Repurposing Inhaled Ibuprofenate, a Non Steroidal Anti‐Inflammatory Drug, as a Potential Adjuvant Treatment for Pneumonia, CARDS and its Aetiological Agent SARS‐CoV‐2
et al., Clinical and Translational Discovery, doi:10.1002/ctd2.204, May 2023
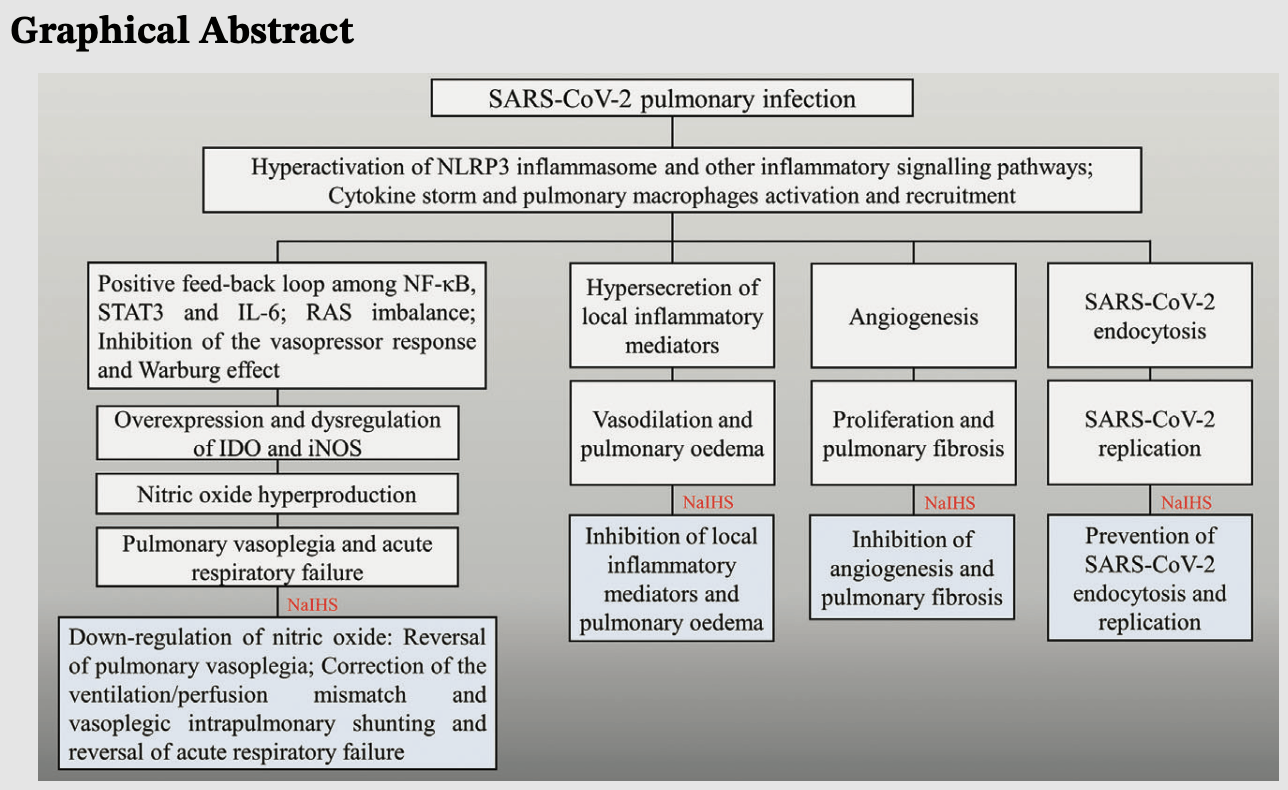
Review of the potential mechanisms of action and therapeutic effects of inhaled sodium ibuprofenate for the treatment of COVID-19 pneumonia. Authors describe potential anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, antiangiogenic, and virucidal effects that may help reverse pulmonary vasoplegia, correct ventilation/perfusion mismatch, and reduce severe hypoxemia and respiratory failure.
1.
Moshawih et al., Evaluating NSAIDs in SARS-CoV-2: Immunomodulatory mechanisms and future therapeutic strategies, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e25734.
Zurita-Lizza et al., 16 May 2023, peer-reviewed, 3 authors.
Contact: zuritachristian70@yahoo.com.ar.
Repurposing Inhaled Ibuprofenate, a Non Steroidal Anti‐Inflammatory Drug, as a Potential Adjuvant Treatment for Pneumonia, CARDS and its Aetiological Agent SARS‐CoV‐2
Clinical and Translational Discovery, doi:10.1002/ctd2.204
In this manuscript, we will describe and highlight the most important potential underlying mechanisms of action of the inhaled sodium ibuprofenate in hypertonic saline formulation-NaIHS aerosolisable, as a probable adjuvant treatment for moderate and severe pneumonia and coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome in COVID-19. In both pathological entities, we will refer exclusively to the pulmonary vasoplegic type and we will describe the following therapeutic effects of NaIHS: antiinflammatory, immunomodulatory and antiangiogenic. The synergistic action of these therapeutic effects anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory together may exert their action at the pulmonary level through the possible reversal of pulmonary vasoplegia and may thereby restore hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction, correcting the uncoupling of the ventilation/ perfusion ratio and vasoplegic intrapulmonary shunting and, above all, it may reverse severe hypoxaemia and acute respiratory failure. We will also mention the potential virucidal effects of NaIHS on severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus 2.
References
Abate, Checkol, Mantefardo, Global prevalence and determinants of mortality among patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Ann Med Surg, doi:10.1016/j.amsu.2021.102204
Ahmad, Rehman, Ahmad, Alkharfy, COVID-19 and thymoquinone: connecting the dots, Phytother Res, doi:10.1002/ptr.6793
Batiha, Dai, Qusti, Common NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitors and COVID-19: Divide and conquer, Sci Afr, doi:10.1016/j.sciaf.2021.e01084
Berre, Boeken, Caramella, Dual-energy CT angiography reveals high prevalence of perfusion defects unrelated to pulmonary embolism in COVID-19 lesions, Insights Imaging, doi:10.1186/s13244-021-00972-0
Bonelli, Tuccillo, Borrelli, Schiattarella, Buonaguro, CDK/CCN and CDKI alterations for cancer prognosis and therapeutic predictivity, Biomed Res Int, doi:10.1155/2014/361020
Boroojerdi, Jabry, Mirarefin, Albalushi, Insights into organoid-based modeling of COVID-19 pathology, Virol J, doi:10.1186/s12985-023-01996-2
Calonico, Tella, Del Valle, Causal inference during a pandemic: evidence on the effectiveness of nebulized ibuprofen as an unproven treatment for COVID-19 in Argentina, doi:10.3386/w30084
Chen, Han, Wang, Vascular and pulmonary effects of ibuprofen on neonatal lung development, Respir Res, doi:10.1186/s12931-023-02342-4
Chilosi, Poletti, Ravaglia, The pathogenic role of epithelial and endothelial cells in early phase COVID-19 pneumonia: victims and partners in crime, Mod Pathol, doi:10.1038/s41379-021-00808-8
Clemente, Freiberger, Ravetti, Beltramo, Garro, An in silico analysis of Ibuprofen enantiomers in high concentrations of sodium chloride with SARS-CoV-2 main protease, J Bio mol Struct Dyn, doi:10.1080/07391102.2021.1872420
De Bruin, Schneider, Reus, Ibuprofen, flurbiprofen, etoricoxib, or paracetamol do not influence ACE2 expression and activity in vitro or in mice and do not exacerbate in-vitro SARS-CoV-2 infection, Int J Mol Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms23031049
Elmaaty, Hamed, Ismail, Computational insights on the potential of some NSAIDs for treating COVID-19: priority set and lead optimization, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules
Elmazoglu, Bek, Saribas, TLR4, Rage, and p-JNK/JNK mediated inflammatory aggression in osteoathritic human chondrocytes are counteracted by redox-sensitive phenolic olive compounds: comparison with ibuprofen, J Tissue EngRegen Med, doi:10.1002/term.3138
García, Porta, Alasino, Muñoz, Beltramo, Ibuprofen, a traditional drug that may impact the course of COVID-19 new effective formulation in nebulisable solution, MedHypotheses, doi:10.1016/j.mehy.110079
Gattinoni, Chiumello, Caironi, COVID-19 pneumonia: different respiratory treatments for different phenotypes?, Intensive Care Med, doi:10.1007/s00134-020-06033-2
Gholamreza-Fahimi, Bisha, Hahn, Cyclooxygenase activity in bradykinin-induced dermal extravasation. A study in mice and humans, Biomed Pharmacother, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109797
Icard, Lincet, Wu, The key role of Warburg effect in SARS-CoV-2 replication and associated inflammatory response, Biochimie, doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2020.11.010
Janssen, Maier, Schiffmann, Evidence of COX-2 independent induction of apoptosis and cell cycle block in human colon carcinoma cells after S-or R-ibuprofen treatment, Eur J Pharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.04.030
Jusman, Sari, Ningsih, Hardiany, Sadikim, Role of hypoxia inducible factor -1 alpha (HIF-1α) in cytoglobin expression and fibroblast proliferation of keloids, Kobe J Med Sci
Kalayan, Cau, Del Valle Cabello, Safety and efficacy of nebulised anti-inflammatory solution of alkaline hypertonic ibuprofen (AHI) for treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection: a compassionate study with a comparator arms, Eur J Respir Med, doi:10.31488/EJRM.132
Kelleni, Early use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in COVID-19 might reverse pathogenesis, prevent complications and improve clinical outcomes, Biomed Pharmacother, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110982
Kelleni, NSAIDs/nitazoxanide/azithromycin repurposed for COVID-19: potential mitigation of the cytokine storm interleukin-6 amplifier via immunomodulatory effects, Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther, doi:10.1080/14787210.2021.1939683
Kulesza, Zielniok, Hawryluk, Paczek, Burdzinska, Ibuprofen in therapeutic concentrations affects the secretion of human bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells, but not their proliferative and migratory capacity, Biomolecules, doi:10.3390/biom12020287
Li, Song, Li, Ibuprofen attenuates interleukin-1βinduced inflammation and actin reorganization via modulation of RhoA signaling in rabbit chondrocytes, Acta BiochimBiophys Sin, doi:10.1093/abbs/gmz101
Liu, Yan, Xue, Prim-O-glucosycimifugin attenuates liver injury in septic mice by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome/caspase-1 signaling cascades in macrophages, Phytomedicine, doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154427
Loganathan, Ramachandran, Shankaran, Nagarajan, Mohan, Host transcriptome-guided drug repurposing for COVID-19 treatment: a meta-analysis based approach, Peer J, doi:10.7717/peerj.9357
Mostafa, Kandeil, Elshaier, FDA approved drugs with potent in vitro antiviral activity against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph13120443
Otto, Krebs, Welker, Inhalationally administered semifluorinated alkanes (SFAs) as drug carriers in an experimental model of acute respiratory distress syndrome, Pharmaceutics, doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics13030431
Palayoor, Tofilon, Coleman, Ibuprofen-mediated reduction of hypoxia-inducible factors HIF-1 alpha and HIF-2 alpha in prostate cancer cells, Clin Cancer Res
Pan, Peng, Tan, Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs potently inhibit the replication of Zika viruses by inducing the degradation of AXL, J Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.01018-18
Perico, Cortinovis, Suter, Remuzzi, Home as the new frontier for the treatment of COVID-19: the case for anti-inflammatory agents, Lancet Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00433-9
Perreau, Suffiotti, Vidal, The cytokines HGF and CXCL13 predict the severity and the mortality in COVID-19 patients, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-021-25191-5
Pizzutto, Upham, Yerkovich, Ab, Inhaled non-steroid anti-inflammatories for children and adults with bronchiectasis, Cochrane Database Syst Rev, doi:10.1002/14651858.CD007525.pub3
Qiao, Wang, Chen, Ibuprofen attenuates cardiac fibrosis in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats, Cardiology, doi:10.1159/000375362
Rainsford, Ibuprofen: pharmacology, efficacy and safety, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-009-0016-x
Salva, Doreski, Giler, Reversal of SARS-CoV-2 induced hypoxia by nebulized sodium ibuprofenate in a compassionate use program, Infect Dis Ther, doi:10.1007/s40121-021-00527-2
Savitz, The kynurenine pathway: a finger in every pie, Mol Psychiatry, doi:10.1038/s41380-019-0414-4
Seltzer, Linking ACE2 and angiotensin II to pulmonary immunovascular dysregulation in SARS-CoV-2 infection, Int J Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.041
Sharma, Dhanjal, Chopra, Targeting eosinophils in chronic respiratory diseases using nanotechnology-based drug delivery, Chem Biol Interact, doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2022.110050
Smart, Fawkes, Goggin, A narrative review of the potential pharmacological influence and safety of ibuprofen on coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19), ACE2, and the immune system: a dichotomy of expectation and reality, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-020-00745-z
Smith, Soti, Jones, Nakagawa, Xue et al., Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are caspase inhibitors, Cell Chem Biol, doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2017.02.003
Thitinarongwate, Nimlamool, Khonsung, Mektrirat, Kunanusorn, Anti-inflammatory activity of essentials oil from zingiber ottensii valeton in animal models, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules27134260
Ts, Li, Schmidt, Cai, Sheppard, Direct block of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator CL(-) channel by niflumic acid, Mol Membr Biol, doi:10.1080/09687680310001597758
Valenzuela, Pedrosa, Garrido-Gil, Interactions between ibuprofen, ACE2, renin-angiotensin system, and Spike protein in the lung. Implications for COVID-19, ClinTransl Med, doi:10.1002/ctm2.371
Vallee, Lecarpentier, Vallee, Targeting the canonical WNT/β-catenin pathway in cancer treatment using non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells8070726
Wang, Qiu, Hou, AXL is a candidate receptor for SARS-CoV-2 that promotes infection of pulmonary and bronchial epithelial cells, Cell Res, doi:10.1038/s41422-020-00460-y
Wiktorowska-Owczarek, Namiecinska, Owczarek, The effect of ibuprofen on bFGF, VEGF secretion and cell proliferation in the presence of LPS in HMEC-1 cells, Acta Pol Pharm
Zapolska-Downar, Naruszewicz, A pleiotropic antiatherogenic action of ibuprofen, Med Sci Monit
Zhou, Zhao, Gan, Use of non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs and adverse outcomes during the COVID-19 pandemic: a systematic review and meta-analysis, EClini-calMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101373
Zumla, Rao, Parida, Inflammation and tuberculosis: host-directed therapies, J Intern Med, doi:10.1111/joim.12256
Zurita-Lizza, Doreski, Potential reversal of pulmonary vasoplegia by inhaled ibuprofenate in COVID-19 pneumonia, Clin Transl Discov, doi:10.1002/ctd2.31
Zurita-Lizza, Rodriguez-Sanchez, Doreski, Blocking the action of NLRP3 inflammasome by inhaled ibuprofenate on pulmonary macrophages infected by SARS-CoV-2, Clin Transl Disc, doi:10.1002/ctd.169
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ctd2.204",
"ISSN": [
"2768-0622",
"2768-0622"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ctd2.204",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:p>In this manuscript, we will describe and highlight the most important potential underlying mechanisms of action of the inhaled sodium ibuprofenate in hypertonic saline formulation‐NaIHS aerosolisable, as a probable adjuvant treatment for moderate and severe pneumonia and coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19)‐associated acute respiratory distress syndrome in COVID‐19. In both pathological entities, we will refer exclusively to the pulmonary vasoplegic type and we will describe the following therapeutic effects of NaIHS: anti‐inflammatory, immunomodulatory and antiangiogenic. The synergistic action of these therapeutic effects anti‐inflammatory and immunomodulatory together may exert their action at the pulmonary level through the possible reversal of pulmonary vasoplegia and may thereby restore hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction, correcting the uncoupling of the ventilation/perfusion ratio and vasoplegic intrapulmonary shunting and, above all, it may reverse severe hypoxaemia and acute respiratory failure. We will also mention the potential virucidal effects of NaIHS on severe acute respiratory syndrome‐coronavirus 2 (SARS‐CoV‐2).</jats:p><jats:p>There are available three retrospective observational studies in moderate and severe COVID‐19 pneumonia, carried out in Argentina, with all three studies concluding that there was a significant reduction in mortality. The most important of these was conducted with the approval of the Institutional Review Board of the National Bureau of Economic Research of Harvard and Columbia Universities, which analysed data from 5146 patients and concluded that NaIHS reduced mortality by 48.7%, although randomized clinical trials are still needed to confirm these emerging data and enable the rise of NaIHS as a new adjuvant treatment.</jats:p><jats:p>Conclusively, we deem essential to reuse known drugs, such as ibuprofen, in COVID‐19, due to the constant emergence of variants and subvariants of concern secondary to mutations and immune escape mechanisms of (SARS‐CoV‐2), since effective medical treatments are currently scarce and many of them are controversial or not available worldwide.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1002/ctd2.204"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2023-03-15"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 1,
"value": "2023-05-06"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 2,
"value": "2023-05-16"
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8969-4261",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Hospital General de Agudos Dr Cosme Argerich, Intensive Care Unit Buenos Aires Argentina"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Zurita‐Lizza",
"given": "Christian Carlos",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Universidad de Buenos Aires (UBA) Buenos Aires Argentina"
}
],
"family": "Rodriguez‐Sanchez",
"given": "Ignacio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Fundación Respirar Clinical Research Unit Buenos Aires Argentina"
}
],
"family": "Doreski",
"given": "Pablo Alexis",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Clinical and Translational Discovery",
"container-title-short": "Clinical and Translational Dis",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"onlinelibrary.wiley.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-17T06:09:39Z",
"timestamp": 1684303779000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-20T11:58:17Z",
"timestamp": 1705751897000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-20T13:08:57Z",
"timestamp": 1705756137914
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "3",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
16
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "3",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-16T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1684195200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/ctd2.204",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1002",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
16
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
16
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mehy.110079",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_2_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/joim.12256",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_3_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.31488/EJRM.132",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_4_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40121‐021‐00527‐2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_5_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3386/w30084",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "e_1_2_10_6_1",
"unstructured": "CalonicoS Di TellaR Lopez del ValleJC Causal inference during a pandemic: evidence on the effectiveness of nebulized ibuprofen as an unproven treatment for COVID‐19 in Argentina. NBER working paper No. 30084 from National Bureau of Economic Research Inc.2022. doi:10.3386/w30084. JEL NO. 11 118 03"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.041",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_7_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.amsu.2021.102204",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_8_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41379‐021‐00808‐8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_9_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00134‐020‐06033‐2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_10_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13244‐021‐00972‐0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_11_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.04.030",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_12_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10787‐009‐0016‐x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_13_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10787‐020‐00745‐z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_14_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/pharmaceutics13030431",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_15_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cbi.2022.110050",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_16_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms23031049",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_17_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110982",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_18_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101373",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_19_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/14651858.CD007525.pub3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_20_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473‐3099(22)00433‐9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_21_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cells8070726",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_22_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ctd.169",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_23_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.sciaf.2021.e01084",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_24_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154427",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_25_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/09687680310001597758",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_26_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chembiol.2017.02.003",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_27_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biom12020287",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_28_1"
},
{
"article-title": "A pleiotropic antiatherogenic action of ibuprofen",
"author": "Zapolska‐Downar D",
"first-page": "837",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Med Sci Monit",
"key": "e_1_2_10_29_1",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/term.3138",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_30_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467‐021‐25191‐5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_31_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ctd2.31",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_32_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41380‐019‐0414‐4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_33_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ctm2.371",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_34_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.6793",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_35_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/14787210.2021.1939683",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_36_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biochi.2020.11.010",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_37_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Role of hypoxia inducible factor ‐1 alpha (HIF‐1α) in cytoglobin expression and fibroblast proliferation of keloids",
"author": "Jusman SWA",
"first-page": "E10",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Kobe J Med Sci",
"key": "e_1_2_10_38_1",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules27134260",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_39_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109797",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_40_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12931‐023‐02342‐4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_41_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000375362",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_42_1"
},
{
"article-title": "The effect of ibuprofen on bFGF, VEGF secretion and cell proliferation in the presence of LPS in HMEC‐1 cells",
"author": "Wiktorowska‐Owczarek A",
"first-page": "889",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Acta Pol Pharm",
"key": "e_1_2_10_43_1",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"article-title": "Ibuprofen‐mediated reduction of hypoxia‐inducible factors HIF‐1 alpha and HIF‐2 alpha in prostate cancer cells",
"author": "Palayoor ST",
"first-page": "3150",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Clin Cancer Res",
"key": "e_1_2_10_44_1",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2014/361020",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_45_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41422‐020‐00460‐y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_46_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.01018‐18",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_47_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12985‐023‐01996‐2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_48_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/abbs/gmz101",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_49_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07391102.2021.1872420",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_50_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_51_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ph13120443",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_52_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7717/peerj.9357",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_53_1"
}
],
"reference-count": 52,
"references-count": 52,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/ctd2.204"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Repurposing Inhaled Ibuprofenate, a Non Steroidal Anti‐Inflammatory Drug, as a Potential Adjuvant Treatment for Pneumonia, CARDS and its Aetiological Agent SARS‐CoV‐2",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/crossmark_policy",
"volume": "3"
}