Real-world Effectiveness of Casirivimab and Imdevimab in Patients With COVID-19 in the Ambulatory Setting: An Analysis of Two Large US National Claims Databases
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.02.28.22270796, Feb 2022
19th treatment shown to reduce risk in
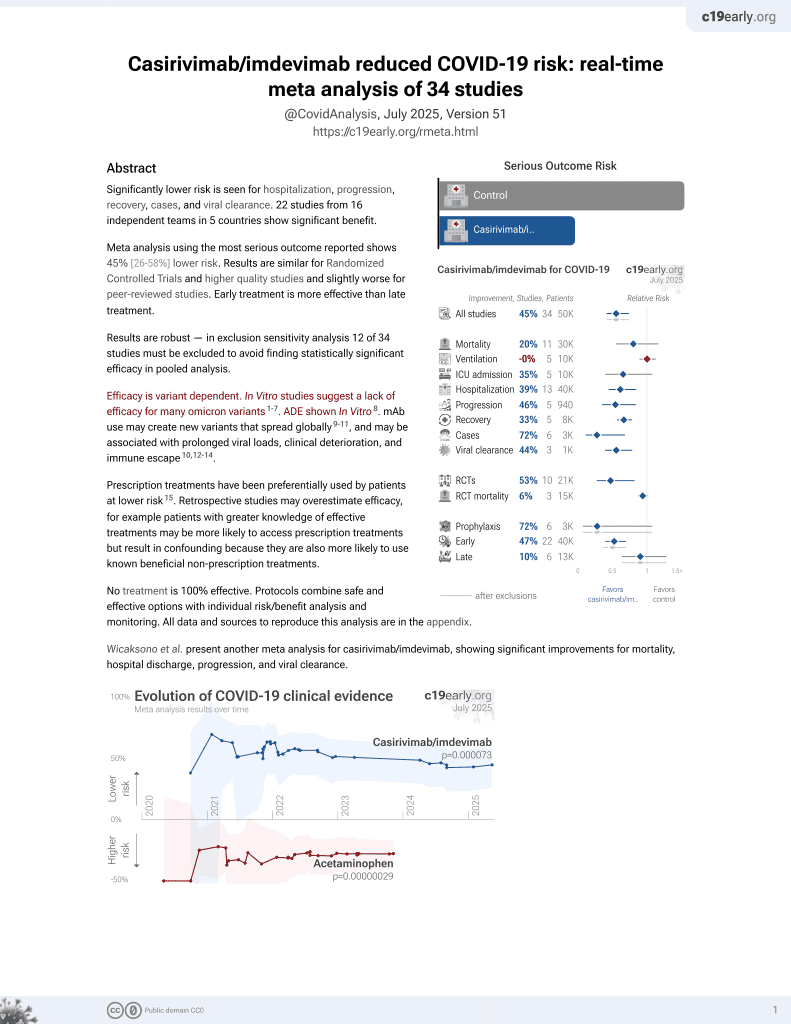
March 2021, now with p = 0.000095 from 34 studies, recognized in 52 countries.
Efficacy is variant dependent.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 4,396 casirivimab/imdevimab patients in the USA, showing lower combined mortality/hospitalization (CDM database) and lower hospitalization (PMTX+ database) with treatment.
Efficacy is variant dependent. In Vitro research suggests a lack of efficacy for many omicron variants1-7.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments8.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
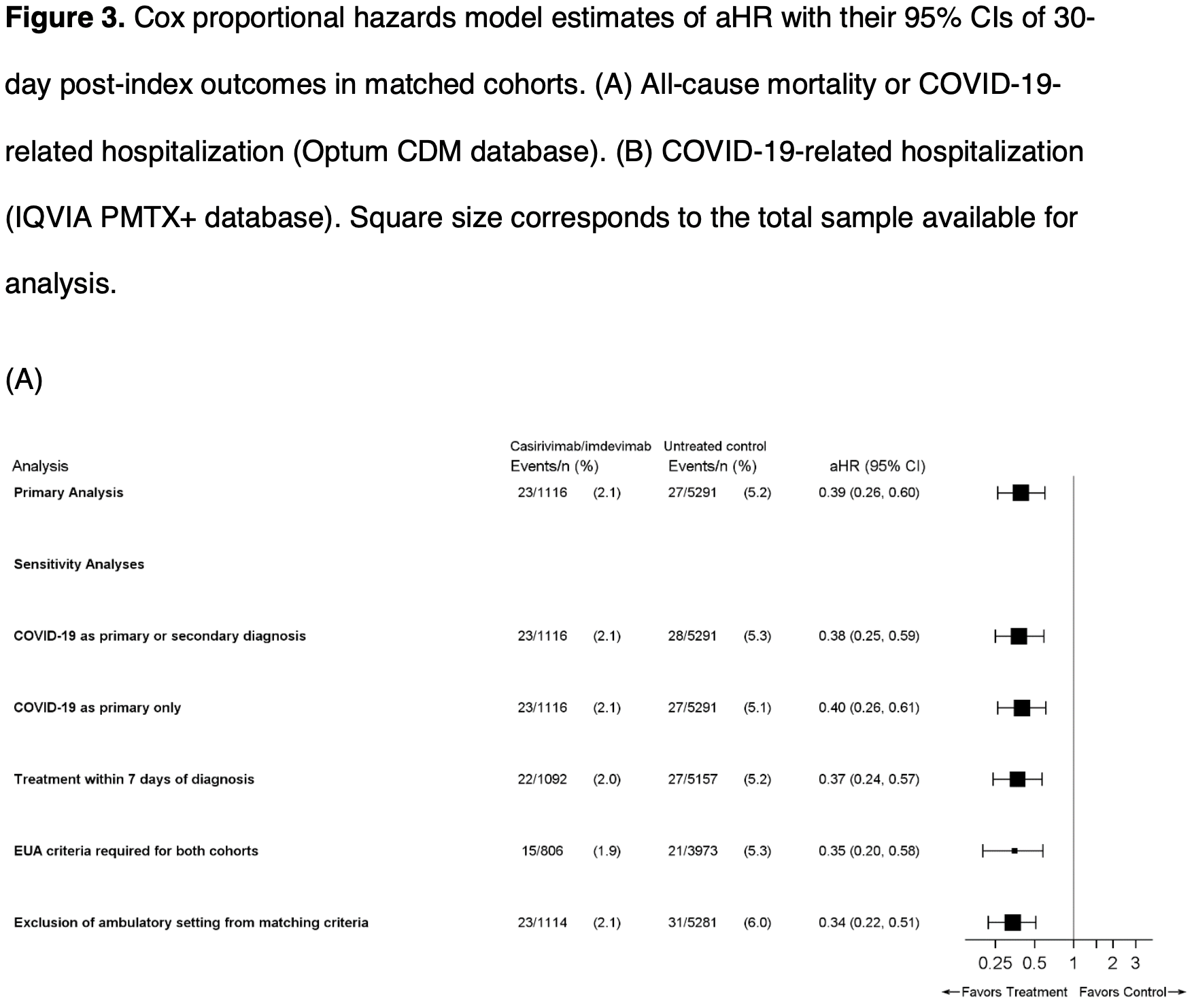
risk of death/hospitalization, 61.0% lower, HR 0.39, p < 0.001, treatment 23 of 1,116 (2.1%), control 27 of 5,291 (0.5%), Optum CDM, Cox proportional hazards.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 61.0% lower, HR 0.39, p < 0.001, treatment 59 of 3,280 (1.8%), control 75 of 16,284 (0.5%), IQVIA PMTX+, Cox proportional hazards.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Liu et al., Striking Antibody Evasion Manifested by the Omicron Variant of SARS-CoV-2, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.14.472719.
2.
Sheward et al., Variable loss of antibody potency against SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 (Omicron), bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.19.473354.
3.
VanBlargan et al., An infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 Omicron virus escapes neutralization by several therapeutic monoclonal antibodies, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.15.472828.
4.
Tatham et al., Lack of Ronapreve (REGN-CoV; casirivimab and imdevimab) virological efficacy against the SARS-CoV 2 Omicron variant (B.1.1.529) in K18-hACE2 mice, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.01.23.477397.
5.
Pochtovyi et al., In Vitro Efficacy of Antivirals and Monoclonal Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Lineages XBB.1.9.1, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5, XBB.1.16, XBB.2.4, BQ.1.1.45, CH.1.1, and CL.1, Vaccines, doi:10.3390/vaccines11101533.
6.
Haars et al., Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Sublineages and Spike Protein Mutations Conferring Resistance against Monoclonal Antibodies in a Swedish Cohort during 2022–2023, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms11102417.
Wei et al., 28 Feb 2022, retrospective, database analysis, USA, preprint, 8 authors, study period December 2020 - June 2021.
Real-world Effectiveness of Casirivimab and Imdevimab in Patients With COVID-19 in the Ambulatory Setting: An Analysis of Two Large US National Claims Databases
doi:10.1101/2022.02.28.22270796
Background: In a phase III clinical trial, casirivimab and imdevimab (CAS+IMD) reduced the composite endpoint of COVID-19-related hospitalizations or all-cause mortality in outpatients at risk of severe disease. This study assessed real-world effectiveness of CAS+IMD. Methods: Data from Optum ® Clinformatics ® Data Mart (CDM) and IQVIA Pharmetrics Plus (PMTX+) were used to identify patients diagnosed with COVID-19 in ambulatory settings between December 2020 and March 2021 (PMTX+) and June 2021 (CDM), and either treated with CAS+IMD or untreated but treatment-eligible under Emergency Use Authorization. CAS+IMD-treated patients were matched to untreated patients and followed up to 30 days for the outcome of all-cause mortality or COVID-19-related hospitalizations (CDM) and COVID-19-related hospitalizations (PMTX+). Kaplan-Meier estimators were used to calculate outcome risks; Cox proportional-hazard models estimated adjusted hazard ratios (aHR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI). Results: For CDM, 1116 CAS+IMD-treated patients were matched to 5294 untreated patients; for PMTX+, 3280 CAS+IMD-treated patients were matched to 16,284 untreated patients. The 30-day outcome risk was 2.1% and 5.3% in treated and untreated cohorts, respectively (CDM), and the 30-day risk of COVID-19-related hospitalization was 1.9% and 4.8%, respectively (PMTX+); translating to a 61% lower adjusted outcome risk (CDM aHR 0.39 (95% CI 0.26-0.60; PMTX+ aHR 0.39 (95% CI 0.30-0.51). The benefit of treatment was maintained across multiple subgroups of highrisk patients; earlier intervention was associated with improved outcomes. .
Conclusions: This real-world study further supports randomized clinical trial findings that treatment with CAS+IMD reduces the risk of hospitalization and mortality in patients infected with susceptible variants. .
A) Diagnosed with or tested positive for COVID-19 during the study period (n=566 755) Received CAS+IMD during the study period (n=1588)
References
Anderson, Smith, Edupuganti, Yan, Masi et al., Effect of Monoclonal Antibody Treatment on Clinical Outcomes in Ambulatory Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019, Open Forum Infect Dis
Bierle, Ganesh, Tulledge-Scheitel, Monoclonal Antibody Treatment of Breakthrough COVID-19 in Fully Vaccinated Individuals with High-Risk Comorbidities, J Infect Dis
Cavazzoni, Coronavirus (COVID-19) Update: FDA Limits Use of Certain Monoclonal Antibodies to Treat COVID-19 Due to the Omicron Variant
Charlson, Pompei, Ales, Mackenzie, A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation, J Chronic Dis
Chilimuri, Mantri, Gurjar, Implementation and outcomes of monoclonal antibody infusion for COVID-19 in an inner-city safety net hospital: A South-Bronx experience, J Natl Med Assoc
Close, Jones, Jentoft, Mcauley, Outcome Comparison of High-Risk Native American Patients Who Did or Did Not Receive Monoclonal Antibody Treatment for COVID-19, JAMA Netw Open
Cooper, Christensen, Salazar, Real-world Assessment of 2,879 COVID-19 Patients Treated with Monoclonal Antibody Therapy: A Propensity Score-Matched Cohort Study, Open Forum Infect Dis
Falcone, Tiseo, Valoriani, Efficacy of Bamlanivimab/Etesevimab and Casirivimab/Imdevimab in Preventing Progression to Severe COVID-19 and Role of Variants of Concern, Infect Dis Ther
Ganesh, Philpot, Bierle, Real-World Clinical Outcomes of Bamlanivimab and Casirivimab-Imdevimab among High-Risk Patients with Mild to Moderate Coronavirus Disease 2019, J Infect Dis
Hall, Wellner, Confidence bands for a survival curve from censored data, Biometrika
Kakinoki, Yamada, Tanino, Effectiveness of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Monoclonal Antibody Infusions in High-Risk Outpatients, Open Forum Infect Dis
Kaplan, Meier, Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations, J Am Stat Assoc
Linden, Samuels, Using balance statistics to determine the optimal number of controls in matching studies, J Eval Clin Pract
Mccreary, Bariola, Wadas, Association of subcutaneous or intravenous route of administration of casirivimab and imdevimab monoclonal antibodies with clinical outcomes in COVID-19, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.11.30.21266756
Planas, Saunders, Maes, Considerable escape of SARS-CoV-2 variant Omicron to antibody neutralization, bioRxiv
Razonable, Aloia, Anderson, A Framework for Outpatient Infusion of Antispike Monoclonal Antibodies to High-Risk Patients with Mild-to-Moderate Coronavirus Disease-19: The Mayo Clinic Model, Mayo Clin Proc
Razonable, Pawlowski, Horo, Casirivimab-Imdevimab treatment is associated with reduced rates of hospitalization among high-risk patients with mild to moderate coronavirus disease-19, EClinicalMedicine
Verderese, Stepanova, Lam, Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibody Treatment Reduces Hospitalization for Mild and Moderate COVID-19: A Real-World Experience, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciab579
Webb, Buckel, Vento, Real-world Effectiveness and Tolerability of Monoclonal Antibody Therapy for Ambulatory Patients With Early COVID-19, Open Forum Infect Dis
Weinreich, Sivapalasingam, Norton, REGEN-COV Antibody Combination and Outcomes in Outpatients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Wilhelm, Widera, Grikscheit, Reduced neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant by vaccine sera and monoclonal antibodies, medRxiv, doi:.org/10.1101/2021.12.07.21267432
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2022.02.28.22270796",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/2022.02.28.22270796",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:p><jats:bold>Background</jats:bold></jats:p><jats:p>In a phase III clinical trial, casirivimab and imdevimab (CAS+IMD) reduced the composite endpoint of COVID-19-related hospitalizations or all-cause mortality in outpatients at risk of severe disease. This study assessed real-world effectiveness of CAS+IMD.</jats:p><jats:p><jats:bold>Methods</jats:bold></jats:p><jats:p>Data from Optum<jats:sup>®</jats:sup> Clinformatics<jats:sup>®</jats:sup> Data Mart (CDM) and IQVIA Pharmetrics Plus (PMTX+) were used to identify patients diagnosed with COVID-19 in ambulatory settings between December 2020 and March 2021 (PMTX+) and June 2021 (CDM), and either treated with CAS+IMD or untreated but treatment-eligible under Emergency Use Authorization. CAS+IMD-treated patients were matched to untreated patients and followed up to 30 days for the outcome of all-cause mortality or COVID-19-related hospitalizations (CDM) and COVID-19-related hospitalizations (PMTX+). Kaplan-Meier estimators were used to calculate outcome risks; Cox proportional-hazard models estimated adjusted hazard ratios (aHR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI).</jats:p><jats:p><jats:bold>Results</jats:bold></jats:p><jats:p>For CDM, 1116 CAS+IMD-treated patients were matched to 5294 untreated patients; for PMTX+, 3280 CAS+IMD-treated patients were matched to 16,284 untreated patients. The 30-day outcome risk was 2.1% and 5.3% in treated and untreated cohorts, respectively (CDM), and the 30-day risk of COVID-19-related hospitalization was 1.9% and 4.8%, respectively (PMTX+); translating to a 61% lower adjusted outcome risk (CDM aHR 0.39 (95% CI 0.26–0.60; PMTX+ aHR 0.39 (95% CI 0.30–0.51). The benefit of treatment was maintained across multiple subgroups of high-risk patients; earlier intervention was associated with improved outcomes.</jats:p><jats:p><jats:bold>Conclusions</jats:bold></jats:p><jats:p>This real-world study further supports randomized clinical trial findings that treatment with CAS+IMD reduces the risk of hospitalization and mortality in patients infected with susceptible variants.</jats:p>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
28
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8766-7769",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Wei",
"given": "Wenhui",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Murdock",
"given": "Dana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jalbert",
"given": "Jessica J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mastey",
"given": "Vera",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sanchez",
"given": "Robert J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hirshberg",
"given": "Boaz",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Weinreich",
"given": "David M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hussein",
"given": "Mohamed",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-03-01T08:15:14Z",
"timestamp": 1646122514000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2022-03-02T21:40:24Z",
"timestamp": 1646257224000
},
"group-title": "Infectious Diseases (except HIV/AIDS)",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2022-03-04T02:11:35Z",
"timestamp": 1646359895326
},
"institution": [
{
"name": "medRxiv"
}
],
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
28
]
]
},
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://syndication.highwire.org/content/doi/10.1101/2022.02.28.22270796",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "246",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
28
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.1101",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
28
]
]
},
"publisher": "Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/nejmoa2108163",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022030213400654000_2022.02.28.22270796v1.1"
},
{
"key": "2022030213400654000_2022.02.28.22270796v1.2",
"unstructured": "U.S. Food & Drug Administration. Fact Sheet for Health Care Providers Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) of Casirivimab and Imdevimab. Revised December 2021. Available at: https://www.fda.gov/media/145611/download. Accessed January 21."
},
{
"key": "2022030213400654000_2022.02.28.22270796v1.3",
"unstructured": "Cavazzoni P. Coronavirus (COVID-19) Update: FDA Limits Use of Certain Monoclonal Antibodies to Treat COVID-19 Due to the Omicron Variant. Available at: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/coronavirus-covid-19-update-fda-limits-use-certain-monoclonal-antibodies-treat-covid-19-due-omicron. Accessed 02/01/2022."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofab512",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2022030213400654000_2022.02.28.22270796v1.4",
"unstructured": "Cooper MH , Christensen PA , Salazar E , et al. Real-world Assessment of 2,879 COVID-19 Patients Treated with Monoclonal Antibody Therapy: A Propensity Score-Matched Cohort Study. Open Forum Infect Dis 2021; 8(11): ofab512."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.10.19.21265222",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2022030213400654000_2022.02.28.22270796v1.5",
"unstructured": "Bierle DM , Ganesh R , Tulledge-Scheitel S , et al. Monoclonal Antibody Treatment of Breakthrough COVID-19 in Fully Vaccinated Individuals with High-Risk Comorbidities. J Infect Dis 2021: Nov 16. [online ahead of print] doi: 0.1093/infdis/jiab570."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiab377",
"article-title": "Real-World Clinical Outcomes of Bamlanivimab and Casirivimab-Imdevimab among High-Risk Patients with Mild to Moderate Coronavirus Disease 2019",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1278",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "J Infect Dis",
"key": "2022030213400654000_2022.02.28.22270796v1.6",
"volume": "224",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.03.010",
"article-title": "A Framework for Outpatient Infusion of Antispike Monoclonal Antibodies to High-Risk Patients with Mild-to-Moderate Coronavirus Disease-19: The Mayo Clinic Model",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1250",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Mayo Clin Proc",
"key": "2022030213400654000_2022.02.28.22270796v1.7",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciab579",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022030213400654000_2022.02.28.22270796v1.8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofab331",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2022030213400654000_2022.02.28.22270796v1.9",
"unstructured": "Webb BJ , Buckel W , Vento T , et al. Real-world Effectiveness and Tolerability of Monoclonal Antibody Therapy for Ambulatory Patients With Early COVID-19. Open Forum Infect Dis 2021; 8(7): ofab331."
},
{
"key": "2022030213400654000_2022.02.28.22270796v1.10",
"unstructured": "Chilimuri S , Mantri N , Gurjar H , et al. Implementation and outcomes of monoclonal antibody infusion for COVID-19 in an inner-city safety net hospital: A South-Bronx experience. J Natl Med Assoc 2021: Sep 11 [online ahead of print] doi: 0.1016/j.jnma.2021.08.036."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.25866",
"article-title": "Outcome Comparison of High-Risk Native American Patients Who Did or Did Not Receive Monoclonal Antibody Treatment for COVID-19",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e2125866",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "2022030213400654000_2022.02.28.22270796v1.11",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.10.10.21264589",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2022030213400654000_2022.02.28.22270796v1.12",
"unstructured": "Kakinoki Y , Yamada K , Tanino Y , et al. Impact of Antibody Cocktail Therapy Combined with Casirivimab and Imdevimab on Clinical Outcome for Covid-19 patients in A Real-Life Setting: A Single Institute Analysis. medRxiv 2021: 2021.10.10.21264589."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofab292",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2022030213400654000_2022.02.28.22270796v1.13",
"unstructured": "Piccicacco N , Zeitler K , Montero J , et al. Effectiveness of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Monoclonal Antibody Infusions in High-Risk Outpatients. Open Forum Infect Dis 2021; 8(7): ofab292."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40121-021-00525-4",
"article-title": "Efficacy of Bamlanivimab/Etesevimab and Casirivimab/Imdevimab in Preventing Progression to Severe COVID-19 and Role of Variants of Concern",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2479",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Infect Dis Ther",
"key": "2022030213400654000_2022.02.28.22270796v1.14",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofab315",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2022030213400654000_2022.02.28.22270796v1.15",
"unstructured": "Anderson B , Smith Z , Edupuganti S , Yan X , Masi CM , Wu HM . Effect of Monoclonal Antibody Treatment on Clinical Outcomes in Ambulatory Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019. Open Forum Infect Dis 2021; 8(7): ofab315."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.11.30.21266756",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022030213400654000_2022.02.28.22270796v1.16"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0021-9681(87)90171-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022030213400654000_2022.02.28.22270796v1.17"
},
{
"key": "2022030213400654000_2022.02.28.22270796v1.18",
"unstructured": "Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Clinical Growth Charts. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/growthcharts/clinical_charts.htm. Accessed November 23."
},
{
"key": "2022030213400654000_2022.02.28.22270796v1.19",
"unstructured": "U.S. Food & Drug Administration. Frequently Asked Questions on the Emergency Use Authorization for Bamlanivimab. Updated 3/24/2021. Available at: https://www.fda.gov/media/143605/download. Accessed January 4."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jep.12072",
"article-title": "Using balance statistics to determine the optimal number of controls in matching studies",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "968",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "J Eval Clin Pract",
"key": "2022030213400654000_2022.02.28.22270796v1.20",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2307/2281868",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022030213400654000_2022.02.28.22270796v1.21"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/biomet/67.1.133",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2022030213400654000_2022.02.28.22270796v1.22"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101102",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2022030213400654000_2022.02.28.22270796v1.23",
"unstructured": "Razonable RR , Pawlowski C , O’Horo JC , et al. Casirivimab-Imdevimab treatment is associated with reduced rates of hospitalization among high-risk patients with mild to moderate coronavirus disease-19. EClinicalMedicine 2021; 40: 101102."
},
{
"key": "2022030213400654000_2022.02.28.22270796v1.24",
"unstructured": "Planas D , Saunders N , Maes P , et al. Considerable escape of SARS-CoV-2 variant Omicron to antibody neutralization. bioRxiv 2021: Dec 15 [preprint] doi.org/0.1101/2021.12.14.472630."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.12.07.21267432",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2022030213400654000_2022.02.28.22270796v1.25",
"unstructured": "Wilhelm A , Widera M , Grikscheit K , et al. Reduced neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant by vaccine sera and monoclonal antibodies. medRxiv 2021: Dec 8 [Preprint] doi.org/10.1101/2021.12.07.21267432."
}
],
"reference-count": 25,
"references-count": 25,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": [
"Real-world Effectiveness of Casirivimab and Imdevimab in Patients With COVID-19 in the Ambulatory Setting: An Analysis of Two Large US National Claims Databases"
],
"type": "posted-content"
}