Molecular Basis of High-Blood-Pressure-Enhanced and High-Fever-Temperature-Weakened Receptor-Binding Domain/Peptidase Domain Binding: A Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study
et al., International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms26073250, Mar 2025
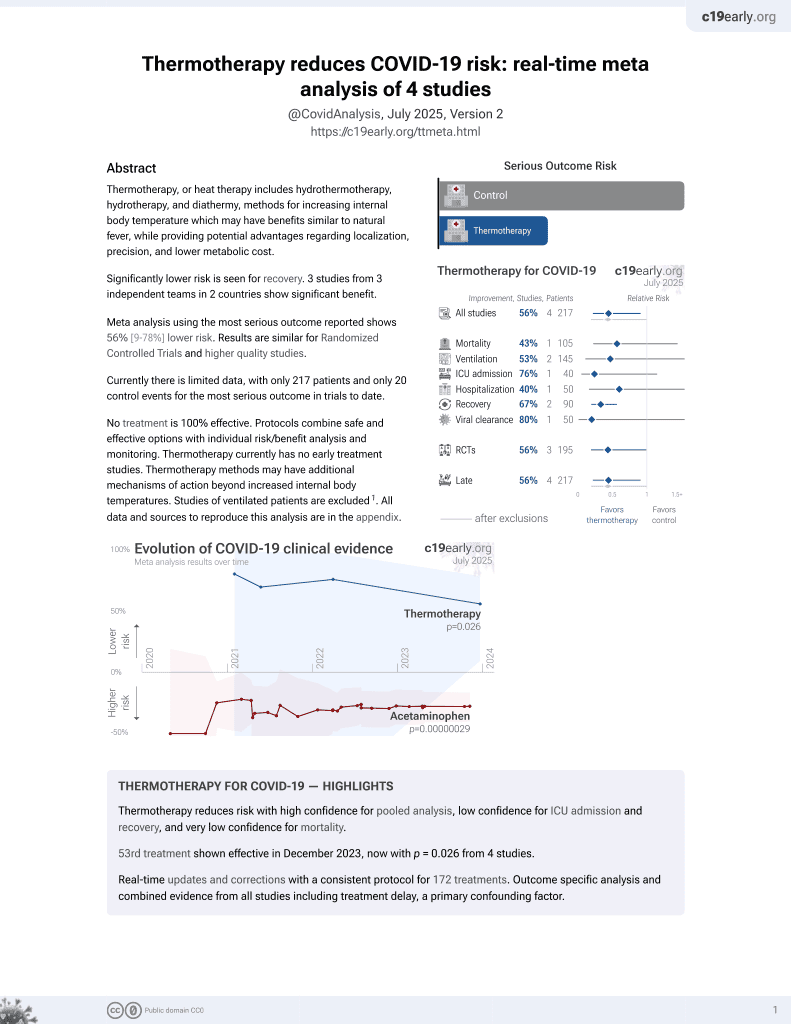
54th treatment shown to reduce risk in
December 2023, now with p = 0.026 from 4 studies.
Lower risk for recovery.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
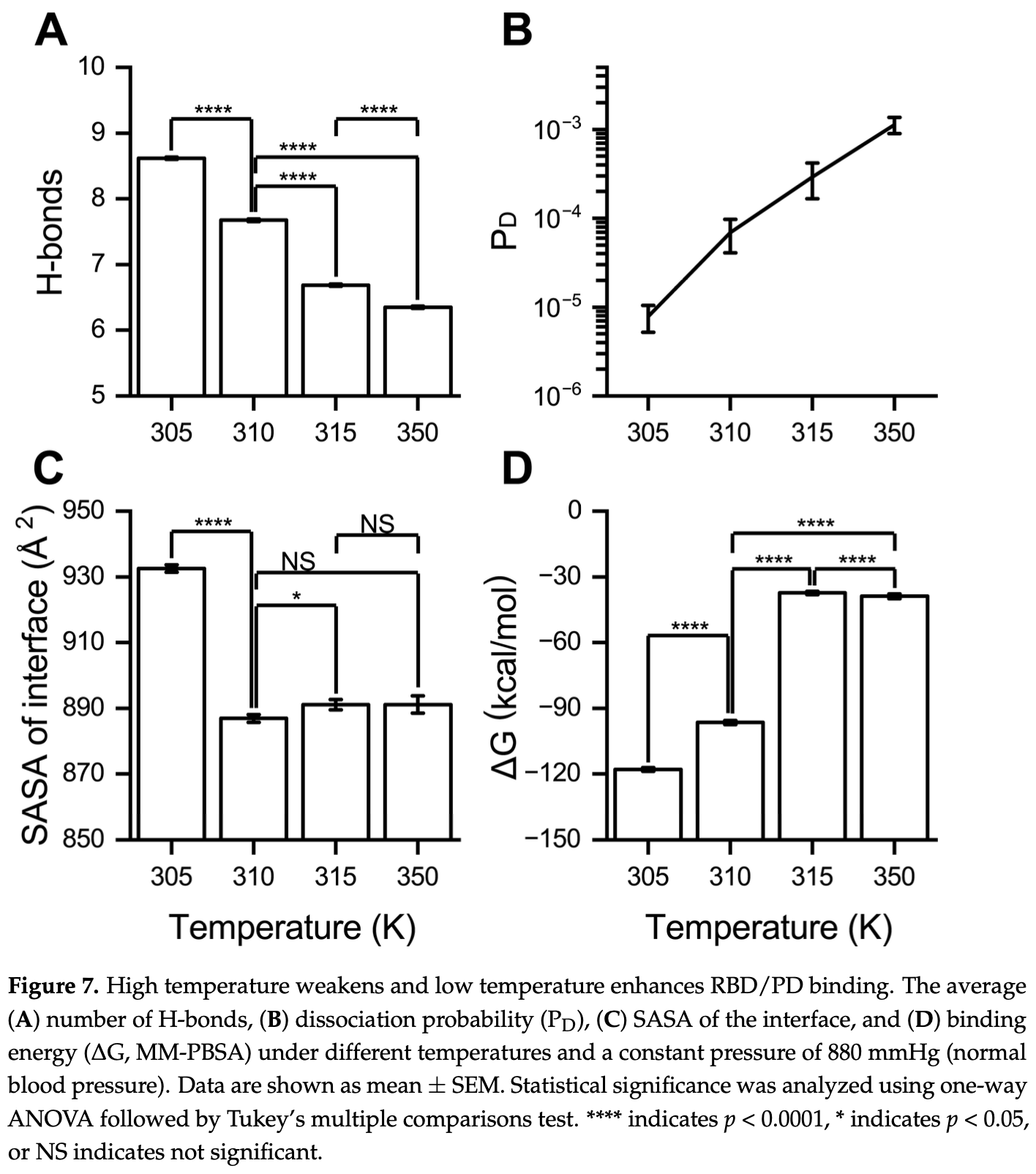
Molecular dynamics simulation study demonstrating that high blood pressure (940 mmHg) enhances and high fever temperature (above 315 K) weakens the binding between SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain (RBD) and the ACE2 receptor peptidase domain (PD). This computational study provides a potential molecular mechanism explaining why hypertension is associated with increased COVID-19 severity and why fever may be protective in early infection. Authors found that high pressure causes curving of the α1-helix in the PD and closer proximity of the β3β4-hairpin to the RBM motif, creating a more compact binding interface. Conversely, high temperatures straighten the α1-helix and move the β3β4-hairpin away from the RBM motif, weakening binding. Low temperature (305 K) enhanced binding similar to high pressure.
3 preclinical studies support the efficacy of thermotherapy for COVID-19:
1.
Xie et al., Molecular Basis of High-Blood-Pressure-Enhanced and High-Fever-Temperature-Weakened Receptor-Binding Domain/Peptidase Domain Binding: A Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms26073250.
Xie et al., 31 Mar 2025, peer-reviewed, 5 authors.
Contact: wujianhua@scut.edu.cn (corresponding author), xiexubin@163.com, zhangyu970724@163.com, yfang@scut.edu.cn, liqh@scut.edu.cn.
In silico studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Molecular Basis of High-Blood-Pressure-Enhanced and High-Fever-Temperature-Weakened Receptor-Binding Domain/Peptidase Domain Binding: A Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study
International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms26073250
The entry and infection of the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 virus (SARS-CoV-2) involve recognition and binding of the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of the virus surface spike protein to the peptidase domain (PD) of the host cellular Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme-2 (ACE2) receptor. ACE2 is also involved in normal blood pressure control. An association between hypertension and COVID-19 severity and fatality is evident, but how hypertension predisposes patients diagnosed with COVID-19 to unfavorable outcomes remains unclear. High temperature early during SARS-CoV-2 infection impairs binding to human cells and retards viral progression. Low body temperature can prelude poor prognosis. In this study, all-atom molecular dynamics simulations were performed to examine the effects of high pressure and temperature on RBD/PD binding. A high blood pressure of 940 mmHg enhanced RBD/PD binding. A high temperature above 315 K significantly weakened RBD/PD binding, while a low temperature of 305 K enhanced binding. The curvature of the PD α1-helix and proximity of the PD β3β4-hairpin tip to the RBM motif affected the compactness of the binding interface and, hence, binding affinity. These findings provide novel insights into the underlying mechanisms by which hypertension predisposes patients to unfavorable outcomes in COVID-19 and how an initial high temperature retards viral progression.
Supplementary Materials: The following supporting information can be downloaded at https: //www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ijms26073250/s1 . Author Contributions: J.W., Y.F. and X.X. designed this research; X.X. performed the molecular dynamics simulations and data analysis; Y.Z. helped with the literature research; X.X., Q.L., J.W. and Y.F. wrote this manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
References
Ashraf, Abokor, Edwards, Waigi, Royfman et al., SARS-CoV-2, ACE2 expression, and systemic organ invasion, Physiol. Genom, doi:10.1152/physiolgenomics.00087.2020
Bai, Tan, Xu, Liu, Huang et al., MolAICal: A soft tool for 3D drug design of protein targets by artificial intelligence and classical algorithm, Brief. Bioinform, doi:10.1093/bib/bbaa161
Benlarbi, Ding, Belanger, Tauzin, Poujol et al., Temperaturedependent Spike-ACE2 interaction of Omicron subvariants is associated with viral transmission, mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.00907-24
Benton, Wrobel, Roustan, Borg, Xu et al., The effect of the D614G substitution on the structure of the spike glycoprotein of SARS-CoV-2, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.2022586118
Boutouyrie, Chowienczyk, Humphrey, Mitchell, Arterial Stiffness and Cardiovascular Risk in Hypertension, Circ. Res, doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.318061
Cao, Tu, Cheng, Yu, Liu et al., Clinical features and short-term outcomes of 102 patients with coronavirus disease 2019 in Wuhan, China, Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa243
Carabelli, Peacock, Thorne, Harvey, Hughes et al., SARS-CoV-2 variant biology: Immune escape, transmission and fitness, Nat. Rev. Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41579-022-00841-7
Crook, Raza, Nowell, Young, Edison, Long covid-mechanisms, risk factors, and management, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.n1648
D'elia, Giaquinto, Zarrella, Rendina, Iaccarino et al., Hypertension and mortality in SARS-COV-2 infection: A meta-analysis of observational studies after 2 years of pandemic, Eur. J. Intern. Med, doi:10.1016/j.ejim.2022.11.018
Dessie, Zewotir, Mortality-related risk factors of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 42 studies and 423,117 patients, BMC Infect. Dis, doi:10.1186/s12879-021-06536-3
Drewry, Hotchkiss, Kulstad, Response to "Body temperature correlates with mortality in COVID-19 patients, Crit. Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-020-03186-w
Díaz-Salinas, Li, Ejemel, Yurkovetskiy, Luban et al., Conformational dynamics and allosteric modulation of the SARS-CoV-2 spike, Elife, doi:10.7554/eLife.75433
Fatteh, Sutherland, Santos, Zeidan, Gastesi et al., Association of hypothermia with increased mortality rate in SARS-CoV-2 infection, Int. J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2021.05.031
Forest-Nault, Koyuturk, Gaudreault, Pelletier, Abbé et al., Impact of the temperature on the interactions between common variants of the SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain and the human ACE2, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-022-15215-5
Gheblawi, Wang, Viveiros, Nguyen, Zhong et al., Angiotensinconverting enzyme 2: SARS-CoV-2 receptor and regulator of the renin-angiotensin system, Circ. Res, doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317015
Glykos, Software news and updates carma: A molecular dynamics analysis program, J. Comput. Chem
Gong, Ding, Benlarbi, Chen, Vezina et al., Temperature influences the interaction between SARS-CoV-2 spike from Omicron subvariants and human ACE2, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v14102178
Hamming, Timens, Bulthuis, Lely, Navis et al., Tissue distribution of ACE2 protein, the functional receptor for SARS coronavirus. A first step in understanding SARS pathogenesis, J. Pathol, doi:10.1002/path.1570
Han, Su, Zhang, Bai, Zheng et al., Molecular insights into receptor binding of recent emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants, Nat. Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-021-26401-w
Hoffmann, Kleine-Weber, Schroeder, Kruger, Herrler et al., SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052
Hu, Zhang, Fei, Zhang, Yao et al., Mechanical activation of spike fosters SARS-CoV-2 viral infection, Cell Res, doi:10.1038/s41422-021-00558-x
Huang, Rauscher, Nawrocki, Ran, Feig et al., CHARMM36m: An improved force field for folded and intrinsically disordered proteins, Nat. Methods, doi:10.1038/nmeth.4067
Huang, Wang, Liu, Liu, Cao et al., COVID-19 patients with hypertension have more severe disease: A multicenter retrospective observational study, Hypertens. Res, doi:10.1038/s41440-020-0485-2
Humphrey, Dalke, Schulten, Vmd, Visual molecular dynamics, J. Mol. Graph, doi:10.1016/0263-7855(96)00018-5
Jian, Wang, Yisimayi, Song, Xu et al., Evolving antibody response to SARS-CoV-2 antigenic shift from XBB to JN.1, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-024-08315-x
Jo, Kim, Iyer, Im, CHARMM-GUI: A web-based graphical user interface for charmm, J. Comput. Chem, doi:10.1002/jcc.20945
Kabia, Li, Jin, Tan, Liu et al., The effects of hypertension on the prognosis of coronavirus disease 2019: A systematic review and meta-analysis on the interactions with age and antihypertensive treatment, J. Hypertens, doi:10.1097/HJH.0000000000003266
Kim, Kim, Choi, Stan, Fever temperatures modulate intraprotein dynamics and enhance the binding affinity between monoclonal antibodies and the spike protein from SARS-CoV-2, Comp. Struct. Biotechnol. J, doi:10.1016/j.csbj.2022.10.045
Kompaniyets, Pennington, Goodman, Rosenblum, Belay et al., Underlying medical conditions and severe illness among 540,667 adults hospitalized with COVID-19, Prev. Chronic Dis, doi:10.5888/pcd18.210123
Lan, Ge, Yu, Shan, Zhou et al., Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain bound to the ACE2 receptor, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2180-5
Li, Li, Sarkar, Zhang, Witham et al., A comprehensive suite for DelPhi software and associated resources, BMC Biophys, doi:10.1186/2046-1682-5-9
Li, Moore, Vasilieva, Sui, Wong et al., Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is a functional receptor for the SARS coronavirus, Nature, doi:10.1038/nature02145
Li, Shi, Gu, Xu, Shu et al., Spike structures, receptor binding, and immune escape of recently circulating SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.2.86, doi:10.1016/j.str.2024.06.012
Li, Xu, Niu, Xie, Zhao et al., Key mechanistic features of the trade-off between antibody escape and host cell binding in the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant spike proteins, EMBO J, doi:10.1038/s44318-024-00062-z
Liu, Liu, Plante, Plante, Xie et al., The N501Y spike substitution enhances SARS-CoV-2 infection and transmission, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-021-04245-0
Liu, Zhou, Dijokaite-Guraliuc, Supasa, Duyvesteyn et al., A structure-function analysis shows SARS-CoV-2 BA.2.86 balances antibody escape and ACE2 affinity, Cell Rep. Med, doi:10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101553
Ncd-Risc, Worldwide trends in hypertension prevalence and progress in treatment and control from 1990 to 2019: A pooled analysis of 1201 population-representative studies with 104 million participants, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01330-1
Oudit, Wang, Viveiros, Kellner, Penninger, Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2-at the heart of the COVID-19 pandemic, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2023.01.039
Park, Lee, Qi, Kern, Lee et al., CHARMM-GUI Glycan Modeler for modeling and simulation of carbohydrates and glycoconjugates, Glycobiology, doi:10.1093/glycob/cwz003
Pettersen, Goddard, Huang, Couch, Greenblatt et al., UCSF Chimera-a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis, J. Comput. Chem, doi:10.1002/jcc.20084
Phillips, Braun, Wang, Gumbart, Tajkhorshid et al., Scalable molecular dynamics with NAMD, J. Comput. Chem, doi:10.1002/jcc.20289
Phillips, Hardy, Maia, Stone, Ribeiro et al., Scalable molecular dynamics on CPU and GPU architectures with NAMD, J. Chem. Phys, doi:10.1063/5.0014475
Prevost, Richard, Gasser, Ding, Fage et al., Impact of temperature on the affinity of SARS-CoV-2 Spike glycoprotein for host ACE2, J. Biol. Chem, doi:10.1016/j.jbc.2021.101151
Rath, Kumar, Investigation of the Effect of Temperature on the Structure of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein by Molecular Dynamics Simulations, Front. Mol. Biosci, doi:10.3389/fmolb.2020.583523
Ravichandran, Grimm, Krüger, Kopp, Infanger et al., SARS-CoV-2 and hypertension, Physiol. Rep, doi:10.14814/phy2.14800
Savoia, Volpe, Kreutz, Hypertension, a moving target in COVID-19: Current views and perspectives, Circ. Res, doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.318054
Schiffrin, How Structure, Mechanics, and Function of the Vasculature Contribute to Blood Pressure Elevation in Hypertension, Can. J. Cardiol, doi:10.1016/j.cjca.2020.02.003
Steiner, Kratzel, Barut, Lang, Aguiar Moreira et al., SARS-CoV-2 biology and host interactions, Nat. Rev. Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41579-023-01003-z
Tadic, Cuspidi, Grassi, Mancia, COVID-19 and arterial hypertension: Hypothesis or evidence?, J. Clin. Hypertens, doi:10.1111/jch.13925
Tharakan, Nomoto, Miyashita, Ishikawa, Body temperature correlates with mortality in COVID-19 patients, Crit. Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-020-03045-8
Tian, Tong, Sun, Shi, Zheng et al., N501Y mutation of spike protein in SARS-CoV-2 strengthens its binding to receptor ACE2, Elife, doi:10.7554/eLife.69091
Tofan, Lenghel, De Camargo, Stan, Fever as an evolutionary agent to select immune complexes interfaces, Immunogenetics, doi:10.1007/s00251-022-01263-8
Towler, Staker, Prasad, Menon, Tang et al., ACE2 X-Ray Structures Reveal a Large Hinge-bending Motion Important for Inhibitor Binding and Catalysis, J. Biol. Chem, doi:10.1074/jbc.M311191200
Turonova, Sikora, Schurmann, Hagen, Welsch et al., In situ structural analysis of SARS-CoV-2 spike reveals flexibility mediated by three hinges, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abd5223
Uriu, Ito, Kosugi, Tanaka, Mugita et al., Transmissibility, infectivity, and immune evasion of the SARS-CoV-2 BA.2.86 variant, Lancet Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00575-3
Vidal-Petiot, Thresholds for hypertension definition, treatment initiation, and treatment targets: Recent guidelines at a glance, Circulation, doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.121.055177
Walls, Park, Tortorici, Wall, Mcguire et al., Structure, function, and antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.058
Wang, Gheblawi, Oudit, Angiotensin converting enzyme 2 a double-edged sword, Circulation, doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.047049
Wang, Horby, Hayden, Gao, A novel coronavirus outbreak of global health concern, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30185-9
Wang, Sun, Wang, Wang, Liu et al., End-point binding free energy calculation with MM/PBSA and MM/GBSA: Strategies and applications in drug design, Chem. Rev, doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00055
Wu, Zhao, Yu, Chen, Wang et al., A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2008-3
Yan, Matuja, Pain, Mcnairy, Etyang et al., Emerging viral infections, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease in Sub-Saharan Africa: A narrative review, Hypertension, doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.121.17949
Yan, Zhang, Li, Xia, Guo et al., Structural basis for the recognition of SARS-CoV-2 by full-length human ACE2, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abb2762
Yang, Yu, Jian, Song, Yisimayi et al., Antigenicity and infectivity characterisation of SARS-CoV-2 BA.2.86, Lancet Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00573-X
Yang, Yu, Xu, Jian, Song et al., Fast evolution of SARS-CoV-2 BA.2.86 to JN.1 under heavy immune pressure, Lancet Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00744-2
Yao, Wu, Fang, Moderate constraint facilitates association and force-dependent dissociation of HA-CD44 complex, Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms24032243
Yu, Lei, Li, Wang, Liu et al., Clinical characteristics, associated factors, and predicting COVID-19 mortality risk: A retrospective study in Wuhan, China, Am. J. Prev. Med, doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2020.05.002
Zhang, Dong, Cao, Yuan, Yang et al., Clinical characteristics of 140 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Wuhan, China, Allergy, doi:10.1111/all.14238
Zhang, Lin, Fang, Wu, Prediction of catch-slip bond transition of Kindlin2/β3 integrin via steered molecular dynamics simulation, J. Chem. Inf. Model, doi:10.1021/acs.jcim.0c00837
Zhang, Wu, Sun, Xue, Shao et al., Association of hypertension with the severity and fatality of SARS-CoV-2 infection: A meta-analysis, Epidemiol. Infect, doi:10.1017/S095026882000117X
Zhou, Yang, Ou, Zhang, Zhang et al., Temperature dependence of the SARS-CoV-2 affinity to human ACE2 determines COVID-19 progression and clinical outcome, Comp. Struct. Biotechnol. J, doi:10.1016/j.csbj.2020.12.005
Zhou, Yu, Du, Fan, Liu et al., Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3
Zhu, Zhang, Wang, Li, Yang et al., A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2001017
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms26073250",
"ISSN": [
"1422-0067"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073250",
"abstract": "<jats:p>The entry and infection of the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 virus (SARS-CoV-2) involve recognition and binding of the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of the virus surface spike protein to the peptidase domain (PD) of the host cellular Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme-2 (ACE2) receptor. ACE2 is also involved in normal blood pressure control. An association between hypertension and COVID-19 severity and fatality is evident, but how hypertension predisposes patients diagnosed with COVID-19 to unfavorable outcomes remains unclear. High temperature early during SARS-CoV-2 infection impairs binding to human cells and retards viral progression. Low body temperature can prelude poor prognosis. In this study, all-atom molecular dynamics simulations were performed to examine the effects of high pressure and temperature on RBD/PD binding. A high blood pressure of 940 mmHg enhanced RBD/PD binding. A high temperature above 315 K significantly weakened RBD/PD binding, while a low temperature of 305 K enhanced binding. The curvature of the PD α1-helix and proximity of the PD β3β4-hairpin tip to the RBM motif affected the compactness of the binding interface and, hence, binding affinity. These findings provide novel insights into the underlying mechanisms by which hypertension predisposes patients to unfavorable outcomes in COVID-19 and how an initial high temperature retards viral progression.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"ijms26073250"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5180-5050",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Institute of Biomechanics, School of Biology and Biological Engineering, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou Higher Education Mega Centre, Panyu District, Guangzhou 510006, China"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Xie",
"given": "Xubin",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Institute of Biomechanics, School of Biology and Biological Engineering, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou Higher Education Mega Centre, Panyu District, Guangzhou 510006, China"
}
],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Yu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2490-8502",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Institute of Biomechanics, School of Biology and Biological Engineering, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou Higher Education Mega Centre, Panyu District, Guangzhou 510006, China"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Fang",
"given": "Ying",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Institute of Biomechanics, School of Biology and Biological Engineering, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou Higher Education Mega Centre, Panyu District, Guangzhou 510006, China"
}
],
"family": "Wu",
"given": "Jianhua",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6133-3114",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Institute of Biomechanics, School of Biology and Biological Engineering, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou Higher Education Mega Centre, Panyu District, Guangzhou 510006, China"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Li",
"given": "Quhuan",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "International Journal of Molecular Sciences",
"container-title-short": "IJMS",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2025-04-01T11:00:45Z",
"timestamp": 1743505245000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2025-04-03T09:34:05Z",
"timestamp": 1743672845000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100001809",
"award": [
"12172137",
"31870928",
"32271360",
"12072117"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "crossref",
"id": "10.13039/501100001809",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "National Natural Science Foundation of China"
},
{
"award": [
"2021A1515010040",
"2023A1515010829"
],
"name": "Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2025-04-03T10:10:26Z",
"timestamp": 1743675026700,
"version": "3.40.3"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "7",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3,
31
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "7",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2025-03-31T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1743379200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/26/7/3250/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "3250",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3,
31
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3,
31
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001017",
"article-title": "A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019",
"author": "Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "727",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_1",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2008-3",
"article-title": "A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "265",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_2",
"volume": "579",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30185-9",
"article-title": "A novel coronavirus outbreak of global health concern",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "470",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.058",
"article-title": "Structure, function, and antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein",
"author": "Walls",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "281",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_4",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor",
"author": "Hoffmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "271",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_5",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 variant biology: Immune escape, transmission and fitness",
"author": "Carabelli",
"first-page": "162",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Microbiol.",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-023-01003-z",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 biology and host interactions",
"author": "Steiner",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "206",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Microbiol.",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2180-5",
"article-title": "Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain bound to the ACE2 receptor",
"author": "Lan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "215",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "581",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abb2762",
"article-title": "Structural basis for the recognition of SARS-CoV-2 by full-length human ACE2",
"author": "Yan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1444",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "367",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317015",
"article-title": "Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: SARS-CoV-2 receptor and regulator of the renin-angiotensin system",
"author": "Gheblawi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1456",
"journal-title": "Circ. Res.",
"key": "ref_10",
"volume": "126",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.047049",
"article-title": "Angiotensin converting enzyme 2 a double-edged sword",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "426",
"journal-title": "Circulation",
"key": "ref_11",
"volume": "142",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature02145",
"article-title": "Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is a functional receptor for the SARS coronavirus",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "450",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_12",
"volume": "426",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/path.1570",
"article-title": "Tissue distribution of ACE2 protein, the functional receptor for SARS coronavirus. A first step in understanding SARS pathogenesis",
"author": "Hamming",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "631",
"journal-title": "J. Pathol.",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "203",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2023.01.039",
"article-title": "Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2-at the heart of the COVID-19 pandemic",
"author": "Oudit",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "906",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "186",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01330-1",
"article-title": "Worldwide trends in hypertension prevalence and progress in treatment and control from 1990 to 2019: A pooled analysis of 1201 population-representative studies with 104 million participants",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "957",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref_15",
"volume": "398",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.14814/phy2.14800",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 and hypertension",
"author": "Ravichandran",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e14800",
"journal-title": "Physiol. Rep.",
"key": "ref_16",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jch.13925",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and arterial hypertension: Hypothesis or evidence?",
"author": "Tadic",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1120",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Hypertens.",
"key": "ref_17",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"article-title": "Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1054",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "ref_18",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5888/pcd18.210123",
"article-title": "Underlying medical conditions and severe illness among 540,667 adults hospitalized with COVID-19, March 2020-March 2021",
"author": "Kompaniyets",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "E66",
"journal-title": "Prev. Chronic Dis.",
"key": "ref_19",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41440-020-0485-2",
"article-title": "COVID-19 patients with hypertension have more severe disease: A multicenter retrospective observational study",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "824",
"journal-title": "Hypertens. Res.",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S095026882000117X",
"article-title": "Association of hypertension with the severity and fatality of SARS-CoV-2 infection: A meta-analysis",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e106",
"journal-title": "Epidemiol. Infect.",
"key": "ref_21",
"volume": "148",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.318054",
"article-title": "Hypertension, a moving target in COVID-19: Current views and perspectives",
"author": "Savoia",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1062",
"journal-title": "Circ. Res.",
"key": "ref_22",
"volume": "128",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-021-06536-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_23",
"unstructured": "Dessie, Z.G., and Zewotir, T. (2021). Mortality-related risk factors of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 42 studies and 423,117 patients. BMC Infect. Dis., 21."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.121.17949",
"article-title": "Emerging viral infections, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease in Sub-Saharan Africa: A narrative review",
"author": "Yan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "898",
"journal-title": "Hypertension",
"key": "ref_24",
"volume": "79",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/HJH.0000000000003266",
"article-title": "The effects of hypertension on the prognosis of coronavirus disease 2019: A systematic review and meta-analysis on the interactions with age and antihypertensive treatment",
"author": "Kabia",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2323",
"journal-title": "J. Hypertens.",
"key": "ref_25",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejim.2022.11.018",
"article-title": "Hypertension and mortality in SARS-COV-2 infection: A meta-analysis of observational studies after 2 years of pandemic",
"author": "Giaquinto",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "28",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Intern. Med.",
"key": "ref_26",
"volume": "108",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cjca.2020.02.003",
"article-title": "How Structure, Mechanics, and Function of the Vasculature Contribute to Blood Pressure Elevation in Hypertension",
"author": "Schiffrin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "648",
"journal-title": "Can. J. Cardiol.",
"key": "ref_27",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.318061",
"article-title": "Arterial Stiffness and Cardiovascular Risk in Hypertension",
"author": "Boutouyrie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "864",
"journal-title": "Circ. Res.",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "128",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41422-021-00558-x",
"article-title": "Mechanical activation of spike fosters SARS-CoV-2 viral infection",
"author": "Hu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1047",
"journal-title": "Cell Res.",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/all.14238",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of 140 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1730",
"journal-title": "Allergy",
"key": "ref_30",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.amepre.2020.05.002",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics, associated factors, and predicting COVID-19 mortality risk: A retrospective study in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Yu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "168",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Prev. Med.",
"key": "ref_31",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa243",
"article-title": "Clinical features and short-term outcomes of 102 patients with coronavirus disease 2019 in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Cao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "748",
"journal-title": "Clin. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_32",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.05.031",
"article-title": "Association of hypothermia with increased mortality rate in SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Fatteh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "167",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_33",
"volume": "108",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00251-022-01263-8",
"article-title": "Fever as an evolutionary agent to select immune complexes interfaces",
"author": "Tofan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "465",
"journal-title": "Immunogenetics",
"key": "ref_34",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-03045-8",
"article-title": "Body temperature correlates with mortality in COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Tharakan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "298",
"journal-title": "Crit. Care",
"key": "ref_35",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.csbj.2022.10.045",
"article-title": "Fever temperatures modulate intraprotein dynamics and enhance the binding affinity between monoclonal antibodies and the spike protein from SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Kim",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5962",
"journal-title": "Comp. Struct. Biotechnol. J.",
"key": "ref_36",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.csbj.2020.12.005",
"article-title": "Temperature dependence of the SARS-CoV-2 affinity to human ACE2 determines COVID-19 progression and clinical outcome",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "161",
"journal-title": "Comp. Struct. Biotechnol. J.",
"key": "ref_37",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-03186-w",
"article-title": "Response to “Body temperature correlates with mortality in COVID-19 patients”",
"author": "Drewry",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "460",
"journal-title": "Crit. Care",
"key": "ref_38",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mbio.00907-24",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_39",
"unstructured": "Benlarbi, M., Ding, S., Belanger, E., Tauzin, A., Poujol, R., Medjahed, H., El, F.O., Bo, Y., Bourassa, C., and Hussin, J. (2024). Temperature-dependent Spike-ACE2 interaction of Omicron subvariants is associated with viral transmission. mBio, 15."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jbc.2021.101151",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_40",
"unstructured": "Prevost, J., Richard, J., Gasser, R., Ding, S., Fage, C., Anand, S.P., Adam, D., Gupta, V.N., Tauzin, A., and Benlarbi, M. (2021). Impact of temperature on the affinity of SARS-CoV-2 Spike glycoprotein for host ACE2. J. Biol. Chem., 297."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v14102178",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_41",
"unstructured": "Gong, S.Y., Ding, S., Benlarbi, M., Chen, Y., Vezina, D., Marchitto, L., Beaudoin-Bussieres, G., Goyette, G., Bourassa, C., and Bo, Y. (2022). Temperature influences the interaction between SARS-CoV-2 spike from Omicron subvariants and human ACE2. Viruses, 14."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-022-15215-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_42",
"unstructured": "Forest-Nault, C., Koyuturk, I., Gaudreault, J., Pelletier, A., L Abbé, D., Cass, B., Bisson, L., Burlacu, A., Delafosse, L., and Stuible, M. (2022). Impact of the temperature on the interactions between common variants of the SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain and the human ACE2. Sci. Rep., 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jcim.0c00837",
"article-title": "Prediction of catch-slip bond transition of Kindlin2/β3 integrin via steered molecular dynamics simulation",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5132",
"journal-title": "J. Chem. Inf. Model.",
"key": "ref_43",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms24032243",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_44",
"unstructured": "Yao, Z., Wu, J., and Fang, Y. (2023). Moderate constraint facilitates association and force-dependent dissociation of HA-CD44 complex. Int. J. Mol. Sci., 24."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.n1648",
"article-title": "Long covid-mechanisms, risk factors, and management",
"author": "Crook",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "n1648",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "ref_45",
"volume": "374",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/physiolgenomics.00087.2020",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2, ACE2 expression, and systemic organ invasion",
"author": "Ashraf",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "51",
"journal-title": "Physiol. Genom.",
"key": "ref_46",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M311191200",
"article-title": "ACE2 X-Ray Structures Reveal a Large Hinge-bending Motion Important for Inhibitor Binding and Catalysis",
"author": "Towler",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "17996",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "ref_47",
"volume": "279",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s44318-024-00062-z",
"article-title": "Key mechanistic features of the trade-off between antibody escape and host cell binding in the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant spike proteins",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1484",
"journal-title": "EMBO J.",
"key": "ref_48",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7554/eLife.69091",
"article-title": "N501Y mutation of spike protein in SARS-CoV-2 strengthens its binding to receptor ACE2",
"author": "Tian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e69091",
"journal-title": "Elife",
"key": "ref_49",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-04245-0",
"article-title": "The N501Y spike substitution enhances SARS-CoV-2 infection and transmission",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "294",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_50",
"volume": "602",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-26401-w",
"article-title": "Molecular insights into receptor binding of recent emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants",
"author": "Han",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6103",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "ref_51",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.str.2024.06.012",
"article-title": "Spike structures, receptor binding, and immune escape of recently circulating SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.2.86, JN.1, EG.5, EG.5.1, and HV.1 sub-variants",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1055",
"journal-title": "Structure",
"key": "ref_52",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00573-X",
"article-title": "Antigenicity and infectivity characterisation of SARS-CoV-2 BA.2.86",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e457",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_53",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00575-3",
"article-title": "Transmissibility, infectivity, and immune evasion of the SARS-CoV-2 BA.2.86 variant",
"author": "Uriu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e460",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_54",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00744-2",
"article-title": "Fast evolution of SARS-CoV-2 BA.2.86 to JN.1 under heavy immune pressure",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e70",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_55",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101553",
"article-title": "A structure-function analysis shows SARS-CoV-2 BA.2.86 balances antibody escape and ACE2 affinity",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "101553",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep. Med.",
"key": "ref_56",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-024-08315-x",
"article-title": "Evolving antibody response to SARS-CoV-2 antigenic shift from XBB to JN.1",
"author": "Jian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "921",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_57",
"volume": "637",
"year": "2025"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmolb.2020.583523",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_58",
"unstructured": "Rath, S.L., and Kumar, K. (2020). Investigation of the Effect of Temperature on the Structure of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein by Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Front. Mol. Biosci., 7."
},
{
"DOI": "10.7554/eLife.75433",
"article-title": "Conformational dynamics and allosteric modulation of the SARS-CoV-2 spike",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e75433",
"journal-title": "Elife",
"key": "ref_59",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abd5223",
"article-title": "In situ structural analysis of SARS-CoV-2 spike reveals flexibility mediated by three hinges",
"author": "Turonova",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "203",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "ref_60",
"volume": "370",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2022586118",
"article-title": "The effect of the D614G substitution on the structure of the spike glycoprotein of SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Benton",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e2022586118",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "ref_61",
"volume": "118",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcc.20945",
"article-title": "CHARMM-GUI: A web-based graphical user interface for charmm",
"author": "Jo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1859",
"journal-title": "J. Comput. Chem.",
"key": "ref_62",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/glycob/cwz003",
"article-title": "CHARMM-GUI Glycan Modeler for modeling and simulation of carbohydrates and glycoconjugates",
"author": "Park",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "320",
"journal-title": "Glycobiology",
"key": "ref_63",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0263-7855(96)00018-5",
"article-title": "VMD: Visual molecular dynamics",
"author": "Humphrey",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "33",
"journal-title": "J. Mol. Graph.",
"key": "ref_64",
"volume": "14",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcc.20289",
"article-title": "Scalable molecular dynamics with NAMD",
"author": "Phillips",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1781",
"journal-title": "J. Comput. Chem.",
"key": "ref_65",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1063/5.0014475",
"article-title": "Scalable molecular dynamics on CPU and GPU architectures with NAMD",
"author": "Phillips",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "44130",
"journal-title": "J. Chem. Phys.",
"key": "ref_66",
"volume": "153",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nmeth.4067",
"article-title": "CHARMM36m: An improved force field for folded and intrinsically disordered proteins",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "71",
"journal-title": "Nat. Methods",
"key": "ref_67",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.121.055177",
"article-title": "Thresholds for hypertension definition, treatment initiation, and treatment targets: Recent guidelines at a glance",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "805",
"journal-title": "Circulation",
"key": "ref_68",
"volume": "146",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcc.20084",
"article-title": "UCSF Chimera-a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis",
"author": "Pettersen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1605",
"journal-title": "J. Comput. Chem.",
"key": "ref_69",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00055",
"article-title": "End-point binding free energy calculation with MM/PBSA and MM/GBSA: Strategies and applications in drug design",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "9478",
"journal-title": "Chem. Rev.",
"key": "ref_70",
"volume": "119",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/2046-1682-5-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_71",
"unstructured": "Li, L., Li, C., Sarkar, S., Zhang, J., Witham, S., Zhang, Z., Wang, L., Smith, N., Petukh, M., and Alexov, E. (2012). DelPhi: A comprehensive suite for DelPhi software and associated resources. BMC Biophys., 5."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/bib/bbaa161",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_72",
"unstructured": "Bai, Q., Tan, S., Xu, T., Liu, H., Huang, J., and Yao, X. (2021). MolAICal: A soft tool for 3D drug design of protein targets by artificial intelligence and classical algorithm. Brief. Bioinform., 22."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcc.20482",
"article-title": "Software news and updates carma: A molecular dynamics analysis program",
"author": "Glykos",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1765",
"journal-title": "J. Comput. Chem.",
"key": "ref_73",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2006"
}
],
"reference-count": 73,
"references-count": 73,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/26/7/3250"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Molecular Basis of High-Blood-Pressure-Enhanced and High-Fever-Temperature-Weakened Receptor-Binding Domain/Peptidase Domain Binding: A Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "26"
}