Vitamin A in resistance to and recovery from infection: relevance to SARS-CoV2
et al., British Journal of Nutrition, doi:10.1017/S0007114521000246, Jan 2021
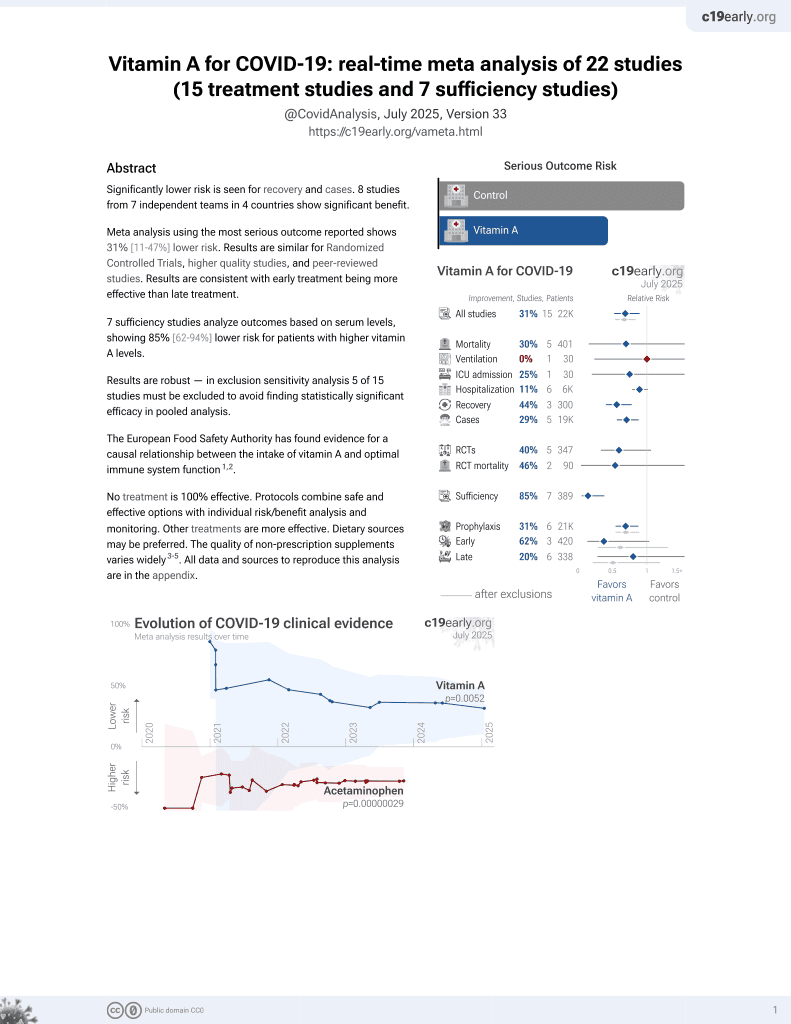
Vitamin A for COVID-19
49th treatment shown to reduce risk in
May 2023, now with p = 0.004 from 14 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Review of the potential benefits of vitamin A for COVID-19, including maintaining innate and adaptive immunity, minimizing inflammation, supporting repair of respiratory epithelium and preventing fibrosis, and counteracting adverse effects of SARS-CoV-2 on the angiotensin system.
1.
Al-Khrasani et al., Do vitamins halt the COVID-19-evoked pro-inflammatory cytokines involved in the development of neuropathic pain?, Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2025.118346.
2.
Sanduzzi Zamparelli et al., Immune-Boosting and Antiviral Effects of Antioxidants in COVID-19 Pneumonia: A Therapeutic Perspective, Life, doi:10.3390/life15010113.
3.
DiGuilio et al., Micronutrient Improvement of Epithelial Barrier Function in Various Disease States: A Case for Adjuvant Therapy, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms23062995.
4.
Stephensen et al., Vitamin A in resistance to and recovery from infection: relevance to SARS-CoV2, British Journal of Nutrition, doi:10.1017/S0007114521000246.
Stephensen et al., 20 Jan 2021, peer-reviewed, 2 authors.
Vitamin A in resistance to and recovery from infection: relevance to SARS-CoV2
British Journal of Nutrition, doi:10.1017/s0007114521000246
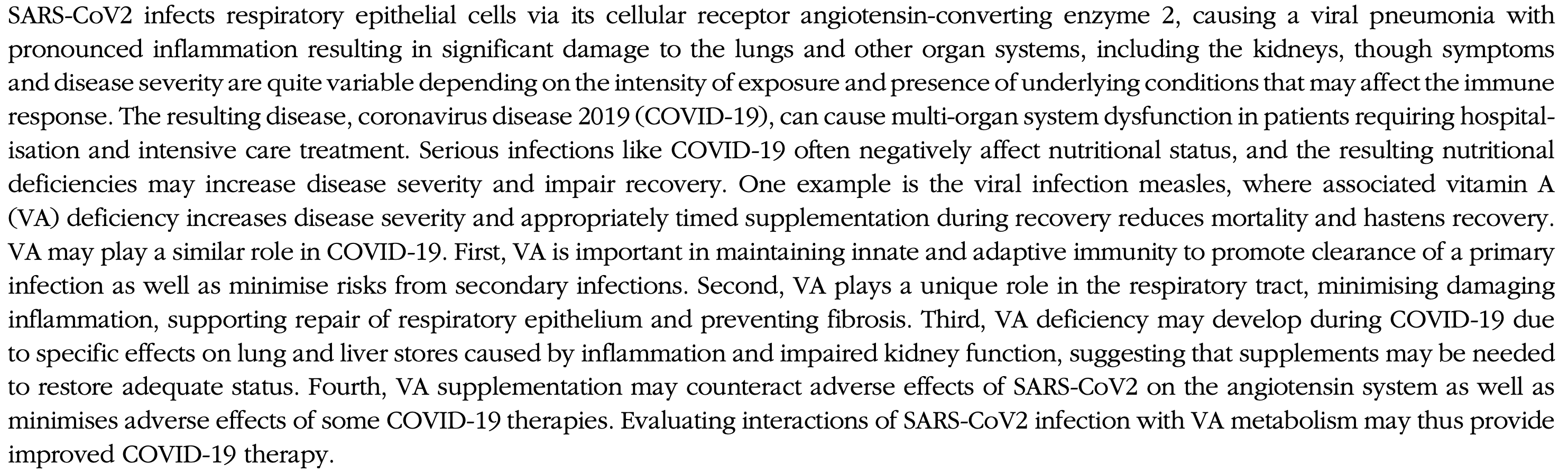
SARS-CoV2 infects respiratory epithelial cells via its cellular receptor angiotensin-converting enzyme 2, causing a viral pneumonia with pronounced inflammation resulting in significant damage to the lungs and other organ systems, including the kidneys, though symptoms and disease severity are quite variable depending on the intensity of exposure and presence of underlying conditions that may affect the immune response. The resulting disease, coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), can cause multi-organ system dysfunction in patients requiring hospitalisation and intensive care treatment. Serious infections like COVID-19 often negatively affect nutritional status, and the resulting nutritional deficiencies may increase disease severity and impair recovery. One example is the viral infection measles, where associated vitamin A (VA) deficiency increases disease severity and appropriately timed supplementation during recovery reduces mortality and hastens recovery. VA may play a similar role in COVID-19. First, VA is important in maintaining innate and adaptive immunity to promote clearance of a primary infection as well as minimise risks from secondary infections. Second, VA plays a unique role in the respiratory tract, minimising damaging inflammation, supporting repair of respiratory epithelium and preventing fibrosis. Third, VA deficiency may develop during COVID-19 due to specific effects on lung and liver stores caused by inflammation and impaired kidney function, suggesting that supplements may be needed to restore adequate status. Fourth, VA supplementation may counteract adverse effects of SARS-CoV2 on the angiotensin system as well as minimises adverse effects of some COVID-19 therapies. Evaluating interactions of SARS-CoV2 infection with VA metabolism may thus provide improved COVID-19 therapy.
References
Ahmed, Jones, Jackson, The interaction of vitamin A deficiency and rotavirus infection in the mouse, Br J Nutr
Aklamati, Mulenga, Dueker, Accelerator mass spectrometry can be used to assess vitamin A metabolism quantitatively in boys in a community setting, J Nutr
Aksoy, Karadag, Wollina, Angiotensin II receptors: impact for COVID-19 severity, Dermatol Ther
Altmann, Boyton, SARS-CoV-2 T cell immunity: specificity, function, durability, and role in protection, Sci Immunol
Aluisio, Perera, Yam, Vitamin A supplementation was associated with reduced mortality in patients with Ebola virus disease during the West African outbreak, J Nutr
Bakdash, Vogelpoel, Van Capel, Retinoic acid primes human dendritic cells to induce gut-homing, IL-10-producing regulatory T cells, Mucosal Immunol
Belvisi, Hele, Birrell, Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma agonists as therapy for chronic airway inflammation, Eur J Pharmacol
Berlin, Gulick, Martinez, Severe Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Bresee, Fischer, Dowell, Vitamin A therapy for children with respiratory syncytial virus infection: a multicenter trial in the United States, Pediatr Infect Dis J
Brooks, Tong, Benedetti, Inhaled aerosolization of all-trans-retinoic acid for targeted pulmonary delivery, Cancer Chemother Pharmacol
Brown, Esterhazy, Sarde, Retinoic acid is essential for Th1 cell lineage stability and prevents transition to a Th17 cell program, Immunity
Catanzaro, Fagiani, Racchi, Immune response in COVID-19: addressing a pharmacological challenge by targeting pathways triggered by SARS-CoV-2, Signal Transduction Targeted Ther
Channappanavar, Fett, Zhao, Virus-specific memory CD8 T cells provide substantial protection from lethal severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection, J Virol
Chen, Liu, Guo, Emerging coronaviruses: genome structure, replication, and pathogenesis, J Med Virol
Cone, Barrier properties of mucus, Adv Drug Delivery Rev
Fan, Liu, Liu, Vitamin A deficiency impairs Mucin expression and suppresses the Mucosal immune function of the respiratory tract in chicks, PLOS ONE
Fang, Karakiulakis, Roth, Are patients with hypertension and diabetes mellitus at increased risk for COVID-19 infection?, Lancet Respir Med
Florindo, Kleiner, Vaskovich-Koubi, Immune-mediated approaches against COVID-19, Nat Nanotechnol
Fung, Liu, Human coronavirus: host-pathogen interaction, Annu Rev Microbiol
Gagliardi, Tieri, Ortona, ACE2 expression and sex disparity in COVID-19, Cell Death Discovery
Gandhi, Lynch, Del Rio, Mild or moderate Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Gieng, Green, Green, Model-based compartmental analysis indicates a reduced mobilization of hepatic vitamin A during inflammation in rats, J Lipid Res
Gori, Leone, Loffredo, COVID-19-related anosmia: the olfactory pathway hypothesis and early intervention, Front Neurol
Gorzkowski, Bevilacqua, Charmillon, Evolution of olfactory disorders in COVID-19 patients, Laryngoscope
Green, Mellanby, Vitamin A as an anti-infective agent, Br Med J
Grotto, Mimouni, Gdalevich, Vitamin A supplementation and childhood morbidity from diarrhea and respiratory infections: a meta-analysis, J Pediatr
Gundra, Girgis, Gonzalez, Vitamin A mediates conversion of monocyte-derived macrophages into tissue-resident macrophages during alternative activation, Nat Immunol
Guo, Brown, Ortiz, Leukocyte homing, fate, and function are controlled by retinoic acid, Physiol Rev
Habiel, Hogaboam, Heterogeneity of fibroblasts and myofibroblasts in pulmonary fibrosis, Curr Pathobiol Rep
Hamming, Cooper, Haagmans, The emerging role of ACE2 in physiology and disease, J Pathol
Headey, Heidkamp, Osendarp, Impacts of COVID-19 on childhood malnutrition and nutrition-related mortality, Lancet
Hikmet, Mear, Edvinsson, The protein expression profile of ACE2 in human tissues, Mol Syst Biol
Hind, Gilthorpe, Stinchcombe, Retinoid induction of alveolar regeneration: from mice to man?, Thorax
Hind, Maden, Retinoic acid induces alveolar regeneration in the adult mouse lung, Eur Respir J
Hoang, Kanjanaumporn, Aeumjaturapat, Olfactory and gustatory dysfunctions in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol
Hoffmann, Begon, Lafon, Influence of glenohumeral joint muscle insertion on moment arms using a finite element model, Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin
Hou, Okuda, Edwards, SARS-CoV-2 reverse genetics reveals a variable infection gradient in the respiratory tract, Cell
Hu, Lee, Asirvatham, Cardiovascular considerations in coronavirus disease 2019 with a special focus on arrhythmia, J Innovations Card Rhythm Manage
Huang, Garcia-Carreras, Hitchings, A systematic review of antibody mediated immunity to coronaviruses: kinetics, correlates of protection, and association with severity, Nat Commun
Huang, Wu, Zheng, Targeting inflammation and cytokine storm in COVID-19, Pharmacolog Res
Hummel, Whitcroft, Rueter, Intranasal vitamin A is beneficial in post-infectious olfactory loss, Eur Arch Oto-Rhino-Laryngol
Hussey, Klein, A randomized, controlled trial of vitamin-A in children with severe measles, N Engl J Med
Iwata, Retinoic acid production by intestinal dendritic cells and its role in T-cell trafficking, Semin Immunol
Johnson, Vinetz, Dexamethasone in the management of Covid-19, BMJ
Koo, Jetten, Belloni, Role of retinoid receptors in the regulation of Mucin gene expression by retinoic acid in human tracheobronchial epithelial cells, Biochem J
Kruglikov, Scherer, The role of adipocytes and adipocyte-like cells in the severity of COVID-19 infections, Obesity
Kuba, Imai, Penninger, Angiotensinconverting enzyme 2 in lung diseases, Curr Opin Pharmacol
Kuba, Imai, Rao, A crucial role of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in SARS coronavirusinduced lung injury, Nat Med
Lai, Treatment of severe acute respiratory syndrome, Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis
Larange, Cheroutre, Retinoic acid and retinoic acid receptors as pleiotropic modulators of the immune system, Annu Rev Immunol
Larson, Guo, Williams, Approaches to assess vitamin A status in settings of inflammation: Biomarkers Reflecting Inflammation and Nutritional Determinants of Anemia (BRINDA) project, Nutrients
Lechien, Chiesa-Estomba, Siati, Olfactory and gustatory dysfunctions as a clinical presentation of mild-to-moderate forms of the coronavirus disease (COVID-19): a multicenter European study, Eur Arch Oto-Rhino-Laryngol
Lee, Park, Jeong, Immunophenotyping of COVID-19 and influenza highlights the role of type I interferons in development of severe COVID-19, Sci Immunol
Li, Wu, Yan, T cell responses to whole SARS coronavirus in humans, J Immunol
Liang, Yi, Wang, Retinoic acid modulates hyperactive T cell responses and protects vitamin A-deficient mice against persistent lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection, J Immunol
Lippman, Lee, Karp, Randomized phase III intergroup trial of isotretinoin to prevent second primary tumors in stage I non-small-cell lung cancer, JNCI-J Nat Cancer Inst
Lo, Kemper, Woodruff, COVID-19: complement, coagulation, and collateral damage, J Immunol
Mangalmurti, Hunter, Cytokine storms: understanding COVID-19, Immunity
Marquez, Chen, Retinoic acid signaling and development of the respiratory system, Sub-Cell Biochem
Martin, Frevert, Innate immunity in the lungs, Proc Am Thorac Soc
Massaro, Massaro, Retinoic acid treatment abrogates elastase-induced pulmonary emphysema in rats, Nat Med
Mcgill, Kelly, Guerra-Maupome, Vitamin A deficiency impairs the immune response to intranasal vaccination and RSV infection in neonatal calves, Sci Rep
Mery, Epaulard, Borel, COVID-19: underlying adipokine storm and angiotensin 1-7 umbrella, Front Immunol
Mokra, Mikolka, Kosutova, Corticosteroids in acute lung injury: the dilemma continues, Int J Mol Sci
Mora, Von Andrian, Role of retinoic acid in the imprinting of gut-homing IgA-secreting cells, Semin Immunol
Murphy, Doty, Duncan, Clinical disorders of olfaction
Murphy, Weaver, Janeway's Immunobiology
Nawijn, Timens, Can ACE2 expression explain SARS-CoV-2 infection of the respiratory epithelia in COVID-19?, Mol Syst Biol
Oliveira, Teixeira, Sato, Impact of retinoic acid on immune cells and inflammatory diseases, Mediators Inflammation
Olson, Vitamin A
Paniri, Hosseini, Rasoulinejad, Molecular effects and retinopathy induced by hydroxychloroquine during SARS-CoV-2 therapy: role of CYP450 isoforms and epigenetic modulations, Eur J Pharmacol
Paquette, Zhang, Vitamin A deficiency enhances ozone-induced lung injury, Am J Physiol
Penkert, Cortez, Karlsson, Vitamin A corrects tissue deficits in diet-induced obese mice and reduces influenza infection after vaccination and challenge, Silver Spring)
Penkert, Surman, Jones, Vitamin A deficient mice exhibit increased viral antigens and enhanced cytokine/chemokine production in nasal tissues following respiratory virus infection despite the presence of FoxP3 þ T cells, Int Immunol
Porzionato, Emmi, Barbon, Sympathetic activation: a potential link between comorbidities and COVID-19, FEBS J
Rawson, Lamantia, A speculative essay on retinoic acid regulation of neural stem cells in the developing and aging olfactory system, Exp Gerontol
Richardson, The physiology of mucus and sputum production in the respiratory system, Nurs Times
Ross, Ambalavanan, Retinoic acid combined with vitamin A synergizes to increase retinyl ester storage in the lungs of newborn and dexamethasone-treated neonatal rats, Neonatology
Ross, Stephensen, Vitamin A and retinoids in antiviral responses, FASEB J
Rubin, Ross, Stephensen, Metabolic effects of inflammation on vitamin A and carotenoids in humans and animal models, Adv Nutr
Sariol, Perlman, Lessons for COVID-19 immunity from other coronavirus infections, Immunity
Schaeffer, Roy, Mukherjee, Uptake of alltrans retinoic acid-containing aerosol by inhalation to lungs in a guinea pig model system -a pilot study, Exp Lung Res
Schuster, Kenyon, Stephensen, Vitamin A deficiency decreases and high dietary vitamin A increases disease severity in the mouse model of asthma, J Immunol
Seo, Jang, Kim, Retinoic acid, acting as a highly specific IgA isotype switch factor, cooperates with TGF-beta1 to enhance the overall IgA response, J Leukocyte Biol
Sharif-Askari, Sharif-Askari, Alabed, Airways expression of SARS-CoV-2 receptor, ACE2, and TMPRSS2 is lower in children than adults and increases with smoking and COPD, Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev
Sodhi, Jenny, Yamaguchi, A dynamic variation of pulmonary ACE2 is required to modulate neutrophilic inflammation in response to pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infection in mice, J Immunol
Stephensen, Alvarez, Kohatsu, Vitamin A is excreted in the urine during acute infection, Am J Clin Nutr
Stephensen, Blount, Schoeb, Vitamin A deficiency impairs some aspects of the host response to influenza A virus infection in BALB/c mice, J Nutr
Stephensen, Franchi, Hernandez, Adverse effects of high-dose vitamin A supplements in children hospitalized with pneumonia, Pediatrics
Stephensen, Lietz, None
Stephensen, Moldoveanu, Gangopadhyay, Vitamin A deficiency diminishes the salivary immunoglobulin A response and enhances the serum immunoglobulin G response to influenza A virus infection in BALB/c mice, J Nutr
Stephensen, Vitamin A, infection, and immune function, Annu Rev Nutr
Subbarao, Mahanty, Respiratory virus infections: understanding COVID-19, Immunity
Tikellis, Thomas, Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) is a key modulator of the renin angiotensin system in health and disease, Int J Pept
Timoneda, Rodríguez-Fernández, Zaragozá, Vitamin A deficiency and the lung, Nutrients
Tsuchida, Friedman, Mechanisms of hepatic stellate cell activation, Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol
Vabret, Britton, Gruber, Immunology of COVID-19: current state of the science, Immunity
Valentine, Davis, Tanumihardjo, Vitamin A isotope dilution predicts liver stores in line with long-term vitamin A intake above the current recommended dietary allowance for young adult women, Am J Clin Nutr
Vellozo, Pereira-Marques, Cabral-Piccin, All-trans retinoic acid promotes an M1-to M2-phenotype shift and inhibits macrophage-mediated immunity to Leishmania major, Front Immunol
Wang, Yu, Kane, Modulation of retinoid signaling: therapeutic opportunities in organ fibrosis and repair, Pharmacol Ther
Xavier-Elsas, Vieira, Masid-De-Brito, The need to consider context in the evaluation of anti-infectious and immunomodulatory effects of vitamin A and its derivatives, Curr Drug Targets
Yadav, Aggarwal, Singh, SARS-CoV-2-host dynamics: increased risk of adverse outcomes of COVID-19 in obesity, Diabetes Metab Syndr
Yang, Peng, Zhu, Persistent memory CD4 þ and CD8 þ T-cell responses in recovered severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) patients to SARS coronavirus M antigen, J Gen Virol
Zhao, Alshukairi, Baharoon, Recovery from the Middle East respiratory syndrome is associated with antibody and T-cell responses, Sci Immunol
Zhong, Huang, Yang, Upregulation of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 by all-trans retinoic acid in spontaneously hypertensive rats, Hypertension
Zhou, Wu, Qin, Association of alltrans retinoic acid treatment with the renin-angiotensin aldosterone system expression in glomerulosclerosis rats, J Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Syst
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1017/s0007114521000246",
"ISSN": [
"0007-1145",
"1475-2662"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/S0007114521000246",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:p>SARS-CoV2 infects respiratory epithelial cells via its cellular receptor angiotensin-converting enzyme 2, causing a viral pneumonia with pronounced inflammation resulting in significant damage to the lungs and other organ systems, including the kidneys, though symptoms and disease severity are quite variable depending on the intensity of exposure and presence of underlying conditions that may affect the immune response. The resulting disease, coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), can cause multi-organ system dysfunction in patients requiring hospitalisation and intensive care treatment. Serious infections like COVID-19 often negatively affect nutritional status, and the resulting nutritional deficiencies may increase disease severity and impair recovery. One example is the viral infection measles, where associated vitamin A (VA) deficiency increases disease severity and appropriately timed supplementation during recovery reduces mortality and hastens recovery. VA may play a similar role in COVID-19. First, VA is important in maintaining innate and adaptive immunity to promote clearance of a primary infection as well as minimise risks from secondary infections. Second, VA plays a unique role in the respiratory tract, minimising damaging inflammation, supporting repair of respiratory epithelium and preventing fibrosis. Third, VA deficiency may develop during COVID-19 due to specific effects on lung and liver stores caused by inflammation and impaired kidney function, suggesting that supplements may be needed to restore adequate status. Fourth, VA supplementation may counteract adverse effects of SARS-CoV2 on the angiotensin system as well as minimises adverse effects of some COVID-19 therapies. Evaluating interactions of SARS-CoV2 infection with VA metabolism may thus provide improved COVID-19 therapy.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"S0007114521000246"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Copyright and Licensing",
"name": "copyright_and_licensing"
},
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© The Author(s), 2021. Published by Cambridge University Press on behalf of The Nutrition Society"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Copyright and Licensing",
"name": "copyright_and_licensing"
},
"label": "License",
"name": "license",
"value": "This is an Open Access article, distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution licence (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted re-use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited."
},
{
"label": "Free to read",
"name": "free",
"value": "This content has been made available to all."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Stephensen",
"given": "C. B.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lietz",
"given": "G.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "British Journal of Nutrition",
"container-title-short": "Br J Nutr",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"cambridge.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2021-01-20T02:40:05Z",
"timestamp": 1611110405000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-12T11:33:56Z",
"timestamp": 1636716836000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-26T05:53:46Z",
"timestamp": 1714110826300
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 42,
"issue": "11",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
20
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "11",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
14
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2021-01-20T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1611100800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.cambridge.org/core/services/aop-cambridge-core/content/view/S0007114521000246",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "56",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1663-1672",
"prefix": "10.1017",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
20
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
20
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
14
]
]
},
"publisher": "Cambridge University Press (CUP)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev.nutr.21.1.167",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/febs.15481",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref42"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30116-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref39"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3109/01902141003790155",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref91"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41565-020-0732-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1099/vir.0.82839-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref61"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-020-0191-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref78"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.addr.2008.09.008",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref32"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/oby.22856",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref48"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/bj3380351",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref35"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2012/256294",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref27"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1096/fasebj.10.9.8801180",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref54"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.05.042",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref51"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jn/nxz142",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref87"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0139131",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref36"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.07.030",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref7"
},
{
"author": "Murphy",
"first-page": "461",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref96",
"volume-title": "Handbook of Olfaction and Gustation",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.2.3537.691",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.181.8.5490",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref64"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.immuni.2020.05.002",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref52"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/intimm/dxv064",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref68"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/09031936.03.00119103",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref18"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/oby.22929",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref88"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.omtm.2020.05.013",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref28"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nm0697-675",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref104"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1389450120666181217095323",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref58"
},
{
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref4",
"unstructured": "4. WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) dashboard. https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed December 2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu10091132",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1067/mpd.2003.116",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref84"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/10255842.2020.1789606",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fneur.2020.00956",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref92"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.immuni.2020.05.004",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref53"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/path.2162",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref23"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pharmthera.2019.107415",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref44"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jn/123.5.823",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref31"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00405-017-4576-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref98"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/lary.28957",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref93"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2018/3067126",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref55"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m2648",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.01505-14",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref62"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3945/ajcn.113.063867",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref83"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-18450-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref65"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15252/msb.20209841",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref22"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-019-51684-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref90"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-3-030-42282-0_6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref43"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu10081100",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref81"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jnci/93.8.605",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref105"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.immuni.2020.06.017",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref77"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJM199007193230304",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref89"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.coph.2006.03.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref25"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000100083",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref103"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.immuni.2015.02.003",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref71"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/01.HYP.0000146400.57221.74",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref37"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1542/peds.101.5.e3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref85"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.1900579",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref26"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ni.3734",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref57"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/sciimmunol.abd1554",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref76"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31647-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref106"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40139-017-0134-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref47"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms20194765",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref100"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1194/jlr.M600528-JLR200",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref16"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10096-005-0004-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref101"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jn/126.1.94",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref67"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105051",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref102"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/sciimmunol.abd6160",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref60"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin A deficiency enhances ozone-induced lung injury",
"author": "Paquette",
"first-page": "L475",
"journal-title": "Am J Physiol",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref30",
"volume": "270",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMcp2009249",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.immuni.2020.07.005",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref50"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrgastro.2017.38",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref46"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2017.01560",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref56"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/00006454-199609000-00008",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref86"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s002800000148",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref99"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.25681",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/dth.13989",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref40"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.1901091",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref72"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejphar.2005.12.048",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref49"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3945/jn.110.125500",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41420-020-0276-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref24"
},
{
"DOI": "10.19102/icrm.2020.110804",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/thx.2008.105437",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref45"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.smim.2008.09.002",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref66"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3945/an.116.014167",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref80"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.180.3.1834",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref70"
},
{
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref79",
"unstructured": "79. Olson JA (1990) Vitamin A. In Present Knowledge in Nutrition, 6th ed., pp. 96–107 [ML Brown, editor]. Washington, DC: International Life Sciences Institute-Nutrition Foundation."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1470320312465220",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref38"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ajcn/60.3.388",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref82"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1079/BJN19900122",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref29"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/mi.2014.64",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref69"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.exger.2006.05.021",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref97"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00405-020-05965-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref95"
},
{
"article-title": "Olfactory and gustatory dysfunctions in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Hoang",
"first-page": "162",
"journal-title": "Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref94",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173454",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref10"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.2000644",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref75"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.01714",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref41"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev-immunol-041015-055427",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref12"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/sciimmunol.aan5393",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref63"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMcp2009575",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nm1267",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref19"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.smim.2008.08.002",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref74"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15252/msb.20209610",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref21"
},
{
"article-title": "The physiology of mucus and sputum production in the respiratory system",
"author": "Richardson",
"first-page": "63",
"journal-title": "Nurs Times",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref34",
"volume": "99",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1513/pats.200508-090JS",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref33"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev-micro-020518-115759",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/physrev.00032.2013",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1189/jlb.0313128",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref73"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1201/9781315533247",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521000246_ref59"
}
],
"reference-count": 106,
"references-count": 106,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.cambridge.org/core/product/identifier/S0007114521000246/type/journal_article"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Vitamin A in resistance to and recovery from infection: relevance to SARS-CoV2",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/policypage",
"volume": "126"
}