The Distinct Regulation of the Vitamin D and Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptors in COVID-19
et al., Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu16050598, Feb 2024
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 136 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
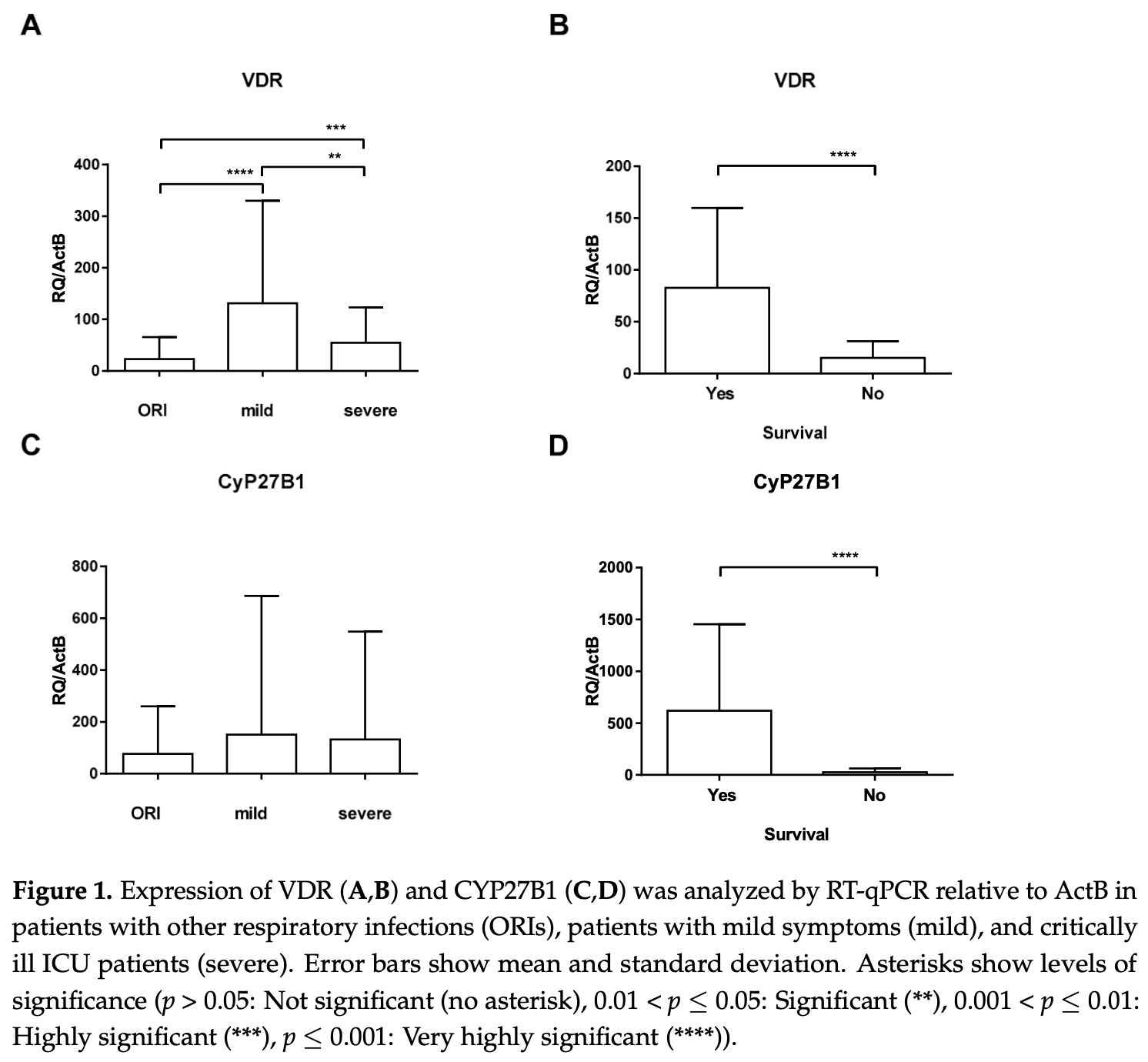
Observational study of 240 COVID-19 patients showing vitamin D receptor (VDR) expression significantly upregulated in mild cases compared to controls, but impaired upregulation in critically ill patients. Patients who died had profound downregulation of VDR and CYP27B1 compared to survivors. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) was significantly upregulated in both mild and critically ill patients. Authors propose evaluating combination treatment with antiviral drugs and vitamin D for potentially improved prognosis.
Robak et al., 22 Feb 2024, retrospective, Austria, peer-reviewed, 5 authors.
Contact: oliver.robak@meduniwien.ac.at (corresponding author), marie-theres.kastner@meduniwien.ac.at, christoph.steininger@meduniwien.ac.at, astrid.voill-glaninger@gesundheitsverbund.at, andre.viveiros@gesundheitsverbund.at.
The Distinct Regulation of the Vitamin D and Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptors in COVID-19
Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu16050598
1) Background: SARS-CoV-2 affects several immune pathways, including the vitamin D (VDR) and the aryl hydrocarbon receptor pathways (AhR). The aim of the study was the evaluation of the VDR and AhR pathways in the blood of COVID-19 patients with regard to the severity of disease. (2) Methods: Observational, single-center, case-control design. A total of 240 samples were selected for exploration. Patients who tested negative for SARS-CoV-2 but suffered from other respiratory infections (ORIs) served as a control group. (3) Results: VDR-specific mRNA in the blood of patients with mild symptoms (131.2 ± 198.6) was significantly upregulated relative to the VDR expression of the ORI group (23.24 ± 42.60; p < 0.0001); however, VDR expression of critically ill patients showed an impaired upregulation (54.73 ± 68.34; p < 0.001). CYP27B1 expression was not significantly regulated during SARS-CoV-2 infection. There was a downregulation of VDR and CYP27B1 compared to survivors. There was no significant difference in 25(OH)-vitamin D3 levels between critically ill patients with regard to survival (24.3 ± 9.4 vs. 27.1 ± 11.3; p = 0.433). ( 4 ) Conclusion: The VDR and AhR pathways are distinctively regulated in patients suffering from COVID-19 depending on the severity of disease. A combination treatment of antiviral drugs and vitamin D substitution should be evaluated for potentially improved prognosis in COVID-19.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Abdollahzadeh, Shushizadeh, Barazandehrokh, Choopani, Azarnezhad et al., Association of Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms and clinical/severe outcomes of COVID-19 patients, Infect. Genet. Evol, doi:10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098
Ao, Kikuta, Ishii, The Effects of Vitamin D on Immune System and Inflammatory Diseases, Biomolecules, doi:10.3390/biom11111624
Apaydin, Polat, Dincer Yazan, Ilgin, Elbasan et al., Effects of vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms on the prognosis of COVID-19, Clin. Endocrinol, doi:10.1111/cen.14664
Azmi, Rismani, Pourmontaseri, Mirzaii, Niknia et al., The role of vitamin D receptor and IL-6 in COVID-19, Mol. Genet. Genomic Med, doi:10.1002/mgg3.2172
Becher, Frerichs, Mortality in COVID-19 is not merely a question of resource availability, Lancet Respir. Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30312-X
Bertoni, Penco, Mollica, Bocca, Prigione et al., Spontaneous NLRP3 inflammasome-driven IL-1-beta secretion is induced in severe COVID-19 patients and responds to anakinra treatment, J. Allergy Clin. Immunol, doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2022.05.029
Cavender, Interactions between endothelial cells and the cells of the immune system, Int. Rev. Exp. Pathol, doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-364932-4.50006-x
Ciarambino, Para, Giordano, Immune system and COVID-19 by sex differences and age, Womens Health, doi:10.1177/17455065211022262
Cutolo, Paolino, Smith, Evidences for a protective role of vitamin D in COVID-19, RMD Open, doi:10.1136/rmdopen-2020-001454
Cutolo, Smith, Paolino, Understanding immune effects of oestrogens to explain the reduced morbidity and mortality in female versus male COVID-19 patients. Comparisons with autoimmunity and vaccination, Clin. Exp. Rheumatol, doi:10.55563/clinexprheumatol/qb05rr
Danese, Dejana, Fiocchi, Immune regulation by microvascular endothelial cells: Directing innate and adaptive immunity, coagulation, and inflammation, J. Immunol, doi:10.4049/jimmunol.178.10.6017
De La Rica, Borges, Gonzalez-Freire, COVID-19: In the Eye of the Cytokine Storm, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.558898
Dunn, Perry, Klein, Mechanisms and consequences of sex differences in immune responses, Nat. Rev. Nephrol, doi:10.1038/s41581-023-00787-w
Gilani, Bin-Jumah, Nadeem, Kazmi, Vitamin D attenuates COVID-19 complications via modulation of proinflammatory cytokines, antiviral proteins, and autophagy, Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther, doi:10.1080/14787210.2021.1941871
Giovannoni, Bosch, Polonio, Torti, Wheeler et al., AHR is a Zika virus host factor and a candidate target for antiviral therapy, Nat. Neurosci, doi:10.1038/s41593-020-0664-0
Giovannoni, Li, Garcia, Quintana, A potential role for AHR in SARS-CoV-2 pathology, Res. Sq, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-25639/v1
Giovannoni, Li, Remes-Lenicov, Davola, Elizalde et al., AHR signaling is induced by infection with coronaviruses, Nat. Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-021-25412-x
Glaros, Larsen, Li, Macrophages and fibroblasts during inflammation, tissue damage and organ injury, Front. Biosci, doi:10.2741/3506
Gunville, Mourani, Ginde, The role of vitamin D in prevention and treatment of infection, Inflamm. Allergy Drug Targets, doi:10.2174/18715281113129990046
Hariharan, Hakeem, Radhakrishnan, Reddy, Rela, The Role and Therapeutic Potential of NF-kappa-B Pathway in Severe COVID-19 Patients, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-020-00773-9
He, Deng, Li, Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): What we know?, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.25766
Klein, Flanagan, Sex differences in immune responses, Nat. Rev. Immunol, doi:10.1038/nri.2016.90
Kmiec, Cyman, Slebioda, Cells of the innate and adaptive immunity and their interactions in inflammatory bowel disease, Adv. Med. Sci, doi:10.1016/j.advms.2016.09.001
Kolls, Garry, Role of the T cell vitamin D receptor in severe COVID-19, Nat. Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41590-021-01098-7
Lescure, Bouadma, Nguyen, Parisey, Wicky et al., Clinical and virological data of the first cases of COVID-19 in Europe: A case series, Lancet Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30200-0
Livak, Schmittgen, Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method, Methods, doi:10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Luo, Li, Jiang, Chen, Wang et al., Targeting JAK-STAT Signaling to Control Cytokine Release Syndrome in COVID-19, Trends Pharmacol. Sci, doi:10.1016/j.tips.2020.06.007
Mcelvaney, Mcevoy, Mcelvaney, Carroll, Murphy et al., Characterization of the Inflammatory Response to Severe COVID-19 Illness, Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med, doi:10.1164/rccm.202005-1583OC
Nehmar, Fauconnier, Alves-Filho, Togbe, Decauwer et al., Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (Ahr)-dependent Il-22 expression by type 3 innate lymphoid cells control of acute joint inflammation, J. Cell Mol. Med, doi:10.1111/jcmm.16433
Notz, Herrmann, Schlesinger, Kranke, Sitter et al., Vitamin D deficiency in critically ill COVID-19 ARDS patients, Clin. Nutr, doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2021.03.001
Pike, Meyer, The vitamin D receptor: New paradigms for the regulation of gene expression by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3, Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am, doi:10.1016/j.rdc.2012.03.004
Reddy, Rogers, Mcauley, Delving beneath the surface of hyperinflammation in COVID-19, Lancet Rheumatol, doi:10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30304-0
Rieder, Groschel, Kastner, Kosulin, Laengle et al., Human cytomegalovirus infection downregulates vitamin-D receptor in mammalian cells, J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2016.08.002
Robak, Kastner, Stecher, Schneider, Andreas et al., Cytomegalovirus Infection Downregulates Vitamin D Receptor in Patients Undergoing Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation, Transplantation, doi:10.1097/TP.0000000000003448
Russo, Morello, Malaguarnera, Piro, Furno et al., Candidate genes of SARS-CoV-2 gender susceptibility, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-01131-7
Russo, Valle, Malaguarnera, Romano, Malaguarnera, Comparison of Vitamin D and Resveratrol Performances in COVID-19, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15112639
Schultheiss, Willscher, Paschold, Gottschick, Klee et al., The IL-1beta, IL-6, and TNF cytokine triad is associated with post-acute sequelae of COVID-19, Cell Rep. Med, doi:10.1016/j.xcrm.2022.100663
Shirvani, Nouri, Sakhinia, Babaloo, Jadideslam et al., The expression and methylation status of vitamin D receptor gene in Behcet's disease, Immun. Inflamm. Dis, doi:10.1002/iid3.275
Siddiqui, Manansala, Abdulrahman, Nasrallah, Smatti et al., Immune Modulatory Effects of Vitamin D on Viral Infections, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12092879
Sun, Lu, Xu, Sun, Pan, Understanding of COVID-19 based on current evidence, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.25722
Turski, Wnorowski, Turski, Turski, Turski, AhR and IDO1 in pathogenesis of COVID-19 and the "Systemic AhR Activation Syndrome:" a translational review and therapeutic perspectives, Restor. Neurol. Neurosci, doi:10.3233/RNN-201042
Vadakedath, Kandi, Mohapatra, Pinnelli, Yegurla et al., Immunological aspects and gender bias during respiratory viral infections including novel Coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19): A scoping review, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.27081
Wu, Zhao, Yu, Chen, Wang et al., A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2008-3
Zhu, Luo, Tian, Yin, Ma et al., Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Promotes IL-10 Expression in Inflammatory Macrophages Through Src-STAT3 Signaling Pathway, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2018.02033
Zhu, Zhang, Wang, Li, Yang et al., A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2001017
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu16050598",
"ISSN": [
"2072-6643"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/nu16050598",
"abstract": "<jats:p>(1) Background: SARS-CoV-2 affects several immune pathways, including the vitamin D (VDR) and the aryl hydrocarbon receptor pathways (AhR). The aim of the study was the evaluation of the VDR and AhR pathways in the blood of COVID-19 patients with regard to the severity of disease. (2) Methods: Observational, single-center, case–control design. A total of 240 samples were selected for exploration. Patients who tested negative for SARS-CoV-2 but suffered from other respiratory infections (ORIs) served as a control group. (3) Results: VDR-specific mRNA in the blood of patients with mild symptoms (131.2 ± 198.6) was significantly upregulated relative to the VDR expression of the ORI group (23.24 ± 42.60; p < 0.0001); however, VDR expression of critically ill patients showed an impaired upregulation (54.73 ± 68.34; p < 0.001). CYP27B1 expression was not significantly regulated during SARS-CoV-2 infection. There was a downregulation of VDR and CYP27B1 compared to survivors. There was no significant difference in 25(OH)-vitamin D3 levels between critically ill patients with regard to survival (24.3 ± 9.4 vs. 27.1 ± 11.3; p = 0.433). (4) Conclusion: The VDR and AhR pathways are distinctively regulated in patients suffering from COVID-19 depending on the severity of disease. A combination treatment of antiviral drugs and vitamin D substitution should be evaluated for potentially improved prognosis in COVID-19.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"nu16050598"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3238-194X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine I, Medical University of Vienna, 1090 Vienna, Austria"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Robak",
"given": "Oliver",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine I, Medical University of Vienna, 1090 Vienna, Austria"
}
],
"family": "Kastner",
"given": "Marie-Theres",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Laboratory Medicine, Klinik Landstraße, 1030 Vienna, Austria"
}
],
"family": "Voill-Glaninger",
"given": "Astrid",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7141-8867",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Laboratory Medicine, Klinik Landstraße, 1030 Vienna, Austria"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Viveiros",
"given": "André",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3500-7205",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine I, Medical University of Vienna, 1090 Vienna, Austria"
},
{
"name": "Karl-Landsteiner Institute for Microbiome Research, Medical University of Vienna, 1090 Vienna, Austria"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Steininger",
"given": "Christoph",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Nutrients",
"container-title-short": "Nutrients",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2024-02-22T13:34:35Z",
"timestamp": 1708608875000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2024-02-22T14:30:13Z",
"timestamp": 1708612213000
},
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"#COVID037"
],
"name": "Medical-Scientific Fund of the Mayor of the Federal Capital Vienna"
},
{
"award": [
"#P33546-B"
],
"name": "Austrian Science Fund"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2024-02-23T00:44:46Z",
"timestamp": 1708649086460
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "5",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
22
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "5",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2024-02-22T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1708560000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/16/5/598/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "598",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
22
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
22
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2008-3",
"article-title": "A new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "265",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_1",
"volume": "579",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001017",
"article-title": "A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019",
"author": "Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "727",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_2",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.25722",
"article-title": "Understanding of COVID-19 based on current evidence",
"author": "Sun",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "548",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): What we know?",
"author": "He",
"first-page": "697",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "ref_4",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30200-0",
"article-title": "Clinical and virological data of the first cases of COVID-19 in Europe: A case series",
"author": "Lescure",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "697",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_5",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30312-X",
"article-title": "Mortality in COVID-19 is not merely a question of resource availability",
"author": "Becher",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "832",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir. Med.",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.558898",
"article-title": "COVID-19: In the Eye of the Cytokine Storm",
"author": "Borges",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "558898",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30304-0",
"article-title": "Delving beneath the surface of hyperinflammation in COVID-19",
"author": "Reddy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e578",
"journal-title": "Lancet Rheumatol.",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/B978-0-12-364932-4.50006-X",
"article-title": "Interactions between endothelial cells and the cells of the immune system",
"author": "Cavender",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "57",
"journal-title": "Int. Rev. Exp. Pathol.",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "32",
"year": "1991"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2741/3506",
"article-title": "Macrophages and fibroblasts during inflammation, tissue damage and organ injury",
"author": "Glaros",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3988",
"journal-title": "Front. Biosci.",
"key": "ref_10",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.advms.2016.09.001",
"article-title": "Cells of the innate and adaptive immunity and their interactions in inflammatory bowel disease",
"author": "Kmiec",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Adv. Med. Sci.",
"key": "ref_11",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.178.10.6017",
"article-title": "Immune regulation by microvascular endothelial cells: Directing innate and adaptive immunity, coagulation, and inflammation",
"author": "Danese",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6017",
"journal-title": "J. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_12",
"volume": "178",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/mgg3.2172",
"article-title": "The role of vitamin D receptor and IL-6 in COVID-19",
"author": "Azmi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e2172",
"journal-title": "Mol. Genet. Genomic Med.",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-01131-7",
"article-title": "Candidate genes of SARS-CoV-2 gender susceptibility",
"author": "Russo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "21968",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biom11111624",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_15",
"unstructured": "Ao, T., Kikuta, J., and Ishii, M. (2021). The Effects of Vitamin D on Immune System and Inflammatory Diseases. Biomolecules, 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/14787210.2021.1941871",
"article-title": "Vitamin D attenuates COVID-19 complications via modulation of proinflammatory cytokines, antiviral proteins, and autophagy",
"author": "Gilani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "231",
"journal-title": "Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther.",
"key": "ref_16",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu15112639",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_17",
"unstructured": "Russo, C., Valle, M.S., Malaguarnera, L., Romano, I.R., and Malaguarnera, L. (2023). Comparison of Vitamin D and Resveratrol Performances in COVID-19. Nutrients, 15."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/rmdopen-2020-001454",
"article-title": "Evidences for a protective role of vitamin D in COVID-19",
"author": "Cutolo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e001454",
"journal-title": "RMD Open",
"key": "ref_18",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/18715281113129990046",
"article-title": "The role of vitamin D in prevention and treatment of infection",
"author": "Gunville",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "239",
"journal-title": "Inflamm. Allergy Drug Targets",
"key": "ref_19",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12092879",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_20",
"unstructured": "Siddiqui, M., Manansala, J.S., Abdulrahman, H.A., Nasrallah, G.K., Smatti, M.K., Younes, N., Althani, A.A., and Yassine, H.M. (2020). Immune Modulatory Effects of Vitamin D on Viral Infections. Nutrients, 12."
},
{
"article-title": "Immune system and COVID-19 by sex differences and age",
"author": "Ciarambino",
"first-page": "17455065211022262",
"journal-title": "Womens Health",
"key": "ref_21",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.27081",
"article-title": "Immunological aspects and gender bias during respiratory viral infections including novel Coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19): A scoping review",
"author": "Vadakedath",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5295",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "ref_22",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41581-023-00787-w",
"article-title": "Mechanisms and consequences of sex differences in immune responses",
"author": "Dunn",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "37",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Nephrol.",
"key": "ref_23",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"article-title": "Understanding immune effects of oestrogens to explain the reduced morbidity and mortality in female versus male COVID-19 patients. Comparisons with autoimmunity and vaccination",
"author": "Cutolo",
"first-page": "383",
"journal-title": "Clin. Exp. Rheumatol.",
"key": "ref_24",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2016.08.002",
"article-title": "Human cytomegalovirus infection downregulates vitamin-D receptor in mammalian cells",
"author": "Rieder",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "356",
"journal-title": "J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol.",
"key": "ref_25",
"volume": "165",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/TP.0000000000003448",
"article-title": "Cytomegalovirus Infection Downregulates Vitamin D Receptor in Patients Undergoing Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation",
"author": "Robak",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1595",
"journal-title": "Transplantation",
"key": "ref_26",
"volume": "105",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "ref_27",
"unstructured": "(2024, February 06). Clinical Spectrum of SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Available online: https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/overview/clinical-spectrum/."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1006/meth.2001.1262",
"article-title": "Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method",
"author": "Livak",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "402",
"journal-title": "Methods",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.rdc.2012.03.004",
"article-title": "The vitamin D receptor: New paradigms for the regulation of gene expression by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3",
"author": "Pike",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "13",
"journal-title": "Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am.",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/iid3.275",
"article-title": "The expression and methylation status of vitamin D receptor gene in Behcet’s disease",
"author": "Shirvani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "308",
"journal-title": "Immun. Inflamm. Dis.",
"key": "ref_30",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nri.2016.90",
"article-title": "Sex differences in immune responses",
"author": "Klein",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "626",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_31",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-25412-x",
"article-title": "AHR signaling is induced by infection with coronaviruses",
"author": "Giovannoni",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5148",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "ref_32",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "AhR and IDO1 in pathogenesis of COVID-19 and the \"Systemic AhR Activation Syndrome:\" a translational review and therapeutic perspectives",
"author": "Turski",
"first-page": "343",
"journal-title": "Restor. Neurol. Neurosci.",
"key": "ref_33",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41593-020-0664-0",
"article-title": "AHR is a Zika virus host factor and a candidate target for antiviral therapy",
"author": "Giovannoni",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "939",
"journal-title": "Nat. Neurosci.",
"key": "ref_34",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10787-020-00773-9",
"article-title": "The Role and Therapeutic Potential of NF-kappa-B Pathway in Severe COVID-19 Patients",
"author": "Hariharan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "91",
"journal-title": "Inflammopharmacology",
"key": "ref_35",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-25639/v1",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_36",
"unstructured": "Giovannoni, F., Li, Z., Garcia, C.C., and Quintana, F.J. (2020). A potential role for AHR in SARS-CoV-2 pathology. Res. Sq."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2018.02033",
"article-title": "Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Promotes IL-10 Expression in Inflammatory Macrophages Through Src-STAT3 Signaling Pathway",
"author": "Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2033",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_37",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jcmm.16433",
"article-title": "Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (Ahr)-dependent Il-22 expression by type 3 innate lymphoid cells control of acute joint inflammation",
"author": "Nehmar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4721",
"journal-title": "J. Cell Mol. Med.",
"key": "ref_38",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tips.2020.06.007",
"article-title": "Targeting JAK-STAT Signaling to Control Cytokine Release Syndrome in COVID-19",
"author": "Luo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "531",
"journal-title": "Trends Pharmacol. Sci.",
"key": "ref_39",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaci.2022.05.029",
"article-title": "Spontaneous NLRP3 inflammasome-driven IL-1-beta secretion is induced in severe COVID-19 patients and responds to anakinra treatment",
"author": "Bertoni",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "796",
"journal-title": "J. Allergy Clin. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_40",
"volume": "150",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.xcrm.2022.100663",
"article-title": "The IL-1beta, IL-6, and TNF cytokine triad is associated with post-acute sequelae of COVID-19",
"author": "Schultheiss",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100663",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep. Med.",
"key": "ref_41",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.202005-1583OC",
"article-title": "Characterization of the Inflammatory Response to Severe COVID-19 Illness",
"author": "McElvaney",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "812",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med.",
"key": "ref_42",
"volume": "202",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41590-021-01098-7",
"article-title": "Role of the T cell vitamin D receptor in severe COVID-19",
"author": "Kolls",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5",
"journal-title": "Nat. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_43",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clnu.2021.03.001",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency in critically ill COVID-19 ARDS patients",
"author": "Notz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3089",
"journal-title": "Clin. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_44",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/cen.14664",
"article-title": "Effects of vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms on the prognosis of COVID-19",
"author": "Apaydin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "819",
"journal-title": "Clin. Endocrinol.",
"key": "ref_45",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098",
"article-title": "Association of Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms and clinical/severe outcomes of COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Abdollahzadeh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "105098",
"journal-title": "Infect. Genet. Evol.",
"key": "ref_46",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 46,
"references-count": 46,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/16/5/598"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "The Distinct Regulation of the Vitamin D and Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptors in COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "16"
}
