High dose vitamin D improves total serum antioxidant capacity and ICU outcome in critically ill patients - a randomized, double-blind clinical trial
et al., European Journal of Integrative Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101271, Dec 2020
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 136 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
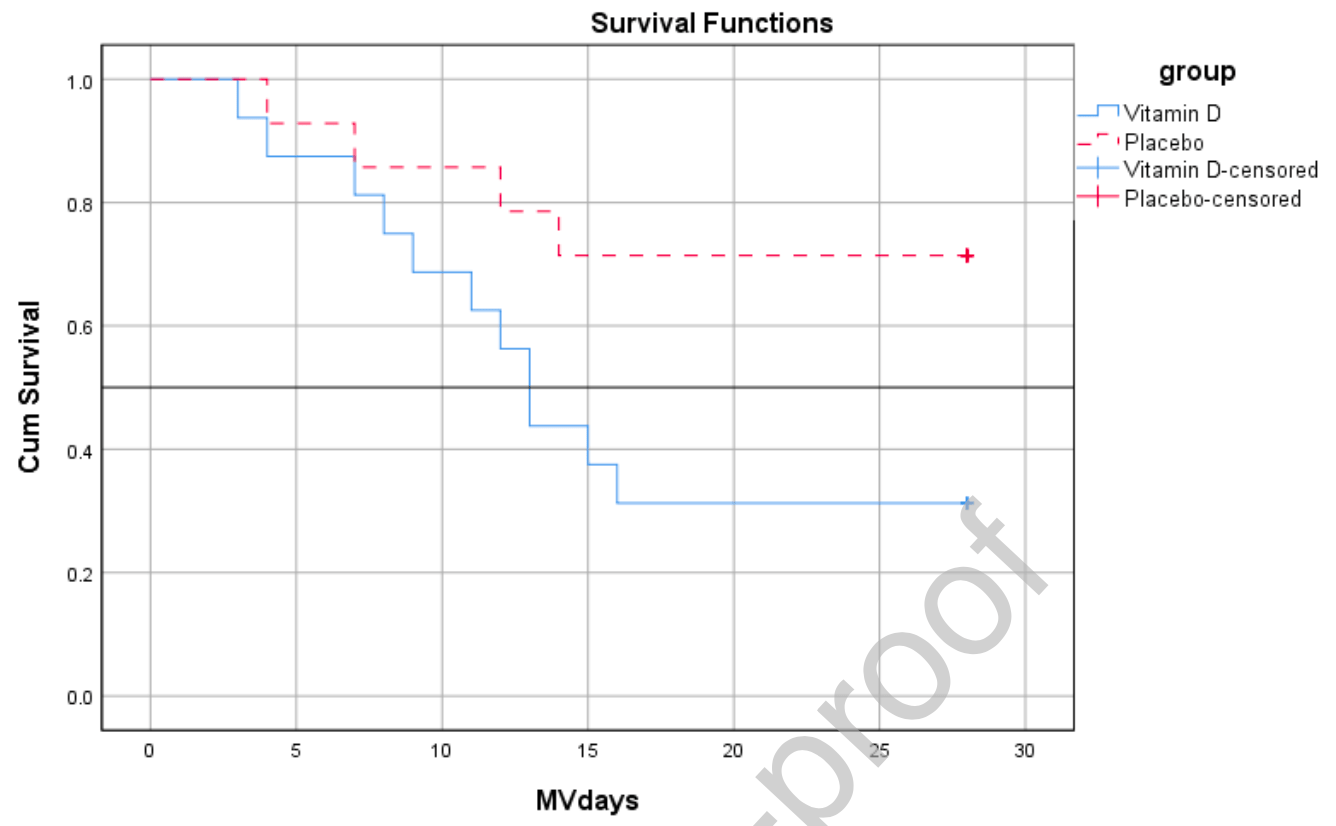
RCT of 30 ventilated ICU patients showing lower mortality with vitamin D treatment, RR 0.36, p = 0.004. Authors do not indicate why the patients were hospitalized or if any of the patients were COVID-19 patients. 300,000 IU intramuscular vitamin D was used.
Cholecalciferol was used in this study.
Meta-analysis shows that late stage treatment with calcitriol / calcifediol (or
paricalcitol, alfacalcidol, etc.) is more effective than cholecalciferol: 66% [47‑78%] lower risk vs. 44% [33‑53%] lower risk.
Cholecalciferol requires two hydroxylation steps to become activated - first
in the liver to calcifediol, then in the kidney to calcitriol. Calcitriol,
paricalcitol, and alfacalcidol are active vitamin D analogs that do not
require conversion. This allows them to have more rapid onset of action
compared to cholecalciferol. The time delay for cholecalciferol to increase
serum calcifediol levels can be 2-3 days, and the delay for converting
calcifediol to active calcitriol can be up to 7 days.
Bolus treatment is less effective.
Pharmacokinetics and the potential side effects of high bolus doses suggest
that ongoing treatment spread over time is more appropriate.
Research has confirmed that lower dose regular treatment with vitamin D is more
effective than intermittent high-dose bolus treatment for various conditions,
including rickets and acute respiratory infections1,2. The biological mechanisms supporting these
findings involve the induction of enzymes such as 24-hydroxylase and
fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) by high-dose bolus treatments. These
enzymes play roles in inactivating vitamin D, which can paradoxically reduce
levels of activated vitamin D and suppress its activation for extended periods
post-dosage. Evidence indicates that 24-hydroxylase activity may remain
elevated for several weeks following a bolus dose, leading to reduced levels
of the activated form of vitamin D. Additionally, FGF23 levels can increase
for at least three months after a large bolus dose, which also contributes to
the suppression of vitamin D activation1.
|
risk of death, 63.5% lower, RR 0.36, p = 0.004, treatment 5 of 16 (31.2%), control 12 of 14 (85.7%), NNT 1.8.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Sistanizad et al., 26 Dec 2020, Randomized Controlled Trial, Iran, peer-reviewed, 8 authors, dosage 300,000IU single dose, intramuscular.
High dose vitamin D improves total serum antioxidant capacity and ICU outcome in critically ill patients - A randomized, double-blind clinical trial
European Journal of Integrative Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101271
Introduction: Mechanical ventilation can increase the rate of free radicals in the systemic circulation due to its effect on the inflammatory system. Previous research has suggested that vitamin D has antioxidant properties. This study aimed to evaluate the effect of vitamin D on total Antioxidant Capacity (TAC) and its relationship with ICU patients' outcomes . Methods: In this prospective randomized clinical trial, 36 ventilated ICU patients were randomly allocated to receive either a single intramuscular vitamin D 300,000 IU or its placebo. Serum Vitamin D and TAC were measured before and on day 7 after the intervention. Clinical Pulmonary Infection Score (CPIS) and sequential organ failure assessment (SOFA) scores were measured daily for seven days and on days 14 and 28. Results: Thirty patients completed the study. The results show that injection of vitamin D leads to a significant increase in the mean changes of vitamin D level on the seventh day of the study ( + 3.5 ± 1.3 vs -0.4 ± 0.2 P = 0.00) and TAC levels (3.2 ± 3.9 vs -2.0 ± 2.6 P = 0.00. ICU length of stay was 18.3 ± 8.4 and 25.4 ± 6.6 days in the intervention and placebo arms of the study. Twelve patients in the placebo group and 5 in the vitamin D group died within the 28 day study period. The duration of mechanical ventilation was 15.7 ± 9.3 vs. 22.6 ± 9.1 days in vitamin D and placebo arms, respectively. Conclusion: : Administration of vitamin D may increase TAC levels and decrease the length of stay and duration of mechanical ventilation in ICU patients.
Author contributions MS: study design, data collection, data analysis, conducting the study, and drafting the manuscript. MK: study design, conducting the study, and supervised the study. MMM, SPS, and SS: study design and conducting the study. FMV: data collection, statistical analysis. HSK: statistical analysis and reviewing the paper. RQG: reviewing the paper, writing the final approval, and data analysis.
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declared that there is no conflict of interest.
Supplementary materials Supplementary material associated with this article can be found, in the online version, at doi: 10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101271 .
References
Amrein, Christopher, Mcnally, Understanding vitamin D deficiency in intensive care patients, Intensive Care Med
Amrein, Papinutti, Mathew, Vila, Parekh, Vitamin D and critical illness: what endocrinology can learn from intensive care and vice versa, Endocr. Connect
Amrein, Schnedl, Holl, Riedl, Christopher et al., Effect of high-dose vitamin D3 on hospital length of stay in critically ill patients with vitamin D deficiency: the VITdAL-ICU randomized clinical trial, Jama
Amrein, Sourij, Wagner, Holl, Pieber et al., Short-term effects of high-dose oral vitamin D3 in critically ill vitamin D deficient patients: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study, Crit. Care
Amrein, Zajic, Schnedl, Waltensdorfer, Fruhwald et al., Vitamin D status and its association with season, hospital and sepsis mortality in critical illness, Crit. Care
Aygencel, Turkoglu, Tuncel, Cand I R, Bildac I et al., Is vitamin D insufficiency associated with mortality of critically ill patients?, Crit. Care Res. Pract
Bacon, Gamble, Horne, Scott, Reid, High-dose oral vitamin D 3 supplementation in the elderly, Osteoporos. Int
Baeke, Takiishi, Korf, Gysemans, Mathieu, Vitamin D: modulator of the immune system, Curr. Opin. Pharmacol
Bikle, Nonclassic actions of vitamin D, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab
Braun, Chang, Mahadevappa, Gibbons, Liu et al., Association of low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and mortality in the critically ill, Crit. Care Med
Chirumbolo, Bjørklund, Sboarina, Vella, The role of vitamin D in the immune system as a pro-survival molecule, Clin. Ther
De Haan, Groeneveld, De Geus, Egal, Struijs, Vitamin D deficiency as a risk factor for infection, sepsis and mortality in the critically ill: systematic review and meta-analysis, Crit. Care
Gorman, Zafirau, Lim, Clarke, Dhamrait et al., High-dose intramuscular vitamin D provides long-lasting moderate increases in serum 25-hydroxvitamin D levels and shorter-term changes in plasma Calcium, J. AOAC Int
Han, Jones, Tangpricha, Brown, Hao et al., High dose vitamin D administration in ventilated intensive care unit patients: a pilot double blind randomized controlled trial, J. Clin. Transl. Endocrinol
Higgins, Wischmeyer, Queensland, Sillau, Sufit et al., Relationship of vitamin D deficiency to clinical outcomes in critically ill patients, J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr
Jeng, Yamshchikov, Judd, Blumberg, Martin et al., Alterations in vitamin D status and anti-microbial peptide levels in patients in the intensive care unit with sepsis, J. Transl. Med
Leyba, Gonzalez, Alonso, Guidelines for specialized nutritional and metabolic support in the critically-ill patient. update. consensus SEMICYUC-SENPE: Septic patient, Nutr. Hosp
Luna, Blanzaco, Niederman, Matarucco, Baredes et al., Resolution of ventilator-associated pneumonia: prospective evaluation of the clinical pulmonary infection score as an early clinical predictor of outcome, Crit. Care Med
Martineau, Jolliffe, Hooper, Greenberg, Aloia et al., Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data, BMJ
Martucci, Mcnally, Parekh, Zajic, Tuzzolino et al., Trying to identify who may benefit most from future vitamin D intervention trials: a post hoc analysis from the VITDAL-ICU study excluding the early deaths, Crit. Care
Matthews, Ahmed, Wilson, Griggs, Danner, Worsening severity of vitamin D deficiency is associated with increased length of stay, surgical intensive care unit cost, and mortality rate in surgical intensive care unit patients, Am. J. Surg
Mcnally, Nama, O'hearn, Sampson, Amrein et al., Vitamin D deficiency in critically ill children: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Crit. Care
Mcnally, Vitamin D as a modifiable risk factor in critical illness: questions and answers provided by observational studies, J. Pediatr
Miri, Kouchek, Dahmardeh, Sistanizad, Effect of high-dose vitamin D on duration of mechanical ventilation in ICU patients, Iran, J. Pharm. Res. IJPR
Miroliaee, Salamzadeh, Shokouhi, Fatemi, Ardehali et al., Effect of vitamin D supplementation on procalcitonin as prognostic biomarker in patients with ventilator associated pneumonia complicated with vitamin D deficiency, Iran, J. Pharm. Res. IJPR
Mistraletti, Paroni, Umbrello, D'amato, Sabbatini et al., Melatonin pharmacological blood levels increase total antioxidant capacity in critically ill patients, Int. J. Mol. Sci
Mokhtari, Hekmatdoost, Nourian, Antioxidant efficacy of vitamin D, J. Parathyr. Dis
Moromizato, Litonjua, Braun, Gibbons, Giovannucci et al., Association of low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and sepsis in the critically ill, Crit. Care Med
Palacios, Gonzalez, Is vitamin D deficiency a major global public health problem?, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol
Perron, Lee, Efficacy of high-dose vitamin D supplementation in the critically ill patients, Inflamm. Allergy-Drug Targets, Formerly Curr. Drug Targets-Inflammation Allergy)
Prietl, Treiber, Pieber, Amrein, Vitamin D and immune function, Nutrients
Quraishi, Bittner, Blum, Mccarthy, Bhan et al., Prospective study of vitamin D status at initiation of care in critically ill surgical patients and risk of 90-day mortality, Crit. Care Med
Quraishi, Mccarthy, Blum, Cobb, Camargo, Plasma 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels at initiation of care and duration of mechanical ventilation in critically ill surgical patients, J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr
Raman, Orun ; Jin, Han, Md, Sc, Vitamin D to improve outcomes by leveraging early treatment: long-term brain outcomes in vitamin D deficient patients (VIOLET-BUD) trial registration
Seligman, Seligman, Teixeira, Comparing the accuracy of predictors of mortality in ventilator-associated pneumonia, J. Bras. Pneumol
Venkatram, Chilimuri, Adrish, Salako, Patel et al., Vitamin D deficiency is associated with mortality in the medical intensive care unit, Crit. Care
Vieth, Critique of the considerations for establishing the tolerable upper intake level for vitamin D: critical need for revision upwards, J. Nutr
Yang, Wang ; Zhonghua, He, Hu, Value of the clinical pulmonary infection score for the prognosis of ventilator-associated pneumonia, J. Tuberc. Respir. Dis
Youssef, Ranasinghe, Grant, Peiris, Vitamin D's potential to reduce the risk of hospital-acquired infections, Dermatoendocrinol
Zajic, Amrein, Vitamin D deficiency in the ICU: a systematic review, Minerva Endocrinol
Zhang, Wan, Sun, Kan, Wang, Association between vitamin D deficiency and mortality in critically ill adult patients: a meta-analysis of cohort studies, Crit. Care
Zittermann, Kuhn, Dreier, Knabbe, Gummert et al., Vitamin D status and the risk of major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events in cardiac surgery, Eur. Heart J
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101271",
"ISSN": [
"1876-3820"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101271",
"alternative-id": [
"S1876382020314529"
],
"article-number": "101271",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "High dose vitamin D improves total serum antioxidant capacity and ICU outcome in critically ill patients - A randomized, double-blind clinical trial"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "European Journal of Integrative Medicine"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101271"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2020 Elsevier GmbH. All rights reserved."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sistanizad",
"given": "Mohammad",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kouchek",
"given": "Mehran",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Miri",
"given": "MirMohammad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Salarian",
"given": "Sara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shojaei",
"given": "Seyedpouzhia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moeini Vasegh",
"given": "Fatemeh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Seifi Kafshgari",
"given": "Hossein",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Qobadighadikolaei",
"given": "Roja",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "European Journal of Integrative Medicine",
"container-title-short": "European Journal of Integrative Medicine",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.com",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.fr",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
12,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2020-12-26T15:48:39Z",
"timestamp": 1608997719000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2021-03-19T12:08:38Z",
"timestamp": 1616155718000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100005851",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2024-02-05T23:24:38Z",
"timestamp": 1707175478536
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 6,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-02-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1612137600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1876382020314529?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1876382020314529?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "101271",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1210/jc.2008-1454",
"article-title": "Nonclassic actions of vitamin D",
"author": "Bikle",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "26",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab.",
"key": "10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101271_bib0001",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1530/EC-18-0184",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and critical illness: what endocrinology can learn from intensive care and vice versa",
"author": "Amrein",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "R304",
"journal-title": "Endocr. Connect.",
"key": "10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101271_bib0002",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.i6583",
"article-title": "Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory tract infections: systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data",
"author": "Martineau",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "i6583",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101271_bib0003",
"volume": "356",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu5072502",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and immune function",
"author": "Prietl",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2502",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101271_bib0004",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-014-0660-4",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency as a risk factor for infection, sepsis and mortality in the critically ill: systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "de Haan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "660",
"journal-title": "Crit. Care.",
"key": "10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101271_bib0005",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clinthera.2017.03.021",
"article-title": "The role of vitamin D in the immune system as a pro-survival molecule",
"author": "Chirumbolo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "894",
"journal-title": "Clin. Ther.",
"key": "10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101271_bib0006",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2013.11.003",
"article-title": "Is vitamin D deficiency a major global public health problem?",
"author": "Palacios",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "138",
"journal-title": "J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101271_bib0007",
"volume": "144",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency in the ICU: a systematic review",
"author": "Zajic",
"first-page": "275",
"journal-title": "Minerva Endocrinol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101271_bib0008",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"article-title": "Efficacy of high-dose vitamin D supplementation in the critically ill patients",
"author": "Perron",
"first-page": "273",
"journal-title": "Inflamm. Allergy-Drug Targets (Formerly Curr. Drug Targets-Inflammation Allergy).",
"key": "10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101271_bib0009",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CCM.0b013e318206ccdf",
"article-title": "Association of low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and mortality in the critically ill",
"author": "Braun",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "671",
"journal-title": "Crit. Care Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101271_bib0010",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00134-015-3937-4",
"article-title": "Understanding vitamin D deficiency in intensive care patients",
"author": "Amrein",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1961",
"journal-title": "Intensive Care Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101271_bib0011",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CCM.0000000000000210",
"article-title": "Prospective study of vitamin D status at initiation of care in critically ill surgical patients and risk of 90-day mortality",
"author": "Quraishi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1365",
"journal-title": "Crit. Care Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101271_bib0012",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-017-1875-y",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency in critically ill children: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "McNally",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "287",
"journal-title": "Crit. Care.",
"key": "10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101271_bib0013",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jped.2013.12.002",
"article-title": "Vitamin D as a modifiable risk factor in critical illness: questions and answers provided by observational studies",
"author": "McNally",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "99",
"journal-title": "J. Pediatr. (Rio. J).",
"key": "10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101271_bib0014",
"volume": "90",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/cc10120",
"article-title": "Short-term effects of high-dose oral vitamin D3 in critically ill vitamin D deficient patients: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study",
"author": "Amrein",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "R104",
"journal-title": "Crit. Care.",
"key": "10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101271_bib0015",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00198-008-0814-9",
"article-title": "High-dose oral vitamin D 3 supplementation in the elderly",
"author": "Bacon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1407",
"journal-title": "Osteoporos. Int.",
"key": "10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101271_bib0016",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jn/136.4.1117",
"article-title": "Critique of the considerations for establishing the tolerable upper intake level for vitamin D: critical need for revision upwards",
"author": "Vieth",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1117",
"journal-title": "J. Nutr.",
"key": "10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101271_bib0017",
"volume": "136",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-019-2472-z",
"article-title": "Trying to identify who may benefit most from future vitamin D intervention trials: a post hoc analysis from the VITDAL-ICU study excluding the early deaths",
"author": "Martucci",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "200",
"journal-title": "Crit. Care.",
"key": "10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101271_bib0018",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CCM.0b013e31829eb7af",
"article-title": "Association of low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and sepsis in the critically ill",
"author": "Moromizato",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "97",
"journal-title": "Crit. Care Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101271_bib0019",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-014-0684-9",
"article-title": "Association between vitamin D deficiency and mortality in critically ill adult patients: a meta-analysis of cohort studies",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "684",
"journal-title": "Crit. Care.",
"key": "10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101271_bib0020",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"article-title": "Antioxidant efficacy of vitamin D",
"author": "Mokhtari",
"first-page": "11",
"journal-title": "J. Parathyr. Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101271_bib0021",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"article-title": "Effect of high-dose vitamin D on duration of mechanical ventilation in ICU patients",
"author": "Miri",
"first-page": "1067",
"journal-title": "Iran. J. Pharm. Res. IJPR.",
"key": "10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101271_bib0022",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"article-title": "High dose vitamin D administration in ventilated intensive care unit patients: a pilot double blind randomized controlled trial",
"author": "Han",
"first-page": "59",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Transl. Endocrinol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101271_bib0023",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"article-title": "Guidelines for specialized nutritional and metabolic support in the critically-ill patient. update. consensus SEMICYUC-SENPE: Septic patient",
"author": "Leyba",
"first-page": "67",
"journal-title": "Nutr. Hosp.",
"key": "10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101271_bib0024",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4161/derm.20789",
"article-title": "Vitamin D's potential to reduce the risk of hospital-acquired infections",
"author": "Youssef",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "167",
"journal-title": "Dermatoendocrinol",
"key": "10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101271_bib0025",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0148607114566276",
"article-title": "Plasma 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels at initiation of care and duration of mechanical ventilation in critically ill surgical patients",
"author": "Quraishi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "273",
"journal-title": "J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr.",
"key": "10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101271_bib0026",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"article-title": "Effect of vitamin D supplementation on procalcitonin as prognostic biomarker in patients with ventilator associated pneumonia complicated with vitamin D deficiency",
"author": "Miroliaee",
"first-page": "1254",
"journal-title": "Iran. J. Pharm. Res. IJPR.",
"key": "10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101271_bib0027",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms18040759",
"article-title": "Melatonin pharmacological blood levels increase total antioxidant capacity in critically ill patients",
"author": "Mistraletti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "759",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Mol. Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101271_bib0028",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2014.13204",
"article-title": "Effect of high-dose vitamin D3 on hospital length of stay in critically ill patients with vitamin D deficiency: the VITdAL-ICU randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Amrein",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1520",
"journal-title": "Jama",
"key": "10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101271_bib0029",
"volume": "312",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1479-5876-7-28",
"article-title": "Alterations in vitamin D status and anti-microbial peptide levels in patients in the intensive care unit with sepsis",
"author": "Jeng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "28",
"journal-title": "J. Transl. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101271_bib0030",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.coph.2010.04.001",
"article-title": "Vitamin D: modulator of the immune system",
"author": "Baeke",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "482",
"journal-title": "Curr. Opin. Pharmacol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101271_bib0031",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"article-title": "Is vitamin D insufficiency associated with mortality of critically ill patients?",
"author": "Aygencel",
"first-page": "2013",
"journal-title": "Crit. Care Res. Pract.",
"key": "10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101271_bib0032",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D to improve outcomes by leveraging early treatment: long-term brain outcomes in vitamin D deficient patients (VIOLET-BUD) trial registration",
"author": "Raman",
"key": "10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101271_bib0033",
"series-title": "https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03733418 Principal Investigator Jin H. Han, MD, M. Sc.",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/eurheartj/ehs468",
"article-title": "Vitamin D status and the risk of major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events in cardiac surgery",
"author": "Zittermann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1358",
"journal-title": "Eur. Heart J.",
"key": "10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101271_bib0034",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0148607112444449",
"article-title": "Relationship of vitamin D deficiency to clinical outcomes in critically ill patients",
"author": "Higgins",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "713",
"journal-title": "J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr.",
"key": "10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101271_bib0035",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.amjsurg.2011.07.021",
"article-title": "Worsening severity of vitamin D deficiency is associated with increased length of stay, surgical intensive care unit cost, and mortality rate in surgical intensive care unit patients",
"author": "Matthews",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "37",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Surg.",
"key": "10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101271_bib0036",
"volume": "204",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/cc13790",
"article-title": "Vitamin D status and its association with season, hospital and sepsis mortality in critical illness",
"author": "Amrein",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "R47",
"journal-title": "Crit. Care.",
"key": "10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101271_bib0037",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/cc10585",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency is associated with mortality in the medical intensive care unit",
"author": "Venkatram",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "R292",
"journal-title": "Crit. Care.",
"key": "10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101271_bib0038",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5740/jaoacint.17-0087",
"article-title": "High-dose intramuscular vitamin D provides long-lasting moderate increases in serum 25-hydroxvitamin D levels and shorter-term changes in plasma Calcium",
"author": "Gorman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1337",
"journal-title": "J. AOAC Int.",
"key": "10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101271_bib0039",
"volume": "100",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"article-title": "Value of the clinical pulmonary infection score for the prognosis of ventilator-associated pneumonia, Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi= Zhonghua Jiehe He Huxi",
"author": "Yang",
"first-page": "751",
"journal-title": "Zazhi= Chinese J. Tuberc. Respir. Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101271_bib0040",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/01.CCM.0000055380.86458.1E",
"article-title": "Resolution of ventilator-associated pneumonia: prospective evaluation of the clinical pulmonary infection score as an early clinical predictor of outcome",
"author": "Luna",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "676",
"journal-title": "Crit. Care Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101271_bib0041",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1590/S1806-37132011000400012",
"article-title": "Comparing the accuracy of predictors of mortality in ventilator-associated pneumonia",
"author": "Seligman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "495",
"journal-title": "J. Bras. Pneumol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.eujim.2020.101271_bib0042",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2011"
}
],
"reference-count": 42,
"references-count": 42,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1876382020314529"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "High dose vitamin D improves total serum antioxidant capacity and ICU outcome in critically ill patients - A randomized, double-blind clinical trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "42"
}
