Analysis of Prior Aspirin Treatment on in-Hospital Outcome of Geriatric COVID-19 Infected Patients
et al., Medicina, doi:10.3390/medicina58111649, Nov 2022
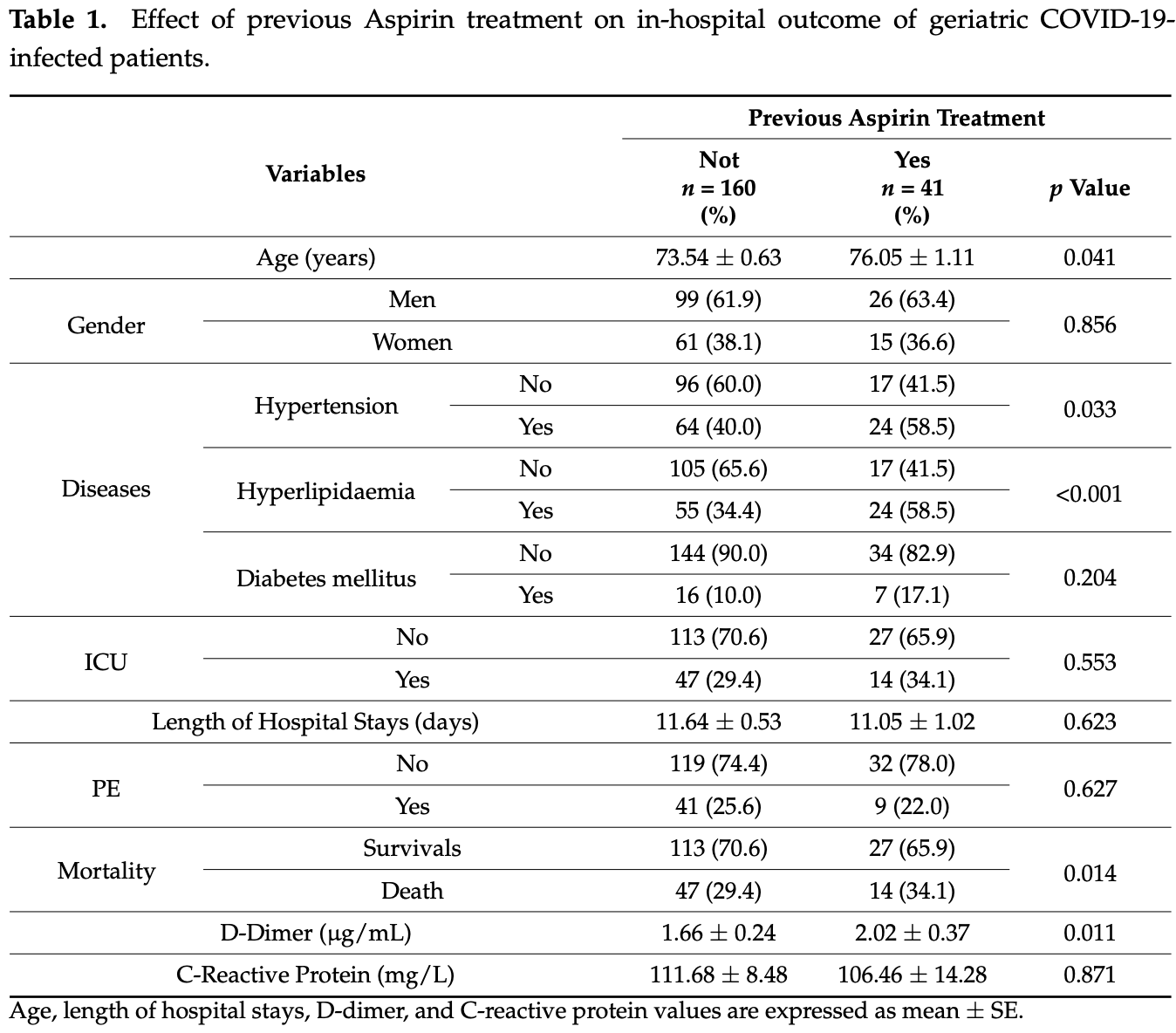
Retrospective 201 consecutive elderly hospitalized patients in Spain, showing higher mortality with aspirin use in unadjusted results. The aspirin group was older and had higher prevalence of hypertension and dyslipidemia. Table 1 shows the same counts for mortality and ICU, but different p values.
This study is excluded in meta-analysis:
unadjusted differences between groups; inconsistent data.
|
risk of death, 16.2% higher, RR 1.16, p = 0.57, treatment 14 of 41 (34.1%), control 47 of 160 (29.4%).
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 16.2% higher, RR 1.16, p = 0.57, treatment 14 of 41 (34.1%), control 47 of 160 (29.4%).
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Zekri-Nechar et al., 15 Nov 2022, retrospective, Spain, peer-reviewed, 10 authors.
Contact: jjzamorano@ucm.es (corresponding author).
Analysis of Prior Aspirin Treatment on in-Hospital Outcome of Geriatric COVID-19 Infected Patients
Medicina, doi:10.3390/medicina58111649
Background and Objectives: Aspirin (ASA) is a commonly used antithrombotic drug that has been demonstrated to reduce venous thromboembolism. The aim was to analyze if geriatric COVID-19 patients undergoing a 100 mg/day Aspirin (ASA) treatment prior to hospitalization differ in hospital outcome compared to patients without previous ASA therapy. Materials and Methods: An observational retrospective study was carried out using an anonymized database including geriatric COVID-19 patients (March to April 2020) admitted to Madrid Hospitals Group. A group of COVID-19 patients were treated with low ASA (100 mg/day) prior to COVID-19 infection. Results: Geriatric ASA-treated patients were older (mean age over 70 years; n = 41), had higher frequency of hypertension and hyperlipidemia, and upon admission had higher D-dimer levels than non-ASAtreated patients (mean age over 73 years; n = 160). However, patients under ASA treatment did not show more frequent pulmonary thromboembolism (PE) than non-ASA-treated patients. ASA-treated geriatric COVID-19-infected patients in-hospital < 30 days all-cause mortality was more frequent than in non-ASA-treated COVID-19 patients. In ASA-treated COVID-19-infected geriatric patients, anticoagulant therapy with low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) significantly reduced need of ICU care, but tended to increase in-hospital < 30 days all-cause mortality. Conclusions: Prior treatment with a low dose of ASA in COVID-19-infected geriatric patients increased frequency of in-hospital < 30 days all-cause mortality, although it seemed to not increase PE frequency despite D-dimer levels upon admission being higher than in non-ASA users. In ASA-treated geriatric COVID-19-infected patients, addition of LMWH therapy reduced frequency of ICU care, but tended to increase in-hospital < 30 days all-cause mortality.
Data Availability Statement: This study was carried out using an anonymized database provided by Madrid Hospitals Group. Data are from COVID-19-infected patients admitted in their hospital net that they made kindly available to some Spanish researchers within the program: COVID-19 data saves lives in Spain.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
References
Alamdari, Afaghi, Rahimi, Tarki, Tavana et al., Mortality Risk Factors among Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients in a Major Referral Center in Iran, Tohoku J. Exp. Med, doi:10.1620/tjem.252.73
Assinger, Platelets and infection-An emerging role of platelets in viral infection, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2014.00649
Becattini, Agnelli, Schenone, Eichinger, Bucherini et al., Aspirin for preventing the recurrence of venous thromboembolism, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1114238
Berenguer, Ryan, Rodríguez-Baño, Jarrín, Carratalà et al., for the COVID-19@Spain Study. Characteristics and predictors of death among 4035 consecutively hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in Spain, Clin. Microbiol. Infect, doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2020.07.024
Brighton, Eikelboom, Mann, Mister, Gallus et al., Low-dose aspirin for preventing recurrent venous thromboembolism, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1210384
Canoglu, Saylan, Therapeutic dosing of low-molecular-weight heparin may decrease mortality in patients with severe COVID-19 infection, Ann. Saudi Med, doi:10.5144/0256-4947.2020.462
Chen, Zhou, Dong, Qu, Gong et al., Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A descriptive study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7
Choi, Kim, Kang, The Potential Role of Dyslipidemia in COVID-19 Severity: An Umbrella Review of Systematic Reviews, J. Lipid Atheroscler, doi:10.12997/jla.2020.9.3.435
Clausen, Sandoval, Spliid, Pihl, Perrett et al., SARS-CoV-2 Infection Depends on Cellular Heparan Sulfate and ACE2, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.09.033
Eikelboom, Hirsh, Weitz, Johnston, Yi et al., Aspirin-resistant thromboxane biosynthesis and the risk of myocardial infarction, stroke, or cardiovascular death in patients at high risk for cardiovascular events, Circulation, doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000013777.21160.07
Glatthaar-Saalmüller, Mair, Saalmüller, Antiviral activity of aspirin against RNA viruses of the respiratory tract-an in vitro study, Influenza Other Respir. Viruses, doi:10.1111/irv.12421
Goligher, Bradbury, Mcverry, Lawler, Berger et al., Therapeutic Anticoagulation with Heparin in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19, N. Engl. J. Med
Gratz, Wiegele, Maleczek, Herkner, Schöchl et al., Risk of Clinically Relevant Venous Thromboembolism in Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Front. Med, doi:10.3389/fmed.2021.647917
Kulkarni, Jenner, Wilkinson, COVID-19 and hypertension, J. Renin. Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst, doi:10.1177/1470320320927851
Lawler, Goligher, Berger, Neal, Mcverry et al., Therapeutic Anticoagulation with Heparin in Noncritically Ill Patients with COVID-19, N. Engl. J. Med
Leentjens, Van Haaps, Wessels, Schutgens, Middeldorp, COVID-19-associated coagulopathy and antithrombotic agents-lessons after 1 year, Lancet Haematol, doi:10.1016/S2352-3026(21)00105-8
Malas, Naazie, Elsayed, Mathlouthi, Marmor et al., Thromboembolism risk of COVID-19 is high and associated with a higher risk of mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis, EClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100639
Martha, Pranata, Lim, Wibowo, Akbar, Active prescription of low-dose aspirin during or prior to hospitalization and mortality in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis of adjusted effect estimates, Int. J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2021.05.016
Nikolich-Zugich, Knox, Rios, Natt, Bhattacharya et al., SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 in older adults: What we may expect regarding pathogenesis, immune responses, and outcomes, Geroscience, doi:10.1007/s11357-020-00186-0
O'brien, Duncan, Kirsh, Allen, King et al., Prevention of pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis with low dose aspirin: Pulmonary Embolism Prevention (PEP) trial, Lancet
Pavoni, Gianesello, Pazzi, Stera, Meconi et al., Venous thromboembolism and bleeding in critically ill COVID-19 patients treated with higher than standard low molecular weight heparin doses and aspirin: A call to action, Thromb. Res, doi:10.1016/j.thromres.2020.09.013
Pranata, Huang, Lim, Wahjoepramono, July, Impact of cerebrovascular and cardiovascular diseases on mortality and severity of COVID-19-systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression, J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis, doi:10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2020.104949
Qin, Dong, Zhang, Hu, Chen et al., Low molecular weight heparin and 28-day mortality among patients with coronavirus disease 2019: A cohort study in the early epidemic era, Thromb. Res, doi:10.1016/j.thromres.2020.11.020
Richardson, Hirsch, Narasimhan, Crawford, Mcginn et al., the Northwell COVID-19 Research Consortium. Presenting Characteristics, Comorbidities, and Outcomes Among 5700 Patients Hospitalized with COVID-19 in the New York City Area, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.6775
Sattar, Mcinnes, Mcmurray, Obesity Is a Risk Factor for Severe COVID-19 Infection: Multiple Potential Mechanisms, Circulation, doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.047659
Signes-Costa, Núñez-Gil, Soriano, Arroyo-Espliguero, Eid et al., Prevalence and 30-Day Mortality in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19 and Prior Lung Diseases, Arch. Bronconeumol, doi:10.1016/j.arbres.2020.11.012
Simes, Becattini, Agnelli, Eikelboom, Kirby et al., INSPIRE Study Investigators (International Collaboration of Aspirin Trials for Recurrent Venous Thromboembolism). Aspirin for the prevention of recurrent venous thromboembolism: The INSPIRE collaboration, Circulation, doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.008828
Speir, Yu, Ferrans, Huang, Epstein, Aspirin attenuates cytomegalovirus infectivity and gene expression mediated by cyclooxygenase-2 in coronary artery smooth muscle cells, Circ. Res, doi:10.1161/01.RES.83.2.210
Tang, Bai, Chen, Gong, Li et al., Anticoagulant treatment is associated with decreased mortality in severe coronavirus disease 2019 patients with coagulopathy, J. Thromb. Haemost, doi:10.1111/jth.14817
Thachil, Tang, Gando, Falanga, Cattaneo et al., ISTH interim guidance on recognition and management of coagulopathy in COVID-19, J. Thromb. Haemost, doi:10.1111/jth.14810
Walz-Cicconi, Weller, Dose-related effect of acetylsalicylic acid on replication of varicella zoster virus in vitro, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.81.16.5223
Wijaya, Andhika, Huang, Purwiga, Budiman, The effects of aspirin on the outcome of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Clin. Epidemiol. Glob. Health, doi:10.1016/j.cegh.2021.100883
Yuan, Chen, Li, Chen, Wang et al., Mortality and pre-hospitalization use of low-dose aspirin in COVID-19 patients with coronary artery disease, J. Cell. Mol. Med, doi:10.1111/jcmm.16198
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/medicina58111649",
"ISSN": [
"1648-9144"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/medicina58111649",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Background and Objectives: Aspirin (ASA) is a commonly used antithrombotic drug that has been demonstrated to reduce venous thromboembolism. The aim was to analyze if geriatric COVID-19 patients undergoing a 100 mg/day Aspirin (ASA) treatment prior to hospitalization differ in hospital outcome compared to patients without previous ASA therapy. Materials and Methods: An observational retrospective study was carried out using an anonymized database including geriatric COVID-19 patients (March to April 2020) admitted to Madrid Hospitals Group. A group of COVID-19 patients were treated with low ASA (100 mg/day) prior to COVID-19 infection. Results: Geriatric ASA-treated patients were older (mean age over 70 years; n = 41), had higher frequency of hypertension and hyperlipidemia, and upon admission had higher D-dimer levels than non-ASA-treated patients (mean age over 73 years; n = 160). However, patients under ASA treatment did not show more frequent pulmonary thromboembolism (PE) than non-ASA-treated patients. ASA-treated geriatric COVID-19-infected patients in-hospital < 30 days all-cause mortality was more frequent than in non-ASA-treated COVID-19 patients. In ASA-treated COVID-19-infected geriatric patients, anticoagulant therapy with low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) significantly reduced need of ICU care, but tended to increase in-hospital < 30 days all-cause mortality. Conclusions: Prior treatment with a low dose of ASA in COVID-19-infected geriatric patients increased frequency of in-hospital < 30 days all-cause mortality, although it seemed to not increase PE frequency despite D-dimer levels upon admission being higher than in non-ASA users. In ASA-treated geriatric COVID-19-infected patients, addition of LMWH therapy reduced frequency of ICU care, but tended to increase in-hospital < 30 days all-cause mortality.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"medicina58111649"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zekri-Nechar",
"given": "Khaoula",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barberán",
"given": "José",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zamorano-León",
"given": "José J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Durbán",
"given": "María",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Andrés-Castillo",
"given": "Alcira",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9869-9240",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Navarro-Cuellar",
"given": "Carlos",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "López-Farré",
"given": "Antonio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5551-5181",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "López-de-Andrés",
"given": "Ana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jiménez-García",
"given": "Rodrigo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Martínez-Martínez",
"given": "Carlos H.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Medicina",
"container-title-short": "Medicina",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-16T07:27:34Z",
"timestamp": 1668583654000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-16T09:38:26Z",
"timestamp": 1668591506000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-17T06:16:42Z",
"timestamp": 1668665802322
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "11",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
15
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "11",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-15T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1668470400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1648-9144/58/11/1649/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1649",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
15
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
15
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2021.647917",
"article-title": "Risk of Clinically Relevant Venous Thromboembolism in Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "647917",
"journal-title": "Front. Med.",
"key": "ref_1",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7",
"article-title": "Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A descriptive study",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "507",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref_2",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.6775",
"article-title": "Presenting Characteristics, Comorbidities, and Outcomes Among 5700 Patients Hospitalized with COVID-19 in the New York City Area",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2052",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11357-020-00186-0",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19 in older adults: What we may expect regarding pathogenesis, immune responses, and outcomes",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "505",
"journal-title": "Geroscience",
"key": "ref_4",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.047659",
"article-title": "Obesity Is a Risk Factor for Severe COVID-19 Infection: Multiple Potential Mechanisms",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4",
"journal-title": "Circulation",
"key": "ref_5",
"volume": "142",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(00)02110-3",
"article-title": "Prevention of pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis with low dose aspirin: Pulmonary Embolism Prevention (PEP) trial",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1295",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "355",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa1114238",
"article-title": "WARFASA Investigators. Aspirin for preventing the recurrence of venous thromboembolism",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1959",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "366",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa1210384",
"article-title": "Low-dose aspirin for preventing recurrent venous thromboembolism",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1979",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "367",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2020.104949",
"article-title": "Impact of cerebrovascular and cardiovascular diseases on mortality and severity of COVID-19-systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "104949",
"journal-title": "J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis.",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.thromres.2020.09.013",
"article-title": "Venous thromboembolism and bleeding in critically ill COVID-19 patients treated with higher than standard low molecular weight heparin doses and aspirin: A call to action",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "313",
"journal-title": "Thromb. Res.",
"key": "ref_10",
"volume": "196",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1620/tjem.252.73",
"article-title": "Mortality Risk Factors among Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients in a Major Referral Center in Iran",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "73",
"journal-title": "Tohoku J. Exp. Med.",
"key": "ref_11",
"volume": "252",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jth.14810",
"article-title": "ISTH interim guidance on recognition and management of coagulopathy in COVID-19",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1023",
"journal-title": "J. Thromb. Haemost.",
"key": "ref_12",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.arbres.2020.11.012",
"article-title": "Prevalence and 30-Day Mortality in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19 and Prior Lung Diseases",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "13",
"journal-title": "Arch. Bronconeumol.",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "ref_14",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization (2022, July 10). Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Outbreak. Regional Office for Europe. Available online: https://www.euro.who.int/en/health-topics/health-emergencies/coronavirus-covid-19/statements/statement-older-people-are-at-highest-risk-from-covid-19,-but-all-must-act-to-prevent-community-spread."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmi.2020.07.024",
"article-title": "Characteristics and predictors of death among 4035 consecutively hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in Spain",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1525",
"journal-title": "Clin. Microbiol. Infect.",
"key": "ref_15",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Platelets and infection—An emerging role of platelets in viral infection",
"first-page": "649",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_16",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"article-title": "Antiviral activity of aspirin against RNA viruses of the respiratory tract-an in vitro study",
"first-page": "85",
"journal-title": "Influenza Other Respir. Viruses",
"key": "ref_17",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.81.16.5223",
"article-title": "Dose-related effect of acetylsalicylic acid on replication of varicella zoster virus in vitro",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5223",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "ref_18",
"volume": "81",
"year": "1984"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/01.RES.83.2.210",
"article-title": "Aspirin attenuates cytomegalovirus infectivity and gene expression mediated by cyclooxygenase-2 in coronary artery smooth muscle cells",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "210",
"journal-title": "Circ. Res.",
"key": "ref_19",
"volume": "83",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.05.016",
"article-title": "Active prescription of low-dose aspirin during or prior to hospitalization and mortality in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis of adjusted effect estimates",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "108",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cegh.2021.100883",
"article-title": "The effects of aspirin on the outcome of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100883",
"journal-title": "Clin. Epidemiol. Glob. Health",
"key": "ref_21",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1470320320927851",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_22",
"unstructured": "Kulkarni, S., Jenner, B.L., and Wilkinson, I. (2020). COVID-19 and hypertension. J. Renin. Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst., 21."
},
{
"DOI": "10.12997/jla.2020.9.3.435",
"article-title": "The Potential Role of Dyslipidemia in COVID-19 Severity: An Umbrella Review of Systematic Reviews",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "435",
"journal-title": "J. Lipid Atheroscler.",
"key": "ref_23",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jcmm.16198",
"article-title": "Mortality and pre-hospitalization use of low-dose aspirin in COVID-19 patients with coronary artery disease",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1263",
"journal-title": "J. Cell. Mol. Med.",
"key": "ref_24",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Thromboembolism risk of COVID-19 is high and associated with a higher risk of mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"first-page": "100639",
"journal-title": "EClinicalMedicine",
"key": "ref_25",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.008828",
"article-title": "INSPIRE Study Investigators (International Collaboration of Aspirin Trials for Recurrent Venous Thromboembolism). Aspirin for the prevention of recurrent venous thromboembolism: The INSPIRE collaboration",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1062",
"journal-title": "Circulation",
"key": "ref_26",
"volume": "130",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.09.033",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Infection Depends on Cellular Heparan Sulfate and ACE2",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1043",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_27",
"volume": "183",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Low molecular weight heparin and 28-day mortality among patients with coronavirus disease 2019: A cohort study in the early epidemic era",
"first-page": "19",
"journal-title": "Thromb. Res.",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "198",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jth.14817",
"article-title": "Anticoagulant treatment is associated with decreased mortality in severe coronavirus disease 2019 patients with coagulopathy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1094",
"journal-title": "J. Thromb. Haemost.",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2352-3026(21)00105-8",
"article-title": "COVID-19-associated coagulopathy and antithrombotic agents-lessons after 1 year",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e524",
"journal-title": "Lancet Haematol.",
"key": "ref_30",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5144/0256-4947.2020.462",
"article-title": "Therapeutic dosing of low-molecular-weight heparin may decrease mortality in patients with severe COVID-19 infection",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "462",
"journal-title": "Ann. Saudi Med.",
"key": "ref_31",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2103417",
"article-title": "Therapeutic Anticoagulation with Heparin in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "777",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_32",
"volume": "385",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2105911",
"article-title": "Therapeutic Anticoagulation with Heparin in Noncritically Ill Patients with COVID-19",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "790",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_33",
"volume": "385",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/01.CIR.0000013777.21160.07",
"article-title": "Aspirin-resistant thromboxane biosynthesis and the risk of myocardial infarction, stroke, or cardiovascular death in patients at high risk for cardiovascular events",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1650",
"journal-title": "Circulation",
"key": "ref_34",
"volume": "105",
"year": "2002"
}
],
"reference-count": 34,
"references-count": 34,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1648-9144/58/11/1649"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Analysis of Prior Aspirin Treatment on in-Hospital Outcome of Geriatric COVID-19 Infected Patients",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "58"
}