Association of Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms and clinical/severe outcomes of COVID-19 patients
et al., Infection, Genetics and Evolution, doi:10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098, Oct 2021
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
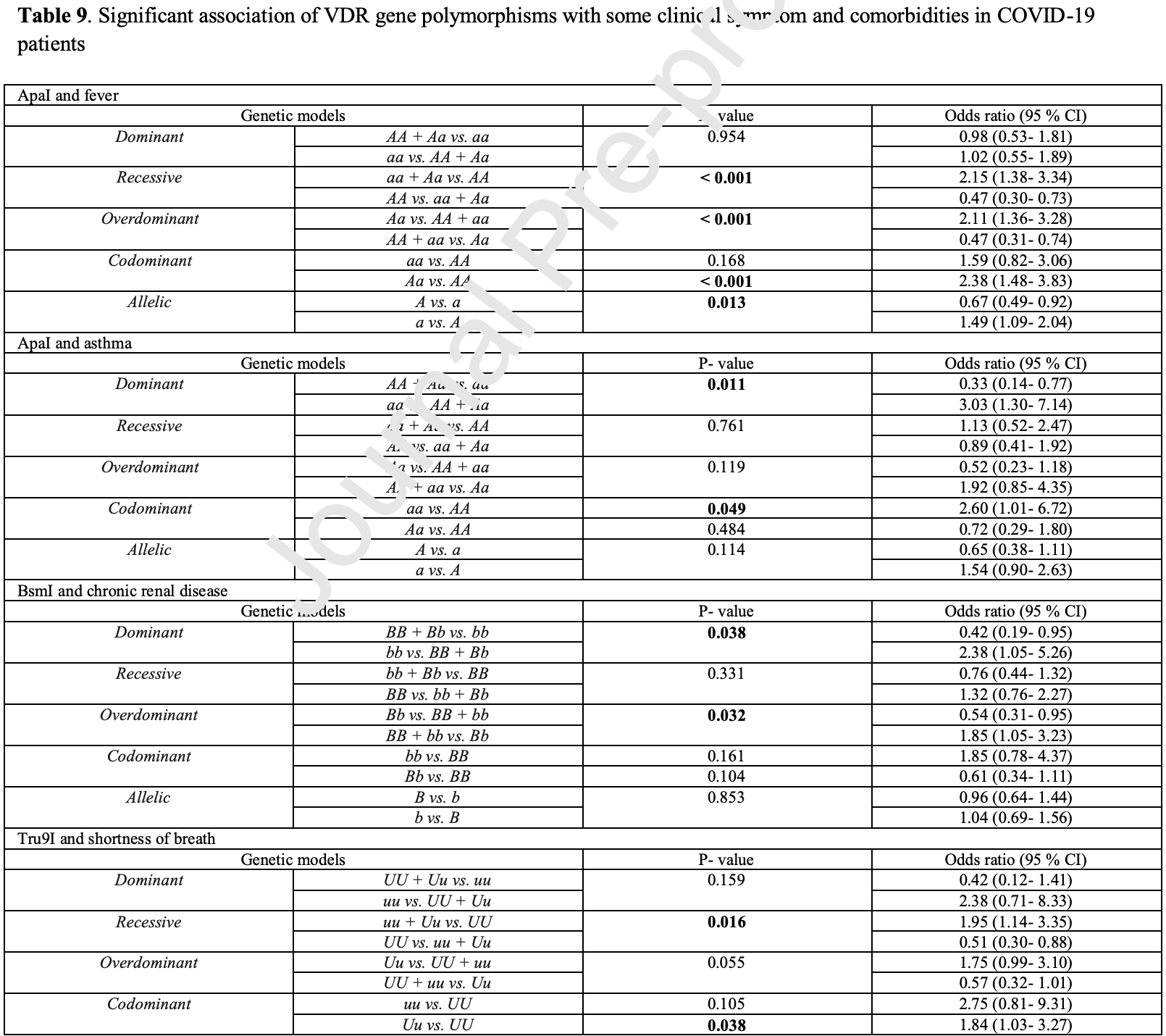
Analysis of 500 hospitalized patients in Iran, showing associations between specific vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms and COVID-19 outcomes.
Abdollahzadeh et al., 2 Oct 2021, peer-reviewed, 9 authors.
Association of Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms and clinical/severe outcomes of COVID-19 patients
Infection, Genetics and Evolution, doi:10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098
Since January 2020 Elsevier has created a COVID-19 resource centre with free information in English and Mandarin on the novel coronavirus COVID-19. The COVID-19 resource centre is hosted on Elsevier Connect, the company's public news and information website. Elsevier hereby grants permission to make all its COVID-19-related research that is available on the COVID-19 resource centre -including this research content -immediately available in PubMed Central and other publicly funded repositories, such as the WHO COVID database with rights for unrestricted research re-use and analyses in any form or by any means with acknowledgement of the original source. These permissions are granted for free by Elsevier for as long as the COVID-19 resource centre remains active.
Conflict of Interest The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Highlights Growing evidence indicated the critical impacts of vitamin D (VD) in prognosis of COVID-19 patients. Significant associations were disclosed for some of the SNPs with severity, signs, symptoms, and coexisting pathologic conditions. VDR gene polymorphisms might thus allow the prioritization of those at greater risk for COVID-19. J o u r n a l P r e -p r o o f
References
Abdollahzadeh, Fard, Rahmani, Moloudi, Azarnezhad, Predisposing role of vitamin D receptor (VDR) polymorphisms in the development of multiple sclerosis: A case-control study, Journal of the neurological sciences
Abdollahzadeh, Pordanjani, Rahmani, Mashayekhi, Azarnezhad et al., Association of VDR gene polymorphisms with risk of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis in an Iranian Kurdish population, International Journal of Neuroscience
Adir, Humbert, Saliba, COVID-19 risk and outcomes in adult asthmatics treated with biologics or systemic corticosteroids: nationwide real-world evidence, Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology
Ali, Role of vitamin D in preventing of COVID-19 infection, progression and severity, Journal of infection and public health
Alzaman, Dawson-Hughes, Nelson, 'alessio, Pittas, Vitamin D status of black and white Americans and changes in vitamin D metabolites after varied doses of vitamin D supplementation. The American journal of clinical nutrition
Amrein, Scherkl, Hoffmann, Neuwersch-Sommeregger, Köstenberger et al., Vitamin D deficiency 2.0: An update on the current status worldwide, European Journal of Clinical Nutrition
Anastassopoulou, Gkizarioti, Patrinos, Tsakris, Human genetic factors associated with susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 disease severity, Human genomics
Aydıngöz, Bingül, Doğru-Abbasoğlu, Vural, Uysal, Analysis of vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms in vitiligo, Dermatology
Aygun, Vitamin D can prevent COVID-19 infection-induced multiple organ damage, Naunynschmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology
Biesalski, Vitamin D deficiency and co-morbidities in COVID-19 patients-A fatal relationship?, NFS Journal
Bizzaro, Antico, Fortunato, Bizzaro, Vitamin D and autoimmune diseases: is vitamin D receptor (VDR) polymorphism the culprit, Isr Med Assoc J
Brar, Pinheiro, Shusterman, Swed, Reshetnyak et al., COVID-19 Severity and Outcomes in Patients With Cancer: A Matched Cohort Study, J Clin Oncol
Cameron, Bermejo-Martin, Danesh, Muller, Kelvin, Human immunopathogenesis of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), Virus research
Carpagnano, Lecce, Quaranta, Zito, Buonamico et al., Vitamin D deficiency as a predictor of poor prognosis in patients with acute respiratory failure due to COVID-19, Journal of endocrinological investigation
Channappanavar, Perlman, Editors, Pathogenic human coronavirus infections: causes and consequences of cytokine storm and immunopathology, Seminars in immunopathology
Chen, Zhou, Dong, Qu, Gong et al., Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study, The Lancet
Cheon, Nam, Lee, Kim, Song et al., Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms and type 1 diabetes mellitus in a Korean population, Pediatrics International
Clendenen, Arslan, Koenig, Enquist, Wirgin et al., Vitamin D receptor polymorphisms and risk of epithelial ovarian cancer, Cancer letters
Colin, Weel, Uitterlinden, Buurman, Birkenhäger et al., Consequences of vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms for growth inhibition of cultured human peripheral blood mononuclear cells by 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3, Clinical endocrinology
Dancer, Parekh, Lax, Souza, Zheng et al., Vitamin D deficiency contributes directly to the acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), Thorax
Dickinson, Perera, Van Der Mei, Ponsonby, Polanowski et al., Past environmental sun exposure and risk of multiple sclerosis: a role for the Cdx-2 Vitamin D receptor variant in this interaction, Multiple Sclerosis Journal
Ebadi, Bhanji, Mazurak, Lytvyak, Mason et al., Severe vitamin D deficiency is a prognostic biomarker in autoimmune hepatitis, Alimentary pharmacology & therapeutics
Fang, Van Meurs, Bergink, Hofman, Van Duijn et al., Cdx-2 polymorphism in the promoter region of the human vitamin D receptor gene determines susceptibility to fracture in the elderly, Journal of Bone and Mineral Research
Faul, Kerley, Love, Neill, Cody et al., Vitamin D deficiency and ARDS after SARS-CoV-2 infection
Frederiksen, Liu, Romanos, Steck, Yin et al., Investigation of the vitamin D receptor gene (VDR) and its interaction with protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 2 gene (PTPN2) on risk of islet autoimmunity and type 1 diabetes: the Diabetes Autoimmunity Study in the Young (DAISY), The Journal of steroid biochemistry and molecular biology
Ghodsi, Keshtkar, Razi, Amoli, Nasli-Esfahani et al., Association of vitamin D receptor gene polymorphism with the occurrence of low bone density, osteopenia, and osteoporosis in patients with type 2 diabetes, Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Baggerly, French et al., Evidence that vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of influenza and COVID-19 infections and deaths, Nutrients
Grasselli, Zangrillo, Zanella, Antonelli, Cabrini et al., Baseline characteristics and outcomes of 1591 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 admitted to ICUs of the Lombardy Region, Italy, Jama
Gómez, Albaiceta, García-Clemente, López-Larrea, Rodríguez et al., Angiotensin-converting enzymes (ACE, ACE2) gene variants and COVID-19 outcome, Gene
Halsall, Osborne, Potter, Pringle, Hutchinson, A novel polymorphism in the 1A promoter region of the vitamin D receptor is associated with altered susceptibilty and prognosis in malignant melanoma, British journal of cancer
Harishankar, Selvaraj, Influence of Cdx2 and TaqI gene variants on vitamin D3 modulated intracellular chemokine positive T-cell subsets in pulmonary tuberculosis, Clinical therapeutics
Henry, Lippi, Chronic kidney disease is associated with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection, International urology and nephrology
Hou, Zhao, Martin, Kallianpur, Chung et al., New insights into genetic susceptibility of COVID-19: an ACE2 and TMPRSS2 polymorphism analysis, BMC medicine
Hribar, Cobbold, Church, Potential Role of Vitamin D in the Elderly to Resist COVID-19 and to Slow Progression of Parkinson's Disease, Brain Sciences
Hussain, Naushad, Ahmed, Alamery, Mohammed et al., Association of vitamin D receptor TaqI and ApaI genetic polymorphisms with nephrolithiasis and end stage renal disease: a meta-analysis, BMC medical genetics
Hustmyer, Deluca, Peacock, Apal, Bsml, Eco RV and Taql polymorphisms at the human vitamin D receptor gene locus in Caucasians, Blacks and Asians, Human molecular genetics
Ilie, Stefanescu, Smith, The role of vitamin D in the prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 infection and mortality, Aging Clinical and Experimental Research
Imai, Kuba, Rao, Huan, Guo et al., Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 protects from severe acute lung failure, Nature
Jurutka, Remus, Whitfield, Thompson, Hsieh et al., The polymorphic N terminus in human vitamin D receptor isoforms influences transcriptional activity by modulating interaction with transcription factor IIB, Molecular endocrinology
Jurutka, Whitfield, Hsieh, Thompson, Haussler et al., Molecular nature of the vitamin D receptor and its role in regulation of gene expression, Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders
Klein, Rosenberg, Reynolds, Zubiri, Rosovsky et al., Impact of Cancer History on Outcomes Among Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19
Kong, Zhu, Shi, Liu, Chen et al., VDR attenuates acute lung injury by blocking Ang-2-Tie-2 pathway and renin-angiotensin system, Molecular endocrinology
Kunadian, Ford, Bawamia, Qiu, Manson, Vitamin D deficiency and coronary artery disease: a review of the evidence, American Heart Journal
Köstner, Denzer, Mueller, Klein, Tilgen et al., The relevance of vitamin D receptor (VDR) gene polymorphisms for cancer: a review of the literature, Anticancer research
Lafaja, Sánchez-Palencia, Palazón, Vitamin D Receptor polymorphisms and risk of enveloped virus infection: a meta-analysis, Gene
Laplana, Royo, Fibla, Vitamin D Receptor polymorphisms and risk of enveloped virus infection: A meta-analysis, Gene
Latini, Agolini, Novelli, Borgiani, Giannini et al., COVID-19 and genetic variants of protein involved in the SARS-CoV-2 entry into the host cells, Genes
Lee, Son, Han, Jung, Park, Impact of comorbid asthma on severity of coronavirus disease (COVID-19), Scientific reports
Liu, Zhang, Wu, Shang, Dong et al., Clinical outcomes of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a large cohort study, Annals of intensive care
Ma, Stampfer, Gann, Hough, Giovannucci et al., Vitamin D receptor polymorphisms, circulating vitamin D metabolites, and risk of prostate cancer in United States physicians, Cancer Epidemiology and Prevention Biomarkers
Mcnally, Sampson, Matheson, Hutton, Little, Vitamin D receptor (VDR) polymorphisms and severe RSV bronchiolitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Pediatric pulmonology
Mehrabani, Shushizadeh, Abazari, Aleagha, Ardalan et al., Association of SHMT1, MAZ, ERG, and L3MBTL3 Gene Polymorphisms with Susceptibility to Multiple Sclerosis, Biochemical genetics
Meltzer, Best, Zhang, Vokes, Arora et al., Association of Vitamin D Deficiency and Treatment with COVID-19 Incidence
Mendy, Apewokin, Wells, Morrow, Factors associated with hospitalization and disease severity in a racially and ethnically diverse population of COVID-19 patients
Meyer, Bornman, Cdx-2 polymorphism in the vitamin D receptor gene (VDR) marks VDR expression in monocyte/macrophages through VDR promoter methylation, Immunogenetics
Miyamoto, -I, Kesterson, Yamamoto, Taketani, Nishiwaki et al., Structural organization of the human vitamin D receptor chromosomal gene and its promoter, Molecular Endocrinology
Mohammadi, Azarnezhad, Khanbabaei, Izadpanah, Abdollahzadeh et al., None
Mohammadi, Azarnezhad, Khanbabaei, Izadpanah, Abdollahzadeh et al., None
Morrison, Qi, Tokita, Kelly, Crofts et al., Prediction of bone density from vitamin D receptor alleles, Nature
Organization, Clinical management of COVID-19: interim guidance
Ovsyannikova, Dhiman, Haralambieva, Vierkant, Byrne et al., Rubella vaccine-induced cellular immunity: evidence of associations with polymorphisms in the Toll-like, vitamin A and D receptors, and innate immune response genes, Human genetics
Parekh, Thickett, Turner, Vitamin D deficiency and acute lung injury. Inflammation & Allergy-Drug Targets (Formerly Current Drug Targets, Inflammation & Allergy)
Park, Lee, Hong, Lim, Koh et al., Effect of vitamin D deficiency in Korean patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome, The Korean journal of internal medicine
Pranata, Lim, Huang, Raharjo, Lukito, Hypertension is associated with increased mortality and severity of disease in COVID-19 pneumonia: a systematic review, meta-analysis and metaregression, JRAAS
Quesada-Gomez, Castillo, Bouillon, Vitamin D Receptor stimulation to reduce Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) in patients with Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 infections: Revised Ms SBMB 2020_166, The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology
Rhodes, Subramanian, Laird, Griffin, Kenny, Perspective: Vitamin D deficiency and COVID-19 severity-plausibly linked by latitude, ethnicity, impacts on cytokines, ACE2 and thrombosis, Journal of internal medicine
Richardson, Hirsch, Narasimhan, Crawford, Mcginn et al., Presenting characteristics, comorbidities, and outcomes among 5700 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in the New
Saccone, Asani, Bornman, Regulation of the vitamin D receptor gene by environment, genetics and epigenetics, Gene
Shi, Liu, Fu, Xu, Wu et al., Vitamin D/VDR signaling attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by maintaining the integrity of the pulmonary epithelial barrier, Molecular medicine reports
Singh, Gupta, Ghosh, Misra, Diabetes in COVID-19: Prevalence, pathophysiology, prognosis and practical considerations, Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome
Singhal, A review of coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19), The Indian Journal of Pediatrics
Sohrabi, Alsafi, Neill, Khan, Kerwan et al., A review of the 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19)
Tabrizi, Moosazadeh, Akbari, Dabbaghmanesh, Mohamadkhani et al., High prevalence of vitamin D deficiency among Iranian population: a systematic review and metaanalysis, Iranian journal of medical sciences
Thickett, Moromizato, Litonjua, Amrein, Quraishi et al., Association between prehospital vitamin D status and incident acute respiratory failure in critically ill patients: a retrospective cohort study, BMJ open respiratory research
Tuoresmäki, Väisänen, Neme, Heikkinen, Carlberg, Patterns of genome-wide VDR locations, PloS one
Valdivielso, Fernandez, Vitamin D receptor polymorphisms and diseases, Clinica chimica acta
Van Etten, Verlinden, Giulietti, Ramos-Lopez, Branisteanu et al., The vitamin D receptor gene FokI polymorphism: functional impact on the immune system, European journal of immunology
Wacker, Holick, Sunlight and Vitamin D: A global perspective for health, Dermatoendocrinology
Wang, Zhang, Zhang, He, Zhu, Distribution of HLA allele frequencies in 82 Chinese individuals with coronavirus disease, Hla
Weir, Thenappan, Bhargava, Chen, Does vitamin D deficiency increase the severity of COVID-19?, Clinical Medicine
Whitfield, Remus, Jurutka, Zitzer, Oza et al., Functionally relevant polymorphisms in the human nuclear vitamin D receptor gene, Molecular and cellular endocrinology
Williamson, Walker, Bhaskaran, Bacon, Bates et al., OpenSAFELY: factors associated with COVID-19 death in 17 million patients, Nature
Wit, Van Doremalen, Falzarano, Munster, SARS and MERS: recent insights into emerging coronaviruses, Nature Reviews Microbiology
Wjst, Variants in the vitamin D receptor gene and asthma, BMC genetics
Xie, Chen, Insight into 2019 novel coronavirus-an updated intrim review and lessons from SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV, International Journal of Infectious Diseases
Xu, Shi, Wang, Zhang, Huang et al., Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome, The Lancet respiratory medicine
Xu, Yang, Chen, Luo, Zhang et al., Vitamin D alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via regulation of the renin-angiotensin system, Molecular medicine reports
Yancy, COVID-19 and African Americans
Yang, Zheng, Gou, Pu, Chen et al., Prevalence of comorbidities and its effects in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2: a systematic review and meta-analysis, International Journal of Infectious Diseases
Zdrenghea, Makrinioti, Bagacean, Bush, Johnston et al., Vitamin D modulation of innate immune responses to respiratory viral infections, Reviews in medical virology
Zemb, Bergman, Jr, Cavalier, Cormier et al., Vitamin D deficiency and COVID-19 pandemic, Journal of Global Antimicrobial Resistance
Zhang, Han, He, Labbe, Hernandez et al., Clinical characteristics and outcomes of COVID-19-infected cancer patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis, JNCI: Journal of the National Cancer Institute
Zhang, Mccullough, Tecson, Vitamin D deficiency in association with endothelial dysfunction: Implications for patients with COVID-19, Reviews in cardiovascular medicine
Zheng, Yang, Hu, Li, Wang et al., Vitamin D attenuates lung injury via stimulating epithelial repair, reducing epithelial cell apoptosis and inhibits TGF-β induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition, Biochemical pharmacology
Zhou, Xu, -D, Li, The association of polymorphisms of the vitamin D receptor gene with psoriasis in the Han population of northeastern China, Journal of Dermatological Science
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098",
"ISSN": [
"1567-1348"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098",
"alternative-id": [
"S1567134821003981"
],
"article-number": "105098",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Association of Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms and clinical/severe outcomes of COVID-19 patients"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Infection, Genetics and Evolution"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2021 Published by Elsevier B.V."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abdollahzadeh",
"given": "Rasoul",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shushizadeh",
"given": "Mohammad Hossein",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Barazandehrokh",
"given": "Mina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Choopani",
"given": "Sepideh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Azarnezhad",
"given": "Asaad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Paknahad",
"given": "Sahereh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pirhoushiaran",
"given": "Maryam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Makani",
"given": "S. Zahra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yeganeh",
"given": "Razieh Zarifian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Al-Kateb",
"given": "Ahmed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Heidarzadehpilehrood",
"given": "Roozbeh",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Infection, Genetics and Evolution",
"container-title-short": "Infection, Genetics and Evolution",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2021-10-04T12:55:10Z",
"timestamp": 1633352110000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2023-04-15T08:34:06Z",
"timestamp": 1681547646000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-14T15:54:56Z",
"timestamp": 1715702096292
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 27,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1638316800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-017",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1638316800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-037",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1638316800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-012",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1638316800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-029",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1638316800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-004",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1638316800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1567134821003981?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1567134821003981?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "105098",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jns.2016.05.053",
"article-title": "Predisposing role of vitamin D receptor (VDR) polymorphisms in the development of multiple sclerosis: a case-control study",
"author": "Abdollahzadeh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "148",
"journal-title": "J. Neurol. Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0005",
"volume": "367",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/00207454.2017.1398158",
"article-title": "Association of VDR gene polymorphisms with risk of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis in an Iranian Kurdish population",
"author": "Abdollahzadeh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "505",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Neurosci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0010",
"volume": "128",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaci.2021.06.006",
"article-title": "COVID-19 risk and outcomes in adult asthmatics treated with biologics or systemic corticosteroids: nationwide real-world evidence",
"author": "Adir",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "361",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J. Allergy Clin. Immunol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0015",
"volume": "148",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiph.2020.06.021",
"article-title": "Role of vitamin D in preventing of COVID-19 infection, progression and severity",
"author": "Ali",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1373",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "J. Infect. Publ. Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0020",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3945/ajcn.115.129478",
"article-title": "Vitamin D status of black and white Americans and changes in vitamin D metabolites after varied doses of vitamin D supplementation",
"author": "Alzaman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "205",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Clin. Nutr.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0025",
"volume": "104",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency 2.0: an update on the current status worldwide",
"author": "Amrein",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Clin. Nutr.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0030",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40246-020-00290-4",
"article-title": "Human genetic factors associated with susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 disease severity",
"author": "Anastassopoulou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Hum. Genom.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0035",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000339340",
"article-title": "Analysis of vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms in vitiligo",
"author": "Aydıngöz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "361",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Dermatology",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0040",
"volume": "224",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D can prevent COVID-19 infection-induced multiple organ damage",
"author": "Aygun",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0045",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nfs.2020.06.001",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency and co-morbidities in COVID-19 patients–A fatal relationship?",
"author": "Biesalski",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "10",
"journal-title": "NFS Journal",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0050",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D and autoimmune diseases: is vitamin D receptor (VDR) polymorphism the culprit",
"author": "Bizzaro",
"first-page": "438",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Isr. Med. Assoc. J.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0055",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1200/JCO.20.01580",
"article-title": "COVID-19 severity and outcomes in patients with Cancer: a matched cohort study",
"author": "Brar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3914",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Oncol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0060",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virusres.2007.02.014",
"article-title": "Human immunopathogenesis of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)",
"author": "Cameron",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "13",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Virus Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0065",
"volume": "133",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency as a predictor of poor prognosis in patients with acute respiratory failure due to COVID-19",
"author": "Carpagnano",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Endocrinol. Investig.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0070",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Pathogenic human coronavirus infections: causes and consequences of cytokine storm and immunopathology",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0075",
"series-title": "Seminars in Immunopathology",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7",
"article-title": "Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "507",
"issue": "10223",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0080",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/ped.12634",
"article-title": "Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms and type 1 diabetes mellitus in a Korean population",
"author": "Cheon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "870",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Pediatr. Int.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0085",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.canlet.2007.11.002",
"article-title": "Vitamin D receptor polymorphisms and risk of epithelial ovarian cancer",
"author": "Clendenen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "209",
"issue": "1–2",
"journal-title": "Cancer Lett.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0090",
"volume": "260",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1046/j.1365-2265.2000.00909.x",
"article-title": "Consequences of vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms for growth inhibition of cultured human peripheral blood mononuclear cells by 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3",
"author": "Colin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "211",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Clin. Endocrinol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0095",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/thoraxjnl-2014-206680",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency contributes directly to the acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)",
"author": "Dancer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "617",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Thorax",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0100",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrmicro.2016.81",
"article-title": "SARS and MERS: recent insights into emerging coronaviruses",
"author": "De Wit",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "523",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Microbiol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0105",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1352458509102459",
"article-title": "Past environmental sun exposure and risk of multiple sclerosis: a role for the Cdx-2 Vitamin D receptor variant in this interaction",
"author": "Dickinson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "563",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Mult. Scler. J.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0110",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/apt.15029",
"article-title": "Severe vitamin D deficiency is a prognostic biomarker in autoimmune hepatitis",
"author": "Ebadi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "173",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0115",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1359/jbmr.2003.18.9.1632",
"article-title": "Cdx-2 polymorphism in the promoter region of the human vitamin D receptor gene determines susceptibility to fracture in the elderly",
"author": "Fang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1632",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "J. Bone Miner. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0120",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"author": "Faul",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0125",
"series-title": "Vitamin D Deficiency and ARDS after SARS-CoV-2 Infection",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2012.08.012",
"article-title": "Investigation of the vitamin D receptor gene (VDR) and its interaction with protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 2 gene (PTPN2) on risk of islet autoimmunity and type 1 diabetes: the Diabetes Autoimmunity Study in the Young (DAISY)",
"author": "Frederiksen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "51",
"journal-title": "J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0130",
"volume": "133",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"article-title": "Association of vitamin D receptor gene polymorphism with the occurrence of low bone density, osteopenia, and osteoporosis in patients with type 2 diabetes",
"author": "Ghodsi",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Diabetes Metab. Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0135",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.gene.2020.145102",
"article-title": "Angiotensin-converting enzymes (ACE, ACE2) gene variants and COVID-19 outcome",
"author": "Gómez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "145102",
"journal-title": "Gene",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0140",
"volume": "762",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12040988",
"article-title": "Evidence that vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of influenza and COVID-19 infections and deaths",
"author": "Grant",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "988",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0145",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.5394",
"article-title": "Baseline characteristics and outcomes of 1591 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 admitted to ICUs of the Lombardy Region, Italy",
"author": "Grasselli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1574",
"issue": "16",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0150",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/sj.bjc.6602006",
"article-title": "A novel polymorphism in the 1A promoter region of the vitamin D receptor is associated with altered susceptibilty and prognosis in malignant melanoma",
"author": "Halsall",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "765",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Br. J. Cancer",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0155",
"volume": "91",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clinthera.2017.04.003",
"article-title": "Influence of Cdx2 and TaqI gene variants on vitamin D3 modulated intracellular chemokine positive T-cell subsets in pulmonary tuberculosis",
"author": "Harishankar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "946",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Clin. Ther.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0160",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"article-title": "Chronic kidney disease is associated with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection",
"author": "Henry",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Int. Urol. Nephrol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0165",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12916-020-01673-z",
"article-title": "New insights into genetic susceptibility of COVID-19: an ACE2 and TMPRSS2 polymorphism analysis",
"author": "Hou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0170",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/brainsci10050284",
"article-title": "Potential role of vitamin D in the elderly to resist COVID-19 and to slow progression of Parkinson’s disease",
"author": "Hribar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "284",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Brain Sciences.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0175",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12881-019-0932-6",
"article-title": "Association of vitamin D receptor TaqI and ApaI genetic polymorphisms with nephrolithiasis and end stage renal disease: a meta-analysis",
"author": "Hussain",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC Med. Genet.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0180",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/hmg/2.4.487",
"article-title": "Apal, Bsml, Eco RV and Taql polymorphisms at the human vitamin D receptor gene locus in Caucasians, Blacks and Asians",
"author": "Hustmyer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "487",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Hum. Mol. Genet.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0185",
"volume": "2",
"year": "1993"
},
{
"article-title": "The role of vitamin D in the prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 infection and mortality",
"author": "Ilie",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Aging Clin. Exp. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0190",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature03712",
"article-title": "Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 protects from severe acute lung failure",
"author": "Imai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "112",
"issue": "7047",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0195",
"volume": "436",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/mend.14.3.0435",
"article-title": "The polymorphic N terminus in human vitamin D receptor isoforms influences transcriptional activity by modulating interaction with transcription factor IIB",
"author": "Jurutka",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "401",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Mol. Endocrinol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0200",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1023/A:1010062929140",
"article-title": "Molecular nature of the vitamin D receptor and its role in regulation of gene expression",
"author": "Jurutka",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "203",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0205",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/mend.11.8.9951",
"article-title": "Structural organization of the human vitamin D receptor chromosomal gene and its promoter",
"author": "K-i",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1165",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Mol. Endocrinol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0210",
"volume": "11",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/onco.13794",
"article-title": "Impact of cancer history on outcomes among hospitalized patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Klein",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "685",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Oncologist",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0215",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/me.2013-1146",
"article-title": "VDR attenuates acute lung injury by blocking Ang-2-Tie-2 pathway and renin-angiotensin system",
"author": "Kong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2116",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Mol. Endocrinol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0220",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"article-title": "The relevance of vitamin D receptor (VDR) gene polymorphisms for cancer: a review of the literature",
"author": "Köstner",
"first-page": "3511",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Anticancer Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0225",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ahj.2013.11.012",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency and coronary artery disease: a review of the evidence",
"author": "Kunadian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "283",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Am. Heart J.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0230",
"volume": "167",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.gene.2018.08.017",
"article-title": "Vitamin D receptor polymorphisms and risk of enveloped virus infection: a meta-analysis",
"author": "Laplana",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "384",
"journal-title": "Gene",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0235",
"volume": "678",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/genes11091010",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and genetic variants of protein involved in the SARS-CoV-2 entry into the host cells",
"author": "Latini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1010",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Genes",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0240",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-020-77791-8",
"article-title": "Impact of comorbid asthma on severity of coronavirus disease (COVID-19)",
"author": "Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0245",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13613-020-00706-3",
"article-title": "Clinical outcomes of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a large cohort study",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Ann. Intensive Care",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0250",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D receptor polymorphisms, circulating vitamin D metabolites, and risk of prostate cancer in United States physicians",
"author": "Ma",
"first-page": "385",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Cancer Epidemiol. Prev. Biomark.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0255",
"volume": "7",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ppul.22877",
"article-title": "Vitamin D receptor (VDR) polymorphisms and severe RSV bronchiolitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "McNally",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "790",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Pediatr. Pulmonol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0260",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10528-018-9894-1",
"article-title": "Association of SHMT1, MAZ, ERG, and L3MBTL3 gene polymorphisms with susceptibility to multiple sclerosis",
"author": "Mehrabani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "355",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Biochem. Genet.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0265",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"article-title": "Association of Vitamin D deficiency and treatment with COVID-19 incidence",
"author": "Meltzer",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0270",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Factors associated with hospitalization and disease severity in a racially and ethnically diverse population of COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Mendy",
"journal-title": "MedRxiv",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0275",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00251-018-1063-5",
"article-title": "Cdx-2 polymorphism in the vitamin D receptor gene (VDR) marks VDR expression in monocyte/macrophages through VDR promoter methylation",
"author": "Meyer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "523",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Immunogenetics",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0280",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.steroids.2020.108615",
"article-title": "Vitamin D receptor genetic polymorphisms and the risk of multiple sclerosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Mohammadi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "108615",
"journal-title": "Steroids",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0285",
"volume": "158",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/367284a0",
"article-title": "Prediction of bone density from vitamin D receptor alleles",
"author": "Morrison",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "284",
"issue": "6460",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0290",
"volume": "367",
"year": "1994"
},
{
"author": "Organization WH",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0295",
"series-title": "Clinical Management of COVID-19: Interim Guidance, 27 May 2020",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00439-009-0763-1",
"article-title": "Rubella vaccine-induced cellular immunity: evidence of associations with polymorphisms in the Toll-like, vitamin A and D receptors, and innate immune response genes",
"author": "Ovsyannikova",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "207",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Hum. Genet.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0300",
"volume": "127",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/18715281113129990049",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency and acute lung injury",
"author": "Parekh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "253",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Inflamm. Allergy Drug Targets",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0305",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3904/kjim.2017.380",
"article-title": "Effect of vitamin D deficiency in Korean patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome",
"author": "Park",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1129",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Korean J. Intern. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0310",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1470320320926899",
"article-title": "Hypertension is associated with increased mortality and severity of disease in COVID-19 pneumonia: a systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression",
"author": "Pranata",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Syst.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0315",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105719",
"article-title": "Vitamin D receptor stimulation to reduce Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) in patients with coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 infections: revised Ms SBMB 2020_166",
"author": "Quesada-Gomez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "105719",
"journal-title": "J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0320",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/joim.13149",
"article-title": "Perspective: vitamin D deficiency and COVID-19 severity–plausibly linked by latitude, ethnicity, impacts on cytokines, ACE2 and thrombosis",
"author": "Rhodes",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "97",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Intern. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0325",
"volume": "289",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.6775",
"article-title": "Presenting characteristics, comorbidities, and outcomes among 5700 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in the New York City area",
"author": "Richardson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2052",
"issue": "20",
"journal-title": "Jama.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0330",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.gene.2015.02.024",
"article-title": "Regulation of the vitamin D receptor gene by environment, genetics and epigenetics",
"author": "Saccone",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "171",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Gene",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0335",
"volume": "561",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3892/mmr.2015.4685",
"article-title": "Vitamin D/VDR signaling attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by maintaining the integrity of the pulmonary epithelial barrier",
"author": "Shi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1186",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Mol. Med. Rep.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0340",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.004",
"article-title": "Diabetes in COVID-19: prevalence, pathophysiology, prognosis and practical considerations",
"author": "Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "303",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0345",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "A review of coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19)",
"author": "Singhal",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Indian J. Pediatr.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0350",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijsu.2020.02.034",
"article-title": "World Health Organization declares global emergency: a review of the 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19)",
"author": "Sohrabi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "71",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Surg.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0355",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "High prevalence of vitamin D deficiency among Iranian population: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Tabrizi",
"first-page": "125",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Iran. J. Med. Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0360",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjresp-2014-000074",
"article-title": "Association between prehospital vitamin D status and incident acute respiratory failure in critically ill patients: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Thickett",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "BMJ Open Respir. Res.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0365",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0096105",
"article-title": "Patterns of genome-wide VDR locations",
"author": "Tuoresmäki",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0370",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cca.2006.02.016",
"article-title": "Vitamin D receptor polymorphisms and diseases",
"author": "Valdivielso",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1–2",
"journal-title": "Clin. Chim. Acta",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0375",
"volume": "371",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/eji.200636043",
"article-title": "The vitamin D receptor gene FokI polymorphism: functional impact on the immune system",
"author": "van Etten",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "395",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Immunol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0380",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4161/derm.24494",
"article-title": "Sunlight and vitamin D: a global perspective for health",
"author": "Wacker",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "51",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Dermato-endocrinology",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0385",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/tan.13941",
"article-title": "Distribution of HLA allele frequencies in 82 Chinese individuals with coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19)",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "194",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Hla",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0390",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7861/clinmed.2020-0301",
"article-title": "Does vitamin D deficiency increase the severity of COVID-19?",
"author": "Weir",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e107",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Clin. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0395",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0303-7207(01)00406-3",
"article-title": "Functionally relevant polymorphisms in the human nuclear vitamin D receptor gene",
"author": "Whitfield",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "145",
"issue": "1–2",
"journal-title": "Mol. Cell. Endocrinol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0400",
"volume": "177",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2521-4",
"article-title": "OpenSAFELY: factors associated with COVID-19 death in 17 million patients",
"author": "Williamson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "430",
"issue": "7821",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0405",
"volume": "584",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1471-2156-6-2",
"article-title": "Variants in the vitamin D receptor gene and asthma",
"author": "Wjst",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC Genet.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0410",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.03.071",
"article-title": "Insight into 2019 novel coronavirus—an updated intrim review and lessons from SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV",
"author": "Xie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "119",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0415",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3892/mmr.2017.7546",
"article-title": "Vitamin D alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via regulation of the renin-angiotensin system",
"author": "Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "7432",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Mol. Med. Rep.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0420",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30076-X",
"article-title": "Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome",
"author": "Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "420",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0425",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.6548",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and African Americans",
"author": "Yancy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1891",
"issue": "19",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0430",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.03.017",
"article-title": "Prevalence of comorbidities and its effects in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "91",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0435",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.1909",
"article-title": "Vitamin D modulation of innate immune responses to respiratory viral infections",
"author": "Zdrenghea",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Rev. Med. Virol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0440",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jgar.2020.05.006",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency and COVID-19 pandemic",
"author": "Zemb",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "133",
"journal-title": "J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0445",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.31083/j.rcm.2020.03.131",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency in association with endothelial dysfunction: implications for patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "339",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Rev. Cardiovasc. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0450",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics and outcomes of COVID-19-infected cancer patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Zhang",
"journal-title": "J. Natl. Cancer Inst.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0455",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bcp.2020.113955",
"article-title": "Vitamin D attenuates lung injury via stimulating epithelial repair, reducing epithelial cell apoptosis and inhibits TGF-β induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition",
"author": "Zheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "113955",
"journal-title": "Biochem. Pharmacol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0460",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jdermsci.2013.08.014",
"article-title": "The association of polymorphisms of the vitamin D receptor gene with psoriasis in the Han population of northeastern China",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "63",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J. Dermatol. Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105098_bb0465",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2014"
}
],
"reference-count": 93,
"references-count": 93,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1567134821003981"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Association of Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms and clinical/severe outcomes of COVID-19 patients",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "96"
}
