COVID-19 Pneumonia and Gut Inflammation: The Role of a Mix of Three Probiotic Strains in Reducing Inflammatory Markers and Need for Oxygen Support
et al., Journal of Clinical Medicine, doi:10.3390/jcm11133758, Jun 2022
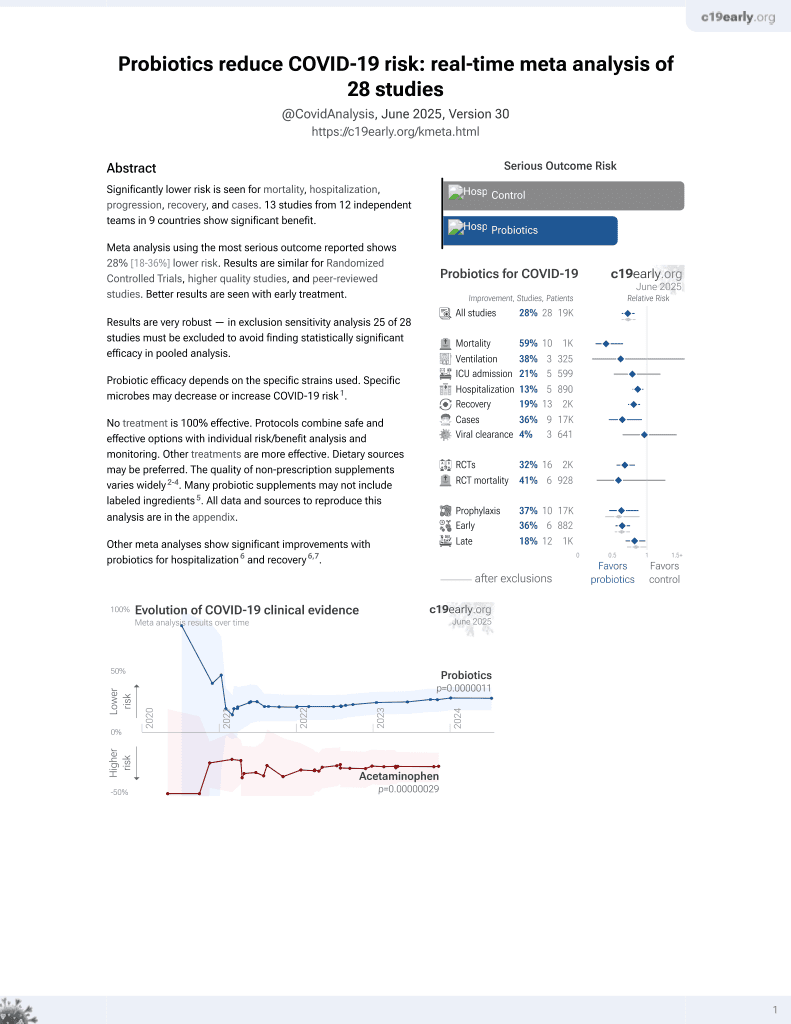
Probiotics for COVID-19
20th treatment shown to reduce risk in
March 2021, now with p = 0.00000044 from 29 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
RCT 80 COVID-19 interstitial pneumonia patients in Italy, 40 treated with probiotics, showing significantly reduced gut inflammatory markers with treatment, and lower ICU admission and mortality, without statistical significance. Bifidobacterium lactis LA 304, lactobacillus salivarius LA 302, and lactobacillus acidophilus LA 201 bid for 10 days.
Probiotic efficacy depends on the specific strains used. Specific microbes may decrease or increase COVID-19 risk1.
Although the 67% lower mortality is not statistically significant, it is consistent with the significant 59% lower mortality [35‑74%] from meta-analysis of the 10 mortality results to date.
|
risk of death, 66.7% lower, RR 0.33, p = 1.00, treatment 0 of 40 (0.0%), control 1 of 40 (2.5%), NNT 40, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 85.7% lower, RR 0.14, p = 0.24, treatment 0 of 40 (0.0%), control 3 of 40 (7.5%), NNT 13, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
hospitalization time, 26.3% lower, relative time 0.74, p = 0.52, treatment mean 14.0 (±6.0) n=40, control mean 19.0 (±10.0) n=40.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Saviano et al., 28 Jun 2022, Randomized Controlled Trial, Italy, peer-reviewed, mean age 59.8, 9 authors.
Contact: veronica.ojetti@policlinicogemelli.it (corresponding author), angela.saviano@policlinicogemelli.it, alessio.migneco@policlinicogemelli.it, flavia.nasella@gmail.com, francesco.franceschi@policlinicogemelli.it, annalisa.potenza@policlinicogemelli.it, claudia.tarli@policlinicogemelli.it, valentina.siciliano@policlinicogemelli.it, carminepetruzziello@live.it.
COVID-19 Pneumonia and Gut Inflammation: The Role of a Mix of Three Probiotic Strains in Reducing Inflammatory Markers and Need for Oxygen Support
Journal of Clinical Medicine, doi:10.3390/jcm11133758
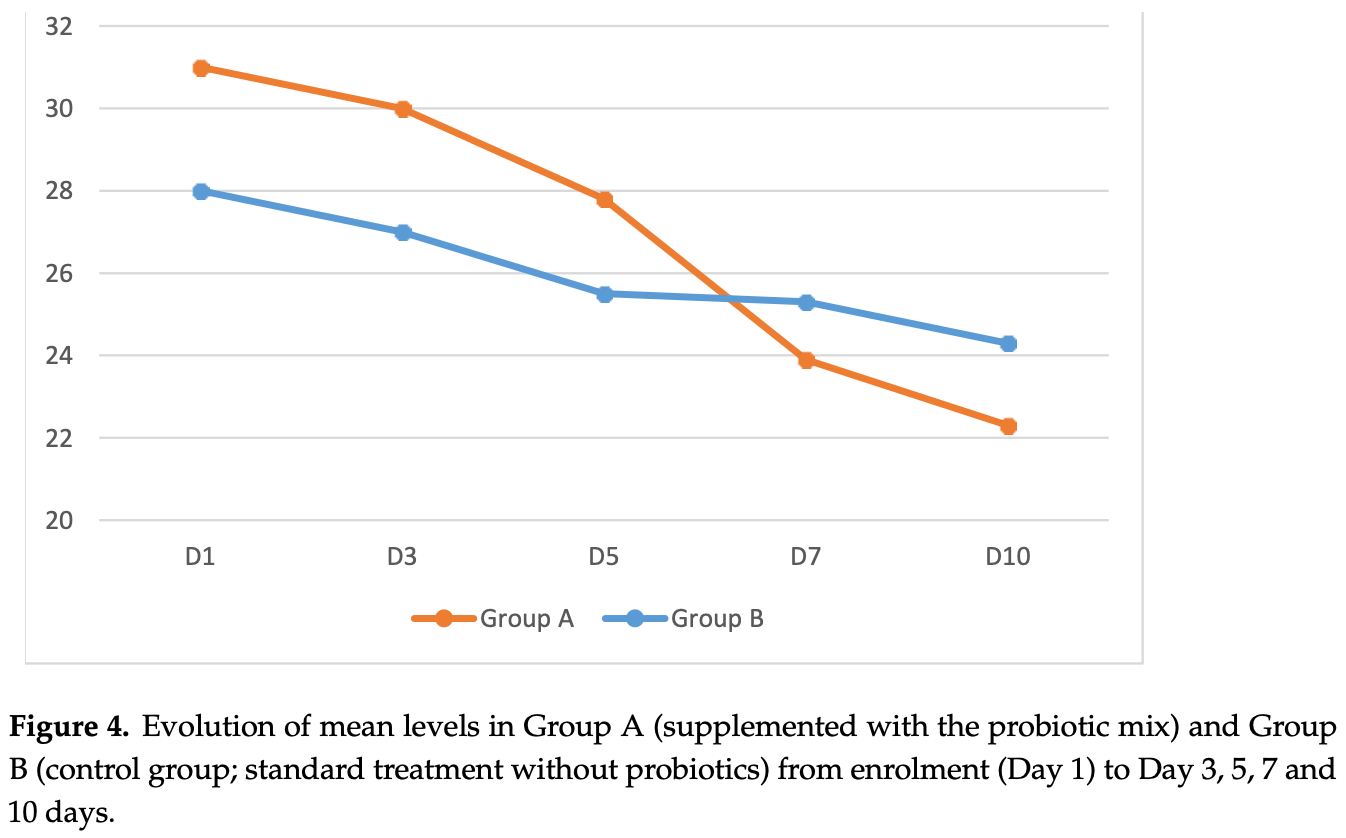
Background: COVID-19 disease, which typically presents with respiratory symptoms, can trigger intestinal inflammation through SARS-CoV-2 replication in the gastrointestinal tract. Supplementation with probiotics may have beneficial effects on gut inflammation due to their analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties. The primary objective of our study was to evaluate the efficacy of a mix of three probiotic strains (Bifidobacterium lactis LA 304, Lactobacillus salivarius LA 302, and Lactobacillus acidophilus LA 201; Lactibiane Iki ® ) in the reduction in fecal calprotectin in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia, compared to a control group. The secondary aim was to evaluate the reduction in oxygen support and length of hospital stay in patients taking the probiotic mix. Patients and Methods: We conducted a prospective randomized controlled trial at Fondazione Policlinico Gemelli, Rome. We enrolled patients with COVID-19 interstitial pneumonia. One group received the probiotic mix twice a day for 10 days in addition to the standard COVID-19 therapy, and a second group received standard COVID-19 therapy without probiotics. We administered oxygen support (through Ventimask or Optiflow ® ) on days (D) 1, 3, 5, 7 and 10, and the level of fecal calprotectin between D3-D5 and D7-D10. Results: A total of 80 patients (44 M/36 F; mean age: 59.8 ± 17.3) were enrolled with a mean value of calprotectin at enrollment of 140 mg/dL. At D7-10, the probiotic group showed a 35% decrease in fecal calprotectin compared to 16% in the control group, a decrease in C-reactive protein (CRP) of 72.7% compared to 62%, and a slight but not significant decrease in oxygen support compared to the control group. Conclusion: Supplementation with a mix of probiotics for 10 days in patients with COVID-19 interstitial pneumonia significantly reduces inflammatory markers.
Institutional Review Board Statement: The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of Fondazione Policlinico Universitario A. Gemelli Hospital, Rome (authorization #ID3786). Informed Consent Statement: Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Conflicts of Interest: All the authors declare no conflict of interests.
References
Channappanavar, Perlman, Pathogenic human coronavirus infections: Causes and consequences of cytokine storm and immunopathology, Semin. Immunopathol, doi:10.1007/s00281-017-0629-x
Cristofori, Dargenio, Miniello, Barone, Francavilla, Anti-Inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Effects of Pro-biotics in Gut Inflammation: A Door to the Body, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.578386
Foligne, Nutten, Grangette, Dennin, Goudercourt et al., Correlation between in vitro and in vivo immunomodulatory properties of lactic acid bacteria, World J. Gastroenterol, doi:10.3748/wjg.v13.i2.236
Gu, Han, Wang, COVID-19: Gastrointestinal Manifestations and Potential Fecal-Oral Transmission, Gastroenterology, doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.02.054
Gutiérrez-Castrellón, Gandara-Martí, Abreu, Nieto-Rufino, López-Orduña et al., Probiotic improves symptomatic and viral clearance in Covid19 outpatients: A randomized, quadruple-blinded, placebo-controlled trial, Gut Microbes, doi:10.1080/19490976.2021.2018899
Hsu, Chia, Lim, The Novel Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) Epidemic, Ann. Acad. Med. Singap, doi:10.47102/annals-acadmedsg.202051
Jin, Cai, Cheng, Wang, Wang, A rapid advice guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of 2019 novel coro-navirus (2019-nCoV) infected pneumonia, Mil. Med. Res
Li, Hsu, Chang, Shih, Combination of Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis Shows a Stronger Anti-Inflammatory Effect than Individual Strains in HT-29 Cells, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu11050969
Ojetti, Saviano, Covino, Acampora, Troiani et al., COVID-19 and intestinal inflammation: Role of fecal calprotectin, Dig. Liver Dis, doi:10.1016/j.dld.2020.09.015
Petruzziello, Marannino, Migneco, Brigida, Saviano et al., The efficacy of a mix of three probiotic strains in reducing abdominal pain and inflammatory biomarkers in acute uncomplicated diverticulitis, Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci, doi:10.1016/S1590-8658(20)30782-9
Ren, Wang, Liu, Guo, Dai, When COVID-19 encounters interstitial lung disease: Challenges and management, Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi
Sánchez, Delgado, Blanco-Míguez, Lourenço, Gueimonde et al., Probiotics, gut microbiota, and their influence on host health and disease, Mol. Nutr. Food Res, doi:10.1002/mnfr.201600240
Wong, Lui, Sung, Covid-19 and the Digestive System, J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol, doi:10.1111/jgh.15047
Yates, Zaccardi, Islam, Baillie, Malcolm et al., Obesity, chronic disease, age, and in-hospital mortality in patients with COVID-19: Analysis of ISARIC clinical characterisation protocol UK cohort, BMC Infect. Dis, doi:10.1186/s12879-021-06466-0
Ye, Zhang, Wang, Huang, Song, Chest CT manifestations of new coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A pictorial review, Eur. Radiol, doi:10.1007/s00330-020-06801-0
Zhang, Li, Wang, Tan, Zhang et al., The Cross-Talk Between Gut Microbiota and Lungs in Common Lung Diseases, Front Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2020.00301
Zhu, Wei, Niu, The novel coronavirus outbreak in Wuhan, China, Glob. Health Res. Policy, doi:10.1186/s41256-020-00135-6
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm11133758",
"ISSN": [
"2077-0383"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/jcm11133758",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Background: COVID-19 disease, which typically presents with respiratory symptoms, can trigger intestinal inflammation through SARS-CoV-2 replication in the gastrointestinal tract. Supplementation with probiotics may have beneficial effects on gut inflammation due to their analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties. The primary objective of our study was to evaluate the efficacy of a mix of three probiotic strains (Bifidobacterium lactis LA 304, Lactobacillus salivarius LA 302, and Lactobacillus acidophilus LA 201; Lactibiane Iki®) in the reduction in fecal calprotectin in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia, compared to a control group. The secondary aim was to evaluate the reduction in oxygen support and length of hospital stay in patients taking the probiotic mix. Patients and Methods: We conducted a prospective randomized controlled trial at Fondazione Policlinico Gemelli, Rome. We enrolled patients with COVID-19 interstitial pneumonia. One group received the probiotic mix twice a day for 10 days in addition to the standard COVID-19 therapy, and a second group received standard COVID-19 therapy without probiotics. We administered oxygen support (through Ventimask or Optiflow®) on days (D) 1, 3, 5, 7 and 10, and the level of fecal calprotectin between D3–D5 and D7–D10. Results: A total of 80 patients (44 M/36 F; mean age: 59.8 ± 17.3) were enrolled with a mean value of calprotectin at enrollment of 140 mg/dl. At D7–10, the probiotic group showed a 35% decrease in fecal calprotectin compared to 16% in the control group, a decrease in C-reactive protein (CRP) of 72.7% compared to 62%, and a slight but not significant decrease in oxygen support compared to the control group. Conclusion: Supplementation with a mix of probiotics for 10 days in patients with COVID-19 interstitial pneumonia significantly reduces inflammatory markers.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"jcm11133758"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saviano",
"given": "Angela",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Potenza",
"given": "Annalisa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Siciliano",
"given": "Valentina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1025-1092",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Petruzziello",
"given": "Carmine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tarli",
"given": "Claudia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Migneco",
"given": "Alessio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nasella",
"given": "Flavia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Franceschi",
"given": "Francesco",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8953-0707",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ojetti",
"given": "Veronica",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of Clinical Medicine",
"container-title-short": "JCM",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-29T05:48:38Z",
"timestamp": 1656481718000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-01T08:06:10Z",
"timestamp": 1656662770000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-01T08:43:28Z",
"timestamp": 1656665008906
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "13",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
28
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "13",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-28T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1656374400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2077-0383/11/13/3758/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "3758",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
28
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
28
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"article-title": "When COVID-19 encounters interstitial lung disease: Challenges and management",
"author": "Ren",
"first-page": "E039",
"journal-title": "Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi",
"key": "ref1",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.47102/annals-acadmedsg.202051",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00330-020-06801-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s41256-020-00135-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref4"
},
{
"article-title": "A rapid advice guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of 2019 novel coro-navirus (2019-nCoV) infected pneumonia",
"author": "Jin",
"first-page": "4",
"journal-title": "Mil. Med. Res.",
"key": "ref5",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jgh.15047",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-021-06466-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00281-017-0629-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dld.2020.09.015",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmicb.2020.00301",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref10"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1590-8658(20)30782-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2020.02.054",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref12"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/mnfr.201600240",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.578386",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/19490976.2021.2018899",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3748/wjg.v13.i2.236",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref16"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu11050969",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref17"
}
],
"reference-count": 17,
"references-count": 17,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2077-0383/11/13/3758"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "COVID-19 Pneumonia and Gut Inflammation: The Role of a Mix of Three Probiotic Strains in Reducing Inflammatory Markers and Need for Oxygen Support",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "11"
}