Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Oxidant Activity of Ultra-Short Wave Diathermy on LPS-Induced Rat Lung Injury
et al., Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine, doi:10.1007/s10517-022-05407-4, Feb 2022
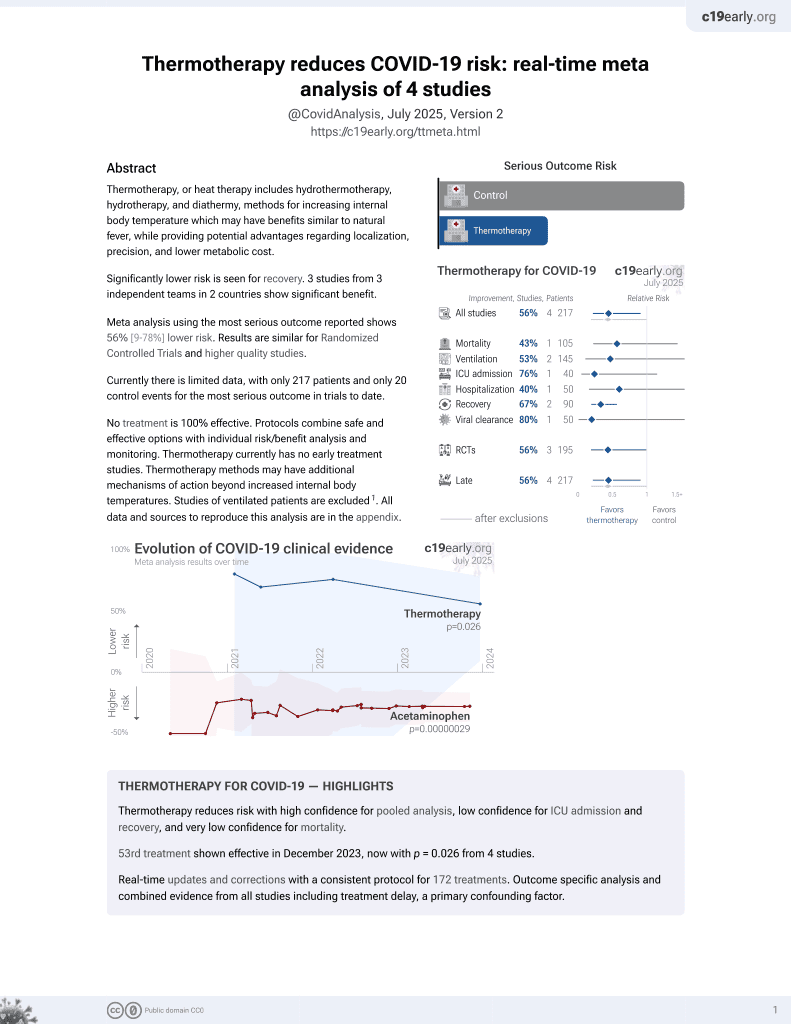
54th treatment shown to reduce risk in
December 2023, now with p = 0.026 from 4 studies.
Lower risk for recovery.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
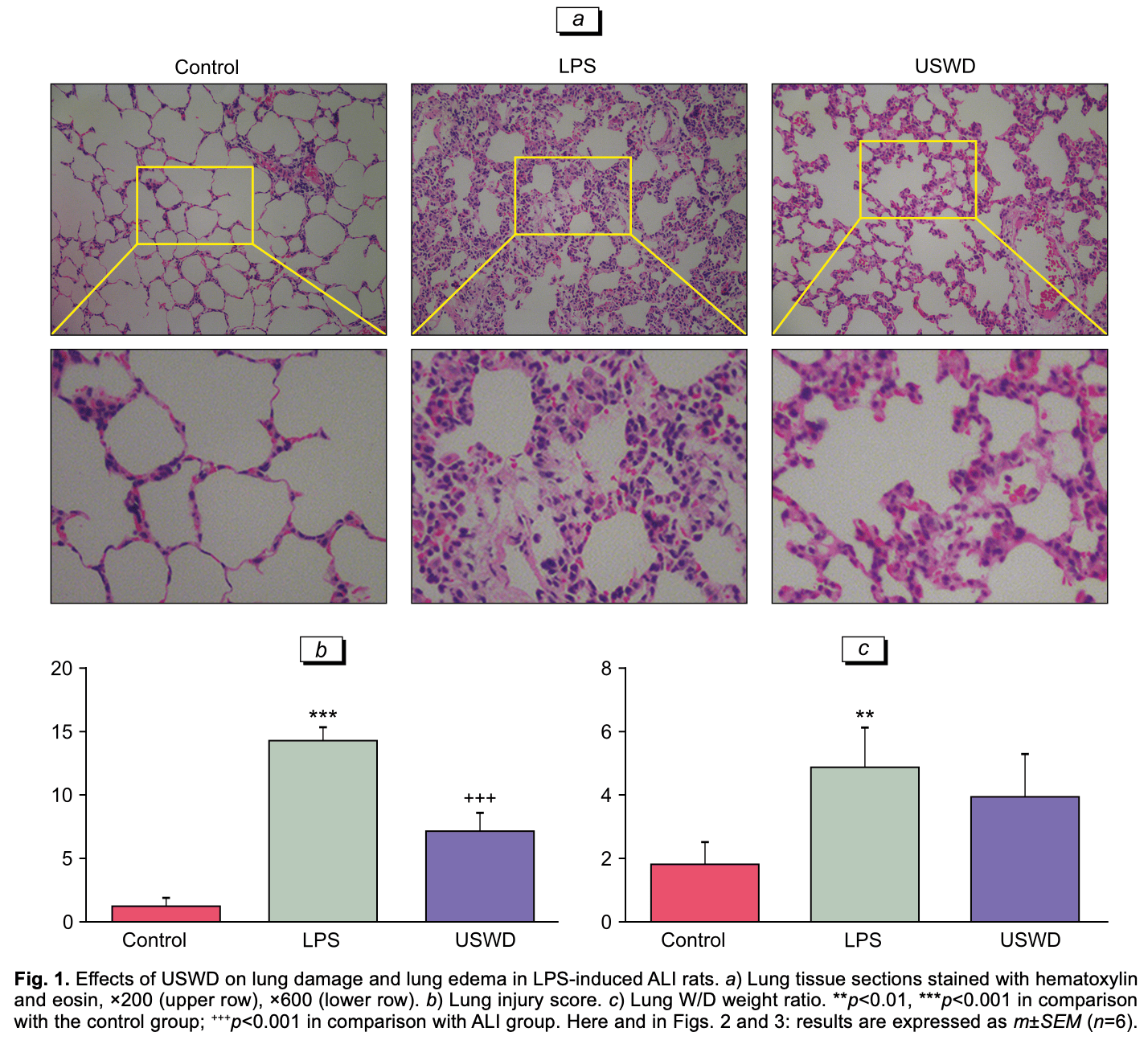
Animal study showing benefit of ultra-short wave diathermy (USWD) in reducing lung injury in a rat model of LPS-induced acute lung injury, a condition similar to COVID-19 acute respiratory distress. Authors found USWD decreased lung edema, injury, and inflammation in LPS-treated rats.
Authors did not measure temperature and it is unknown how much the observed benefit is due to the thermal effects of UWSD versus other potential mechanisms of action.
3 preclinical studies support the efficacy of thermotherapy for COVID-19:
1.
Xie et al., Molecular Basis of High-Blood-Pressure-Enhanced and High-Fever-Temperature-Weakened Receptor-Binding Domain/Peptidase Domain Binding: A Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms26073250.
Wu et al., 17 Feb 2022, peer-reviewed, 11 authors.
Contact: wangtong60621@163.com (corresponding author).
Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Oxidant Activity of Ultra-Short Wave Diathermy on LPS-Induced Rat Lung Injury
Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine, doi:10.1007/s10517-022-05407-4
We studied the lung-protective effect and mechanisms of the anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of ultra-short-wave diathermy (USWD) in a rat model of LPS-induced acute lung injury. Histological examination of the lung tissues was performed and the levels of oxidative stress-related factors and inflammatory cytokines were measured. It was shown that the lung injury score, the lung wet-to-dry weight ratio (W/D), oxidative stress-related factors malondialdehyde and acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 4 (ACSL4), and inflammatory cytokines were increased after LPS administration, while USWD treatment reduced these parameters. In addition, superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase 4 were decreased in rats with LPS-induced acute lung injury, while USWD therapy up-regulated the expression of these enzymes. Thus, USWD could antagonize lung injury by inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammatory response in rats with acute lung injury. USWD can be a promising adjunctive treatment to counter oxidative stress and inflammation and a potential therapeutic candidate for the treatment of patients with this pathology.
References
Dong, Yuan, Accelerated inflammation and oxidative stress induced by LPS in acute lung injury: Ιnhibition by ST1926, Int. J. Mol. Med, doi:10.3892/ijmm.2018.3574
Go, Ferroptosis: Role of lipid peroxidation, iron and ferritinophagy, Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj, doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2017.05.019
Imai, Matsuoka, Kumagai, Sakamoto, Koumura, Lipid Peroxidation-Dependent Cell Death Regulated by GPx4 and Ferroptosis, Curr. Top Microbiol. Immunol, doi:10.1007/82_2016_508
Kellner, Noonepalle, Lu, Srivastava, Zemskov et al., ROS Signaling in the Pathogenesis of Acute Lung Injury (ALI) and Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS), Adv. Exp. Med. Biol, doi:10.1007/978-3-319-63245-2_8
Lei, Wei, Song, Li, Zhang et al., Cordycepin inhibits LPS-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting inflammation and oxidative stress, Eur. J. Pharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2017.10.029
Li, Cao, Xiao, Shang, Tan et al., Inhibitor of apoptosis-stimulating protein of p53 inhibits ferroptosis and alleviates intestinal ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute lung injury, Cell. Death Differ, doi:10.1038/s41418-020-0528-x
Li, Li, Leng, Xiong, Xia, Ferroptosis Is Involved in Diabetes Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Through Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, DNA Cell. Biol, doi:10.1089/dna.2019.5097
Li, Wu, Wang, Ma, Zhai et al., Dapk1 improves inflammation, oxidative stress and autophagy in LPSinduced acute lung injury via p38MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway, Mol. Immunol, doi:10.1016/j.mo-limm.2020.01.014
Mowery, Terzian, Nelson, Acute lung injury, Curr. Probl. Surg, doi:10.1016/j.cp-surg.2020.100777
Shields, Gormley, Hare, Short-wave diathermy: current clinical and safety practices, Physiother. Res. Int, doi:10.1002/pri.259
Wang, Deng, Dong, Huang, Li et al., Eriodictyol ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by suppressing the inflammatory COX-2/NLRP3/NF-κB pathway in mice, J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol, doi:10.1002/jbt.22434
Wang, Feng, Zhao, Zhang, Zhang, Ultrashortwave radiation promotes the recovery of spinal cord injury by inhibiting inflammation via suppression of the MK2/TNF-α pathway, Int. J. Mol. Med, doi:10.3892/ijmm.2018.3786
Wang, Jia, Cao, Feng, Na et al., HUCMSCs transplantation combined with ultrashort wave therapy attenuates neuroinflammation in spinal cord injury through NUR77/NF-κB pathway, Life Sci, doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118958
Xu, Li, Cheng, Yang, Wang, Inhibition of ACSL4 attenuates ferroptotic damage after pulmonary ischemia-reperfusion, FASEB J, doi:10.1096/fj.202001758R
Yu, Jones, Dean, Laakso, Ultra-shortwave diathermy -a new purported treatment for management of patients with COVID-19, Physiother. Theory Pract, doi:10.1080/09593985.2020.1757264
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10517-022-05407-4",
"ISSN": [
"0007-4888",
"1573-8221"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10517-022-05407-4",
"alternative-id": [
"5407"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "7 April 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 2,
"value": "17 February 2022"
},
{
"label": "Free to read",
"name": "free",
"value": "This content has been made available to all."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wu",
"given": "Q.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Qu",
"given": "M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhong",
"given": "P.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zeng",
"given": "Y.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Q.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Ting",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "D.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhou",
"given": "J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Tong",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine",
"container-title-short": "Bull Exp Biol Med",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-17T10:14:57Z",
"timestamp": 1645092897000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-03-01T01:28:58Z",
"timestamp": 1646098138000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-20T10:55:43Z",
"timestamp": 1700477743510
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 1,
"issue": "4",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "4",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.springer.com/tdm",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1643673600000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.springer.com/tdm",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1643673600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s10517-022-05407-4.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10517-022-05407-4/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s10517-022-05407-4.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"page": "423-429",
"prefix": "10.1007",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
17
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.3892/ijmm.2018.3574",
"author": "Z Dong",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3405",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Mol. Med.",
"key": "5407_CR1",
"unstructured": "Dong Z, Yuan Y. Accelerated inflammation and oxidative stress induced by LPS in acute lung injury: Ιnhibition by ST1926. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018;41(6):3405-3421. doi: https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2018.3574",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/82_2016_508",
"author": "H Imai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "143",
"journal-title": "Curr. Top Microbiol. Immunol.",
"key": "5407_CR2",
"unstructured": "Imai H, Matsuoka M, Kumagai T, Sakamoto T, Koumura T. Lipid Peroxidation-Dependent Cell Death Regulated by GPx4 and Ferroptosis. Curr. Top Microbiol. Immunol. 2017;403:143- 170. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/82_2016_508",
"volume": "403",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-3-319-63245-2_8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "5407_CR3",
"unstructured": "Kellner M, Noonepalle S, Lu Q, Srivastava A, Zemskov E, Black S.M. ROS Signaling in the Pathogenesis of Acute Lung Injury (ALI) and Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS). Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017;967:105-137. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-63245-2_8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbagen.2017.05.019",
"author": "GO Latunde-Dada",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1893",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj.",
"key": "5407_CR4",
"unstructured": "Latunde-Dada GO. Ferroptosis: Role of lipid peroxidation, iron and ferritinophagy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2017;1861(8):1893-1900. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2017.05.019",
"volume": "1861",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejphar.2017.10.029",
"author": "J Lei",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "110",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Pharmacol.",
"key": "5407_CR5",
"unstructured": "Lei J, Wei Y, Song P, Li Y, Zhang T, Feng Q, Xu G. Cordycepin inhibits LPS-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting inflammation and oxidative stress. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018;818:110-114. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2017.10.029",
"volume": "818",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.molimm.2020.01.014",
"author": "T Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "13",
"journal-title": "Mol. Immunol.",
"key": "5407_CR6",
"unstructured": "Li T, Wu YN, Wang H, Ma JY, Zhai SS, Duan J. Dapk1 improves inflammation, oxidative stress and autophagy in LPSinduced acute lung injury via p38MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway. Mol. Immunol. 2020;120:13-22. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2020.01.014",
"volume": "120",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/dna.2019.5097",
"author": "W Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "210",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "DNA Cell. Biol.",
"key": "5407_CR7",
"unstructured": "Li W, Li W, Leng Y, Xiong Y, Xia Z. Ferroptosis Is Involved in Diabetes Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Through Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. DNA Cell. Biol. 2020;39(2):210- 225. doi: https://doi.org/10.1089/dna.2019.5097",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41418-020-0528-x",
"author": "Y Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2635",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Cell. Death Differ.",
"key": "5407_CR8",
"unstructured": "Li Y, Cao Y, Xiao J, Shang J, Tan Q, Ping F, Huang W, Wu F, Zhang H, Zhang X. Inhibitor of apoptosis-stimulating protein of p53 inhibits ferroptosis and alleviates intestinal ischemia/ reperfusion-induced acute lung injury. Cell. Death Differ. 2020;27(9):2635-2650. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-020-0528-x",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cpsurg.2020.100777",
"author": "NT Mowery",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "100777",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Curr. Probl. Surg.",
"key": "5407_CR9",
"unstructured": "Mowery NT, Terzian WTH, Nelson AC. Acute lung injury. Curr. Probl. Surg. 2020;57(5):100777. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpsurg.2020.100777",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/pri.259",
"author": "N Shields",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "191",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Physiother. Res. Int.",
"key": "5407_CR10",
"unstructured": "Shields N, Gormley J, O’Hare N. Short-wave diathermy: current clinical and safety practices. Physiother. Res. Int. 2002;7(4):191-202. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/pri.259",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3892/ijmm.2018.3786",
"author": "N Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1909",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Mol. Med.",
"key": "5407_CR11",
"unstructured": "Wang N, Feng Z, Zhao W, Zhang Z, Zhang L. Ultrashortwave radiation promotes the recovery of spinal cord injury by inhibiting inflammation via suppression of the MK2/TNF-α pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018;42(4):1909-1916. doi: https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2018.3786",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118958",
"author": "S Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "118958",
"journal-title": "Life Sci.",
"key": "5407_CR12",
"unstructured": "Wang S, Jia Y, Cao X, Feng S, Na L, Dong H, Gao J, Zhang L. HUCMSCs transplantation combined with ultrashort wave therapy attenuates neuroinflammation in spinal cord injury through NUR77/NF-κB pathway. Life Sci. 2021;267:118958. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118958",
"volume": "267",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jbt.22434",
"author": "X Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e22434",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol.",
"key": "5407_CR13",
"unstructured": "Wang X, Deng R, Dong J, Huang L, Li J, Zhang B. Eriodictyol ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by suppressing the inflammatory COX-2/NLRP3/NF-κB pathway in mice. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2020;34(3):e22434. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/jbt.22434",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1096/fj.202001758R",
"author": "Y Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "16262",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "FASEB J.",
"key": "5407_CR14",
"unstructured": "Xu Y, Li X, Cheng Y, Yang M, Wang R. Inhibition of ACSL4 attenuates ferroptotic damage after pulmonary ischemia-reperfusion. FASEB J. 2020;34(12):16262-16275. doi: https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.202001758R",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/09593985.2020.1757264",
"author": "HP Yu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "559",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Physiother. Theory Pract.",
"key": "5407_CR15",
"unstructured": "Yu HP, Jones AY, Dean E, Liisa Laakso E. Ultra-shortwave diathermy — a new purported treatment for management of patients with COVID-19. Physiother. Theory Pract. 2020;36(5):559-563. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/09593985.2020.1757264",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 15,
"references-count": 15,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s10517-022-05407-4"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Biochemistry, Genetics and Molecular Biology",
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Oxidant Activity of Ultra-Short Wave Diathermy on LPS-Induced Rat Lung Injury",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "172"
}