Casirivimab and Imdevimab for the Treatment of Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19
et al., The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiac320, NCT04426695, Nov 2021 (preprint)
19th treatment shown to reduce risk in
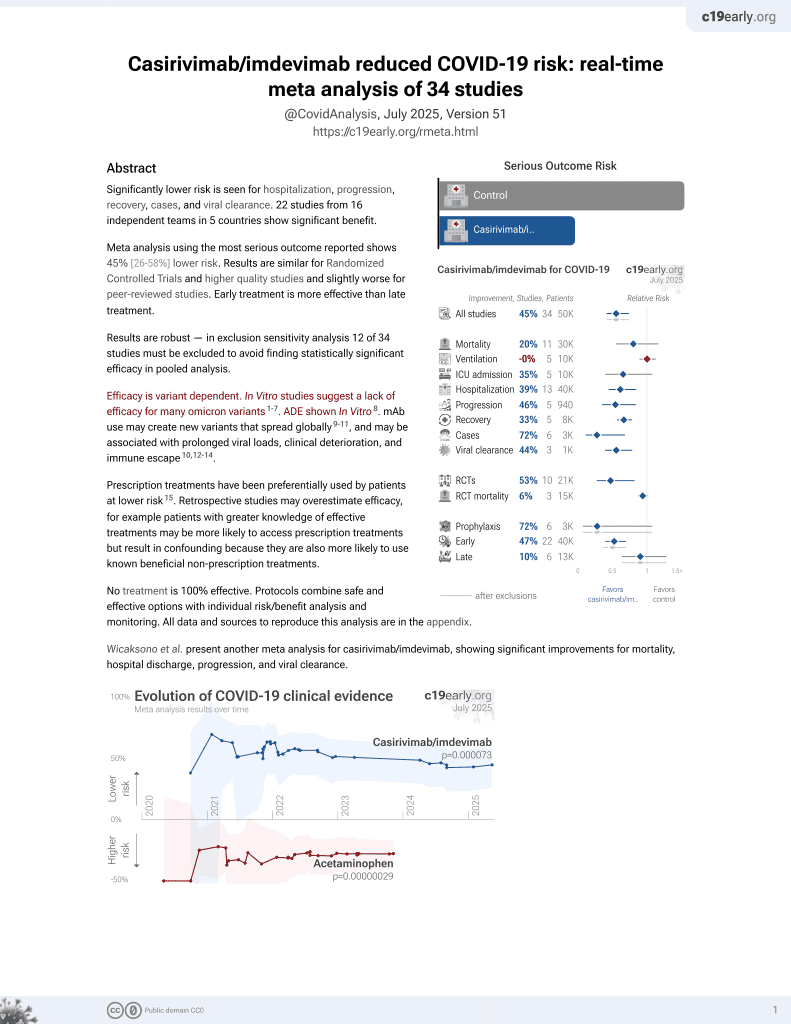
March 2021, now with p = 0.000095 from 34 studies, recognized in 52 countries.
Efficacy is variant dependent.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
RCT 2,252 hospitalized patients. Results for 1,336 patients on low-flow or no supplemental oxygen are reported, showing lower mortality with casirivimab/imdevimab treatment. Cohorts 2&3 (high-intensity oxygen and mechanical ventilation) were paused mid-trial due to increased deaths in the treatment arm and only mortality results are reported.
Efficacy is variant dependent. In Vitro research suggests a lack of efficacy for many omicron variants1-7.
|
risk of death, 3.1% lower, RR 0.97, p = 0.92, treatment 804, control 393, all cohorts combined.
|
|
risk of death, 35.9% lower, RR 0.64, p = 0.02, treatment 59 of 804 (7.3%), control 45 of 393 (11.5%), NNT 24, day 28, mFAS, cohort 1.
|
|
risk of death, 56.9% higher, RR 1.57, p = 0.08, treatment 44 of 110 (40.0%), control 13 of 51 (25.5%), cohort 2.
|
|
risk of death, 3.1% lower, RR 0.97, p = 1.00, treatment 13 of 23 (56.5%), control 7 of 12 (58.3%), NNT 55, cohort 3.
|
|
risk of death/intubation, 30.9% lower, RR 0.69, p = 0.03, treatment 82 of 804 (10.2%), control 58 of 393 (14.8%), NNT 22, day 1-29, mFAS, cohort 1.
|
|
risk of no hospital discharge, 30.2% lower, RR 0.70, p = 0.02, treatment 90 of 804 (11.2%), control 63 of 393 (16.0%), NNT 21, day 1-29, mFAS, cohort 1.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Conflicts of interest:
research funding from the drug patent holder, employee of the drug patent holder.
1.
Liu et al., Striking Antibody Evasion Manifested by the Omicron Variant of SARS-CoV-2, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.14.472719.
2.
Sheward et al., Variable loss of antibody potency against SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 (Omicron), bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.19.473354.
3.
VanBlargan et al., An infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 Omicron virus escapes neutralization by several therapeutic monoclonal antibodies, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.15.472828.
4.
Tatham et al., Lack of Ronapreve (REGN-CoV; casirivimab and imdevimab) virological efficacy against the SARS-CoV 2 Omicron variant (B.1.1.529) in K18-hACE2 mice, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.01.23.477397.
5.
Pochtovyi et al., In Vitro Efficacy of Antivirals and Monoclonal Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Lineages XBB.1.9.1, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5, XBB.1.16, XBB.2.4, BQ.1.1.45, CH.1.1, and CL.1, Vaccines, doi:10.3390/vaccines11101533.
Somersan-Karakaya et al., 8 Nov 2021, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, multiple countries, peer-reviewed, median age 62.0, 34 authors, study period 10 June, 2020 - 9 April, 2021, average treatment delay 6.0 days, trial NCT04426695 (history).
Casirivimab and Imdevimab for the Treatment of Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19
doi:10.1093/infdis/jiac320/6650790
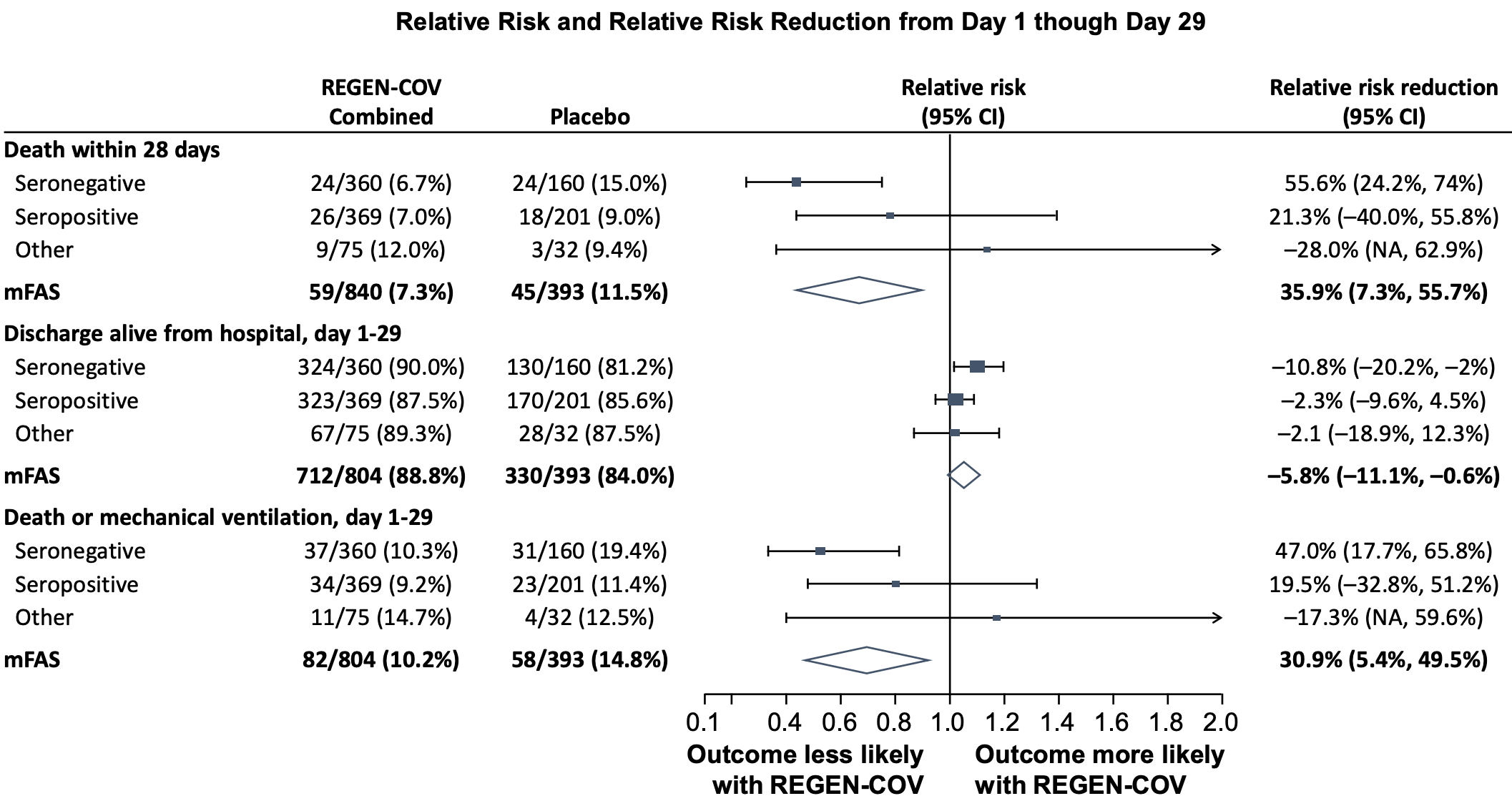
Background: The open-label RECOVERY study reported improved survival in hospitalized, SARS-CoV-2 seronegative patients treated with casirivimab and imdevimab (CAS+IMD).
Methods: In this phase I/II/III, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial conducted prior to widespread circulation of Delta and Omicron, hospitalized COVID-19 patients were randomized (1:1:1) to 2.4 g or 8.0 g CAS+IMD or placebo, and characterized at baseline for viral load and SARS-CoV-2 serostatus. Results: 1336 patients on low-flow or no supplemental (low-flow/no) oxygen were treated. The primary endpoint was met: in seronegative patients, the least-squares mean difference (CAS+IMD versus placebo) for time-weighted average change from baseline in viral load through day 7 was -0.28 log 10 copies/mL (95% CI, -0.51 to -0.05; P=.0172). The primary clinical analysis of death or mechanical ventilation (death/MV) from day 6-29 in patients with high viral load had a strong positive trend but did not reach significance. CAS+IMD numerically reduced all-cause mortality in seronegative patients through day 29 (relative risk reduction, 55.6%; 95% CI, 24.2-74.0). No safety concerns were noted.
Conclusions: In hospitalized COVID-19 patients on low-flow/no oxygen, CAS+IMD reduced viral load and likely improves clinical outcomes in the overall population, with the benefit driven by seronegative patients, and no harm observed in seropositive patients.
Notes Forest plot shows relative risk and relative risk reduction with 95% CIs for CAS+IMD combined dose analysis (2.4 g and 8.0 g) versus placebo. Parameters examined include death within 28 days, discharge alive from hospital from days 1 to 29, and death or mechanical ventilation from days 1 to 29. For all populations, the mFAS was comprised of patients who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 at baseline. Populations analyzed include patients who tested negative for all SARS-CoV-2 antibodies at baseline (seronegative mFAS), patients who tested positive for any SARS-CoV-2 antibody at baseline (seropositive mFAS), those with borderline, inconclusive or missing baseline serology (other), and the overall population regardless of serostatus (overall mFAS). For the proportion of death within 28 days and the proportion of death or mechanical ventilation with 28 days, the lower bounds of the CI of the relative risk reduction were -342.0% and -241.0%, respectively, which are presented as "NA" in the figure . Abbreviations: CAS+IMD, casirivimab and imdevimab; CI, confidence interval; mFAS, modified full analysis set; SARS-CoV-2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.
References
Baum, Fulton, Wloga, Antibody cocktail to SARS-CoV-2 spike protein prevents rapid mutational escape seen with individual antibodies, Science
Copin, Baum, Wloga, The monoclonal antibody combination REGEN-COV protects against SARS-CoV-2 mutational escape in preclinical and human studies, Cell
Goyal, Choi, Pinheiro, Clinical characteristics of Covid-19 in New York City, N Engl J Med
Group, Lundgren, Grund, A neutralizing monoclonal antibody for hospitalized patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Group, Lundgren, Grund, Clinical and virological response to a neutralizing monoclonal antibody for hospitalized patients with COVID-19, medRxiv
Guan, Ni, Hu, Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China, N Engl J Med
Hansen, Baum, Pascal, Studies in humanized mice and convalescent humans yield a SARS-CoV-2 antibody cocktail, Science
Horby, Lim, Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Li, Zhang, Hu, Effect of convalescent plasma therapy on time to clinical improvement in patients with severe and life-threatening COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Marconi, Ramanan, De Bono, Efficacy and safety of baricitinib for the treatment of hospitalised adults with COVID-19 (COV-BARRIER): a randomised, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial, Lancet Respir Med
O'brien, Forleo-Neto, Musser, Subcutaneous REGEN-COV antibody combination for Covid-19 prevention, medRxiv
O'brien, Forleo-Neto, Musser, Subcutaneous REGEN-COV antibody combination to prevent Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Plains, Center, Plains, Ny, Schelker et al., Former employee of Regeneron Pharmaceuticals
Richardson, Hirsch, Narasimhan, Presenting characteristics, comorbidities, and outcomes among 5700 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in the New York City area, JAMA
Rosas, Brau, Waters, Tocilizumab in hospitalized patients with severe Covid-19 pneumonia, N Engl J Med
Sharun, Tiwari, Dhama, Emran, Rabaan et al., Emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants: impact on vaccine efficacy and neutralizing antibodies, Hum Vaccin Immunother
Verderese, Stepanova, Lam, Neutralizing monoclonal antibody treatment reduces hospitalization for mild and moderate COVID-19: A real-world experience, Clin Infect Dis
Weinreich, Sivapalasingam, Norton, REGEN-COV antibody combination and outcomes in outpatients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Weinreich, Sivapalasingam, Norton, REGN-COV2, a neutralizing antibody cocktail, in outpatients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiac320",
"ISSN": [
"0022-1899",
"1537-6613"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jiac320",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Background</jats:title>\n <jats:p>The open-label RECOVERY study reported improved survival in hospitalized, SARS-CoV-2 seronegative patients treated with casirivimab and imdevimab (CAS + IMD).</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>In this phase I/II/III, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial conducted prior to widespread circulation of Delta and Omicron, hospitalized COVID-19 patients were randomized (1:1:1) to 2.4 g or 8.0 g CAS + IMD or placebo, and characterized at baseline for viral load and SARS-CoV-2 serostatus.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>1336 patients on low-flow or no supplemental (low-flow/no) oxygen were treated. The primary endpoint was met: in seronegative patients, the least-squares mean difference (CAS + IMD versus placebo) for time-weighted average change from baseline in viral load through day 7 was –0.28 log10 copies/mL (95% CI, –0.51 to –0.05; P = .0172). The primary clinical analysis of death or mechanical ventilation (death/MV) from day 6–29 in patients with high viral load had a strong positive trend but did not reach significance. CAS + IMD numerically reduced all-cause mortality in seronegative patients through day 29 (relative risk reduction, 55.6%; 95% CI, 24.2–74.0). No safety concerns were noted.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title>\n <jats:p>In hospitalized COVID-19 patients on low-flow/no oxygen, CAS + IMD reduced viral load and likely improves clinical outcomes in the overall population, with the benefit driven by seronegative patients, and no harm observed in seropositive patients.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. , Tarrytown, NY , USA"
}
],
"family": "Somersan-Karakaya",
"given": "Selin",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Brown University , Providence, RI , USA"
}
],
"family": "Mylonakis",
"given": "Eleftherios",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "NYC Health + Hospitals/Lincoln, The Bronx, NY , USA"
}
],
"family": "Menon",
"given": "Vidya P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "The Oregon Clinic , Portland, OR , USA"
},
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. , Tarrytown, NY , USA"
}
],
"family": "Wells",
"given": "Jason C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. , Tarrytown, NY , USA"
}
],
"family": "Ali",
"given": "Shazia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. , Tarrytown, NY , USA"
}
],
"family": "Sivapalasingam",
"given": "Sumathi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. , Tarrytown, NY , USA"
}
],
"family": "Sun",
"given": "Yiping",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. , Tarrytown, NY , USA"
}
],
"family": "Bhore",
"given": "Rafia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. , Tarrytown, NY , USA"
}
],
"family": "Mei",
"given": "Jingning",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. , Tarrytown, NY , USA"
}
],
"family": "Miller",
"given": "Jutta",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. , Tarrytown, NY , USA"
}
],
"family": "Cupelli",
"given": "Lisa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. , Tarrytown, NY , USA"
}
],
"family": "Forleo-Neto",
"given": "Eduardo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. , Tarrytown, NY , USA"
}
],
"family": "Hooper",
"given": "Andrea T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. , Tarrytown, NY , USA"
}
],
"family": "Hamilton",
"given": "Jennifer D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. , Tarrytown, NY , USA"
}
],
"family": "Pan",
"given": "Cynthia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. , Tarrytown, NY , USA"
}
],
"family": "Pham",
"given": "Viet",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. , Tarrytown, NY , USA"
}
],
"family": "Zhao",
"given": "Yuming",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. , Tarrytown, NY , USA"
}
],
"family": "Hosain",
"given": "Romana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. , Tarrytown, NY , USA"
}
],
"family": "Mahmood",
"given": "Adnan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. , Tarrytown, NY , USA"
}
],
"family": "Davis",
"given": "John D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. , Tarrytown, NY , USA"
}
],
"family": "Turner",
"given": "Kenneth C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. , Tarrytown, NY , USA"
}
],
"family": "Kim",
"given": "Yunji",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. , Tarrytown, NY , USA"
}
],
"family": "Cook",
"given": "Amanda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. , Tarrytown, NY , USA"
}
],
"family": "Kowal",
"given": "Bari",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. , Tarrytown, NY , USA"
}
],
"family": "Soo",
"given": "Yuhwen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. , Tarrytown, NY , USA"
}
],
"family": "DiCioccio",
"given": "A Thomas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. , Tarrytown, NY , USA"
}
],
"family": "Geba",
"given": "Gregory P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. , Tarrytown, NY , USA"
}
],
"family": "Stahl",
"given": "Neil",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. , Tarrytown, NY , USA"
}
],
"family": "Lipsich",
"given": "Leah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. , Tarrytown, NY , USA"
}
],
"family": "Braunstein",
"given": "Ned",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. , Tarrytown, NY , USA"
}
],
"family": "Herman",
"given": "Gary A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. , Tarrytown, NY , USA"
}
],
"family": "Yancopoulos",
"given": "George D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. , Tarrytown, NY , USA"
}
],
"family": "Weinreich",
"given": "David M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"name": "for the COVID-19 Phase 2/3 Hospitalized Trial Team",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "The Journal of Infectious Diseases",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-27T16:59:39Z",
"timestamp": 1658941179000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-27T16:59:39Z",
"timestamp": 1658941179000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-27T17:41:30Z",
"timestamp": 1658943690399
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
27
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "am",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-27T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1658880000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/jid/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/infdis/jiac320/45108752/jiac320.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "am",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/jid/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/infdis/jiac320/45108752/jiac320.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "286",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1093",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
27
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
27
]
]
},
"publisher": "Oxford University Press (OUP)",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/jid/advance-article/doi/10.1093/infdis/jiac320/6650790"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Immunology and Allergy"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Casirivimab and Imdevimab for the Treatment of Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article"
}