrie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mitchard",
"given": "Sarah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ramos",
"given": "Lidia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "White",
"given": "Katie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Johnson",
"given": "Toby",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Headdon",
"given": "William",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Spencer",
"given": "Stephen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "White",
"given": "Alison",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Howie",
"given": "Lucy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Smith",
"given": "Natalie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Riddell",
"given": "Phillip",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hierons",
"given": "Sarah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Evans",
"given": "Gabrielle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Didiodato",
"given": "Giulio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Igric",
"given": "Ana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cruise",
"given": "Kelly",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ding",
"given": "Ian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Shelep",
"given": "Victoria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pietersen",
"given": "Debra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pokhrel",
"given": "Sujata",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Reay",
"given": "Michael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jenkins",
"given": "Steve",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Watts",
"given": "Angela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Traverse",
"given": "Eleanor",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jennings",
"given": "Stacey",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Anumakonda",
"given": "Vikram",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Tuckwell",
"given": "Caroline",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Harrow",
"given": "Kath",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Matthews",
"given": "Julie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McGarry",
"given": "Karen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Moore",
"given": "Vanessa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Smith",
"given": "Lucie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Summerfield",
"given": "Anna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Dark",
"given": "Paul",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Harvey",
"given": "Alice",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Doonan",
"given": "Reece",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McMorrow",
"given": "Liam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Knowles",
"given": "Karen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pendlebury",
"given": "Jessica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lee",
"given": "Stephanie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Perez",
"given": "Jane",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Marsden",
"given": "Tracy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Taylor",
"given": "Melanie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Michael",
"given": "Angiy ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Collis",
"given": "Matthew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Claxton",
"given": "Andrew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Habeichi",
"given": "Wadih",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Horner",
"given": "Dan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Slaughter",
"given": "Melanie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Thomas",
"given": "Vicky",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Proudfoot",
"given": "Nicola",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Keatley",
"given": "Claire",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mclaughlan",
"given": "Danielle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Donnison",
"given": "Phil",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Casey",
"given": "Ruth",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Irving",
"given": "Ben",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Matimba-Mupaya",
"given": "Wadzanai",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Reed",
"given": "Catherine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Anthony",
"given": "Alpha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Trim",
"given": "Fiona",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cambalova",
"given": "Lenka",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Robertson",
"given": "Debra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wilson",
"given": "Anna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Eapen",
"given": "Beena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hulme",
"given": "Jonathan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kannan",
"given": "Santhana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kinney",
"given": "Fiona",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Senya",
"given": "Ho",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hayes",
"given": "Anne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Diridis",
"given": "Kristina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ramamurthi",
"given": "Balaji",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bleasdale",
"given": "John",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mokhtar",
"given": "Nabih",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Newbould",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Arora",
"given": "Anand",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Saluja",
"given": "Rupali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sharma",
"given": "Deepak",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Haiba",
"given": "Khalid",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Donnelly",
"given": "Kieran",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sherwood",
"given": "Nick",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Joseph",
"given": "Sibet",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Potter",
"given": "Sarah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Henry",
"given": "Lavinia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ratnam",
"given": "Valli",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gill",
"given": "Mandy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kirk",
"given": "Jill",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Shelton",
"given": "Sarah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Schweikert",
"given": "Sacha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wibrow",
"given": "Bradley",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mevavala",
"given": "Bhaumik",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Asif",
"given": "Namra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Khoso",
"given": "Nasir",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Taqdees",
"given": "Huda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Frey",
"given": "Christian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Scano",
"given": "Riccardo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McKee",
"given": "Madeleine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Murphy",
"given": "Peter",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Thomas",
"given": "Matt",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Worner",
"given": "Ruth",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Faulkner",
"given": "Beverley",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gendall",
"given": "Emma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hayes",
"given": "Kati",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Blakemore",
"given": "Hayley",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Borislavova",
"given": "Borislava",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Smith",
"given": "Kerry",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Stephens",
"given": "Deanna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Deshpande",
"given": "Kush",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "van Haren",
"given": "Frank",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Konecny",
"given": "Pam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Inskip",
"given": "Deborah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Tung",
"given": "Raymond",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hayes",
"given": "Leanne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Murphy",
"given": "Lorna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Neill",
"given": "Andy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Reidy",
"given": "Bryan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "O’Dwyer",
"given": "Michael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ryan",
"given": "Donal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ainscough",
"given": "Kate",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hamilton-Davies",
"given": "Colin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Chan",
"given": "Carmen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mfuko",
"given": "Celina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Abbass",
"given": "Hakam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mandadapu",
"given": "Vineela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Leaver",
"given": "Susannah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Patel",
"given": "Kamal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Farnell-Ward",
"given": "Sarah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Saluzzio",
"given": "Romina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rawlins",
"given": "Sam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sicat",
"given": "Christine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Fernandes",
"given": "Edna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "De Keulenaer",
"given": "Bart",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ferrier",
"given": "Janet",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Fysh",
"given": "Ed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Dawda",
"given": "Ashlish",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Al-Hazzani",
"given": "Waleed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ligori",
"given": "Tania",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Soth",
"given": "Mark",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Clarke",
"given": "France",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Matic",
"given": "Karlo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Copland",
"given": "Mary",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hoad",
"given": "Neala",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sawyer",
"given": "Ashley",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Banach",
"given": "Dorota",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Fernández de Pinedo Artaraz",
"given": "Ziortza ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cabreros",
"given": "Leilani",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Latham",
"given": "Victoria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wong",
"given": "Jenny",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gurung",
"given": "Anita",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mohammed",
"given": "Amal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jepson",
"given": "Eleanor",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kruisselbrink",
"given": "Rebecca",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Brochard",
"given": "Laurent",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Burns",
"given": "Karen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sandhu",
"given": "Gyan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Khalid ",
"given": "Imrana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "White",
"given": "Ian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Croft",
"given": "Maria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Holland",
"given": "Nicky",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pereira",
"given": "Rita",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Frost",
"given": "Victoria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wells",
"given": "Karen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Chin",
"given": "Teri",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Aquino",
"given": "Maia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Nair",
"given": "Priya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Buscher",
"given": "Hergen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Reynolds",
"given": "Claire",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Campion",
"given": "Alexandra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hall",
"given": "Amelia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Santamaria",
"given": "John",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Haydon",
"given": "Tim",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Homes",
"given": "Jennifer",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Zaki",
"given": "Ahmed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Johnson",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Garrard",
"given": "Hywel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Juhaz",
"given": "Vera",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Brown",
"given": "Louise",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pemberton",
"given": "Abigail",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Roy",
"given": "Alistair",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rostron",
"given": "Anthony",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Woods",
"given": "Lindsey",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cornell",
"given": "Sarah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Amaral",
"given": "Andre",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Angriman",
"given": "Federico",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cuthbertson",
"given": "Brian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Fowler",
"given": "Rob",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Piquette",
"given": "Dominique",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Scales",
"given": "Damon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Tillman",
"given": "Bourke",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Marinoff ",
"given": "Nicole",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kaur",
"given": "Navjot",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Adeel",
"given": "Zoya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kamra",
"given": "Maneesha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Khan",
"given": "Hamzah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Murali",
"given": "Deeptha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ruxandra",
"given": "Pinto",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sabananthan",
"given": "Thivya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sugumaran",
"given": "Thuva",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Garrett",
"given": "Peter",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Murray",
"given": "Lauren",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Brailsford",
"given": "Jane",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pillai",
"given": "Suresh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Harford",
"given": "Rachel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ivatt",
"given": "Helen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Evans",
"given": "Debra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Richards",
"given": "Suzanne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Roberts",
"given": "Eilir",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bowen",
"given": "James",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ainsworth",
"given": "James",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Williams",
"given": "Marie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kuitunen",
"given": "Anne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Karlsson",
"given": "Sari",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vahtera",
"given": "Annukka",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kiiski",
"given": "Heikki",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ristimäki",
"given": "Sanna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Albrett",
"given": "Jonathan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jackson",
"given": "Carolyn",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kirkham",
"given": "Simon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Tamme",
"given": "Kadri",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Reinhard",
"given": "Veronika",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ellervee",
"given": "Anneli",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Põldots",
"given": "Liisi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rennit",
"given": "Pille",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Svitškar",
"given": "Nikolai",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Jonathan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Miller",
"given": "Amanda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McCracken",
"given": "Phoebe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Young",
"given": "Meredith",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Board",
"given": "Jasmin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Martin",
"given": "Emma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kasipandian",
"given": "Vidya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Patel",
"given": "Amit",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Allibone",
"given": "Suzanne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mary-Genetu",
"given": "Roman",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "English",
"given": "Shane",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Seely",
"given": "Andrew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McIntyre",
"given": "Lauralyn",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Watpool",
"given": "Irene",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Porteous",
"given": "Rebecca",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Miezitis",
"given": "Sydney",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Haines",
"given": "Jessica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Brady",
"given": "Kara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vale",
"given": "Cassandra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Shekar",
"given": "Kiran",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lavana",
"given": "Jayshree",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Parmar",
"given": "Dinesh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Peake",
"given": "Sandra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Williams",
"given": "Patricia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kurenda",
"given": "Catherine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wijewardena",
"given": "Gayathri",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hormis",
"given": "Anil",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Walker",
"given": "Rachel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Collier",
"given": "Dawn",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kimpton",
"given": "Sarah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Oakley",
"given": "Susan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Graham",
"given": "Cheryl",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Maynard",
"given": "Victoria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bhagani",
"given": "Sanjay",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "De Neef",
"given": "Mark",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Garcia",
"given": "Sara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Maharajh",
"given": "Amitaa ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Nandani",
"given": "Aarti",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Dobson",
"given": "Jade",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Fernando",
"given": "Gloria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Eastgate",
"given": "Christine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gomez",
"given": "Keith",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Abdi",
"given": "Zakee",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pakou",
"given": "Glykeria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Tatham",
"given": "Kate",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jhanji",
"given": "Shaman",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Black",
"given": "Ethel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Dela Rosa",
"given": "Arnold",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Howle",
"given": "Ryan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Baikady",
"given": "Ravishankar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Tully",
"given": "Redmond",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Drummond",
"given": "Andrew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Dearden",
"given": "Joy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Philbin",
"given": "Jennifer",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Munt",
"given": "Sheila",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gopal",
"given": "Shameer",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pooni",
"given": "Jagtar-Singh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ganguly",
"given": "Saibal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Smallwood",
"given": "Andrew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Metherell",
"given": "Stella",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Naeem",
"given": "Anas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Fagan",
"given": "Laura",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Turner",
"given": "Elizabeth",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mariappa",
"given": "Vasanth",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Smith",
"given": "Judith",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Foulds",
"given": "Angela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Revill",
"given": "Adam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bhattarai",
"given": "Binita",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Maharjan",
"given": "Sabi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Maharjan",
"given": "Radhika",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Phuyal",
"given": "Aarti",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Shrestha",
"given": "Namrata",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Meijer",
"given": "Karina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Postma",
"given": "Douwe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Thedinga",
"given": "Karen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "de Jonge",
"given": "Evert",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wigbers",
"given": "Jeanette",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "del Prado",
"given": "Michael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cremer",
"given": "Olaf",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mulier",
"given": "Jelle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rademaker",
"given": "Emma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Peters",
"given": "Anna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Romberg",
"given": "Birgit",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Leavis",
"given": "Helen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Schutgens",
"given": "Roger",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Troeman",
"given": "Darren",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "van Opdorp",
"given": "Marjolein",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Besten",
"given": "Henny",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Brakké",
"given": "Karen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Barber",
"given": "Russell",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hilldrith",
"given": "Anette",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sloan",
"given": "Andrew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Okubanjo",
"given": "Maryanne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Francis",
"given": "Olesya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Barker",
"given": "Stephanie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Butler",
"given": "Susan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hewitt",
"given": "Claire",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lee",
"given": "Kelvin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Tavares",
"given": "Silvia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kluge",
"given": "Stefan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Nierhaus",
"given": "Axel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jarczak",
"given": "Dominik",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Roedl ",
"given": "Kevin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kochanek",
"given": "Matthias",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rueß-Paterno",
"given": "Giusi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mc-Kenzie",
"given": "Josette",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Eichenauer",
"given": "Dennis",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Shimabukuro-Vornhagen",
"given": "Alexander",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Göpel",
"given": "Siri",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Eisenbeis",
"given": "Simone",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rissen",
"given": "Reimer",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Conzelmann",
"given": "Nadine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wilcox",
"given": "Elizabeth",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "del Sorbo",
"given": "Lorenzo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Abdelhady",
"given": "Hesham",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Romagnuolo ",
"given": "Tina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Simpson",
"given": "Scott",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Maiden",
"given": "Matthew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Horton",
"given": "Michelle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Trickey",
"given": "Jemma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Brohi",
"given": "Farooq",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jagannathan",
"given": "Vijay",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Clark",
"given": "Michele",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Purvis",
"given": "Sarah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wetherill",
"given": "Bill",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Dushianthan",
"given": "Ahilanandan ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cusack",
"given": "Rebecca",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "de Courcy-Golder",
"given": "Kim",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Salmon",
"given": "Karen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Burnish",
"given": "Rachel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Smith",
"given": "Simon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jackson",
"given": "Susan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ruiz",
"given": "Winningtom ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Duke",
"given": "Zoe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Johns",
"given": "Magaret ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Male",
"given": "Michelle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gladas",
"given": "Kirsty",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Virdee",
"given": "Satwinder ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Swabe",
"given": "Jacqueline",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Tomlinson",
"given": "Helen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Baker",
"given": "Alice",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Carter",
"given": "Michael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Roberts",
"given": "Belinda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Greene",
"given": "Emma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rohde",
"given": "Gernot",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Grünewaldt",
"given": "Achim",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bojunga",
"given": "Jörg",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Petros",
"given": "Sirak",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pasieka",
"given": "Bastian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kunz",
"given": "Kevin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Laudi",
"given": "Sven",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Seidel",
"given": "Antje",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ullmann",
"given": "Hannah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Schlegel",
"given": "Christian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Weismann",
"given": "Dirk",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Frey",
"given": "Anna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Drayss",
"given": "Maria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Goebeler",
"given": "M.E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Flor",
"given": "Thomas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Fragner",
"given": "Gertrud",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wahl",
"given": "Nadine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Totzke",
"given": "Juliane",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sayehli",
"given": "Cyrus",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bewley",
"given": "Jeremy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sweet",
"given": "Katie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Grimmer",
"given": "Lisa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Johnson",
"given": "Rebekah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wyatt",
"given": "Rachel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Morgan",
"given": "Karen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Varghese",
"given": "Siby",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Willis",
"given": "Joanna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Stratton",
"given": "Emma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kyle",
"given": "Laura",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Putensen",
"given": "Daniel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Drury",
"given": "Kay",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Skorko",
"given": "Agnieszka",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Dell",
"given": "Abbie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wright",
"given": "Kim",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Webster",
"given": "Denise",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Corcoran",
"given": "Kathleen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kolovou",
"given": "Angeliki",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Efford",
"given": "Georgia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McCullagh",
"given": "Liz",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bremmer",
"given": "Pamela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ward",
"given": "Geraldine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bassford",
"given": "Christopher",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sligl",
"given": "Wendy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Baig",
"given": "Nadia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rewa",
"given": "Oleksa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bagshaw",
"given": "Sean",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Markota",
"given": "Andrej",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kalamar",
"given": "Žiga",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Svenšek",
"given": "Franc",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Marinšek",
"given": "Martin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Fluher",
"given": "Jure",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jerenec",
"given": "Katja",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kit",
"given": "Barbara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Živko",
"given": "Iris",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Linstrum",
"given": "Kelsey",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Basile",
"given": "Kim",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Stavor",
"given": "Dara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Burbee",
"given": "Dylan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McNamara",
"given": "Amanda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wunderley",
"given": "Renee",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bensen",
"given": "Nicole",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Richardson",
"given": "Aaron",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Adams",
"given": "Peter",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vita",
"given": "Tina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Buhay",
"given": "Megan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Scholl",
"given": "Denise",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gilliam",
"given": "Matthew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Winters",
"given": "James",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Doherty",
"given": "Kaleigh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Berryman",
"given": "Emily",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ghaffari",
"given": "Mehrdad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Marroquin",
"given": "Oscar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Quinn",
"given": "Kevin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Garrard",
"given": "William",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kalchthaler",
"given": "Kyle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Beard",
"given": "Gregory",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Skrtich",
"given": "Aimee",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bagavathy",
"given": "Kavitha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Drapola",
"given": "Debra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wells",
"given": "Alan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bryan-Morris",
"given": "Kayla",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Arnold",
"given": "John",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Reynolds",
"given": "Bob",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hussain",
"given": "Mahwish",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Dunsavage",
"given": "Janice",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Saiyed",
"given": "Salim",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hernandez",
"given": "Erik",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Goldman",
"given": "John",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Brown",
"given": "Cynthia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Comp",
"given": "Susan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Raczek",
"given": "James",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Morris",
"given": "Jenny",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vargas Jr.",
"given": "Jesus",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Weiss",
"given": "Daniel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hensley",
"given": "Joseph",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kochert",
"given": "Erik",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wnuk",
"given": "Chris",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Nemeth",
"given": "Christopher",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mowery",
"given": "Brent",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hutchinson",
"given": "Christina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Winters",
"given": "Lauren",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McAdams",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Walker",
"given": "Gena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Minnier",
"given": "Tami",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wisniewski",
"given": "Mary",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mayak",
"given": "Katelyn",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McCreary",
"given": "Erin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Martin",
"given": "Elise",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bariola",
"given": "Ryan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Viehman",
"given": "Alex",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Daley",
"given": "Jessica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lopus",
"given": "Alyssa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Schmidhofer",
"given": "Mark",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ambrosino",
"given": "Richard",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Keen",
"given": "Sherbrina ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Toffalo",
"given": "Sue",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Stambaugh",
"given": "Martha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Trimmer",
"given": "Ken",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Perri",
"given": "Reno",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Casali",
"given": "Sherry",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Medva",
"given": "Rebecca",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Massar",
"given": "Brent",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Beyerl",
"given": "Ashley",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Burkey",
"given": "Jason",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Keeler",
"given": "Sheryl",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lowery",
"given": "Maryalyce",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Oncea",
"given": "Lynne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Daugherty",
"given": "Jason",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sevilla",
"given": "Chanthou",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Woelke",
"given": "Amy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Dice",
"given": "Julie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Weber",
"given": "Lisa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Roth",
"given": "Jason",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ferringer",
"given": "Cindy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Beer",
"given": "Deborah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Fesz",
"given": "Jessica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Carpio",
"given": "Lillian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Colin",
"given": "Gwenhael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Zinzoni",
"given": "Vanessa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Maquigneau",
"given": "Natacha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Henri-Lagarrigue",
"given": "Matthieu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pouplet",
"given": "Caroline",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Reill",
"given": "Lorenz",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Distler",
"given": "Michael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Maselli",
"given": "Astrid",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Martynoga",
"given": "Robert",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Trask",
"given": "Kara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Butler",
"given": "Amelia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Newlands",
"given": "Jessica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Henderson",
"given": "Kelly",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Attwood",
"given": "Ben",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Parsons",
"given": "Penny",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Campbell",
"given": "Bridget",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Smith",
"given": "Alex",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hakak",
"given": "Sheeba",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Murphy",
"given": "Aisling",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Joyce",
"given": "Kirsten",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Page",
"given": "Valerie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Zhao",
"given": "Xiao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Oza",
"given": "Deepali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Abrahamson",
"given": "Gail",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sheath",
"given": "Ben",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ellis",
"given": "Chiara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Guanco",
"given": "Mark",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hoxha",
"given": "Elvira",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hegazy",
"given": "Ahmed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Nordin",
"given": "Nazril",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Denham",
"given": "Lynn",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Young",
"given": "Paul",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lesona",
"given": "Eden",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Navarra",
"given": "Leanlove",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Delaney",
"given": "Kirsha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Marmol",
"given": "Joy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Latino",
"given": "Reece",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Qiu",
"given": "Shan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Monaghan",
"given": "Maree",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rhodes",
"given": "Jonathan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Anderson",
"given": "Thomas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Morris",
"given": "Sheila",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Madani",
"given": "Yasser",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Nayyar",
"given": "Vineet",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bowen",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kong",
"given": "Jing",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Monzon",
"given": "Angelica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Fuchs",
"given": "Ralph",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lambert",
"given": "Bridget",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Tai",
"given": "Charlotte",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Thomas",
"given": "Amy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Keen",
"given": "Alexandra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Tierney",
"given": "Carey",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Omer",
"given": "Nimca",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bacon",
"given": "Gina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Evans",
"given": "Amy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Binnie",
"given": "Alexandra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Powell",
"given": "Elizabeth",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McMillan",
"given": "Alexandra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Luk",
"given": "Tracy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Aref",
"given": "Noah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Denmade",
"given": "Craig",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sadera",
"given": "Girendra ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jacob",
"given": "Reni",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "Cathy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hughes",
"given": "Debbie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Elgendy",
"given": "Ahmad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Geng",
"given": "Wenli",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Digby",
"given": "Stephen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Southern",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Reddy",
"given": "Harsha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hulse",
"given": "Sarah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Campbell",
"given": "Andrew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Garton",
"given": "Mark",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Watkins",
"given": "Claire",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Smuts",
"given": "Sara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "The",
"given": "Stephanie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Smith",
"given": "Oliver",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Harris",
"given": "John",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Quinn",
"given": "Alison",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Simpson",
"given": "Benjamin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McMillan",
"given": "Catherine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Finch",
"given": "Cheryl",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hill",
"given": "Claire",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cooper",
"given": "Josh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Brittain",
"given": "Michael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Teo",
"given": "Hoon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Waddington",
"given": "Natalia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Budd",
"given": "Joanna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Small",
"given": "Charlotte",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "O’Leary",
"given": "Ryan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Birch",
"given": "Janine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Collins",
"given": "Emma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Holland",
"given": "Andrew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Alexander",
"given": "Peter",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Felton",
"given": "Tim",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ferguson",
"given": "Susan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sellers",
"given": "Katharine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ward",
"given": "Luke",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bentley",
"given": "Andrew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Fiouni",
"given": "Sofia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Yates",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Birkinshaw",
"given": "Isobel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kell",
"given": "Kay",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Scott",
"given": "Zoe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pearson",
"given": "Harriet",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wittekamp",
"given": "Bastiaan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Grady",
"given": "Bart",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Platenkamp",
"given": "Ellen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hashmi",
"given": "Madiha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ali",
"given": "Maryam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hassan",
"given": "Noor",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Panjwani",
"given": "Ashok",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Umrani",
"given": "Zulfiqar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Shaikh",
"given": "Mohiuddin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Siddiqui",
"given": "Ayesha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ain",
"given": "Quratul",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kanwal",
"given": "Darakhshan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "van Bree",
"given": "Sjoerd",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bouw-Ruiter",
"given": "Marianne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Osinga",
"given": "Margreet",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": " van Zanten ",
"given": "Arthur",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Adhikari",
"given": "Neill KJ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Annane",
"given": "Djillali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Battista",
"given": "Marie-Claude",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cohen",
"given": "Dian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cook",
"given": "Deborah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Day",
"given": "Andrew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Guyatt",
"given": "Gordon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Heyland",
"given": "Daren",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kanji",
"given": "Salmaan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Tirupakuzhi Vijayaraghavan",
"given": "Bharath Kumar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lamontagne",
"given": "Francois",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Masse",
"given": "Marie-Helene",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McGuinness",
"given": "Shay",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Menard",
"given": "Julie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Parke",
"given": "Rachael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pinto",
"given": "Ruxandra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sprague",
"given": "Sheila",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bouffard",
"given": "Lucie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gritsas",
"given": "Ari",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Buckingham",
"given": "Lisa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Têtu",
"given": "Amélie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Malenfant",
"given": "Francis",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Turcotte",
"given": "Pierre",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Al-Beidh",
"given": "Farah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Angus",
"given": "Derek",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Annane",
"given": "Djillai",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Arabi",
"given": "Yaseen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Beane",
"given": "Abigail",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Berry",
"given": "Scott",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bhimani",
"given": "Zahra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bonten",
"given": "Marc",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bradbury",
"given": "Charlotte",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Brunkhorst",
"given": "Franck",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Burrell",
"given": "Aidan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Buxton",
"given": "Meredith",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cecconi",
"given": "Maurizio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cheng",
"given": "Allen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cove",
"given": "Matthew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Derde",
"given": "Lennie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Escourt",
"given": "Lise",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Goossens",
"given": "Herman",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gordon",
"given": "Anthony",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Green",
"given": "Camron",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Haniffa",
"given": "Rashan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hill",
"given": "Thomas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Huang",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ichihara",
"given": "Nao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lawler",
"given": "Patrick",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Marshall",
"given": "John",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McArthur",
"given": "Colin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McAuley",
"given": "Daniel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McGQuilten",
"given": "Zoe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McVerry",
"given": "Bryan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mouncey",
"given": "Paul",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Murthy",
"given": "Srinivas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Nichol",
"given": "Alistair",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Parker",
"given": "Jane",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Reyes",
"given": "Luis Felipe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rowan",
"given": "Kathryn",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Saito",
"given": "Hiroki",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Santos",
"given": "Marlene",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Seymour",
"given": "Christopher",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Shankar-Hari",
"given": "Manu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Turgeon",
"given": "Alexis",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Turner",
"given": "Anne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Webb",
"given": "Steve",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Zarychanski",
"given": "Ryan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McEldrew",
"given": "Rebecca",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "KC",
"given": "Shirish",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Tolppa",
"given": "Timo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rashan",
"given": "Sumayyah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Singh",
"given": "Vanessa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "van Bentum-Puijk",
"given": "Wilma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Brugman",
"given": "Curt",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Groeneveld",
"given": "Erika",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jafarzadeh",
"given": "Mina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jongenelen",
"given": "Irene",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Keijzer-Timmers",
"given": "Nicole",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kester",
"given": "Esmee",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Koelink",
"given": "Maaike",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Okundaye",
"given": "Clementina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Parker",
"given": "Lorraine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Patil",
"given": "Sonal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Peters",
"given": "Svenja",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rietveld",
"given": "Ilse",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sayada",
"given": "Sarah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Smit ",
"given": "Albertine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "van Amerongen",
"given": "Roosmarijn",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vermont - van der Staaij",
"given": "Janine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Doran",
"given": "Peter",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Anjum",
"given": "Aisha ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Au",
"given": "Carly",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lane",
"given": "Janis-Best",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Fagboden",
"given": "Elizabeth",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Barton",
"given": "Frances",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Charles",
"given": "Walton",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Miller",
"given": "Lorna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Parry-Billings",
"given": "Karen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Peters",
"given": "Sam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Richards-Belle",
"given": "Alvin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Saull",
"given": "Michelle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sprinckmoller",
"given": "Stefan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wiley",
"given": "Daisy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Darnell",
"given": "Robert",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Stronach",
"given": "Lucy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wada",
"given": "Asako",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Beqaj",
"given": "Besa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Forbes",
"given": "Andrew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Green",
"given": "Cameron",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Heritier",
"given": "Stephane",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hills",
"given": "Thomas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McEldrew",
"given": "Bec",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McQuilten",
"given": "Zoe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Trapani",
"given": "Tony",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Manoharan",
"given": "Venika",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Dondrop",
"given": "Arjen M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Bin Hasan",
"given": "Mohd Shahnaz",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jayakumar",
"given": "Devachandran",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kalla",
"given": "Ismail ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Murray",
"given": "Lyle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Siika",
"given": "Wangari",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Brunkhorst",
"given": "Frank",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ehrmann",
"given": "Stephan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Povoa",
"given": "Pedro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Horvat",
"given": "Chrisptopher",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Doi",
"given": "Yohei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Fujitani",
"given": "Shigeki",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Honda",
"given": "Hitoshi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Jindai",
"given": "Kazuaki",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kamata",
"given": "Kazuhiro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kato",
"given": "Hideaki",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kunishima",
"given": "Hiroyuki",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Nakazono",
"given": "Kenichi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Shintani",
"given": "Ayumi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Yamagishi",
"given": "Yoshiaki",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Yamashita",
"given": "Chizuru",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Beasley",
"given": "Richard",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Daneman",
"given": "Nick",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Fowler",
"given": "Robert",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McGloughlin",
"given": "Steve",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Paterson",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hullegie",
"given": "Sebastiaan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Litton",
"given": "Edward",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Murphy",
"given": "Srinivas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Venkatesh",
"given": "Bala",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "de Jong",
"given": "Menno",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Uyeki",
"given": "Tim",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Baillie",
"given": "Kenneth",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Netea",
"given": "Mihai",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Orr",
"given": "Katrina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Patanwala",
"given": "Asad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Tong",
"given": "Steve",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cooper",
"given": "Nichola",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Galea",
"given": "James",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ogungbenro",
"given": "Kayode",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Patawala",
"given": "Asad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Tong",
"given": "Steven",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Youngstein",
"given": "Taryn",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Carrier",
"given": "Marc",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Fergusson",
"given": "Dean",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Goligher",
"given": "Ewan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hunt",
"given": "Beverley",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kumar",
"given": "Anand",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Laffan",
"given": "Mike",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lother",
"given": "Sylvain",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Middledorp",
"given": "Saskia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Neal",
"given": "Matthew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Stanworth",
"given": "Simon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Anstey",
"given": "Matthew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "de Man",
"given": "Angelique",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Udy",
"given": "Andrew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Abraham",
"given": "Jacinta",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Arnold",
"given": "Donald",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Begin",
"given": "Phillipe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Charlewood",
"given": "Richard",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Chasse",
"given": "Michael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Cooper",
"given": "Jamie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Coyne",
"given": "Mark",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Daly",
"given": "James",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Estcourt",
"given": "Lise",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gosbell",
"given": "Iain",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Harvala-Simmonds",
"given": "Heli",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hills",
"given": "Tom",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "MacLennan",
"given": "Sheila",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McDyer",
"given": "John",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Menon",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pridee",
"given": "Nicole",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Roberts",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Thomas",
"given": "Helen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Tinmouth",
"given": "Alan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Triulzi",
"given": "Darrell",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Walsh",
"given": "Tim",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wood",
"given": "Erica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Calfee",
"given": "Carolyn",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "O’Kane",
"given": "Cecilia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Shyamsundar",
"given": "Murali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Sinha",
"given": "Pratik",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Thompson",
"given": "Taylor",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Young",
"given": "Ian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ferguson",
"given": "Niall",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Hodgson",
"given": "Carol",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Neto",
"given": "Ary",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Orford",
"given": "Neil",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Phua",
"given": "Jason",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Baron",
"given": "Rebecca",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Epelman",
"given": "Slava ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ezekowitz",
"given": "Justin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Frankfurter",
"given": "Claudia ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Gommans",
"given": "Frank ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kwan",
"given": "Yvonne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Kim",
"given": "Edy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Leaf",
"given": "David ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Owen",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Pollock",
"given": "Katrina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Puskarich",
"given": "Michael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Vaduganathan",
"given": "Muthiah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "van Kimmenade",
"given": "Roland",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Harrison",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Higgins",
"given": "Alisa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lampro",
"given": "Lamprini",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mason",
"given": "Alexina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Mila de la Fuente",
"given": "Gema",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Leffelaar",
"given": "Evelien",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Schotsman",
"given": "Joost",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Boyd",
"given": "Craig",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Harland",
"given": "Cain",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Shearer",
"given": "Audrey",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Wren",
"given": "Jess",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Clermont",
"given": "Giles",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ricketts",
"given": "Daniel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Fazla",
"given": "Fathima",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Muvindi",
"given": "Himasha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Ishani",
"given": "Pramodya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Rashan",
"given": "Aasiyah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Udayanga",
"given": "Ishara ",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Detry",
"given": "Michelle",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Fitzgerald",
"given": "Mark",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lewis",
"given": "Roger",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "McGlothlin",
"given": "Anna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Saunders",
"given": "Christina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Berry",
"given": "Lindsay",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The LOVIT-COVID Investigators, on behalf of the Canadian Critical Care Trials Group, and the REMAP-CAP Investigators"
}
],
"family": "Lorenzi",
"given": "Elizabeth",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Critical Care Medicine, Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, Toronto, Ontario, Canada"
},
{
"name": "Interdepartmental Division of Critical Care Medicine, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada"
}
],
"family": "Adhikari",
"given": "Neill K. J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Critical Care Medicine, Ziauddin University, Karachi, Pakistan"
}
],
"family": "Hashmi",
"given": "Madiha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Critical Care Medicine, Apollo Hospitals, Chennai, India"
},
{
"name": "George Institute for Global Health India, New Delhi"
}
],
"family": "Tirupakuzhi Vijayaraghavan",
"given": "Bharath Kumar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Centre for Inflammation Research, Institute for Regeneration and Repair, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, Scotland"
},
{
"name": "Mahidol Oxford Tropical Medicine Research Unit, Bangkok, Thailand"
}
],
"family": "Haniffa",
"given": "Rashan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Centre for Inflammation Research, Institute for Regeneration and Repair, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, Scotland"
},
{
"name": "Mahidol Oxford Tropical Medicine Research Unit, Bangkok, Thailand"
}
],
"family": "Beane",
"given": "Abi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Australian and New Zealand Intensive Care Research Centre, School of Public Health and Preventive Medicine, Monash University, Melbourne, Australia"
},
{
"name": "St John of God Health Care, Perth, Australia"
}
],
"family": "Webb",
"given": "Steve A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania"
},
{
"name": "University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania"
}
],
"family": "Angus",
"given": "Derek C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Anaesthetics, Pain Medicine, and Intensive Care, Imperial College London, London, England"
},
{
"name": "St Mary’s Hospital, Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust, London, England"
}
],
"family": "Gordon",
"given": "Anthony C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada"
},
{
"name": "Department of Critical Care, St Joseph’s Healthcare Hamilton, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada"
},
{
"name": "Department of Health Research Methods, Evidence, and Impact, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada"
}
],
"family": "Cook",
"given": "Deborah J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Health Research Methods, Evidence, and Impact, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada"
}
],
"family": "Guyatt",
"given": "Gordon H.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Berry Consultants LLC, Austin, Texas"
}
],
"family": "Berry",
"given": "Lindsay R.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Berry Consultants LLC, Austin, Texas"
}
],
"family": "Lorenzi",
"given": "Elizabeth",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Intensive Care National Audit and Research Centre, London, England"
}
],
"family": "Mouncey",
"given": "Paul R.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Intensive Care National Audit and Research Centre, London, England"
}
],
"family": "Au",
"given": "Carly",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Critical Care Medicine, Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre, Toronto, Ontario, Canada"
}
],
"family": "Pinto",
"given": "Ruxandra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Research Centre of the Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Sherbrooke, Sherbrooke, Quebec, Canada"
}
],
"family": "Ménard",
"given": "Julie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Surgery, McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada"
}
],
"family": "Sprague",
"given": "Sheila",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Research Centre of the Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Sherbrooke, Sherbrooke, Quebec, Canada"
}
],
"family": "Masse",
"given": "Marie-Hélène",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Medicine, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania"
}
],
"family": "Huang",
"given": "David T.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Critical Care Medicine, Queen’s University, Kingston, Ontario, Canada"
}
],
"family": "Heyland",
"given": "Daren K.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Australian and New Zealand Intensive Care Research Centre, School of Public Health and Preventive Medicine, Monash University, Melbourne, Australia"
},
{
"name": "Faculty of Medicine, Nursing, and Health Sciences, Monash University, Clayton, Australia"
},
{
"name": "University College Dublin, Dublin, Ireland"
},
{
"name": "Alfred Health, Melbourne, Australia"
}
],
"family": "Nichol",
"given": "Alistair D.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Critical Care Medicine, Auckland City Hospital, Auckland, New Zealand"
}
],
"family": "McArthur",
"given": "Colin J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Intensive Care Medicine, Amsterdam University Medical Centers, Amsterdam, the Netherlands"
}
],
"family": "de Man",
"given": "Angelique",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Imperial College London, London, England"
}
],
"family": "Al-Beidh",
"given": "Farah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "UVSQ University Paris Saclay, Institut-Hospitalo Universitaire Prometheus, Paris, France"
},
{
"name": "Médecine Intensive-Réanimation, Hôpital Raymond-Poincaré, Garches, France"
}
],
"family": "Annane",
"given": "Djillali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Sir Charles Gairdner Hospital, Nedlands, Australia"
},
{
"name": "University of Western Australia, Perth"
}
],
"family": "Anstey",
"given": "Matthew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "King Saud bin Abdulaziz University for Health Sciences, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia"
},
{
"name": "King Abdullah International Medical Research Center, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia"
}
],
"family": "Arabi",
"given": "Yaseen M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Research Centre of the Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Sherbrooke, Sherbrooke, Quebec, Canada"
}
],
"family": "Battista",
"given": "Marie-Claude",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Berry Consultants LLC, Austin, Texas"
}
],
"family": "Berry",
"given": "Scott",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "St Michael’s Hospital, Unity Health Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada"
}
],
"family": "Bhimani",
"given": "Zahra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Julius Center for Health Sciences and Primary Care, University Medical Center Utrecht, Utrecht, the Netherlands"
},
{
"name": "European Clinical Research Alliance on Infectious Diseases, Utrecht, the Netherlands"
}
],
"family": "Bonten",
"given": "Marc J. M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University of Bristol, Bristol, England"
}
],
"family": "Bradbury",
"given": "Charlotte A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Critical Care Medicine, School of Medicine, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania"
}
],
"family": "Brant",
"given": "Emily B.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Anaesthesiology and Intensive Care Medicine, Jena University Hospital, Jena, Germany"
}
],
"family": "Brunkhorst",
"given": "Frank M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Alfred Health, Melbourne, Australia"
},
{
"name": "Australian and New Zealand Intensive Care Research Centre, Department of Epidemiology and Preventive Medicine, Monash University, Melbourne, Australia"
}
],
"family": "Burrell",
"given": "Aidan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Global Coalition for Adaptive Research, Larkspur, California"
}
],
"family": "Buxton",
"given": "Meredith",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Biomedical Sciences, Humanitas University, Milan, Italy"
},
{
"name": "IRCCS Humanitas Research Hospital, Milan, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Cecconi",
"given": "Maurizio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Monash Infectious Disease, Monash Health and School of Clinical Sciences, Monash University, Clayton, Australia"
},
{
"name": "School of Public Health and Preventive Medicine, Monash University, Melbourne, Australia"
}
],
"family": "Cheng",
"given": "Allen C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Bishop’s University, Sherbrooke, Quebec, Canada"
},
{
"name": "Massawippi Valley Foundation, Ayer’s Cliff, Quebec, Canada"
}
],
"family": "Cohen",
"given": "Dian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore, Singapore"
}
],
"family": "Cove",
"given": "Matthew E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Kingston Health Sciences Centre and Queen’s University, Kingston, Ontario, Canada"
}
],
"family": "Day",
"given": "Andrew G.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "European Clinical Research Alliance on Infectious Diseases, Utrecht, the Netherlands"
},
{
"name": "Intensive Care Centre, University Medical Centre Utrecht, Utrecht, the Netherlands"
}
],
"family": "Derde",
"given": "Lennie P. G.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Berry Consultants LLC, Austin, Texas"
}
],
"family": "Detry",
"given": "Michelle A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Haematology, NHS Blood and Transplant, Bristol, England"
},
{
"name": "Radcliffe Department of Medicine, University of Oxford, Oxford, England"
}
],
"family": "Estcourt",
"given": "Lise J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Imperial Clinical Trials Unit, Imperial College London, London, England"
}
],
"family": "Fagbodun",
"given": "Elizabeth O.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Berry Consultants LLC, Austin, Texas"
}
],
"family": "Fitzgerald",
"given": "Mark",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Laboratory of Medical Microbiology, University of Antwerp, Antwerp, Belgium"
}
],
"family": "Goossens",
"given": "Herman",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Australian and New Zealand Intensive Care Research Centre, School of Public Health and Preventive Medicine, Monash University, Melbourne, Australia"
}
],
"family": "Green",
"given": "Cameron",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Australian and New Zealand Intensive Care Research Centre, School of Public Health and Preventive Medicine, Monash University, Melbourne, Australia"
}
],
"family": "Higgins",
"given": "Alisa M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical Research Institute of New Zealand, Wellington"
}
],
"family": "Hills",
"given": "Thomas E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, School of Medicine, Jikei University, Tokyo, Japan"
}
],
"family": "Ichihara",
"given": "Nao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Dr Kamakshi Memorial Hospital Apollo, Chennai, India"
}
],
"family": "Jayakumar",
"given": "Devachandran",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Ottawa Hospital, Ottawa, Ontario, Canada"
},
{
"name": "Ottawa Hospital Research Institute, Ottawa, Ontario, Canada"
}
],
"family": "Kanji",
"given": "Salmaan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "South City Hospital, Karachi, Pakistan"
}
],
"family": "Khoso",
"given": "Muhammad Nasir",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University Health Network, Toronto, Ontario, Canada"
},
{
"name": "University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada"
},
{
"name": "McGill University Health Centre, Montreal, Quebec, Canada"
}
],
"family": "Lawler",
"given": "Patrick R.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Berry Consultants LLC, Austin, Texas"
}
],
"family": "Lewis",
"given": "Roger J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Fiona Stanley Hospital, Department of Intensive Care Unit, University of Western Australia, Perth"
}
],
"family": "Litton",
"given": "Edward",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Surgery, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada"
}
],
"family": "Marshall",
"given": "John C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Queen’s University of Belfast, Belfast, Northern Ireland"
},
{
"name": "Centre for Infection and Immunity, Royal Victoria Hospital, Belfast, Northern Ireland"
}
],
"family": "McAuley",
"given": "Daniel F.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Berry Consultants LLC, Austin, Texas"
}
],
"family": "McGlothlin",
"given": "Anna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical Research Institute of New Zealand, Wellington"
},
{
"name": "Auckland City Hospital, Cardiothoracic and Vascular Intensive Care Unit, Auckland, New Zealand"
},
{
"name": "Australian and New Zealand Intensive Care Research Centre, Monash University, Melbourne, Australia"
}
],
"family": "McGuinness",
"given": "Shay P.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Monash University, Monash Health, Clayton, Australia"
}
],
"family": "McQuilten",
"given": "Zoe K.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania"
}
],
"family": "McVerry",
"given": "Bryan J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pediatrics, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada"
}
],
"family": "Murthy",
"given": "Srinivas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical Research Institute of New Zealand, Wellington"
},
{
"name": "Auckland City Hospital, Cardiothoracic and Vascular Intensive Care Unit, Auckland, New Zealand"
},
{
"name": "School of Nursing, University of Auckland, Auckland, New Zealand"
}
],
"family": "Parke",
"given": "Rachael L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Faculty of Medicine, Nursing, and Health Sciences, Monash University, Clayton, Australia"
}
],
"family": "Parker",
"given": "Jane C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases, Universidad de La Sabana, Chia, Colombia"
},
{
"name": "Department of Critical Care Medicine, Clinica Universidad de La Sabana, Chia, Colombia"
}
],
"family": "Reyes",
"given": "Luis Felipe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Intensive Care National Audit and Research Centre, London, England"
}
],
"family": "Rowan",
"given": "Kathryn M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Emergency and Critical Care Medicine, St Marianna University Yokohama Seibu Hospital, Yokohama, Japan"
}
],
"family": "Saito",
"given": "Hiroki",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "National Institute of Cardiovascular Diseases, Karachi, Pakistan"
}
],
"family": "Salahuddin",
"given": "Nawal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Critical Care, St Michael’s Hospital, Toronto, Ontario, Canada"
}
],
"family": "Santos",
"given": "Marlene S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Berry Consultants LLC, Austin, Texas"
}
],
"family": "Saunders",
"given": "Christina T.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Critical Care Medicine, School of Medicine, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania"
}
],
"family": "Seymour",
"given": "Christopher W.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Institute for Regeneration and Repair, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, Scotland"
},
{
"name": "Royal Infirmary of Edinburgh, NHS Lothian, Edinburgh, Scotland"
}
],
"family": "Shankar-Hari",
"given": "Manu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "National Intensive Care Surveillance, Colombo, Sri Lanka"
}
],
"family": "Tolppa",
"given": "Timo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Australian and New Zealand Intensive Care Research Centre, Monash University, Melbourne, Australia"
}
],
"family": "Trapani",
"given": "Tony",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Anesthesiology and Critical Care, Université Laval, Quebec City, Quebec, Canada"
},
{
"name": "Population Health and Optimal Health Practices Research Unit, Departments of Traumatology, Emergency Medicine, and Critical Care Medicine, Université Laval Research Center, CHU de Québec-Université Laval, Quebec City, Quebec, Canada"
}
],
"family": "Turgeon",
"given": "Alexis F.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Medical Research Institute of New Zealand, Wellington"
}
],
"family": "Turner",
"given": "Anne M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Australian and New Zealand Intensive Care Research Centre, Monash University, Melbourne, Australia"
},
{
"name": "Department of Intensive Care and Hyperbaric Medicine, Alfred Hospital, Melbourne, Australia"
}
],
"family": "Udy",
"given": "Andrew A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Internal Medicine, Radboud University Medical Center, Nijmegen, the Netherlands"
}
],
"family": "van de Veerdonk",
"given": "Frank L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, Canada"
}
],
"family": "Zarychanski",
"given": "Ryan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Research Centre of the Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Sherbrooke, Sherbrooke, Quebec, Canada"
},
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Université de Sherbrooke, Sherbrooke, Quebec, Canada"
}
],
"family": "Lamontagne",
"given": "François",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "JAMA",
"container-title-short": "JAMA",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2023-10-25T12:30:56Z",
"timestamp": 1698237056000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-26T16:01:42Z",
"timestamp": 1703606502000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-19T09:42:08Z",
"timestamp": 1710841328447
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 7,
"issue": "18",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
14
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "18",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
14
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/articlepdf/2811212/jama_adhikari_2023_oi_230127_1702498690.6766.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "10",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1745",
"prefix": "10.1001",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
14
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
14
]
]
},
"publisher": "American Medical Association (AMA)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m3379",
"article-title": "A living WHO guideline on drugs for COVID-19.",
"author": "Lamontagne",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "m3379",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "joi230127r2",
"volume": "370",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00372-5",
"article-title": "The global COVID-19 treatment divide.",
"author": "Usher",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "779",
"issue": "10327",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "joi230127r3",
"volume": "399",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.202005-1829OC",
"article-title": "Use of hydrocortisone, ascorbic acid, and thiamine in adults with septic shock.",
"author": "Vail",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1531",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Am J Respir Crit Care Med",
"key": "joi230127r4",
"volume": "202",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2019.22176",
"article-title": "Effect of vitamin C, hydrocortisone, and thiamine vs hydrocortisone alone on time alive and free of vasopressor support among patients with septic shock: the VITAMINS randomized clinical trial.",
"author": "Fujii",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "423",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "joi230127r5",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.24505",
"article-title": "Effect of vitamin C, thiamine, and hydrocortisone on ventilator- and vasopressor-free days in patients with sepsis: the VICTAS randomized clinical trial.",
"author": "Sevransky",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "742",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "joi230127r6",
"volume": "325",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2200644",
"article-title": "Intravenous vitamin C in adults with sepsis in the intensive care unit.",
"author": "Lamontagne",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2387",
"issue": "25",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "joi230127r7",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12113286",
"article-title": "The emerging role of vitamin C in the prevention and treatment of COVID-19.",
"author": "Carr",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3286",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "joi230127r9",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-03249-y",
"article-title": "Vitamin C levels in patients with SARS-CoV-2-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome.",
"author": "Chiscano-Camón",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "522",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "joi230127r10",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14194217",
"article-title": "Vitamin C supplementation for the treatment of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis.",
"author": "Olczak-Pruc",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4217",
"issue": "19",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "joi230127r11",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1513/AnnalsATS.202003-192SD",
"article-title": "The REMAP-CAP (Randomized Embedded Multifactorial Adaptive Platform for Community-acquired Pneumonia) study: rationale and design.",
"author": "Angus",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "879",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Ann Am Thorac Soc",
"key": "joi230127r12",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021436",
"article-title": "Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19.",
"author": "Horby",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "693",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "joi230127r13",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2105911",
"article-title": "Therapeutic anticoagulation with heparin in noncritically ill patients with Covid-19.",
"author": "ATTACC, ACTIV-4a Investigators, and REMAP-CAP Investigators",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "790",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "joi230127r14",
"volume": "385",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2103417",
"article-title": "Therapeutic anticoagulation with heparin in critically ill patients with Covid-19.",
"author": "REMAP-CAP, ACTIV-4a, and ATTACC Investigators",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "777",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "joi230127r15",
"volume": "385",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2022.23257",
"article-title": "Long-term (180-day) outcomes in critically ill patients with COVID-19 in the REMAP-CAP randomized clinical trial.",
"author": "Higgins",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "39",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "joi230127r16",
"volume": "329",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/cc10110",
"article-title": "Persistent organ dysfunction plus death: a novel, composite outcome measure for critical care trials.",
"author": "Heyland",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "R98",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "joi230127r17",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30483-7",
"article-title": "A minimal common outcome measure set for COVID-19 clinical research.",
"author": "WHO Working Group on the Clinical Characterisation and Management of COVID-19 Infection",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e192",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "joi230127r18",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2019.11825",
"article-title": "Effect of vitamin C infusion on organ failure and biomarkers of inflammation and vascular injury in patients with sepsis and severe acute respiratory failure: the CITRIS-ALI randomized clinical trial.",
"author": "Fowler",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1261",
"issue": "13",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "joi230127r19",
"volume": "322",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00134-022-06869-w",
"article-title": "Coronavirus disease 2019 subphenotypes and differential treatment response to convalescent plasma in critically ill adults: secondary analyses of a randomized clinical trial.",
"author": "Fish",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1525",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Intensive Care Med",
"key": "joi230127r20",
"volume": "48",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.f2304",
"article-title": "Influence of trial sample size on treatment effect estimates: meta-epidemiological study.",
"author": "Dechartres",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "f2304",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "joi230127r21",
"volume": "346",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2019.14607",
"article-title": "Effect of selepressin vs placebo on ventilator- and vasopressor-free days in patients with septic shock: the SEPSIS-ACT randomized clinical trial.",
"author": "Laterre",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1476",
"issue": "15",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "joi230127r22",
"volume": "322",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0197-2456(83)90029-6",
"article-title": "The Coronary Drug Project: monitoring of the data for evidence of adverse or beneficial treatment effects.",
"author": "Canner",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "467",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Control Clin Trials",
"key": "joi230127r23",
"volume": "4",
"year": "1983"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.290.2.238",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of tifacogin (recombinant tissue factor pathway inhibitor) in severe sepsis: a randomized controlled trial.",
"author": "Abraham",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "238",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "joi230127r24",
"volume": "290",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0197-2456(02)00273-8",
"article-title": "Be skeptical about unexpected large apparent treatment effects: the case of an MRC AML12 randomization.",
"author": "Wheatley",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "66",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Control Clin Trials",
"key": "joi230127r25",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMra1510061",
"article-title": "Adaptive designs for clinical trials.",
"author": "Bhatt",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "65",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "joi230127r26",
"volume": "375",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jclinepi.2022.11.002",
"article-title": "An overview of methodological considerations regarding adaptive stopping, arm dropping, and randomization in clinical trials.",
"author": "Granholm",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "45",
"journal-title": "J Clin Epidemiol",
"key": "joi230127r27",
"volume": "153",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1479-5876-12-32",
"article-title": "Phase I safety trial of intravenous ascorbic acid in patients with severe sepsis.",
"author": "Fowler",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "32",
"journal-title": "J Transl Med",
"key": "joi230127r28",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.0444",
"article-title": "Geographical representation of low- and middle-income countries in randomized clinical trials for COVID-19.",
"author": "Ramanan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "joi230127r29",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m1847",
"article-title": "Waste in COVID-19 research.",
"author": "Glasziou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "m1847",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "joi230127r30",
"volume": "369",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "joi230127r1",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization. COVID-19 dashboard. Accessed March 30, 2023. https://covid19.who.int/"
},
{
"key": "joi230127r8",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization. A coordinated global research roadmap: 2019 novel coronavirus. Published March 12, 2020. Accessed October 6, 2023. https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/a-coordinated-global-research-roadmap"
}
],
"reference-count": 30,
"references-count": 30,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2811212"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [
"Two Harmonized Randomized Clinical Trials"
],
"title": "Intravenous Vitamin C for Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "330"
}
adhikari2
